|
A-class Destroyer (1913)
The A class as designated in 1913 was a heterogeneous group of torpedo boat destroyers (TBDs) built for the Royal Navy in the mid-1890s. Some 42 vessels were constructed to the individual designs of their builders to meet Admiralty specifications, the only uniting feature being a specified top speed of . In fact the initial six vessels were generally differentiated by a slightly lower speed and were often referred to as "26-knotters" to distinguish them from the following batch of thirty-six vessels; all fifteen surviving "27-knotter" vessels were classified by the Admiralty as the A class in 1913 to provide some system to the naming of HM destroyers. All of the "26-knotters" and most of the "27-knotters" had been lost or scrapped before the 1913 classification (and so – strictly speaking – never survived to become 'A' class), but for convenience all 42 ships are listed below. The number of funnels varied from one to four. All vessels had a distinctive "turtleback" foreca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-class Destroyer (1913)
The B class as designated in 1913 was a heterogeneous group of torpedo boat destroyers (TBDs) built for the Royal Navy in the late 1890s. They were constructed to the individual designs of their builders to meet Admiralty specifications, the uniting feature being a specified top speed of and four funnels, although the funnel spacings differed between ships. All "30 knotter" vessels with four funnels were classified by the Admiralty as the B class in 1913 to provide some system to the naming of HM destroyers. At the same time all "30 knotter" vessels with three funnels were classified by the Admiralty as the and those with two funnels became the . Fourteen vessels were built by Laird Brothers at Birkenhead (in 1903 to become part of Cammell Laird, Birkenhead), seven by Palmers Shipbuilding and Iron Company at Hebburn-on-Tyne, and one each by Armstrong Whitworth at Walker-on-Tyne, William Doxford and Sons at Sunderland, and J & G Thomson (later to become John Brown and Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
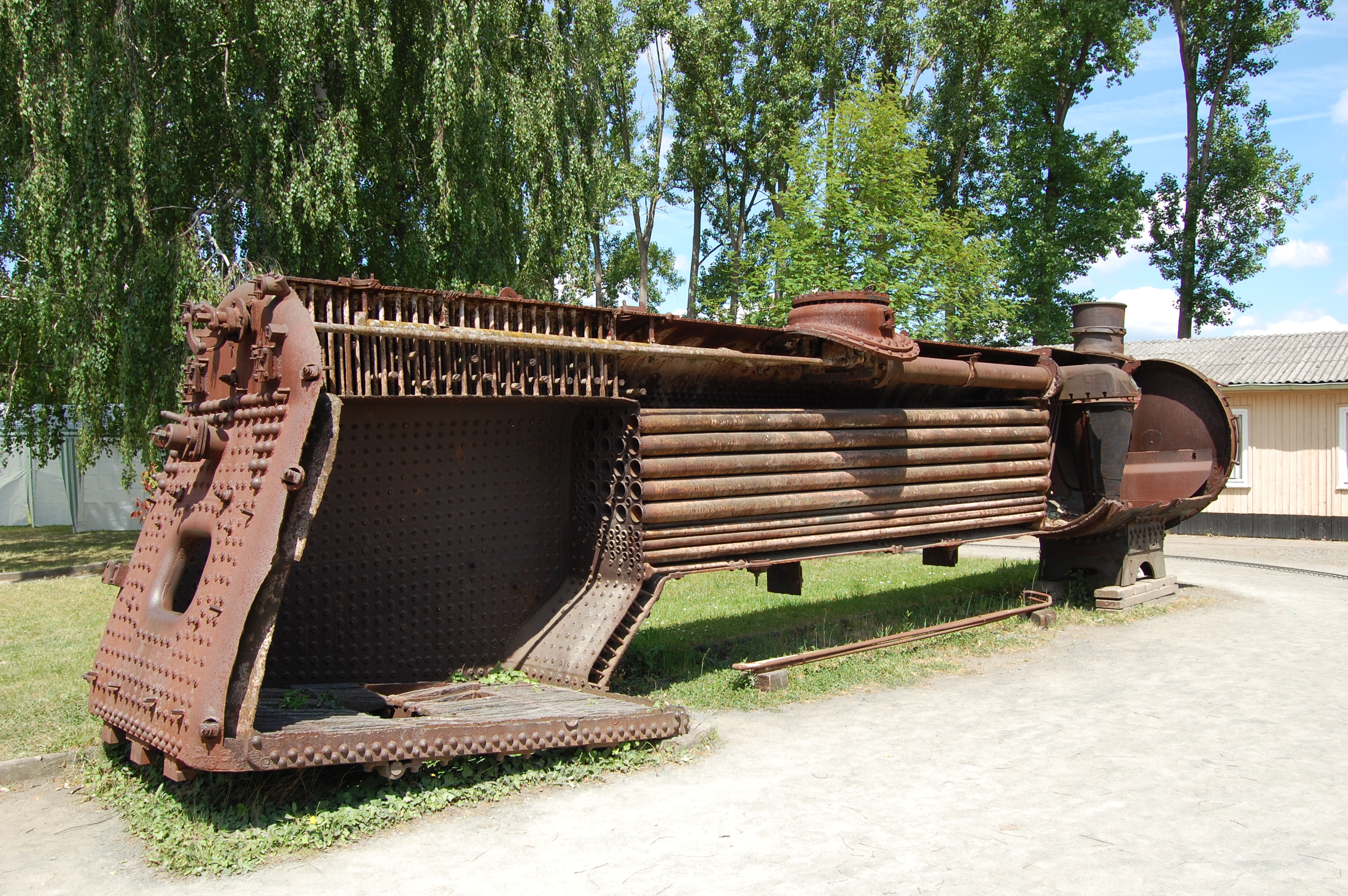
Fire-tube Boiler
A fire-tube boiler is a type of boiler invented in 1828 by Marc Seguin, in which hot gases pass from a fire through one or more tubes running through a sealed container of water. The heat of the gases is transferred through the walls of the tubes by thermal conduction, heating the water and ultimately creating steam. The fire-tube boiler developed as the third of the four major historical types of boilers: low-pressure tank or " haystack" boilers, flued boilers with one or two large flues, fire-tube boilers with many small tubes, and high-pressure water-tube boilers. Their advantage over flued boilers with a single large flue is that the many small tubes offer far greater heating surface area for the same overall boiler volume. The general construction is as a tank of water penetrated by tubes that carry the hot flue gases from the fire. The tank is usually cylindrical for the most part—being the strongest practical shape for a pressurized container—and this cylindrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
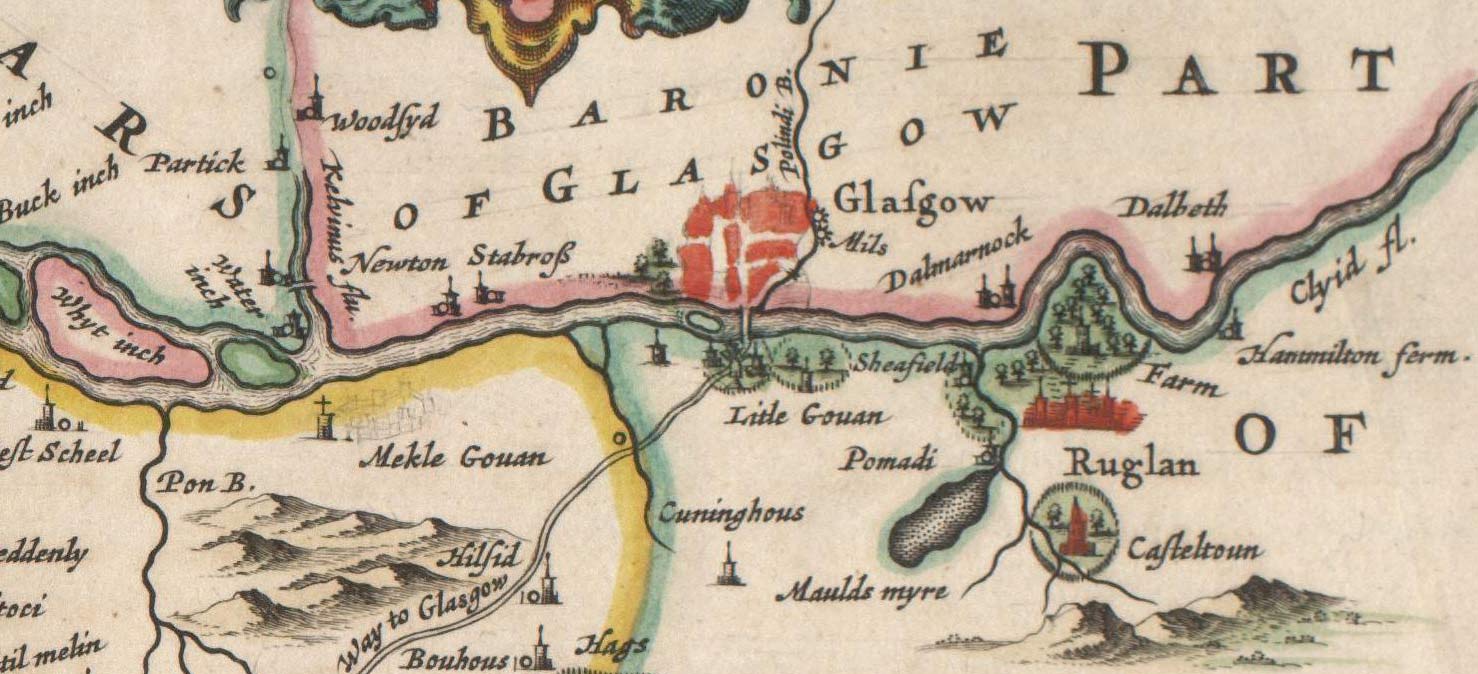
Govan
Govan ( ; Cumbric: ''Gwovan''; Scots language, Scots: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh now part of southwest Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite the mouth of the River Kelvin and the district of Partick. Historically it was part of the Lanarkshire, County of Lanark. In the early medieval period, the site of the present Govan Old Parish Church, Govan Old churchyard was established as a Christian centre for the Brittonic Peoples, Brittonic Kingdom of Alt Clut (Dumbarton Rock) and its successor realm, the Kingdom of Strathclyde. This latter kingdom, established in the aftermath of the Viking siege and capture of Alt Clut by Vikings from Dublin in 870, created the stone sculptures known today as the The Govan Stones, Govan Stones. Govan was the site of a ford and later a ferry which linked the area with Partick for seasonal cattle drovers. In the ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairfield Shipbuilding And Engineering Company
The Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company, Limited, was a Scottish shipbuilding company in the Govan area on the Clyde in Glasgow. Fairfields, as it is often known, was a major warship builder, turning out many vessels for the Royal Navy and other navies through the First World War and the Second World War. It also built many transatlantic liners, including record-breaking ships for the Cunard Line and Canadian Pacific, such as the Blue Riband-winning sisters RMS ''Campania'' and RMS ''Lucania''. At the other end of the scale, Fairfields built fast cross-channel mail steamers and ferries for locations around the world. These included ships for the Bosporus crossing in Istanbul and some of the early ships used by Thomas Cook for developing tourism on the River Nile. John Elder & Co and predecessors Millwright Randolph & Elliott Charles Randolph founded the company as Randolph & Co. He had been an apprentice at the Clyde shipyard of Robert Napier, and at Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paisley, Renfrewshire
Paisley ( ; ; ) is a large town situated in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Located north of the Gleniffer Braes, the town borders the city of Glasgow to the east, and straddles the banks of the White Cart Water, a tributary of the River Clyde. It serves as the administrative centre for the Renfrewshire council areas of Scotland, council area, and is the largest town in the counties of Scotland, historic county of the Renfrewshire (historic), same name. It is often cited as "Scotland's largest town" and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, fifth largest settlement in the country, although it does not have city status. The town became prominent in the 12th century, with the establishment of Paisley Abbey, an important religious hub which formerly had control over other local churches. Paisley expanded significantly during the Industrial Revolution as a result of its location beside White Cart Water, with access to the Clyde and nearby ore, mineral and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanna, Donald & Wilson
Hanna, Donald and Wilson were a Scottish engineering and shipbuilding firm which flourished in the Victorian era. Reid & Hanna The general engineering firm of Reid & Hanna was founded in 1816 in Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, Scotland. Paisley had become an important industrial town in the late 18th century. By the mid-19th century weaving would become the town's principal industry. Of course the textile industry created opportunities for local machine factories and / or repair shops. Reid & Hanna might have been a company that just catered to the needs of the local textiles industry. Paisley was also a traditional center for shipbuilding. It is connected to the River Clyde, Clyde by the modest River Cart. When ships became too big for the River Cart, the local maritime industry adapted to building small vessels, specialising, or building "knock down" vessels. In July 1834 Reid & Hanna were reported to have finished a very beautiful sheet iron gig for use on the Paisley Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cowes
Cowes () is an England, English port, seaport town and civil parish on the Isle of Wight. Cowes is located on the west bank of the estuary of the River Medina, facing the smaller town of East Cowes on the east bank. The two towns are linked by the Cowes Floating Bridge, a cable ferry, chain ferry. Cowes has a population of 14,370 according to the United Kingdom Census 2021, 2021 Census. Charles Godfrey Leland's 19th-century verses describe the towns poetically as "The two great Cowes that in loud thunder roar/This on the eastern, that the western shore". Cowes has been seen as a home for international yacht racing since the founding of the Royal Yacht Squadron in 1815. It gives its name to the world's oldest regular regatta, Cowes Week, which occurs annually in the first week of August. Later, powerboat races are held. Much of the town's architecture is still heavily influenced by the style of ornate building that Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert popularised. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkenhead
Birkenhead () is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, Merseyside, England. The town is on the Wirral Peninsula, along the west bank of the River Mersey, opposite Liverpool. It lies within the Historic counties of England, historic county boundaries of Cheshire, and became part of Merseyside in 1974. At the 2021 United Kingdom census, 2021 census, the built up area as defined by the Office for National Statistics had a population of 109,835. Birkenhead Priory and the Mersey Ferry were established in the 12th century. In the 19th century, Birkenhead expanded greatly as a consequence of the Industrial Revolution, leading to a shipbuilding firm which became Cammell Laird. A Great Float, seaport was established. As the town grew, Birkenhead Park and Hamilton Square were laid out. The first street tramway in Britain was built, followed by the Mersey Railway which connected Birkenhead and Liverpool through the world's first railway tunnel beneath a tidal estuary. In the sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laird Brothers
Cammell Laird is a British shipbuilding company. It was formed from the merger of Laird Brothers of Birkenhead and Johnson Cammell & Co of Sheffield at the turn of the twentieth century. The company also built railway rolling stock until 1929, when that side of the business was separated and became part of the Metropolitan-Cammell Carriage & Wagon Company. History Formation from merger of Laird Company and Cammell & Co. The Laird Company was founded by William Laird, who had established the Birkenhead Iron Works in 1824. When he was joined by his son, John Laird in 1828, their first ship was an iron barge. John realised that the techniques of making boilers could be applied to making ships. The company soon became pre-eminent in the manufacture of iron ships and also made major advances in propulsion. In 1860, John Laird was joined in the business by his three sons, renaming the company John Laird, Sons & Co. The sons continued the business after their father's death in 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar, London
