Synchronous conferencing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
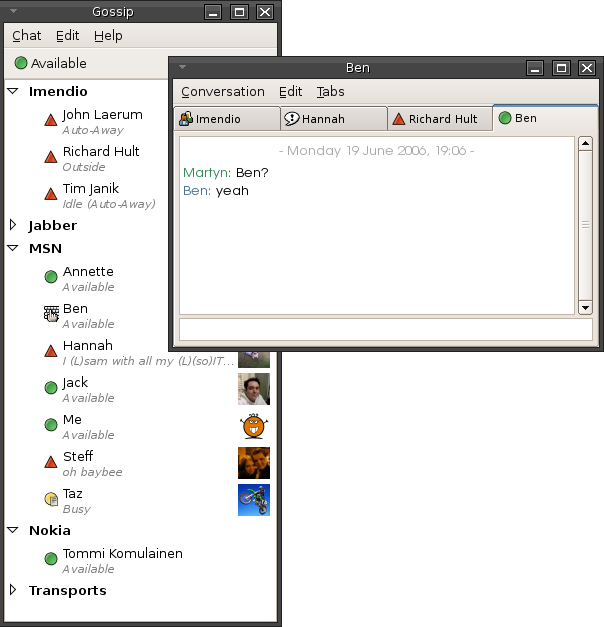 Online chat is any direct text-, audio- or video-based (
Online chat is any direct text-, audio- or video-based (
 Online chat is any direct text-, audio- or video-based (
Online chat is any direct text-, audio- or video-based (webcam
A webcam is a video camera which is designed to record or stream to a computer or computer network. They are primarily used in Videotelephony, video telephony, live streaming and social media, and Closed-circuit television, security. Webcams can b ...
s), one-on-one or one-to-many ( group) chat (formally also known as synchronous conferencing), using tools such as instant messenger
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
s, Internet Relay Chat
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for Many-to-many, group communication in discussion forums, called ''#Channels, channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via instant mess ...
(IRC), talkers and possibly MUD
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
s or other online game
An online game is a video game that is either partially or primarily played through the Internet or any other computer network available. Online games are ubiquitous on modern gaming platforms, including PCs, consoles and mobile devices, a ...
s. Online chat includes web-based applications that allow communication – often directly addressed, but anonymous between users in a multi-user environment. Web conferencing
Web conferencing is used as an umbrella term for various types of online conferencing and collaborative services including webinars (web seminars), webcasts, and web meetings. Sometimes it may be used also in the more narrow sense of the peer-l ...
is a more specific online service, that is often sold as a service, hosted on a web server controlled by the vendor. Online chat may address point-to-point communications as well as multicast
In computer networking, multicast is a type of group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast differs from ph ...
communications from one sender to multiple receivers and voice and video chat, or may be a feature of a web conferencing
Web conferencing is used as an umbrella term for various types of online conferencing and collaborative services including webinars (web seminars), webcasts, and web meetings. Sometimes it may be used also in the more narrow sense of the peer-l ...
service.
''Online chat'' in a narrower sense is any kind of communication
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not onl ...
over the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the Global network, global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a internetworking, network of networks ...
that offers a real-time transmission of text
Text may refer to:
Written word
* Text (literary theory)
In literary theory, a text is any object that can be "read", whether this object is a work of literature, a street sign, an arrangement of buildings on a city block, or styles of clothi ...
messages from sender to receiver. Chat messages are generally short in order to enable other participants to respond quickly. Thereby, a feeling similar to a spoken conversation is created, which distinguishes chatting from other text-based online communication forms such as Internet forums and email
Electronic mail (usually shortened to email; alternatively hyphenated e-mail) is a method of transmitting and receiving Digital media, digital messages using electronics, electronic devices over a computer network. It was conceived in the ...
. The expression ''online chat'' comes from the word '' chat'' which means "informal conversation".
Synchronous conferencing or synchronous computer-mediated communication (SCMC) is any form of computer-mediated communication
Computer-mediated communication (CMC) is defined as any human communication that occurs through the use of two or more electronic devices. While the term has traditionally referred to those communications that occur via computer-mediated forma ...
that occurs in real-time; that is, there is no significant delay between sending and receiving messages. SCMC includes real-time forms of text, audio, and video communication. SCMC has been highly studied in the context of e-learning
Educational technology (commonly abbreviated as edutech, or edtech) is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning and teaching. When referred to with its abbreviation, "EdTech" ...
.
History
The first online chat system was called Talkomatic, created by Doug Brown and David R. Woolley in 1973 on the PLATO System at theUniversity of Illinois
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United ...
. It offered several channels, each of which could accommodate up to five people, with messages appearing on all users' screens character-by-character as they were typed. Talkomatic was popular among PLATO users into the mid-1980s. In 2014, Brown and Woolley released a web-based version of Talkomatic.
The first online system to use the actual command "chat" was created for The Source in 1979 by Tom Walker and Fritz Thane of Dialcom, Inc.
Other chat platforms flourished during the 1980s. Among the earliest with a GUI was BroadCast, a Macintosh
Mac is a brand of personal computers designed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 1984. The name is short for Macintosh (its official name until 1999), a reference to the McIntosh (apple), McIntosh apple. The current product lineup inclu ...
extension that became especially popular on university
A university () is an educational institution, institution of tertiary education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. ''University'' is derived from the Latin phrase , which roughly ...
campuses in America and Germany.
The first transatlantic Internet chat took place between Oulu, Finland and Corvallis, Oregon
Corvallis ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Benton County, Oregon, Benton County in central western Oregon, United States. It is the principal city of the Corvallis, Oregon Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Benton Co ...
in February 1989.
The first dedicated online chat service that was widely available to the public was the CompuServe CB Simulator in 1980, created by CompuServe
CompuServe, Inc. (CompuServe Information Service, Inc., also known by its initialism CIS or later CSi) was an American Internet company that provided the first major commercial online service provider, online service. It opened in 1969 as a times ...
executive Alexander "Sandy" Trevor in Columbus, Ohio
Columbus (, ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities in Ohio, most populous city of the U.S. state of Ohio. With a 2020 United States census, 2020 census population of 905,748, it is the List of United States ...
. Ancestors include network chat software such as UNIX "talk" used in the 1970s.
Chat is implemented in multiple video-conferencing tools. A study of chat use during work-related videoconferencing found that chat during meetings allows participants to communicate without interrupting the meeting, plan action around common resources, and enables greater inclusion. The study also found that chat can cause distractions and information asymmetries between participants.
Types
According to the type of media used, synchronous conferencing can be divided into * audio conferencing: only audio is used * video conferencing: Both audio (voice) and video and pictures are used. According to the number of access point used, synchronous conferencing can be divided into * point-to-point: Only two computers are connected end to end. * multi-point: Two or more than two computers are connected.Methods
Some of the methods used in synchronous conferencing are: * Chat (text only): Multiple participants can be logged into the conference and can interactively share resources and ideas. There is also an option to save the chat and archive it for later review. * Voice (telephone or voice-over IP): This is a conference call between the instructor and the participating students where they can speak through a built-in microphone or a headset. *Video conferencing
Videotelephony (also known as videoconferencing or video calling) is the use of audio signal, audio and video for simultaneous two-way communication. Today, videotelephony is widespread. There are many terms to refer to videotelephony. ''Vide ...
: This may or may not require the participants to have their webcams running. Usually, a video conference involves a live feed from a classroom or elsewhere or content.
* Web conferencing
Web conferencing is used as an umbrella term for various types of online conferencing and collaborative services including webinars (web seminars), webcasts, and web meetings. Sometimes it may be used also in the more narrow sense of the peer-l ...
: This includes Webinar (Web-based seminar) as well. Unlike in video conferencing, participants of web conferencing can access a wider variety of media elements. Web conferences are comparatively more interactive and usually incorporate chat sessions as well.
* Virtual worlds: In this setup, students can meet in the virtual world and speak with each other through headsets and VoIP. This can make learning more productive and engaging when the students can navigate the worlds and operate in their avatar.
Synchronous vs asynchronous conferencing
Both synchronous andasynchronous conferencing
Asynchronous conferencing or asynchronous computer-mediated communication (asynchronous CMC) is the formal term used in science, in particular in computer-mediated communication, collaboration and learning, to describe technologies where there is ...
are online conferencing where the participants can interact while being physically located at different places in the world. Asynchronous conferencing allows the students to access the learning material at their convenience while synchronous conferencing requires that all participants including the instructor and the students be online at the time of the conference.
While synchronous conferencing enables real-time interaction of the participants, asynchronous conferencing allows participants to post messages and others can respond to it at any convenient time. Sometimes a combination of both synchronous and asynchronous conferencing is used. Both methods give a permanent record of the conference.
Critical factors for effective implementation
There are four critical factors identified for implementing synchronous conferencing for effective instruction to the students * Video and audio quality which depends on technical factors like higher bandwidth and processing capabilities of the system. * Training time depends on the familiarity and proficiency of the instructors and the students with the technology. * Teaching strategies depend on the adaptability of the instructors to the new methods, preparing appropriate and effective training materials, and motivating students. * Direct meeting of the instructor and the students.Synchronous conferencing in higher education
Synchronous conferencing in education helps in the delivery of content through digital media. Since this is real-time teaching, it also brings the benefits of face-to-face teaching in distance learning. Multiple higher education institutions offer well-designed quality e-learning opportunities. Some of the advantages of synchronous conferencing in education are: * Helps the students to connect with not only their teachers and peers but also with recognized experts in the field regardless of the geographical distance and different time zones. * Provides opportunities for both the teachers and the students to expand their knowledge outside the classroom. * Helps students who are home-bound or limited mobility to connect with their classrooms and participate in learning. * Helps the faculties to conduct classes when they are not able to come to classes due to an emergency. * Supports real-time collaboration, interaction, and immediate feedback * Encourage students to learn together and in turn, develop cultural understanding * Personalized learning experience for the students * Real-time discussion opportunities for students promoting student engagement * Active interaction can lead to an associated community of like-minded students * Saves travel expenses and timeImplementation of educational technology
The tools for implementing synchronous conferencing depend on the type of educational problem addressed. This is in turn decides the method of synchronous conferencing to be used and the tool to be used in the learning context. The tool selected addresses the problem of improving the learning outcomes which cannot be solved with an asynchronous environment. There are a number of tools and platforms available for synchronous conferencing. * Smartphone applications * Web conferencing tools * Video conferencing tools * Video and hangout platforms * Shared whiteboards The selection of tools and platforms also depends on the group size which depends on the activity for the course design.Chatiquette
The term '' chatiquette'' (chat etiquette) is a variation of netiquette (Internet etiquette) and describes basic rules of online communication. These conventions or guidelines have been created to avoid misunderstandings and to simplify the communication between users. Chatiquette varies from community to community and generally describes basic courtesy. As an example, it is considered rude to write only in upper case, because it appears as if the user is shouting. The word "chatiquette" has been used in connection with various chat systems (e.g.Internet Relay Chat
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for Many-to-many, group communication in discussion forums, called ''#Channels, channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via instant mess ...
) since 1995.
Chatrooms can produce a strong sense of online identity
Internet identity (IID), also online identity, online personality, online persona or internet persona, is a social identity that an Internet user establishes in online communities and websites. It may also be an actively constructed presentatio ...
leading to impression of subculture.
Chats are valuable sources of various types of information, the automatic processing of which is the object of chat/text mining
Text mining, text data mining (TDM) or text analytics is the process of deriving high-quality information from text. It involves "the discovery by computer of new, previously unknown information, by automatically extracting information from differe ...
technologies.
Limitations
Some limitations for synchronous conferencing in learning are: * Disjointed discussions, not connected in time * Lack of effective moderation and/or clear guidelines for learners * Difficulty in collaborating on online projects * Lack of proper communication with the instructor and students. * Technical issues may arise if not analysed and planned in advance * Lack of familiarity with the tools * Limited time to complete the learning activity and to incorporate interactions with the learnersSocial criticism
Criticism of online chatting andtext messaging
Text messaging, or texting, is the act of composing and sending electronic messages, typically consisting of alphabetic and numeric characters, between two or more users of mobile phones, tablet computers, smartwatches, desktops/laptops, or ...
include concern that they replace proper English with shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to Cursive, longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Gr ...
or with an almost completely new hybrid language.
Writing is changing as it takes on some of the functions and features of speech. Internet chat room
The term chat room, or chatroom (and sometimes group chat; abbreviated as GC), is primarily used to describe any form of synchronous conferencing, occasionally even asynchronous conferencing. The term can thus mean any technology, ranging from ...
s and rapid real-time teleconferencing
A teleconference or telecon is a live exchange of information among several people remote from one another but linked by a communications system. Terms such as audio conferencing, telephone conferencing, and phone conferencing are also sometime ...
allow users to interact with whoever happens to coexist in cyberspace
Cyberspace is an interconnected digital environment. It is a type of virtual world popularized with the rise of the Internet. The term entered popular culture from science fiction and the arts but is now used by technology strategists, security ...
. These virtual interactions involve us in 'talking' more freely and more widely than ever before. With chatrooms replacing multiple face-to-face conversations, it is necessary to be able to have quick conversation as if the person were present, so some learn to type as quickly as they would normally speak. Some critics are wary that this casual form of speech is being used so much that it will slowly take over common grammar; however, such a change has yet to be seen.
With the increasing population of online chatrooms there has been a massive growth of new words created or slang words, a number of them documented on the website Urban Dictionary
''Urban Dictionary'' is a crowdsourced English-language online dictionary for slang words and phrases. The website was founded in 1999 by Aaron Peckham. Originally, ''Urban Dictionary'' was intended as a dictionary of slang or cultural word ...
. Sven Birkerts wrote:"as new electronic modes of communication provoke similar anxieties amongst critics who express concern that young people are at risk, endangered by a rising tide of information over which the traditional controls of print media and the guardians of knowledge have no control on it".In Guy Merchant's journal article Teenagers in Cyberspace: An Investigation of Language Use and Language Change in Internet Chatrooms; Merchant says
"that teenagers and young people are in the leading the movement of change as they take advantage of the possibilities of digital technology, drastically changing the face of literacy in a variety of media through their uses of mobile phone text messages, e-mails, web-pages and on-line chatrooms. This new literacy develops skills that may well be important to the labor market but are currently viewed with suspicion in the media and by educationalists.Merchant also says "Younger people tend to be more adaptable than other sectors of society and, in general, quicker to adapt to new technology. To some extent they are the innovators, the forces of change in the new communication landscape." In this article he is saying that young people are merely adapting to what they were given.
Synchronous conferencing protocols
Synchronous conferencing protocols include: *IRC
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called '' channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat ...
(Internet Relay Chat)
* PSYC (Protocol for Synchronous Conferencing)
* SILC (Secure Internet Live Conferencing protocol)
* XMPP
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (abbreviation XMPP, originally named Jabber) is an Open standard, open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML (Ext ...
(Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol)
* SIMPLE (instant messaging protocol)
SIMPLE, the Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions, is an instant messaging (IM) and presence protocol suite based on Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) managed by the Internet Engineering Task Force. ...
(Session Initiation Protocol for Instant Messaging and Presence Leveraging Extensions)
Software and protocols
The following are common chat programs and protocols: * AIM (No longer available) * Camfrog *Campfire
A campfire is a fire at a campsite that provides light and warmth, and heat for cooking. It can also serve as a beacon, and an insect and predator deterrent. Established campgrounds often provide a stone or steel fire ring for safety. Campfires ...
* Discord
Discord is an instant messaging and Voice over IP, VoIP social platform which allows communication through Voice over IP, voice calls, Videotelephony, video calls, text messaging, and digital media, media. Communication can be private or take ...
* XMPP
Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (abbreviation XMPP, originally named Jabber) is an Open standard, open communication protocol designed for instant messaging (IM), presence information, and contact list maintenance. Based on XML (Ext ...
* Flock
* Gadu-Gadu
* Google Talk
Google Talk was an instant messaging service that provided both text and voice communication. The instant messaging service was variously referred to colloquially as Gchat, Gtalk, or Gmessage among its users.
Google Talk was also the name o ...
(No longer available)
* I2P-Messenger (anonymous, end-to-end encrypted IM for the I2P network)
* ICQ (OSCAR)
* ICB
* IRC
IRC (Internet Relay Chat) is a text-based chat system for instant messaging. IRC is designed for group communication in discussion forums, called '' channels'', but also allows one-on-one communication via private messages as well as chat ...
* Line
* Mattermost
* Apple Messages
* Teams
A team is a group of individuals (human or non-human) working together to achieve their goal.
As defined by Professor Leigh Thompson (academic), Leigh Thompson of the Kellogg School of Management, " team is a group of people who are interd ...
* Paltalk
* RetroShare (encrypted, decentralized)
* Signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
(encrypted messaging protocol and software)
* SILC
* Skype
Skype () was a proprietary telecommunications application operated by Skype Technologies, a division of Microsoft, best known for IP-based videotelephony, videoconferencing and voice calls. It also had instant messaging, file transfer, ...
* Slack
* Talk
* Talker
* TeamSpeak (TS)
* Telegram
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas pi ...
* QQ
* The Palace
''The Palace'' is a British drama television series that aired on ITV (TV network), ITV in 2008. Produced by Company Pictures for the ITV network, it was created by Tom Grieves and follows a fictional British Royal Family in the aftermath of t ...
(encrypted, decentralized)
* WebChat Broadcasting System (WBS)
* WeChat
WeChat or Weixin in Chinese ( zh, c=微信, p=Wēixìn , l=micro-message) is an instant messaging, social media, and mobile payment mobile app, app developed by Tencent. First released in 2011, it became the world's largest standalone mobile a ...
* WhatsApp
WhatsApp (officially WhatsApp Messenger) is an American social media, instant messaging (IM), and voice-over-IP (VoIP) service owned by technology conglomerate Meta. It allows users to send text, voice messages and video messages, make vo ...
* Windows Live Messenger
* Yahoo! Messenger (No longer available)
Chat programs supporting multiple protocols:
* Adium
* Google+ Hangouts
* IBM Sametime
* Kopete
* Miranda NG
* Pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified form of contact language that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn f ...
* Quiet Internet Pager
* Trillian
* Windows Live Messenger
Web sites with browser-based chat services:
* Chat-Avenue
* Convore (No longer available)
* Cryptocat
Cryptocat is a discontinued open-source software, open-source Application software, desktop application intended to allow encrypted online chatting available for Microsoft Windows, Windows, OS X, and Linux. It uses end-to-end encryption to secur ...
* eBuddy
* Facebook
Facebook is a social media and social networking service owned by the American technology conglomerate Meta Platforms, Meta. Created in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with four other Harvard College students and roommates, Eduardo Saverin, Andre ...
* FilmOn
* Gmail
Gmail is the email service provided by Google. it had 1.5 billion active user (computing), users worldwide, making it the largest email service in the world. It also provides a webmail interface, accessible through a web browser, and is also ...
* Google+
Google+ (sometimes written as Google Plus, stylized as G+ or g+) was a Social networking service, social network owned and operated by Google until it ceased operations in 2019. The network was launched on June 28, 2011, in an attempt to challe ...
(No longer available)
* Chat Television (No longer available)
* MeBeam
* Meebo (No longer available)
* Mibbit
Mibbit was a web-based client for web browsers that supports Internet Relay Chat (IRC), Yahoo! Messenger, and Twitter. It is developed by Jimmy Moore and is designed around the Ajax model with a user interface written in JavaScript. It is th ...
(No longer available)
* Omegle (no longer available)
* Talkomatic
* Tinychat
* Tokbox (No longer available)
* Trillian
* Userplane (No longer available)
* Woo Media
Woo Media was an online chat and video social network which offered a variety of interactive sites that provided live social entertainment through a computer or mobile device.
The company raised $17 million in venture capital from several investo ...
(No longer available)
* Zumbl (No longer available)
See also
*Asynchronous conferencing
Asynchronous conferencing or asynchronous computer-mediated communication (asynchronous CMC) is the formal term used in science, in particular in computer-mediated communication, collaboration and learning, to describe technologies where there is ...
* Chat room
The term chat room, or chatroom (and sometimes group chat; abbreviated as GC), is primarily used to describe any form of synchronous conferencing, occasionally even asynchronous conferencing. The term can thus mean any technology, ranging from ...
* Collaborative software
Collaborative software or groupware is application software designed to help people working on a common task to attain their goals. One of the earliest definitions of groupware is "intentional group processes plus software to support them."
Regar ...
* Instant messaging
Instant messaging (IM) technology is a type of synchronous computer-mediated communication involving the immediate ( real-time) transmission of messages between two or more parties over the Internet or another computer network. Originally involv ...
* Internet forum
* MUD
Mud (, or Middle Dutch) is loam, silt or clay mixed with water. Mud is usually formed after rainfall or near water sources. Ancient mud deposits hardened over geological time to form sedimentary rock such as shale or mudstone (generally cal ...
s (Multi-User Dungeons)
* Online dating service
* Real-time text
Real-time text (RTT) is text transmitted instantly as it is typed or created. Recipients can immediately read the message while it is being written, without waiting.
Real-time text is used for conversational text, in collaboration, and in live cap ...
* Videotelephony
Videotelephony (also known as videoconferencing or video calling) is the use of audio signal, audio and video for simultaneous two-way communication. Today, videotelephony is widespread. There are many terms to refer to videotelephony. ''Vide ...
* Voice chat
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Online Chat Internet culture