|
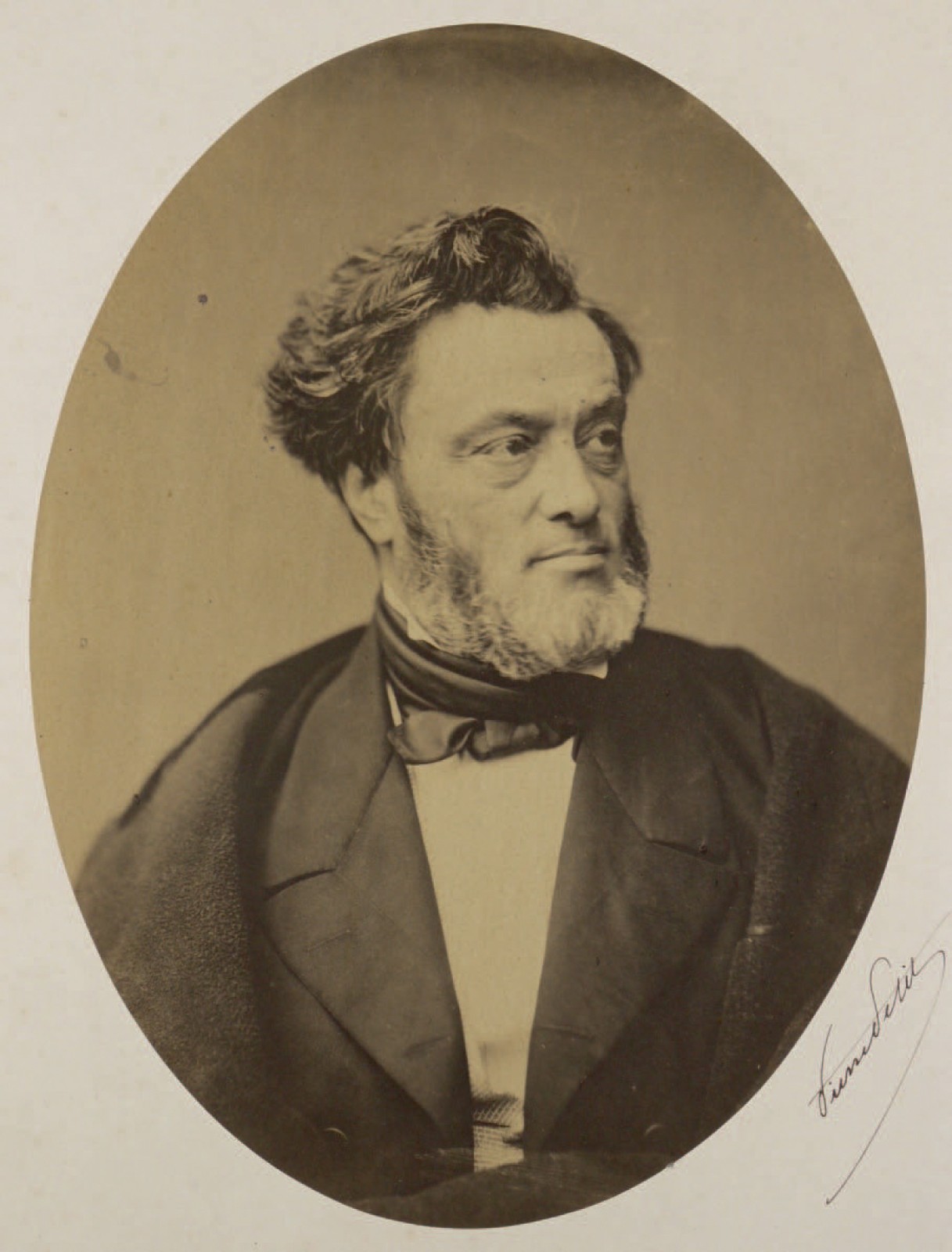
Émile Ollivier
Olivier Émile Ollivier (; 2 July 182520 August 1913) was a French statesman. Starting as an avid republican opposed to Emperor Napoleon III, he pushed the Emperor toward liberal reforms and in turn came increasingly into Napoleon's grip. He entered the cabinet and was the prime minister when Napoleon fell. Biography Émile Ollivier was born in Marseille. His father, Démosthène Ollivier (1799–1884), was a vehement opponent of the July Monarchy, and was returned by Marseille to the Constituent Assembly in 1848 which established a republic. The father's opposition to Louis Napoleon led to his banishment after the coup d'état of December 1851, and he returned to France only in 1860. With the establishment of the Second Republic, his father's influence with Ledru-Rollin secured for Émile Ollivier the position of commissary-general of the of Bouches-du-Rhône. Ollivier, then twenty-three, had just been called to the Parisian bar. Less radical in his political opinions th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Prime Minister Of France
The prime minister of France (), officially the prime minister of the French Republic (''Premier ministre de la République française''), is the head of government of the French Republic and the leader of its Council of Ministers. The prime minister is the holder of the second-highest office in France, after the president of France. The president, who appoints but cannot dismiss the prime minister, can request resignation. The Government of France, including the prime minister, can be dismissed by the National Assembly. Upon appointment, the prime minister proposes a list of ministers to the president. Decrees and decisions signed by the prime minister, like almost all executive decisions, are subject to the oversight of the administrative court system. Some decrees are taken after advice from the Council of State (), over which the prime minister is entitled to preside. Ministers defend the programmes of their ministries to the prime minister, who makes budgetary choices. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bouches-du-RhĂ´ne
Bouches-du-Rhône ( ; , ; ; "the Mouths of the Rhône") is a Departments of France, department in southern France. It borders Vaucluse to the north, Gard to the west and Var (department), Var to the east. The Mediterranean Sea lies to the south. Its Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city is Marseille; other important cities include Aix-en-Provence, Arles, Martigues and Aubagne. Marseille, France's second-largest city, has one of the largest Containerization, container ports in the country. It prides itself on being France's oldest city, founded by Greek settlers from Phocaea around 600 BC. Bouches-du-Rhône is the most populous department of the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region, with 2,043,110 inhabitants as of 2019.Populations légales 2019: 13 Bouches-du-Rhône< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Minister Of National Education (France)
The Ministry of National Education and Youth, or simply Ministry of National Education, as the title has changed several times in the course of the Fifth Republic, is the cabinet member in the Government of France who oversees the country's public educational system and supervises agreements and authorisations for private teaching organisations. The ministry's headquarters is located in the 18th century Hôtel de Rochechouart on the Rue de Grenelle in the 7th arrondissement of Paris. . Ministry of National Education. Retrieved on 6 May 2011. "Ministère de l’éducation nationale, de la jeunesse et de la vie associative Secrétariat général – Délégation à la communication 110 rue de Grenelle 75007 Paris" As education is France's large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Duc De Morny
Charles Auguste Louis Joseph de Morny, 1st Duc de Morny (; 15/16 September 181110 March 1865) was a French statesman. Biography Morny was born in Switzerland, and was the extra-marital son of Hortense de Beauharnais (the wife of Louis Bonaparte and queen of Holland) and Charles Joseph, Comte de Flahaut, making him half-brother of Emperor Napoleon III and grandson of Talleyrand. His birth was duly registered in a misleading certificate, which made him the legitimate son of Auguste Jean Hyacinthe Demorny, and born in Paris on 23 October 1811, and described as a landowner of Saint-Domingue. M. Demorny was in fact an officer in the Prussian army and a native of the French colony of St. Domingue (now Haiti), though he owned no land there or elsewhere. Morny was educated by his grandmother, AdelaĂŻde Filleul. After a brilliant school and college career the future duc de Morny received a commission in the army, and the next year he entered the staff college. The comte de Morny, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexandre Joseph Colonna, Count Walewski
Alexandre Florian Joseph, Count Colonna-Walewski (; ; 4 May 181027 September 1868), also Count of the Empire, was a Polish and French politician and diplomat, the unacknowledged son of French emperor Napoleon I. He is best known for his position as foreign minister of France under his cousin Napoleon III and for his diplomatic efforts presiding over the Congress of Paris, which created peace in the Crimean War and laid the base for modern international law of the sea with the Paris Declaration Respecting Maritime Law. Early years ''Alexandre Florian Joseph Colonna Walewski'' was born on May 4, 1810, at Walewice, near Warsaw, to Countess Maria Walewska, the Polish noblewoman and mistress of Napoleon Bonaparte. His mother conceived him while residing near Schönbrunn Palace in Vienna, where Napoleon was temporarily staying. When Marie requested to give birth in Paris, Napoleon insisted she return to her husband's estate in Poland. Count Athanasius Walewski, nearly eighty years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Étienne Vacherot
Étienne Vacherot (29 July 180928 July 1897) was a French philosophical writer. Life Vacherot was born of peasant parentage at Torcenay, near Langres in the Haute-Marne ''département'' of France. He was educated at the École Normale Supérieure, and returned there as director of studies in 1838, after some years spent in provincial schoolmasterships. In 1839 he succeeded his master Victor Cousin as professor of philosophy at the Sorbonne. His ''Histoire critique de l'école d'Alexandrie'' (3 vols. 1846–51), was his first and best-known work. It drew on him attacks from the Clerical party which led to his suspension in 1851. Shortly afterwards he refused to swear allegiance to the new imperial government, and was dismissed from his post. His work ''La Démocratie'' (1859) led to a political prosecution and imprisonment. This work in turn cites Léon Ollé-Laprune, ''Étienne Vacherot'' (Paris, 1898). On 7 March 1868 he was elected to the Académie des sciences morales et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ernest Picard
Louis Joseph Ernest Picard (24 December 1821 – 13 May 1877) was a French politician. Life Louis Joseph Ernest Picard was born in Paris, France, Paris. After taking his doctorate in law in 1846 he joined the Parisian bar. Elected to the ''corps législatif'' in 1858, he became a follower of Émile Ollivier. As Ollivier moved towards the government standpoint, Picard, one of the members of the group known as ''Les Cinq'', veered more to the Left-wing politics, left. In the 1860s Picard was an active member of the Conférence Molé, as were Léon Gambetta, Clément Laurier and Léon Renault. At that time the Molé met in the Café Procope in the Rue de l'Ancienne-Comédie, the oldest coffee house in Paris. In 1868 he founded a weekly democratic journal, ''L'Electeur libre'', and in 1869 was elected both for Hérault and Paris, electing to sit for the former. From 4 September 1870 he held the portfolio of finance in the government of National Defence. In January 1871 he accompa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jules Favre
Jules Claude Gabriel Favre (21 March 1809 – 20 January 1880) was a French statesman and lawyer. After the establishment of the Third Republic in September 1870, he became one of the leaders of the Moderate Republicans in the National Assembly. Early years He was born in Lyon, and began his career as a lawyer. From the time of the Revolution of 1830, he openly declared himself a republican, and in political trials he took the opportunity to express this opinion. After the Revolution of 1848 he was elected deputy for Lyon to the Constituent Assembly, where he sat among the Moderate Republicans, voting against the socialists. When Louis Napoleon was elected President of France, Favre openly opposed him.On 2 December 1851 he tried with Victor Hugo and others to organize armed resistance in the streets of Paris. After the ''coup d'état'', he withdrew from politics, returned to the legal profession, distinguishing himself by his defence of Felice Orsini, the perpetrator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alfred Darimon
Alfred may refer to: Arts and entertainment *''Alfred J. Kwak'', Dutch-German-Japanese anime television series * ''Alfred'' (Arne opera), a 1740 masque by Thomas Arne * ''Alfred'' (Dvořák), an 1870 opera by AntonĂn Dvořák *"Alfred (Interlude)" and "Alfred (Outro)", songs by Eminem from the 2020 album '' Music to Be Murdered By'' Business and organisations * Alfred, a radio station in Shaftesbury, England *Alfred Music, an American music publisher * Alfred University, New York, U.S. * The Alfred Hospital, a hospital in Melbourne, Australia People * Alfred (name) includes a list of people and fictional characters called Alfred * Alfred the Great (848/49 – 899), or Alfred I, a king of the West Saxons and of the Anglo-Saxons Places Antarctica * Mount Alfred (Antarctica) Australia * Alfredtown, New South Wales * County of Alfred, South Australia Canada * Alfred and Plantagenet, Ontario ** Alfred, Ontario, a community in Alfred and Plantagenet * Alfred Island, Nunavut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
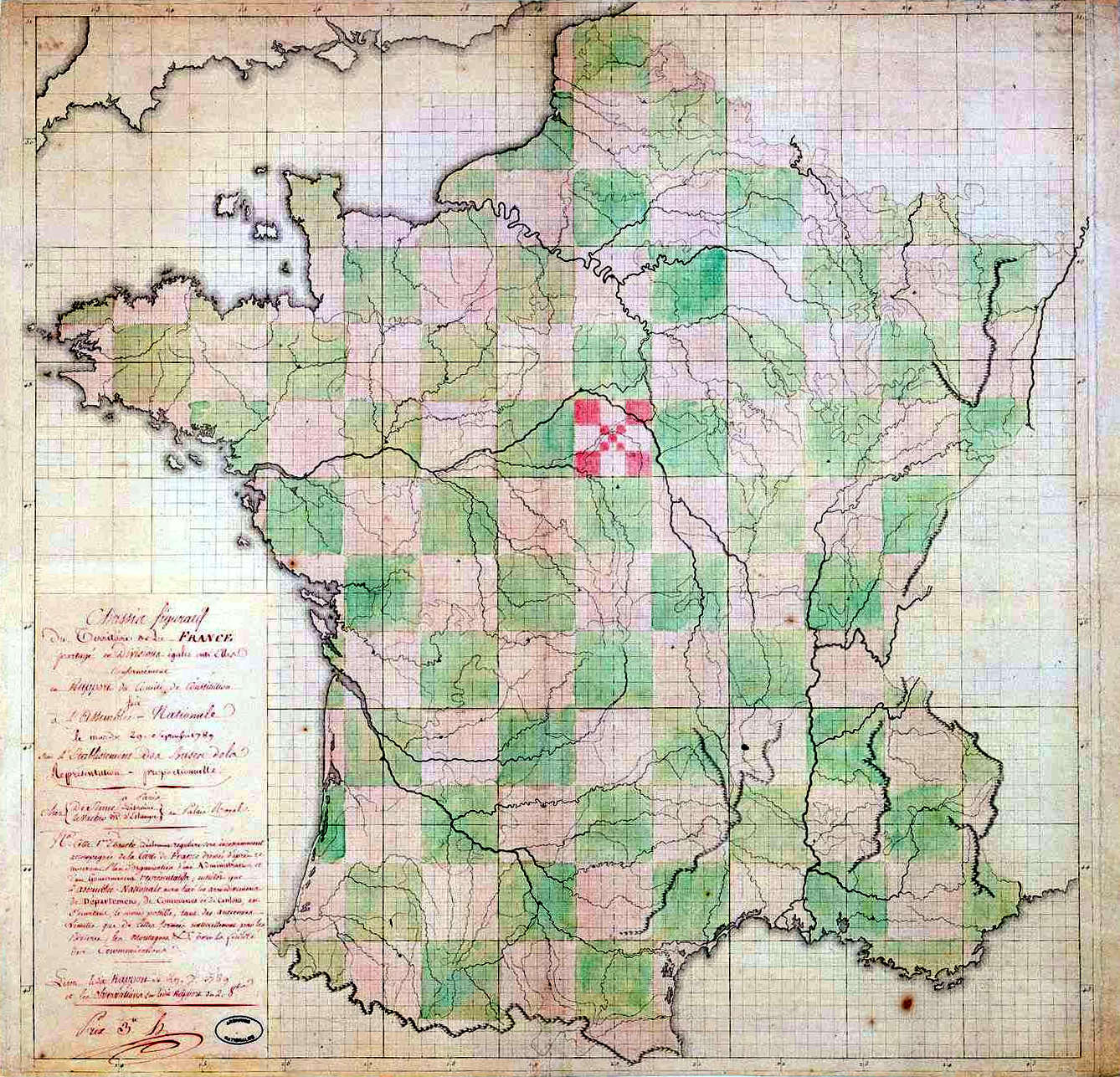
DĂ©partement
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level (" territorial collectivities"), between the administrative regions and the communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 arrondissements and 2,054 cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called general councils ( , ). Each council has a president. Their main areas of responsibility include the management of a number of social and welfare allowances, of junior hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Seine (département)
Seine is a former department of France, which encompassed Paris and its immediate suburbs. It was the only enclaved department of France, being surrounded entirely by the former Seine-et-Oise department. Its prefecture was Paris and its INSEE number was 75. The Seine department was disbanded in 1968 and its territory divided among four new departments: Paris, Hauts-de-Seine, Seine-Saint-Denis and Val-de-Marne. '' La DĂ©pĂŞche'', 10 July 2014. General characteristics From 1929 to its abolition in 1968, the department consiste ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Haute-Marne
Haute-Marne (; English: Upper Marne) is a department in the Grand Est region of Northeastern France. Named after the river Marne, its prefecture is Chaumont. In 2019, it had a population of 172,512.Populations légales 2019: 52 Haute-Marne INSEE History Haute-Marne is one of the original 83 departments created during the French Revolution on March 4, 1790. It was created from parts of the former provinces of ,[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |