|
Alchemical Symbols (Unicode)
Alchemical symbols were used to denote chemical elements and compounds, as well as alchemical apparatus and processes, until the 18th century. Although notation was partly standardized, style and symbol varied between alchemists. Lüdy-Tenger published an inventory of 3,695 symbols and variants, and that was not exhaustive, omitting for example many of the symbols used by Isaac Newton. This page therefore lists only the most common symbols. Three primes According to Paracelsus (1493–1541), the three primes or ''tria prima'' – of which material substances are immediately composed – are: * Sulfur or soul, the principle of combustibility: 🜍 () * Mercury or spirit, the principle of fusibility and volatility: ☿ () * Salt or body, the principle of non-combustibility and non-volatility: 🜔 () Four basic elements Western alchemy makes use of the four classical elements. The symbols used for these are: * Air 🜁 () * Earth 🜃 () * Fire 🜂 () * Water 🜄 () Seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemical Symbols
Alchemical symbols were used to denote chemical elements and compounds, as well as alchemy, alchemical apparatus and processes, until the 18th century. Although notation was partly standardized, style and symbol varied between alchemists. Lüdy-Tenger published an inventory of 3,695 symbols and variants, and that was not exhaustive, omitting for example many of the symbols used by Isaac Newton. This page therefore lists only the most common symbols. Three primes According to Paracelsus (1493–1541), the three primes or ''tria prima'' – of which material substances are immediately composed – are: * Sulfur or soul, the principle of combustibility: 🜍 () * Mercury (element), Mercury or Spirit (animating force), spirit, the principle of fusibility and Volatility (chemistry), volatility: ☿ () * Salt (chemistry), Salt or Physical object, body, the principle of non-combustibility and non-volatility: 🜔 () Four basic elements Western alchemy makes use of the four classical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
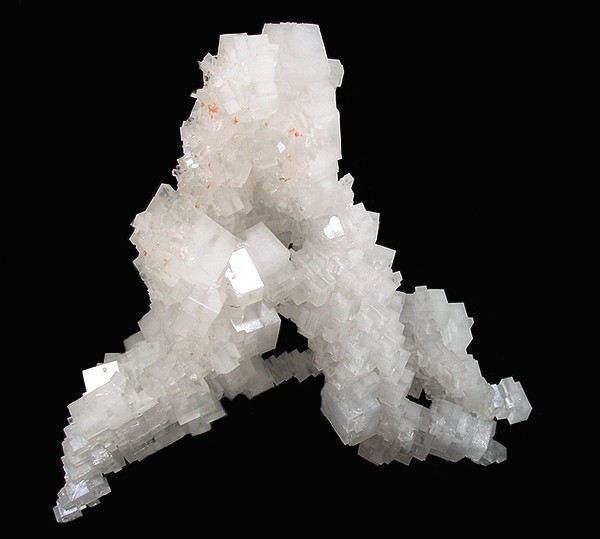
Salt (chemistry)
In chemistry, a salt or ionic compound is a chemical compound consisting of an assembly of positively charged ions ( cations) and negatively charged ions ( anions), which results in a compound with no net electric charge (electrically neutral). The constituent ions are held together by electrostatic forces termed ionic bonds. The component ions in a salt can be either inorganic, such as chloride (Cl−), or organic, such as acetate (). Each ion can be either monatomic, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl−) in sodium chloride, or polyatomic, such as ammonium () and carbonate () ions in ammonium carbonate. Salts containing basic ions hydroxide (OH−) or oxide (O2−) are classified as bases, such as sodium hydroxide and potassium oxide. Individual ions within a salt usually have multiple near neighbours, so they are not considered to be part of molecules, but instead part of a continuous three-dimensional network. Salts usually form crystalline structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
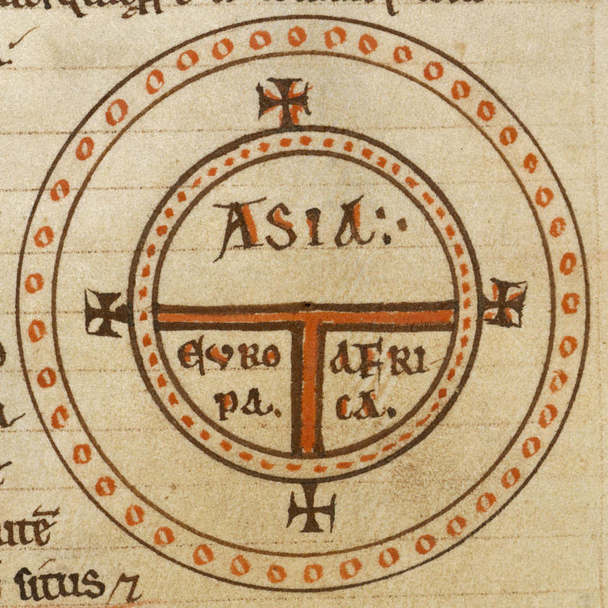
Classical Planet
A classical planet is an astronomical object that is visible to the naked eye and moves across the sky and its backdrop of fixed stars (the common stars which seem still in contrast to the planets), appearing as wandering stars. Visible to humans on Earth there are seven classical planets (the seven luminaries). They are from brightest to dimmest: the Sun, the Moon, Venus, Jupiter, Mercury, Mars and Saturn. Greek astronomers such as Geminus and Ptolemy recorded these classical planets during classical antiquity, introducing the term ''planet'', which means 'wanderer' in Greek ( and ), expressing the fact that these objects move across the celestial sphere relative to the fixed stars. Therefore, the Greeks were the first to document the astrological connections to the planets' visual detail. Through the use of telescopes other celestial objects like the classical planets were found, starting with the Galilean moons in 1610. Today the term ''planet'' is used considerably di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metals Of Antiquity
