Transylvanian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in
''The Hungarians: A Thousand Years of Victory in Defeat''
C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2003, page 146; After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors."Transylvania"
(2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009"Diploma Leopoldinum"
(2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009 During the
(Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV) After the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the separate status of Transylvania ceased, it was incorporated again into the
 The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the
The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the 
 Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the
Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the  The Holidays in Romania, national holiday of
The Holidays in Romania, national holiday of
''Hungarians in Transylvania between 1870 and 1995''
Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999, pp. 30-34 were living on the Romanian side of the border, mainly in the Székely Land of Eastern Transylvania, and along the newly created border. In August 1940, by the
In August 1940, by the
the Armistice Agreement with Romania
(Article 19); and the 1947 Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Treaty of Paris reaffirmed the borders between Romania and Hungary, as originally defined in the Treaty of Trianon, 27 years earlier, thus confirming the return of Northern Transylvania to Romania. From 1947 to 1989, Transylvania, along with the rest of Romania, was Socialist Republic of Romania, under a communist regime. The ethnic clashes of Târgu Mureș occurred between ethnic
File:Sarmisegetusa Regia - Templele patrulatere mici - Zona sacra – Gradistea Muntelui, Muntii Sureanu, Hunedoara, Romania 19.JPG, Ruins of Sarmizegetusa Regia
File:Castrum Apulum 2011 - Porta Principalis Dextra-1.jpg, Roman city of Alba Iulia#Ancient times, Apulum
File:Lanzedelli - Târg în Transilvania 3.jpg, A market scene in Transylvania, 1818
File:Original_Photo_National_Museum_of_Union-Alba_Iulia.jpg, The National Assembly in


 The Transylvanian Plateau, high, is drained by the Mureș River, Mureș, Someș River, Someș, Criș River, Criș, and Olt River, Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern Carpathians, Eastern, Southern Carpathians, Southern and Apuseni Mountains, Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains. The area includes the Transylvanian Plain. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, though geographically the two are not identical.
Ethnographic areas:
* Transylvania proper:
** Mărginimea Sibiului (Szeben-hegyalja)
** Transylvanian Plain (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség)
** Țara Bârsei (Burzenland/Barcaság)
**
** Țara Călatei (Kalotaszeg)
** (Kővár)
** Țara Făgărașului (Fogaras)
** Țara Hațegului (Hátszeg)
**
**
** Țara Moților
** Țara Năsăudului (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke)
**
**
** Ținutul Secuiesc (Székelyföld/Székely Land)
*
The Transylvanian Plateau, high, is drained by the Mureș River, Mureș, Someș River, Someș, Criș River, Criș, and Olt River, Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern Carpathians, Eastern, Southern Carpathians, Southern and Apuseni Mountains, Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains. The area includes the Transylvanian Plain. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, though geographically the two are not identical.
Ethnographic areas:
* Transylvania proper:
** Mărginimea Sibiului (Szeben-hegyalja)
** Transylvanian Plain (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség)
** Țara Bârsei (Burzenland/Barcaság)
**
** Țara Călatei (Kalotaszeg)
** (Kővár)
** Țara Făgărașului (Fogaras)
** Țara Hațegului (Hátszeg)
**
**
** Țara Moților
** Țara Năsăudului (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke)
**
**
** Ținutul Secuiesc (Székelyföld/Székely Land)
*
File:Biserica Mihail.JPG, Cluj-Napoca ( hu, Kolozsvár, german: Klausenburg)
File:Brasov, Romania (26523347959).jpg,
 Official censuses with information on Transylvania's population have been conducted since the 18th century. On May 1, 1784 the Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II called for the first official census of the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Empire, including Transylvania. The data was published in 1787, and this census showed only the overall population (1,440,986 inhabitants). :hu:Fényes Elek, Fényes Elek, a 19th-century Hungarian statistician, estimated in 1842 that in the population of Transylvania for the years 1830–1840 the majority were 62.3%
Official censuses with information on Transylvania's population have been conducted since the 18th century. On May 1, 1784 the Emperor Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor, Joseph II called for the first official census of the Habsburg monarchy, Habsburg Empire, including Transylvania. The data was published in 1787, and this census showed only the overall population (1,440,986 inhabitants). :hu:Fényes Elek, Fényes Elek, a 19th-century Hungarian statistician, estimated in 1842 that in the population of Transylvania for the years 1830–1840 the majority were 62.3%
 Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably lignite, iron, lead, manganese, gold, copper, natural gas, salt, and sulfur.
Transylvania's GDP (nominal) is 194 billion$ and its GDP per capita measures around 24,500$. Transylvania's Human Development Index is ranked 0.890, which makes Transylvania the 2nd most developed region in Romania after Bucharest-Ilfov and makes it comparable to countries like Czech Republic, Poland and Estonia.
There are large iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries. Stock raising, agriculture, wine production and fruit growing are important occupations. Agriculture is widespread in the Transylvanian Plateau, including growing cereals, vegetables, viticulture and breeding cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry. Timber is another valuable resource.
Information technology, IT, electronics and Automotive industry, automotive industries are important in urban and university centers like Cluj-Napoca (Robert Bosch GmbH, Emerson Electric), Timișoara (Alcatel-Lucent, Flextronics and Continental AG),
Transylvania is rich in mineral resources, notably lignite, iron, lead, manganese, gold, copper, natural gas, salt, and sulfur.
Transylvania's GDP (nominal) is 194 billion$ and its GDP per capita measures around 24,500$. Transylvania's Human Development Index is ranked 0.890, which makes Transylvania the 2nd most developed region in Romania after Bucharest-Ilfov and makes it comparable to countries like Czech Republic, Poland and Estonia.
There are large iron and steel, chemical, and textile industries. Stock raising, agriculture, wine production and fruit growing are important occupations. Agriculture is widespread in the Transylvanian Plateau, including growing cereals, vegetables, viticulture and breeding cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry. Timber is another valuable resource.
Information technology, IT, electronics and Automotive industry, automotive industries are important in urban and university centers like Cluj-Napoca (Robert Bosch GmbH, Emerson Electric), Timișoara (Alcatel-Lucent, Flextronics and Continental AG),
 The culture of Transylvania is complex, due to its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, having incorporated significant Hungarian (see Hungarians in Romania) and German (see Germans of Romania) influences.
With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian Gothic style is preserved to this day in monuments such as the Biserica Neagră, Black Church in
The culture of Transylvania is complex, due to its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, having incorporated significant Hungarian (see Hungarians in Romania) and German (see Germans of Romania) influences.
With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian Gothic style is preserved to this day in monuments such as the Biserica Neagră, Black Church in

 * Bran Castle, also known as Count Dracula, Dracula's Castle
* The medieval cities of
* Bran Castle, also known as Count Dracula, Dracula's Castle
* The medieval cities of
 The first heraldic representations of Transylvania date from the 16th century. The Transylvanian Diet, Diet of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations (Unio Trium Nationum (Union of the Three Nations)) in Flag and coat of arms of Transylvania, Transylvania's coat of arms. It depicted a black eagle (Turul) on a blue background, representing the
The first heraldic representations of Transylvania date from the 16th century. The Transylvanian Diet, Diet of 1659 codified the representation of the privileged nations (Unio Trium Nationum (Union of the Three Nations)) in Flag and coat of arms of Transylvania, Transylvania's coat of arms. It depicted a black eagle (Turul) on a blue background, representing the
File:Coa Transylvania Country History v4.svg, Coat of arms of Transylvania by Levinus Hulsius (1596)
File:SigismundBathory1597.jpg, Coat of arm of Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania (1586–1598, 1598–1599, 1601–1602)
File:Stema Mihai Viteazul.jpg, Seal of Michael the Brave during his personal union of Wallachia, Moldavia and Transylvania (1599–1600)
File:COA Bathory Zsofia.jpg, Coat of arms of Sophia Báthory, List of Transylvanian royal consorts, Princess of Transylvania (1642–1657, 1657–1658, 1659–1660)
File:Coat of arms of Transilvania in Stematographia.jpg, Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hristofor Žefarović (1741)
File:Wappen Großfürstentum Siebenbürgen.png, Coat of arms of Transylvania by Hugo Gerard Ströhl
File:Erdely-Cimere-1765.jpg, Coat of arms of Transylvania (1765)
File:Kreisregierung Vorarlberg.jpg, Coat of arms of Transylvania in an Austrian Empire, Austrian coat of arms (1850)
File:Coa Hungary Country History Mid (1867).svg, alt=kingdom hungary 1867, Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the
 Following the publication of Emily Gerard's ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his Gothic fiction, gothic horror novel '' Dracula'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with vampires. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel ''The Witch of Portobello'', the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani people, Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklós Bánffy, ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. Among the first actors to portray Count Dracula, Dracula Dracula (1931 English-language film), in film was Bela Lugosi, who was born in Lugos (now Lugoj), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called ''Hotel Transylvania''. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in ''Europa Universalis IV''.
Following the publication of Emily Gerard's ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his Gothic fiction, gothic horror novel '' Dracula'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with vampires. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel ''The Witch of Portobello'', the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani people, Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklós Bánffy, ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. Among the first actors to portray Count Dracula, Dracula Dracula (1931 English-language film), in film was Bela Lugosi, who was born in Lugos (now Lugoj), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called ''Hotel Transylvania''. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in ''Europa Universalis IV''.
Transylvania Guidebook
* Patrick Leigh Fermor, ''Between the Woods and the Water'' (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986. * *
Radio Transsylvania International
Katherine Lovatt, in ''Central Europe Review'', Vol. 1, No. 14, 27 September 1999.
by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany
''Transylvania,Its Products and its People''
, by Charles Boner, 1865
Transylvanian Family History Database
{{Authority control Transylvania, Historical regions Historical regions in the Kingdom of Hungary Historical regions in Romania
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
, encompassing central Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
. To the east and south its natural border
A natural border is a border between states or their subdivisions which is concomitant with natural formations such as rivers or mountain ranges. The "doctrine of natural boundaries" developed in Western culture in the 18th century being based u ...
is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains
The Apuseni Mountains ( ro, Munții Apuseni, hu, Erdélyi-középhegység) is a mountain range in Transylvania, Romania, which belongs to the Western Romanian Carpathians, also called ''Occidentali'' in Romanian. Their name translates from Ro ...
. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Rom ...
and Maramureș
or Marmaroshchyna ( ro, Maramureș ; uk, Мармарощина, Marmaroshchyna; hu, Máramaros) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, alon ...
, and occasionally Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
.
Transylvania is known for the scenery of its Carpathian landscape and its rich history. It also contains Romania's second-largest city, Cluj-Napoca, and other iconic cities and towns such as Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
, Sibiu, Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 census. It lies on the Mureș River, the ...
, Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
and Sighișoara
Sighișoara (; hu, Segesvár ; german: Schäßburg ; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Schäsbrich''; yi, שעסבורג, Shesburg; la, Castrum Sex) is a city on the Târnava Mare River in Mureș County, Romania. Located in the historic region of Transy ...
. It is also the home of some of Romania's UNESCO World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
such as the Villages with fortified churches, the Historic Centre of Sighișoara
The Historic Centre of Sighișoara (''Sighișoara Citadel'') is the old historic center of the town of Sighișoara (german: Schäßburg, hu, Segesvár), Romania, built in the 12th century by Saxon settlers. It is an inhabited medieval citadel that ...
, the Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains
Built in murus dacicus style, the six Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains (), in Romania, were created in the 1st centuries BC and AD as protection against Roman conquest, and played an important role during the Roman-Dacian wars.
Their ...
and the Roșia Montană Mining Cultural Landscape.
It was under the rule of the Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
, part of the Dacian Kingdom
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It t ...
(168 BC–106 AD), Roman Dacia (106–271), the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, the Hunnic Empire (4th–5th centuries), the Kingdom of the Gepids (5th–6th centuries), the Avar Khaganate (6th–9th centuries), the Slavs, and the 9th century First Bulgarian Empire. During the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the Hungarian conquerors, and Gyula's family from seven chieftains of the Hungarians ruled it in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary
Stephen I, also known as King Saint Stephen ( hu, Szent István király ; la, Sanctus Stephanus; sk, Štefan I. or Štefan Veľký; 975 – 15 August 1038), was the last Grand Prince of the Hungarians between 997 and 1000 or 1001, and the ...
asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords. He personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III
Gyula III, also Iula or Gyula the Younger, Geula or Gyla, was an early medieval ruler in Transylvania ( – 1003/1004). Around 1003, he and his family were attacked, dispossessed and captured by King Stephen I of Hungary (1000/1001-1038). The name ...
and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
in 1002; it then belonged to the Lands of the Hungarian Crown
The "Lands of the Hungarian Crown"Laszlo PéterHungary's Long Nineteenth Century: Constitutional and Democratic Traditions in a European Perspective BRILL, 2012, pp. 51–56 was the titular expression of Hungarian pretensions to the various territo ...
until 1918.
After the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
in 1526 it belonged to the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom, from which the Principality of Transylvania emerged in 1570 by the Treaty of Speyer. During most of the 16th and 17th centuries, the principality was a vassal state of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
; however, the principality had dual suzerainty ( Ottoman and Habsburg).
In 1690, the Habsburg monarchy gained possession of Transylvania through the Hungarian crown
The Hungarian Crown ( pl, Korona Węgierska) was a part of the Polish Crown Jewels. It was made in the 16th century, resembling the Crown of Saint Stephen, as a private crown of John II Sigismund Zápolya.
History
The original Hungarian Regali ...
.Paul Lendvai, Ann Major''The Hungarians: A Thousand Years of Victory in Defeat''
C. Hurst & Co. Publishers, 2003, page 146; After the failure of Rákóczi's War of Independence in 1711, Habsburg control of Transylvania was consolidated, and Hungarian Transylvanian princes were replaced with Habsburg imperial governors."Transylvania"
(2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009"Diploma Leopoldinum"
(2009). ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Retrieved July 7, 2009 During the
Hungarian Revolution of 1848
The Hungarian Revolution of 1848 or fully Hungarian Civic Revolution and War of Independence of 1848–1849 () was one of many European Revolutions of 1848 and was closely linked to other revolutions of 1848 in the Habsburg areas. Although t ...
, the Hungarian government proclaimed union with Transylvania in the April Laws
The April Laws, also called March Laws, were a collection of laws legislated by Lajos Kossuth with the aim of modernizing the Kingdom of Hungary into a parliamentary democracy, nation state. The imperative program included Hungarian control o ...
of 1848. After the failure of the revolution, the March Constitution of Austria The March Constitution, Imposed March Constitution or Stadion Constitution (German: ' or ') was an "irrevocable" constitution of the Austrian Empire promulgated by Minister of the Interior Count Stadion between 4 March and 7 March 1849 until it was ...
decreed that the Principality of Transylvania be a separate crown land entirely independent of Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
.Austrian Constitution of 4 March 1849(Section I, Art. I and Section IX., Art. LXXIV) After the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, the separate status of Transylvania ceased, it was incorporated again into the
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(Transleithania
The Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen ( hu, a Szent Korona Országai), informally Transleithania (meaning the lands or region "beyond" the Leitha River) were the Hungarian territories of Austria-Hungary, throughout the latter's entire exis ...
) as part of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Transylvania became part of Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
by the Treaty of Trianon in 1920. In 1940, Northern Transylvania reverted to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the ...
as a result of the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
, but it was reclaimed by Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
after the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
In popular culture, Transylvania is commonly associated with vampires because of the influence of Bram Stoker's 1897 novel '' Dracula'' and the many subsequent books and films that have been inspired by the tale.
Etymology
The earliest known reference to Transylvania appears in aMedieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functione ...
document of the Kingdom of Hungary in 1075 as , meaning "beyond the forest" ( meaning "beyond" or "on the far side of" and the accusative case of () "woods, forest"). Transylvania, with an alternative Latin prepositional prefix, means "on the other side of the woods". Hungarian historians claim that the Medieval Latin form , later , was a direct translation from the Hungarian form .Engel, Pál (2001). ''Realm of St. Stephen: History of Medieval Hungary, 895–1526 (International Library of Historical Studies)'', page 24, London: I.B. Taurus. That also was used as an alternative name in German ("beyond the forest") (13th–14th centuries) and Ukrainian ().
Historical names of Transylvania are:
* bg, Седмиградско, Sedmigradsko,
* hr, Sedmogradska, (hist.),
* german: Siebenbürgen (),
* hu, Erdély ()
* la, Ultrasilvania,
* pl, Siedmiogród,
* rom, Transilvaniya
* ro, Ardeal (), ()
* russian: Трансильвания, Transil'vaniya,
* sr, Ердељ/Erdelj, sr, Трансилванија/Transilvanija
* sk, Ardieľ, Sedmohradsko
* Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjen''
* tr, Erdel, Erdelistan
* uk, Семигород, Semyhorod, ,
* yi, זיבנבערגן, Zibnbergn, ,
* The German name means "seven castles", after the seven (ethnic German
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
) Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania ( ...
' cities in the region. This is also the origin of the region's name in many other languages, such as the Croatian , the Bulgarian (), Polish , Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
(), and Ukrainian ().
* The Hungarian form was first mentioned in the 12th-century as (in modern script ) or . The word means forest in Hungarian, and the word denotes a region in connection with this, similarly to the Hungarian name for Muntenia (, or land lying ahead of the snow-capped mountains). , , are derived from Hungarian .
* An occurrence of the form ''Ardeliu'' in a Church Slavonic document written by a Romanian chancellery is attested in 1432. The Romanian is derived from the Hungarian .
History
 The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the
The first known civilization to inhabit the territory was the Agathyrsi
The Agathyrsi ( Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a people belonging to the Scythian cultures. The Agathyrsi were a people of mixed Iranian Scythic and Geto-Thracian origin whose bulk were Thracian while their aristocracy was closely related to ...
belonging to the Scythic cultures. From the 4th century BC Celtic La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
came to domination. The indigenous Dacian tribes engaged in politics from the 1st century BC and united under King Burebista forming their kingdom Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
.
The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
made heavy efforts to seize the territory from King Decebalus, resulting in the formation of Roman Dacia in 106, after Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
's costly and bloody wars. During Roman rule, the territory, depleted of its indigenous population, was repopulated with Latin colonists and its rich resource stock was systematically exploited. However, due to the growing threat of East Germanic
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the ...
and Carpic invasions, Emperor Aurelian
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited th ...
withdrew his legions and evacuated the citizens south of the Lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
in 275, after which the province was occupied by the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
. In 376, a powerful nomadic people, the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, defeated and shattered the Goths, settling down in the area. After the death of King Attila, their empire disintegrated and the Gepids conquered the region in 455, under King Ardaric. For two centuries, the Gepids controlled Transylvania. They waged successful war against the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
, and less successful against the Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths ( la, Ostrogothi, Austrogothi) were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who ...
in Pannonia. They were successfully defeated by the Lombards
The Lombards () or Langobards ( la, Langobardi) were a Germanic people who ruled most of the Italian Peninsula from 568 to 774.
The medieval Lombard historian Paul the Deacon wrote in the '' History of the Lombards'' (written between 787 an ...
and Avars in 567. In the following years, the Avars took full control over Transylvania, heavily settling the area with Slavic tribes who accepted their suzerainty. The expansion of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
, however imposed a growing threat on them and crushed their khaganate in the Avar Wars. The Avars and Slavs, although decreased seriously, continued to inhabit the Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large Sedimentary basin, basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The Geomorphology, geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewh ...
. The First Bulgarian Empire annexed Southern Transylvania. Smaller Slavic polities were also present, nevertheless they could hardly keep their independence.
In the late 9th century, Transylvania was reached and conquered by the Hungarian conquerors. There is an ongoing scholarly debate over the demographics in Transylvania in this time. According to the theory of Daco-Roman Continuity, Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
continuously lived on the territory for the past 2500 years. Opponents of this hypothesis point to the lack of written, archaeological and linguistic evidence to support this. Hungarian medieval chronicles claimed that the Székely people descended of the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
who remained in Transylvania, and later allying with the returning Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
conquered together the Carpathian Basin
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large Sedimentary basin, basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The Geomorphology, geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewh ...
. According to the ''Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', is the earliest book about Hungarian history which has survived for posterity. Its genre is not chronicle, but ''gesta'', meaning "deeds" or "acts", which is a medieval entertaining li ...
'', the Vlach (''Blacorum, Blacus'') leader Gelou
Gelou ( ro, Gelu; hu, Gyalu) was the Vlach ruler of Transylvania at the time of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin around 900 AD, according to the ''Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', i ...
ruled part of Transylvania before the Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
arrived, historians debate whether he was a historical person or an imaginary figure. The gyulas from the seven chieftains of the Hungarians governed Transylvania in the 10th century. King Stephen I of Hungary asserted his claim to rule all lands dominated by Hungarian lords, he personally led his army against his maternal uncle Gyula III
Gyula III, also Iula or Gyula the Younger, Geula or Gyla, was an early medieval ruler in Transylvania ( – 1003/1004). Around 1003, he and his family were attacked, dispossessed and captured by King Stephen I of Hungary (1000/1001-1038). The name ...
and Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
in 1002. Place names derived from the Hungarian tribes evidence that major Hungarian groups settled in Transylvania from the 950s. In the 12th and 13th centuries, Southeast and Northeast Transylvania was settled by Saxon colonists. After the Battle of Kosovo and Ottoman arrival at the Hungarian border, thousands of Vlach
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other Easter ...
and Serbian refugees came to Transylvania.
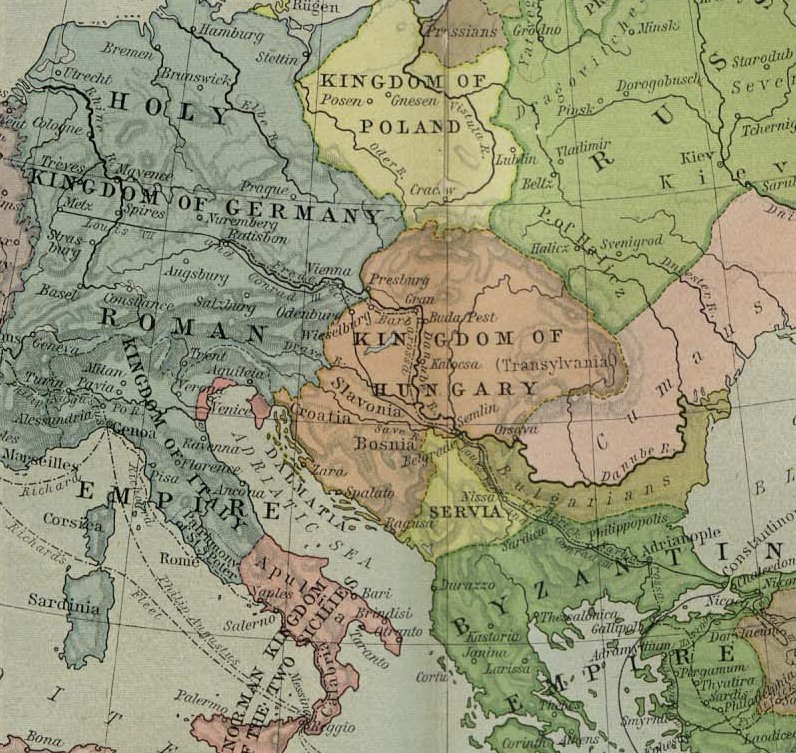
 Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the
Between 1002 and 1526, Transylvania was part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, led by a voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the ...
appointed by the King of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 175 ...
. After the Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács (; hu, mohácsi csata, tr, Mohaç Muharebesi or Mohaç Savaşı) was fought on 29 August 1526 near Mohács, Kingdom of Hungary, between the forces of the Kingdom of Hungary and its allies, led by Louis II, and thos ...
in 1526, Transylvania became part of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom. Later, in 1570, the kingdom transformed into the Principality of Transylvania by the Treaty of Speyer, which was ruled primarily by Calvinist
Calvinism (also called the Reformed Tradition, Reformed Protestantism, Reformed Christianity, or simply Reformed) is a major branch of Protestantism that follows the theological tradition and forms of Christian practice set down by John Ca ...
Hungarian princes Hungarian may refer to:
* Hungary, a country in Central Europe
* Kingdom of Hungary, state of Hungary, existing between 1000 and 1946
* Hungarians, ethnic groups in Hungary
* Hungarian algorithm, a polynomial time algorithm for solving the assignme ...
. The Eastern Hungarian king became the first prince of Transylvania
The Prince of Transylvania ( hu, erdélyi fejedelem, german: Fürst von Siebenbürgen, la, princeps Transsylvaniae, ro, principele TransilvanieiFallenbüchl 1988, p. 77.) was the head of state of the Principality of Transylvania from the last d ...
, according to the treaty, the Principality of Transylvania continued to be part of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
in the sense of public law, which stressed in a highly significant way that John Sigismund's possessions belonged to the Holy Crown of Hungary
The Holy Crown of Hungary ( hu, Szent Korona; sh, Kruna svetoga Stjepana; la, Sacra Corona; sk, Svätoštefanská koruna , la, Sacra Corona), also known as the Crown of Saint Stephen, named in honour of Saint Stephen I of Hungary, was the ...
and he was not permitted to alienate them.
The Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
acquired the territory shortly after the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna; pl, odsiecz wiedeńska, lit=Relief of Vienna or ''bitwa pod Wiedniem''; ota, Beç Ḳalʿası Muḥāṣarası, lit=siege of Beç; tr, İkinci Viyana Kuşatması, lit=second siege of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mou ...
in 1683. In 1687, the rulers of Transylvania recognized the suzerainty of the Habsburg emperor Leopold I, and the region was officially attached to the Habsburg Empire. The Habsburgs acknowledged Principality of Transylvania as one of the Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen
The Lands of the Crown of Saint Stephen ( hu, a Szent Korona Országai), informally Transleithania (meaning the lands or region "beyond" the Leitha, Leitha River) were the Hungarian territories of Austria-Hungary, throughout the latter's ent ...
, but the territory of principality was administratively separated from Habsburg Hungary and subjected to the direct rule of the emperor's governors. In 1699 the Ottomans legally acknowledged their loss of Transylvania in the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by the ...
; however, some anti-Habsburg elements within the principality submitted to the emperor only in the 1711 Peace of Szatmár, and Habsburg control over Principality of Transylvania was consolidated. The Grand Principality of Transylvania
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and co ...
was reintroduced 54 years later in 1765.
The Hungarian revolution against the Habsburgs started in 1848. The revolution in the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
grew into a war for the total independence from the Habsburg dynasty
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
. Julius Jacob von Haynau
Julius Jakob Freiherr von Haynau (14 October 1786 – 14 March 1853) was an Austrian general who suppressed insurrectionary movements in Italy and Hungary in 1848 and later. While a hugely effective military leader, he also gained renown as an agg ...
, the leader of the Austrian army was appointed plenipotentiary to restore order in Hungary after the conflict. He ordered the execution of The 13 Hungarian Martyrs of Arad and Prime Minister Lajos Batthyány, Batthyány was executed the same day in Pest, Hungary, Pest. After a series of serious Austrian defeats in 1849, the Austrian Empire, empire came close to the brink of collapse. Thus, the new young emperor Franz Joseph I of Austria, Franz Joseph I had to call for Russian help in the name of the Holy Alliance. Czar Nicholas, I answered, and sent 200,000 men strong army with 80,000 auxiliary forces. Finally, the joint army of Russian and Austrian forces defeated the Hungarian forces. After the restoration of Habsburg power, Hungary was placed under martial law. Following the Hungarian Army's surrender at Világos (now Șiria, Romania) in 1849, their revolutionary banners were taken to Russia by the Tsarist troops and were kept there both under the Tsarist and Communist systems (in 1940 the Soviet Union offered the banners to the Horthy government).
After the Ausgleich of 1867, the Principality of Transylvania was once again abolished. The territory then became part of Transleithania,"Transylvania", Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2008. an addition to the newly established Austro-Hungarian Empire. Romanian intellectuals issued the Blaj Pronouncement in protest.
The region was the site of an important Battle of Transylvania, battle during World War I, which caused the replacement of the German Chief of Staff, temporarily ceased German offensives on all the other fronts and created a unified Central Powers command under the German Kaiser. Following defeat in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Austria-Hungary disintegrated. Elected representatives of the Romanians, ethnic Romanians from Transylvania, Banat, Crișana and Maramureș backed by the Hungarian–Romanian War, mobilization of Romanian troops, proclaimed Union of Transylvania with Romania, Union with Romania on 1 December 1918. The ''Proclamation of Union'' of Alba Iulia was adopted by the Deputies of the Romanians from Transylvania and supported one month later by the vote of the Deputies of the Saxons from Transylvania.
Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, the Great Union Day (also called ''Unification Day'') occurring on December 1, celebrates this event. The holiday was established after the Romanian Revolution, and marks the unification not only of Transylvania but also of the provinces of Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
, Bessarabia and Bukovina with the Kingdom of Romania, Romanian Kingdom. These other provinces had all joined with the Kingdom of Romania a few months earlier. In 1920, the Treaty of Trianon established new borders, much of the proclaimed territories became part of Romania. Hungary protested against the new state borders, as they did not follow the real ethnic boundaries, for over 1.3 or 1.6 million Hungarian people, representing 25.5 or 31.6% of the Transylvanian population (depending on statistics used),Varga, E. Árpád''Hungarians in Transylvania between 1870 and 1995''
Translation by Tamás Sályi, Budapest, March 1999, pp. 30-34 were living on the Romanian side of the border, mainly in the Székely Land of Eastern Transylvania, and along the newly created border.
 In August 1940, by the
In August 1940, by the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
, with the arbitration of Germany and Italy, Hungary gained Northern Transylvania (including parts of Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Rom ...
and Maramureș
or Marmaroshchyna ( ro, Maramureș ; uk, Мармарощина, Marmaroshchyna; hu, Máramaros) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, alon ...
) totaling over 40% of the territory lost in 1920. This award did not solve the nationality problem, as over 1.15–1.3 million Romanians (or 48% to more than 50% of the population of the ceded territory) remained in Northern Transylvania while 0.36–0.8 million Hungarians (or 11% to more than 20% of the population) continued to reside in Southern Transylvania. The Second Vienna Award was voided on 12 September 1944 by the Allied Commission througthe Armistice Agreement with Romania
(Article 19); and the 1947 Paris Peace Treaties, 1947, Treaty of Paris reaffirmed the borders between Romania and Hungary, as originally defined in the Treaty of Trianon, 27 years earlier, thus confirming the return of Northern Transylvania to Romania. From 1947 to 1989, Transylvania, along with the rest of Romania, was Socialist Republic of Romania, under a communist regime. The ethnic clashes of Târgu Mureș occurred between ethnic
Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
and Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
in March 1990 after the Romanian Revolution, fall of the communist regime and became the most notable inter-ethnic incident in the post-communist era.
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
(December 1, 1918), declaring the Union of Transylvania with Romania
Geography and ethnography

 The Transylvanian Plateau, high, is drained by the Mureș River, Mureș, Someș River, Someș, Criș River, Criș, and Olt River, Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern Carpathians, Eastern, Southern Carpathians, Southern and Apuseni Mountains, Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains. The area includes the Transylvanian Plain. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, though geographically the two are not identical.
Ethnographic areas:
* Transylvania proper:
** Mărginimea Sibiului (Szeben-hegyalja)
** Transylvanian Plain (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség)
** Țara Bârsei (Burzenland/Barcaság)
**
** Țara Călatei (Kalotaszeg)
** (Kővár)
** Țara Făgărașului (Fogaras)
** Țara Hațegului (Hátszeg)
**
**
** Țara Moților
** Țara Năsăudului (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke)
**
**
** Ținutul Secuiesc (Székelyföld/Székely Land)
*
The Transylvanian Plateau, high, is drained by the Mureș River, Mureș, Someș River, Someș, Criș River, Criș, and Olt River, Olt rivers, as well as other tributaries of the Danube. This core of historical Transylvania roughly corresponds with nine counties of modern Romania. The plateau is almost entirely surrounded by the Eastern Carpathians, Eastern, Southern Carpathians, Southern and Apuseni Mountains, Romanian Western branches of the Carpathian Mountains. The area includes the Transylvanian Plain. Other areas to the west and north are widely considered part of Transylvania. In common reference, the Western border of Transylvania has come to be identified with the present Romanian-Hungarian border, settled in the 1920 Treaty of Trianon, though geographically the two are not identical.
Ethnographic areas:
* Transylvania proper:
** Mărginimea Sibiului (Szeben-hegyalja)
** Transylvanian Plain (Câmpia Transilvaniei/Mezőség)
** Țara Bârsei (Burzenland/Barcaság)
**
** Țara Călatei (Kalotaszeg)
** (Kővár)
** Țara Făgărașului (Fogaras)
** Țara Hațegului (Hátszeg)
**
**
** Țara Moților
** Țara Năsăudului (Nösnerland/Naszód vidéke)
**
**
** Ținutul Secuiesc (Székelyföld/Székely Land)
* Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
**
* Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Rom ...
**
* Maramureș historical region, Maramureș
** Țara Oașului (Avasság)
** (Lápos-vidék)
Administrative divisions
The area of the historical Voivodeship is . The regions granted to Romania in 1920 covered 23 counties including nearly (102,787–103,093 km2 in Hungarian sources and 102,282 km2 in contemporary Romanian documents). Nowadays, due to the several administrative reorganisations, the territory covers 16 Counties of Romania, counties (Romanian language, Romanian: ''județ''), with an area of , in central and northwest Romania. The 16 counties are: Alba County, Alba, Arad County, Arad, Bihor County, Bihor, Bistrița-Năsăud County, Bistrița-Năsăud, Brașov County, Brașov, Caraș-Severin County, Caraș-Severin, Cluj County, Cluj, Covasna County, Covasna, Harghita County, Harghita, Hunedoara County, Hunedoara, Maramureș County, Maramureș, Mureș County, Mureș, Sălaj County, Sălaj, Satu Mare County, Satu Mare, Sibiu County, Sibiu, and Timiș County, Timiș. Transylvania contains both largely urban counties, such as Brașov and Hunedoara counties, as well as largely rural ones, such as Bistrița-Năsăud and Sălaj counties. Since 1998, Romania has been divided into eight Development regions of Romania, development regions, acting as divisions that coordinate and implement socio-economic development at regional level. Six counties (Alba, Brașov, Covasna, Harghita, Mureș and Sibiu) form the Centru (development region), Centru development region, other six counties (Bihor, Bistrița-Năsăud, Cluj, Maramureș, Satu Mare, Sălaj) form the Nord-Vest (development region), Nord-Vest development region, while four (Arad, Caraș-Severin, Hunedoara, Timiș) form the Vest (development region), Vest development region.Cities
Cluj-Napoca, commonly known as Cluj, is the second most populous city in Romania (as of 2011 census), after the national capital Bucharest, and the seat of Cluj County. From 1790 to 1848 and from 1861 to 1867, it was the official capital of theGrand Principality of Transylvania
Grand may refer to:
People with the name
* Grand (surname)
* Grand L. Bush (born 1955), American actor
* Grand Mixer DXT, American turntablist
* Grand Puba (born 1966), American rapper
Places
* Grand, Oklahoma
* Grand, Vosges, village and co ...
. Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
is an important tourist destination, being the largest city in a mountain resorts area, and a central location, suitable for exploring Romania, with the distances to several tourist destinations (including the Black Sea resorts, the monasteries in northern Moldavia, and the wooden churches of Maramureș region, Maramureș) being similar.
Sibiu is one of the most important cultural centres of Romania and was designated the European Capital of Culture for the year 2007, along with the city of Luxembourg (city), Luxembourg, and it was formerly the centre of the Transylvanian Saxon culture and between 1692 and 1791 and 1849–65 was the capital of the Principality of Transylvania.
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
is a city located on the Mureș River in Alba County, and since the High Middle Ages, the city has been the seat of Transylvania's Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Alba Iulia, Roman Catholic diocese. Between 1541 and 1690 it was the capital of the Eastern Hungarian Kingdom and the latter Principality of Transylvania. Alba Iulia also has historical importance because at the end of World War I, representatives of the Romanian population of Transylvania gathered in Alba Iulia on 1 December 1918 to proclaim the Union of Transylvania with Romania, union of Transylvania with the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
. In Transylvania, there are many medieval smaller towns such as Sighișoara
Sighișoara (; hu, Segesvár ; german: Schäßburg ; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Schäsbrich''; yi, שעסבורג, Shesburg; la, Castrum Sex) is a city on the Târnava Mare River in Mureș County, Romania. Located in the historic region of Transy ...
, Mediaș, Sebeș, and Bistrița.
Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
( hu, Brassó, german: Kronstadt)
File:Sibiu 200811 800px.jpg, Sibiu (german: Hermannstadt, hu, Nagyszeben)
File:Arad City Hall (30112380741).jpg, Arad
File:Cetatea Alba Carolina Ansamblul fortificației „Cetatea Alba Iulia 16.jpg, Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
( hu, Gyulafehérvár, german: Karlsburg), defense wall of Alba Carolina Citadel
File:Palatul Culturii (Targu Mures).jpg, Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 census. It lies on the Mureș River, the ...
( hu, Marosvásárhely, german: Neumarkt am Mieresch)
File:Timisoara - Catholic Dome in Union Square.jpg, Timișoara ( hu, Temesvár, german: Temeschburg)
File:Primăria și Centrul Municipiului Oradea.JPG, Oradea ( hu, Nagyvárad, german: Großwardein)
File:Sighisoara. Biserica din deal.jpg, Sighișoara
Sighișoara (; hu, Segesvár ; german: Schäßburg ; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Schäsbrich''; yi, שעסבורג, Shesburg; la, Castrum Sex) is a city on the Târnava Mare River in Mureș County, Romania. Located in the historic region of Transy ...
( hu, Segesvár, german: Schäßburg)
File:Biserica Sfânta Margareta.jpg, Mediaș ( hu, Medgyes, german: Mediasch)
File:Bistrița de sus.jpg, Bistrița (german: Bistritz, hu, Beszterce)
File:Sebes evangelical church 3.JPG, Sebeș (german: Mülbach, hu, Szászsebes)
File:Centrul Vechi Baia Mare.jpg, Baia Mare ( hu, Nagybánya, german: Frauenbach)
File:Dévai vármegyeház.jpeg, Deva
File:Sighetul Marmatiei - Palatul Culturii.jpg, Sighetu Marmației
File:2011-IMG 4425.jpg, Turda
File:Sepsiszentgyorgyi reformatus vartemplom.jpg, Sfântu Gheorghe Fortress
File:Aiud-Turnul dogarilor si biserica reformata-2.JPG, Aiud Citadel
Population
Historical population
Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
and 23.3% Hungarian people, Hungarians.
In the last quarter of the 19th century, the Hungarian population of Transylvania increased from 24.9% in 1869 to 31.6%, as indicated in the 1910 Hungarian census (the majority of the History of the Jews in Hungary, Jewish population reported Hungarian as their primary language, so they were also counted as ethnically Hungarian in the 1910 census). At the same time, the percentage of the Romanian population decreased from 59.0% to 53.8% and the percentage of the German population decreased from 11.9% to 10.7%, for a total population of 5,262,495. Magyarization policies greatly contributed to this shift.
The percentage of the Romanian majority has significantly increased since the declaration of the union of Transylvania with Romania after World War I in 1918. The proportion of Hungarians in Transylvania was in steep decline as more of the region's inhabitants moved into urban areas, where the pressure to assimilate and Romanianize was greater. The expropriation of the estates of Magyar magnates, the distribution of the lands to the Romanian peasants, and the policy of cultural Romanianization that followed the Treaty of Trianon were major causes of friction between Hungary and Romania. Other factors include the emigration of non-Romanian peoples, assimilation and internal migration within Romania (estimates show that between 1945 and 1977, some 630,000 people moved from the Romanian Old Kingdom, Old Kingdom to Transylvania, and 280,000 from Transylvania to the Old Kingdom, most notably to Bucharest).
Current population
According to the results of the Demographics of Romania, 2011 Population Census, the total population of Transylvania was 6,789,250 inhabitants and the ethnic groups were: Romanians – 70.62%, Hungarians – 17.92%, Roma – 3.99%, Ukrainians – 0.63%, Germans – 0.49%, other – 0.77%. Some 378,298 inhabitants (5.58%) have not declared their ethnicity. The ethnic Hungarian population of Transylvania form a majority in the counties of Covasna County, Covasna (73.6%) and Harghita County, Harghita (84.8%). The Hungarians are also numerous in the following counties: Mureș (37.8%), Satu Mare (34.5%), Bihor (25.2%), and Sălaj (23.2%).Economy
Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
, Sibiu, Oradea and Arad. The cities of Cluj Napoca and Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 census. It lies on the Mureș River, the ...
are connected with a strong medicine, medical tradition, and according to the same classifications top performance hospitals exist there.
Native brands include: Roman (vehicle manufacturer), Roman of Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
(trucks and buses), Azomureș of Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 census. It lies on the Mureș River, the ...
(fertilizers), Terapia Ranbaxy, Terapia of Cluj-Napoca (pharmaceuticals), Banca Transilvania of Cluj-Napoca (finance), Romgaz and Transgaz of Mediaș (natural gas), Jidvei wines, Jidvei of Alba county (alcoholic beverages), Timișoreana of Timișoara (alcoholic beverages) and others.
The Jiu Valley, located in the south of Hunedoara County, has been a major mining area throughout the second half of the 19th century and the 20th century, but many mines were closed down in the years following the collapse of the communist regime, forcing the region to diversify its economy.
During the Second World War, Transylvania (the Southern/Romanian half, as the region was divided during the war) was crucial to the Romanian defense industry. Transylvanian factories built until 1945 over 1,000 warplanes and over 1,000 artillery pieces of all types, among Southern Transylvania#Armaments industry, others.
Culture
 The culture of Transylvania is complex, due to its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, having incorporated significant Hungarian (see Hungarians in Romania) and German (see Germans of Romania) influences.
With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian Gothic style is preserved to this day in monuments such as the Biserica Neagră, Black Church in
The culture of Transylvania is complex, due to its varied history and longstanding multiculturalism, having incorporated significant Hungarian (see Hungarians in Romania) and German (see Germans of Romania) influences.
With regard to architecture, the Transylvanian Gothic style is preserved to this day in monuments such as the Biserica Neagră, Black Church in Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
(14th and 15th centuries) and a number of other cathedrals, as well as the Bran Castle in Brașov County (14th century), the Hunyad Castle in Hunedoara (15th century).
Notable writers such as Emil Cioran, Lucian Blaga, George Coșbuc, Ioan Slavici, Octavian Goga, Liviu Rebreanu, Endre Ady, Elek Benedek, Elie Wiesel and Károly Kós were born in Transylvania. Liviu Rebreanu wrote the novel ''Ion'', which introduces the reader to a depiction of the life of Romanian peasants and intellectuals of Transylvania at the turn of the 20th century. Károly Kós was one of the most important writers supporting the movement of Transylvanianism.
Religion
Transylvania has a very rich and unique religious history from the other regions of Europe. Since the Protestant Reformation, different Christian denominations have been coexisting in this religious melting pot, including Romanian Orthodox, other Eastern Orthodox, Catholic Church in Romania, Latin Catholic and Romanian Greek Catholic Church, Romanian Greek Catholic, Lutheran, Reformed tradition, Reformed, and Unitarianism, Unitarian branches. Other faiths also are present, including Jews and Muslims. Under the Habsburgs, Transylvania served as a place for "religious undesirables". People who arrived in Transylvania included those that did not conform to the Catholic Church and were sent here forcibly, as well as many religious refugees. Transylvania has a long history of religious tolerance. This has been ensured by its religious pluralism. Christianity is the largest religion in Transylvania. Transylvania has also been (and still is) a center for Christian denominations other than Eastern Orthodoxy, the form of Christianity that most Romanians currently follow. As such, there are significant numbers of inhabitants of Transylvania that follow Roman Catholicism in Romania, Latin Catholicism and Romanian Greek Catholic Church, Greek Catholicism, and Protestantism in Romania, Protestantism. Even though before 1948, the population of Transylvania split between Eastern Orthodox, Greek Catholic other forms of Christianity, during the Communist Period the Orthodox Church was much more favored by the state which has led to Eastern Orthodoxy being the religion of the majority of Transylvanians.Earl A. Pope, "Protestantism in Romania", in Sabrina Petra Ramet (ed.), ''Protestantism and Politics in Eastern Europe and Russia: The Communist and Postcommunist Eras'', Duke University Press, Durham, 1992, p.158-160. Babeș-Bolyai University, UBB, located in Cluj-Napoca is the only university in Europe that has four faculties of theology (Orthodox, Reformed, Roman Catholic, and Greek Catholic). There are also small denominations like adventism, Jehovah's Witnesses and more. Others * Nowadays, there is a very small number of Muslims (Islam) and Jews (Judaism), but back in 1930, with 191,877 inhabitants, Jews represented 3.46% of Transylvania's population. * Atheists, agnostics and unaffiliated account for 0.27% of Transylvania's population. ''Data refers to extended Transylvania (withBanat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
, Crișana
Crișana ( hu, Körösvidék, german: Kreischgebiet) is a geographical and historical region in north-western Romania, named after the Criș (Körös) River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru, and Crișul Repede. In Rom ...
and Maramureș
or Marmaroshchyna ( ro, Maramureș ; uk, Мармарощина, Marmaroshchyna; hu, Máramaros) is a geographical, historical and cultural region in northern Romania and western Ukraine. It is situated in the northeastern Carpathians, alon ...
).''
Tourist attractions

 * Bran Castle, also known as Count Dracula, Dracula's Castle
* The medieval cities of
* Bran Castle, also known as Count Dracula, Dracula's Castle
* The medieval cities of Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
, Cluj-Napoca (European Youth Capital 2015), Sibiu (European Capital Of Culture in 2007), Târgu Mureș
Târgu Mureș (, ; hu, Marosvásárhely ) is the seat of Mureș County in the historical region of Transylvania, Romania. It is the 16th largest Romanian city, with 134,290 inhabitants as of the 2011 census. It lies on the Mureș River, the ...
and Sighișoara
Sighișoara (; hu, Segesvár ; german: Schäßburg ; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Schäsbrich''; yi, שעסבורג, Shesburg; la, Castrum Sex) is a city on the Târnava Mare River in Mureș County, Romania. Located in the historic region of Transy ...
(World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site and alleged birthplace of Vlad Dracula)
* The city of Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
and the nearby Poiana Brașov ski resort
* The city of Hunedoara with the 14th century Corvin Castle
* The citadel and the Art Nouveau city centre of Oradea
* The Densuș Church, the oldest church in Romania that still holds services
* The Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains
Built in murus dacicus style, the six Dacian Fortresses of the Orăștie Mountains (), in Romania, were created in the 1st centuries BC and AD as protection against Roman conquest, and played an important role during the Roman-Dacian wars.
Their ...
, including Sarmizegetusa Regia (World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site)
* The Roman forts including Sarmizegetusa Ulpia Traiana, Porolissum, Apulum (castra), Apulum, Potaissa (castra), Potaissa and Drobeta (castra), Drobeta
* The Red Lake (Romania), Red Lake (also known as Lake Ghilcoș)
* The Turda Gorge natural reserve
* The Râșnov Citadel in Râșnov
* The Maramureș region
** The Merry Cemetery, Merry Cemetery of Săpânța (the only one of that kind in the world)
** The Wooden Churches of Maramureș, Wooden Churches (World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site)
** The cities of Baia Mare and Sighetu Marmației
** The villages in the Maramureș County, Iza, Maramureș County, Mara, and Maramureș County, Viseu valleys
* Villages with fortified churches in Transylvania, The Saxon fortified churches (World Heritage Site, UNESCO World Heritage Site)
* The Apuseni Mountains:
** Țara Moților
** Peștera Urșilor, The Bears Cave
** Scărișoara Cave in Alba County, the third largest glacier cave in the world
* The Rodna Mountains
* The Salina Turda Salt Mine: according to Business Insider—one of the ten "coolest underground places in the world".
Festivals and events
Film festivals
* Transilvania International Film Festival, Cluj-Napoca – Romania's biggest film festival * Gay Film Nights, Cluj-Napoca * Comedy Cluj, Cluj-Napoca * Humor Film Festival, TimișoaraMusic festivals
* Golden Stag Festival,Brașov
Brașov (, , ; german: Kronstadt; hu, Brassó; la, Corona; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Kruhnen'') is a city in Transylvania, Romania and the administrative centre of Brașov County.
According to the latest Romanian census (2011), Brașov has a pop ...
* Gărâna Jazz Festival, Gărâna
* Peninsula / Félsziget Festival, Târgu-Mureș
* Untold Festival, Cluj-Napoca – Romania's biggest music festival
* Toamna Muzicală Clujeană, Cluj-Napoca
* Artmania Festival, Sibiu
* Rockstadt Extreme Fest, Râșnov
* Electric Castle Festival, Bontida, Cluj-Napoca
Others
* Sighișoara Medieval Festival, Sighișoara * Sibiu International Theatre Festival * Festivalul Medieval Cetăți Transilvane SibiuHistorical coat of arms of Transylvania
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
, the Sun and the Moon representing the Székelys, and seven red towers on a yellow background representing the Transylvanian Saxons#Fortification of the towns, seven fortified cities of the Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons (german: Siebenbürger Sachsen; Transylvanian Saxon: ''Siweberjer Såksen''; ro, Sași ardeleni, sași transilvăneni/transilvani; hu, Erdélyi szászok) are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania ( ...
. The flag and coat of arms of Transylvania were granted by Queen Maria Theresa in 1765, when she established a Principality of Transylvania (1711–1867), Grand Principality within the Habsburg monarchy.
In 1596, Levinus Hulsius created a coat of arms for Transylvania, consisting of a shield with a rising eagle in the upper field and seven hills with towers on top in the lower field. He published it in his work "''Chronologia''", issued in Nuremberg the same year. The seal from 1597 of Sigismund Báthory, Prince of Transylvania, reproduced the new coat of arms with some slight changes: in the upper field the eagle was flanked by a sun and a moon and in the lower field the hills were replaced by simple towers. The coat of arms of Sigismund Báthory beside the coat of arms of the Báthory family, included the Transylvanian, Wallachia and Moldavian coat of arms, he used the title List of princes of Transylvania, Prince of Transylvania, Wallachia and Moldavia. A short-lived heraldic representation of Transylvania is found on the seal of Michael the Brave. Besides the Wallachian eagle and the Flag and coat of arms of Moldavia, Moldavian aurochs, Transylvania is represented by two lions holding a sword standing on seven hills. Hungarian Transylvanian princes used the symbols of the Flag and coat of arms of Transylvania, Transylvanian coat of arms usually with the Coat of arms of Hungary, Hungarian coat of arms since the 16th century because Transylvanian princes maintained their claims to the throne of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
.
While neither symbol has official status in present-day Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, the Flag and coat of arms of Transylvania, Transylvanian coat of arms is marshalled within the national Coat of arms of Romania, it was also a component of the Coat of arms of Hungary.
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(1867–1915)
File:Wappen Ungarische Länder 1867 (Mittel).png, Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(1867–1915)
File:Wappen Ungarische Länder 1915 (Mittel).png, Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
(1915–1918)
File:Kingdom of Romania - Medium CoA.svg, Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
(1921–1947)
File:Coat of arms of Romania.svg, Coat of arms of Transylvania in the coat of arms of Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
(2016)
In popular culture
 Following the publication of Emily Gerard's ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his Gothic fiction, gothic horror novel '' Dracula'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with vampires. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel ''The Witch of Portobello'', the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani people, Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklós Bánffy, ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. Among the first actors to portray Count Dracula, Dracula Dracula (1931 English-language film), in film was Bela Lugosi, who was born in Lugos (now Lugoj), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called ''Hotel Transylvania''. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in ''Europa Universalis IV''.
Following the publication of Emily Gerard's ''The Land Beyond the Forest'' (1888), Bram Stoker wrote his Gothic fiction, gothic horror novel '' Dracula'' in 1897, using Transylvania as a setting. With its success, Transylvania became associated in the English- and Spanish-speaking world with vampires. Since then it has been represented in fiction and literature as a land of mystery and magic. For example, in Paulo Coelho's novel ''The Witch of Portobello'', the main character, Sherine Khalil, is described as a Transylvanian orphan with a Romani people, Romani mother, in an effort to add to the character's exotic mystique. The so-called Transylvanian trilogy of historical novels by Miklós Bánffy, ''The Writing on the Wall'', is an extended treatment of the 19th- and early 20th-century social and political history of the country. Among the first actors to portray Count Dracula, Dracula Dracula (1931 English-language film), in film was Bela Lugosi, who was born in Lugos (now Lugoj), in present-day Romania. There is also an American animated movie franchise called ''Hotel Transylvania''. The Principality of Transylvania is also a playable nation in ''Europa Universalis IV''.
See also
* Prehistory of Transylvania * Siebenbürgenlied, an unofficial anthem for Transylvania * TransylvanianismNotes
References
Further reading
* András Bereznay, ''Erdély történetének atlasza'' (''Historical Atlas of Transylvania''), with text and 102 map plates, the first ever historical atlas of Transylvania (Méry Ratio, 2011; ) * * Zoltán Farkas and Judit SósTransylvania Guidebook
* Patrick Leigh Fermor, ''Between the Woods and the Water'' (New York Review of Books Classics, 2005; ). Fermor travelled across Transylvania in the summer of 1934, and wrote about it in this account first published more than 50 years later, in 1986. * *
External links
Radio Transsylvania International
Katherine Lovatt, in ''Central Europe Review'', Vol. 1, No. 14, 27 September 1999.
by Dr. Konrad Gündisch, Oldenburg, Germany
''Transylvania,Its Products and its People''
, by Charles Boner, 1865
Transylvanian Family History Database
{{Authority control Transylvania, Historical regions Historical regions in the Kingdom of Hungary Historical regions in Romania