Variable gauge on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Variable gauge systems allow railway vehicles to travel between two railways with different
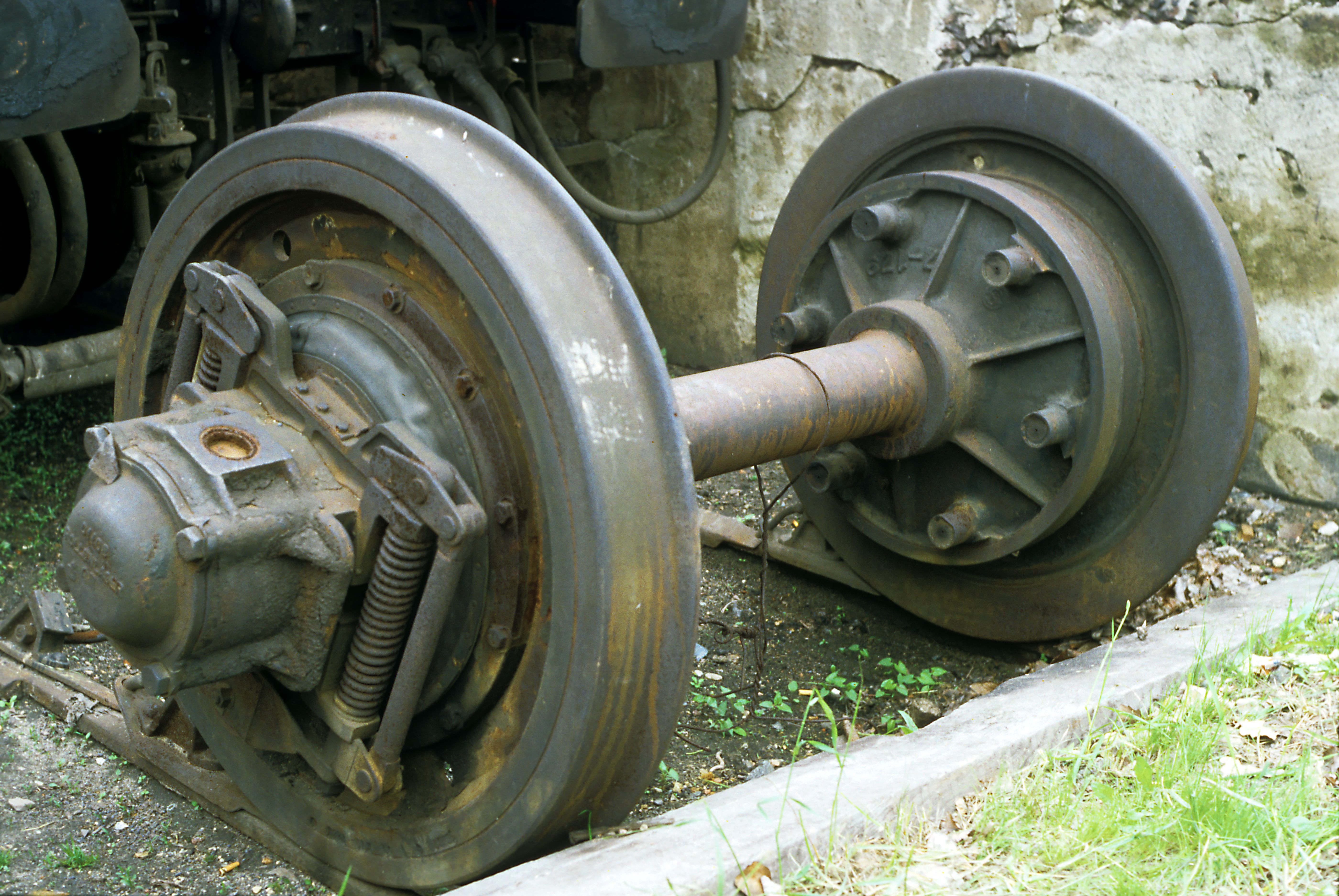 There are several variable gauge axle systems:
* Talgo-RD (from Talgo).
** The Talgo system has been in revenue service in Portbou and
There are several variable gauge axle systems:
* Talgo-RD (from Talgo).
** The Talgo system has been in revenue service in Portbou and
File:Free Gauge Train GCT-01 at kamogawa.jpg, The first-generation "Gauge Change Train" EMU in May 2003
File:Gauge Changing Train 20120912.jpg, The second-generation "Gauge Change Train" EMU in September 2012
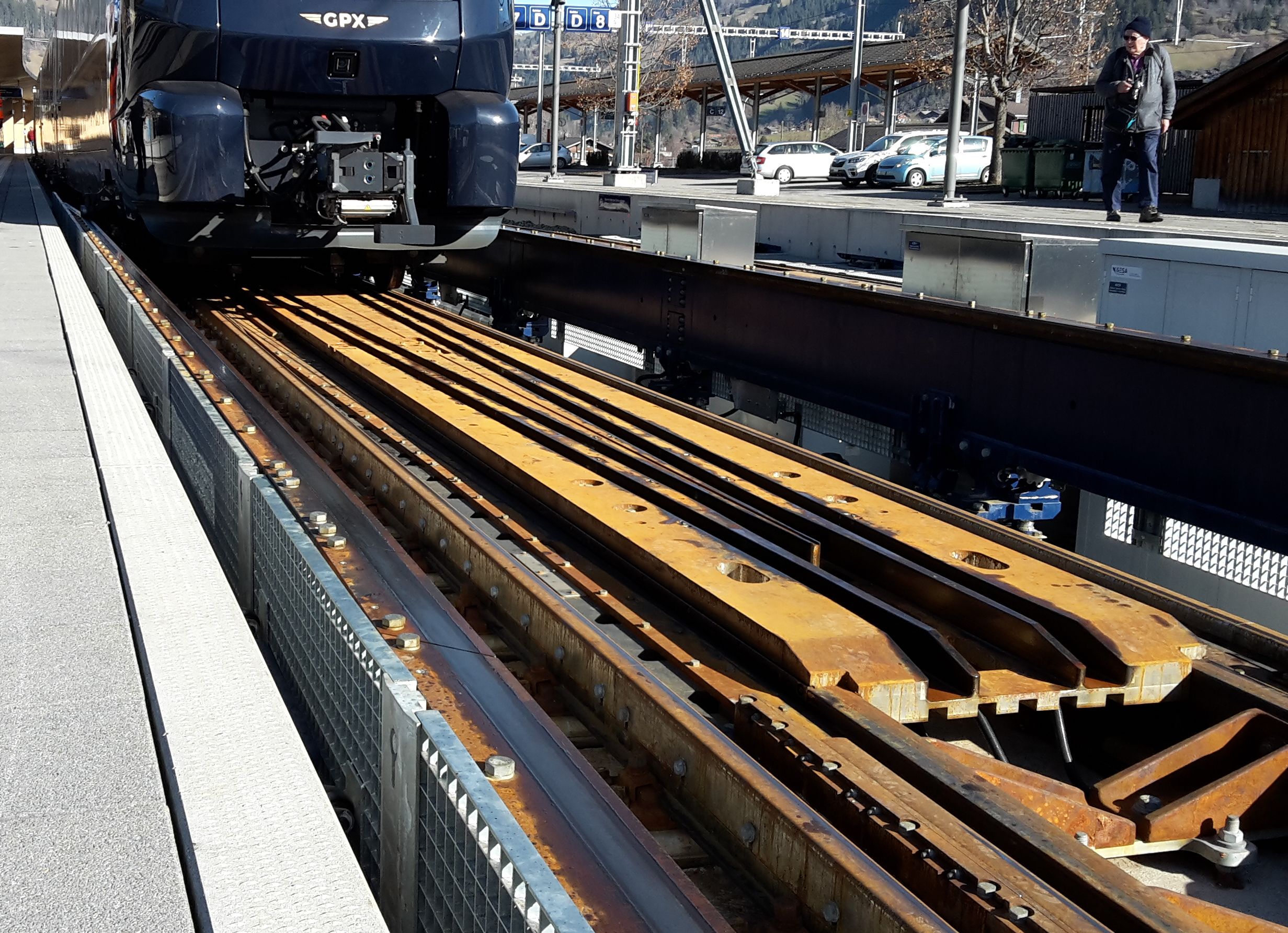 Variable gauge bogies are implemented on the Montreux–Gstaad–Zweisimmen–Spiez–Interlaken line. Trains automatically switch from to at
Variable gauge bogies are implemented on the Montreux–Gstaad–Zweisimmen–Spiez–Interlaken line. Trains automatically switch from to at
A train axle system with variable gauge wheels
patent EP1112908, assigned to Talgo SA.
patent EP0873929, assigned to Railway Technical Research Institute.
patent US5787814, assigned to Talgo SA.
Variable-Gauge Wagon Wheelsets – Brief Article
International Railway Journal, July, 1999
European Automatic Track Gauge Changeover Systems
UIC-backed study of different variable gauge systems
Talgo's variable gauge system explained
(in French)
Talgo's Variable gauge system in action
Close-up view of MOB's variable bogie in action
UA report
* http://osjd.plaske.ua/en/doklad/wishnevski.doc
Ukraine
Automatic gauge changing systems in Spain
{{Navbox track gauge Track gauges Rolling stock Vehicle technology International rail transport
track gauge
In rail transport, track gauge is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have Wheelset (rail transport), wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges ...
s. Vehicles are equipped with variable gauge axles (VGA). The gauge is altered by driving the train through a gauge changer installed at the break of gauge
With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge (the distance between the rails, or between the wheels of trains designed to run on those rails) meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and railroad car, rolling stock g ...
which moves the wheels to the gauge desired.
Variable gauge systems exist within the internal network of Spain, and are installed on international links between Spain/France (Spanish train), Sweden/Finland (Swedish train), Poland/Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
(Polish train) and Poland/Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
(Polish train).
A system for changing gauge without the need to stop is in widespread use for passenger traffic in Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, for services run on a mix of dedicated high-speed lines (using Standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
) and older lines (using Iberian gauge). Similar systems for freight traffic are still in their infancy, as the higher axle weight increases the technological challenge. Although several alternatives exist, including transferring freight, replacing individual wheels and axles, bogie exchange, transporter flatcars or the simple transshipment of freight or passengers, they are impractical, thus a cheap and fast system for changing gauge would be beneficial for cross-border freight traffic.
Alternative names include ''Gauge Adjustable Wheelsets'' (GAW), ''Automatic Track Gauge Changeover Systems'' (ATGCS/AGCS), ''Rolling Stock Re-Gauging System'' (RSRS), ''Rail Gauge Adjustment System'' (RGAS), ''Shifting wheelset'', ''Variable Gauge Rolling Truck'', ''track gauge change'' and ''track change wheelset''.
Overview
Variable gauge axles help solve the problem of abreak-of-gauge
With railways, a break of gauge occurs where a line of one track gauge (the distance between the rails, or between the wheels of trains designed to run on those rails) meets a line of a different gauge. Trains and rolling stock generally canno ...
without having to resort to dual gauge
Dual gauge railroad track has three or four rails, allowing vehicles of two track gauges to run on it.
Signalling and sidings are more expensive to install on dual gauge tracks than on two single gauge tracks. Dual gauge is used when there i ...
tracks or transshipment
Transshipment, trans-shipment or transhipment is the shipment of goods or containers to an intermediate destination, then to another destination.
One possible reason for transshipment is to change the means of transport during the journey (e.g. ...
. Systems allow the adjustment between two gauges. No gauge changer designs supporting more than two gauges are used.
Systems
 There are several variable gauge axle systems:
* Talgo-RD (from Talgo).
** The Talgo system has been in revenue service in Portbou and
There are several variable gauge axle systems:
* Talgo-RD (from Talgo).
** The Talgo system has been in revenue service in Portbou and Irun
Irun (, ) is a town of the Bidasoaldea region in the province of Gipuzkoa in the Basque Autonomous Community, Spain.
History
It lies on the foundations of the ancient Oiasso, cited as a Roman- Vasconic town.
During the Spanish Civil War, ...
, on the Spanish-French border, since 1969
** It is used on the Strizh train (swift) between Moscow and Berlin.
** From 2014 for freight wagons up to 22.5 tonne axleloads
* CAF-BRAVA (from Construcciones y Auxiliar de Ferrocarriles
Construcciones y Auxiliar de Ferrocarriles (Grupo CAF, ) is a Spanish publicly listed company which manufactures railway vehicles and equipment and buses through its Solaris Bus & Coach subsidiary. It is based in Beasain, Basque Autonomous Comm ...
)
** The BRAVA system was originally designed in 1968 by the Vevey Company in Switzerland. The system was originally called the "Vevey axle". The design was subsequently obtained and improved by Construcciones y Auxiliar de Ferrocarriles (CAF).
* DB Cargo
DB Cargo (; previously known as Railion and DB Schenker Rail) is an international transport and logistics company. It is responsible for all of the rail freight transport activities of the German railway company Deutsche Bahn (the DB Group) bo ...
–Knorr-Bremse
Knorr-Bremse AG is a German manufacturer of braking systems for rail and commercial vehicles that has operated since 1905. Other products in the company's portfolio include intelligent door systems, control components, air conditioning system ...
. being developed in 2002 for use between Europe and Russia.
* DBAG
(, ; abbreviated as DB or DB AG ) is the national railway company of Germany, and a state-owned enterprise under the control of the German government. Headquartered in the Bahntower in Berlin, it is a joint-stock company ( AG).
DB was fou ...
– Rafil Type V for freight (from ' for Deutsche Bahn).
* Japan Railways
The Japan Railways Group, commonly known as the or simply JR, is a network of railway companies in Japan formed after the division and privatization of the government-owned Japanese National Railways (JNR) on April 1, 1987. The group comprise ...
RTRI (from the Japan Railway Technical Research Institute
, or , is the technical research company under the Japan Railways group of companies.
Overview
RTRI was established in its current form in 1986 just before Japanese National Railways (JNR) was privatised and split into separate JR group compan ...
) to be used on motorised axles.
* PKP SUW 2000
SUW 2000 is a Polish variable gauge system that allows trains to cross a break of gauge. It is interoperable with the German Rafil Type V system (built by the Radsatzfabrik Ilsenburg).
History
The SUW 2000 system was designed by Ryszard Suwalski. ...
system produced by ZNTK Poznań for Polish State Railways
The Polish State Railways ( , abbr.: PKP S.A.) is a Polish state-owned holding company (legally a sole-shareholder company of the State Treasury) comprising the rail transport holdings of the country's formerly dominant namesake railway oper ...
.
*Montreux–Lenk im Simmental line
The Montreux–Lenk im Simmental line is a metre-gauge electric railway line in Switzerland run by the Montreux Oberland Bernois Railway (MOB) and links Montreux on Lake Geneva by way of Les Avants, Montbovon, Rossinière, Château-d'Œx, Rou ...
, also developed by Prose of Winterthur
Winterthur (; ) is a city in the canton of Zurich in northern Switzerland. With over 120,000 residents, it is the country's List of cities in Switzerland, sixth-largest city by population, as well as its ninth-largest agglomeration with about 14 ...
in 2022 (/). Strictly speaking, this is not a variable gauge ''axle'' system; the bogie wheels are individually suspended without a connecting axle, and their gauge can be adjusted. Furthermore, while the gauge is being changed, the height of the body is changed by 200 mm to match the difference in the platform heights on the two different gauge railways comprising the '' GoldenPass Express''.
Compatibility
The variable gauge systems are not themselves all compatible. The SUW 2000 and Rafil Type V systems are interoperable, as are TALGO-RD and CAF-BRAVA. In 2009, at Roda de Barà nearTarragona
Tarragona (, ; ) is a coastal city and municipality in Catalonia (Spain). It is the capital and largest town of Tarragonès county, the Camp de Tarragona region and the province of Tarragona. Geographically, it is located on the Costa Daurada ar ...
, a Unichanger capable of handling four different VGA systems was under development.
International traffic
VGA is particularly important with international railway traffic because gauge changes tend to occur more often at international borders.Features
Different systems have different limitations, for example, some can be used on carriages and wagons only and are unsuitable for motive power, while others require that rolling stock is unloaded before going through the gauge changer. When one of the gauges is narrow there may not be enough space between the wheels for the Brakes, Gauge Changer and the Traction Motors.= Maximum speed
= The maximum speed of the trains equipped with the different technologies varies. Only CAF and Talgo produce high-speed VGA, allowing speeds up to 330 km/h.= Speed changing
= The Talgo RD GC changes gauge at a speed of so a train takes only 24 seconds to convert.Gauge changer
A gauge changer is a device which forces the gauge adjustment in the wheels. Designs consist of a pair of running rails that gradually vary in width between the two gauges, combined with other rails and levers to perform the following steps, using Talgo RD as an example: # Verify that all vehicles in train are suitable for Gauge Change. # Support on – takes weight off lock and on the guide rails. # Unlock. # Move wheels to new position. # Relock. # Support off – put weight back on lock from the guide rails. # Verify correct operation and generate statistics. Use ECPB power, supervisory or Digital automatic coupling ( DAC) cables. In the Spanish Talgo-RD system, a constant spray of water is used to lubricate the metal surfaces, to reduce heat and wear. A Talgo RD gauge changer is long and wide.Limitations
At present the choice of gauge is limited to two out of three of and broad gauges and . With narrow gauges such as as found atZweisimmen
Zweisimmen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Obersimmental-Saanen (administrative district), Obersimmental-Saanen administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland.
History
Zweisimmen is first mentioned in 1228 ...
, Switzerland, there is less room between the wheels for the gauge change mechanism, the traction motors, and the brakes. The diameter of the wheels also limits the axleload to no more than 22.5 tonnes.
Operation
A variable gaugemultiple unit
A multiple-unit train (or multiple unit (MU)) is a self-propelled train composed of one or more Coach (rail), carriages joined, and where one or more of the carriages have the means of propulsion built in. By contrast, a locomotive-hauled ...
, or a train including a variable gauge locomotive (e.g. Talgo 250) and rolling stock, may drive straight across a gauge changer. Normally the locomotive will not be able to change gauge, meaning that it must move out of the way whilst the remainder of the train itself passes through. On the opposite side, a new locomotive of the other gauge will couple to the train.
A Talgo train with a locomotive can drive across a gauge change at 1 axle per second at a speed of about .
A train (or an individual car) can be pushed halfway across the gauge-changer, uncoupled, and then (once far enough across) coupled to the new locomotive and pulled the rest of the way. A long length of wire-rope with hooks on the end means that the process can be asynchronous, with the rope used to bridge across the length of the gauge changer (to temporarily couple the arriving cars and receiving locomotive, although without braking control from the locomotive to the train vehicles).
On long-distance trains in Spain and night trains crossing from Spain into France, the arriving locomotive stops just short of the gauge changer, uncouples and moves into a short siding out of the way. Gravity then moves the train through the gauge changer at a controlled low speed. The new locomotive is coupled onto the front only after the full train has finished passing through the changer.
From 2014 gauge changing systems for freight wagons were being developed.
Countries
Australia
In 1933, as many as 140 inventions were offered to Australia railways to overcome the breaks of gauge between the different states. None was accepted. About 20 of these devices were adjustable wheels/axles of some kind or another, which may be analogous to the modernVGA
Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the IBM PC compatible industry within three years. T ...
. VGA systems were mostly intended for Broad Gauge and Standard Gauge lines.
Break of Gauge stations were installed at Port Pirie
Port Pirie is a small city on the east coast of the Spencer Gulf in South Australia, north of the state capital, Adelaide. Port Pirie is the largest city and the main retail centre of the Mid North region of South Australia. The city has an ex ...
, Peterborough
Peterborough ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in the City of Peterborough district in the Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire, England. The city is north of London, on the River Nene. A ...
and Albury
Albury (; ) is a major regional city that is located in the Murray River, Murray region of New South Wales, Australia. It is part of the twin city of Albury–Wodonga, Albury-Wodonga and is located on the Hume Highway and the northern side of ...
; these were fairly manual in operation. The newest installation was at Dry Creek and was of a more automatic design. The Talgo RD design is even more automatic and efficient.
Belarus/Poland
A Talgo gauge changing facility is installed at Brest near the Belarusian-Polish border. It is used byRussian Railways
Russian Railways or RZD () is a Russian fully state-owned vertically integrated railway company, both managing infrastructure and operating freight and passenger train services and has a near-monopoly on long-distance train travel in Russia.
...
' fast trains connecting Moscow and Berlin.
Orders for 7 Talgo VGA trainsets placed were placed in 2011. The trains under the brand " Strizh" are in service since 2016.
Canada
Variable gauge axles were used for a while on theGrand Trunk Railway
The Grand Trunk Railway (; ) was a Rail transport, railway system that operated in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian provinces of Quebec and Ontario and in the List of states and territories of the United States, American sta ...
in the 1860s in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
to connect and standard gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), international gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the ...
without transshipment. Five hundred vehicles were fitted with "adjustable gauge trucks" but following heavy day-in, day-out use the system proved unsatisfactory, particularly in cold and snowy weather. The system used telescoping axles with wide hubs that allowed the wheels to be squeezed or stretched apart through a gauge-changer, after holding pins had been manually released.
Railway operations over the Niagara Bridge were also complicated.
Finland/Sweden
In 1999, a gauge-changer was installed atTornio
Tornio (; ; ; ) is a city and municipalities of Finland, municipality in Lapland, Finland. The city forms a cross-border Twin cities, twin city together with Haparanda on the Swedish side. The municipality covers an area of , of which is wat ...
at the Finnish end of the dual-gauge section between Haparanda
Haparanda (; Meänkieli and Finnish: ''Haaparanta'', ) is a locality and the seat of Haparanda Municipality in Norrbotten County, Sweden. It is adjacent to Tornio, Finland. Haparanda has a population of 9,166 inhabitants (2024).
Haparanda is ...
and Tornio, for use with variable gauge freight wagons. The Tornio gauge changer is a ''Rafil'' design from Germany; a similar ''Talgo-RD'' gauge changer at the Haparanda end used to exist, but was removed as it required de-icing in winter.
Train ferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry Railroad car, railway vehicles, as well as their cargoes and passengers. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with Track (rail transport), railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the f ...
traffic operated by SeaRail and arriving from Germany and Sweden by sea used bogie exchange facilities in the Port of Turku.
Georgia
A new gauge changer has been put in place in Akhalkalaki for Baku-Tbilisi-Kars railway. Northwestern end has rails apart, southeastern end has rails apart. Both bogie exchange and variable gauge adapters are provided.Japan
The "Gauge Change Train" is a project started in Japan in the 1990s to investigate the feasibility of producing anelectric multiple unit
An electric multiple unit or EMU is a multiple-unit train consisting of self-propelled carriages using electricity as the motive power. An EMU requires no separate locomotive, as electric traction motors are incorporated within one or a number o ...
(EMU) train capable of operating both the Shinkansen
The , colloquially known in English as the bullet train, is a network of high-speed railway lines in Japan. It was initially built to connect distant Japanese regions with Tokyo, the capital, to aid economic growth and development. Beyond lon ...
high-speed network at and the original network at . See .
The first-generation train was tested from 1998 to 2006, including on the US High-speed Test Track in 2002. The second-generation train, intended to run at a maximum speed of , was test-run in various locations in Japan between 2006 and 2013. A third-generation train has been undergoing reliability trials since 2014 in preparation for potential introduction to service on the planned Kyushu Shinkansen
The is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed railway network. It is an extension of the San'yō Shinkansen from Honshu connecting the city of Fukuoka (Hakata Station) in the north of Japan's Kyushu Island to the city of Kagoshima (Kagoshima-Chuo Sta ...
extension to Nagasaki.Gallery
Lithuania/Poland
A gauge changing facility of the PolishSUW 2000
SUW 2000 is a Polish variable gauge system that allows trains to cross a break of gauge. It is interoperable with the German Rafil Type V system (built by the Radsatzfabrik Ilsenburg).
History
The SUW 2000 system was designed by Ryszard Suwalski. ...
system is installed at Mockava
Mockava is a village in Lithuania six km from the border with Poland. The Mockava Railway Station is located northeast of Mockava in the village of .
According to the 2011 census, the population of Mockava was 59.
Transport
The Rail Baltica p ...
north of the Lithuanian-Polish border. VGA passenger trains between Lithuania and Poland were running between October 1999 and May 2005, and VGA goods trains between early 2000s and 2009.
Poland/Ukraine
There are two gauge changing facilities of the Polish SUW 2000 system installed on the Polish-Ukrainian border, one of them in Dorohusk (Poland) on the Warsaw-Kiyv line, another in Mostyska (Ukraine) on the Kraków-Lviv line. On 14 December 2003 VGA passenger trains were introduced betweenKraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
(Poland) and Lviv
Lviv ( or ; ; ; see #Names and symbols, below for other names) is the largest city in western Ukraine, as well as the List of cities in Ukraine, fifth-largest city in Ukraine, with a population of It serves as the administrative centre of ...
(Ukraine) instead of bogie exchange. VGA saves about 3 hours compared to bogie exchange. The trains last ran in 2016.
Spain
Spain is the largest user of variable gauge systems. This is because of the need to connect older mainlines built to Iberian gauge and extensive newhigh-speed rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated railway track, tracks. While there is ...
way lines and connections to France, using the standard gauge. Two gauge changes are installed on lines to France and at all entrances/exits leading between the high-speed network and older lines. There are also significant lengths of secondary lines but these are not connected to the main network.
In February 2004, RENFE placed orders for:
* Forty-five CAF/Alstom 25 kV AC/3 kV DC, variable gauge EMUs for 250 km/h regional services, between October 2006 and May 2009 (€580 million)
* Twenty-six 25 kV AC variable gauge trains for long-distance services using two Bombardier power cars and Talgo Series VII trailer cars (€370 million) Gauges involved are and .
* Olmedo to Medina del Campo
Medina del Campo is a town and municipality of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. Part of the Province of Valladolid, it is the centre of a farming area.
It lies on the banks of the Zapardiel river, in the centre of t ...
in Valladolid
Valladolid ( ; ) is a Municipalities of Spain, municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and ''de facto'' capital of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile and León. It is also the capital of the pr ...
, Spanish test track.
* November 2008 – High Speed trainset for Cadiz to Warsaw
Warsaw, officially the Capital City of Warsaw, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the Vistula, River Vistula in east-central Poland. Its population is officially estimated at ...
.Railway Gazette International
''Railway Gazette International'' is a British monthly business magazine and news website covering the railway, metro, light rail and tram industries worldwide. Available by annual subscription, the magazine is read in over 140 countries by tran ...
November 2008, p. 881
* July 2009 – Talgo 250 supplied with Voith Turbo SZH-692 gauge change final drives.
There is also a circular test track in Spain.
Switzerland
 Variable gauge bogies are implemented on the Montreux–Gstaad–Zweisimmen–Spiez–Interlaken line. Trains automatically switch from to at
Variable gauge bogies are implemented on the Montreux–Gstaad–Zweisimmen–Spiez–Interlaken line. Trains automatically switch from to at Zweisimmen
Zweisimmen is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the Obersimmental-Saanen (administrative district), Obersimmental-Saanen administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland.
History
Zweisimmen is first mentioned in 1228 ...
. The bogie has no axles, which allow the bogie half frames holding the wheels on both sides to slide sideways relative to each other. The EV09-Prose gauge changer at Zweisimmen was satisfactorily tested on 19 June 2019. The system, designed to allow operation on both Montreux Oberland Bernois Railway's (MOB) 1000mm gauge line and BLS AG
BLS AG is a Swiss railway company created by the 2006 merger of BLS Lötschbergbahn and Regionalverkehr Mittelland AG. Its ownership is divided, with 55.8% of it owned by the canton of Berne, and 21.7% by the Swiss Confederation. It has two ma ...
1435mm gauge infrastructure, was first implemented on 11 December 2022. Moreover, while the gauge is being automatically changed at Zweisimmen, the air spring mounted on the bogie cross member is automatically adjusted by 200 mm to match the body height with the platform height on the MOB or BLS AG portion of the GoldenPass Express.
United Kingdom
John Fowler mentions in 1886 at attempt by the GWR to develop a "telescopical" axle. Trams ran betweenLeeds
Leeds is a city in West Yorkshire, England. It is the largest settlement in Yorkshire and the administrative centre of the City of Leeds Metropolitan Borough, which is the second most populous district in the United Kingdom. It is built aro ...
() and Bradford
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city in West Yorkshire, England. It became a municipal borough in 1847, received a city charter in 1897 and, since the Local Government Act 1972, 1974 reform, the city status in the United Kingdo ...
( gauge) following a successful trial in 1906 using Bradford tram car number 124. The system was later patented by – GB190601695 (A) of 1906. This system was improved again in patent GB190919655 (A) of 1909 by introducing a locking system acting on the wheel and axle rather than just the wheel rim. This provided a more effective grip where the wheel was free to move along the splined axle.
Comparison with bogie exchange
Time taken
In VGA, the train is pulled through the "adjuster" at about without any need to uncouple the wagons or disconnect (and test) the brake equipment. Alternatively, as the train need not be uncoupled, the locomotive may pull the coupled carriages all together. See Talgo Gauge Changer.Locomotives
Steam locomotive are generally not gauge convertible on-the-fly. While diesel locomotives can be bogie exchanged, this is not normally done owing to the complexity in the reconnection of cables and hoses. In Australia, some locomotives are transferred between gauges. The transfer might happen every few months, but not for an individual trip. By 2004, variable gauge electric passenger locomotives were available from Talgo. It is not clear if variable gauge freight locomotives are available.Electric
* L-9202 is an experimental high speedBo-Bo
B-B and Bo-Bo are the AAR wheel arrangement, Association of American Railroads (AAR) and British classifications of wheel arrangement for railway locomotives with four axles in two individual bogies. They are equivalent to the B′B′ and Bo′B ...
dual voltage ( 3 kV DC/25 kV AC
Railway electrification systems using alternating current (AC) at are used worldwide, especially for high-speed rail. It is usually supplied at the standard utility frequency (typically 50 or 60Hz), which simplifies traction substations. The dev ...
) VGA locomotive.
* Talgo 250 locomotives were also planned to haul dual-voltage variable-gauge trainsets from Montpellier
Montpellier (; ) is a city in southern France near the Mediterranean Sea. One of the largest urban centres in the region of Occitania (administrative region), Occitania, Montpellier is the prefecture of the Departments of France, department of ...
from the border to Barcelona and Madrid. Two Talgo 250 power cars haul 11 passenger trailer cars.
* EMU
Weight
* A gauge adjustable bogie complete with wheelsets weighs a total of about one ton/tonne more than a conventional bogie and normally must usedisc brakes
Disc or disk may refer to:
* Disk (mathematics), a two dimensional shape, the interior of a circle
* Disk storage
* Optical disc
* Floppy disk
Music
* Disc (band), an American experimental music band
* ''Disk'' (album), a 1995 EP by Moby
Other ...
, which cool more slowly.
History
* 1915. C. W. Prosser. – Argus * 1921. C. R. Prosser. – Argus Friday 8 July 1921 * 1922. J. Grieve. – Argus 19 July 1922See also
*Alvia
Alvia is a High-speed rail, high-speed train service in Spain offered by Renfe Operadora on long-distance routes with a top speed of . The trains have the ability to use both Iberian gauge and standard gauge, which allows them to travel on the rece ...
* Axle exchange
* Bogie exchange
* Bradford Corporation Tramways
* Dual couplings
* Gauge Change Train (Japan)
* Interoperability
Interoperability is a characteristic of a product or system to work with other products or systems. While the term was initially defined for information technology or systems engineering services to allow for information exchange, a broader de ...
* Ramsey car-transfer apparatus
* Strizh
* SUW 2000
SUW 2000 is a Polish variable gauge system that allows trains to cross a break of gauge. It is interoperable with the German Rafil Type V system (built by the Radsatzfabrik Ilsenburg).
History
The SUW 2000 system was designed by Ryszard Suwalski. ...
a form of VGA
References
Further reading
* *External links
A train axle system with variable gauge wheels
patent EP1112908, assigned to Talgo SA.
patent EP0873929, assigned to Railway Technical Research Institute.
patent US5787814, assigned to Talgo SA.
Variable-Gauge Wagon Wheelsets – Brief Article
International Railway Journal, July, 1999
European Automatic Track Gauge Changeover Systems
UIC-backed study of different variable gauge systems
Talgo's variable gauge system explained
(in French)
Talgo's Variable gauge system in action
Close-up view of MOB's variable bogie in action
UA report
* http://osjd.plaske.ua/en/doklad/wishnevski.doc
Ukraine
Automatic gauge changing systems in Spain
{{Navbox track gauge Track gauges Rolling stock Vehicle technology International rail transport