The metals of antiquity are the seven metals which humans had identified and found use for in prehistoric times in Africa, Europe and throughout Asia: gold, silver, copper, tin, lead, iron, and mercury (element), mercury. Zinc, arsenic, and antimony were also known during antiquity, but they were not recognised as distinct metals until later. A special case is platinum; it was known to native South Americans around the time Europe was going through classical antiquity, but was unknown to Europeans until the 18th century. Thus, at most eleven elemental metals and metalloids were known by the end of antiquity; this contrasts greatly with the situation today, with over 90 elemental metals known. Bismuth only began to be recognised as distinct around 1500 by the European and Incan civilisations. The first elemental metal with a clearly identifiable discoverer is cobalt, discovered in 1735 by Georg Brandt, by which time the Scientific Revolution was in full swing. (Even then, cobalt m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arms Of The Royal Society Of Chemistry
Arms or ARMS may refer to: * Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to: People * Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader Coat of arms or weapons *Armaments or weapons **Firearm *Coat of arms **In this sense, "arms" is a common element in pub names Enterprises * Amherst Regional Middle School *Arms Corporation, originally named Dandelion, a defunct Japanese animation studio who operated from 1996 to 2020 * TRIN (finance) or Arms Index, a short-term stock trading index *Australian Relief & Mercy Services, a part of Youth With A Mission Arts and entertainment *ARMS (band), an American indie rock band formed in 2004 * ''Arms'' (album), a 2016 album by Bell X1 * "Arms" (song), a 2011 song by Christina Perri from the album ''lovestrong'' * ''Arms'' (video game), a 2017 fighting video game for the Nintendo Switch *ARMS Charity Concerts, a series of charitable rock concerts in support of Action into Research for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Symbol (alchemical)
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water (classical Element)
Water is one of the classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy along with air, earth and fire, in the Asian Indian system '' Panchamahabhuta'', and in the Chinese cosmological and physiological system '' Wu Xing''. In contemporary esoteric traditions, it is commonly associated with the qualities of emotion and intuition. Greek and Roman tradition Water was one of many ''archai'' proposed by the Pre-socratics, most of whom tried to reduce all things to a single substance. However, Empedocles of Acragas (c. 495 – c. 435 BC) selected four archai for his four roots: air, fire, water and earth. Empedocles roots became the four classical elements of Greek philosophy. Plato (427–347 BC) took over the four elements of Empedocles. In the Timaeus, his major cosmological dialogue, the Platonic solid associated with water is the icosahedron which is formed from twenty equilateral triangles. This makes water the element with the greatest number of sides, which Plato regarded as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Symbol (alchemical)
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion reaction when the fuel reaches its ignition point temperature. Flames from hydrocarbon fuels consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce plasma. The color and intensity of the flame depend on the type of fuel and composition of the surrounding gases. Fire, in its most common form, has the potential to result in conflagration, which can lead to permanent physical damage. It directly impacts land-based ecological systems worldwide. The positive effects of fire include stimulating plant growth and maintaining ecological balance. Its negative effects include hazards to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water contamination. When fire removes protective vegetation, heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire (classical Element)
Fire is one of the four classical elements along with earth, water and air in ancient Greek philosophy and science. Fire is considered to be both hot and dry and, according to Plato, is associated with the tetrahedron. Greek and Roman tradition Fire is one of the four classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy and science. It was commonly associated with the qualities of energy, assertiveness, and passion. In one Greek myth, Prometheus stole ''fire'' from the gods to protect the otherwise helpless humans, but was punished for this charity. Fire was one of many '' archai'' proposed by the pre-Socratics, most of whom sought to reduce the cosmos, or its creation, to a single substance. Heraclitus considered ''fire'' to be the most fundamental of all elements. He believed fire gave rise to the other three elements: "All things are an interchange for fire, and fire for all things, just like goods for gold and gold for goods." Diels-Kranz B90 (Freeman 9481970p. 45. He had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Symbol (alchemical)
A variety of symbols or iconographic conventions are used to represent Earth, whether in the sense of planet Earth, or the inhabited world, or as a classical element. A circle representing the round world, with the rivers of Garden of Eden separating the four corners of the world, or rotated 45° to suggest the four continents, remains a common pictographic convention to express the notion of "worldwide". The current astronomical symbols for the planet are a circle with an intersecting cross, 20px, 🜨, alt=An equilateral cross enclosed in a circle, and a ''globus cruciger'', 20px, ♁. Although the International Astronomical Union (IAU) now discourages the use of planetary symbols, this is an exception, being used in abbreviations such as ''M''🜨 or ''M''♁ for Earth mass. History The earliest type of symbols are allegories, personifications or deifications, mostly in the form of an Earth goddess (in the case of Egyptian mythology a god, Geb). Before the recognition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth (classical Element)
Earth is one of the classical elements, in some systems being one of the four along with air, fire, and water. European tradition Earth is one of the four classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy and science. It was commonly associated with qualities of heaviness, matter and the terrestrial world. Due to the hero cults, and chthonic underworld deities, the element of ''earth'' is also associated with the sensual aspects of both life and death in later occultism. Empedocles of Acragas proposed four '' archai'' by which to understand the cosmos: ''fire'','' air'', ''water'', and ''earth''. Plato (427–347 BCE) believed the elements were geometric forms (the platonic solids) and he assigned the cube to the element of ''earth'' in his dialogue '' Timaeus''. Aristotle (384–322 BCE) believed ''earth'' was the heaviest element, and his theory of '' natural place'' suggested that any ''earth–laden'' substances, would fall quickly, straight down, towards the center ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Symbol (alchemical)
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosphere is the outer region of a star, which includes the layers above the opaque photosphere; stars of low temperature might have outer atmospheres containing compound molecules. The atmosphere of Earth is composed of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), argon (0.9%), carbon dioxide (0.04%) and trace gases. Most organisms use oxygen for respiration; lightning and bacteria perform nitrogen fixation which produces ammonia that is used to make nucleotides and amino acids; plants, algae, and cyanobacteria use carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. The layered composition of the atmosphere minimises the harmful effects of sunlight, ultraviolet radiation, solar wind, and cosmic rays and thus protects the organisms from genetic damage. The current composition o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |