|
ؤگuraؤ‘ I Balإ،iؤ‡
ؤگuraؤ‘ I Balإ،iؤ‡ ( sr-cyr, ذ‚رƒر€ذ°ر’ I ذ‘ذ°ذ»رˆذ¸ر›; ) was the Lord of Zeta between 1362 and 13 January 1378. He was the eldest of the three sons of Balإ،a I, and belonged to the Balإ،iؤ‡ family. Life ؤگuraؤ‘ was the eldest son of Balإ،a, a petty nobleman who held one village during the rule of Emperor Stefan Duإ،an (r. 1331–1355) and was said to be "kin to Nemanja". The family started taking Lower Zeta sometime following the death of Duإ،an in 1355. In 1362 the brothers murdered ؤگuraإ، Ilijiؤ‡ who had held Upper Zeta, and were then recognized as (provincial lords) of Zeta in charters of Stefan Uroإ، V (r. 1355–1371). In 1363, ؤگuraؤ‘ declared war against the Thopias, an Albanian noble family which controlled northern Albania. The Matarangos, an Albanian noble family which controlled southern Albania, were allied with the Balإ،iؤ‡s as a result of a quarrel with the Thopias in the south. In the spring of 1364, Karl Thopia took ؤگuraؤ‘ captive due to a skirmish, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mrnjavؤچeviؤ‡ Family
The House of Mrnjavؤچeviؤ‡ ( sr-Cyrl, ذœر€رڑذ°ذ²ر‡ذµذ²ذ¸ر›, Mrnjavؤچeviؤ‡i / ذœر€رڑذ°ذ²ر‡ذµذ²ذ¸ر›ذ¸, ) was a medieval Serbian noble house during the Serbian Empire, its fall, and the subsequent years when it held a region of present-day Macedonia region. The house ruled a province from its base at Prilep (in modern North Macedonia) from 1366 to 1395. Vukaإ،in Mrnjavؤچeviؤ‡ was a military commander in the army of Emperor Duإ،an the Mighty ( 1331-1355) and co-ruler of Serbia as king, with Emperor Uroإ، the Weak ( 1355-1371). After Uroإ،' death, the Serbian Empire crumbled, as the nobility could not agree on its rightful successor. Vukaإ،in's son, Marko Kraljeviؤ‡, ruled his hereditary lands as titular ''King of Serbs and Greeks''. History Origin The family's progenitor, after whom historiography names it, was Mrnjava, a financial chancellor (''kaznac'', chamberlain) who served King Stefan Uroإ، I and his wife, Queen Helen of Anjou at the court at Trebinje (in Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stefan Uroإ، V
Saint Stefan Uroإ، V ( sr-Cyrl, ذ،ر‚ذµر„ذ°ذ½ ذ£ر€ذ¾رˆ V, ; 13362/4 December 1371), known in historiography and folk tradition as Uroإ، the Weak (), was the Emperor of the Serbs, second Emperor (Tsar#Serbia, Tsar) of the Serbian Empire (1355–1371), and before that he was Serbian King and co-ruler (since 1346) with his father, Emperor Stefan Duإ،an. Early life Stefan Uroإ، V was the only son of Stefan Uroإ، IV Duإ،an by Helena of Bulgaria, Empress of Serbia, Helena of Bulgaria, the sister of Ivan Alexander of Bulgaria. He had been crowned as king (second highest title) in the capacity of heir and co-ruler after Duإ،an was crowned emperor in 1346. Although by the time of his succession as sole ruler and emperor in 1355 Stefan Uroإ، V was no longer a minor, he remained heavily dependent on his mother and various members of the court. Reign file:Loza Nemanjica Decani c 2.jpg, left, 200px, Depiction in the Serbian Orthodox Monastery of Visoki Deؤچani, Serbia The account of the conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serbian Perper
The first mention of a "Serbian dinar" dates back to the reign of Stefan Nemanjiؤ‡ in 1214. Until the fall of the Serbian Despotate in 1459, most of the Serbian rulers minted silver dinar coins. Emperor Stefan Duإ،an adopted the Byzantine ''hyperpyron'' (perper), a large unit of currency: the imperial tax was one perper per year per house.Vladimir ؤ†oroviؤ‡ذکرپر‚ذ¾ر€ذ¸رکذ° رپر€ذ؟رپذ؛ذ¾ذ³ ذ½ذ°ر€ذ¾ذ´ذ°: V. The first Serbian dinars, like many other Southern European coins, replicated Venetian grosso, including characters in Latin (the word ''dux'' replaced with the word ''rex''). For many years it was one of the main export articles of medieval Serbia, considering the relative abundance of silver coming from Serbian mines. While multiple foreign currencies circulated medieval Serbia, medieval dinar nevertheless maintained stable value from early thirteen till the mid fourteen century when 24 dinars were exchanged for 1 gold coin ducat. Venetians were weary of this, and Dante Alighier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ducat
The ducat ( ) coin was used as a trade coin in Europe from the later Middle Ages to the 19th century. Its most familiar version, the gold ducat or sequin containing around of 98.6% fine gold, originated in Venice in 1284 and gained wide international acceptance over the centuries. Similarly named silver ducatons also existed. The gold ducat circulated along with the Florentine florin and preceded the modern British pound sterling. Predecessors The word ''ducat'' is from Medieval Latin ''ducalis'' = "relating to a duke (or dukedom)", and initially meant "duke's coin" or a "duchy's coin". The first issue of scyphate billon coins modelled on Byzantine ''trachea'' was made by King Roger II of Sicily as part of the Assizes of Ariano (1140). It was to be a valid issue for the whole kingdom. The first issue bears the figure of Christ and the Latin inscription ''Sit tibi, Christe, datus, quem tu regis iste ducatus'' (meaning "O Christ, let this duchy, which you rule, be dedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bar, Montenegro
Bar (Montenegrin language, Montenegrin: Bar, ذ‘ذ°ر€, , ) is a town and seaport in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is the capital of the Bar Municipality and a center for tourism. According to the 2023 census, the city proper had 15,868 inhabitants, while the total population of Bar Municipality was 46,171. Name Bar is supposed to be a shortened Slavic variant of ''Antivari''. The name is thought to be derived from the Latin ''Antibarum'' or ''Antibari'', which later in Greek was transformed into ''Antivأ،rion / Antivari'' due to its pronunciation. "Antibari", meaning "opposite Bari", is a name taken because of it is location across the Adriatic Sea from Bari in Italy. Variations are in Italian language, Italian, ''Antivari / Antibari''; in Albanian language, Albanian, ''Tivari'' or ''Tivar''; in Turkish language, Turkish, ''Bar''; in Greek language, Greek, خکخ·خ²خ¬دپخ¹خ؟خ½, ''Thivأ،rion'', خ‘خ½د„خ¹خ²خ¬دپخ¹خ؟خ½, ''Antivأ،rion''; in Latin, ''Antibarium''. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kotor
Kotor (Cyrillic script, Cyrillic: ذڑذ¾ر‚ذ¾ر€, ), historically known as Cattaro (from Italian language, Italian: ), is a town in Coastal Montenegro, Coastal region of Montenegro. It is located in a secluded part of the Bay of Kotor. The city has a population of 13,347 and is the administrative center of Kotor Municipality. The old Mediterranean port of Kotor is surrounded by fortifications of Kotor, fortifications built during the Republic of Venice, Venetian period. It is located on the Bay of Kotor (''Boka Kotorska''), one of the most indented parts of the Adriatic Sea. Some have called it the southernmost fjord in Europe, but it is a ria, a submerged river canyon. Together with the nearly overhanging limestone cliffs of Orjen and Lovؤ‡en, Kotor and its surrounding area form an impressive landscape. Since the early 2000s Kotor has seen an increase in tourists, many of them coming by cruise ship. Visitors are attracted to the natural environment of the Bay of Kotor and the old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Capetian House Of Anjou
The Capetian House of Anjou, or House of Anjou-Sicily, or House of Anjou-Naples was a royal house and cadet branch of the Capetian dynasty. It is one of three separate royal houses referred to as ''Angevin'', meaning "from Anjou" in France. Founded by Charles I of Anjou, the youngest son of Louis VIII of France, the Capetian king first ruled the Kingdom of Sicily during the 13th century. The War of the Sicilian Vespers later forced him out of the island of Sicily, leaving him with the southern half of the Italian Peninsula, known as the Kingdom of Naples. The house and its various branches would go on to influence much of the history of Southern and Central Europe during the Middle Ages until it became extinct in 1435. Historically, the house ruled the Counties of Anjou, Maine, Touraine, Provence and Forcalquier; the Principalities of Achaea and Taranto; and the Kingdoms of Sicily, Naples, Hungary, Croatia, Albania and Poland. Rise of Charles I and his sons A younge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Durrأ«s
Durrأ«s ( , ; sq-definite, Durrأ«si) is the List of cities and towns in Albania#List, second most populous city of the Albania, Republic of Albania and county seat, seat of Durrأ«s County and Durrأ«s Municipality. It is one of Albania's oldest list of oldest continuously inhabited cities, continuously inhabited cities, with roughly 2,500 years of recorded history. It is located on a flat plain along the Albanian Adriatic Sea Coast between the mouths of the Erzen River, Erzen and Ishأ«m (river), Ishأ«m at the southeastern corner of the Adriatic Sea. Durrأ«s' climate is profoundly influenced by a seasonal Mediterranean climate. Durrأ«s was founded under the name of Epidamnos around the 7th century BC, by Ancient Greece, ancient Greek colonists from Corinth and Korkyra (polis), Corcyra in cooperation with the Taulantii, a local Illyrians, Illyrian tribe. Also known as Dyrrachium, Durrأ«s developed as it became an integral part of the Roman Empire and its successor the Byzantine Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mati River
The Mat ( sq-definite, Mati) is a river in north-central Albania. Its overall length is , while its catchment surface is . Its average discharge is . The main tributary is the Fan, flowing from the northeast, while the Mat flows from the southwest down to the confluence with Fan and then towards the Adriatic Sea. Etymology The Albanian name ''mat'' originally meant "elevated location", "mountain place". Today's meaning in Albanian, "river bank, river shore", is a consequence of a secondary change through the common use of both the terms ''mal'', "mountain" and ''breg'', "shore", giving the meaning of "elevation". The river was recorded by Roman writer Vibius Sequester (4th or 5th century AD) as ''Mathis'', following a hellenized graphic mode of the term ''mat''. It appeared in written records also as ''Mathia'' in 1380. Overview The Mat originates from the confluence of several streams within the karstic mountains in Martanesh, where it forms deep gorges and canyons. Rising i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Balإ،a II
Balإ،a Balإ،iؤ‡ ( sr-cyr, ذ‘ذ°ذ»رˆذ° ذ‘ذ°ذ»رˆذ¸ر›; ; died 18 September 1385) or Balإ،a II was the Lord of Lower Zeta from 1378 to 1385. He was a member of the Balإ،iؤ‡ noble family, which ruled Zeta (with Scutari) from 1362 to 1421. Early life Balإ،a II was the youngest of three sons of Balإ،a I. According to Mavro Orbini, ''Balإ،a'', the progenitor of the Balإ،iؤ‡ family, was a petty nobleman who held only one village in the area of Lake Skadar during the rule of Emperor Duإ،an the Mighty (r. 1331 to 1355). Only after the death of the emperor, during the subsequent weak rule of Emperor Uroإ، V, Balإ،a together with his friends and his three sons ( Stracimir, ؤگuraؤ‘ and Balإ،a II) gained power in Lower Zeta, which had previously been the lands of ''gospodin'' إ½arko (fl. 1336 to 1360). Balإ،a's people then turned for Upper Zeta, which was held by ؤگuraإ، Ilijiؤ‡ and his relatives; the Balإ،iؤ‡ brothers murdered ؤگuraإ،, and had some of his relatives imprisoned. Balإ،a died t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
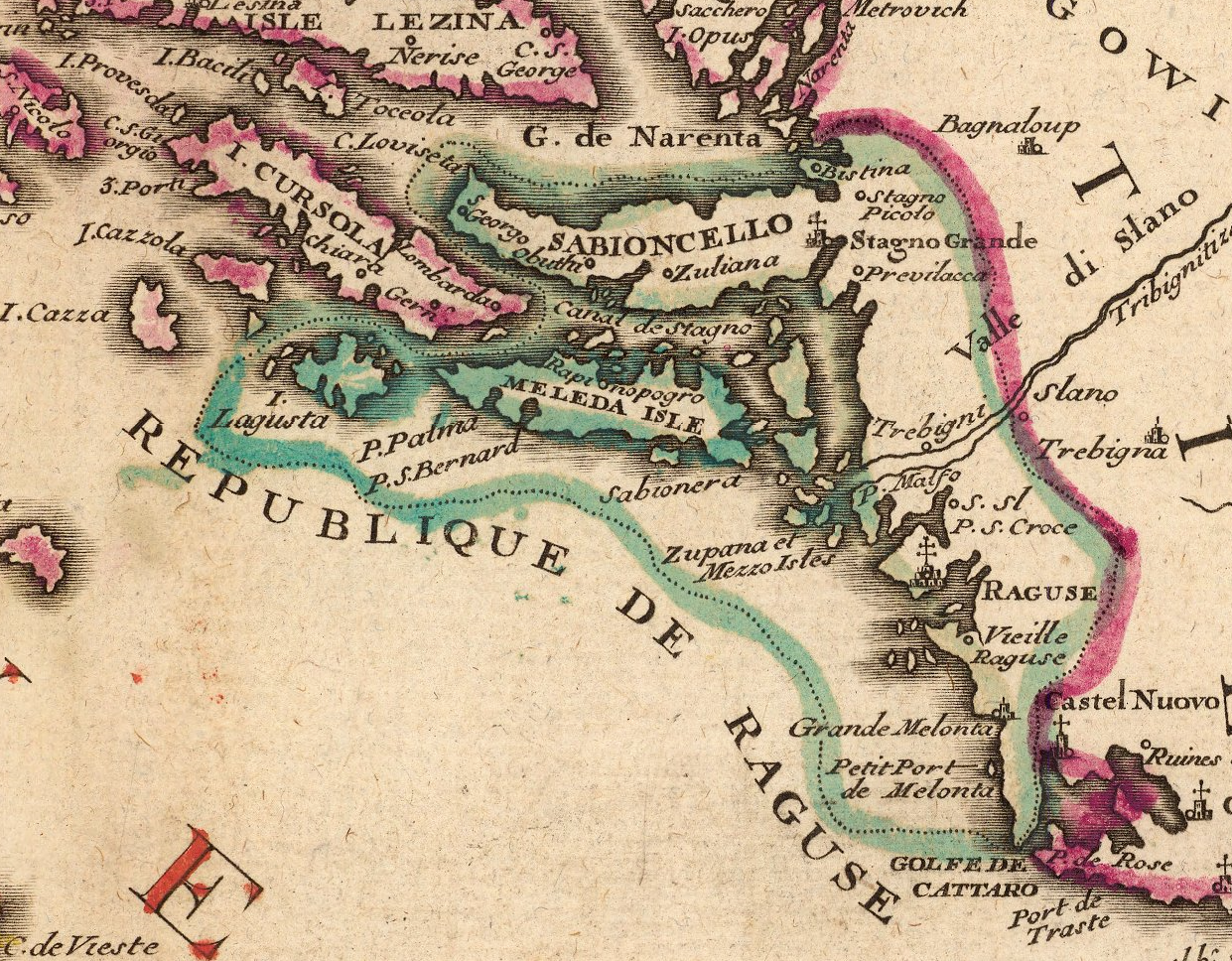
Republic Of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa, or the Republic of Dubrovnik, was an maritime republics, aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' in Italian and Latin; ''Raguxa'' in Venetian) in South Dalmatia (today in southernmost Croatia) that carried that name from 1358 until 1808. It reached its commercial peak in the 15th and the 16th centuries, before being conquered by Napoleon's First French Empire, French Empire and formally annexed by the Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Napoleonic Kingdom of Italy in 1808. It had a population of about 30,000 people, of whom 5,000 lived within the city walls. Its motto was "'", a Latin phrase which can be translated as "Liberty is not well sold for all the gold". Names Originally named ' (Latin for "Ragusan municipality" or "community"), in the 14th century it was renamed ' (Latin for ''Ragusan Republic''), first mentioned in 1385. It was nevertheless a Republic under its previous name, although its Rector was appointed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Karl Thopia
Karl Thopia (; – January 1388) sometimes written as Charles Thopia, was an Albanian feudal prince and warlord who ruled Albanian domains from 1358 until the first Ottoman conquest of Albania in 1388. Thopia usually maintained good relations with the Roman Curia. Family The first mention of the Thopia is from 1329, when Tanusio Thopia was mentioned as one of the counts of Albania. In 1338, Tanusio was mentioned as Count of Mat (conte di Matia). According to Karl Hopf, Tanusio's son or brother Andrea I, as told by Gjon Muzaka (fl. 1510), had fallen in love with an illegitimate daughter of King Robert of Naples when her ship, en route to the Principality of the Morea to be wed with the ''bailli'', had stopped at Durrأ«s where they met. Andrea abducted and married her, and they had two sons, Karl and George. Karl was named after his great great grandfather Charles I of Anjou. King Robert, enraged, under the pretext of reconciliation had the couple invited to Naples wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |