|
Abramowitz And Stegun
''Abramowitz and Stegun'' (''AS'') is the informal name of a 1964 mathematical reference work edited by Milton Abramowitz and Irene Stegun of the United States National Bureau of Standards (NBS), now the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Its full title is ''Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables''. A digital successor to the Handbook was released as the " Digital Library of Mathematical Functions" (DLMF) on 11 May 2010, along with a printed version, the '' NIST Handbook of Mathematical Functions'', published by Cambridge University Press. Overview Since it was first published in 1964, the 1046-page ''Handbook'' has been one of the most comprehensive sources of information on special functions, containing definitions, identities, approximations, plots, and tables of values of numerous functions used in virtually all fields of applied mathematics. The notation used in the ''Handbook'' is the '' de facto'' standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Milton Abramowitz
Milton Abramowitz (19 February 1915 – 5 July 1958) was an American mathematician at the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) who, with Irene Stegun, edited a classic book of mathematical tables called '' Handbook of Mathematical Functions'', widely known as "Abramowitz and Stegun". Abramowitz was born in Brooklyn, NY, in 1915. He received a B. A. and M. A. from Brooklyn College (1937, 1940) and in 1948 received a Ph.D. in Mathematics from New York University. He joined the NBS Math Tables Project in 1938, and was later Chief of the Computation Laboratory of the NBS Applied Mathematics Division. In 1958, he died while mowing the lawn of his home in suburban Washington, when the heat caused a heart attack. In his memory, the Abramowitz Award is granted by the University of Maryland, College Park to students "for superior competence and promise in the field of mathematics and its applications." Winners of this award include Charles Fefferman and Sergey Brin. At the time of Abra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical science laboratory programs that include nanoscale science and technology, engineering, information technology, neutron research, material measurement, and physical measurement. From 1901 to 1988, the agency was named the National Bureau of Standards. History Background The Articles of Confederation, ratified by the colonies in 1781, provided: The United States in Congress assembled shall also have the sole and exclusive right and power of regulating the alloy and value of coin struck by their own authority, or by that of the respective states—fixing the standards of weights and measures throughout the United States. Article 1, section 8, of the Constitution of the United States, ratified in 1789, granted these powers to the new Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hypergeometric Functions
In mathematics, the Gaussian or ordinary hypergeometric function 2''F''1(''a'',''b'';''c'';''z'') is a special function represented by the hypergeometric series, that includes many other special functions as specific or limiting cases. It is a solution of a second-order linear ordinary differential equation (ODE). Every second-order linear ODE with three regular singular points can be transformed into this equation. For systematic lists of some of the many thousands of published identities involving the hypergeometric function, see the reference works by and . There is no known system for organizing all of the identities; indeed, there is no known algorithm that can generate all identities; a number of different algorithms are known that generate different series of identities. The theory of the algorithmic discovery of identities remains an active research topic. History The term "hypergeometric series" was first used by John Wallis in his 1655 book ''Arithmetica Infinitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Coulomb Wave Function
In mathematics, a Coulomb wave function is a solution of the Coulomb wave equation, named after Charles-Augustin de Coulomb. They are used to describe the behavior of charged particles in a Coulomb potential and can be written in terms of confluent hypergeometric functions or Whittaker functions of imaginary argument. Coulomb wave equation The Coulomb wave equation for a single charged particle of mass m is the Schrödinger equation with Electric potential energy#One point charge q in the presence of one point charge Q, Coulomb potential :\left(-\hbar^2\frac+\frac\right) \psi_(\vec) = \frac \psi_(\vec) \,, where Z=Z_1 Z_2 is the product of the charges of the particle and of the field source (in units of the elementary charge, Z=-1 for the hydrogen atom), \alpha is the fine-structure constant, and \hbar^2k^2/(2m) is the energy of the particle. The solution, which is the Coulomb wave function, can be found by solving this equation in parabolic coordinates :\xi= r + \vec\cdot\hat, \qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Confluent Hypergeometric Function
In mathematics, a confluent hypergeometric function is a solution of a confluent hypergeometric equation, which is a degenerate form of a hypergeometric differential equation where two of the three regular singularities merge into an irregular singularity. The term ''confluent'' refers to the merging of singular points of families of differential equations; ''confluere'' is Latin for "to flow together". There are several common standard forms of confluent hypergeometric functions: * Kummer's (confluent hypergeometric) function , introduced by , is a solution to Kummer's differential equation. This is also known as the confluent hypergeometric function of the first kind. There is a different and unrelated Kummer's function bearing the same name. * Tricomi's (confluent hypergeometric) function introduced by , sometimes denoted by , is another solution to Kummer's equation. This is also known as the confluent hypergeometric function of the second kind. * Whittaker functions (for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Struve Function
In mathematics, the Struve functions , are solutions of the non-homogeneous Bessel's differential equation: : x^2 \frac + x \frac + \left (x^2 - \alpha^2 \right )y = \frac introduced by . The complex number α is the order of the Struve function, and is often an integer. And further defined its second-kind version \mathbf_\alpha(x) as \mathbf_\alpha(x)=\mathbf_\alpha(x)-Y_\alpha(x), where Y_\alpha(x) is the Bessel function#Bessel functions of the second kind : Y.CE.B1, Neumann function. The modified Struve functions are equal to and are solutions of the non-homogeneous Bessel's differential equation: : x^2 \frac + x \frac - \left (x^2 + \alpha^2 \right )y = \frac And further defined its second-kind version \mathbf_\alpha(x) as \mathbf_\alpha(x)=\mathbf_\alpha(x)-I_\alpha(x), where I_\alpha(x) is the Bessel function#Modified Bessel functions: Iα, KαBessel function#Bessel functions of the second kind : Y.CE.B1, modified Bessel function. Definitions Since this is a Ordinar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bessel Function
Bessel functions, named after Friedrich Bessel who was the first to systematically study them in 1824, are canonical solutions of Bessel's differential equation x^2 \frac + x \frac + \left(x^2 - \alpha^2 \right)y = 0 for an arbitrary complex number \alpha, which represents the ''order'' of the Bessel function. Although \alpha and -\alpha produce the same differential equation, it is conventional to define different Bessel functions for these two values in such a way that the Bessel functions are mostly smooth functions of \alpha. The most important cases are when \alpha is an integer or half-integer. Bessel functions for integer \alpha are also known as cylinder functions or the cylindrical harmonics because they appear in the solution to Laplace's equation in cylindrical coordinates. Spherical Bessel functions with half-integer \alpha are obtained when solving the Helmholtz equation in spherical coordinates. Applications Bessel's equation arises when finding separa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Legendre Function
In physical science and mathematics, the Legendre functions , and associated Legendre functions , , and Legendre functions of the second kind, , are all solutions of Legendre's differential equation. The Legendre polynomials and the associated Legendre polynomials are also solutions of the differential equation in special cases, which, by virtue of being polynomials, have a large number of additional properties, mathematical structure, and applications. For these polynomial solutions, see the separate Wikipedia articles. Legendre's differential equation The general Legendre equation reads \left(1 - x^2\right) y'' - 2xy' + \left[\lambda(\lambda+1) - \frac\right] y = 0, where the numbers and may be complex, and are called the degree and order of the relevant function, respectively. The polynomial solutions when is an integer (denoted ), and are the Legendre polynomials ; and when is an integer (denoted ), and is also an integer with are the associated Legendre polynomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
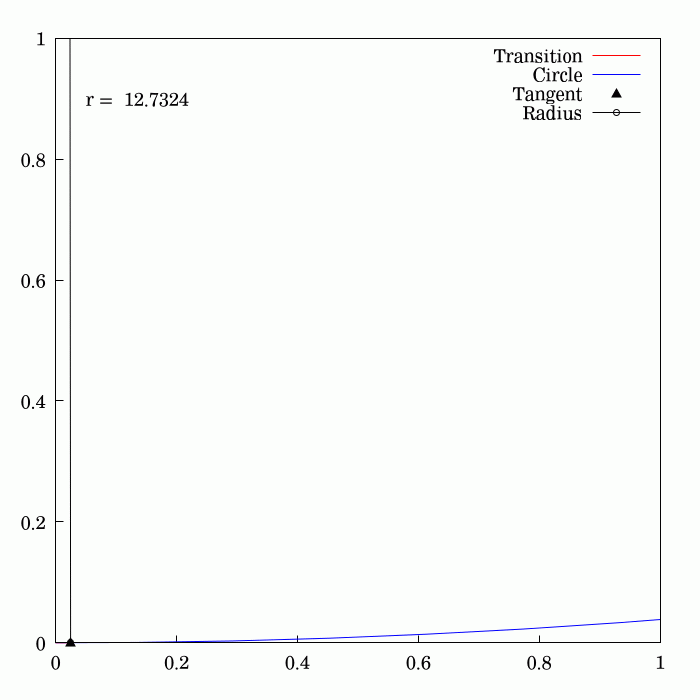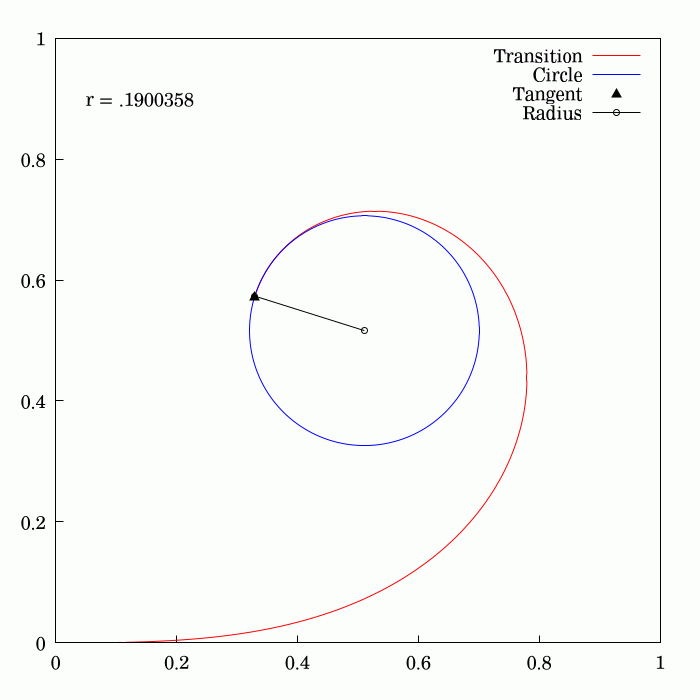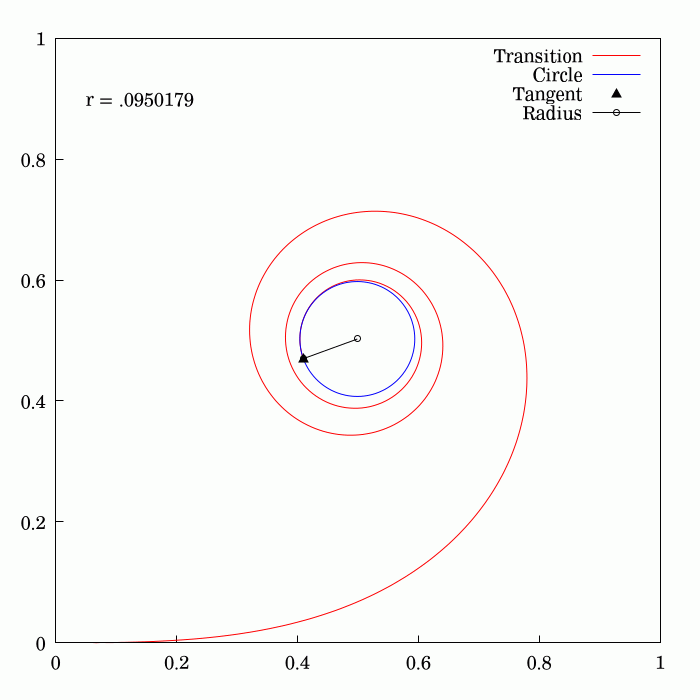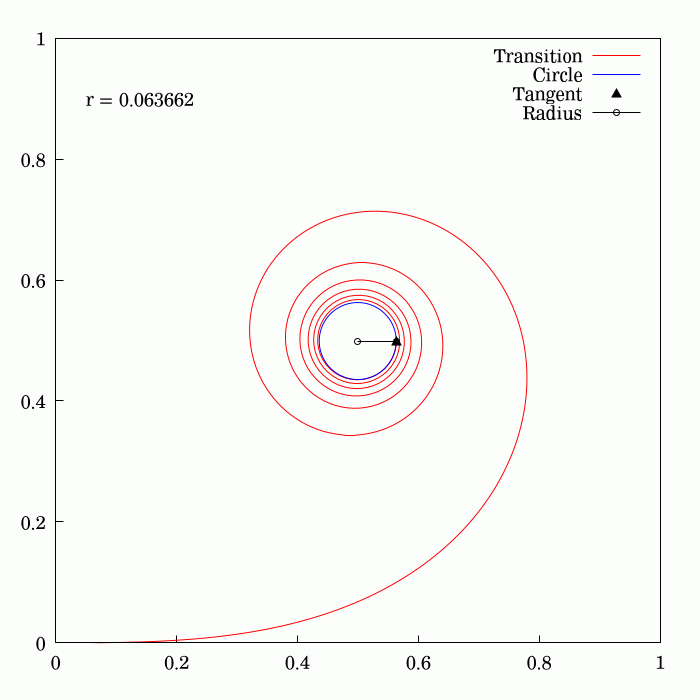
Fresnel Integral
250px, Plots of and . The maximum of is about . If the integrands of and were defined using instead of , then the image would be scaled vertically and horizontally (see below). The Fresnel integrals and are two transcendental functions named after Augustin-Jean Fresnel that are used in optics and are closely related to the error function (). They arise in the description of near-field Fresnel diffraction phenomena and are defined through the following integral representations: S(x) = \int_0^x \sin\left(t^2\right)\,dt, \quad C(x) = \int_0^x \cos\left(t^2\right)\,dt. The parametric curve is the Euler spiral or clothoid, a curve whose curvature varies linearly with arclength. The term Fresnel integral may also refer to the complex definite integral \int_^\infty e^ dx = \sqrte^ where is real and positive; this can be evaluated by closing a contour in the complex plane and applying Cauchy's integral theorem. Definition 250px, Fresnel integrals with arguments in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Error Function
In mathematics, the error function (also called the Gauss error function), often denoted by , is a function \mathrm: \mathbb \to \mathbb defined as: \operatorname z = \frac\int_0^z e^\,\mathrm dt. The integral here is a complex Contour integration, contour integral which is path-independent because \exp(-t^2) is Holomorphic function, holomorphic on the whole complex plane \mathbb. In many applications, the function argument is a real number, in which case the function value is also real. In some old texts, the error function is defined without the factor of \frac. This nonelementary integral is a sigmoid function, sigmoid function that occurs often in probability, statistics, and partial differential equations. In statistics, for non-negative real values of , the error function has the following interpretation: for a real random variable that is normal distribution, normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation \frac, is the probability that falls in the range . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gamma Function
In mathematics, the gamma function (represented by Γ, capital Greek alphabet, Greek letter gamma) is the most common extension of the factorial function to complex numbers. Derived by Daniel Bernoulli, the gamma function \Gamma(z) is defined for all complex numbers z except non-positive integers, and for every positive integer z=n, \Gamma(n) = (n-1)!\,.The gamma function can be defined via a convergent improper integral for complex numbers with positive real part: \Gamma(z) = \int_0^\infty t^ e^\textt, \ \qquad \Re(z) > 0\,.The gamma function then is defined in the complex plane as the analytic continuation of this integral function: it is a meromorphic function which is holomorphic function, holomorphic except at zero and the negative integers, where it has simple Zeros and poles, poles. The gamma function has no zeros, so the reciprocal gamma function is an entire function. In fact, the gamma function corresponds to the Mellin transform of the negative exponential functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Exponential Integral
In mathematics, the exponential integral Ei is a special function on the complex plane. It is defined as one particular definite integral of the ratio between an exponential function and its argument. Definitions For real non-zero values of ''x'', the exponential integral Ei(''x'') is defined as : \operatorname(x) = -\int_^\infty \fract\,dt = \int_^x \fract\,dt. The Risch algorithm shows that Ei is not an elementary function. The definition above can be used for positive values of ''x'', but the integral has to be understood in terms of the Cauchy principal value due to the singularity of the integrand at zero. For complex values of the argument, the definition becomes ambiguous due to branch points at 0 and Instead of Ei, the following notation is used, :E_1(z) = \int_z^\infty \frac\, dt,\qquad, (z), 0. Properties Several properties of the exponential integral below, in certain cases, allow one to avoid its explicit evaluation through the definition ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |