Sremska Mitrovica on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sremska Mitrovica (; sr-Cyrl, Сремска Митровица, hu, Szávaszentdemeter, la, Sirmium) is a
 During
During
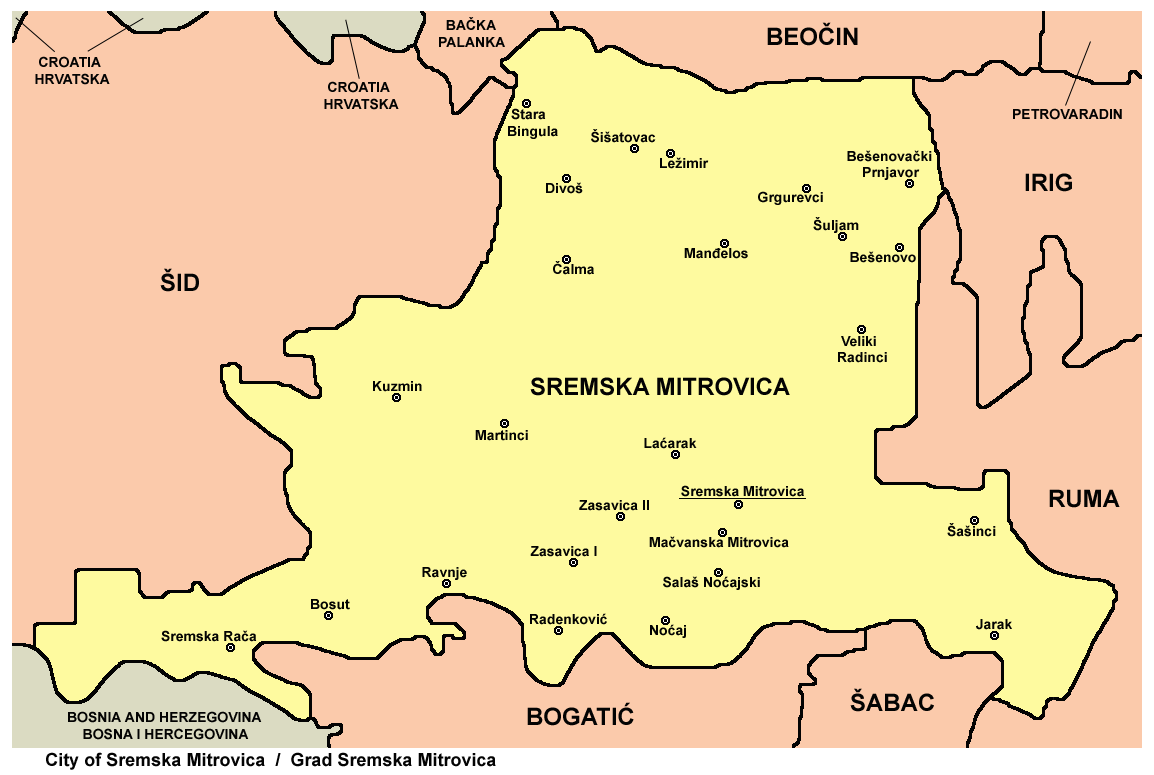
 The city of Sremska Mitrovica includes the town of
The city of Sremska Mitrovica includes the town of
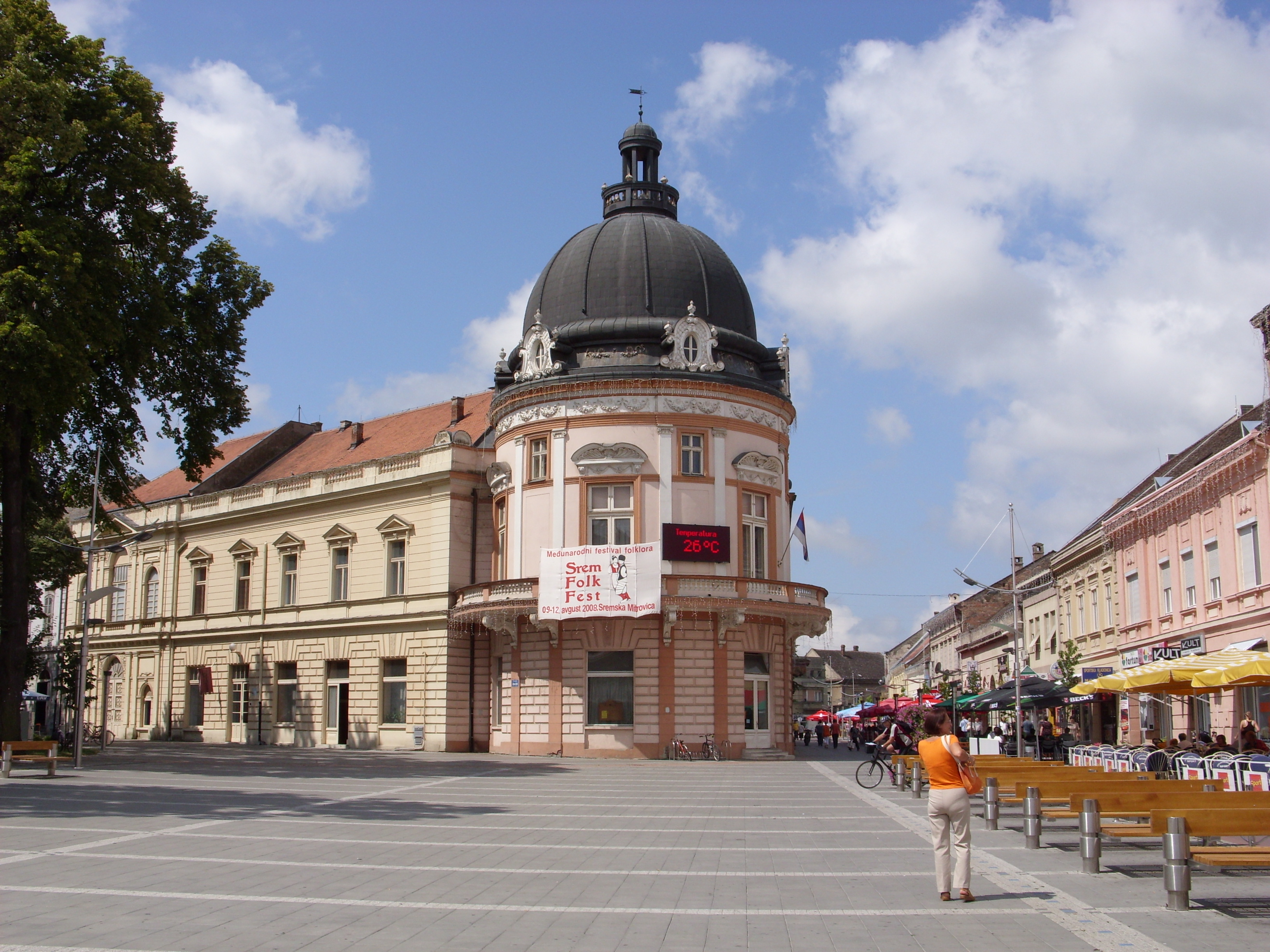
 The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):
The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):
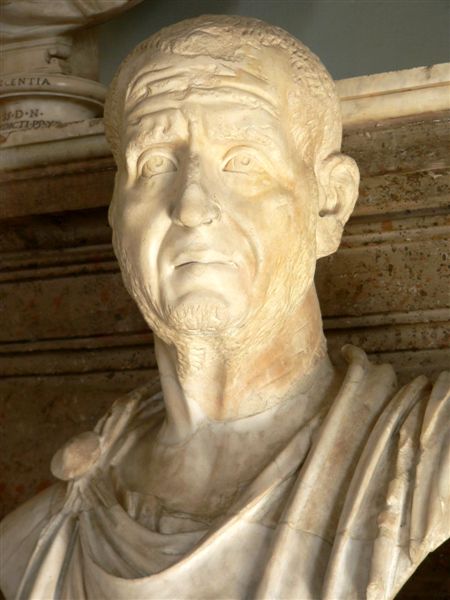 Ten Roman emperors were born in the city and its environs:
* Decius Traian (249–51)
*
Ten Roman emperors were born in the city and its environs:
* Decius Traian (249–51)
*
Sremska Mitrovica.org - info, news about Sremska MitrovicaInformation portal on culture, sport and fun in Sremska Mitrovica
{{Authority control Populated places in Srem District Populated places in Syrmia Syrmia County Municipalities and cities of Vojvodina
city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
and the administrative center of the Srem District in the autonomous province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
. It is situated on the left bank of the Sava river
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
. , the city has a total population of 37,751 inhabitants, while its administrative area has a population of 79,940 inhabitants.
As Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrian ...
, it was a capital of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
during the Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
of 4th century CE. Ten Roman emperors were born in or near this city, Emperors Herennius Etruscus
Quintus Herennius Etruscus Messius Decius (died June 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251, ruling jointly under his father Decius. His father was proclaimed emperor by his troops in September 249 while in Pannonia and Moesia, in opposition to ...
(251), Hostilian
Hostilian ( la, Gaius Valens Hostilianus Messius Quintus; died 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251. Hostilian was born to Decius and Herennia Etruscilla at an unknown date and elevated to Caesar (title), ''caesar'' in 250 by Decius. After De ...
(251), Decius Traian (249–251), Claudius Gothicus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – January/April 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle ...
(268–270), Quintillus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius Quintillus (died 270) was a Roman emperor. He was a brother of Emperor Claudius Gothicus, whom he succeeded after Claudius' death in 270. Quintillus' claim to be emperor was challenged by Aurelian, who was proclaimed e ...
(270), Aurelian (270–275), Probus (276–282), Maximian (285–310), Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
(337–361) and Gratian
Gratian (; la, Gratianus; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and w ...
(367–383).
Name
The modern town name is ''Sremska Mitrovica'' ( sr, Сремска Митровица). The Hungarian name was ''Szávaszentdemeter'' while in Croatian it is referred to as ''Srijemska Mitrovica''. Mitrovica stems from Saint Demetrius or "Sveti Dimitrije" in Serbian. Sremska Mitrovica means ''Mitrovica of Syrmia'' with Sremska distinguishing it fromKosovska Mitrovica
Mitrovica ( sq-definite, Mitrovicë; sr-cyrl, Митровица) or Kosovska Mitrovica ( sr-cyrl, Косовска Митровица) is a city and municipality located in Kosovo. Settled on the banks of Ibar and Sitnica rivers, the city is ...
.
The name of the city during the reign of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
was Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrian ...
. Beginning in 1180 AD the name changed from "Civitas Sancti Demetrii" to "Dmitrovica", "Mitrovica", and finally to the present form - "Sremska Mitrovica".
History
Ancient Sirmium
Sremska Mitrovica is one of the oldest cities in Europe. Archaeologists have found a trace of organizedhuman
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
life dating from 5000 BC onwards. Ionian jewellery dating to 500BC was excavated in the city. When the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
conquered the city in the 1st century BC, Sirmium already was a settlement with a long tradition. In the 1st century, Sirmium gained a status of a colony of the citizens of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, and became a very important military and strategic location in Pannonia province. The war expeditions of Roman emperors Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
, Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
, and Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – January/April 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle ...
, were prepared in Sirmium.
In 103, Pannonia was split into two provinces: Pannonia Superior
Pannonia Superior, lit. Upper Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Carnuntum. It was one on the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pan ...
and Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia ...
, and Sirmium became the capital city of the latter. In 296, Diocletian implemented a new territorial division of Pannonia. Instead of previous two provinces, there were four new provinces established in former territory of original Pannonia: Pannonia Prima
Pannonia Prima was an ancient Roman province. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of Emperor Diocletian. Previously, it was a part of the province of Pannonia Superior, which, along with Pannonia Inferior, was gradually divided into ...
, Pannonia Valeria
The Pannonia Valeria or simply Valeria, also known as Pannonia Ripensis, was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of emperor Diocletian, in a division of Pannonia Inferior. The capital of the p ...
, Pannonia Savia
Pannonia Savia or simply Savia, also known as Pannonia Ripariensis, was a Late Roman province. It was formed in the year 295, during the Tetrarchy reform of Roman emperor Diocletian, and assigned to the civil diocese of Pannonia, which was atta ...
and Pannonia Secunda
Pannonia Secunda was one of the provinces of the Roman Empire. It was formed in the year 296, during the reign of emperor Diocletian. The capital of the province was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica). Pannonia Secunda included parts of present-da ...
. Capital city of Pannonia Secunda was Sirmium.
In 293, with the establishment of tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
, the Roman Empire was split into four parts; Sirmium became one of the four capital cities of the Empire, the other three being Augusta Treverorum
Trier in Rhineland-Palatinate, whose history dates to the Roman Empire, is often claimed to be the oldest city in Germany. Traditionally it was known in English by its French name of Treves.
Prehistory
The first traces of human settlement in ...
, Mediolanum
Mediolanum, the ancient city where Milan now stands, was originally an Insubrian city, but afterwards became an important Roman city in northern Italy. The city was settled by the Insubres around 600 BC, conquered by the Romans in 222 BC, and ...
, and Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; el, Νικομήδεια, ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocleti ...
(modern Trier
Trier ( , ; lb, Tréier ), formerly known in English as Trèves ( ;) and Triers (see also names in other languages), is a city on the banks of the Moselle in Germany. It lies in a valley between low vine-covered hills of red sandstone in the ...
, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city h ...
and Izmit). During the tetrarchy, Sirmium was the capital of emperor Galerius
Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. During his reign he campaigned, aided by Diocletian, against the Sasanian Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across th ...
. With the establishment of praetorian prefectures in 318, the capital of the prefecture of Illyricum was Sirmium.
Beginning in the 4th century, the city was an important Christian centre, and was a seat of the Episcopate of Sirmium. Four Christian councils
A council is a group of people who come together to consult, deliberate, or make decisions. A council may function as a legislature, especially at a town, city or county/ shire level, but most legislative bodies at the state/provincial or nati ...
were held in Sirmium. At the end of the 4th century, Sirmium was brought under the sway of the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, and later, was again annexed to the Eastern Roman Empire. In 441, Sirmium was conquered by the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, and after this conquest, it remained for more than a century in the hands of various Germanic tribes, such were Eastern Goths and Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
.
For a short time, Sirmium was the center of the Gepide State and the king Cunimund
Cunimund (died 567) was the last king of the Gepids, falling in the Lombard–Gepid War (567) against the Lombards and Pannonian Avars.
War with the Lombards Background
The Gepids had held the important city of Sirmium (now Sremska Mitrovica, Se ...
minted golden coins in it. After 567, Sirmium was again incorporated into Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
. The city was conquered and destroyed by Avars in 582. This event marked the end of the period of late Antiquity in the history of Sirmium.
11 luxurious golden belts of Avar handicraft dating to the 6th century was excavated in the vicinity.
After the Avar conquest
For the next two centuries Sirmium was a place of little importance. At the end of the 8th century, Sirmium belonged to the Frankish State. The historical role of Sirmium increased again in the 9th century, when it was part of the Bulgarian Empire. Pope Adrian II gave St Methodius the title of Archbishop of Sirmium. After having adopted Christianity, the Bulgarians restored in Sirmium the Christian Episcopate, having in mind old Christian traditions and the reputation this city had in the ancient world. In the 11th century, Sirmium was a residence ofSermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. ...
, a duke of Syrmia, who was a vassal of the Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
Samuil
Samuel (also Samuil; bg, Самуил, ; mk, Самоил/Самуил, ; Old Church Slavonic: Самоилъ; died October 6, 1014) was the Tsar (''Emperor'') of the First Bulgarian Empire from 997 to 6 October 1014. From 977 to 997, he was ...
. After 1018, the city was again included into the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, and since the end of the 11th century, Sirmium was a subject of a dispute between the Byzantine Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, until 1180 when the Byzantine Empire gave up Sirmium, surrendering it to the Kingdom of Hungary. In the 11th century, a Byzantine province named Theme of Sirmium
The Theme of Sirmium ( el, θέμα Σιρμίου) was a Byzantine administrative unit ( theme), which existed in present-day Serbia, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina in the 11th century. Its capital was Sirmium (today Sremska Mitrovica).
Backg ...
had its capital in this city.
For a while, about 1451, the city was in possession of the Serbian despot Đurađ Branković
Đurađ Branković (; sr-cyr, Ђурађ Бранковић; hu, Brankovics György; 1377 – 24 December 1456) was the Serbian Despot from 1427 to 1456. He was one of the last Serbian medieval rulers. He was a participant in the battle of Anka ...
. In 1521 the city came into Ottoman hands and it remained under the Ottoman rule for almost two centuries. According to Ottoman traveler Evliya Çelebi
Derviş Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi ( ota, اوليا چلبى), was an Ottoman explorer who travelled through the territory of the Ottoman Empire and neighboring lands over a period of forty years, recording ...
, Mitrovica had been conquered by the Bosnian sanjak bey Husrev-bey
Gazi Husrev-beg ( ota, غازى خسرو بك, ''Gāzī Ḫusrev Beğ''; Modern Turkish: ''Gazi Hüsrev Bey''; 1480–1541) was an Ottoman Bosnian sanjak-bey (governor) of the Sanjak of Bosnia in 1521–1525, 1526–1534, and 1536–1541. He w ...
. It was renamed as "Dimitrofça".
The name of the mayor of the city was Dimitar and since the middle of the 16th century, the city was mostly populated with Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. According to the 1566/69 data, the population of the city was composed of 592 Muslim and 30 Christian houses, while according to the 1572 data, it was composed of 598 Muslim and 18 Christian houses.
According to the 1573 data, the city had 17 mosques and no Christian church. During the Ottoman rule, Sremska Mitrovica was the largest settlement in Syrmia, and was the administrative center of the Ottoman Sanjak of Syrmia
Sanjak of Syrmia ( tr, Sirem sancağı, sr, Sremski sandžak/Сремски санџак, hr, Srijemski sandžak) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire formed in 1541. It was located in the Syrmia region and was part o ...
. It was temporarily occupied by Austrian troops between 1688 and 1690. They finally took it in 1717 and took possession of it after signing Treaty of Passarowitz
The Treaty of Passarowitz, or Treaty of Požarevac, was the peace treaty signed in Požarevac ( sr-cyr, Пожаревац, german: Passarowitz), a town that was in the Ottoman Empire but is now in Serbia, on 21 July 1718 between the Ottoman ...
in 1718.
With the establishment of the Habsburg administration in 1718, the Muslim population fled from the city and was replaced with Serbian, Croatian, and German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
settlers. According to the 1765 data, the population of the city numbered 809 people, of whom 514 were Serbs and 290 Catholics.
Sremska Mitrovica was part of the Habsburg Military Frontier
The Military Frontier (german: Militärgrenze, sh-Latn, Vojna krajina/Vojna granica, Војна крајина/Војна граница; hu, Katonai határőrvidék; ro, Graniță militară) was a borderland of the Habsburg monarchy and ...
(Slavonian Krajina
The Slavonian Military Frontier ( hr, Slavonska vojna krajina or ; german: Slawonische Militärgrenze; sr, Славонска војна крајина; hu, Szlavón határőrvidék) was a district of the Military Frontier, a territory in the ...
). In 1848-49, it was part of the Serbian Voivodship, a Serb autonomous region within Austrian Empire, but in 1849, it was returned under administration of the Military Frontier. With the abolition of the Slavonian Military Frontier in 1881, Sremska Mitrovica was included into Syrmia County, which was part of the Kingdom of Croatia-Slavonia within Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
.
According to the 1910 census, the population of the city numbered 12,909 people, of which 8,793 spoke the Serbo-Croatian language (4,878 of those spoke Serbian and 3,915 spoke Croatian) and 2,341 German. The administrative area of the city (which did not included the city itself) had 32,012 inhabitants, of which 28,093 spoke Serbo-Croatian (27,022 of those spoke Serbian and 1,071 spoke Croatian) and 2,324 German.
After the First World War
In 1918, the Austro-Hungarian monarchy collapsed and the Syrmia region first became a part of the newly formedState of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs
The State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( sh, Država Slovenaca, Hrvata i Srba / ; sl, Država Slovencev, Hrvatov in Srbov) was a political entity that was constituted in October 1918, at the end of World War I, by Slovenes, Croats and Serbs ( ...
, and then, on 24 November 1918, the assembly of Syrmia in Ruma
Ruma (; hu, Árpatarló) is a town and municipality in the Srem District of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, Serbia. As of 2011, the town has a population of 30,076, while the municipality has a population of 54,339.
History
Traces of org ...
decided most of Syrmia (including Mitrovica) would join the Kingdom of Serbia.
Subsequently, on 1 December 1918, Kingdom of Serbia united with the Kingdom of Montenegro
The Kingdom of Montenegro ( sr, Краљевина Црна Горa, Kraljevina Crna Gora) was a monarchy in southeastern Europe, present-day Montenegro, during the tumultuous period of time on the Balkan Peninsula leading up to and during World ...
and the State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs to form the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(renamed to Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
in 1929). Between 1918-22, Sremska Mitrovica was part of the Syrmia County, between 1922-29 part of the Syrmia Oblast, between 1929-31 part of the Drina Banovina, and, between 1931–41, part of the Danube Banovina.
 During
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the city was occupied by Axis
An axis (plural ''axes'') is an imaginary line around which an object rotates or is symmetrical. Axis may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Axis of rotation: see rotation around a fixed axis
* Axis (mathematics), a designator for a Cartesian-coordinat ...
troops and was attached to the Independent State of Croatia
The Independent State of Croatia ( sh, Nezavisna Država Hrvatska, NDH; german: Unabhängiger Staat Kroatien; it, Stato indipendente di Croazia) was a World War II-era puppet state of Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. It was established in p ...
. During that time its name was changed to ''Hrvatska Mitrovica'' (meaning ''Croatian Mitrovica''). One of the largest Nazi concentration/death camps in the Independent State of Croatia existed in Sremska Mitrovica and as many as 10,000 victims (Serbs, Jews, and antifascists) were killed here.
The Serbian Jewish population was to be interned in a concentration camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
built first in Jarak and then at Zasavica. However, both locations proved to be too flooded for construction. The Germans had to abandon these locations and use Sajmište, which resulted in the destruction of 83% of Serbian Jewry.
In the Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
in Sremska Mitrovica Prison, some Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
n prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
were kept in this prison. The main prison facility; the largest known in Serbia, was open from November 1991 to August 1992 and was a scene where many prisoners were killed, torture
Torture is the deliberate infliction of severe pain or suffering on a person for reasons such as punishment, extracting a confession, interrogation for information, or intimidating third parties. Some definitions are restricted to acts c ...
d, abused and rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault usually involving sexual intercourse or other forms of sexual penetration carried out against a person without their consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or ...
d.
Beginning in 1944, the town was part of the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital ...
within the new Socialist Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugo ...
and, from 1945, within the Socialist Republic of Serbia. From 1992 to 2003 it was part of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
Serbia and Montenegro ( sr, Cрбија и Црна Гора, translit=Srbija i Crna Gora) was a country in Southeast Europe located in the Balkans that existed from 1992 to 2006, following the breakup of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yu ...
, which was then transformed into the state union of Serbia and Montenegro. Since the 2006 independence of Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
, Sremska Mitrovica is part of an independent Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
.
Inhabited places

 The city of Sremska Mitrovica includes the town of
The city of Sremska Mitrovica includes the town of Mačvanska Mitrovica
Mačvanska Mitrovica (Serbian Cyrillic: Мачванска Митровица, ) is a town located in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Srem District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The town has a Serb ...
, and several villages. Villages on the northern bank of the river Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
, in the region of Syrmia:
*Bešenovački Prnjavor
Bešenovački Prnjavor () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Syrmia District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and it is the smallest village in the municipality - its pop ...
* Bešenovo
* Bosut
* Čalma
* Divoš
*Grgurevci
Grgurevci () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, Syrmia District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and, according to the census, had a population of 1,312 people as of 2002.
Nam ...
*Jarak
Jarak () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, Syrmia District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 2,235 people (2002 census).
Name
In Serbian, the vil ...
* Kuzmin
* Laćarak
* Ležimir
*Manđelos
Manđelos () is a village located in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Syrmia District of Vojvodina, Serbia. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,533 people (2002 census).
Name
In Serbian, the village ...
*Martinci
Martinci () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, Srem District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 3,639 people (2002 census).
Krofnijada jedina u Srbij ...
* Sremska Rača
* Stara Bingula
* Šašinci
*Šišatovac
Šišatovac () is a village located in the municipality of Sremska Mitrovica, Serbia. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbers 211 people (as of 2011). Near the village is the Šišatovac monastery, one of 16 Serbian Ort ...
* Šuljam
*Veliki Radinci
Veliki Radinci () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Syrmia District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,426 people (2011 census).
Name
I ...
Villages on the southern bank of the river Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
, in the region of Mačva
Mačva ( sr-Cyrl, Мачва, ; hu, Macsó) is a geographical and historical region in the northwest of Central Serbia, on a fertile plain between the Sava and Drina rivers. The chief town is Šabac. The modern Mačva District of Serbia is nam ...
:
* Noćaj
*Radenković
Radenković () is a village in Serbia. It is located in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Srem District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,086 people (2002 census). Although part of ...
* Ravnje
* Salaš Noćajski
*Zasavica I
Zasavica I (), also known as Zasavica () or Gornja Zasavica (), is a village in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in Serbian province of Vojvodina. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 772 people (2011 census).
G ...
*Zasavica II
Zasavica II ( sr-Cyrl, Засавица II), also known as Donja Zasavica (), is a village in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, in the Vojvodina province of Serbia. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 608 people ...
Demographics
According to the 2011 census results, the city administrative area has a population of 79,940 inhabitants.Ethnic groups
Most of the settlements in the city have an ethnic Serb majority. Ethnically mixed settlement with relative Serb majority is Stara Bingula. The main concentration of ethnic minorities is in the urban area of the city. The ethnic composition of the city:Religion
In 2002, the population of city of Sremska Mitrovica included 76,290Orthodox Christians
Orthodoxy (from Greek: ) is adherence to correct or accepted creeds, especially in religion.
Orthodoxy within Christianity refers to acceptance of the doctrines defined by various creeds and ecumenical councils in Antiquity, but different Churc ...
, 3,935 Roman Catholics, 252 Protestants and 106 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
. Orthodox Christians in Sremska Mitrovica are belonging to the Eparchy of Syrmia of the Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches.
The majori ...
. Catholics belong to the Diocese of Syrmia, which has its seat in Sremska Mitrovica.
Climate
Sremska Mitrovica has a humid subtropical climate bordering very closely on ahumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Dfb'') as well as an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Cfb'').
Economy
 The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):
The following table gives a preview of total number of registered people employed in legal entities per their core activity (as of 2018):
Sport
*KAF Sirmium Legionaries KAF, Kaf or Kafs may refer to:
Places
* Mount Qaf or Kaf, a mythical place in medieval Islamic cosmology
* Kaf, a city in Al Jawf Province, Saudi Arabia
* Kandahar International Airport or Kandahar Air Field (KAF), near Kandahar, Afghanistan
O ...
, an American Football club from Sremska Mitrovica. This is the first club of American Football in Serbia.
*FK Srem
FK Srem () is a football club based in Sremska Mitrovica, Vojvodina, Serbia. They compete in the Sremska Mitrovica City League, the seventh tier of the national league system.
History
The club was founded as Građanski in 1919. They initially c ...
, a football club from Sremska Mitrovica.
*KK Val
KK, K.K., kK, k.k., or other sequences of two k's with or without punctuation may refer to:
Arts and media
*KK, the production code for the 1967 ''Doctor Who'' serial ''The Faceless Ones''
* "KK" (song), a 2014 song by Wiz Khalifa
* Kk. or Kirk ...
, a canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
club from Sremska Mitrovica.
Famous and notable residents
Roman emperors
 Ten Roman emperors were born in the city and its environs:
* Decius Traian (249–51)
*
Ten Roman emperors were born in the city and its environs:
* Decius Traian (249–51)
*Herennius Etruscus
Quintus Herennius Etruscus Messius Decius (died June 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251, ruling jointly under his father Decius. His father was proclaimed emperor by his troops in September 249 while in Pannonia and Moesia, in opposition to ...
(251-51)
*Hostilian
Hostilian ( la, Gaius Valens Hostilianus Messius Quintus; died 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251. Hostilian was born to Decius and Herennia Etruscilla at an unknown date and elevated to Caesar (title), ''caesar'' in 250 by Decius. After De ...
(251-51)
*Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – January/April 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle ...
(268-270)
*Quintillus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius Quintillus (died 270) was a Roman emperor. He was a brother of Emperor Claudius Gothicus, whom he succeeded after Claudius' death in 270. Quintillus' claim to be emperor was challenged by Aurelian, who was proclaimed e ...
(270)
* Aurelian (270–75)
* Probus (276–82)
*Maximianus Herculius
Maximian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maximianus; c. 250 – c. July 310), nicknamed ''Herculius'', was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then ''Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his ...
(285–310)
*Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
(337–61)
*Gratian
Gratian (; la, Gratianus; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and w ...
(367–83)
The last emperor of the united Roman Empire, Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
(378–95), became emperor in Sirmium. The usurpers Ingenuus
Ingenuus was a Roman military commander, the imperial legate in Pannonia, who became a usurper to the throne of the emperor Gallienus when he led a brief and unsuccessful revolt in the year 260. Appointed by Gallienus himself,Leadbetter, ww.rom ...
and Regalianus
P. C. Regalianus (died 260/261), also known as Regalian, was Roman usurper for a few months in 260 and/or 261, during the Crisis of the Third Century, a period of intense political instability in the Roman Empire. Regalianus was acclaimed emperor ...
also declared themselves emperors in this city (in 260) and many other Roman emperors spent some time in Sirmium including Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
who might have written parts of his famous work ''Meditations
''Meditations'' () is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from AD 161 to 180, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy.
Marcus Aurelius wrote the 12 books of the ''Meditations'' in Koine ...
'' in the city.
Classical antiquity
*Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
, Roman emperor (161-180), used Sirmium as a residence in between pannonian military campaigns 170-180
* Maximinus, Roman emperor (235-238), ruled from residence in Sirmium.
*Herennius Etruscus
Quintus Herennius Etruscus Messius Decius (died June 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251, ruling jointly under his father Decius. His father was proclaimed emperor by his troops in September 249 while in Pannonia and Moesia, in opposition to ...
, Roman emperor (251), born in Sirmium.
*Hostilian
Hostilian ( la, Gaius Valens Hostilianus Messius Quintus; died 251) was briefly Roman emperor in 251. Hostilian was born to Decius and Herennia Etruscilla at an unknown date and elevated to Caesar (title), ''caesar'' in 250 by Decius. After De ...
, Roman emperor (251), born in Sirmium
* Decius Traian, Roman emperor (249-251), born in village Budalia
Martinci () is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Sremska Mitrovica municipality, Srem District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 3,639 people (2002 census).
Krofnijada jedina u Srb ...
near Sirmium.
*Ingenuus
Ingenuus was a Roman military commander, the imperial legate in Pannonia, who became a usurper to the throne of the emperor Gallienus when he led a brief and unsuccessful revolt in the year 260. Appointed by Gallienus himself,Leadbetter, ww.rom ...
, Roman emperor (260), proclaimed himself emperor in Sirmium.
*Regalianus
P. C. Regalianus (died 260/261), also known as Regalian, was Roman usurper for a few months in 260 and/or 261, during the Crisis of the Third Century, a period of intense political instability in the Roman Empire. Regalianus was acclaimed emperor ...
, Roman emperor (260), proclaimed himself emperor in Sirmium.
*Claudius II
Marcus Aurelius Claudius "Gothicus" (10 May 214 – January/April 270), also known as Claudius II, was Roman emperor from 268 to 270. During his reign he fought successfully against the Alemanni and decisively defeated the Goths at the Battle ...
, Roman emperor (268-270), born in Sirmium and spent most of his life there.
*Quintillus
Marcus Aurelius Claudius Quintillus (died 270) was a Roman emperor. He was a brother of Emperor Claudius Gothicus, whom he succeeded after Claudius' death in 270. Quintillus' claim to be emperor was challenged by Aurelian, who was proclaimed e ...
, Roman emperor (270), born in Sirmium
* Aurelian, Roman emperor (270-275), born in Sirmium.
* Probus, Roman emperor (276-282), born in Sirmium.
*Maximianus Herculius
Maximian ( la, Marcus Aurelius Valerius Maximianus; c. 250 – c. July 310), nicknamed ''Herculius'', was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was ''Caesar'' from 285 to 286, then ''Augustus'' from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his ...
, Roman emperor (285-310), born near Sirmium.
*Galerius
Gaius Galerius Valerius Maximianus (; 258 – May 311) was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. During his reign he campaigned, aided by Diocletian, against the Sasanian Empire, sacking their capital Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across th ...
, Roman emperor (305-311), ruled as Caesar during the Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their juniors colleagues and designated successors, the '' caesares'' ...
from residence in Sirmium (293-296).
*Crispus
Flavius Julius Crispus (; 300 – 326) was the eldest son of the Roman emperor Constantine I, as well as his junior colleague ( ''caesar'') from March 317 until his execution by his father in 326. The grandson of the ''augustus'' Constantius I ...
, a Caesar of the Roman Empire. He was proclaimed Caesar in Sirmium in 317.
* Constantine II, a Caesar of the Roman Empire. He was proclaimed Caesar in Sirmium in 317.
*Vetranio
Vetranio (died c. 356) was a Roman soldier, statesman and co-Emperor, a native of the province of Moesia (in modern Serbia).
Life and career Early life
Vetranio was born in the Roman province of Moesia to low-born parents, sometime in the ...
n, Roman emperor. Proclaimed himself emperor in Sirmium (in 350).
*Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
, Roman emperor (337-361), born in Sirmium.
*Gratian
Gratian (; la, Gratianus; 18 April 359 – 25 August 383) was emperor of the Western Roman Empire from 367 to 383. The eldest son of Valentinian I, Gratian accompanied his father on several campaigns along the Rhine and Danube frontiers and w ...
, Roman emperor (367-383), born in Sirmium.
*Theodosius I the Great
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
, Roman emperor (378-395). He became emperor in Sirmium.
*Valerius Licinius
Valerius Licinianus Licinius (c. 265 – 325) was Roman emperor from 308 to 324. For most of his reign he was the colleague and rival of Constantine I, with whom he co-authored the Edict of Milan, AD 313, that granted official toleration to C ...
, prefect of the Diocese of Pannonia
The Diocese of Pannonia ( la, Dioecesis Pannoniarum, lit. "Diocese of the Pannonias"), from 395 known as the Diocese of Illyricum, was a diocese of the Late Roman Empire. The seat of the ''vicarius'' (governor of the diocese) was Sirmium.
Hist ...
with residence in Sirmium (308-314).
*Aurelius Victor
Sextus Aurelius Victor (c. 320 – c. 390) was a historian and politician of the Roman Empire. Victor was the author of a short history of imperial Rome, entitled ''De Caesaribus'' and covering the period from Augustus to Constantius II. The work ...
, prefect of the Pannonia Secunda province, wrote a ''History of Rome'' under the emperor Julian.
*Leontius
Leontius ( el, Λεόντιος, Leóntios; – 15 February 706), was Byzantine emperor from 695 to 698. Little is known of his early life, other than that he was born in Isauria in Asia Minor. He was given the title of ''patrikios'', and ma ...
, prefect in Sirmium (426).
Middle ages
*Cunimund
Cunimund (died 567) was the last king of the Gepids, falling in the Lombard–Gepid War (567) against the Lombards and Pannonian Avars.
War with the Lombards Background
The Gepids had held the important city of Sirmium (now Sremska Mitrovica, Se ...
, king of the Gepids with residence in Sirmium.
*Sermon
A sermon is a religious discourse or oration by a preacher, usually a member of clergy. Sermons address a scriptural, theological, or moral topic, usually expounding on a type of belief, law, or behavior within both past and present contexts. ...
, duke of Syrmia (11th century).
Modern period
*Mira Banjac
Mira Banjac ( sr-Cyrl, Мира Бањац; born 4 November 1929) is a Serbian actress.
She won a number of awards, including an award for her work in Mamaroš from Brasil and Golden Medal for Merits of Republic of Serbia.
Selected filmograph ...
, Serbian actress
* Vaso Čubrilović, Serbian historian
* Robert Frangeš-Mihanović, Croatian sculptor
* Petar Gburčik, Serbian scientist
*Nikola Hristić
Nikola Hristić (Sremska Mitrovica, 10 August 1818 – Belgrade, 26 November 1911) was a Serbian politician who served as Prime Minister of Serbia for four terms.
Biography
Hristić was born and educated in Sremska Mitrovica. In 1840 he came ...
(1818–1911), Serbian politician
* Branislav Ivanović, Serbian footballer
*Siniša Kovačević
Siniša Kovačević (Serbian Cyrillic: Синиша Ковачевић, ; born 30 May 1954) is a Serbian author, playwright, politician and professor of the Belgrade Academy of Arts.
Biography
Kovačević was born on 30 May 1954 in the northern ...
, Serbian author
*Petar Kralj
Petar Kralj ( sr-cyr, Петар Краљ; 4 April 1941 – 10 November 2011) was a Serbian theater, film and television actor.
Biography
Kralj was born in Zagreb to a Serb family from Banija. During World War II his family fled to Syrmia, ...
, Serbian actor
*Mileva Marić
Mileva Marić ( sr-cyr, Милева Марић; 19 December 1875 – 4 August 1948), sometimes called Mileva Marić-Einstein ( sr-cyr, Милева Марић-Ајнштајн, Mileva Marić-Ajnštajn), was a Serbian physicist and mathematicia ...
, Serbian scientist
*Đorđe Marković Koder
Đorđe Marković Koder ( Cyrillic: Ђорђе Марковић Кодер) (1806 – April 30, 1891) was a Serbian poet born in Austrian Empire. Misunderstood, largely forgotten and often considered a marginal figure in Serbian poetry, criticize ...
(1806–1891), Serbian writer
*Dejan Milovanović
Dejan Milovanović ( sr-Cyrl, Дејан Миловановић; born 21 January 1984) is a Serbian retired professional footballer.
Personal
He is the son of Đorđe Milovanović, a member of Red Star Belgrade in the late 1970s and early to mi ...
, Serbian footballer
*Stjepan Musulin
Stjepan Musulin (1885 in Sremska Mitrovica – 1969) was a Croatian linguist, comparative Slavicist, philologist, lexicographer and translator.
Life
Musulin translated from the Polish and Czech languages. He is recognized as one of the gre ...
, Croatian linguist and lexicographer
* Milijana Nikolić, operatic mezzo-soprano
* Boško Palkovljević Pinki, People's Hero of Yugoslavia
*Veljko Petrović
Veljko Petrović ( sr-cyr, Вељко Петровић, ; c. 1780 – 1813), known simply as Hajduk Veljko (Хајдук Вељко, ǎjduːk v̞ɛ̌ːʎkɔ, was one of the '' vojvodas'' (military commanders) of the Serbian Revolutionary force ...
, Serbian poet
*Igor Pisanjuk
Igor Pisanjuk ( uk, Ігор Писанюк; sr-Cyrl, Игор Писањук; born 24 October 1989) is a footballer who played in the Nemzeti Bajnokság I, Nemzeti Bajnokság II, and the Canadian Soccer League. Pisanjuk was born in Serbia and ...
(1989), Canadian football player
*Mirjana Puhar
The 21st cycle of ''America's Next Top Model'' (subtitled as ''America's Next Top Model: Guys & Girls'') premiered on August 18, 2014 and it is the 15th season to air on The CW. It was the second season to feature male and female contestants. Ty ...
(1995-2015), Serbian - American model
*Ilarion Ruvarac
Ilarion (Jovan) Ruvarac ( sr, Иларион Руварац; September 1, 1832 — August 8, 1905) was a Serbian historian and Orthodox priest, a member of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts (first Serbian Learned Society and Serbian Roya ...
(1832–1905), Serbian Churchman and historian
*Mara Švel-Gamiršek Mara Švel-Gamiršek, also known as ''Mara Schwell'' (3 January 1900 – 7 December 1975) was Croatian writer from Syrmia. Beside prose, she also wrote poetry.
Early life and education
Mara Švel-Gamiršek was born in Sremska Mitrovica, Kingd ...
(1900–1975), Croatian writer
* Dragana Tomašević, Serbian discus thrower
*Zlatko Tomčić
Zlatko Tomčić (; born 10 July 1945) is a Croatian politician who served as President of the Croatian Peasant Party from 1994 to 2005, as Speaker of the Croatian Parliament from 2000 to 2003, as a representative in the Croatian Parliament, and as ...
, Croatian politician
*Slavko Vorkapić
Slavoljub "Slavko" Vorkapić ( sr-Cyrl, Славољуб "Славко" Воркапић; March 17, 1894 – October 20, 1976), known in English as Slavko Vorkapich, was a Serbian-born Hollywood montagist, an independent cinematic artist, chair ...
, Serbian-American film director and editor
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Sremska Mitrovica is twinned with: *Banja Luka
Banja Luka ( sr-Cyrl, Бања Лука, ) or Banjaluka ( sr-Cyrl, Бањалука, ) is the second largest city in Bosnia and Herzegovina and the largest city of Republika Srpska. Banja Luka is also the ''de facto'' capital of this entity. I ...
, Bosnia-Herzegovina
* Dunaújváros
Dunaújváros (; also known by other #Etymology and names, alternative names) is an industrial city in Fejér County, Central Hungary. It is a city with county rights. Situated 70 kilometres (43 miles) south of Budapest on the Danube, the city i ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
See also
*List of cities, towns and villages in Vojvodina
This is a list of cities, towns and villages in Vojvodina, a province of Serbia.
List of largest cities and towns in Vojvodina
List of urban settlements in Vojvodina
List of all urban settlements (cities and towns) in Vojvodina with populati ...
*List of cities in Serbia
, plural: ) is elected through popular vote, elected by their citizens in local elections. Also, the presidents of the municipalities are often referred to as "mayors" in everyday usage. There are 29 cities (, singular: ), each having an assembly a ...
*Councils of Sirmium The Councils of Sirmium were the five episcopal councils held in Sirmium in 347, 351, 357, 358 and finally in 375 or 378. The third—the most important of the councils—marked a temporary compromise between Arianism and the Western bishops of the ...
* Sremska Mitrovica railway station
References
External links
*Sremska Mitrovica.org - info, news about Sremska Mitrovica
{{Authority control Populated places in Srem District Populated places in Syrmia Syrmia County Municipalities and cities of Vojvodina