|
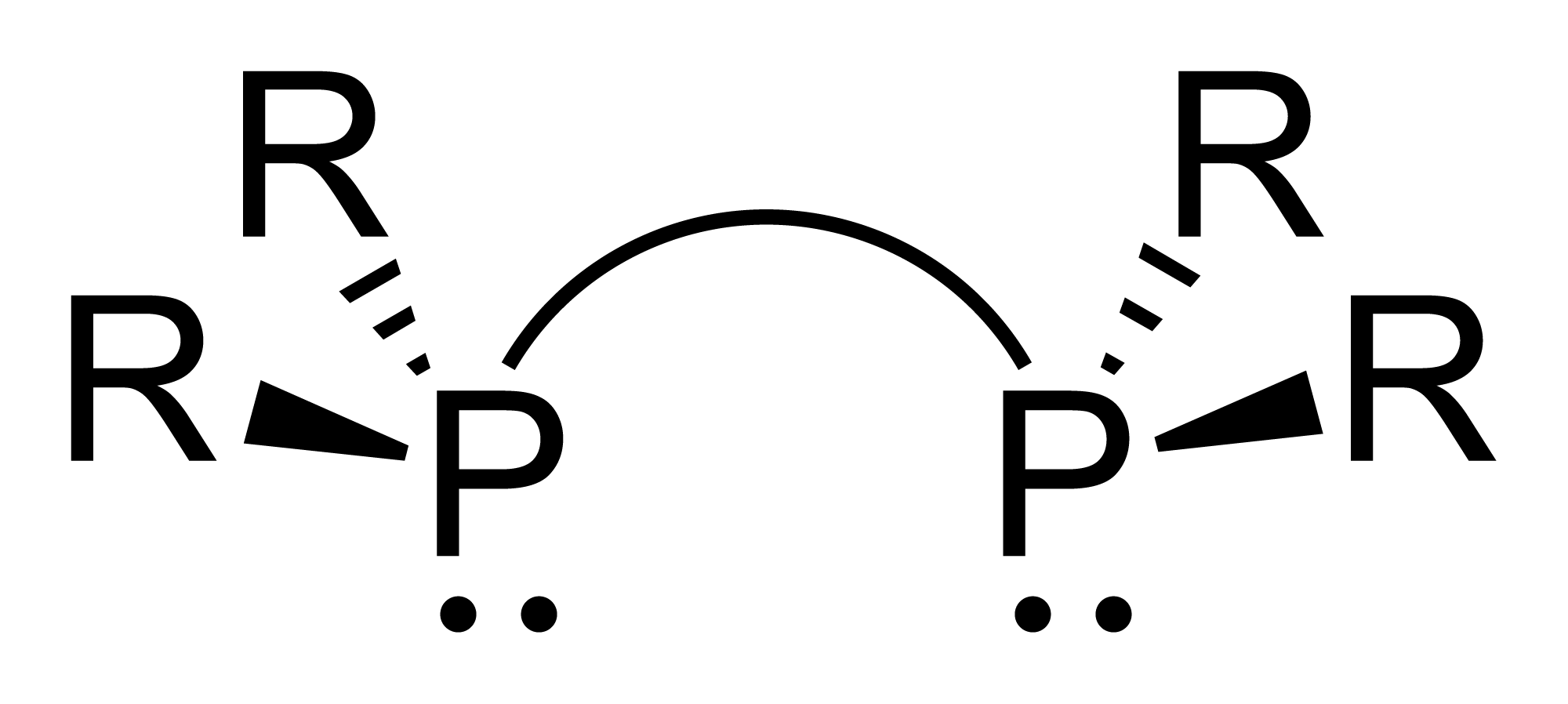
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula PhP(CH)PPh. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is classified as a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry and homogeneous catalysis. The diphosphine can be prepared by the reaction of lithium diphenylphosphide and 1,3-dichloropropane (Ph = CH): : 2 PhPLi + CHCl → PhP(CH)PPh + 2 LiCl However, it can be synthesised via a much more controllable (and cheaper) route, via metal-halogen exchange and then metathesis: :Br(CH)Br + 2 BuLi → Li(CH)Li + 2 BuBr :Li(CH)Li + 2 PCl → ClP(CH)PCl + 2 LiCl :ClP(CH)PCl + 4 PhLi → PhP(CH)PPh + 4 LiCl Coordination chemistry and use as co-catalyst The diphosphine serves as a bidentate ligand forming six-membered CPM chelate ring with a natural bite angle of 91°. For example, the complex dichloro(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane)nic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyketone
Polyketones are a family of high-performance thermoplastic polymers. The polar ketone groups in the polymer backbone of these materials gives rise to a strong attraction between polymer chains, which increases the material's melting point (255 °C for copolymer (carbon monoxide ethylene), 220 °C for terpolymer (carbon monoxide, ethylene, propylene). Trade names include Poketone, Carilon, Karilon, Akrotek, and Schulaketon. Such materials also tend to resist solvents and have good mechanical properties. Unlike many other engineering plastics, aliphatic polyketones such as Shell Chemicals' Carilon are relatively easy to synthesize and can be derived from inexpensive monomers. Carilon is made with a palladium(II) catalyst from ethylene and carbon monoxide. A small fraction of the ethylene is generally replaced with propylene to reduce the melting point somewhat. Shell Chemical commercially launched Carilon thermoplastic polymer in the U.S. in 1996, but discontinued it in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
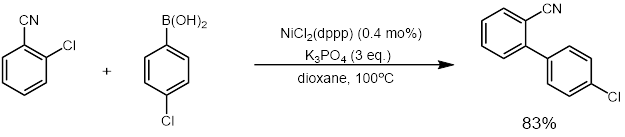
Dichloro(1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane)nickel
Dichloro ,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propaneickel a coordination complex with the formula NiCl2(dppp); where dppp is the diphosphine 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane. It is used as a catalyst in organic synthesis. The compound is a bright orange-red crystalline powder. Structure and properties While the electronic and solid-state structure of the chloride congener is not known (due to low solubility in common analytical solvents), several studies have been carried out on the bromo and iodo derivatives. The complexes display a temperature-dependent interconversion between square-planar and tetrahedral geometries (diamagnetic and paramagnetic) in polar organic solvents (Keq between 1-3.68, depending on the solvent and temperature). In contrast, dichloro(1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane)nickel adopts a static square-planar (diamagnetic) structure in solution. Preparation NiCl2(dppp) is prepared by combining equal molar portions of nickel(II) chloride hexahydrate with 1,3-bis(diphe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphosphines
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts. Synthesis 222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines. From phosphide building blocks Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Chemistry
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of chemical bond, bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing chemical compound, compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Block (periodic table), Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A Ligand#Polydentate and polyhapto ligand motifs and nomenclature, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Catalysis
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts. Examples Acid catalysis The proton is a pervasive homogeneous catalyst because water is the most common solvent. Water forms protons by the process of self-ionization of water. In an illustrative case, acids accelerate (catalyze) the hydrolysis of esters: :CH3CO2CH3 + H2O CH3CO2H + CH3OH At neutral pH, aqueous solutions of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Diphenylphosphide
Lithium diphenylphosphide contains lithium and the organophosphorus anion with the formula (C6H5)2PLi. It is an air-sensitive solid that is used in the preparation of diphenylphosphino compounds. As an ether complex, the lithium salt is dark red. Synthesis and reactions The lithium, sodium, and potassium salts are prepared by reduction of chlorodiphenylphosphine, triphenylphosphine, or tetraphenyldiphosphine with alkali metals (M): :(C6H5)2PCl + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MCl :(C6H5)3P + 2 M → (C6H5)2PM + MC6H5 :(C6H5)4P2 + 2 M → 2 (C6H5)2PM They can also be obtained by deprotonation of diphenylphosphine. With water, the salts convert to diphenylphosphine: :(C6H5)2PLi + H2O → (C6H5)2PH + LiOH With halocarbons, the salts react to give tertiary phosphines: :(C6H5)2PM + RX → (C6H5)2PR + MX When treated with metal halides, lithium diphenylphosphide gives transition metal phosphido complexes A transition metal phosphido complex is a coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidentate Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bite Angle
In coordination chemistry the bite angle is the ligand–metal–ligand bond angle of coordination complex containing a bidentate ligand. This geometric parameter is used to classify chelating ligands, including those in organometallic complexes. It is most often discussed in terms of catalysis, as changes in bite angle can affect not just the activity and selectivity of a catalytic reaction but even allow alternative reaction pathways to become accessible. Although the parameter can be applied generally to any chelating ligand, it is commonly applied to describe diphosphine ligands, as they can adopt a wide range of bite angles. Diamines Diamines form a wide range of coordination complexes. They typically form 5- and 6-membered chelate rings. Examples of the former include ethylenediamine and 2,2′-bipyridine. Six-membered chelate rings are formed by 1,3-diaminopropane. The bite angle in such complexes is usually near 90°. Longer chain diamines, which are "floppy", tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-sensitive
Air sensitivity is a term used, particularly in chemistry, to denote the reactivity of chemical compounds with some constituent of air. Most often, reactions occur with atmospheric oxygen (O2) or water vapor (H2O), although reactions with the other constituents of air such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), and nitrogen (N2) are also possible. Method A variety of air-free techniques have been developed to handle air-sensitive compounds. Two main types of equipment are gloveboxes and Schlenk lines. Glove boxes are sealed cabinets filled with an inert gas such as argon or nitrogen. Normal laboratory equipment can be set up in the glovebox, and manipulated by the use of gloves that penetrate its walls. The atmosphere can be regulated to approximately atmospheric pressure and set to be pure nitrogen or other gas with which the chemicals will not react. Chemicals and equipment can be transferred in and out via an airlock. A Schlenk line is a vacuum and inert-gas dual-man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel(II) Chloride
Nickel(II) chloride (or just nickel chloride) is the chemical compound NiCl2. The anhydrous salt is yellow, but the more familiar hydrate NiCl2·6H2O is green. Nickel(II) chloride, in various forms, is the most important source of nickel for chemical synthesis. The nickel chlorides are deliquescent, absorbing moisture from the air to form a solution. Nickel salts have been shown to be carcinogenic to the lungs and nasal passages in cases of long-term inhalation exposure. Production and syntheses The largest scale production of nickel chloride involves the extraction with hydrochloric acid of nickel matte and residues obtained from roasting refining nickel-containing ores. Nickel chloride is not usually prepared in the laboratory because it is inexpensive and has a long shelf-life. Heating the hexahydrate in the range 66–133.°C gives the yellowish dihydrate, NiCl2·2H2O. The hydrates convert to the anhydrous form upon heating in thionyl chloride or by heating under a stre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumada Coupling
In organic chemistry, the Kumada coupling is a type of cross coupling reaction, useful for generating carbon–carbon bonds by the reaction of a Grignard reagent and an organic halide. The procedure uses transition metal catalysts, typically nickel or palladium, to couple a combination of two alkyl, aryl or vinyl groups. The groups of Robert Corriu and Makoto Kumada reported the reaction independently in 1972. The reaction is notable for being among the first reported catalytic cross-coupling methods. Despite the subsequent development of alternative reactions (Suzuki, Sonogashira, Stille, Hiyama, Negishi), the Kumada coupling continues to be employed in many synthetic applications, including the industrial-scale production of aliskiren, a hypertension medication, and polythiophenes, useful in organic electronic devices. History The first investigations into the catalytic coupling of Grignard reagents with organic halides date back to the 1941 study of cobalt catalyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




4-3D-balls.png)
-3D-balls.png)

_complexes_in_aqueous_solution.jpg)
