|
Akkaya, Çukurca
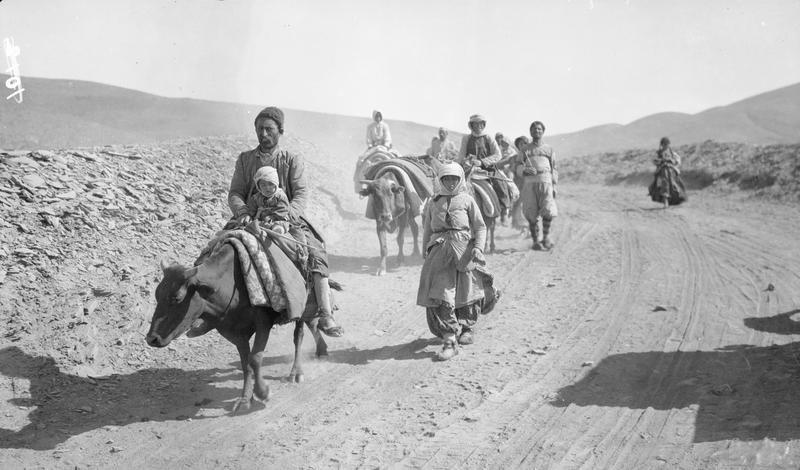
Akkaya (; ) is a village in the Çukurca District in Hakkâri Province in Turkey. The village is populated by Kurds of the Alan tribe and had a population of 755 in 2023. The four hamlets of Dağdibi (), Sarıyer (), Dikenli () and Kunaklı () are attached to Akkaya. Dikenli and Kunaklı are unpopulated. History Sārāspīdōn (today called Akkaya) was historically inhabited by Assyrian people and located in the Upper Tyari district in the Hakkari region. It had two churches and was served as part of the diocese of the Patriarch of the Church of the East. According to the English missionary George Percy Badger, the village was inhabited by 80 Assyrian families in 1850, all of whom belonged to the Church of the East and were served by two priests. Badger recorded that the villagers possessed 3000 sheep, 150 oxen, and 160 muskets; he also noted lead was mined at the village for use in the production of bullets. By 1877, there were 50 Assyrians families at Sārāspīdōn with two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
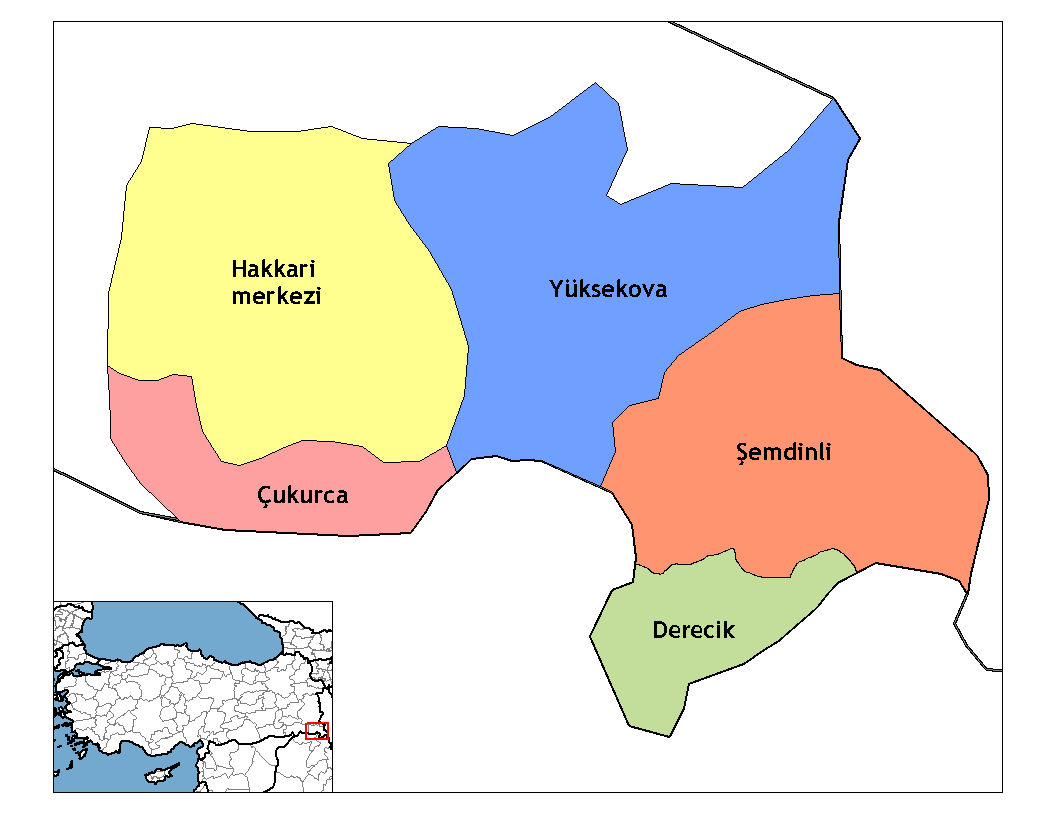
Çukurca District
Çukurca District is a district in the Hakkâri Province of Turkey. The district had a population of 17,734 in 2023 with the town of Çukurca as its seat. Its area is 725 km2. And Çukurca has border with iraqi Kurdistan at the south point of there border The current district governor (''kaymakam)'' is Hasan Kurt. The district has more unpopulated settlements than populated ones. The district was established in 1953. Settlements There is one municipality in Çukurca District: * Çukurca () The district has sixteen villages of which eight are unpopulated: # Akkaya () # Cevizli () # Çağlayan () # Çayırlı () # Çığlı () # Çınarlı () # Dede () # Gündeş () # Işıklı () # Kavaklı () # Kavuşak () # Kayalık () # Kazan () # Kurudere () # Narlı () # Üzümlü () There are moreover thirty-four hamlets A hamlet is a human settlement that is smaller than a town or village. This is often simply an informal description of a smaller settlement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of The East
The Church of the East ( ) or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church, the Chaldean Church or the Nestorian Church, is one of three major branches of Eastern Christianity, Eastern Nicene Christianity that arose from the Christological controversies in the Christianity in the 5th century, 5th century and the Christianity in the 6th century, 6th century, alongside that of Miaphysitism (which came to be known as the Oriental Orthodox Churches) and Chalcedonian Christianity (from which Catholicism, Eastern Orthodoxy and Protestantism would arise). Having its origins in Mesopotamia during the time of the Parthian Empire, the Church of the East developed its own unique form of Christian theology and East Syriac Rite, liturgy. During the early modern period, a series of Schism#Christianity, schisms gave rise to rival patriarchates, sometimes two, sometimes three. In the latter half of the 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Assyrian Communities In Hakkâri Province
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to develop a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurdish Settlements In Hakkâri Province
Kurdish may refer to: *Kurds or Kurdish people *Kurdish language **Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji) **Central Kurdish (Sorani) **Southern Kurdish ** Laki Kurdish *Kurdish alphabets *Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes: **Southern Kurdistan **Eastern Kurdistan **Northern Kurdistan **Western Kurdistan See also * Kurd (other) *Kurdish literature *Kurdish music *Kurdish rugs *Kurdish cuisine *Kurdish culture *Kurdish nationalism Kurdish nationalism () is a nationalist political movement which asserts that Kurds are a nation and espouses the creation of an independent Kurdistan from Iran, Iraq, Syria, and Turkey. Early Kurdish nationalism had its roots in the Ottoman ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Statistical Institute
Turkish Statistical Institute (commonly known as TurkStat; or TÜİK) is the Turkish government agency commissioned with producing official statistics on Turkey, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It was founded in 1926 and headquartered in Ankara. Formerly named as the State Institute of Statistics (Devlet İstatistik Enstitüsü (DİE)), the institute was renamed as the Turkish Statistical Institute on November 18, 2005. See also * List of Turkish provinces by life expectancy References External linksOfficial website of the institute National statistical services Statistical Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ... Organizations established in 1926 Organizations based in Ankara {{Sci-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayfo
The Sayfo (, ), also known as the Seyfo or the Assyrian genocide, was the mass murder and deportation of Assyrian people, Assyrian/Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan province by Ottoman Army (1861–1922), Ottoman forces and some Kurdish tribes during World War I. The Assyrians were divided into mutually antagonistic churches, including the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Assyrian Church of the East, and the Chaldean Catholic Church. Before World War I, they largely lived in mountainous and remote areas of the Ottoman Empire and Persia, some of which were effectively Stateless society, stateless. The Ottoman Empire's nineteenth-century centralization efforts led to increased violence and danger for the Assyrians. Mass killing of Assyrian civilians began during the Persian campaign (World War I), Ottoman occupation of Azerbaijan from January to May 1915, during which massacres were committed by Ottoman forces and pro-Ottoman Kur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris Peace Conference
Agreements and declarations resulting from meetings in Paris include: Listed by name Paris Accords may refer to: * Paris Accords, the agreements reached at the end of the London and Paris Conferences in 1954 concerning the post-war status of Germany. '' or parallel conferences for peace in Korea and in Indochina, see Berlin Conference (1954) and 1954 Geneva Conference]'' * Paris Peace Accords, in 1973, ending United States involvement in the Vietnam War * Paris Agreement, the 2015 agreement related to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, sometimes called the Paris Accords Paris Agreement /h2> may refer to: * Paris Agreements about the status of West Germany reached at the London and Paris Conferences in 1954. '' or parallel conferences for peace in Korea and in Indochina, see Berlin Conference (1954) and 1954 Geneva Conference]'' * 1991 Paris Peace Agreements, related to the Cambodian–Vietnamese War * Paris Agreement, international treaty on climate chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Lewes Cutts
Edward Lewes Cutts was an English writer, antiquarian and curate, specialising in archaeology and the study of ecclesiastical history. Life and church career Cutts was born on 2 March 1824 in Sheffield. He was the son of John Priston Cutts, an optician, and Mary, daughter of Robert Waterhouse. He was educated at Sheffield Collegiate School and graduated B.A. at Queens' College, Cambridge, in 1848. Being ordained in the same year, he was curate successively of Ide Hill, Kent, until 1850, of Coggeshall, Essex, until 1857, and of Kelvedon until 1859, and was perpetual curate of Billericay until 1865. He had already acted also as local organising secretary of the Additional Curates Society, and on leaving Billericay became general secretary of the society in London, resigning in 1871, on presentation to the vicarage of Holy Trinity, Haverstock Hill. In 1876 Cutts was selected by the Archbishops of Canterbury and York to visit the East and inquire into the position of the Syrian an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its Amphoterism, amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Lead compounds, Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighter members of the carbon group. Exceptions are mostly limited ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Percy Badger
George Percy Badger (6 April 1815 – 21 February 1888) was an English Anglican missionary, and a scholar of oriental studies. He is mainly known for his doctrinal and historical studies about the Church of the East. Life ''George Percy Badger'' was born at Chelmsford on 6 April 1815. His father served in the British Army and in 1821 his regiment was transferred in Malta. After his father's death in 1823, George's mother decided to raise her sons in Malta, thus George Badger passed there his youth where he learned the Maltese language and Arabic, which he studied also in Beirut from 1835. On 8 January 1840 Badger married Maria Wilcox in Valletta. He returned to England in 1841, and after some theological studies at the Church Missionary College, Islington, he was ordained Anglican priest in 1842. For his knowledge of the Near East he was appointed by the Archbishop of Canterbury as delegate to the Christians of Church of the East in Mesopotamia and Kurdistan, and in this work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakkâri Province
Hakkâri Province (, ; ), is a province in the southeast of Turkey. The administrative centre is the city of Hakkâri. Its area is 7,095 km2, and its population is 287,625 (2023). The current Governor is Ali Çelik. The province encompasses 8 municipalities, 140 villages and 313 hamlets. The province is a stronghold for Kurdish nationalism and a hotspot in the Kurdish–Turkish conflict. Districts Hakkâri province is divided into five districts (capital district in bold): * Çukurca District * Derecik District (since 2018) * Hakkâri District * Şemdinli District * Yüksekova District Demographics Hakkari Province is located in Turkish Kurdistan and has an overwhelmingly Kurdish population. The province is tribal and most of the Kurds adhere to the Shafiʽi school of Sunni Islam with the Naqshbandi order having a strong presence around Şemdinli. The Kurdish tribes in the province include the Doski, Ertuşi, Gerdi, Herki, Jirki and Pinyaniş. The area had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |