|
ß╣×
Macron below is a combining diacritical mark that is used in various orthographies. A non-combining form is . It is not to be confused with , and . The difference between "macron below" and "low line" is that the latter results in an unbroken underline when it is run together: compare a╠▒ß©çc╠▒ and a╠▓b╠▓c╠▓ (only the latter should look like abc). Unicode Macron below character Unicode defines several characters for the macron below: There are many similar marks covered elsewhere: * Spacing underscores, including ** ** * Combining underlines, including ** ** ** ; ** ** ** * International Phonetic Alphabet mark for Relative articulation#Advanced and retracted, retracted or backed articulation: ** ** Precomposed characters Various precomposed character, precomposed letters with a macron below are defined in Unicode: Note that the Unicode character names of precomposed characters whose Canonical decomposition, decompositions contain use "WITH LINE BELOW" rather t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combining Diacritical Mark
In digital typography, combining characters are Character (computing), characters that are intended to modify other characters. The most common combining characters in the Latin script are the combining diacritic, diacritical marks (including combining accents). Unicode also contains many precomposed characters, so that in many cases it is possible to use both combining diacritics and precomposed characters, at the user's or application's choice. This leads to a requirement to perform Unicode normalization before comparing two Unicode strings and to carefully design encoding converters to correctly map all of the valid ways to represent a character in Unicode to a legacy encoding to avoid data loss. In Unicode, the main block of combining diacritics for European languages and the International Phonetic Alphabet is U+0300ÔÇôU+036F. Combining diacritical marks are also present in many other blocks of Unicode characters. In Unicode, diacritics are always added after the main char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egyptian Language
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian (; ), is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century. Egyptian is one of the earliest known written languages, first recorded in the hieroglyphic script in the late 4th millennium BC. It is also the longest-attested human language, with a written record spanning over 4,000 years. Its classical form, known as " Middle Egyptian," served as the vernacular of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt and remained the literary language of Egypt until the Roman period. By the time of classical antiquity, the spoken language had evolved into Demotic, and by the Roman era, diversified into various Coptic dialects. These were eventually supplanted by Arabic after the Muslim conquest of Egypt, although Bohairic Coptic rem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seri Language
Seri () is an indigenous language spoken by between 716La situación sociolingüística de la lengua seri en 2006. and 900 Seri people in Punta Chueca and El Desemboque, two villages on the coast of Sonora, Mexico. The language is generally considered an isolate, but attempts have been made to include it in the theoretical Hokan language family. No concrete evidence has been found for connections to other languages. The earliest records of the Seri language are from 1692, but the population has remained fairly isolated. Extensive work on Seri began in 1951 by Edward and Mary Beck Moser with the Summer Institute of Linguistics. The language is viable within its community and is used freely in daily life. Exceptions include primary and secondary school, some parts of local church services, and communications with Spanish speakers outside of the Seri community. Most members of the community, including youth, are fluent in their language, but the population of speakers is small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Script
The Tamil script ( ) is an abugida script that is used by Tamils and Tamil language, Tamil speakers in India, Sri Lanka, Malaysia, Singapore and elsewhere to write the Tamil language. It is one of the official scripts of the Indian Republic. Certain minority languages such as Saurashtra language, Saurashtra, Badaga language, Badaga, Irula language, Irula and Paniya language, Paniya are also written in the Tamil script. Characteristics The Tamil script has 12 vowels (, , "soul-letters"), 18 consonants (, , "body-letters") and one special character, the (, ). is called "Ó«àÓ«òÓ»ìÓ«òÓ»ü", ''akku,'' and is classified in Tamil orthography as being neither a consonant nor a vowel. However, it is listed at the end of the vowel set. The script is Syllabary, syllabic, not alphabetic, and is written from left to right. History The Tamil script, like the other Brahmic scripts, is thought to have evolved from the original Brahmi script. The earliest inscriptions which are accepted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transliteration
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus '' trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek  and  the digraph , Cyrillic  , Armenian  or Latin  . For instance, for the Greek term , which is usually translated as 'Hellenic Republic', the usual transliteration into the Latin script (romanization) is ; and the Russian term , which is usually translated as 'Russian Republic', can be transliterated either as or alternatively as . Transliteration is the process of representing or intending to represent a word, phrase, or text in a different script or writing system. Transliterations are designed to convey the pronunciation of the original word in a different script, allowing readers or speakers of that script to approximate the sounds and pronunciation of the original word. Transliterations do not change the pronunciation of the word. Thus, in the Greek above example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M─üori Language
M─üori (; endonym: 'the M─üori language', commonly shortened to ) is an Eastern Polynesian languages, Eastern Polynesian language and the language of the M─üori people, the indigenous population of mainland New Zealand. The southernmost member of the Austronesian language family, it is related to Cook Islands M─üori, Tuamotuan language, Tuamotuan, and Tahitian language, Tahitian. The M─üori Language Act 1987 gave the language recognition as one of New Zealand's official languages. There are regional dialects of the M─üori language. Prior to contact with Europeans, M─üori lacked a written language or script. Written M─üori now uses the Latin script, which was adopted and the spelling standardised by Northern M─üori in collaboration with English Protestant clergy in the 19th century. In the second half of the 19th century, European children in rural areas spoke M─üori with M─üori children. It was common for prominent parents of these children, such as government officials, to us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Korean Alphabet
The Korean alphabet is the modern writing system for the Korean language. In North Korea, the alphabet is known as (), and in South Korea, it is known as (). The letters for the five basic consonants reflect the shape of the speech organs used to pronounce them. They are systematically modified to indicate phonetic features. The vowel letters are systematically modified for related sounds, making Hangul a featural writing system. It has been described as a syllabic alphabet as it combines the features of alphabetic and syllabic writing systems. Hangul was created in 1443 by Sejong the Great, the fourth king of the Joseon dynasty. The alphabet was made as an attempt to increase literacy by serving as a complement to Hanja, which were Chinese characters used to write Literary Chinese in Korea by the 2nd century BCE, and had been adapted to write Korean by the 6th century CE. Modern Hangul orthography uses 24 basic letters: 14 consonant letters and 10 vowel le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiceless Uvular Stop
The voiceless uvular plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. It is pronounced like a voiceless velar plosive , except that the tongue makes contact not on the soft palate but on the uvula. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is q. There is also the voiceless pre-uvular plosiveInstead of "pre-uvular", it can be called "advanced uvular", "fronted uvular", "post-velar", "retracted velar" or "backed velar". For simplicity, this article uses only the term "pre-uvular". in some languages, which is articulated slightly more front compared with the place of articulation of the prototypical uvular consonant, though not as front as the prototypical velar consonant. The International Phonetic Alphabet does not have a separate symbol for that sound, though it can be transcribed as or (both symbols denote an advanced ) or ( retracted ). The equivalent X-SAMPA symbols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
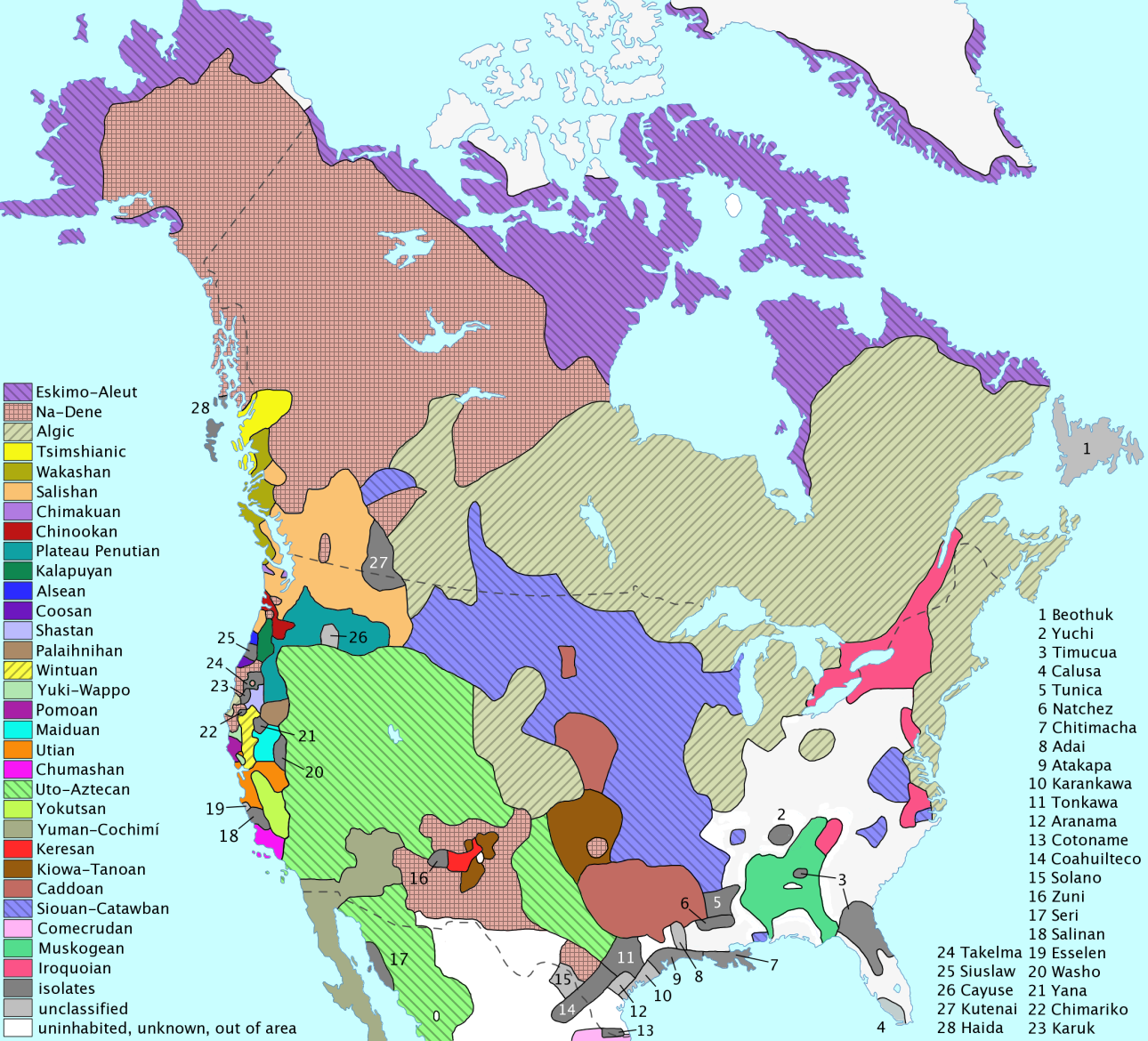
Pacific Northwest Languages
The Pacific Northwest languages are the indigenous languages of the Pacific Northwest of North America. This is a geographic term and does not imply any common heritage for these languages. In fact, the Pacific Northwest is an area of exceptional linguistic diversity and contains languages belonging to a large number of (apparently) unrelated families. However, the close proximity of multiple languages has created many opportunities for mutual interaction, with the result that the Pacific Northwest forms a linguistic area, with many areal features that are shared across language families. These include animacy hierarchies and case markers that cliticize to the end of the word before the noun phrase being marked for case. The linguistic area is centered on the Salishan, Wakashan and Chimakuan families. Some features are also shared with Tsimshianic, Chinookan and Sahaptian languages, as well as Kutenai, a language isolate. These languages are well known for their co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haida Language
Haida (', ', ', ') is the language of the Haida people, spoken in the Haida Gwaii archipelago off the coast of western Canada and on Prince of Wales Island in Alaska. An endangered language, Haida currently has 24 native speakers, though revitalization efforts are underway. At the time of the European arrival at in 1774, it is estimated that Haida speakers numbered about 15,000. Epidemics soon led to a drastic reduction in the Haida population, which became limited to three villages: Masset, Skidegate, and Hydaburg. Positive attitudes towards assimilation combined with the ban on speaking Haida in residential schools led to a sharp decline in the use of the Haida language among the Haida people, and today almost all ethnic Haida use English to communicate. Classification of the Haida language is a matter of controversy, with some linguists placing it in the Na-Den├® language family and others arguing that it is a language isolate. Haida itself is split between Northern a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlingit Language
The Tlingit language ( ; ' ) is an Indigenous language of the northwestern coast of North America, which is spoken by the Tlingit people of Southeast Alaska and Western Canada and is a branch of the Na-Dene language family. Extensive effort is being put into revitalization programs in Southeast Alaska to revive and preserve the Tlingit language and culture. Missionaries of the Russian Orthodox Church were the first to develop a written version of Tlingit by using the Cyrillic script to record and translate it when the Russian Empire had contact with Alaska and the coast of North America down to Sonoma County, California. After the Alaska Purchase, English-speaking missionaries from the United States developed a written version of the language with the Latin alphabet. History The history of Tlingit is poorly known, mostly because there is no written record until the first contact with Europeans around the 1790s. Documentation was sparse and irregular until the early 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaph (letter)
Kaph (also spelled kaf) is the eleventh letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''k─üp'' Éñè, Hebrew ''k─üp╠ä'' , Aramaic ''k─üp'' Éíè, Syriac ''k─üp╠ä'' ▄ƒ, and Arabic ''k─üf'' (in abjadi order The Abjad numerals, also called Hisab al-Jummal (, ), are a decimal alphabetic numeral system/ alphanumeric code, in which the 28 letters of the Arabic alphabet are assigned numerical values. They have been used in the Arabic-speaking world si ...). It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian ɬïÔÇÄ, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and Ge╩¢ez script, Ge'ez . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek alphabet, Greek Kappa (letter), kappa (╬Ü), Latin alphabet, Latin K, and Cyrillic script, Cyrillic Ka (Cyrillic), ðÜ. Origin Kaph is thought to be derived from a pictogram of a hand (in both modern Arabic and Hebrew language, modern Hebrew, kaph means "palm" or "grip"), though in Arabic the ''a'' in the name of the letter (┘âϺ┘ü) is pronounced lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |