|
أپnyos Jedlik
أپnyos Istvأ،n Jedlik (1800 – 1895) was a Hungarian inventor, engineer, physicist, and Benedictine priest. He was also a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and author of several books. He is considered by Hungarians and Slovaks to be the unsung father of the dynamo and electric motor. Career He was born in Szimإ‘, Kingdom of Hungary (today Zemnأ©, Slovakia). His parents were Ferenc Jedlik and Rozأ،lia Szabأ³. His mother was a member of a Hungarian noble family, while his paternal grandfather was of Slovak origin moving in 1720 from Liptأ³ County to Szimإ‘. ("It is likely that the Jedlik family arrived from Liptأ³ by boat on the River Vأ،g in 1720 and started to live in Szimإ‘.") Jedlik's education began at high schools in Nagyszombat (today Trnava) and Pozsony (today Bratislava). In 1817 he became a Benedictine, and from that time continued his studies at the schools of that order, where he was known by his Latin name . In 1818-20 he studied humanities at the Ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kingdom Of Hungary (1526–1867)
The Kingdom of Hungary between 1526 and 1867 existed as a state outside the Holy Roman Empire, but part of the lands of the Habsburg monarchy that became the Austrian Empire in 1804. After the Battle of Mohأ،cs in 1526, the country was ruled by two crowned kings ( John I and Ferdinand I). Initially, the exact territory under Habsburg rule was disputed because both rulers claimed the whole kingdom. This unsettled period lasted until 1570 when John Sigismund Zأ،polya (John II) abdicated as King of Hungary in Emperor Maximilian II's favor. In the early stages, the lands that were ruled by the Habsburg Hungarian kings were regarded as both the "Kingdom of Hungary" and "Royal Hungary". Royal Hungary was the symbol of the continuity of formal law after the Ottoman occupation, because it could preserve its legal traditions, but in general, it was ''de facto'' a Habsburg province.Raphael PataThe Jews of Hungary: History, Culture, Psychology Wayne State University Press, 1996, p. 153 T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
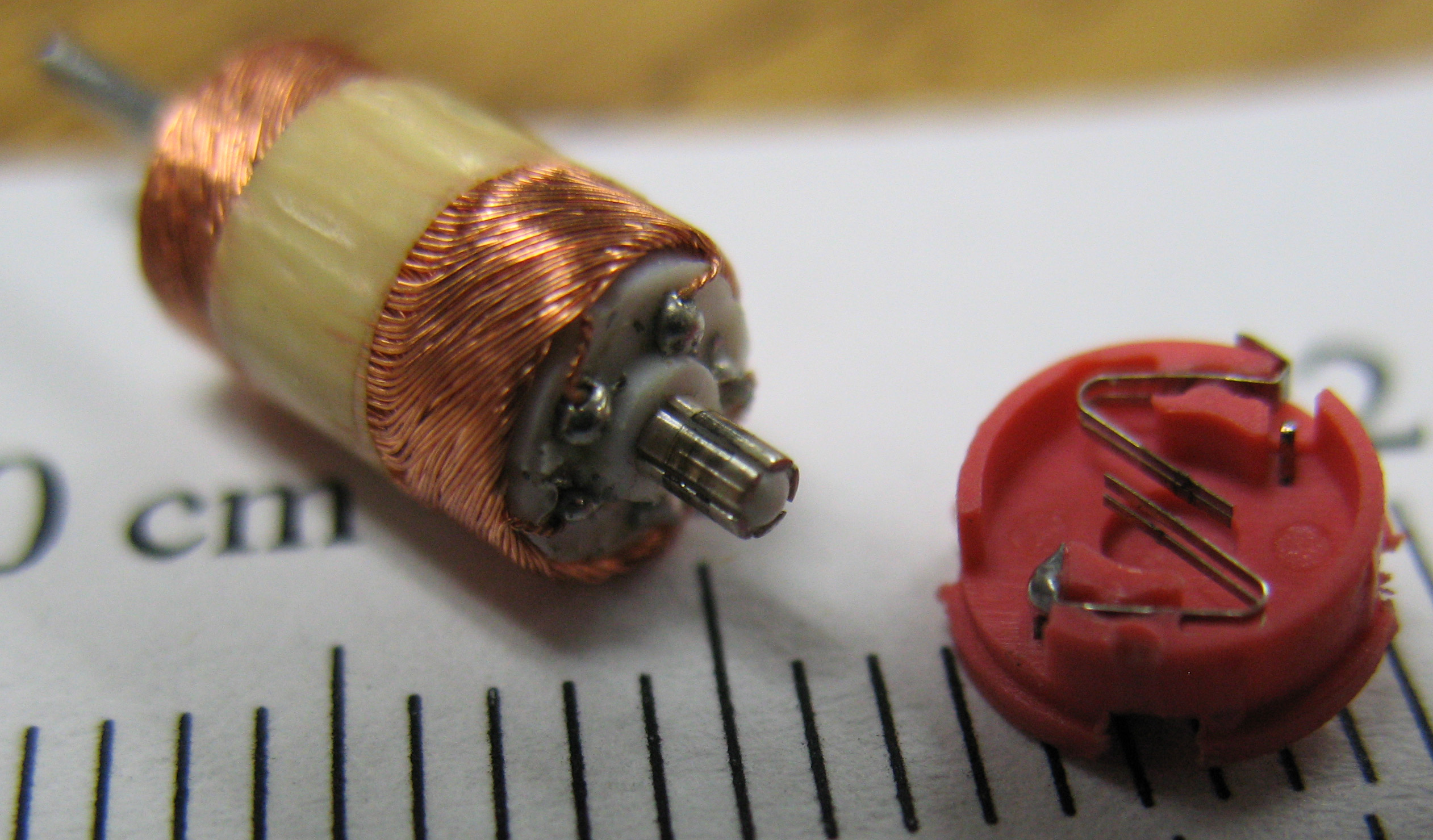
Commutator (electric)
A commutator is a rotary switch, electrical switch in certain types of electric motors and electrical generators that periodically reverses the Current (electricity), current direction between the rotor and the external circuit. It consists of a cylinder composed of multiple metal contact segments on the rotating armature (electrical engineering), armature of the machine. Two or more electrical contacts called "brush (electric), brushes" made of a soft conductive material like carbon press against the commutator, making sliding contact with successive segments of the commutator as it rotates. The windings (coils of wire) on the armature (electrical engineering), armature are connected to the commutator segments. Commutators are used in direct current (DC) machines: dynamos (DC generators) and many DC motors as well as universal motors. In a motor the commutator applies electric current to the windings. By reversing the current direction in the rotating windings each half turn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Armature (electrical Engineering)
In electrical engineering, the armature is the winding (or set of windings) of an electric machine which carries alternating current. The armature windings conduct Alternating current, AC even on Direct current, DC machines, due to the Commutator (electric), commutator action (which periodically reverses current direction) or due to electronic commutation, as in Brushless DC electric motor, brushless DC motors. The armature can be on either the Rotor (electric), rotor (rotating part) or the stator (field coil, stationary part), depending on the type of electric machine. Shapes of Armature (electrical engineering), armature used in motors include double-T and triple-T armatures. The armature windings interact with the magnetic field (magnetic flux) in the air-gap; the magnetic field is generated either by permanent magnets, or electromagnets formed by a conducting coil. The armature must carry electric current, current, so it is always a electrical conductor, conductor or a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
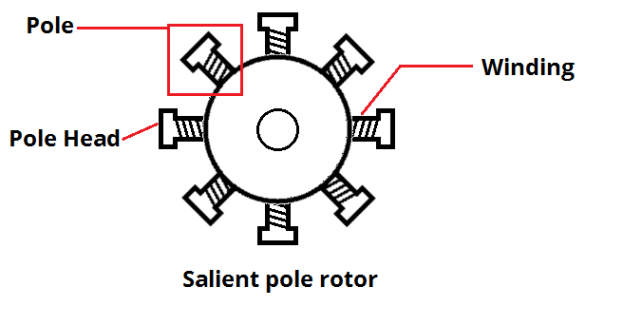
Stator
The stator is the stationary part of a rotary system, found in electric generators, electric motors, sirens, mud motors, or biological rotors (such as bacterial flagella or ATP synthase). Energy flows through a stator to or from the rotating component of the system, the rotor. In an electric motor, the stator provides a magnetic field that drives the rotating armature; in a generator, the stator converts the rotating magnetic field to electric current. In fluid powered devices, the stator guides the flow of fluid to or from the rotating part of the system. Design Motor stators are made either from iron/steel or from a printed circuit board (PCB). Originally applied to low-power applications, PCB stators can be lighter, smaller, and less noisy. One design embeds thin copper traces in the PCB stator that serve as the windings. The traces are interleaved with epoxy-glass laminates, that insulate each coil from its neighbors. An air core replaces the traditional iron core ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
DC Electric Motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate Laplace force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may also be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be brushed or brushless, single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase, axial or radial flux, and may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Standardized electric motors provide power for industrial use. The larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional electric current, flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor (material), conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, electrical insulation, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron beam, electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A archaism, term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains Electronics, electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hans Christian أکrsted
Hans Christian أکrsted (; 14 August 1777 – 9 March 1851), sometimes Transliteration, transliterated as Oersted ( ), was a Danish chemist and physicist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields. This phenomenon is known as Oersted's law. He also discovered aluminium, a chemical element. A leader of the Danish Golden Age, أکrsted was a close friend of Hans Christian Andersen and the brother of politician and jurist Anders Sandأ¸e أکrsted, who served as Prime Minister of Denmark from 1853 to 1854. Early life and studies أکrsted was born in Rudkأ¸bing in 1777. As a young boy he developed an interest in science while working for his father, who was a pharmacist in the Rudkأ¸bing Pharmacy, town's pharmacy. He and his brother Anders Sandأ¸e أکrsted, Anders received most of their early education through self-study at home, going to Copenhagen in 1793 to take entrance exams for the University of Copenhagen, where both brothers excelled academically. By 1796, أکrst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gergely Czuczor
Gergely Czuczor (17 December 1800 – 9 September 1866) was a Hungarian Benedictine monk, a poet and linguist, member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. Baptized Istvأ،n (the Hungarian equivalent of ''Stephen'') he took Gergely (''Gregory'') as his religious name. As down-to-earth common sense a poet as Petإ‘fi: his national poems also quickly became folk songs and popular. Both poets tended to emulate the rhythm of folk songs in their poems, which served the Nationalist cause in the popular common sense way. He participated in the fight for freedom against Habsburg The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ... rule. One of his most famous poems, "Riadأ³" i.e. 'Alarm', was published in Kossuth's newspaper on 21 December 1848 while the Austrian troops were already closi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |