Tranylcypromine trifluoperazine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tranylcypromine, sold under the brand name Parnate among others,Drugs.co
Page accessed April 17, 2016 is a
Tranylcypromine
Llast updated October 28, 2015 It is also used in depression that is not responsive to reuptake inhibitor antidepressants, such as the


Page accessed April 17, 2016 is a
monoamine oxidase inhibitor
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, espe ...
(MAOI). More specifically, tranylcypromine acts as nonselective
Functional selectivity (or “agonist trafficking”, “biased agonism”, “biased signaling”, "ligand bias" and “differential engagement”) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a referen ...
and irreversible
Irreversible may refer to:
* Irreversible process, in thermodynamics, a process that is not reversible
*'' Irréversible'', a 2002 film
* ''Irréversible'' (soundtrack), soundtrack to the film ''Irréversible''
* An album recorded by hip-hop artis ...
inhibitor
Inhibitor or inhibition may refer to:
In biology
* Enzyme inhibitor, a substance that binds to an enzyme and decreases the enzyme's activity
* Reuptake inhibitor, a substance that increases neurotransmission by blocking the reuptake of a neurotra ...
of the enzyme monoamine oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first ...
(MAO). It is used as an antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medication used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain conditions, and to help manage addictions. Common side-effects of antidepressants include dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, hea ...
and anxiolytic agent in the clinical treatment of mood and anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a cluster of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal function are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause physi ...
s, respectively.
Tranylcypromine is a propylamine formed from the cyclization of amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
's side chain; therefore, it is classified as a substituted amphetamine
Substituted amphetamines are a class of compounds based upon the amphetamine structure; it includes all derivative compounds which are formed by replacing, or substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the amphetamine core structure with sub ...
.
Medical uses
Tranylcypromine is used to treat major depressive disorder, including atypical depression, especially when there is an anxiety component, typically as a second-line treatment.UK Electronic medicines compendiumTranylcypromine
Llast updated October 28, 2015 It is also used in depression that is not responsive to reuptake inhibitor antidepressants, such as the
SSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
, TCAs, or bupropion
Bupropion, sold under the brand names Wellbutrin and Zyban among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the case ...
.
Systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
s and meta-analyses have reported that tranylcypromine is significantly more effective in the treatment of depression than placebo and has efficacy over placebo similar to that of other antidepressants such as tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and we ...
s.
Contraindications
Contraindications include: * Porphyria * Cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease * Pheochromocytoma * Tyramine, found in several foods, is metabolized by MAO. Ingestion and absorption of tyramine causes extensive release of norepinephrine, which can rapidly increase blood pressure to the point of causing hypertensive crisis. * Concomitant use of serotonin-enhancing drugs, includingSSRIs
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are a class of drugs that are typically used as antidepressants in the treatment of major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and other psychological conditions.
SSRIs increase the extracellul ...
, serotonergic TCAs, dextromethorphan, and meperidine may cause serotonin syndrome.
* Concomitant use of MRAs, including fenfluramine
Fenfluramine, sold under the brand name Fintepla, is a serotonergic medication used for the treatment of seizures associated with Dravet syndrome and Lennox–Gastaut syndrome.https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2022/212102s003lb ...
, amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
, and pseudoephedrine
Pseudoephedrine (PSE) is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It may be used as a nasal/sinus decongestant, as a stimulant, or as a wakefulness-promoting agent in higher doses.
It was first characteri ...
may cause toxicity via serotonin syndrome or hypertensive crisis.
* L-DOPA given without carbidopa may cause hypertensive crisis.
Dietary restrictions
Tyramine is a biogenic amine produced as a (generally undesirable) byproduct during the fermentation of certain tyrosine-rich foods. It is rapidly metabolized by MAO-A in those not taking MAO-inhibiting drugs. Individuals sensitive to tyramine-induced hypertension may experience an uncomfortable, yet fleeting, increase in blood pressure after ingesting relatively small amounts of tyramine. Advances in food safety standards in most nations, as well as the widespread use of starter-cultures shown to result in undetectable to low levels of tyramine in fermented products has rendered concerns of serious hypertensive crises rare in those consuming a modern diet. Those treated with MAOIs should still exercise caution, particularly at home, if it is unclear whether food has been properly refrigerated. Since tyramine-producing microbes also produce compounds to which humans have a natural aversion, disposal of any questionable food—particularly meats—should be sufficient to avoid hypertensive crises.Adverse effects
Incidence of adverse effects Very common (>10% incidence) adverse effects include: * Dizziness secondary to orthostatic hypotension (17%) Common (1-10% incidence) adverse effects include: * Tachycardia (5–10%) * Hypomania (7%) *Paresthesia
Paresthesia is an abnormal sensation of the skin (tingling, pricking, chilling, burning, numbness) with no apparent physical cause. Paresthesia may be transient or chronic, and may have any of dozens of possible underlying causes. Paresthesias ar ...
(5%)
* Weight loss (2%)
* Confusion (2%)
* Dry mouth (2%)
* Sexual function disorders (2%)
* Hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
(1–2 hours after ingestion) (2%)
* Rash (2%)
* Urinary retention (2%)
Other (unknown incidence) adverse effects include:
* Increased/decreased appetite
* Blood dyscrasias
* Chest pain
* Diarrhea
* Edema
Edema, also spelled oedema, and also known as fluid retention, dropsy, hydropsy and swelling, is the build-up of fluid in the body's Tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may include skin which feels t ...
* Hallucinations
* Hyperreflexia
* Insomnia
* Jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
* Leg cramps
* Myalgia
Myalgia (also called muscle pain and muscle ache in layman's terms) is the medical term for muscle pain. Myalgia is a symptom of many diseases. The most common cause of acute myalgia is the overuse of a muscle or group of muscles; another likel ...
* Palpitations
Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart.
Symptoms include a rapi ...
* Sensation of cold
* Suicidal ideation
Suicidal ideation, or suicidal thoughts, means having thoughts, ideas, or ruminations about the possibility of ending one's own life.World Health Organization, ''ICD-11 for Mortality and Morbidity Statistics'', ver. 09/2020MB26.A Suicidal ideatio ...
* Tremor
Of note, there has not been found to be a correlation between sex and age below 65 regarding incidence of adverse effects.
Tranylcypromine is not associated with weight gain and has a low risk for hepatotoxicity compared to the hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
MAOIs.
It is generally recommended that MAOIs be discontinued prior to anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
; however, this creates a risk of recurrent depression. In a retrospective observational cohort study, patients on tranylcypromine undergoing general anesthesia had a lower incidence of intraoperative hypotension, while there was no difference between patients not taking an MAOI regarding intraoperative incidence of bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, a ...
, tachycardia, or hypertension. The use of indirect sympathomimetic drugs or drugs affecting serotonin reuptake, such as meperidine or dextromethorphan poses a risk for hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
and serotonin syndrome respectively; alternative agents are recommended. Other studies have come to similar conclusions. Pharmacokinetic interactions with anesthetics are unlikely, given that tranylcypromine is a high-affinity substrate for CYP2A6
Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and ...
and does not inhibit CYP enzymes at therapeutic concentrations.
Tranylcypromine abuse
Abuse is the improper usage or treatment of a thing, often to unfairly or improperly gain benefit. Abuse can come in many forms, such as: physical or verbal maltreatment, injury, assault, violation, rape, unjust practices, crimes, or other t ...
has been reported at doses ranging from 120 to 600 mg per day. It is thought that higher doses have more amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
-like effects and abuse is promoted by the fast onset and short half-life of tranylcypromine.
Cases of suicidal ideation and suicidal behaviours have been reported during tranylcypromine therapy or early after treatment discontinuation.
Symptoms of tranylcypromine overdose are generally more intense manifestations of its usual effects.
Interactions
In addition to contraindicated concomitant medications, tranylcypromine inhibitsCYP2A6
Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and ...
, which may reduce the metabolism and increase the toxicity of substrates of this enzyme, such as:
* Dexmedetomidine
* nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is used fo ...
* TSNAs (found in cured tobacco products, including cigarette
A cigarette is a narrow cylinder containing a combustible material, typically tobacco, that is rolled into thin paper for smoking. The cigarette is ignited at one end, causing it to smolder; the resulting smoke is orally inhaled via the opp ...
s)
* Valproate
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors prevent neuronal uptake of tyramine and may reduce its pressor
An antihypotensive agent, also known as a vasopressor agent or simply vasopressor, or pressor, is any substance, whether endogenous or a medication, that tends to raise low blood pressure. Some antihypotensive drugs act as vasoconstrictors to inc ...
effects.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Tranylcypromine acts as a nonselective and irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase. Regarding the isoforms of monoamine oxidase, it shows slight preference for the MAOB isoenzyme overMAOA
Monoamine oxidase A, also known as MAO-A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MAOA'' gene. This gene is one of two neighboring gene family members that encode mitochondrial enzymes which catalyze the oxidative deamination of amines, ...
. This leads to an increase in the availability of monoamines, such as serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
, norepinephrine, and dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
, epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
as well as a marked increase in the availability of trace amines, such as tryptamine, octopamine, and phenethylamine
Phenethylamine (PEA) is an organic compound, natural monoamine alkaloid, and trace amine, which acts as a central nervous system stimulant in humans. In the brain, phenethylamine regulates monoamine neurotransmission by binding to trace amin ...
. The clinical relevance of increased trace amine availability is unclear.
It may also act as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor at higher therapeutic doses. Compared to amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
, tranylcypromine shows low potency as a dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
releasing agent, with even weaker potency for norepinephrine and serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vas ...
release.
Tranylcypromine has also been shown to inhibit the histone demethylase, BHC110/LSD1
Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (LSD1) also known as lysine (K)-specific demethylase 1A (KDM1A) is a protein in humans that is encoded by the KDM1A gene. LSD1 is a flavin-dependent monoamine oxidase, which can demethylate mono- and di-me ...
. Tranylcypromine inhibits this enzyme with an IC50 < 2 μM, thus acting as a small molecule inhibitor of histone demethylation with an effect to derepress the transcriptional activity of BHC110/LSD1 target genes. The clinical relevance of this effect is unknown.
Tranylcypromine has been found to inhibit CYP46A1 at nanomolar concentrations. The clinical relevance of this effect is unknown.

Pharmacokinetics
Tranylcypromine reaches its maximum concentration (tmax) within 1–2 hours. After a 20 mg dose, plasma concentrations reach at most 50-200 ng/mL. While its half-life is only about 2 hours, its pharmacodynamic effects last several days to weeks due to irreversible inhibition of MAO. Metabolites of tranylcypromine include 4-hydroxytranylcypromine, ''N''-acetyltranylcypromine, and ''N''-acetyl-4-hydroxytranylcypromine, which are less potent MAO inhibitors than tranylcypromine itself.Amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
was once thought to be a metabolite of tranylcypromine, but has not been shown to be.
Tranylcypromine inhibits CYP2A6
Cytochrome P450 2A6 (abbreviated CYP2A6) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system, which is involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. CYP2A6 is the primary enzyme responsible for the oxidation of nicotine and ...
at therapeutic concentrations.
Chemistry

Synthesis
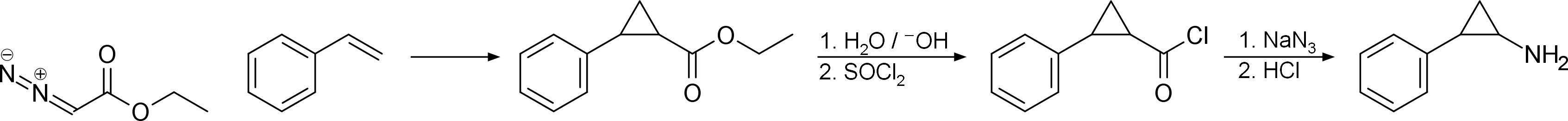
History
Tranylcypromine was originally developed as ananalog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
of amphetamine
Amphetamine (contracted from alpha- methylphenethylamine) is a strong central nervous system (CNS) stimulant that is used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. It is also commonly used ...
. Although it was first synthesized in 1948, its MAOI action was not discovered until 1959. Precisely because tranylcypromine was not, like isoniazid and iproniazid, a hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
derivative, its clinical interest increased enormously, as it was thought it might have a more acceptable therapeutic index than previous MAOIs.
The drug was introduced by Smith, Kline and French
Smith, Kline & French (SKF) was an American pharmaceutical company.
History
In 1830, John K. Smith opened a drugstore in Philadelphia, and his younger brother, George, joined him in 1841 to form John K Smith & Co. In 1865, Mahlon Kline joined ...
in the United Kingdom in 1960, and approved in the United States in 1961. It was withdrawn from the market in February 1964 due to a number of patient deaths involving hypertensive crises with intracranial bleeding. However, it was reintroduced later that year with more limited indications and specific warnings of the risks.
Research
Tranylcypromine is known to inhibitLSD1
Lysine-specific histone demethylase 1A (LSD1) also known as lysine (K)-specific demethylase 1A (KDM1A) is a protein in humans that is encoded by the KDM1A gene. LSD1 is a flavin-dependent monoamine oxidase, which can demethylate mono- and di-me ...
, an enzyme that selectively demethylates two lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
s found on histone H3
Histone H3 is one of the five main histones involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminal tail, H3 is involved with the structure of the nucleosomes of the 'beads on a stri ...
. Genes promoted downstream of LSD1 are involved in cancer cell growth and metastasis, and several tumor cells express high levels of LSD1. Tranylcypromine analogues with more potent and selective LSD1 inhibitory activity are being researched in the potential treatment of cancers.
Tranylcypromine may have neuroprotective properties applicable to the treatment of Parkinson's disease, similar to the MAO-B inhibitors selegiline
Selegiline, also known as L-deprenyl and sold under the brand names Eldepryl and Emsam among others, is a medication which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and major depressive disorder. It is provided in the form of a capsule or ...
and rasagiline. As of 2017, only one clinical trial in Parkinsonian patients has been conducted, which found some improvement initially and only slight worsening of symptoms after a 1.5 year followup.
See also
* Tranylcypromine/trifluoperazineReferences
{{GlaxoSmithKline Cyclopropanes CYP2D6 inhibitors Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents Substituted amphetamines Substances discovered in the 1940s