|
Paisley, Renfrewshire
Paisley ( ; ; ) is a large town situated in the west central Lowlands of Scotland. Located north of the Gleniffer Braes, the town borders the city of Glasgow to the east, and straddles the banks of the White Cart Water, a tributary of the River Clyde. It serves as the administrative centre for the Renfrewshire council areas of Scotland, council area, and is the largest town in the counties of Scotland, historic county of the Renfrewshire (historic), same name. It is often cited as "Scotland's largest town" and is the List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, fifth largest settlement in the country, although it does not have city status. The town became prominent in the 12th century, with the establishment of Paisley Abbey, an important religious hub which formerly had control over other local churches. Paisley expanded significantly during the Industrial Revolution as a result of its location beside White Cart Water, with access to the Clyde and nearby ore, mineral and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxing The Compass
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 "points" (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points or compass directions are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose * The four cardinal direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Areas Of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" (), which are all governed by single-tier authorities designated as "councils". They have the option under the Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Scotland) Act 1997 of being known (but not re-designated) as a "''comhairle''" when opting for a Gaelic name; only ''Comhairle nan Eilean Siar'' (Council of the Western Isles) has chosen this option, whereas the Highland Council (''Comhairle na Gàidhealtachd'') has adopted its Gaelic form alongside its English equivalent, informally. The council areas have been in existence since 1 April 1996, under the provisions of the Local Government etc. (Scotland) Act 1994. Historically, Scotland was divided into 34 counties or shires. Although these no longer have any administrative function, they are still used to some extent in Scotland for cultural and geographical purposes, and some of the current council areas are named after them. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
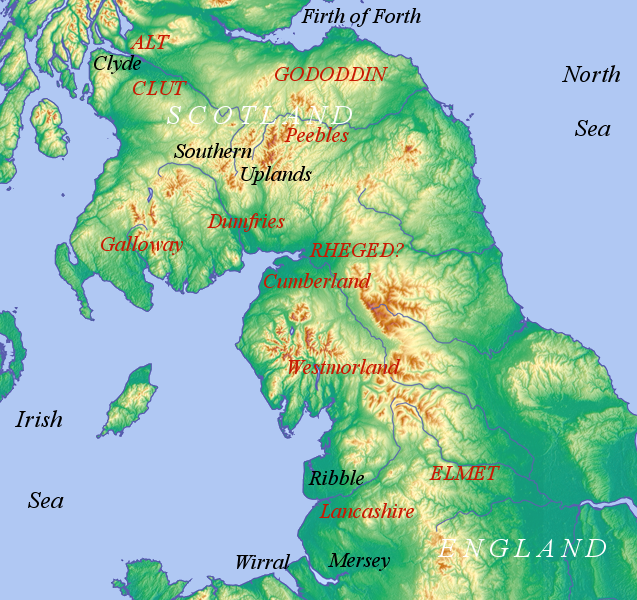
Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the other Brittonic languages. Place-name evidence suggests Cumbric may also have been spoken as far south as Pendle and the Yorkshire Dales. The prevailing view is that it became extinct in the 12th century, after the incorporation of the Kingdom of Strathclyde into the Kingdom of Scotland. Problems with terminology Dauvit Broun sets out the problems with the various terms used to describe the Cumbric language and its speakers.Broun, Dauvit (2004): 'The Welsh identity of the kingdom of Strathclyde, ca 900-ca 1200', ''Innes Review'' 55, pp 111–80. The people seem to have called themselves the same way that the Welsh called themselves (most likely from reconstructed Brittonic meaning "fellow countrymen"). The Welsh and the Cumbric-speaki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittonic Languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; ; ; and ) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic languages; the other is Goidelic. It comprises the extant languages Breton, Cornish, and Welsh. The name ''Brythonic'' was derived by Welsh Celticist John Rhys from the Welsh word , meaning Ancient Britons as opposed to an Anglo-Saxon or Gael. The Brittonic languages derive from the Common Brittonic language, spoken throughout Great Britain during the Iron Age and Roman period. In the 5th and 6th centuries emigrating Britons also took Brittonic speech to the continent, most significantly in Brittany and Britonia. During the next few centuries, in Celtic language decline in England, much of Britain the language was replaced by Old English and Scottish Gaelic, with the remaining Common Brittonic language splitting into regional dialects, eventually evolving into Welsh, Cornish, Breton, Cumbric, and probably Pictish. Welsh and Breton continue to be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coates Memorial Church, Paisley, Scotland LOC 3449508871 , a villa ...
Coates may refer to: People *Coates (surname) Places United Kingdom * Coates, Cambridgeshire * Coates, Gloucestershire * Coates, Lancashire * Coates, Nottinghamshire * Coates, West Sussex * Coates by Stow, in Lincolnshire * Coates Castle, a Grade II listed manor in West Sussex United States * Coates, Minnesota Other * Coates graph, a kind of flow graph associated with the solution of a system of linear equations * Coates Hire, an Australian equipment hire company * Coates (supercomputer), a supercomputer at Purdue University * Coates' disease, occasional spelling for Coats' disease, a rare human eye disorder See also * Coate (other) * Cotes (other) * Coats (other) * Great Coates Great Coates is a Villages in the UK, village and civil parish in North East Lincolnshire, England. It is to the north-west and adjoins the Grimsby urban area, and is served by Great Coates railway station. The northern part of the parish exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Glasgow
Greater Glasgow is an urban settlement in Scotland consisting of all localities which are physically attached to the city of Glasgow, forming with it a single contiguous urban area (or conurbation). It does not relate to municipal government boundaries, and its territorial extent is defined by National Records of Scotland, which determines settlements in Scotland for census and statistical purposes. Greater Glasgow had a population of 1,199,629 at the time of the 2001 UK Census making it the largest urban area in Scotland and the fifth- largest in the United Kingdom. However, the population estimate for the Greater Glasgow 'settlement' (a chain of continuously populated postcodes) in mid-2016 was 985,290—the reduced figure explained by the removal of the Motherwell & Wishaw (124,790), Coatbridge & Airdrie (91,020), and Hamilton (83,730) settlement areas east of the city due to small gaps between the populated postcodes. The 'new towns' of Cumbernauld (which had a 2016 sett ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paisley (design)
Paisley or paisley pattern is an ornamental textile design using the ''Buta (ornament), boteh'' () or ''buta'', a teardrop-shaped motif with a curved upper end. Of Culture of Iran, Persian origin, paisley designs became popular in the West in the 18th and 19th centuries, following imports of post-Mughal Empire versions of the design from India, especially in the form of Kashmir shawls, and were then replicated locally. The English name for the patterns comes from the town of Paisley, Renfrewshire, Paisley, in the west of Scotland, a centre for textiles where paisley designs were reproduced using Jacquard machine, jacquard looms. The pattern is still commonly seen in Britain and other English-speaking countries on neckties, waistcoats, and scarves, and remains popular in other items of clothing and textiles in Iran and South Asia, South and Central Asian countries. Origins Some design scholars believe the ''buta'' is the convergence of a stylized floral spray and a Cupressus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paisley Shawl
Paisley shawls were a fashionable item of women's clothing in Europe during the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Many were made of intricately woven and delicate wool, as well as examples being printed onto silks, wools, and cotton. These pieces were highly decorative. Although now known as the Paisley (design), Paisley pattern, the teardrop motif originated in Persia and India, becoming popular in Europe—and synonymous with Paisley, Renfrewshire, therefore earning name-association with the town—in the nineteenth century. History The Paisley shawl has its antecedents in the Kashmir shawl, produced in Kashmir, since the eleventh century, and more intensively in central Asia in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries. In the eighteenth century, travel, trade, and colonisation, namely by the British East India Company, saw examples of Kashmir shawls brought back to Europe. Around 1805, the first shawls in imitation of Kashmir originals were produced in Paisley, Renfr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products are created with one of three basic weaves: plain weave, satin weave, or twill weave. Woven cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical War
The Radical War, also known as the Scottish Insurrection of 1820, was a week of strikes and unrest in Scotland, a culmination of Radical demands for reform in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland which had become prominent in the early years of the French Revolution, but had then been repressed during the long Napoleonic Wars. An economic downturn after the wars ended brought increasing unrest, but the root cause was the Industrial Revolution. Artisan workers, particularly weavers in Scotland, sought action to force the government to enact Luddite protective restrictions. Gentry fearing revolutionary horrors recruited militia and the government deployed an apparatus of spies, informers and agents provocateurs to stamp out the movement. A ''Committee of Organisation for Forming a Provisional Government'' put placards around the streets of Glasgow late on Saturday 1 April, calling for an immediate national strike. On Monday, 3 April, work stopped in a wide area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radicalism (historical)
Radicalism (from French ) was a political movement representing the leftward flank of liberalism between the late 18th and early 20th century. Certain aspects of the movement were precursors to a wide variety of modern-day movements, ranging from '' laissez-faire'' to social liberalism, social democracy, civil libertarianism, and modern progressivism. This ideology is commonly referred to as "radicalism" but is sometimes referred to as radical liberalism, or classical radicalism, to distinguish it from radical politics. Its earliest beginnings are to be found during the English Civil War with the Levellers and later the Radical Whigs. During the 19th century in the United Kingdom, continental Europe and Latin America, the term ''radical'' came to denote a progressive liberal ideology inspired by the French Revolution. Radicalism grew prominent during the 1830s in the United Kingdom with the Chartists and in Belgium with the Revolution of 1830, then across Europe in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succeeding the Second Agricultural Revolution. Beginning in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain around 1760, the Industrial Revolution had spread to continental Europe and the United States by about 1840. This transition included going from craft production, hand production methods to machines; new Chemical industry, chemical manufacturing and Puddling (metallurgy), iron production processes; the increasing use of Hydropower, water power and Steam engine, steam power; the development of machine tools; and rise of the mechanisation, mechanised factory system. Output greatly increased, and the result was an unprecedented rise in population and population growth. The textile industry was the first to use modern production methods, and textiles b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |