|
бјҳПҒОұП„ОҝПғОёОӯОҪО·ПӮ
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; вҖ“ ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria. His work is comparable to the study of geography, and he introduced some of the terminology, even coining the terms geography and geographer. He is best known for being the first person known to calculate the Earth's circumference, which he did by using the extensive survey results he could access in his role at the Library. His calculation was remarkably accurate (his error margin turned out to be less than 1%). He was the first to calculate Earth's axial tilt, which similarly proved to have remarkable accuracy. He created the first global projection of the world, incorporating parallels and meridians based on the available geographic knowledge of his era. Eratosthenes was the founder of scientific chronology; he used Egyptian and Persian records to estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrene, Libya
Cyrene, also sometimes anglicization of names, anglicized as Kyrene, was an ancient Greeks, ancient Greek Greek colonization, colony and ancient Romans, Roman Cities of the Roman Empire, city near present-day Shahhat in northeastern Libya in North Africa. It was part of the Pentapolis (North Africa), Pentapolis, an important group of five cities in the region, and gave the area its classical and early modern name Cyrenaica. Cyrene lies on a ridge of the Jebel Akhdar (Libya), Jebel Akhdar uplands. The archaeological remains cover several hectares and include several monumental temples, stoas, theatres, bathhouses, churches, and palatial residences. The city is surrounded by the Necropolis of Cyrene. Since 1982, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city's port was Apollonia, Cyrenaica, Apollonia (Marsa Sousa), located about to the north. The city was attributed to Apollo and the legendary etymology, etymon Cyrene (mythology), Cyrene by the Greeks themselves but it was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eratosthenes' Map Of The World
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries Common Era, BCE still based on the flat Earth paradigm. World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period. The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy world map, Ptolemy's world map (2nd century CE), which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages. Since Ptolemy, knowledge of the approximate size of the Earth allowed cartographers to estimate the extent of their geographical knowledge, and to indicate parts of the planet known to exist but not yet explored as ''terra incognita''. With the Age of Discovery, during the 15th to 18th centuries, world maps became increasingly accurate; exploration of Antarctica, Australia, and the European exploration of Africa, interior of Africa by western mapmakers was left to the 19th and early 20th century. Antiq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berenice
Berenice (, ''BerenГӯkД“'') is the Ancient Macedonian form of the Attic Greek name ''PherenikД“'', which means "bearer of victory" . Berenika, priestess of Demeter in Lete ca. 350 BC, is the oldest epigraphical evidence. The Latin variant Veronica is a direct transliteration. The name also has the form Bernice. Many historical figures bear the name Berenice: Ancient world Ptolemaic and Seleucid queens and royal daughters in Cyrenaica and Egypt * Berenice I of Egypt ( вҖ“ between 279 and 268 BC), mother of Magas of Cyrene and wife of Ptolemy I of Egypt * Berenice Syra ( вҖ“ 246 BC), daughter of Ptolemy II of Egypt and wife of Seleucid monarch Antiochus II Theos * Berenice II of Egypt (267 or 266 BC вҖ“ 221 BC), daughter of Magas of Cyrene, wife of Ptolemy III of Egypt and traditional namesake of the constellation Coma Berenices * Berenice III of Egypt (120вҖ“80 BC), daughter of Ptolemy IX of Egypt; she first married Ptolemy X of Egypt, and later Ptolemy XI of Egypt * Bere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tocra
Tocra, Taucheira or Tukrah, is a town on the coast of the Marj District in the Cyrenaica region of northeastern Libya, founded by Cyrene. It lay 200 stadia west of Ptolemais. Today it is a coastal town west of Marj. History Founded by the Greeks and considered by some to be part of the Pentapolis of Cyrenaica, at a later period it became a Roman colony (Tab. Peut.), and was fortified by Justinian I. (Procop. ''de Aed.'' vi. 3.) Taucheira was particularly noted for the worship of Cybele, in honour of whom an annual festival was celebrated. (Synes. Ep. 3.) In the city fortifications from the Hellenistic, Roman and Byzantine periods have been found. Name Taucheira, Teucheira, Tauchira or Teuchira (Greek: , ,). Under the Ptolemies it obtained the name of Arsinoe (ArsinoГ«) (Greek: ), after Arsinoe II of Egypt, named by her brother and husband, Ptolemy Philadelphus. Later it became known as Tocra or Tukrah or Tokara, and then Al Quriyah or El Agouriya in Arabic. It is the same t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentapolis (North Africa)
A pentapolis (from Greek ''penta-'', 'five' and ''polis'', 'city') is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities. Cities in the ancient world probably formed such groups for political, commercial and military reasons, as happened later with the Cinque Ports in England. Significant historical cases * The Philistine Pentapolis: Gaza, Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, and Gath, all combined to make Philistia. * In the biblical Holy Land, describes the region where five citiesвҖ” Sodom, Gomorrah, Zoara, Admah and ZeboimвҖ”united to resist the invasion of Chedorlaomer, and of which four were shortly after destroyed. * The DoricвҖ”or Dorian Pentapolis: Kos, on the island of the same name in the Aegean Sea; Knidos, in Caria on the west coast of Asia Minor; Lindus, Ialysus and Camirus, all three on Rhodes. * The Phrygian Pentapolis: Eukarpia, Hierapolis, Otrus, Bruzus, and Stectorium. * The Pontic Pentapolis: Apollonia, Callatis, Mesembria, Odessos, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrene (city)
Cyrene, also sometimes anglicized as Kyrene, was an ancient Greek colony and Roman city near present-day Shahhat in northeastern Libya in North Africa. It was part of the Pentapolis, an important group of five cities in the region, and gave the area its classical and early modern name Cyrenaica. Cyrene lies on a ridge of the Jebel Akhdar uplands. The archaeological remains cover several hectares and include several monumental temples, stoas, theatres, bathhouses, churches, and palatial residences. The city is surrounded by the Necropolis of Cyrene. Since 1982, it has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city's port was Apollonia (Marsa Sousa), located about to the north. The city was attributed to Apollo and the legendary etymon Cyrene by the Greeks themselves but it was probably actually colonized by settlers from Thera (modern Santorini) in the late seventh century BC. It was initially ruled by a dynasty of monarchs called the Battiads, who grew rich and powerful as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suda
The ''Suda'' or ''Souda'' (; ; ) is a large 10th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine encyclopedia of the History of the Mediterranean region, ancient Mediterranean world, formerly attributed to an author called Soudas () or Souidas (). It is an encyclopedic lexicon, written in Medieval Greek, Greek, with 30,000 entries, many drawing from ancient sources that have since been lost, and often derived from Christianity in the Middle Ages, medieval Christian compilers. Title The exact spelling of the title is disputed. The transmitted title (''paradosis'') is "Suida", which is also attested in Eustathius of Thessalonica, Eustathius' commentary on Homer's epic poems; several conjectures have been made, both defending it and trying to correct it in "Suda". * Paul Maas (classical scholar), Paul Maas advocated for the spelling, connecting it to the Latin verb , the second-person singular imperative of , "to sweat". * Franz Dölger also defended , tracing its origins back to Byzantine mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
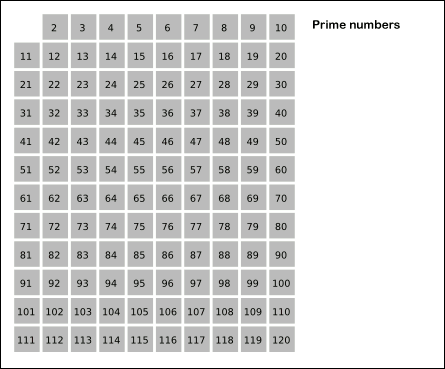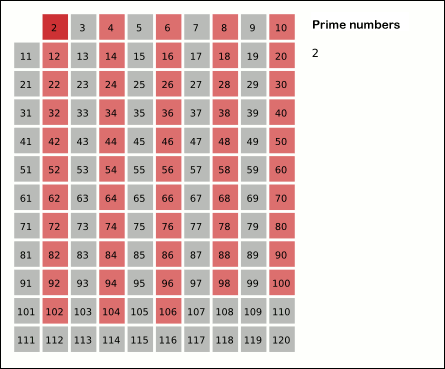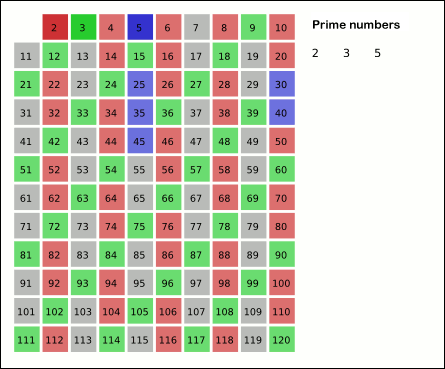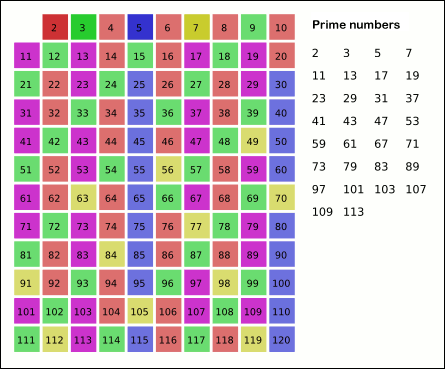
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 Г— 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorization, factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow primality test, method of checking the primality of a given number , called trial division, tests whether is a multiple of any integer between 2 and . Faster algorithms include the MillerвҖ“Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieve Of Eratosthenes
In mathematics, the sieve of Eratosthenes is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to any given limit. It does so by iteratively marking as composite number, composite (i.e., not prime) the multiples of each prime, starting with the first prime number, 2. The multiples of a given prime are generated as a sequence of numbers starting from that prime, with arithmetic progression, constant difference between them that is equal to that prime.Horsley, Rev. Samuel, F. R. S., "' or, The Sieve of Eratosthenes. Being an account of his method of finding all the Prime Numbers,''Philosophical Transactions'' (1683вҖ“1775), Vol. 62. (1772), pp. 327вҖ“347 This is the sieve's key distinction from using trial division to sequentially test each candidate number for divisibility by each prime. Once all the multiples of each discovered prime have been marked as composites, the remaining unmarked numbers are primes. The earliest known reference to the sieve (, ''kГіskinon EratosthГ©n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example, rational numbers), or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory can often be understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects, such as the Riemann zeta function, that encode properties of the integers, primes or other number-theoretic objects in some fashion (analytic number theory). One may also study real numbers in relation to rational numbers, as for instance how irrational numbers can be approximated by fractions (Diophantine approximation). Number theory is one of the oldest branches of mathematics alongside geometry. One quirk of number theory is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troy
Troy (/; ; ) or Ilion (; ) was an ancient city located in present-day Hisarlik, Turkey. It is best known as the setting for the Greek mythology, Greek myth of the Trojan War. The archaeological site is open to the public as a tourist destination, and was added to the List of World Heritage Sites in Turkey, UNESCO World Heritage list in 1998. Troy was repeatedly destroyed and rebuilt during its 4000 years of occupation. As a result, the site is divided into nine Stratigraphy (archaeology), archaeological layers, each corresponding to a city built on the ruins of the previous. Archaeologists refer to these layers using Roman numerals, Troy I being the earliest and Troy IX being the latest. Troy was first settled around 3600 BC and grew into a small fortified city around 3000 BC (Troy I). Among the early layers, Troy II is notable for its wealth and imposing architecture. During the Late Bronze Age, Troy was called Wilusa and was a vassal of the Hittite Empire. The final layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |