|
ĂĂłrisjökull
ĂĂłrisjökull or ThĂłrisjökull (, Icelandic for "ThĂłris's glacier") is a small glacier and volcano in western-central Iceland, to the southwest of Langjökull glacier. It has an elevation of . Kaldidalur lies in the foreground. Position ĂŸĂłrisjökull is situated between Langjökull glacier and the shield volcano Ok to its east. The "Cold valley" (translation of Kaldidalur) is lying between them with its famous highland road of the same name. The volcano The glacier volcano ĂĂłrisjökull is a tuya from the Ice Age (in Iceland from 100,000 years ago til about 10,000 years ago). Its mountain part consists mainly of hyaloclastites. The glacier was part of Langjökull glacier probably til the end of the 18th century. Some geological research was made again on the ĂĂłrisjökull and PrestahnĂșkur area in 2009 and it shows clearly active volcanic fissures under the glacier which are part of the PrestahnĂșkur volcanic system (see weblink, Icelandic Meteorological Institute). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaciers Of Iceland
The glaciers and ice caps of Iceland covered 11% of the land area of the country, up to about 2008. this was down to 10%. They have a considerable impact on its landscape and meteorology. Glaciers are also contributing to the Icelandic economy, with a tourist market that includes glacier trips on snowmobiles and glacier hiking tours. However, the recent loss of ice due to climate change is an increasing concern in Icelandic society. Description Glaciers can both grow in size and regress depending upon several factors of which climate and precipitation in the glaciers catchment are the most important. About 7,000 years ago, the Pleistocene ice from the last Ice Age over Iceland disappeared almost entirely, so the current glaciers in Iceland are not that old. In the case of Iceland as several large glaciers are over active volcanoes, geothermal melting can be a substantial component of the glacier ice mass balance. Accordingly Iceland's glacier area varies from year to year and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PrestahnĂșkur
The peak PrestahnĂșkur () with a height of , is in the Western Volcanic Zone to the west of the Highlands of Iceland to the west of Langjökull glacier, or to be more specific, to the west of Geitlandsjökull glacier, a part of the Langjökull. The volcano PrestahnĂșkur includes the terrain under the Geitlandsjökull glacier continuous to the peak and also includes fissure fields to its north and south. The volcanic system The central volcano PrestahnĂșkur consists of a rhyolite tuya that was formed entirely under ice, and has been dated as 89 ± 24 , but another dating is about 60 ka. Two vents have been found. At the base of the northern flank is a geothermal area, with the rhyolite and hot springs suggesting that a long-lived magma chamber is or has been present. There has been intermittent seismic activity, mostly in an area about wide centred at the central volcano, but as no dyke intrusions have been observed, so it is unproven that the volcano is active. In 2009 g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaldidalur
The Kaldadalsvegur (, ) is the shortest of the highland tracks traversing the Highlands of Iceland, therefore the nickname "highlands for beginners" . Its name derives from the valley it crosses: '':is:Kaldidalur, Kaldidalur'' means "cold dale/valley". Sometimes the Kaldadalsvegur is referred to as simply "the Kaldidalur". The route begins a bit to the north of Ăingvellir and to the west of the volcano SkjaldbreiĂ°ur, which really comes up to its name (meaning ''broad shield''). The track continues between the glaciers ĂĂłrisjökull and Ok (glacier), Ok and leads up to the north. To the east of Reykholt, Western Iceland, Reykholt it comes near the ''Reykholtsdalur'' to HĂșsafell. Then it continues up to ''Hvammstangi'' at the ''MiĂ°fjörĂ°ur''. Signed as route 550 (formerly F550), the track is 40 kilometers long, and has no unbridged river crossings. (The Kaldadalsvegur is ''not'' an Roads in Iceland, F road, and a four-wheel-drive vehicle is ''not'' legally required to tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langjökull
Langjökull (, Icelandic for "long glacier") is the second largest ice cap in Iceland (), after Vatnajökull. It is situated in the west of the Icelandic interior or Highlands of Iceland and can be seen clearly from Haukadalur. It covers the higher parts of the Langjökull volcanic system. Its volume is and the ice is up to thick. The highest point of the ice cap (at ''Baldjökull'' at the northern end of Langjökull) is about above sea level. In the past, the largest recorded surface area was in 1840. Situation and form The glacier is roughly parallel to the direction of the country's active volcanic zone: north-east to south-west. It is about long and wide, and has a slightly narrower point roughly between the lake HvĂtĂĄrvatn on the Kjölur mountain road to the east and the ĂrĂstapajökull glacier to the west, near another smaller glacier, EirĂksjökull, which is not quite connected to Langjökull. It is the nearest large glacier to ReykjavĂk. The area o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaloclastite
Hyaloclastite is a volcanoclastic accumulation or breccia consisting of glass (from the Greek ''hyalus'') fragments (clasts) formed by quench fragmentation of lava flow surfaces during submarine or subglacial extrusion. It occurs as thin margins on the lava flow surfaces and between pillow lavas as well as in thicker deposits, more commonly associated with explosive, volatile-rich eruptions as well as steeper topography. Hyaloclastites form during volcanic eruptions under water, under ice or where subaerial flows reach the sea or other bodies of water. It commonly has the appearance of angular flat fragments sized between a millimeter to few centimeters. The fragmentation occurs by the force of the volcanic explosion, or by thermal shock and spallation during rapid cooling. Several mineraloids are found in hyaloclastite masses. Sideromelane is a basalt glass rapidly quenched in water. It is transparent and pure, lacking the iron oxide crystals dispersed in the more comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
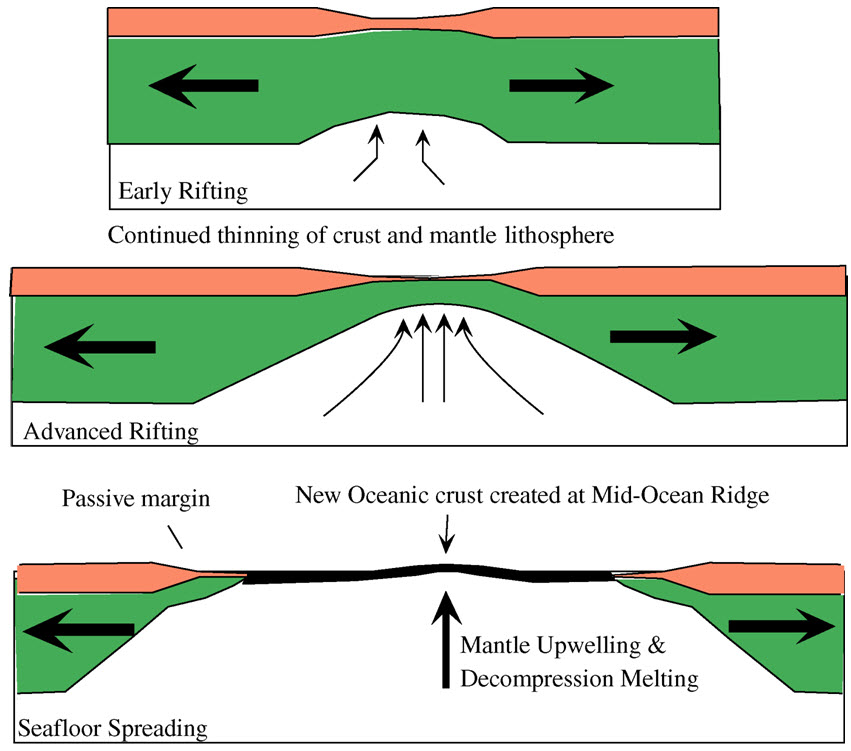
West Volcanic Zone Of Iceland
The geological deformation of Iceland is the way that the rocks of the island of Iceland are changing due to tectonic forces. The geological deformation help to explain the location of earthquakes, volcanoes, fissures, and the shape of the island. Iceland is the largest landmass () situated on an oceanic ridge. It is an elevated plateau of the sea floor, situated at the crossing of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the Greenland-Iceland-Scotland ridge. It lies along an oceanic divergent plate boundary: the western part of Iceland sits on the North American Plate and the eastern part sits on the Eurasian Plate. The Reykjanes Ridge of the Mid-Atlantic ridge system in this region crosses the island from southwest and connects to the Kolbeinsey Ridge in the northeast. Iceland is geologically young: all rocks there were formed within the last 25 million years. It started forming in the Early Miocene sub-epoch, but the oldest rocks found at the surface of Iceland are from the Middle Miocene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
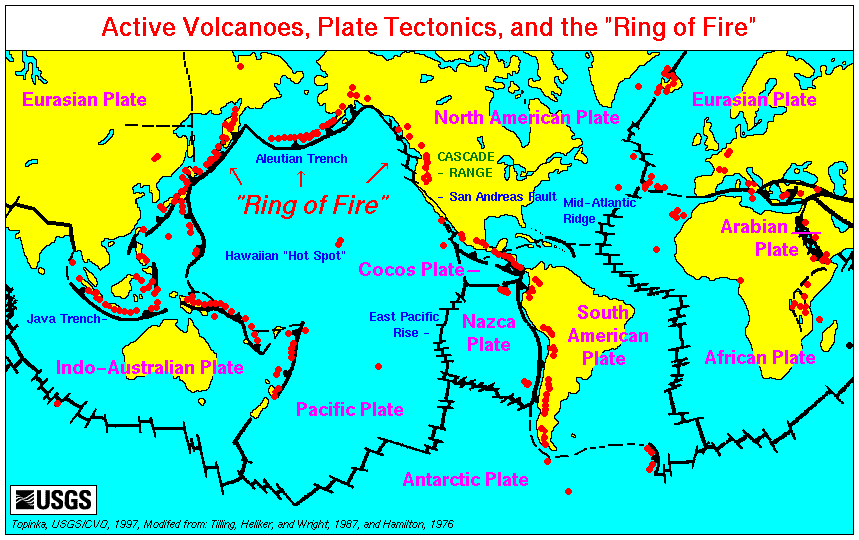
Active Volcanoes
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Volcanoes
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''Ice Age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek () 'most' and (; Latinized as ) 'new'. The aridification and cooling trends of the preceding Neogene were continued in the Pleistocene. The climate was strongly variable depending on the glacial cycle, oscillating between cold glacial periods and warmer interglacials, with the sea levels being up to lower th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuyas Of Iceland
A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided volcano formed when lava erupts through a thick glacier or ice sheet. They are rare worldwide, being confined to regions which were covered by glaciers and had active volcanism during the same period. As lava that erupts under a glacier cools very quickly and cannot travel far, it piles up into a steep-sided hill. If the eruption continues long enough, it either melts all the ice or emerges through the top of the ice and then creates normal-looking lava flows that make a flat cap on top of the hill. Discovering and dating the lava flows in a tuya has proven useful in reconstructing past glacial ice extents and thicknesses. Formation Tuyas are a type of subglacial volcano that consists of nearly horizontal beds of lava capping outward-dipping beds of fragmental volcanic rocks, and they often rise in isolation above a surrounding plateau. Tuyas are found in Iceland, British Columbia, the Santiam Pass region in Oregon, the Tyva Republic in eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grettis Saga
''Grettis saga Ăsmundarsonar'' (modern , reconstructed ), also known as ''Grettla'', ''Grettir's Saga'' or ''The Saga of Grettir the Strong'', is one of the Icelanders' sagas. It details the life of Grettir Ăsmundarson, a bellicose Icelandic outlaw, and is set in the eleventh century. Overview ''Grettis saga'' is considered one of the Sagas of Icelanders (''Ăslendingasögur''), which were written down in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries and record stories of events that supposedly took place between the ninth and the eleventh centuries in Iceland. The earliest manuscript of ''Grettis saga'' was written down some time just before 1400 CE, and the saga is thought to have been composed in its current form in the fourteenth century, making it a relatively late addition to the genre.. Introduction. ''The Saga of Grettir the Strong'', p. ix The author is unknown but it is believed that the saga may have been based on a previous account of Grettir's life written by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |