|
Water (classical Element)
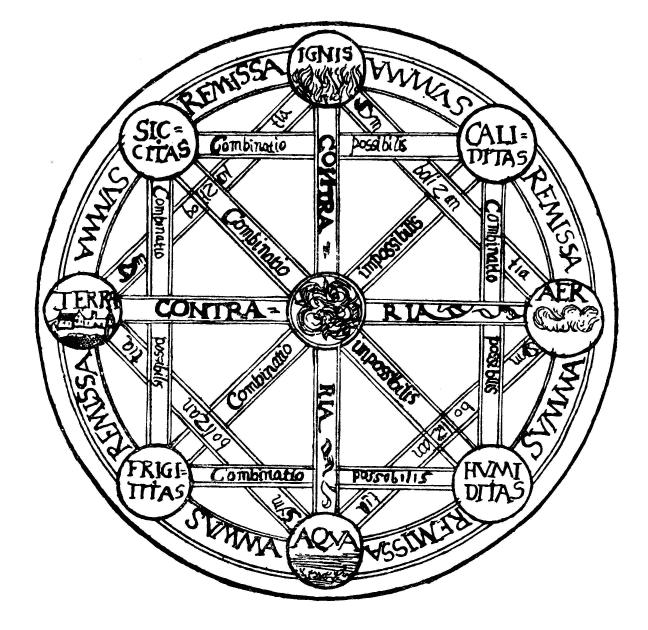
Water is one of the classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy along with air, earth and fire, in the Asian Indian system '' Panchamahabhuta'', and in the Chinese cosmological and physiological system '' Wu Xing''. In contemporary esoteric traditions, it is commonly associated with the qualities of emotion and intuition. Greek and Roman tradition Water was one of many ''archai'' proposed by the Pre-socratics, most of whom tried to reduce all things to a single substance. However, Empedocles of Acragas (c. 495 – c. 435 BC) selected four archai for his four roots: air, fire, water and earth. Empedocles roots became the four classical elements of Greek philosophy. Plato (427–347 BC) took over the four elements of Empedocles. In the Timaeus, his major cosmological dialogue, the Platonic solid associated with water is the icosahedron which is formed from twenty equilateral triangles. This makes water the element with the greatest number of sides, which Plato regarded as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the elements to be divisible into infinitely small pieces without changing their nature. While the classification of the material world in ancient India, Hellenistic Egypt, and ancient Greece into air, earth, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icosahedron
In geometry, an icosahedron ( or ) is a polyhedron with 20 faces. The name comes . The plural can be either "icosahedra" () or "icosahedrons". There are infinitely many non- similar shapes of icosahedra, some of them being more symmetrical than others. The best known is the ( convex, non- stellated) regular icosahedron—one of the Platonic solids—whose faces are 20 equilateral triangles. Regular icosahedra There are two objects, one convex and one nonconvex, that can both be called regular icosahedra. Each has 30 edges and 20 equilateral triangle faces with five meeting at each of its twelve vertices. Both have icosahedral symmetry. The term "regular icosahedron" generally refers to the convex variety, while the nonconvex form is called a ''great icosahedron''. Convex regular icosahedron The convex regular icosahedron is usually referred to simply as the ''regular icosahedron'', one of the five regular Platonic solids, and is represented by its Schläfli symbol , contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its atomic nucleus, nucleus. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, known as isotopes of the element. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules. Some elements form Homonuclear molecule, molecules of atoms of said element only: e.g. atoms of hydrogen (H) form Diatomic molecule, diatomic molecules (H). Chemical compounds are substances made of atoms of different elements; they can have molecular or non-molecular structure. Mixtures are materials containing different chemical substances; that means (in case of molecular substances) that they contain different types of molecules. Atoms of one element can be transformed into atoms of a different element in nuclear reactions, which change an atom's at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alchemy
Alchemy (from the Arabic word , ) is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practised in China, India, the Muslim world, and Europe. In its Western form, alchemy is first attested in a number of pseudepigraphical texts written in Greco-Roman Egypt during the first few centuries AD.. Greek-speaking alchemists often referred to their craft as "the Art" (τέχνη) or "Knowledge" (ἐπιστήμη), and it was often characterised as mystic (μυστική), sacred (ἱɛρά), or divine (θɛíα). Alchemists attempted to purify, mature, and perfect certain materials. Common aims were chrysopoeia, the transmutation of " base metals" (e.g., lead) into "noble metals" (particularly gold); the creation of an elixir of immortality; and the creation of panaceas able to cure any disease. The perfection of the human body and soul was thought to result from the alchemical ''magnum opus'' ("Great Work"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West
West is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''vest'' in Romanian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב (maarav) 'west' from עֶרֶב (erev) 'evening'. West is sometimes abbreviated as W. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femininity
Femininity (also called womanliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and Gender roles, roles generally associated with women and girls. Femininity can be understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there is also some evidence that some behaviors considered feminine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent femininity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is Sex and gender distinction, conceptually distinct from both the Female, female biological sex and from womanhood, as all humans can exhibit feminine and masculine traits, regardless of sex and gender. Traits traditionally cited as feminine include gracefulness, gentleness, empathy, humility, and Sensitivity (human), sensitivity, though traits associated with femininity vary across societies and individuals, and are influenced by a variety of social and cultural factors. Overview and history Despite the terms ''femininity'' and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Medicine Of Western Europe
In the Middle Ages, the medicine of Western Europe was composed of a mixture of existing ideas from antiquity. In the Early Middle Ages, following the fall of the Western Roman Empire, standard medical knowledge was based chiefly upon surviving Ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman texts, preserved in monasteries and elsewhere. Medieval medicine is widely misunderstood, thought of as a uniform attitude composed of placing hopes in the church and God to heal all sicknesses, while sickness itself exists as a product of destiny, sin, and Astrology, astral influences as physical causes. But, especially in the second half of the medieval period (c. 1100–1500 AD), medieval medicine became a formal body of theoretical knowledge and was institutionalized in universities. Medieval medicine attributed illnesses, and disease, not to sinful behavior, but to natural causes, and sin was connected to illness only in a more general sense of the view that disease manifested in humanity as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlegm
Phlegm (; , ''phlégma'', "inflammation", "humour caused by heat") is mucus produced by the respiratory system, excluding that produced by the throat nasal passages. It often refers to respiratory mucus expelled by coughing, otherwise known as sputum. Phlegm, and mucus as a whole, is in essence a water-based gel consisting of glycoproteins, immunoglobulins, lipids and other substances. Its composition varies depending on climate, genetics, and state of the immune system. Its color can vary from transparent to pale or dark yellow and green, from light to dark brown, and even to dark grey depending on the contents. The body naturally produces about 1 quart (about 1 litre) of phlegm every day to capture and clear substances in the air and bacteria from the nose and throat. Distinction between mucus and phlegm Contrary to popular misconception and misuse, mucus and phlegm are not always the same. Mucus Mucus is a normal protective layering around the airway, eye, nasal turbinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Humours
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers. Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 17th century and it was definitively disproved with the discovery of microbes. Origin The concept of "humors" may have origins in Ancient Egyptian medicine, or Mesopotamia, though it was not systemized until ancient Greek thinkers. The word ''humor'' is a translation of Greek , (literally 'juice' or ' sap', metaphorically 'flavor'). Early texts on Indian Ayurveda medicine presented a theory of three or four humors (doṣas), which they sometimes linked with the five elements (): earth, water, fire, air, and space. The concept of "humors" (chemical systems regulating human behaviour) became more prominent from the writing of medical theorist Alcmaeon of Croton (c. 540–500 BC). His list of humors was longer and included fundamental elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine In Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek medicine was a compilation of theories and practices that were constantly expanding through new ideologies and trials. The Greek term for medicine was ''iatrikē'' (). Many components were considered in ancient Greek medicine, intertwining the spiritual with the physical. Specifically, the ancient Greeks believed health was affected by the humors, geographic location, social class, diet, trauma, beliefs, and mindset. Early on the ancient Greeks believed that illnesses were "divine punishments" and that healing was a "gift from the Gods". As trials continued wherein theories were tested against symptoms and results, the pure spiritual beliefs regarding "punishments" and "gifts" were replaced with a foundation based in the physical, i.e., cause and effect. Asclepieia Asclepius was espoused as the first physician, and myth placed him as the son of Apollo. Temples dedicated to the healer-god Asclepius, known as '' Asclepieia'' (; sing. Ἀσκληπιεῖον ''Ascl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Symbol (alchemical)
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as a solvent). It is vital for all known forms of life, despite not providing food energy or organic micronutrients. Its chemical formula, , indicates that each of its molecules contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms, connected by covalent bonds. The hydrogen atoms are attached to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.45°. In liquid form, is also called "water" at standard temperature and pressure. Because Earth's environment is relatively close to water's triple point, water exists on Earth as a solid, a liquid, and a gas. It forms precipitation in the form of rain and aerosols in the form of fog. Clouds consist of suspended droplets of water and ice, its solid state. When finely divided, crystalline ice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublunary Sphere
In Aristotelian physics and Greek astronomy, the sublunary sphere is the region of the geocentric cosmos below the Moon, consisting of the four classical elements: earth, water, air, and fire. The sublunary sphere was the realm of changing nature. Beginning with the Moon, up to the limits of the universe, everything (to classical astronomy) was permanent, regular and unchanging—the region of aether where the planets and stars are located. Only in the sublunary sphere did the powers of physics hold sway. Evolution of concept Plato and Aristotle helped to formulate the original theory of a sublunary sphere in antiquity, the idea usually going hand in hand with geocentrism and the concept of a spherical Earth. Avicenna carried forward into the Middle Ages the Aristotelian idea of generation and corruption being limited to the sublunary sphere. Medieval scholastics like Thomas Aquinas, who charted the division between celestial and sublunary spheres in his work ''Summa Theolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |