Diphosphines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
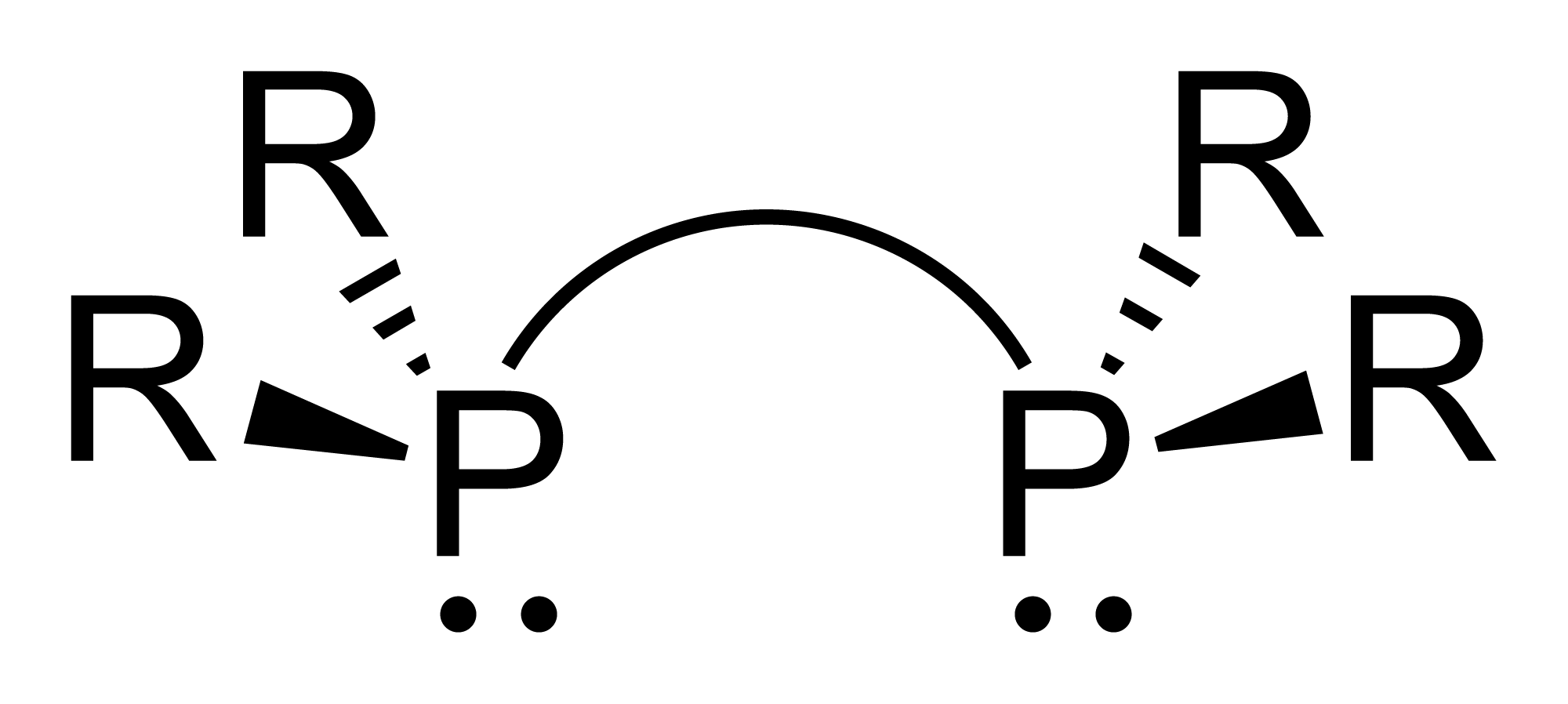 Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are
(from which abbreviation derived) !Structure !Bite Angle , - , dppm , 1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane , , 73
, -
, dmpe
,
, 73
, -
, dmpe
,  ,
, -
, dippe
,
,
, -
, dippe
,  ,
, -
, dppbz
,
,
, -
, dppbz
,
 Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are
Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compound
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective in ...
s most commonly used as bidentate phosphine
Phosphine ( IUPAC name: phosphane) is a colorless, flammable, highly toxic compound with the chemical formula , classed as a pnictogen hydride. Pure phosphine is odorless, but technical grade samples have a highly unpleasant odor like rotti ...
ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule ( functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's ele ...
s in inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemis ...
and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating. A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.
Synthesis
222px, Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is a popular building block for the preparation of diphosphines.From phosphide building blocks
Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal): :Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl Diphosphine ligands can also be prepared from dilithiated reagents and chlorophosphines: :XLi2 + 2 ClPAr2 → X(PAr2)2 + 2 LiCl (X = hydrocarbon backbone) This approach is suitable for installing two dialkylphosphino groups, using reagents such as chlorodiisopropylphosphine. Another popular method, suitable for preparing unsymmetrical diphosphines, involves the addition of secondary phosphines to vinylphosphines: :Ph2PH + 2 CH2=CHPAr2 → Ph2PCH2-CH2PAr2 (2-Lithiophenyl)diphenylphosphine can be used also to give unsymmetrical diphosphines. The lithiated reagent is available from(2-bromophenyl)diphenylphosphine
(2-Bromophenyl)diphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (CHBr)P(CH). It is a white crystalline solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound is used as a precursor to the 2-lithiated derivative of tri ...
:
:Ph2P(C6H4Br) + BuLi → Ph2P(C6H4Li) + BuBr
:Ph2P(C6H4Li) + R2PCli → Ph2P(C6H4PR2) + LiCl
From bis(dichlorophosphine) precursors
Many diphosphines are prepared from compounds of the type X(PCl2)2 where X = (CH2)n or C6H4. The key reagents are1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane
1,2-Bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH2PCl2)2. A colorless liquid, it is a precursor to chelating diphosphines.
Synthesis and reactions
It is prepared by the reaction of ethylene, white phosphorus, a ...
and 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)benzene
1,2-Bis(dichlorophosphino)benzene is an organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H4(PCl2)2. A viscous colorless liquid, it is a precursor to chelating diphosphines of the type C6H4(PR2)2.
It is prepared from 1,2-dibromobenzene by sequential li ...
.
164px, 1,2-Bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane is a key intermediate in the synthesis of 1,2-bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane.
Chain length and coordinating properties
The short-chain diphosphine dppm tends to promote metal-metal interactions as illustrated by A-frame complexes. When the two phosphine substituents are linked by two to four carbon centres, the resulting ligands often chelate rings with a single metal. A common diphosphine ligand is dppe, which forms a five-membered chelate ring with most metals. Some diphosphines, such as the extraordinary case of ''t''Bu2P(CH2)10P''t''Bu2, give macrocyclic complexes with as many as 72 atoms in a ring.Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. ''Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text'', 4th ed.; Wiley-Interscience Publications: New York, NY, 1980; p.246. To position phosphine donor groups trans on a coordination sphere, several atoms are required to link the donor centres and long-chain diphosphines are typically floppy and do not chelate well. This challenge has been resolved by the long but rigid diphosphine SPANphos. The bite angle of the diphosphine influences the reactivity of the metal center. Some examples of non-chelating diphosphine also exist. Due to steric effect, these phosphorus atoms can not react with anything except a proton. It can be changed from non-chelating to chelating diphosphine by tuning the length of the linking arm.Representative ligands
Particularly common diphosphine ligands are shown in the table below:http://old.iupac.org/reports/provisional/abstract04/RB-prs310804/TableVII-3.04.pdf {, class="sortable wikitable" style="background-color:#ffffff;" !Abbreviation !Common name(from which abbreviation derived) !Structure !Bite Angle , - , dppm , 1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane ,
 , 73
, -
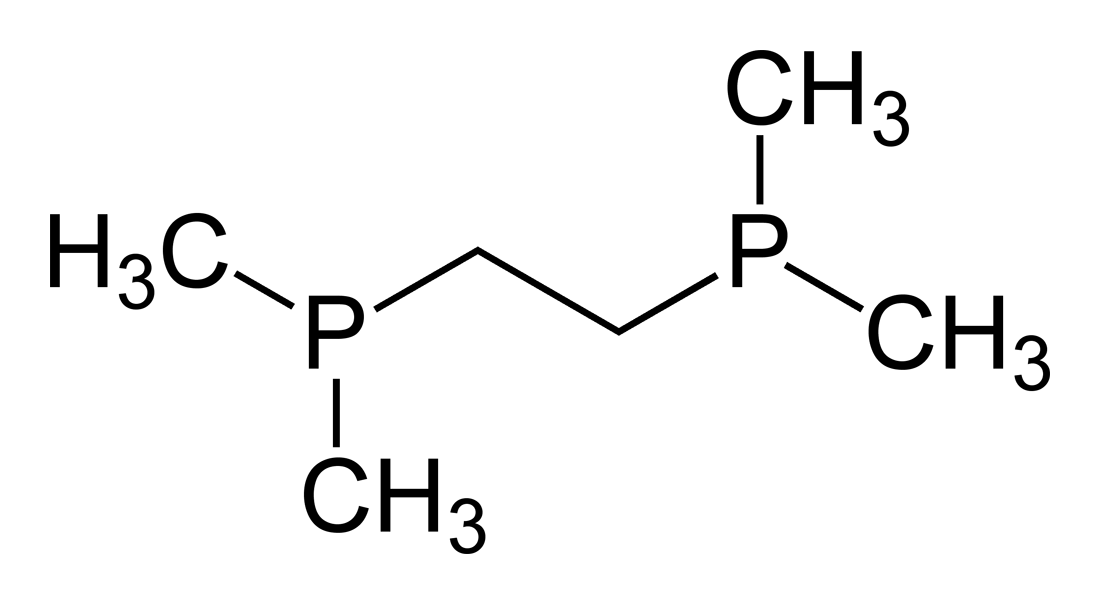
, dmpe
,
, 73
, -
, dmpe
, 1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane
1,2-Bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane (dmpe) is a diphosphine ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a colorless, air-sensitive liquid that is soluble in organic solvents. With the formula (CHPMe), dmpe is used as a compact strongly basic spectator l ...
,  ,
, -
, dippe
,
,
, -
, dippe
, 1,2-Bis(diisopropylphosphino)ethane
1,2-Bis(diisopropylphosphino)ethane (dippe) is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. This compound is similar to the ligand 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane
1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus co ...
,  ,
, -
, dppbz
,
,
, -
, dppbz
, 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene
1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)benzene (dppbz) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula C6H4(PPh2)2 ( Ph = C6H5). Classified as a diphosphine ligand, it is a common bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry
A coordination complex consists ...
,
,
, -
, dppe
, 1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane
1,2-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (PhPCH) (Ph = phenyl). It is a commonly used bidentate ligand in coordination chemistry. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents.
Preparation ...
,
, 86
, -
, DIPAMP
, derivative of phenylanisylmethylphosphine
,
,
, -
, dcpe
, Bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)ethane
Bis(dicyclohexylphosphino)ethane, abbreviated dcpe, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H11)2PCH2CH2P(C6H11)2. It is a white solid that is soluble in nonpolar organic solvents. The compound is used as a bulky and highly basic dip ...
,
,
, -
, dppp
, 1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane
1,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula PhP(CH)PPh. The compound is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is slightly air-sensitive, degrading in air to the phosphine oxide. It is ...
,
, 91
, -
, dppb
, 1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane
1,4-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane (dppb) is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (Ph2PCH2CH2)2. It is less commonly used in coordination chemistry than other diphosphine ligands such as dppe. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic ...
,
, 94
, -
, DIOP
, (S,S)-DIOP (O-isopropylidene-2,3-dihydroxy-1,4-bis(diphenylphosphino)butane)
,
,
, -
, Chiraphos
, 2,3-Bis(diphenylphosphino)butane
Chiraphos is a chiral diphosphine employed as a ligand in organometallic chemistry. This bidentate ligand chelates metals via the two phosphine groups. Its name is derived from its description — being both ''chiral'' and a ''phosphine''. As ...
,
,
, -
, BINAP
, 2,2'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1'-binaphthyl
,
, 93
, -
, Xantphos
, 4,5-Bis(diphenylphosphino)-9,9-dimethylxanthene
,
, 108
, -
, DPEphos
, Bis 2-diphenylphosphino)phenylether
,
, 104
, -
, SPANphos
, 4,4,4',4',6,6'-Hexamethyl-2,2'-spirobichromane-8,8'-diylbis(diphenylphosphane)
,
,
, -
, SEGPHOS
SEGPHOS is a chiral ligand developed by Takasago that is used in asymmetric synthesis. It was developed after BINAP
BINAP (2,2′-bis(diphenylphosphino)-1,1′-binaphthyl) is an organophosphorus compound. This chiral diphosphine ligand is w ...
, 4,4'-Bi-1,3-benzodioxole-5,5'-diylbis(diphenylphosphane)
,
,
, -
, dppf
, 1,1'-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene
1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene, commonly abbreviated dppf, is an organophosphorus compound commonly used as a ligand in homogeneous catalysis. It contains a ferrocene moiety in its backbone, and is related to other bridged diphosphines such ...
,
, 99
, -
, Me-DuPhos
, 1,2-Bis(2,5-dimethylphospholano)benzene
,
,
, -
, Josiphos
, (Diphenylphosphino)ferrocenyl-ethyldicyclohexylphosphine1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes
, ]
,
, -
, P2N2
, 1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes
1,5-Diaza-3,7-diphosphacyclooctanes are organophosphorus compounds with the formula 'NCHP(R)CH often abbreviated PN. They are air-sensitive white solids that are soluble in organic solvents. The ligands exist as meso and d,l-diastereomers, but o ...
,
,
References