Kingdom Of Hungary (1526–1867) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Kingdom of Hungary between 1526 and 1867 existed as a state outside the
The Jews of Hungary: History, Culture, Psychology
Wayne State University Press, 1996, p. 153 The Hungarian nobility forced Vienna to admit that Hungary was a special unit of the Habsburg lands and had to be ruled in
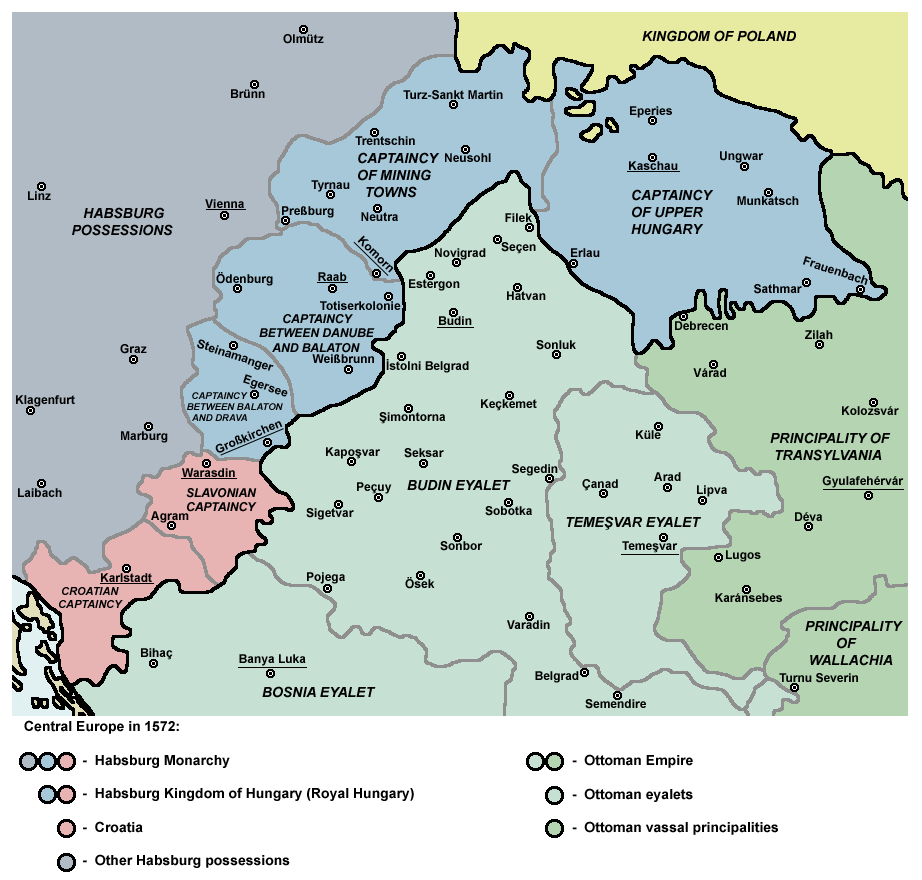 Royal Hungary (1526–1699), (, ), was the name of the portion of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary where the
Royal Hungary (1526–1699), (, ), was the name of the portion of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary where the
Conflict and chaos in Eastern Europe
Palgrave Macmillan, 1995, p. 62
 The
The

 As the Habsburgs' control of the Turkish possessions started to increase, the ministers of Leopold I argued that he should rule Hungary as conquered territory. At the Diet of "Royal Hungary" in Pressburg, in 1687, the Emperor promised to observe all laws and privileges. Nonetheless, the hereditary succession of the Habsburgs was recognized, and the nobles' right of resistance was abrogated. In 1690 Leopold began redistributing lands freed from the Turks. Protestant nobles and all other
As the Habsburgs' control of the Turkish possessions started to increase, the ministers of Leopold I argued that he should rule Hungary as conquered territory. At the Diet of "Royal Hungary" in Pressburg, in 1687, the Emperor promised to observe all laws and privileges. Nonetheless, the hereditary succession of the Habsburgs was recognized, and the nobles' right of resistance was abrogated. In 1690 Leopold began redistributing lands freed from the Turks. Protestant nobles and all other
Austerlitz, 1805. december 2. A három császár csatája – magyar szemmel
In: Eszmék, forradalmak, háborúk. Vadász Sándor 80 éves, ELTE, Budapest, 2010 p. 557 By the start of the 19th century, the aim of Hungary's agricultural producers had shifted from subsistence farming and small-scale production for local trade to cash-generating, large-scale production for a wider market. Road and waterway improvements cut transportation costs, while urbanization in Austria,
File:Gróf Széchenyi István.jpg,
 After the
After the
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, but part of the lands of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
that became the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
in 1804. After the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
in 1526, the country was ruled by two crowned kings ( John I and Ferdinand I). Initially, the exact territory under Habsburg rule was disputed because both rulers claimed the whole kingdom. This unsettled period lasted until 1570 when John Sigismund Zápolya (John II) abdicated as King of Hungary in Emperor Maximilian II's favor.
In the early stages, the lands that were ruled by the Habsburg Hungarian kings were regarded as both the "Kingdom of Hungary" and "Royal Hungary". Royal Hungary was the symbol of the continuity of formal law after the Ottoman occupation, because it could preserve its legal traditions, but in general, it was ''de facto'' a Habsburg province.Raphael PataThe Jews of Hungary: History, Culture, Psychology
Wayne State University Press, 1996, p. 153 The Hungarian nobility forced Vienna to admit that Hungary was a special unit of the Habsburg lands and had to be ruled in
conformity
Conformity or conformism is the act of matching attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors to social group, group norms, politics or being like-minded. Social norm, Norms are implicit, specific rules, guidance shared by a group of individuals, that guide t ...
with its own special laws. However, Hungarian historiography positioned Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
in a direct continuity with the medieval Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from 1000 to 1946 and was a key part of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526-1918. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the Coro ...
in pursuance of the advancement of Hungarian interests.
Under the terms of the Treaty of Karlowitz, which ended the Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War () or The Last Crusade, also called in Ottoman sources The Disaster Years (), was a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League (1684), Holy League consisting of the Holy Roman Empire, Polish–Lith ...
in 1699, the Ottomans ceded nearly all of Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary () encompassed the parts of the Kingdom of Hungary which were under the rule of the Ottoman Empire from the occupation of Buda in 1541 until the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The territory was incorporated into the empire, under ...
. The new territories were united with the territory of the Kingdom of Hungary, and although its powers were mostly formal, the Diet of Hungary in Pressburg ruled the lands.
Two major Hungarian rebellions were the Rákóczi's War of Independence in the early 18th century and the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848, also known in Hungary as Hungarian Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many Revolutions of 1848, European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in ...
and marked important shifts in the evolution of the polity. The kingdom became a dual monarchy in 1867, known as Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
.
Royal Hungary (1526–1699)
 Royal Hungary (1526–1699), (, ), was the name of the portion of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary where the
Royal Hungary (1526–1699), (, ), was the name of the portion of the medieval Kingdom of Hungary where the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout Europe d ...
were recognized as Kings of Hungary
The King of Hungary () was the Monarchy, ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Magyarország apostoli királya'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 ...
in the wake of the Ottoman victory at the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; , ) took place on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, in the Kingdom of Hungary. It was fought between the forces of Hungary, led by King Louis II of Hungary, Louis II, and the invading Ottoman Empire, commanded by Suleima ...
(1526) and the subsequent partition of the country.
Temporary territorial division between the rival rulers John I and Ferdinand I occurred only in 1538, under the Treaty of Nagyvárad
The Treaty of Nagyvárad (or Treaty of Grosswardein) was a secret peace agreement between Emperor Ferdinand I and John Szapolyai, rival claimants to the Kingdom of Hungary, signed in Grosswardein / Várad (modern-day Oradea, Romania) on Februa ...
, when the Habsburgs got the northern and western parts of the country (Royal Hungary), with the new capital Pressburg (Pozsony, now Bratislava
Bratislava (German: ''Pressburg'', Hungarian: ''Pozsony'') is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Slovakia, Slovak Republic and the fourth largest of all List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river Danube. ...
). John I secured the eastern part of the kingdom (known as the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom
The Eastern Hungarian Kingdom ( ) is a modern term coined by some historians to designate the realm of John Zápolya and his son John Sigismund Zápolya, who contested the claims of the House of Habsburg to rule the Kingdom of Hungary from 1526 ...
). The Habsburg monarchs needed the economic power of Hungary for the Ottoman wars. During the Ottoman wars the territory of the former Kingdom of Hungary was reduced by around 60 per cent. Despite these enormous territorial and demographic losses, the smaller and heavily war torn Royal Hungary was as important as the Austrian hereditary lands or the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted o ...
in the late 16th century.
The territory of present-day Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
and northwestern Transdanubia
Transdanubia ( ; , or ', ) is a traditional region of Hungary. It is also referred to as Hungarian Pannonia, or Pannonian Hungary.
Administrative divisions Traditional interpretation
The borders of Transdanubia are the Danube River (north and ...
were parts of this polity, while control of the region of northeastern Hungary often shifted between Royal Hungary and the Principality of Transylvania. The central territories of the medieval Hungarian kingdom were annexed by the Ottoman Empire for 150 years (see Ottoman Hungary
Ottoman Hungary () encompassed the parts of the Kingdom of Hungary which were under the rule of the Ottoman Empire from the occupation of Buda in 1541 until the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699. The territory was incorporated into the empire, under ...
).
In 1570, John Sigismund Zápolya abdicated as King of Hungary in Emperor Maximilian II's favor under the terms of the Treaty of Speyer.
The term "Royal Hungary" fell into disuse after 1699, and the Habsburg kings referred to the newly enlarged country by the more formal term "Kingdom of Hungary".
Habsburg kings
The Habsburgs, an influential dynasty of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, were elected Kings of Hungary
The King of Hungary () was the Monarchy, ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Magyarország apostoli királya'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 ...
.
Royal Hungary became a part of the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
and enjoyed little influence in Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
. The Habsburg king directly controlled Royal Hungary's financial, military, and foreign affairs, and imperial troops guarded its borders. The Habsburgs avoided filling the office of palatine
A palatine or palatinus (Latin; : ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman Empire, Roman times.
to prevent the holders amassing too much power. In addition, the so-called Turkish question divided the Habsburgs and the Hungarians: Vienna wanted to maintain peace with the Ottomans; the Hungarians wanted the Ottomans ousted. As the Hungarians recognized the weakness of their position, many became anti-Habsburg. They complained about foreign rule, the behaviour of foreign garrisons, and the Habsburgs' recognition of Turkish suzerainty in the Principality of Transylvania. This was usually under the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
, however, it often had dual vassalage -Ottoman Turkish sultans and the Habsburg Hungarian kings- in the 16th and 17th centuries).Dennis P. HupchickConflict and chaos in Eastern Europe
Palgrave Macmillan, 1995, p. 62
Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, who were persecuted in Royal Hungary, considered the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
a greater menace than the Turks, however.
The Austrian branch of Habsburg monarchs needed the economic power of Hungary for the Ottoman wars. During the Ottoman wars the territory controlled by the Kingdom of Hungary shrank by around 60%. Despite these enormous territorial and demographic losses, the smaller, heavily war-torn Royal Hungary had remained as economically important to the Habsburg rulers as the Austrian hereditary lands or the Bohemian crownlands even in the late 16th century. Out of all his countries, the depleted Kingdom of Hungary was, at that time, Ferdinand I's largest source of revenue.
Reformation
 The
The Reformation
The Reformation, also known as the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation, was a time of major Theology, theological movement in Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the p ...
spread quickly, and by the early 17th century hardly any noble families remained Catholic. In Royal Hungary, the majority of the population became Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
by the end of the 16th century.
Archbishop Péter Pázmány reorganized Royal Hungary's Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and led a Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also sometimes called the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to, and as an alternative to or from similar insights as, the Protestant Reformations at the time. It w ...
that reversed the Protestants' gains in Royal Hungary, using persuasion rather than intimidation. The Reformation caused rifts between Catholics, who often sided with the Habsburgs, and Protestants, who developed a strong national identity and became rebels in Austrian eyes. Chasms also developed between the mostly Catholic magnates and the mainly Protestant lesser nobles.
Kingdom of Hungary in the early modern period until 1848
18th century

 As the Habsburgs' control of the Turkish possessions started to increase, the ministers of Leopold I argued that he should rule Hungary as conquered territory. At the Diet of "Royal Hungary" in Pressburg, in 1687, the Emperor promised to observe all laws and privileges. Nonetheless, the hereditary succession of the Habsburgs was recognized, and the nobles' right of resistance was abrogated. In 1690 Leopold began redistributing lands freed from the Turks. Protestant nobles and all other
As the Habsburgs' control of the Turkish possessions started to increase, the ministers of Leopold I argued that he should rule Hungary as conquered territory. At the Diet of "Royal Hungary" in Pressburg, in 1687, the Emperor promised to observe all laws and privileges. Nonetheless, the hereditary succession of the Habsburgs was recognized, and the nobles' right of resistance was abrogated. In 1690 Leopold began redistributing lands freed from the Turks. Protestant nobles and all other Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former pa ...
thought disloyal by the Habsburgs lost their estates, which were given to foreigners. Vienna controlled the foreign affairs, defense, tariffs, and other functions.
The repression of Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
and the land seizures frustrated the Hungarians, and in 1703 a peasant uprising sparked an eight-year rebellion against Habsburg rule. In Transylvania, which became part of Hungary again at the end of the 17th century (as a province, called " Principality of Transylvania" with the Diet seated at Gyulafehérvár), the people united under Francis II Rákóczi, a Roman Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
magnate. Most of Hungary soon supported Rákóczi, and the Hungarian Diet voted to annul the Habsburgs' right to the throne. Fortunes turned against the Hungarians, however, when the Habsburgs made peace in the west and turned their full force against them. The war ended in 1711, when Count Károlyi, General of the Hungarian Armies agreed to the Treaty of Szatmár. The treaty contained the emperor's agreement to reconvene the Diet in Pressburg and to grant an amnesty for the rebels.
Leopold's successor, King Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
(1711–40), began building a workable relationship with Hungary after the Treaty of Szatmár. Charles asked the approval of the Diet for the Pragmatic Sanction
A pragmatic sanction is a sovereign's solemn decree on a matter of primary importance and has the force of fundamental law. In the late history of the Holy Roman Empire, it referred more specifically to an edict issued by the Emperor.
When used ...
, under which the Habsburg monarch was to rule Hungary not as emperor, but as a king subject to the restraints of Hungary's constitution and laws. He hoped that the Pragmatic Sanction would keep the Habsburg Empire intact if his daughter, Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the ...
, succeeded him. The Diet approved the Pragmatic Sanction in 1723, and Hungary thus agreed to become a hereditary monarchy under the Habsburgs for as long as their dynasty existed. In practice, however, Charles and his successors governed almost autocratically, controlling Hungary's foreign affairs, defense, and finance but lacking the power to tax the nobles without their approval.
Charles organized the country under a centralized administration and in 1715 established a standing army under his command, which was entirely funded and manned by the non-noble population. This policy reduced the nobles' military obligation without abrogating their exemption from taxation. Charles also banned conversion to Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, required civil servants to profess Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
, and forbade Protestant students to study abroad.
Maria Theresa (1741–80) faced an immediate challenge from Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
's Frederick II when she became head of the House of Habsburg, facing the First Silesian War. In 1741 she appeared before the Diet of Pressburg holding her newborn son and entreated Hungary's nobles to support her. They stood behind her and helped secure her rule. Maria Theresa later took measures to reinforce links with Hungary's magnates. She established special schools to attract Hungarian nobles to Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
.
Under Charles and Maria Theresa, Hungary experienced further economic decline. Centuries of Ottoman occupation and war had reduced Hungary's population drastically, and large parts of the country's southern half were almost deserted. A labor shortage developed as landowners restored their estates. In response, the Habsburgs began to colonize Hungary with large numbers of peasants from all over Europe, especially Slovaks, Serbs, Croatians, and Germans. Many Jews also immigrated from Vienna and the empire's Polish lands near the end of the 18th century. Hungary's population more than tripled to 8 million between 1720 and 1787. However, only 39 percent of its people were Magyars, who lived mainly in the center of the country.
In the first half of the 18th century, Hungary had an agricultural economy that employed 90 percent of the population. The nobles failed to use fertilizers, roads were poor and rivers blocked, and crude storage methods caused huge losses of grain. Barter had replaced money transactions, and little trade existed between towns and the serfs. After 1760 a labor surplus developed. The serf population grew, pressure on the land increased, and the serfs' standard of living declined. Landowners began making greater demands on new tenants and began violating existing agreements. In response, Maria Theresa issued her Urbarium of 1767 to protect the serfs by restoring their freedom of movement and limiting the corvée
Corvée () is a form of unpaid forced labour that is intermittent in nature, lasting for limited periods of time, typically only a certain number of days' work each year. Statute labour is a corvée imposed by a state (polity), state for the ...
. Despite her efforts and several periods of strong demand for grain, the situation worsened. Between 1767 and 1848, many serfs left their holdings. Most became landless farmworkers because a lack of industrial development meant few opportunities for work in the towns.
Joseph II (1780–90), a dynamic leader strongly influenced by the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment (also the Age of Reason and the Enlightenment) was a Europe, European Intellect, intellectual and Philosophy, philosophical movement active from the late 17th to early 19th century. Chiefly valuing knowledge gained th ...
, shook Hungary from its malaise when he inherited the throne from his mother, Maria Theresa. In the framework of Josephinism, Joseph sought to centralize control of the empire and to rule it by decree as an enlightened despot. He refused to take the Hungarian coronation oath to avoid being constrained by Hungary's constitution. In 1781–82 Joseph issued a Patent of Toleration, followed by an Edict of Tolerance which granted Protestants and Orthodox Christians full civil rights and Jews freedom of worship. He decreed that German replace Latin as the kingdom's official language and granted the peasants the freedom to leave their holdings, to marry, and to place their children in trades. Hungary, Slavonia
Slavonia (; ) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria County, Istria, one of the four Regions of Croatia, historical regions of Croatia. Located in the Pannonian Plain and taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with f ...
, Croatia
Croatia, officially the Republic of Croatia, is a country in Central Europe, Central and Southeast Europe, on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. It borders Slovenia to the northwest, Hungary to the northeast, Serbia to the east, Bosnia and Herze ...
, the Military Frontier and Transylvania
Transylvania ( or ; ; or ; Transylvanian Saxon dialect, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen'') is a List of historical regions of Central Europe, historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and ...
became a single imperial territory under one administration, called the Kingdom of Hungary or " Lands of the Crown of St. Stephen". When the Hungarian nobles again refused to waive their exemption from taxation, Joseph banned imports of Hungarian manufactured goods into Austria and began a survey to prepare for the imposition of a general land tax.
Joseph's reforms outraged nobles and clergy of Hungary, and the peasants of the country grew dissatisfied with taxes, conscription, and requisitions of supplies. Hungarians perceived Joseph's language reform as German cultural hegemony
In Marxist philosophy, cultural hegemony is the dominance of a culturally diverse society by the ruling class who shape the culture of that society—the beliefs and explanations, perceptions, values, and mores—so that the worldview of the rul ...
, and they reacted by insisting on the right to use their own tongue. As a result, Hungarian lesser nobles sparked a renaissance of the Hungarian language and culture, and a cult of national dance and costume flourished. The lesser nobles questioned the loyalty of the magnates, of whom less than half were ethnic Hungarians, and even those had become French- and German-speaking courtiers. The Hungarian national reawakening subsequently triggered national revivals among the Slovak, Romanian, Serbian, and Croatian minorities within Hungary and Transylvania, who felt threatened by both German and Hungarian cultural hegemony. These national revivals later blossomed into the nationalist movements of the 19th and 20th centuries that contributed to the empire's ultimate collapse.
Late in his reign, Joseph led a costly, ill-fated campaign against the Turks that weakened his empire. On January 28, 1790, three weeks before his death, the emperor issued a decree cancelling all of his reforms except the Patent of Toleration, peasant reforms, and the abolition of the religious orders.
Joseph's successor, Leopold II (1790–92), re-introduced the bureaucratic technicality which viewed Hungary as a separate country under a Habsburg king. In 1791 the Diet passed Law X, which stressed Hungary's status as an independent kingdom ruled only by a king legally crowned according to Hungarian laws. Law X later became the basis for demands by Hungarian reformers for statehood in the period from 1825 to 1849. New laws again required approval of both the Habsburg king and the Diet, and Latin was restored as the official language. The peasant reforms remained in effect, however, and Protestants remained equal before the law. Leopold died in March 1792 just as the French Revolution was about to degenerate into the Reign of Terror
The Reign of Terror (French: ''La Terreur'', literally "The Terror") was a period of the French Revolution when, following the creation of the French First Republic, First Republic, a series of massacres and Capital punishment in France, nu ...
and send shock waves through the royal houses of Europe.
First half of the 19th century
Enlightened absolutism ended in Hungary under Leopold's successor, Francis II (ruled 1792–1835), who developed an almost abnormal aversion to change, bringing Hungary decades of political stagnation. In 1795 the Hungarian police arrested Ignác Martinovics and several of the country's leading thinkers for plotting aJacobin
The Society of the Friends of the Constitution (), renamed the Society of the Jacobins, Friends of Freedom and Equality () after 1792 and commonly known as the Jacobin Club () or simply the Jacobins (; ), was the most influential political cl ...
kind of revolution to install a radical democratic, egalitarian political system in Hungary. Thereafter, Francis resolved to extinguish any spark of reform that might ignite a revolution. The execution of the alleged plotters silenced any reform advocates among the nobles, and for about three decades reform ideas remained confined to poetry and philosophy. The magnates, who also feared that the influx of revolutionary ideas might precipitate a popular uprising, became a tool of the crown and seized the chance to further burden the peasants.
In 1804 Francis II, who was also the Holy Roman Emperor and ruler of the other dynastic lands of the Habsburg dynasty, founded the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire, officially known as the Empire of Austria, was a Multinational state, multinational European Great Powers, great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the Habsburg monarchy, realms of the Habsburgs. Duri ...
, in which Hungary and all his other dynastic lands were included. In doing so he created a formal overarching structure for the Habsburg Monarchy, that had functioned as a composite monarchy
A composite monarchy (or composite state) is a historical category, introduced by H. G. Koenigsberger in 1975 and popularised by Sir John H. Elliott, that describes early modern states consisting of several countries under one ruler, sometimes ...
for about three hundred years before. He himself became Francis I (''Franz I.''), the first Emperor of Austria
The emperor of Austria (, ) was the ruler of the Austrian Empire and later the Austro-Hungarian Empire. The hereditary imperial title and office was proclaimed in 1804 by Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, a member of the House of Habsburg-Lorr ...
(''Kaiser von Österreich''), ruling from 1804 to 1835, so later he was named the one and only ''Doppelkaiser'' (double emperor) in history. The workings of the overarching structure and the status of the new '' Kaiserthum''’s component lands at first stayed much as they had been under the composite monarchy that existed before 1804. This was especially demonstrated by the status of the Kingdom of Hungary, whose affairs remained to be administered by its own institutions (King and Diet) as they had been under the composite monarchy, in which it had always been considered a separate Realm. Article X of 1790, which was added to Hungary's constitution during the phase of the composite monarchy uses the Latin phrase "Regnum Independens". In the new situation, therefore, no Imperial institutions were involved in its internal government.József ZacharAusterlitz, 1805. december 2. A három császár csatája – magyar szemmel
In: Eszmék, forradalmak, háborúk. Vadász Sándor 80 éves, ELTE, Budapest, 2010 p. 557 By the start of the 19th century, the aim of Hungary's agricultural producers had shifted from subsistence farming and small-scale production for local trade to cash-generating, large-scale production for a wider market. Road and waterway improvements cut transportation costs, while urbanization in Austria,
Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, and Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
and the need for supplies for the Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Napoleonic Wars
, partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars
, image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg
, caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battl ...
boosted demand for foodstuffs and clothing. Hungary became a major grain and wool exporter. New lands were cleared, and yields rose as farming methods improved. Hungary did not reap the full benefit of the boom, however, because most of the profits went to the magnates, who considered them not as capital for investment but as a means of adding luxury to their lives. As expectations rose, goods such as linen and silverware, once considered luxuries, became necessities. The wealthy magnates had little trouble balancing their earnings and expenditures, but many lesser nobles, fearful of losing their social standing, went into debt to finance their spending.
Napoleon's final defeat brought recession. Grain prices collapsed as demand dropped, and debt ensnared much of Hungary's lesser nobility. Poverty forced many lesser nobles to work to earn a livelihood, and their sons entered education institutions to train for civil service or professional careers. The decline of the lesser nobility continued despite the fact that by 1820 Hungary's exports had surpassed wartime levels. As the number of lesser nobles who earned diplomas increased, the bureaucracy and professions became saturated, leaving a host of disgruntled graduates without jobs. Members of this new intelligentsia quickly became enamored of radical political ideologies emanating from Western Europe and organized themselves to effect changes in Hungary's political system.
Francis rarely called the Diet into session (usually only to request men and supplies for war) without hearing complaints. Economic hardship brought the lesser nobles' discontent to a head by 1825, when Francis finally convoked the Diet after a fourteen-year hiatus. Grievances were voiced, and open calls for reform were made, including demands for less royal interference in the nobles' affairs and for wider use of the Hungarian language.
The first great figure of the reform era came to the fore during the 1825 convocation of the Diet. Count István Széchenyi
Count István Széchenyi de Sárvár-Felsővidék (, ; archaically English: Stephen Széchenyi; 21 September 1791 – 8 April 1860) was a Hungarian politician, political theorist, and writer. Widely considered one of the greatest statesme ...
, a magnate from one of Hungary's most powerful families, shocked the Diet when he delivered the first speech in Hungarian ever uttered in the upper chamber and backed a proposal for the creation of a Hungarian academy of arts and sciences by pledging a year's income to support it. In 1831 angry nobles burned Szechenyi's book Hitel (Credit), in which he argued that the nobles' privileges were both morally indefensible and economically detrimental to the nobles themselves. Szechenyi called for an economic revolution and argued that only the magnates were capable of implementing reforms. Szechenyi favored a strong link with the Habsburg Empire and called for the abolition of entail and serfdom, taxation of landowners, financing of development with foreign capital, the establishment of a national bank, and introduction of wage labor. He inspired such projects as the construction of the Széchenyi Chain Bridge linking Buda
Buda (, ) is the part of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary, that lies on the western bank of the Danube. Historically, “Buda” referred only to the royal walled city on Castle Hill (), which was constructed by Béla IV between 1247 and ...
and Pest. Szechenyi's reform initiatives ultimately failed because they were targeted at the magnates, who were not inclined to support change, and because the pace of his program was too slow to attract disgruntled lesser nobles.
The most popular of Hungary's great reform leaders, Lajos Kossuth
Lajos Kossuth de Udvard et Kossuthfalva (; ; ; ; 19 September 1802 – 20 March 1894) was a Hungarian nobleman, lawyer, journalist, politician, statesman and governor-president of the Kingdom of Hungary during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, r ...
, addressed passionate calls for change to the lesser nobles. Kossuth was the son of a landless, lesser nobleman of Protestant background. He practiced law with his father before moving to Pest. There he published commentaries on the Diet's activities, which made him popular with young, reform-minded people. Kossuth was imprisoned in 1836 for treason. After his release in 1840, he gained quick notoriety as the editor of a liberal party newspaper. Kossuth argued that only political and economic separation from Austria would improve Hungary's plight. He called for broader parliamentary democracy, rapid industrialization, general taxation, economic expansion through exports, and the abolition of privileges (equality before the law) and serfdom. But Kossuth was also a Hungarian patriotic whose rhetoric provoked the strong resentment of Hungary's minority ethnic groups. Kossuth gained support among liberal lesser nobles, who constituted an opposition minority in the Diet. They sought reforms with increasing success after Francis's death in 1835 and the succession of Ferdinand V (1835–48). In 1844 a law was enacted making Hungarian the country's exclusive official language.
István Széchenyi
Count István Széchenyi de Sárvár-Felsővidék (, ; archaically English: Stephen Széchenyi; 21 September 1791 – 8 April 1860) was a Hungarian politician, political theorist, and writer. Widely considered one of the greatest statesme ...
, the first great figure of the reform era
File:Flag_of_Hungarian_Revolution_of_1848.png, Revolutionary flag, 1848–49
File:Great coat of arms of Hungary (1849).svg, Arms of Hungary, 1849
File:Kossuth1848.png, Lajos Kossuth
Lajos Kossuth de Udvard et Kossuthfalva (; ; ; ; 19 September 1802 – 20 March 1894) was a Hungarian nobleman, lawyer, journalist, politician, statesman and governor-president of the Kingdom of Hungary during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, r ...
, the most popular of Hungary's great reform leaders
1848–1867
 After the
After the Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848, also known in Hungary as Hungarian Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many Revolutions of 1848, European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in ...
, the emperor revoked Hungary's constitution and assumed absolute control. Emperor Franz Joseph
Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I ( ; ; 18 August 1830 – 21 November 1916) was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the ruler of the Grand title of the emperor of Austria, other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 1848 until his death ...
divided the country into four distinct territories: Hungary, Transylvania, Croatia-Slavonia, and Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( ; sr-Cyrl, Војводина, ), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an Autonomous administrative division, autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies withi ...
(also known as the Banat). German and Bohemian administrators managed the government, and German became the language of administration and higher education. The non-Magyar minorities of Hungary received little for their support of Austria during the turmoil. A Croat reportedly told a Hungarian: "We received as a reward what the Magyars got as a punishment."
Hungarian public opinion split over the country's relations with Austria. Some Hungarians held out hope for full separation from Austria; others wanted an accommodation with the Habsburgs, provided that they respected Hungary's constitution and laws. Ferenc Deák became the main advocate for accommodation. Deak upheld the legality of the April laws and argued that their amendment required the Hungarian Diet's consent. He also held that the dethronement of the Habsburgs was invalid. As long as Austria ruled absolutely, Deak argued, Hungarians should do no more than passively resist illegal demands.
The first crack in Franz Joseph's neo-absolutist rule developed in 1859, when the forces of Sardinia-Piedmont and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
defeated Austria at the Battle of Solferino
The Battle of Solferino (referred to in Italy as the Battle of Solferino and San Martino) on 24 June 1859 resulted in the victory of the allied Second French Empire, French army under Napoleon III and the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia, Piedmont- ...
. The defeat convinced Franz Joseph that national and social opposition to his government was too strong to be managed by decree from Vienna. Gradually he recognized the necessity of concessions towards Hungary, and Austria and Hungary thus moved towards a compromise.
In 1866 the Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
ns defeated the Austrians in the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War (German: ''Preußisch-Österreichischer Krieg''), also known by many other names,Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Second War of Unification, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), ''Deutsc ...
, further underscoring the weakness of the Habsburg Empire. Negotiations between the emperor and the Hungarian leaders were intensified and finally resulted in the Compromise of 1867, which created the Dual Monarchy of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, also referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy or the Habsburg Monarchy, was a multi-national constitutional monarchy in Central Europe#Before World War I, Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. A military ...
, also known as the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Demography
See also
* List of Hungarian rulersNotes
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Kingdom of Hungary (1526-1867) .1526 Kingdom of Hungary 1526 Kingdom of Hungary 1526 Kingdom of Hungary 1526Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
Hungary 1526
Kingdom of Hungary 1526
Kingdom of Hungary 1526
Kingdom of Hungary 1526
.Kingdom of Hungary
.Kingdom of Hungary
.Kingdom of Hungary
.Kingdom of Hungary 1526
Hungary (1526-1867)