|
265 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 265 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Gurges and Vitulus (or, less frequently, year 489 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 265 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Greece * Although the Egyptian fleet blockades the Saronic Gulf, the Macedonian King Antigonus II defeats the Spartans and kills the king of Sparta, Areus I near Corinth, after which he besieges Athens. * Acrotatus II succeeds his father Areus I as king of Sparta. Italy * Hiero II threatens to renew his attack on the Mamertines. They appeal to Carthage and receive the support of a Carthaginian garrison. The Mamertines also appeal to the Romans who are also willing to help. * The Battle of Messana (265- 264 BCE) takes place as the first military clash between the Roman Republic and Cart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Areus I
Areus I (; 320 or 312 – 265 BC) was Agiad King of Sparta from 309 to 265 BC. His reign is noted for his attempts to transform Sparta into a Hellenistic period, Hellenistic kingdom and to recover its former pre-eminence in Ancient Greece, Greece, notably against the kings Antigonus II Gonatas, Antigonos Gonatas of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonia and Pyrrhus of Epirus, Pyrrhus of Epirus (ancient state), Epirus. The first part of Areus' reign was dominated by the influence of his uncle and regent Cleonymus of Sparta, Cleonymus, a skilled general who campaigned in Greece and abroad at the head of mercenary armies. Areus' first record in the scanty ancient sources took place in 281 BC, when he led an alliance of Greek city-states to challenge Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedonian control over Greece, but was rapidly defeated by the Aetolian League, Aitolian League (allied with Macedonia). In 275 BC, Cleonymus defected to Pyrrhus of Epirus, who launched an invasion of the Pel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Roman Calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. Although the term is primarily used for Rome's pre-Julian calendars, it is often used inclusively of the Julian calendar established by Julius Caesar in 46 BC. According to most Roman accounts, #Romulus, their original calendar was established by their Roman legend, legendary list of kings of Rome, first king Romulus. It consisted of ten months, beginning in spring with March and leaving winter as an unassigned span of days before the next year. These months each had 30 or 31 days and ran for 38 nundinal cycles, each forming a kind of eight-day weeknine days inclusive counting, counted inclusively in the Roman mannerand ending with religious rituals and a Roman commerce, public market. This fixed calendar bore traces of its origin as an observational calendar, observational lunar calendar, lunar one. In particular, the most important days of each monthits kalends, nones (calendar), nones, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Battle Of Messana
The Battle of Messana in 264 BC was the first military clash between the Roman Republic and Carthage. It marked the start of the First Punic War. In that period, and after the recent successes in southern Italy, Sicily became of increasing strategic importance to Rome. Background The Greek historian Polybius states in Book One of '' The Histories'': "Even after long consideration, the (Roman) Senate did not approve the proposal to send help to Messana; they took the view that any advantage which would result from relieving the place would be counterbalanced by the inconsistency of such an action. However, the people who had suffered grievously from the wars that had just ended and were in dire need of rehabilitation of every kind, were inclined to listen to the consuls. These men, besides stressing the national advantages Rome could secure if she intervened, also dwelt on the great gains which would clearly accrue to every individual citizen from the spoils of war, and so a resol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ziaelas Of Bithynia
Ziaelas (; lived c. 265 BC – 228 BC, reigned c. 254 BC – 228 BC), third king of Bithynia, was a son of Nicomedes I and Ditizele. Life Following the death of Nicomedes I, his second wife Etazeta of Bithynia acted as regent on behalf of her infant sons. Nicomedes' adult son from his first marriage Ziaelas, was denied the chance to ascend the throne, leading him to flee to Armenia and take refuge at the court of King Arsames I in Sophene. Upon his father's death he immediately endeavored to regain his rights by force, and returned, aided by some Galatians. Although Etazeta was supported by neighboring cities and Antigonus II Gonatas, Ziaelas rapidly conquered Bithynia, forcing Etazeta and her sons to escape to the court of Antigonus in about 254 BC. During the Fraternal War between Seleucus II Callinicus and Antiochus Hierax, he seized the opportunity to attack the latter, trying to conquer Asia Minor They later became allies and his daughter, born c. 245 BC, married Hiera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
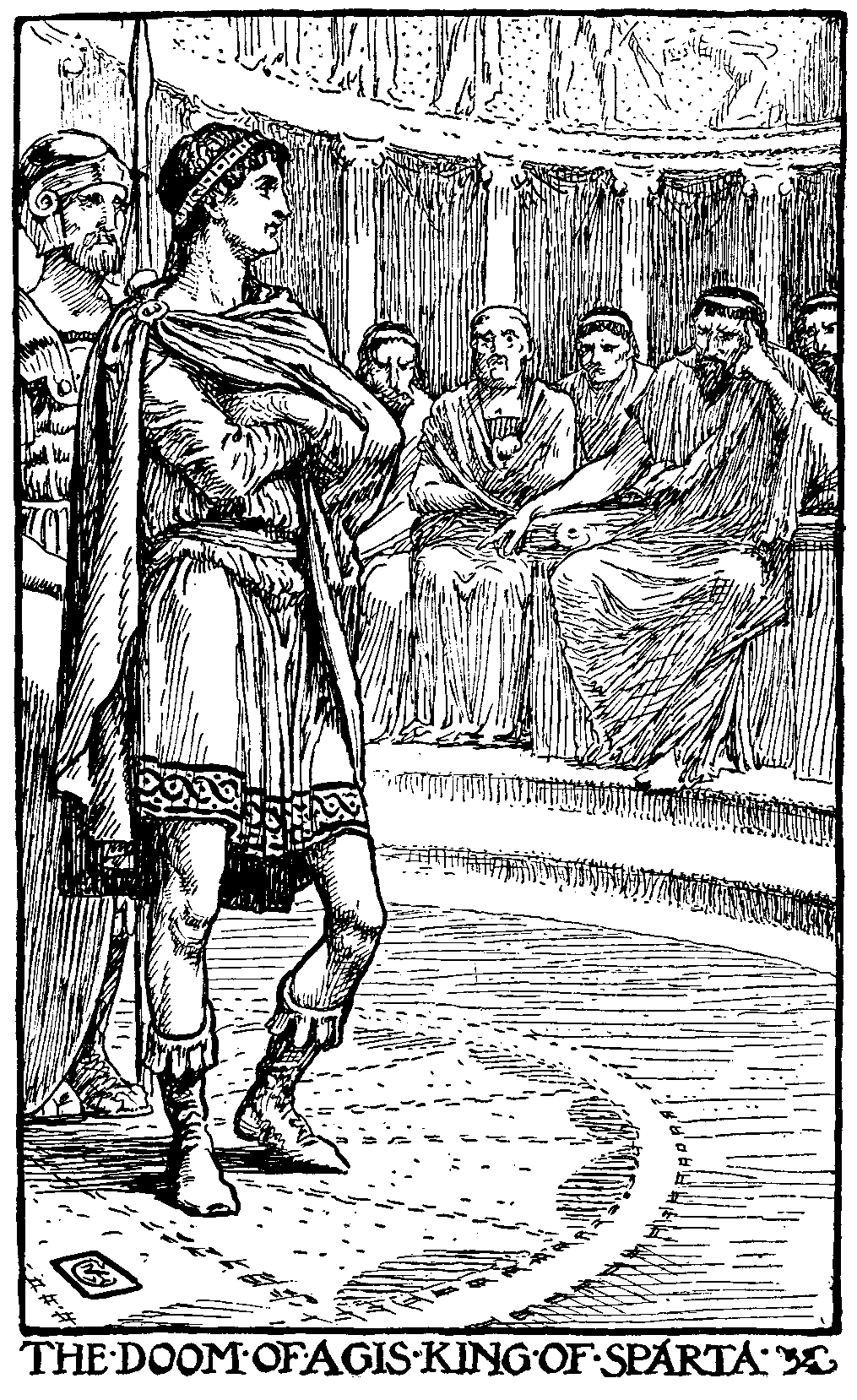
Agis IV
Agis IV (; c. 265 BC – 241 BC), the elder son of Eudamidas II, was the 25th king of the Kings of Sparta, Eurypontid dynasty of Sparta. Posterity has reckoned him an idealistic but impractical monarch. Family background and accession Agis was the son of Eudamidas II () and grandson of Archidamus IV (), who belonged to the List of kings of Sparta, Eurypontid dynasty, one of the two royal families of Sparta (the other being the Agiads). The reign of Agis marks a re-emergence of the Eurypontids, who had disappeared from the records since the defeat of Archidamus IV against Demetrius I of Macedon, Demetrios Poliorketes in 294. His father is indeed the most obscure of all the Spartan kings, perhaps due to a mental or physical disability. Eudamidas II's dates of reign are therefore very conjectural. The traditional year of his death is c.245, but he may have died earlier (up to 263), in which case a regent was appointed during Agis' minority, as he was born c.265. The most likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile Delta, Nile River delta. Founded in 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilisation, eventually replacing Memphis, Egypt, Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" and "Pearl of the Mediterranean Coast" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and petroleum, oil pipeline transport, pipelines from Suez. The city extends about along the northern coast of Egypt and is the largest city on the Mediterranean, the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second-largest in Egypt (after Cairo), the List of largest cities in the Arab world, fourth- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenistic Sicily, Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, based on his surviving work, he is considered one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity, and one of the greatest mathematicians of all time. Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and mathematical analysis, analysis by applying the concept of the Cavalieri's principle, infinitesimals and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove many geometry, geometrical theorem, theorems, including the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Archimedes' other math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archimedes' Screw
The Archimedes' screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest documented hydraulic machines. It was so-named after the Greek mathematician Archimedes who first described it around 234 BC, although the device had been developed in Egypt earlier in the century. It is a reversible hydraulic machine that can be operated both as a pump or a power generator. As a machine used for lifting water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches, water is lifted by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe. In the modern world, Archimedes screw pumps are widely used in wastewater treatment plants and for dewatering low-lying regions. Run in reverse, Archimedes screw turbines act as a new form of small hydroelectric powerplant that can be applied even in low head sites. Such generators operate in a wide range of flows (0.01 m^3/s to 14.5 m^3/s) and heads (0.1 m to 10 m), including low heads and moderate flow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Li Mu
Li Mu (; died 229 BC), personal name Zuo (繓), courtesy name Mu (牧), was a Chinese military General of the State of Zhao during the Warring States period. He is regarded by Chinese folklore as one of the four Greatest Generals of the Late Warring States period, along with Bai Qi, Wang Jian, and Lian Po. He is widely considered as one of the best defensive tacticians commanders of ancient warfare. Life In 265 BC, Li Mu was stationed in Yanmen Commandery and ordered to defend northwestern commanderies of Yanshan (雁山) and Daijun (代郡) from raids instigated by the Xiongnu (匈奴) and other tribes. He initially adopted an extremely defensive strategy, for which he was accused of cowardice and thereafter replaced by a more aggressive general. The Zhao state prepared an army of 1,300 war chariots, 13,000 cavalry, 50,000 infantry and 100,000 archers. The army was scattered in the countryside. The Xiongnu sent a small force to raid the border, and Li Mu pretended to be de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
State Of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the tripartite division of Jin, along with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military reforms initiated during the reign of King Wuling, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas in the modern provinces of Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei, and Yan, as well as various nomadic peoples including the Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei province. Zhao was home to the administrative philosopher Shen Dao, Confucian Xun Kuang, and Gongsun Long, who is affiliated to the school of names. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao clan within Jin had been accumulating power for centuries, including annexing the Baidi state of Dai in the mid-5th At the end of the Spring and Autumn period, Jin was d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges (consul 265 BC)
Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges was Roman consul in 265 BC, and died of wounds received in battle at Volsinii, where he had been sent to help put down a revolt. There is some uncertainty as to his identity.Broughton, pp. 200–202. Controversy Traditionally the consul of 265 has been identified as the same Quintus Fabius Maximus Gurges who had previously been consul in 292 and 276 BC. This Gurges was the son of Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus, and is usually regarded as the father of Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus. Livy describes Verrucosus as the grandson of Rullianus, and thus the son of Gurges, but passages in Plutarch and Pliny referring to Verrucosus as the great-grandson of Rullianus imply the existence of an intervening generation. Although Verrucosus is said to have served as an augur for sixty-two years at the time of his death in 203 BC, and thus would have been at least a young man in 265, the interval between his first consulship, in 233 BC, and that of Gurges, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |