|
I2P
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is an anonymous network layer (implemented as a mix network) that allows for censorship-resistant, peer-to-peer communication. Anonymous connections are achieved by encrypting the user's traffic (by using end-to-end encryption), and sending it through a volunteer-run network of roughly 55,000 computers distributed around the world. Given the high number of possible paths the traffic can transit, a third party watching a full connection is unlikely. The software that implements this layer is called an "I2P router", and a computer running I2P is called an "I2P node". I2P is free and open sourced, and is published under multiple licenses. Technical design I2P is beta software since 2003, when it started as a fork of Freenet. The software's developers emphasize that bugs are likely to occur in the beta version and that peer review has been insufficient to date. However, they believe the code is now reasonably stable and well-develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garlic Routing
Garlic routing is a variant of onion routing that encrypts multiple messages together to make it more difficult for attackers to perform traffic analysis and to increase the speed of data transfer. Michael J. Freedman defined "garlic routing" as an extension of onion routing, in which multiple messages are bundled together. He called each message a "bulb", whereas I2P calls them "garlic cloves". All messages, each with their own delivery instructions, are exposed at the endpoint. This allows the efficient bundling of an onion routing "reply block" with the original message. Garlic routing is one of the key factors that distinguishes I2P from Tor and other privacy or encryption networks. The name alludes to the garlic plant, whose structure this protocol resembles. "Garlic routing" was first coined by Michael J. Freedman in Roger Dingledine's Free Haven Master's thesis Section 8.1.1 (June 2000), as derived from Onion Routing. However, the garlic routing implementation in I2P d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
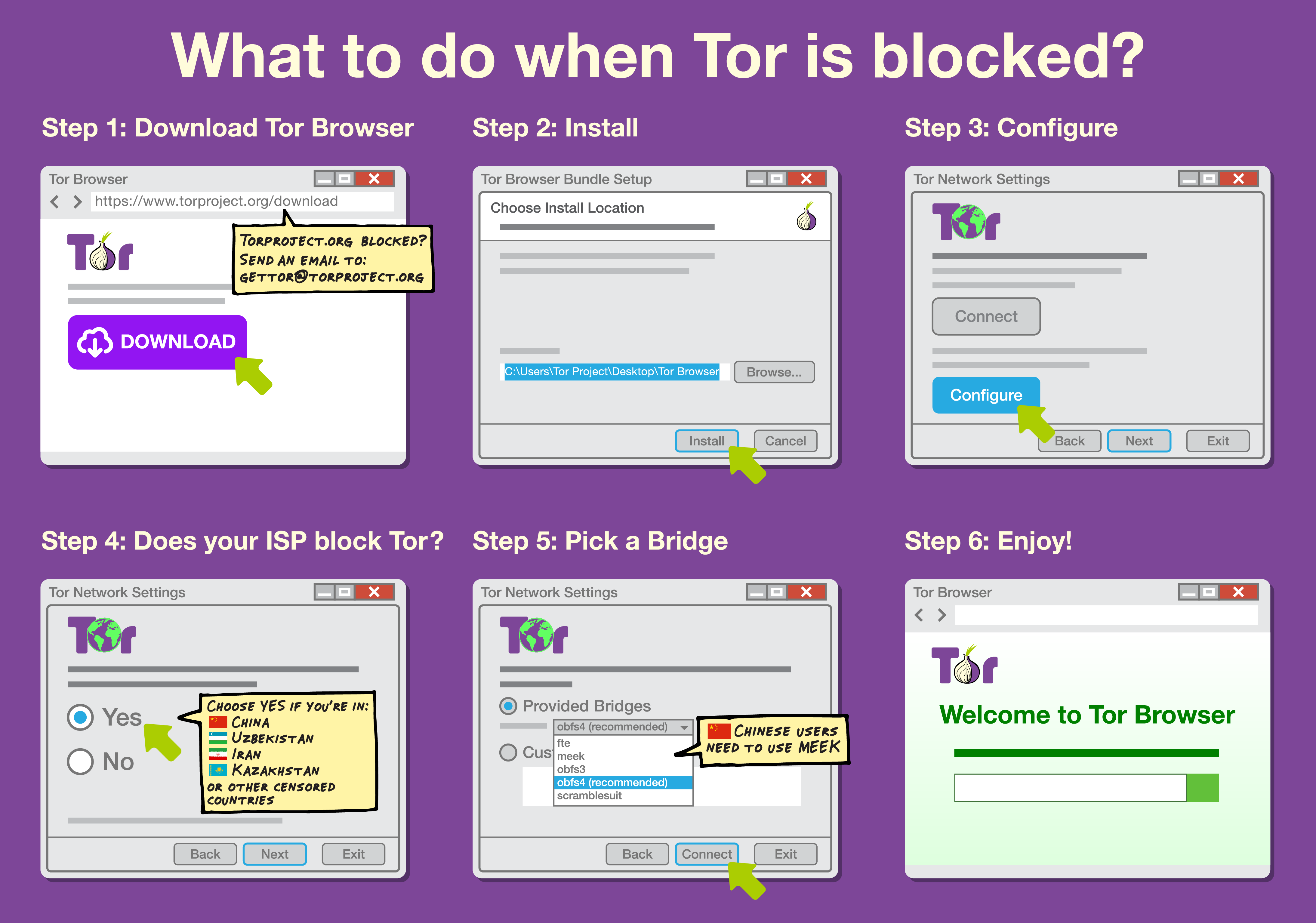
Internet Censorship Circumvention
Internet censorship circumvention is the use of various methods and tools to bypass internet censorship. Various techniques and methods are used to bypass Internet censorship, and have differing ease of use, speed, security, and risks. Some methods, such as the use of alternate DNS servers, evade blocking by using an alternate address or address lookup system to access the site. Techniques using website mirrors or archive sites rely on other copies of the site being available at different locations. Additionally, there are solutions that rely on gaining access to an Internet connection that is not subject to filtering, often in a different jurisdiction not subject to the same censorship laws, using technologies such as proxying, virtual private networks, or anonymization networks. An arms race has developed between censors and developers of circumvention software, resulting in more sophisticated blocking techniques by censors and the development of harder-to-detect tools by re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network. They are said to form a peer-to-peer network of nodes. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the file sharing system Napster, originally released in 1999. The concept has inspired new structures and philosophies in many areas of human interaction. In such social contexts, peer-to-peer as a meme refers to the egalitari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anonymity Application
Anonymity describes situations where the acting person's identity is unknown. Some writers have argued that namelessness, though technically correct, does not capture what is more centrally at stake in contexts of anonymity. The important idea here is that a person be non-identifiable, unreachable, or untrackable. Anonymity is seen as a technique, or a way of realizing, a certain other values, such as privacy, or liberty. Over the past few years, anonymity tools used on the dark web by criminals and malicious users have drastically altered the ability of law enforcement to use conventional surveillance techniques. An important example for anonymity being not only protected, but enforced by law is the vote in free elections. In many other situations (like conversation between strangers, buying some product or service in a shop), anonymity is traditionally accepted as natural. There are also various situations in which a person might choose to withhold their identity. Acts of char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overlay Network
An overlay network is a computer network that is layered on top of another network. Structure Nodes in the overlay network can be thought of as being connected by virtual or logical links, each of which corresponds to a path, perhaps through many physical links, in the underlying network. For example, distributed systems such as peer-to-peer networks and client–server applications are overlay networks because their nodes run on top of the Internet. The Internet was originally built as an overlay upon the telephone network, while today (through the advent of VoIP), the telephone network is increasingly turning into an overlay network built on top of the Internet. Uses Enterprise networks Enterprise private networks were first overlaid on telecommunication networks such as Frame Relay and Asynchronous Transfer Mode packet switching infrastructures but migration from these (now legacy) infrastructures to IP based MPLS networks and virtual private networks started (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mix Network
Mix networks are routing protocols that create hard-to-trace communications by using a chain of proxy servers known as ''mixes'' which take in messages from multiple senders, shuffle them, and send them back out in random order to the next destination (possibly another mix node). This breaks the link between the source of the request and the destination, making it harder for eavesdroppers to trace end-to-end communications. Furthermore, mixes only know the node that it immediately received the message from, and the immediate destination to send the shuffled messages to, making the network resistant to malicious mix nodes. Each message is encrypted to each proxy using public key cryptography; the resulting encryption is layered like a Russian doll (except that each "doll" is of the same size) with the message as the innermost layer. Each proxy server strips off its own layer of encryption to reveal where to send the message next. If all but one of the proxy servers are compromis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freenet
Freenet is a peer-to-peer platform for censorship-resistant, anonymous communication. It uses a decentralized distributed data store to keep and deliver information, and has a suite of free software for publishing and communicating on the Web without fear of censorship.What is Freenet? , ''Freenet: The Free network official website''.Taylor, Ian J. ''From P2P to Web Services and Grids: Peers in a Client/Server World''. London: Springer, 2005. Both Freenet and some of its associated tools were originally designed by Ian Clarke, who defined Freenet's goal as providing [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Development Stage
A software release life cycle is the sum of the stages of development and maturity for a piece of computer software ranging from its initial development to its eventual release, and including updated versions of the released version to help improve the software or fix software bugs still present in the software. There are several models for such a life cycle. A common method is that suggested by Microsoft, which divides software development into five phases: Pre-alpha, Alpha, Beta, Release candidate, and Stable. Pre-alpha refers to all activities performed during the software project before formal testing. The alpha phase generally begins when the software is feature complete but likely to contain several known or unknown bugs. The beta phase generally begins when the software is deemed feature complete, yet likely to contain several known or unknown bugs. Software in the production phase will generally have many more bugs in it than completed software, as well as speed/performan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Bug
A software bug is an error, flaw or fault (technology), fault in the design, development, or operation of computer software that causes it to produce an incorrect or unexpected result, or to behave in unintended ways. The process of finding and correcting bugs is termed "debugging" and often uses formal techniques or tools to pinpoint bugs. Since the 1950s, some computer systems have been designed to deter, detect or auto-correct various computer bugs during operations. Bugs in software can arise from mistakes and errors made in interpreting and extracting users' requirements, planning a program's software architecture, design, writing its source code, and from interaction with humans, hardware and programs, such as operating systems or Library (computing), libraries. A program with many, or serious, bugs is often described as ''buggy''. Bugs can trigger errors that may have ripple effects. The effects of bugs may be subtle, such as unintended text formatting, through to more o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implementation
Implementation is the realization of an application, or execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, or policy. Industry-specific definitions Computer science In computer science, an implementation is a realization of a technical specification or algorithm as a program, software component, or other computer system through computer programming and deployment. Many implementations may exist for a given specification or standard. For example, web browsers contain implementations of World Wide Web Consortium-recommended specifications, and software development tools contain implementations of programming languages. A special case occurs in object-oriented programming, when a concrete class implements an interface; in this case the concrete class is an ''implementation'' of the interface and it includes methods which are ''implementations'' of those methods specified by the interface. Information technology In the information technology d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer Review
Peer review is the evaluation of work by one or more people with similar competencies as the producers of the work ( peers). It functions as a form of self-regulation by qualified members of a profession within the relevant field. Peer review methods are used to maintain quality standards, improve performance, and provide credibility. In academia, scholarly peer review is often used to determine an academic paper's suitability for publication. Peer review can be categorized by the type of activity and by the field or profession in which the activity occurs, e.g., medical peer review. It can also be used as a teaching tool to help students improve writing assignments. Henry Oldenburg (1619–1677) was a German-born British philosopher who is seen as the 'father' of modern scientific peer review. Professional Professional peer review focuses on the performance of professionals, with a view to improving quality, upholding standards, or providing certification. In academia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet. IP has the task of delivering packets from the source host to the destination host solely based on the IP addresses in the packet headers. For this purpose, IP defines packet structures that encapsulate the data to be delivered. It also defines addressing methods that are used to label the datagram with source and destination information. IP was the connectionless datagram service in the original Transmission Control Program introduced by Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn in 1974, which was complemented by a connection-oriented service that became the basis for the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). The Internet protocol suite is therefore often referred to as ''TCP/IP''. The first major version of IP, Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |