Constellations historic ptolemaic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A constellation is an area on the
 The oldest Babylonian catalogues of stars and constellations date back to the beginning of the
The oldest Babylonian catalogues of stars and constellations date back to the beginning of the
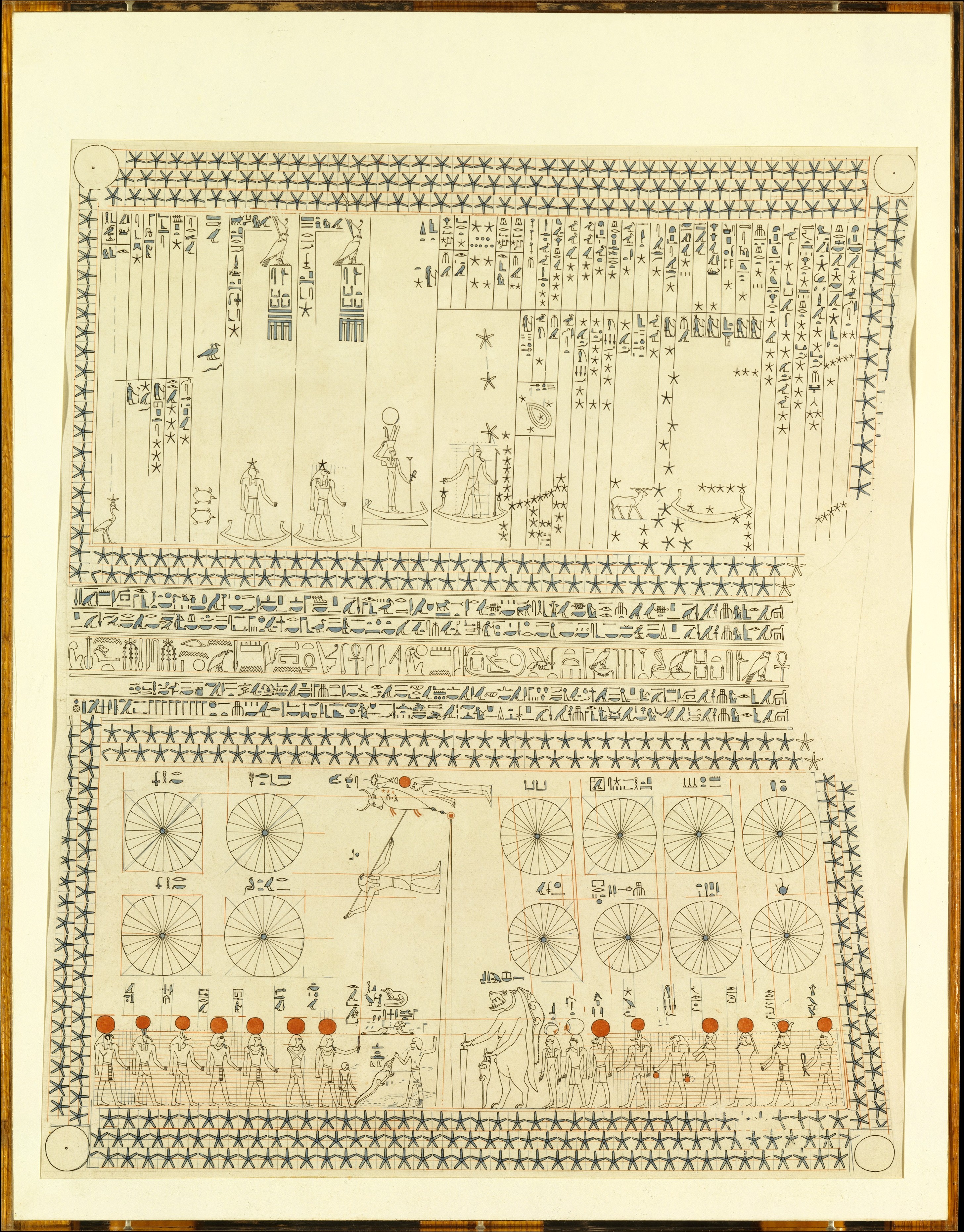 There is only limited information on ancient Greek constellations, with some fragmentary evidence being found in the '' Works and Days'' of the Greek poet
There is only limited information on ancient Greek constellations, with some fragmentary evidence being found in the '' Works and Days'' of the Greek poet
 The southern sky, below about −65°
The southern sky, below about −65°
File:Hipparcos Catalogue equirectangular plot.svg, Equirectangular plot of declination vs right ascension of stars brighter than apparent magnitude 5 on the Hipparcos Catalogue, coded by spectral type and apparent magnitude, relative to the modern constellations and the ecliptic.
The boundaries developed by Delporte used data that originated back to epoch
File:Emu public.jpg, The ''

IAU: The Constellations
including high quality maps.
Atlascoelestis
di Felice Stoppa.
Celestia
free 3D realtime space-simulation (OpenGL)
Stellarium
realtime sky rendering program (OpenGL)
Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center Files on official IAU constellation boundaries
Interactive Sky Charts
(Java applets allowing navigation through the entire sky with variable star detail, optional constellation lines)
Studies of Occidental Constellations and Star Names to the Classical Period: An Annotated Bibliography
Greco-Roman constellation myths
Neave Planetarium
Adobe Flash interactive web browser planetarium and stardome with realistic movement of stars and the planets. * Audio – Cain/Gay (2009
Astronomy Cast
Constellations
The Greek Star-Map
short essay by Gavin White
Bucur D. The network signature of constellation line figures
PLOS ONE 17(7): e0272270 (2022). A comparative analysis on the structure of constellation line figures across 56 sky cultures. {{Authority control Constellations Celestial cartography Constellations Concepts in astronomy
celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
in which a group of visible star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation
Creation may refer to:
Religion
*''Creatio ex nihilo'', the concept that matter was created by God out of nothing
* Creation myth, a religious story of the origin of the world and how people first came to inhabit it
* Creationism, the belief tha ...
, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation.
The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellations in the far southern sky
The southern celestial hemisphere, also called the Southern Sky, is the southern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies south of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere, on which seemingly fixed stars form constellations, appears ...
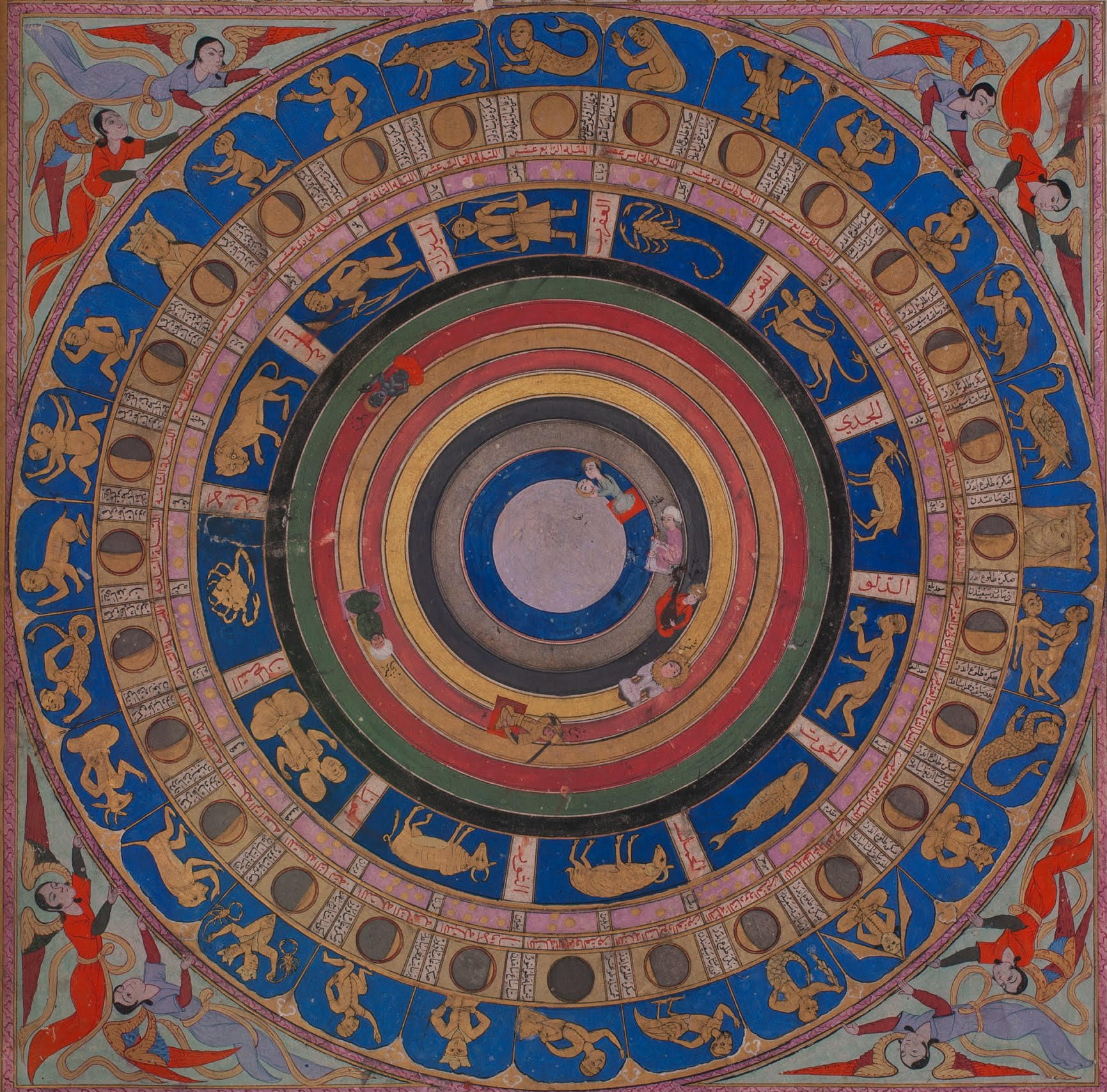
were added from the 15th century until the mid-18th century when European explorers began traveling to the Southern Hemisphere. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traverse). The origins of the zodiac remain historically uncertain; its astrological divisions became prominent 400 BC in Babylonian or Chaldea
Chaldea () was a small country that existed between the late 10th or early 9th and mid-6th centuries BCE, after which the country and its people were absorbed and assimilated into the indigenous population of Babylonia. Semitic-speaking, it was ...
n astronomy.
In 1922, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) formally accepted the modern list of 88 constellations, and in 1928 adopted official constellation boundaries that together cover the entire celestial sphere. Any given point in a celestial coordinate system lies in one of the modern constellations. Some astronomical naming systems include the constellation where a given celestial object is found to convey its approximate location in the sky. The Flamsteed designation of a star, for example, consists of a number and the genitive form of the constellation's name.
Other star patterns or groups called asterisms are not constellations under the formal definition, but are also used by observers to navigate the night sky. Asterisms may be several stars within a constellation, or they may share stars with more than one constellation. Examples of asterisms include the teapot within the constellation Sagittarius, or the big dipper in the constellation of Ursa Major.
Terminology
The word ''constellation'' comes from the Late Latin term , which can be translated as "set of stars"; it came into use in Middle English during the 14th century. The Ancient Greek word for constellation is ἄστρον (''astron''). These terms historically referred to any recognisable pattern of stars whose appearance was associated with mythological characters or creatures, earthbound animals, or objects. Over time, among European astronomers, the constellations became clearly defined and widely recognised. Today, there are 88 IAU designated constellations. A constellation or star that never sets below thehorizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This line divides all viewing directions based on whether i ...
when viewed from a particular latitude on Earth is termed circumpolar. From the North Pole or South Pole, all constellations south or north of the celestial equator are circumpolar. Depending on the definition, equatorial constellations may include those that lie between declinations 45° north and 45° south, or those that pass through the declination range of the ecliptic or zodiac ranging between 23½° north, the celestial equator, and 23½° south.
Stars in constellations can appear near each other in the sky, but they usually lie at a variety of distances away from the Earth. Since each star has its own independent motion, all constellations will change slowly over time. After tens to hundreds of thousands of years, familiar outlines will become unrecognizable. Astronomers can predict the past or future constellation outlines by measuring individual stars' common proper motions or cpm by accurate astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, the Milky Way.
His ...
and their radial velocities by astronomical spectroscopy
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and othe ...
.
Identification
The 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union as well as those that cultures have recognized throughout history are imagined figures and shapes derived from the patterns of stars in the observable sky. Many officially recognized constellations are based in the imaginations of ancient, Near Eastern and Mediterranean mythologies.H.A. Rey
Hans Augusto (H.A.) Rey (né Reyersbach; September 16, 1898 – August 26, 1977) was a German-born American illustrator and author, known best for the '' Curious George'' series of children's picture books that he and his wife Margret Rey creat ...
, who wrote popular books on astronomy, pointed out the imaginative nature of the constellations and their mythological, artistic basis, and the practical use of identifying them through definite images, according to the classical names they were given.
History of the early constellations
Lascaux Caves, Southern France
It has been suggested that the 17,000-year-oldcave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,000 ye ...
s in Lascaux Southern France depict star constellations such as Taurus, Orion's Belt, and the Pleiades. However, this view is not generally accepted among scientists.
Mesopotamia
Inscribed stones and clay writing tablets from Mesopotamia (in modern Iraq) dating to 3000 BC provide the earliest generally accepted evidence for humankind's identification of constellations. It seems that the bulk of the Mesopotamian constellations were created within a relatively short interval from around 1300 to 1000 BC. Mesopotamian constellations appeared later in many of the classical Greek constellations.Ancient Near East
 The oldest Babylonian catalogues of stars and constellations date back to the beginning of the
The oldest Babylonian catalogues of stars and constellations date back to the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, most notably the ''Three Stars Each'' texts and the '' MUL.APIN'', an expanded and revised version based on more accurate observation from around 1000 BC. However, the numerous Sumerian names in these catalogues suggest that they built on older, but otherwise unattested, Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ian traditions of the Early Bronze Age.
The classical Zodiac is a revision of Neo-Babylonian
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bein ...
constellations from the 6th century BC. The Greeks adopted the Babylonian constellations in the 4th century BC. Twenty Ptolemaic constellations are from the Ancient Near East. Another ten have the same stars but different names.
Biblical scholar E. W. Bullinger
Ethelbert William Bullinger (15 December 1837 – 6 June 1913) was an Anglican clergyman, biblical scholar, and ultradispensationalist theologian.
Early life
He was born in Canterbury, Kent, England, the youngest of five children of William ...
interpreted some of the creatures mentioned in the books of Ezekiel
Ezekiel (; he, יְחֶזְקֵאל ''Yəḥezqēʾl'' ; in the Septuagint written in grc-koi, Ἰεζεκιήλ ) is the central protagonist of the Book of Ezekiel in the Hebrew Bible.
In Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, Ezekiel is acknow ...
and Revelation as the middle signs of the four-quarters of the Zodiac, with the Lion as Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
, the Bull as Taurus, the Man representing Aquarius
Aquarius may refer to:
Astrology
* Aquarius (astrology), an astrological sign
* Age of Aquarius, a time period in the cycle of astrological ages
Astronomy
* Aquarius (constellation)
* Aquarius in Chinese astronomy
Arts and entertainment ...
, and the Eagle standing in for Scorpio. The biblical Book of Job
The Book of Job (; hbo, אִיּוֹב, ʾIyyōḇ), or simply Job, is a book found in the Ketuvim ("Writings") section of the Hebrew Bible (Tanakh), and is the first of the Poetic Books in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. Scholars ar ...
also makes reference to a number of constellations, including "bier", "fool" and "heap" (Job 9:9, 38:31–32), rendered as "Arcturus, Orion and Pleiades" by the KJV, but ''‘Ayish'' "the bier" actually corresponding to Ursa Major. The term ''Mazzaroth
''Mazzaroth'' (Hebrew Transliteration: מַזָּרוֹת ''Mazzārōṯ'', LXX Μαζουρωθ, ''Mazourōth'') is a Biblical Hebrew Word found in the Book of Job (38:32) and literally meaning "constellations," according to 10th-century biblic ...
'' , translated as ''a garland of crowns'', is a '' hapax legomenon'' in Job 38:32, and it might refer to the zodiacal constellations.
Classical antiquity
 There is only limited information on ancient Greek constellations, with some fragmentary evidence being found in the '' Works and Days'' of the Greek poet
There is only limited information on ancient Greek constellations, with some fragmentary evidence being found in the '' Works and Days'' of the Greek poet Hesiod
Hesiod (; grc-gre, Ἡσίοδος ''Hēsíodos'') was an ancient Greek poet generally thought to have been active between 750 and 650 BC, around the same time as Homer. He is generally regarded by western authors as 'the first written poet i ...
, who mentioned the "heavenly bodies". Greek astronomy essentially adopted the older Babylonian system in the Hellenistic era, first introduced to Greece by Eudoxus of Cnidus
Eudoxus of Cnidus (; grc, Εὔδοξος ὁ Κνίδιος, ''Eúdoxos ho Knídios''; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer, mathematician, scholar, and student of Archytas and Plato. All of his original works are lost, though some fragments are ...
in the 4th century BC. The original work of Eudoxus is lost, but it survives as a versification by Aratus, dating to the 3rd century BC. The most complete existing works dealing with the mythical origins of the constellations are by the Hellenistic writer termed pseudo-Eratosthenes
The ''Catasterismi'' or ''Catasterisms'' (Greek Καταστερισμοί ''Katasterismoi'', "Constellations" or "Placings Among the Stars"), is a lost work attributed to Eratosthenes of Cyrene. It was a comprehensive compendium of astral myt ...
and an early Roman writer styled pseudo- Hyginus. The basis of Western astronomy as taught during Late Antiquity and until the Early Modern period is the ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canoni ...
'' by Ptolemy, written in the 2nd century.
In the Ptolemaic Kingdom, native Egyptian tradition of anthropomorphic figures represented the planets, stars, and various constellations. Some of these were combined with Greek and Babylonian astronomical systems culminating in the Zodiac of Dendera; it remains unclear when this occurred, but most were placed during the Roman period between 2nd to 4th centuries AD. The oldest known depiction of the zodiac showing all the now familiar constellations, along with some original Egyptian constellations, decans, and planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young ...
. Ptolemy's ''Almagest'' remained the standard definition of constellations in the medieval period both in Europe and in Islamic astronomy.
Ancient China
Ancient China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapte ...
had a long tradition of observing celestial phenomena. Nonspecific Chinese star names, later categorized in the twenty-eight mansions, have been found on oracle bones from Anyang
Anyang (; ) is a prefecture-level city in Henan province, China. The northernmost city in Henan, Anyang borders Puyang to the east, Hebi and Xinxiang to the south, and the provinces of Shanxi and Hebei to its west and north respectively.
It had a ...
, dating back to the middle Shang dynasty. These constellations are some of the most important observations of Chinese sky, attested from the 5th century BC. Parallels to the earliest Babylonian (Sumerian) star catalogues suggest that the ancient Chinese system did not arise independently.
Three schools of classical Chinese astronomy in the Han period are attributed to astronomers of the earlier Warring States period. The constellations of the three schools were conflated into a single system by Chen Zhuo, an astronomer of the 3rd century ( Three Kingdoms period). Chen Zhuo's work has been lost, but information on his system of constellations survives in Tang period records, notably by Qutan Xida
Gautama Siddha, (fl. 8th century) astronomer, astrologer and compiler of History of India, Indian descent, known for leading the compilation of the ''Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era'' during the Tang Dynasty. He was born in Chang'an, and h ...
. The oldest extant Chinese star chart dates to that period and was preserved as part of the Dunhuang Manuscripts. Native Chinese astronomy flourished during the Song dynasty, and during the Yuan dynasty became increasingly influenced by medieval Islamic astronomy
Islamic astronomy comprises the astronomical developments made in the Islamic world, particularly during the Islamic Golden Age (9th–13th centuries), and mostly written in the Arabic language. These developments mostly took place in the Middle ...
(see Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era). As maps were prepared during this period on more scientific lines, they were considered as more reliable.
A well-known map from the Song period is the Suzhou Astronomical Chart, which was prepared with carvings of stars on the planisphere of the Chinese sky on a stone plate; it is done accurately based on observations, and it shows the supernova of the year of 1054 in Taurus.
Influenced by European astronomy during the late Ming dynasty, charts depicted more stars but retained the traditional constellations. Newly observed stars were incorporated as supplementary to old constellations in the southern sky, which did not depict the traditional stars recorded by ancient Chinese astronomers. Further improvements were made during the later part of the Ming dynasty by Xu Guangqi and Johann Adam Schall von Bell, the German Jesuit and was recorded in Chongzhen Lishu (Calendrical Treatise of Chongzhen period, 1628). Traditional Chinese star maps incorporated 23 new constellations with 125 stars of the southern hemisphere of the sky based on the knowledge of Western star charts; with this improvement, the Chinese Sky was integrated with the World astronomy.
Early modern astronomy
Historically, the origins of the constellations of the northern and southern skies are distinctly different. Most northern constellations date to antiquity, with names based mostly on Classical Greek legends. Evidence of these constellations has survived in the form of star charts, whose oldest representation appears on the statue known as the Farnese Atlas, based perhaps on the star catalogue of the Greek astronomer Hipparchus. Southern constellations are more modern inventions, sometimes as substitutes for ancient constellations (e.g. Argo Navis). Some southern constellations had long names that were shortened to more usable forms; e.g. Musca Australis became simply Musca. Some of the early constellations were never universally adopted. Stars were often grouped into constellations differently by different observers, and the arbitrary constellation boundaries often led to confusion as to which constellation a celestial object belonged. Before astronomers delineated precise boundaries (starting in the 19th century), constellations generally appeared as ill-defined regions of the sky. Today they now follow officially accepted designated lines ofright ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
and declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
based on those defined by Benjamin Gould in epoch 1875.0 in his star catalogue ''Uranometria Argentina''.
The 1603 star atlas " Uranometria" of Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, a ...
assigned stars to individual constellations and formalized the division by assigning a series of Greek and Latin letters to the stars within each constellation. These are known today as Bayer designation
A Bayer designation is a stellar designation in which a specific star is identified by a Greek or Latin letter followed by the genitive form of its parent constellation's Latin name. The original list of Bayer designations contained 1,564 stars. ...
s. Subsequent star atlases led to the development of today's accepted modern constellations.
Origin of the southern constellations
 The southern sky, below about −65°
The southern sky, below about −65° declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
, was only partially catalogued by ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Greeks, Chinese, and Persian astronomers of the north. The knowledge that northern and southern star patterns differed goes back to Classical writers, who describe, for example, the African circumnavigation expedition commissioned by Egyptian Pharaoh Necho II in c. 600 BC and those of Hanno the Navigator
Hanno the Navigator (sometimes "Hannon"; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤀 , ; ) was a Carthaginian explorer of the fifth century BC, best known for his naval exploration of the western coast of Africa. The only source of his voyage is a ''periplus'' transla ...
in c. 500 BC.
The history of southern constellations is not straightforward. Different groupings and different names were proposed by various observers, some reflecting national traditions or designed to promote various sponsors. Southern constellations were important from the 14th to 16th centuries, when sailors used the stars for celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface of ...
. Italian explorers who recorded new southern constellations include Andrea Corsali, Antonio Pigafetta, and Amerigo Vespucci.
Many of the 88 IAU-recognized constellations in this region first appeared on celestial globes developed in the late 16th century by Petrus Plancius, based mainly on observations of the Dutch navigators Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser
Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser (occasionally Petrus Theodorus; – 11 September 1596) was a Dutch navigator and celestial cartographer who mapped several constellations on the southern celestial hemisphere.
Voyages and star observation
Little is ...
and Frederick de Houtman
Frederick de Houtman ( – 21 October 1627) was a Dutch explorer, navigator, and colonial governor who sailed on the first Dutch expedition to the East Indies from 1595 until 1597, during which time he made observations of the southern cel ...
. These became widely known through Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, a ...
's star atlas '' Uranometria'' of 1603. Fourteen more were created in 1763 by the French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille, who also split the ancient constellation Argo Navis into three; these new figures appeared in his star catalogue, published in 1756.
Several modern proposals have not survived. The French astronomers Pierre Lemonnier and Joseph Lalande
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
, for example, proposed constellations that were once popular but have since been dropped. The northern constellation Quadrans Muralis
Quadrans Muralis (Latin for ''mural quadrant'') was a former constellations, constellation created by the French astronomer Jérôme Lalande in 1795. It depicted a wall-mounted quadrant with which he and his nephew Michel Lefrançois de Lalande ha ...
survived into the 19th century (when its name was attached to the Quadrantid meteor shower), but is now divided between Boötes
Boötes ( ) is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from la, Boōtēs, which comes from grc-gre, Βοώτης, Boṓtēs ...
and Draco
Draco is the Latin word for serpent or dragon.
Draco or Drako may also refer to:
People
* Draco (lawgiver) (from Greek: Δράκων; 7th century BC), the first lawgiver of ancient Athens, Greece, from whom the term ''draconian'' is derived
* D ...
.
88 modern constellations
A list of 88 constellations was produced for the International Astronomical Union in 1922. It is roughly based on the traditional Greek constellations listed by Ptolemy in his ''Almagest'' in the 2nd century and Aratus' work ''Phenomena'', with early modern modifications and additions (most importantly introducing constellations covering the parts of the southern sky unknown to Ptolemy) by Petrus Plancius (1592, 1597/98 and 1613), Johannes Hevelius (1690) and Nicolas Louis de Lacaille (1763), who introduced fourteen new constellations. Lacaille studied the stars of the southern hemisphere from 1751 until 1752 from theCape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is t ...
, when he was said to have observed more than 10,000 stars using a refracting telescope.
In 1922, Henry Norris Russell
Henry Norris Russell ForMemRS HFRSE FRAS (October 25, 1877 – February 18, 1957) was an American astronomer who, along with Ejnar Hertzsprung, developed the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (1910). In 1923, working with Frederick Saunders, he deve ...
produced a list of 88 constellations with three-letter abbreviations for them. However, these constellations did not have clear borders between them. In 1928, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) formally accepted 88 modern constellations
In contemporary astronomy, 88 constellations are recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Each constellation is a region of the sky, bordered by arcs of right ascension and declination. Together they cover the celestial sphere ...
, with contiguous boundaries along vertical and horizontal lines of right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the (hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When paired w ...
and declination
In astronomy, declination (abbreviated dec; symbol ''δ'') is one of the two angles that locate a point on the celestial sphere in the equatorial coordinate system, the other being hour angle. Declination's angle is measured north or south of the ...
developed by Eugene Delporte that, together, cover the entire celestial sphere; this list was finally published in 1930. Where possible, these modern constellations usually share the names of their Graeco-Roman predecessors, such as Orion, Leo
Leo or Léo may refer to:
Acronyms
* Law enforcement officer
* Law enforcement organisation
* ''Louisville Eccentric Observer'', a free weekly newspaper in Louisville, Kentucky
* Michigan Department of Labor and Economic Opportunity
Arts an ...
or Scorpius. The aim of this system is area-mapping, i.e. the division of the celestial sphere into contiguous fields. Out of the 88 modern constellations, 36 lie predominantly in the northern sky, and the other 52 predominantly in the southern.
B1875.0
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to pe ...
, which was when Benjamin A. Gould
Benjamin Apthorp Gould (September 27, 1824 – November 26, 1896) was a pioneering American astronomer. He is noted for creating the ''Astronomical Journal'', discovering the Gould Belt, and for founding of the Argentine National Observatory an ...
first made his proposal to designate boundaries for the celestial sphere, a suggestion on which Delporte based his work. The consequence of this early date is that because of the precession of the equinoxes, the borders on a modern star map, such as epoch J2000, are already somewhat skewed and no longer perfectly vertical or horizontal. This effect will increase over the years and centuries to come.
Symbols
The constellations have no official symbols, though those of the ecliptic may take the signs of the zodiac. Symbols for the other modern constellations, as well as older ones that still occur in modern nomenclature, have occasionally been published.Dark cloud constellations
The Great Rift, a series of dark patches in the Milky Way, is more visible and striking in the southern hemisphere than in the northern. It vividly stands out when conditions are otherwise so dark that the Milky Way's central region casts shadows on the ground. Some cultures have discerned shapes in these patches and have given names to these "dark cloud constellations". Members of the Inca civilization identified various dark areas ordark nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection nebu ...
e in the Milky Way as animals and associated their appearance with the seasonal rains. Australian Aboriginal astronomy also describes dark cloud constellations, the most famous being the "emu in the sky" whose head is formed by the Coalsack, a dark nebula, instead of the stars.
Emu
The emu () (''Dromaius novaehollandiae'') is the second-tallest living bird after its ratite relative the ostrich. It is endemic to Australia where it is the largest native bird and the only extant member of the genus ''Dromaius''. The emu' ...
in the sky'' – a constellation defined by dark clouds rather than by stars. The head of the emu is the Coalsack with the Southern Cross directly above. Scorpius is to the left.
File:Coricancha museum marker graphically explaining the Inca astronomical system.jpg, Inca dark cloud constellations in the Mayu (Celestial River), also known as the Milky Way. The Southern Cross is above Yutu, while the eyes of the Llama are Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from α Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or α Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centaur ...
and Beta Centauri.
See also
* Celestial cartography *Constellation family
Constellation families are collections of constellations sharing some defining characteristic, such as proximity on the celestial sphere, common historical origin, or common mythological theme. In the Western tradition, most of the northern ...
* Former constellations
Former constellations are old historical Western constellations that for various reasons are no longer widely recognised or are not officially recognised by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Prior to 1930, many of these defunct conste ...
* IAU designated constellations
* Lists of stars by constellation
* Constellations listed by Johannes Hevelius
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
* Constellations listed by Lacaille
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
* Constellations listed by Petrus Plancius
* Constellations listed by Ptolemy
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellati ...
References
Further reading
Mythology, lore, history, and archaeoastronomy
* Allen, Richard Hinckley. (1899) ''Star-Names And Their Meanings'', G. E. Stechert, New York, hardcover; reprint 1963 as ''Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning'', Dover Publications, Inc., Mineola, NY, softcover. * Olcott, William Tyler. (1911); ''Star Lore of All Ages'',G. P. Putnam's Sons
G. P. Putnam's Sons is an American book publisher based in New York City, New York. Since 1996, it has been an imprint of the Penguin Group.
History
The company began as Wiley & Putnam with the 1838 partnership between George Palmer Putnam and J ...
, New York, hardcover; reprint 2004 as ''Star Lore: Myths, Legends, and Facts'', Dover Publications, Inc., Mineola, NY, softcover.
* Kelley, David H. and Milone, Eugene F. (2004) ''Exploring Ancient Skies: An Encyclopedic Survey of Archaeoastronomy'', Springer, hardcover.
* Ridpath, Ian. (2018) ''Star Tales'' 2nd ed., Lutterworth Press, softcover.
* Staal, Julius D. W. (1988) ''The New Patterns in the Sky: Myths and Legends of the Stars'', McDonald & Woodward Publishing Co., hardcover, softcover.
*
*
Atlases and celestial maps
General and nonspecialized – entire celestial heavens
* Becvar, Antonin. ''Atlas Coeli''. Published as ''Atlas of the Heavens'', Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, with coordinate grid transparency overlay. * Norton, Arthur Philip. (1910) '' Norton's Star Atlas'', 20th Edition 2003 as ''Norton's Star Atlas and Reference Handbook'', edited by Ridpath, Ian, Pi Press, , hardcover. * National Geographic Society. (1957, 1970, 2001, 2007) ''The Heavens'' (1970), Cartographic Division of the National Geographic Society (NGS), Washington, DC, two-sided large map chart depicting the constellations of the heavens; as a special supplement to the August 1970 issue of ''National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
''. Forerunner map as ''A Map of The Heavens'', as a special supplement to the December 1957 issue. Current version 2001 (Tirion), with 2007 reprint.
* Sinnott, Roger W. and Perryman, Michael A.C. (1997) ''Millennium Star Atlas
The ''Millennium Star Atlas'' was constructed as a collaboration between
a team at '' Sky & Telescope'' led by Roger Sinnott, and the European Space Agency's Hipparcos project, led by Michael Perryman. This 1997 work was the first sky atlas to i ...
'', Epoch 2000.0, Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, and European Space Agency (ESA), ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands. Subtitle: "An All-Sky Atlas Comprising One Million Stars to Visual Magnitude Eleven from the Hipparcos and Tycho Catalogues and Ten Thousand Nonstellar Objects". 3 volumes, hardcover, . Vol. 1, 0–8 Hours (Right Ascension), hardcover; Vol. 2, 8–16 Hours, hardcover; Vol. 3, 16–24 Hours, hardcover. Softcover version available. Supplemental separate purchasable coordinate grid transparent overlays.
* Tirion, Wil; et al. (1987) ''Uranometria 2000.0'', Willmann-Bell, Inc., Richmond, VA, 3 volumes, hardcover. Vol. 1 (1987): "The Northern Hemisphere to −6°", by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and George Lovi, hardcover, printed boards. Vol. 2 (1988): "The Southern Hemisphere to +6°", by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport and George Lovi, hardcover, printed boards. Vol. 3 (1993) as a separate added work: ''The Deep Sky Field Guide to Uranometria 2000.0'', by Murray Cragin, James Lucyk, and Barry Rappaport, hardcover, printed boards. 2nd Edition 2001 as collective set of 3 volumes – Vol. 1: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Atlas'', by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and Will Remaklus, hardcover, printed boards; Vol. 2: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Atlas'', by Wil Tirion, Barry Rappaport, and Will Remaklus, hardcover, printed boards; Vol. 3: ''Uranometria 2000.0 Deep Sky Field Guide'' by Murray Cragin and Emil Bonanno, , hardcover, printed boards.
* Tirion, Wil and Sinnott, Roger W. (1998) ''Sky Atlas 2000.0'', various editions. 2nd Deluxe Edition, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England.
Northern celestial hemisphere and north circumpolar region
* Becvar, Antonin. (1962) ''Atlas Borealis 1950.0'', Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Praha, Czechoslovakia, 1st Edition, elephant folio hardcover, with small transparency overlay coordinate grid square and separate paper magnitude legend ruler. 2nd Edition 1972 and 1978 reprint, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Prague, Czechoslovakia, and Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, oversize folio softcover spiral-bound, with transparency overlay coordinate grid ruler.Equatorial, ecliptic, and zodiacal celestial sky
* Becvar, Antonin. (1958) ''Atlas Eclipticalis 1950.0'', Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Praha, Czechoslovakia, 1st Edition, elephant folio hardcover, with small transparency overlay coordinate grid square and separate paper magnitude legend ruler. 2nd Edition 1974, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Prague, Czechoslovakia, and Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, oversize folio softcover spiral-bound, with transparency overlay coordinate grid ruler.Southern celestial hemisphere and south circumpolar region
* Becvar, Antonin. ''Atlas Australis 1950.0'', Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Praha, Czechoslovakia, 1st Edition, hardcover, with small transparency overlay coordinate grid square and separate paper magnitude legend ruler. 2nd Edition, Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences (Ceskoslovenske Akademie Ved), Prague, Czechoslovakia, and Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA, oversize folio softcover spiral-bound, with transparency overlay coordinate grid ruler.Catalogs
* Becvar, Antonin. (1959) ''Atlas Coeli II Katalog 1950.0'', Praha, 1960 Prague. Published 1964 as ''Atlas of the Heavens – II Catalogue 1950.0'', Sky Publishing Corporation, Cambridge, MA * Hirshfeld, Alan and Sinnott, Roger W. (1982) ''Sky Catalogue 2000.0'', Cambridge University Press and Sky Publishing Corporation, 1st Edition, 2 volumes. both vols., and vol. 1. "Volume 1: Stars to Magnitude 8.0", (Cambridge) and hardcover, softcover. Vol. 2 (1985) – "Volume 2: Double Stars, Variable Stars, and Nonstellar Objects", (Cambridge) hardcover, (Cambridge) softcover. 2nd Edition (1991) with additional third author François Ochsenbein, 2 volumes, . Vol. 1: (Cambridge) hardcover; (Cambridge) softcover . Vol. 2 (1999): (Cambridge) softcover and 0-933346-38-7 softcover – reprint of 1985 edition. * Yale University Observatory. (1908, et al.) '' Catalogue of Bright Stars'', New Haven, CN. Referred to commonly as "Bright Star Catalogue". Various editions with various authors historically, the longest term revising author as (Ellen) Dorrit Hoffleit. 1st Edition 1908. 2nd Edition 1940 by Frank Schlesinger andLouise F. Jenkins
Louise Freeland Jenkins (July 5, 1888 – May 9, 1970) was an American astronomer who compiled a valuable catalogue of stars within 10 parsecs of the sun, as well as editing the 3rd edition of the Yale Bright Star Catalogue.
She was born in Fit ...
. 3rd Edition (1964), 4th Edition, 5th Edition (1991), and 6th Edition (pending posthumous) by Hoffleit.
External links
IAU: The Constellations
including high quality maps.
Atlascoelestis
di Felice Stoppa.
Celestia
free 3D realtime space-simulation (OpenGL)
Stellarium
realtime sky rendering program (OpenGL)
Strasbourg Astronomical Data Center Files on official IAU constellation boundaries
Interactive Sky Charts
(Java applets allowing navigation through the entire sky with variable star detail, optional constellation lines)
Studies of Occidental Constellations and Star Names to the Classical Period: An Annotated Bibliography
Greco-Roman constellation myths
Neave Planetarium
Adobe Flash interactive web browser planetarium and stardome with realistic movement of stars and the planets. * Audio – Cain/Gay (2009
Astronomy Cast
Constellations
The Greek Star-Map
short essay by Gavin White
Bucur D. The network signature of constellation line figures
PLOS ONE 17(7): e0272270 (2022). A comparative analysis on the structure of constellation line figures across 56 sky cultures. {{Authority control Constellations Celestial cartography Constellations Concepts in astronomy