Poplar is a district in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets. It is located five miles (8 km) east of Charing Cross and lies on the western bank of the River Lea. Poplar is identified as a major district centre in the London Plan, with its centre being Chrisp Street Market, a significant commercial and retail centre surrounded by extensive residential development. Originally part of the Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, the ''Hamlet of Poplar'' had become an autonomous area of Stepney by the 17th century, and an independent parish in 1817, the Parish and later Metropolitan Borough of Poplar. After a series of mergers, Poplar became part of the London Borough of Tower Hamlets in 1965. History Origin and administrative history Poplar was formerly part of the Manor and Ancient Parish of Stepney, and was first recorded in either 1327''The History of the Countryside'', Oliver Rackham, 1986, p207 or 1350. It took its name from the Black Poplar trees which once flourished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yarrow Shipbuilders
Yarrow Shipbuilders Limited (YSL), often styled as simply Yarrows, was a major shipbuilding firm based in the Scotstoun district of Glasgow on the River Clyde. It is now part of BAE Systems Surface Ships, owned by BAE Systems, which has also operated the nearby Kvaerner Govan, Govan shipyard (formerly Fairfields) since 1999. History Origins in London The company was founded by Alfred Yarrow, later Sir Alfred Yarrow, Yarrow Baronets, 1st Baronet, in the year 1865 as Yarrow & Company, Limited. Originally it was based at Folly Wall, Poplar, London, Poplar, then in 1898 as the company grew, Yarrow moved his shipyard to London Yard, Cubitt Town.History of London Yard by Angela Brown and Ron Coverson, 2001 Hundreds of steam launches, lake and river vessels, and eventually the Royal Navy's first destroyers, the , were built at Yarro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiswick
Chiswick ( ) is a district in West London, split between the London Borough of Hounslow, London Boroughs of Hounslow and London Borough of Ealing, Ealing. It contains Hogarth's House, the former residence of the 18th-century English artist William Hogarth, Chiswick House, a neo-Palladian villa regarded as one of the finest in England and Fuller's Brewery, London's largest and oldest brewery. In a meander of the River Thames used for competitive and recreational rowing, with several rowing clubs on the river bank, the finishing post for the Boat Race is just downstream of Chiswick Bridge. Old Chiswick was an St Nicholas Church, Chiswick, ancient parish in the county of Middlesex, with an agrarian and fishing economy beside the river; from the Early Modern period, the wealthy built imposing riverside houses on Chiswick Mall. Having good communications with London, Chiswick became a popular country retreat and part of the suburban growth of London in the late 19th and early 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |