|
─Éura┼Ī Iliji─ć
─Éura┼Ī Iliji─ć ( sr-Cyrl, ąéčāčĆą░čł ąśą╗ąĖčśąĖčø, 1326ŌĆō62) was a Serbian commander and nobleman who served the Serbian monarchs Stefan De─Źanski (r. 1321ŌĆō1331), Stefan Du┼Īan (r. 1331ŌĆō1355) and Uro┼Ī V (r. 1355ŌĆō1371), from 1326 until his death in 1362. He had the title of ''─Źelnik'' ("head"), and governed Upper Zeta. He is an ancestor of the Crnojevi─ć noble family (a branch of the ─Éura┼Īevi─ć). Origin and early life ─Éura┼Ī was born in Zeta (crown land), Zeta, the son of Ilija, and grandson of ─Éura┼Ī Vran─Źi─ć. His grandfather served King Stefan Milutin (r. 1282ŌĆō1321) with the court title of ''stavilac'', while his father had the title of ''kefalija'', and governed Zeta. It has been claimed that ─Éura┼Ī had two brothers, Nikola and Vladin, or one brother, Nikola Vladin. King Stefan De─Źanski's confirmation on the rights of Ragusan merchants dating to March 25, 1326, was attended by ''vojvoda'' Mladen, ''tep─Źija'' Vladoje, and ''─Źelnik ''─īelnik'' ( sr-Cyrl, čćą ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dominus (title)
''Dominus'' is the Latin word for Lord or owner. was used primarily as an imperial title during the era of the Roman Empire (25 BC ŌĆō 1453 AD) and was also the Latin title of the feudal, superior and mesne, lords. Dominus was also used as an ecclesiastical and academic title during that time. The ecclesiastical title was translated from the French into English as , making it a common prefix for parsons before the Reformation. This is evident by the character's name Sir Hugh Evans in Shakespeare's '' Merry Wives of Windsor''. The title , is still used in modetn times for those with a Bachelor of Arts degree. The shortened form for Dominus ŌĆō '' Dom'' ŌĆō has remained in use in modern times as a prefix of honor for ecclesiastics of the Catholic Church, and members of religious orders, especially for those of the monastic Order of Saint Benedict, the Benedictines, who have professed perpetual religious vows. The Spanish equivalents of and the French equivalent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gradislav Voj┼Īi─ć
Gradislav Voj┼Īi─ć (; 1284ŌĆō1327) was a Serbian nobility in the Middle Ages, Serbian nobleman who served the Serbian Kings Stefan Uro┼Ī II Milutin (r. 1282ŌĆō1321) and Stefan Uro┼Ī III (r. 1322ŌĆō1331). He was the first known ''─Źelnik'' of the Serbian court, in the nearest circle of the King, mentioned serving the first time in 1284 and the second time in 1327. The ''─Źelnik'' was entrusted with the security of Church property from the Serbian nobility, nobility, and appeared in the role of a judge or executor of the King's decisions, in disputes between Serbian Orthodox Church, the Church and the nobility. Life He was born in the mid-13th century. Gradislav is mentioned in 1284, as serving King Stefan Milutin as ''─Źelnik''. The latter account also mentions a gift worth 400 Hyperpyron, perpers to the King, and 26 perpers to Gradislav. Gradislav is the first known ''─Źelnik'' (č湥ą╗ąĮąĖą║, roughly "head, chief") that served a Serbian ruler. He was in the nearest circle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Michigan Press
The University of Michigan Press is a university press that is a part of Michigan Publishing at the University of Michigan Library. It publishes 170 new titles each year in the humanities and social sciences. Titles from the press have earned numerous awards, including Lambda Literary Awards, the PEN/Faulkner Award, the Joe A. Callaway Award, and the Nautilus Book Award. The press has published works by authors who have been awarded the Pulitzer Prize, the National Humanities Medal and the Nobel Prize in Economics. History From 1858 to 1930, the University of Michigan had no organized entity for its scholarly publications, which were generally conference proceedings or department-specific research. The University Press was established in 1930 under the university's Graduate School, and in 1935, Frank E. Robbins, assistant to university president Alexander G. Ruthven, was appointed as the managing editor of the University Press. He would hold this position until 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Branko (─Źelnik)
Branko ( sr-cyr, ąæčĆą░ąĮą║ąŠ; 1306ŌĆō19) was a Serbian nobleman with the title of ''─Źelnik'', serving King Stefan Milutin (r. 1282ŌĆō1321). He was among the witnesses mentioned in the charter issued to the Ratac Monastery by Milutin in 1306, alongside noblemen ''kaznac'' Miroslav and ''┼Šupan'' Vladislav, holding the title of ''─Źelnik''. He is still in this position in an edict dated 1319. During the reign of Milutin, the title holder was entrusted with the security of property belonging to the Church from the aristocrats, so the holder appeared in the role of a judge or executor of the ruler's decisions, in disputes between the church and the nobility. At that time the title of ''─Źelnik'' was of a higher rank than ''┼Šupan'' and ''stavilac'', but lower than ''kaznac'' and ''tep─Źija'', with '' vojvoda'' being the supreme title. It is unclear if there was one or several with that title at the court at that time. He was preceded by Gradislav Voj┼Īi─ć and succeeded by ─Éura┼Ī ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
─Éura─æ I Bal┼Īi─ć
─Éura─æ I Bal┼Īi─ć ( sr-cyr, ąéčāčĆą░čÆ I ąæą░ą╗čłąĖčø; ) was the Lord of Zeta between 1362 and 13 January 1378. He was the eldest of the three sons of Bal┼Īa I, and belonged to the Bal┼Īi─ć family. Life ─Éura─æ was the eldest son of Bal┼Īa, a petty nobleman who held one village during the rule of Emperor Stefan Du┼Īan (r. 1331ŌĆō1355) and was said to be "kin to Nemanja". The family started taking Lower Zeta sometime following the death of Du┼Īan in 1355. In 1362 the brothers murdered ─Éura┼Ī Iliji─ć who had held Upper Zeta, and were then recognized as (provincial lords) of Zeta in charters of Stefan Uro┼Ī V (r. 1355ŌĆō1371). In 1363, ─Éura─æ declared war against the Thopias, an Albanian noble family which controlled northern Albania. The Matarangos, an Albanian noble family which controlled southern Albania, were allied with the Bal┼Īi─ćs as a result of a quarrel with the Thopias in the south. In the spring of 1364, Karl Thopia took ─Éura─æ captive due to a skirmish, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains more than 1,300 islands, mostly located along its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of . The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although acqua alta, larger amplitudes occur occasionally. The Adriatic's salinity is lower than the Mediterranean's because it collects a third of the fresh water flowing into the Mediterranean, acting as a dilution basin. The surface water temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Lake Skadar
Lake Skadar or Lake Scutari (, ; cnr-Cyrl-Latn, ąĪą║ą░ą┤ą░čĆčüą║ąŠ čśąĄąĘąĄčĆąŠ, Skadarsko jezero, )also called Lake Shkodra (and ''Lake Shkod├½r'')lies on the border of Albania and Montenegro, and is the largest lake in Southern Europe. It is named after the Albanian city of Shkod├½r which lies at its southeastern coast. It is a karst lake. The Montenegrin section of the lake and surrounding land have been designated as a national park, while the Albanian part constitutes a nature reserve and a Ramsar site. Geography Lake Skadar is the largest lake in the Balkan Peninsula with a surface area that seasonally fluctuates between and . Lake Skadar itself is located in the western Balkan region. The lake is located in the border area between Montenegro and Albania, the Montenegrin share of the area of the lake is larger than the Albanian one. The lake's water level also varies seasonally from above sea level. The lake extends northwest to southeast, and it is approximately l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Republic Of Venice
The Republic of Venice, officially the Most Serene Republic of Venice and traditionally known as La Serenissima, was a sovereign state and Maritime republics, maritime republic with its capital in Venice. Founded, according to tradition, in 697 by Paolo Lucio Anafesto, over the course of its History of the Republic of Venice, 1,100 years of history it established itself as one of the major European commercial and naval powers. Initially extended in the ''Dogado'' area (a territory currently comparable to the Metropolitan City of Venice), during its history it annexed a large part of Northeast Italy, Istria, Dalmatia, the coasts of present-day Montenegro and Albania as well as numerous islands in the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and eastern Ionian Sea, Ionian seas. At the height of its expansion, between the 13th and 16th centuries, it also governed Crete, Cyprus, the Peloponnese, a number of List of islands of Greece, Greek islands, as well as several cities and ports in the eastern Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
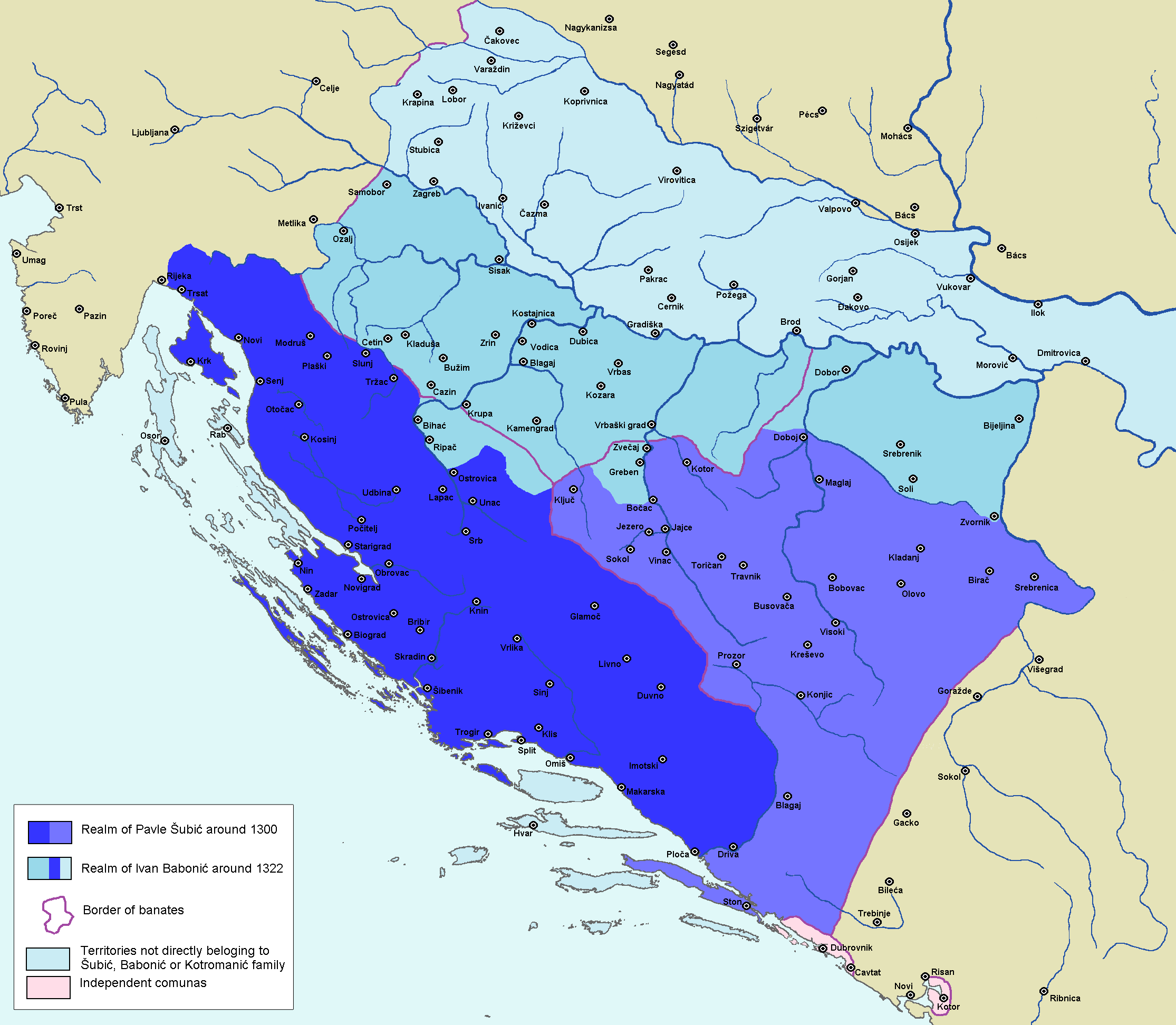
Mladen III ┼Āubi─ć
Mladen III ┼Āubi─ć () ( 1315 ŌĆō Trogir, 1 May 1348) was a member of the Croatian ┼Āubi─ć noble family, who ruled from Klis Fortress. He was in possession of Klis, Omi┼Ī and Skradin. He is also known as Shield of the Croats (Clipeus Croatorum), according to the Latin epitaph in verse on his grave in Trogir Cathedral. Ruler He formally succeeded his father Juraj II ┼Āubi─ć upon his early death, though the territories were initially controlled by his mother Lelka until he reached adulthood in 1332. She continued to have considerable influence on his politics afterwards. He successfully warred against the coalition of Dalmatian cities Split, Trogir and ┼Āibenik under Republic of Venice and the nobility under Duke of Knin, Ivan Nelipi─ć, whom he pressured to return Ostrovica in 1335. He also strengthened his position by ousting opposition of Ivan Juri┼Īi─ć, Budislav Ugrini─ć and Hran Gradini─ć within his clan either through military or diplomatic means. He later also allowed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jelena Nemanji─ć ┼Āubi─ć
Jelena ┼Āubi─ć (Serbian Cyrillic: ąłąĄą╗ąĄąĮą░ ą©čāą▒ąĖčø; Jelena Nemanji─ć ┼Āubi─ć (ąłąĄą╗ąĄąĮą░ ąØąĄą╝ą░čÜąĖčø ą©čāą▒ąĖčø)) was the daughter of Stefan Uro┼Ī III De─Źanski of Serbia and the half-sister of Stefan Du┼Īan. She was married to the Croatian magnate Mladen III ┼Āubi─ć, Prince of Bribir from the noble ┼Āubi─ć family. They ruled from Klis Fortress in Dalmatia. After Mladen III ┼Āubi─ć's death, she ruled as his widow over Skradin and Klis. After the death of Prince Mladen III (1348), the Dalmatian cities of Klis and Skradin were ruled by Jelena, in the name of their son Mladen IV. She had many opponents, beginning from 1351. Firstly, from the wife of Paul III, Catherine Dandolo from Venice, then Jelena ┼Āubi─ć, the mother of Ban Tvrtko I of Bosnia. The mother of Tvrtko was openly supported by King Louis I of Hungary Louis I, also Louis the Great (; ; ) or Louis the Hungarian (; 5 March 132610 September 1382), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1342 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Skradin
Skradin is a small town in the ┼Āibenik-Knin County of Croatia. It is located near the Krka (Croatia), Krka river and at the entrance to the Krka National Park, from ┼Āibenik and from Split, Croatia, Split. The main attraction of the park, Slapovi Krke, is a series of waterfalls, the biggest of which, Skradinski buk, was named after Skradin. History During Classical antiquity, Antiquity, the city was known as ''Scardon'' and ''Scardona'', a name attested in the writings of Strabo and Procopius (), Pliny the Elder () and Ptolemy (). Before the Roman Empire, Roman conquest, the settlement was Illyrians, Illyrian, with the particularity of having the locally recurring suffix ''-ona''. The prevailing theory links the root of the Illyrian toponym to a term meaning "steep", as a derivation of ''*sko/ard(h)-'', and it has been compared with the ┼Āar mountains, Scardus mountains in southern Illyria. p. 363. After an initial development in Vulgar Latin in the form ''-una'', the Illyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |