Soghdiana on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sogdia ( Sogdian: ) or Sogdiana was an ancient
 Achaemenid ruler
Achaemenid ruler
World History Encyclopedia
'. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
Roxane
" ''Articles on Ancient History''. Page last modified 17 August 2015. Retrieved 29 August 2016.Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), ''Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century'', London: Sphinx Fine Art, p. 87, . was the mother of
 Finally Sogdia was occupied by
Finally Sogdia was occupied by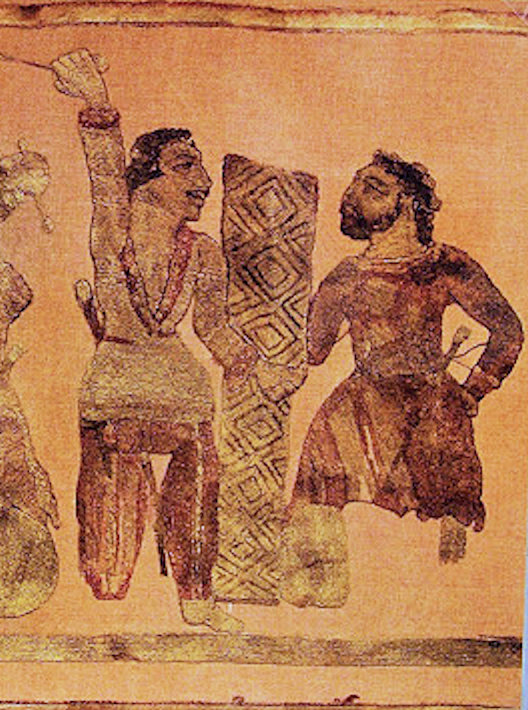  Zhang Qian also reported:
From the 1st century AD, the Yuezhi morphed into the powerful
Zhang Qian also reported:
From the 1st century AD, the Yuezhi morphed into the powerful
 The
The  The wealth of the Sasanian ransoms and tributes to the Hephthalites may have been reinvested in Sogdia, possibly explaining the prosperity of the region from that time. Sogdia, at the center of a new
The wealth of the Sasanian ransoms and tributes to the Hephthalites may have been reinvested in Sogdia, possibly explaining the prosperity of the region from that time. Sogdia, at the center of a new

 The Umayyads
The Umayyads
 It appears, however, that direct trade with the Sogdians remained limited in light of the small amount of Roman currency, Roman and Byzantine coinage, Byzantine coins found in Central Asian and Chinese archaeological sites belonging to this era. Although Sino-Roman relations, Roman embassies apparently reached Han China from 166 AD onwards, and the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans imported Han Chinese silk while the Han-dynasty Chinese imported Roman glasswares as discovered in their tombs, Valerie Hansen (2012) wrote that no Roman coins from the Roman Republic (507–27 BC) or the Principate (27 BC – 330 AD) era of the Roman Empire have been found in China.Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 97, . However, Warwick Ball (2016) upends this notion by pointing to a hoard of sixteen Roman coins found at Xi'an, China (formerly Chang'an), dated to the reigns of various emperors from Tiberius (14–37 AD) to Aurelian (270–275 AD).Warwick Ball (2016), ''Rome in the East: Transformation of an Empire'', 2nd edition, London & New York: Routledge, , p. 154. The earliest gold Solidus (coin), ''solidus'' coins from the Eastern Roman Empire found in China date to the reign of Byzantine emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450) and altogether only forty-eight of them have been found (compared to thirteen-hundred silver coins) in Xinjiang and the rest of China. The use of silver coins in Turfan persisted long after the Tang campaign against Karakhoja and Chinese conquest of 640, with a gradual adoption of Ancient Chinese coinage, Chinese bronze coinage over the course of the 7th century. The fact that these Eastern Roman coins were almost always found with Monetary history of Iran, Sasanian Persian silver coins and Eastern Roman gold coins were used more as ceremonial objects like talismans, confirms the pre-eminent importance of Greater Iran in Chinese Silk Road commerce of Central Asia compared to Eastern Rome.
It appears, however, that direct trade with the Sogdians remained limited in light of the small amount of Roman currency, Roman and Byzantine coinage, Byzantine coins found in Central Asian and Chinese archaeological sites belonging to this era. Although Sino-Roman relations, Roman embassies apparently reached Han China from 166 AD onwards, and the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans imported Han Chinese silk while the Han-dynasty Chinese imported Roman glasswares as discovered in their tombs, Valerie Hansen (2012) wrote that no Roman coins from the Roman Republic (507–27 BC) or the Principate (27 BC – 330 AD) era of the Roman Empire have been found in China.Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 97, . However, Warwick Ball (2016) upends this notion by pointing to a hoard of sixteen Roman coins found at Xi'an, China (formerly Chang'an), dated to the reigns of various emperors from Tiberius (14–37 AD) to Aurelian (270–275 AD).Warwick Ball (2016), ''Rome in the East: Transformation of an Empire'', 2nd edition, London & New York: Routledge, , p. 154. The earliest gold Solidus (coin), ''solidus'' coins from the Eastern Roman Empire found in China date to the reign of Byzantine emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450) and altogether only forty-eight of them have been found (compared to thirteen-hundred silver coins) in Xinjiang and the rest of China. The use of silver coins in Turfan persisted long after the Tang campaign against Karakhoja and Chinese conquest of 640, with a gradual adoption of Ancient Chinese coinage, Chinese bronze coinage over the course of the 7th century. The fact that these Eastern Roman coins were almost always found with Monetary history of Iran, Sasanian Persian silver coins and Eastern Roman gold coins were used more as ceremonial objects like talismans, confirms the pre-eminent importance of Greater Iran in Chinese Silk Road commerce of Central Asia compared to Eastern Rome.
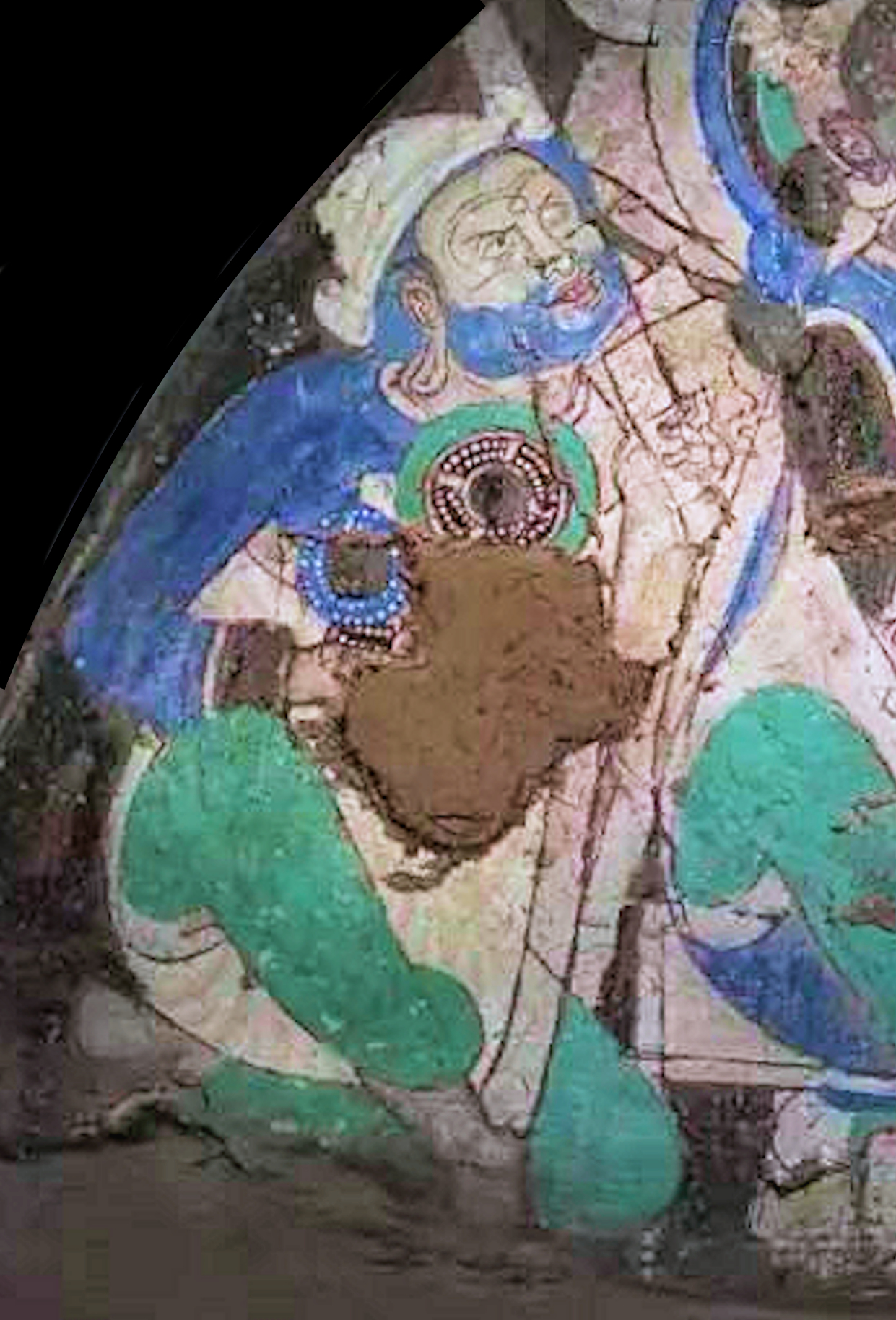 The Kizil Caves near Kucha, mid-way in the Tarim Basin, record many scenes of traders from Central Asia in the 5-6th century: these combine influence from the Eastern Iran sphere, at that time occupied by the
The Kizil Caves near Kucha, mid-way in the Tarim Basin, record many scenes of traders from Central Asia in the 5-6th century: these combine influence from the Eastern Iran sphere, at that time occupied by the
File:Dragon-King_Mabi_saving_traders,_Kizil_cave_14.jpg, Dragon-King Mabi saving traders, Cave 14, Kizil Caves
File:Dragon-King_Mabi_saving_traders,_Kizil_cave_17.jpg, Two-headed dragon capturing traders, Cave 17
Sab leading the way, Kizil Cave 17.jpg, Sab leading the way for the 500 traders, Kizil Cave 17.
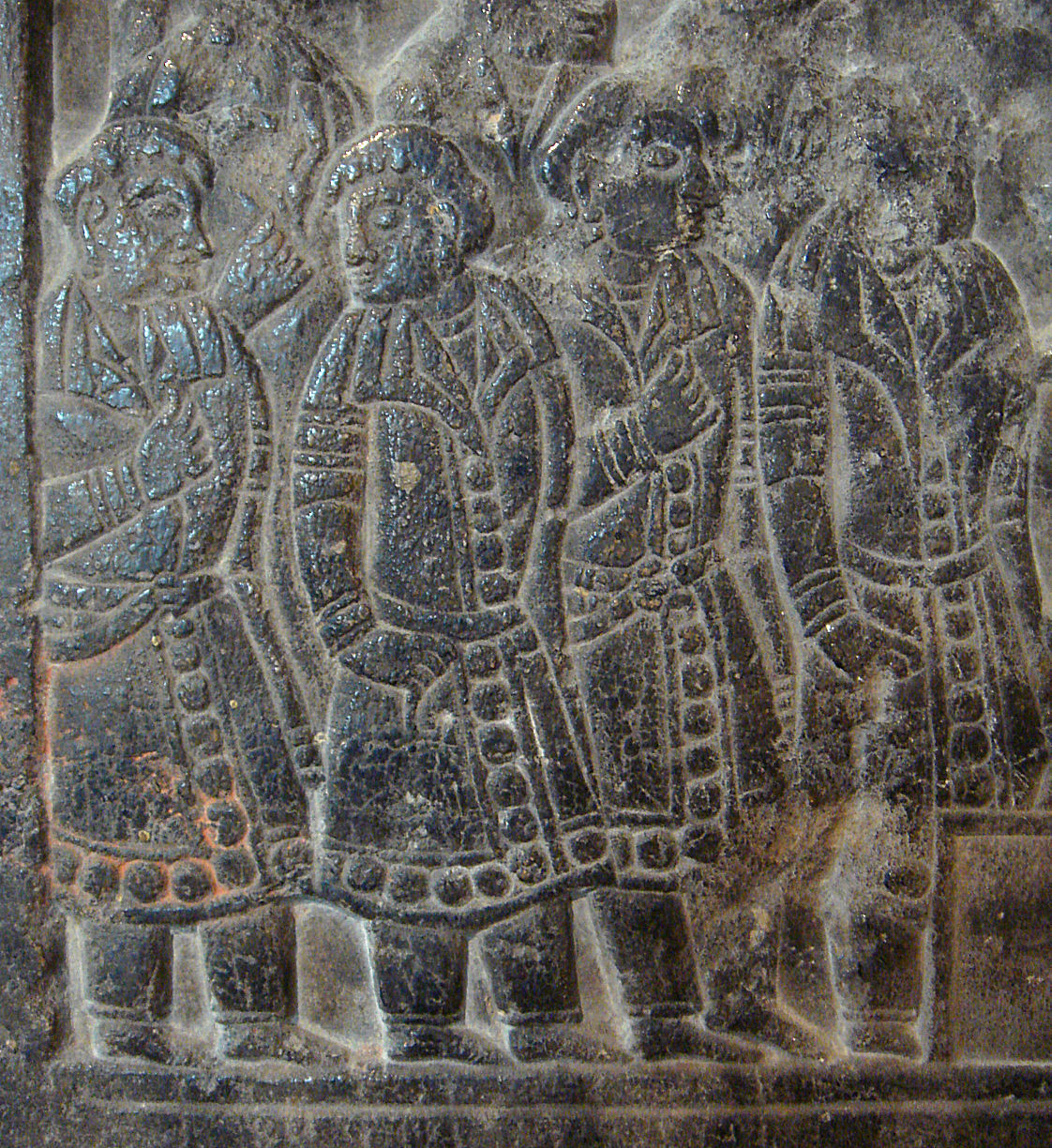
 In addition to being merchants, monks, and government officials, Sogdians also served as soldiers in the Tang military.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 135. An Lushan, whose father was Sogdian and mother a Gokturk, rose to the position of a military governor (''jiedushi'') in the northeast before leading the An Lushan Rebellion (755 – 763 AD), which split the loyalties of the Sogdians in China. The An Lushan rebellion was supported by many Sogdians, and in its aftermath many of them were slain or changed their names to escape their Sogdian heritage, so that little is known about the Sogdian presence in North China since that time. The former Yan rebel general Gao Juren of Goguryeo descent ordered a mass slaughter of West Asian (Central Asian)
In addition to being merchants, monks, and government officials, Sogdians also served as soldiers in the Tang military.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 135. An Lushan, whose father was Sogdian and mother a Gokturk, rose to the position of a military governor (''jiedushi'') in the northeast before leading the An Lushan Rebellion (755 – 763 AD), which split the loyalties of the Sogdians in China. The An Lushan rebellion was supported by many Sogdians, and in its aftermath many of them were slain or changed their names to escape their Sogdian heritage, so that little is known about the Sogdian presence in North China since that time. The former Yan rebel general Gao Juren of Goguryeo descent ordered a mass slaughter of West Asian (Central Asian)  During the Tang and subsequent Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, Five Dynasties and Song Dynasty, a large community of Sogdians also existed in the multicultural ''entrepôt'' of Dunhuang, Gansu, a major center of Buddhist learning and home to the Buddhist Mogao Caves. Although Dunhuang and the Hexi Corridor were captured by the Tibetan Empire after the An Lushan Rebellion, in 848 the ethnic Han Chinese general Zhang Yichao (799–872) managed to wrestle control of the region from Era of Fragmentation, the Tibetans during their civil war, establishing the Guiyi Circuit under Emperor Xuānzong of Tang (r. 846–859).''Zizhi Tongjian'', :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷249, vol. 249. Although the region occasionally fell under the rule of different states, it retained its multilingual nature as evidenced by an abundance of manuscripts (religious and secular) in Chinese language, Chinese and Tibetan languages, Tibetan, but also Sogdian, Saka language, Khotanese (another Eastern Iranian language native to Western Regions, the region), Uyghur language, Uyghur, and Sanskrit.
There were nine prominent Sogdian clans (昭武九姓). The names of these clans have been deduced from the Chinese surnames listed in a Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang-era Dunhuang manuscript (Pelliot chinois 3319V). Each "clan" name refers to a different city-state as the Sogdian used the name of their hometown as their Chinese surname. Of these the most common Sogdian surname throughout China was Shí (surname), Shí (石, generally given to those from Chach, modern
During the Tang and subsequent Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, Five Dynasties and Song Dynasty, a large community of Sogdians also existed in the multicultural ''entrepôt'' of Dunhuang, Gansu, a major center of Buddhist learning and home to the Buddhist Mogao Caves. Although Dunhuang and the Hexi Corridor were captured by the Tibetan Empire after the An Lushan Rebellion, in 848 the ethnic Han Chinese general Zhang Yichao (799–872) managed to wrestle control of the region from Era of Fragmentation, the Tibetans during their civil war, establishing the Guiyi Circuit under Emperor Xuānzong of Tang (r. 846–859).''Zizhi Tongjian'', :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷249, vol. 249. Although the region occasionally fell under the rule of different states, it retained its multilingual nature as evidenced by an abundance of manuscripts (religious and secular) in Chinese language, Chinese and Tibetan languages, Tibetan, but also Sogdian, Saka language, Khotanese (another Eastern Iranian language native to Western Regions, the region), Uyghur language, Uyghur, and Sanskrit.
There were nine prominent Sogdian clans (昭武九姓). The names of these clans have been deduced from the Chinese surnames listed in a Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang-era Dunhuang manuscript (Pelliot chinois 3319V). Each "clan" name refers to a different city-state as the Sogdian used the name of their hometown as their Chinese surname. Of these the most common Sogdian surname throughout China was Shí (surname), Shí (石, generally given to those from Chach, modern
 The Sogdians spoke an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language called Sogdian, closely related to Bactrian language, Bactrian, Khwarezmian language, Khwarazmian, and the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese Saka language, widely spoken Eastern Iranian languages of Central Asia in ancient times.Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, p 323. Sogdian was also prominent in the oasis city-state of Turfan in the Tarim Basin region of Northwest China (in modern Xinjiang). Judging by the Sogdian Bugut inscription of Mongolia written c. 581, the Sogdian language was also an official language of the First Turkic Khaganate established by the Gokturks.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 9, .
Sogdian was written largely in three scripts: the Sogdian alphabet, the Syriac alphabet, and the Manichaean alphabet, each derived from the Aramaic alphabet, which had been widely used in both the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires of ancient Iran.Christoph Baumer (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, p. 202–203, . The Sogdian alphabet formed the basis of the Old Uyghur alphabet of the 8th century, which in turn was used to create the Mongolian script of the early
The Sogdians spoke an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language called Sogdian, closely related to Bactrian language, Bactrian, Khwarezmian language, Khwarazmian, and the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese Saka language, widely spoken Eastern Iranian languages of Central Asia in ancient times.Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, p 323. Sogdian was also prominent in the oasis city-state of Turfan in the Tarim Basin region of Northwest China (in modern Xinjiang). Judging by the Sogdian Bugut inscription of Mongolia written c. 581, the Sogdian language was also an official language of the First Turkic Khaganate established by the Gokturks.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 9, .
Sogdian was written largely in three scripts: the Sogdian alphabet, the Syriac alphabet, and the Manichaean alphabet, each derived from the Aramaic alphabet, which had been widely used in both the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires of ancient Iran.Christoph Baumer (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, p. 202–203, . The Sogdian alphabet formed the basis of the Old Uyghur alphabet of the 8th century, which in turn was used to create the Mongolian script of the early
 Early medieval Sogdian costumes can be divided in two periods: Hephthalite, Hephtalitic (5th and 6th centuries) and Turkic (7th and early 8th centuries). The latter did not become common immediately after the political dominance of the Gökturks but only in c. 620 when, especially following Western Turkic Khaganate, Western Turkic Khagan Tong Yabghu Qaghan, Ton-jazbgu's reforms, Sogd was Turkized and the local nobility was officially included in the Khaganate's administration.
For both sexes clothes were tight-fitted, and narrow waists and wrists were appreciated. The silhouettes for grown men and young girls emphasized wide shoulders and narrowed to the waist; the silhouettes for female aristocrats were more complicated. The Sogdian clothing underwent a thorough process of Islamization in the ensuing centuries, with few of the original elements remaining. In their stead, turbans, kaftans, and sleeved coats became more common.
Early medieval Sogdian costumes can be divided in two periods: Hephthalite, Hephtalitic (5th and 6th centuries) and Turkic (7th and early 8th centuries). The latter did not become common immediately after the political dominance of the Gökturks but only in c. 620 when, especially following Western Turkic Khaganate, Western Turkic Khagan Tong Yabghu Qaghan, Ton-jazbgu's reforms, Sogd was Turkized and the local nobility was officially included in the Khaganate's administration.
For both sexes clothes were tight-fitted, and narrow waists and wrists were appreciated. The silhouettes for grown men and young girls emphasized wide shoulders and narrowed to the waist; the silhouettes for female aristocrats were more complicated. The Sogdian clothing underwent a thorough process of Islamization in the ensuing centuries, with few of the original elements remaining. In their stead, turbans, kaftans, and sleeved coats became more common.
A Mathematic Expression of Art: Sino-Iranian and Uighur Textile Interactions and the Turfan Textile Collection in Berlin
" in Rudolf G. Wagner and Monica Juneja (eds), ''Transcultural Studies'', Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg, No 1 (2014), pp 134–163 In addition to Puranas, Puranic cults, there were five Hindu deities known to have been worshipped in Sogdiana. These were Brahma, Indra, Shiva, Mahadeva (Shiva), Narayana, and Vaishravana; the gods Brahma, Indra, and Shiva were known by their Sogdian names Zravan, Adbad and Veshparkar, respectively. Durga, a mother goddess in Shaktism, may be represented in Sogdian art as a four-armed goddess riding atop a lion. As seen in an 8th-century mural from Panjakent, portable fire altars can be "associated" with Mahadeva (Buddhism), Mahadeva-Veshparkar, Brahma-Zravan, and Indra-Abdab, according to Braja Bihārī Kumar.Braja Bihārī Kumar (2007). "India and Central Asia: Links and Interactions," in J.N. Roy and B.B. Kumar (eds), ''India and Central Asia: Classical to Contemporary Periods'', 3–33. New Delhi: Published for Astha Bharati Concept Publishing Company. , p. 8. Among the Sogdian Christians known in China from inscriptions and texts were An Yena, a Christian from An country (Bukhara). Mi Jifen a Christian from Mi country (Maymurgh), Kang Zhitong, a Sogdian Christian cleric from Kang country (Samarkand), Mi Xuanqing a Sogdian Christian cleric from Mi country (Maymurgh), Mi Xuanying, a Sogdian Christian cleric from Mi country (Maymurgh), An Qingsu, a Sogdian Christian monk from An country (Bukhara). When visiting Yuan Dynasty, Yuan-era Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China during the late 13th century, the Venice, Venetian explorer and merchant Marco Polo noted that Europeans in Medieval China, a large number of Christian churches had been built there. His claim is confirmed by a Chinese text of the 14th century explaining how a Sogdian named Mar-Sargis from Samarkand founded six Church of the East in China, Nestorian Christian churches there, in addition to one in Hangzhou during the second half of the 13th century. Nestorian Christianity had existed in China earlier during the Tang Dynasty when a Persian monk named Alopen came to Chang'an in 653 to Proselytism, proselytize, as described in a dual Chinese and Syriac language inscription from Chang'an (modern Xi'an), dated to the year 781. Within the Syriac inscription is a list of priests and monks, one of whom is named Gabriel, the archdeacon of "Xumdan" and "Sarag", the Sogdian names for the Chinese capital cities Chang'an and
When visiting Yuan Dynasty, Yuan-era Zhenjiang, Jiangsu, China during the late 13th century, the Venice, Venetian explorer and merchant Marco Polo noted that Europeans in Medieval China, a large number of Christian churches had been built there. His claim is confirmed by a Chinese text of the 14th century explaining how a Sogdian named Mar-Sargis from Samarkand founded six Church of the East in China, Nestorian Christian churches there, in addition to one in Hangzhou during the second half of the 13th century. Nestorian Christianity had existed in China earlier during the Tang Dynasty when a Persian monk named Alopen came to Chang'an in 653 to Proselytism, proselytize, as described in a dual Chinese and Syriac language inscription from Chang'an (modern Xi'an), dated to the year 781. Within the Syriac inscription is a list of priests and monks, one of whom is named Gabriel, the archdeacon of "Xumdan" and "Sarag", the Sogdian names for the Chinese capital cities Chang'an and
 In 1916, the French Sinologist and historian Paul Pelliot used Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang Chinese manuscripts excavated from Dunhuang, Gansu to identify an ancient Sogdian colony south of Lop Nur in Xinjiang (Northwest China), which he argued was the base for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism and Nestorian Christianity in China.Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S., p. 148. In 1926, Japanese scholar Kuwabara compiled evidence for Sogdians in Chinese historical sources, and by 1933, Chinese historian Xiang Da published his ''Tang Chang'an and Central Asian Culture'', detailing the Sogdian influence on Chinese social religious life in the History of Xi'an, Tang-era Chinese capital city. The Canadian Sinologist Edwin G. Pulleyblank published an article in 1952, demonstrating the presence of a Sogdian colony founded in Six Hu Prefectures of the Ordos Loop during the Chinese Tang period, composed of Sogdians and Turkic peoples who migrated from the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, Mongolian steppe. The Japanese historian Ikeda on wrote an article in 1965, outlining the history of the Sogdians inhabiting Dunhuang from the beginning of the 7th century, analyzing lists of their Chinese surname, Sinicized names and the role of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism in their religious life. Yoshida Yutaka and Kageyama Etsuko, Japanese ethnographers and linguists of the Sogdian language, were able to reconstruct Sogdian names from forty-five different Chinese transliterations, noting that these were common in Turfan whereas Sogdians living closer to the center of Chinese civilization for generations adopted traditional Chinese names.
In 1916, the French Sinologist and historian Paul Pelliot used Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang Chinese manuscripts excavated from Dunhuang, Gansu to identify an ancient Sogdian colony south of Lop Nur in Xinjiang (Northwest China), which he argued was the base for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism and Nestorian Christianity in China.Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S., p. 148. In 1926, Japanese scholar Kuwabara compiled evidence for Sogdians in Chinese historical sources, and by 1933, Chinese historian Xiang Da published his ''Tang Chang'an and Central Asian Culture'', detailing the Sogdian influence on Chinese social religious life in the History of Xi'an, Tang-era Chinese capital city. The Canadian Sinologist Edwin G. Pulleyblank published an article in 1952, demonstrating the presence of a Sogdian colony founded in Six Hu Prefectures of the Ordos Loop during the Chinese Tang period, composed of Sogdians and Turkic peoples who migrated from the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, Mongolian steppe. The Japanese historian Ikeda on wrote an article in 1965, outlining the history of the Sogdians inhabiting Dunhuang from the beginning of the 7th century, analyzing lists of their Chinese surname, Sinicized names and the role of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism in their religious life. Yoshida Yutaka and Kageyama Etsuko, Japanese ethnographers and linguists of the Sogdian language, were able to reconstruct Sogdian names from forty-five different Chinese transliterations, noting that these were common in Turfan whereas Sogdians living closer to the center of Chinese civilization for generations adopted traditional Chinese names.
 * An Chongrong (安重榮), a general of the China's Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
*
* An Chongrong (安重榮), a general of the China's Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
*
A Mathematic Expression of Art: Sino-Iranian and Uighur Textile Interactions and the Turfan Textile Collection in Berlin
" in Rudolf G. Wagner and Monica Juneja (eds.), ''Transcultural Studies'', Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg, No 1 (2014), pp. 134–163. . ** * Ghafurov, Babadjan, "Tajiks", published in USSR, Russia, Tajikistan * Peter B. Golden (2011), ''Central Asia in World History'', Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, p. 47, . * Hanks, Reuel R. (2010), ''Global Security Watch: Central Asia'', Santa Barbara, Denver, Oxford: Praeger. * Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, . * Hansson, Anders, (1996), ''Chinese Outcasts: Discrimination and Emancipation in Late Imperial China'', Leiden, New York, Koln: E.J. Brill, . * Holt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Copenhagen, Cologne: E. J. Brill, . * Howard, Michael C. (2012), ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies: the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', Jefferson: McFarland & Company. * Hucker, Charles O. (1975). ''China's Imperial Past: An Introduction to Chinese History and Culture''. Stanford: Stanford University Press. . * A.F.P. Hulsewé, Hulsewé, A.F.P. (1986). "Ch'in and Han law," in Denis Twitchett and Michael Loewe (eds.), ''The Cambridge History of China: Volume I: the Ch'in and Han Empires, 221 B.C. – A.D. 220'', pp 520–544 Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Ibbotson, Sophie and Max Lovell-Hoare (2016), ''Uzbekistan'', 2nd edition, Bradt Travel Guides Ltd, . * Braja Bihārī Kumar (2007). "India and Central Asia: Links and Interactions," in J.N. Roy and B.B. Kumar (eds.), ''India and Central Asia: Classical to Contemporary Periods'', 3–33. New Delhi: Published for Astha Bharati Concept Publishing Company. . * Litvinski, B. A., A. H. Jalilov, A. I. Kolesnikov (1999), "The Arab Conquest", in ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia: Volume III, the Crossroads of Civilizations: A.D. 250–750'', B. A. Litvinski, Zhang Guangda, and R. Shabani Samghabadi (eds.). Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, pp. 449–472. * Liu, Xinru, "The Silk Road: Overland Trade and Cultural Interactions in Eurasia", in ''Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History'', ed. Michael Adas, American Historical Association, Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2001. * Magill, Frank N. et al. (eds.) (1998). ''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography, Volume 1.'' Pasadena; Chicago; London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, Salem Press, . * Michon, Daniel (2015). ''Archaeology and Religion in Early Northwest India: History, Theory, Practice'', London, New York, New Delhi: Routledge, . * * Nourzhanov, Kirill, Christian Bleuer (2013), ''Tajikistan: a Political and Social History'', Canberra: Australian National University Press, . * Prevas, John (2004), ''Envy of the Gods: Alexander the Great's Ill-Fated Journey across Asia'', Da Capo Press. * Ramirez-Faria, Carlos, (2007), ''Concise Encyclopedia of World History'', New Delhi: Atlantic Publishers & Distributors, . * * Rong, Xinjiang, "The Sogdian Caravan as Depicted in the Relieves of the Stone Sarcophagus from Shi's Tomb of the Northern Zhou" in ''Chinese Archaeology''. Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 181–185, ISSN (Online) 2160–5068, ISSN (Print) 5004–4295, DOI: 10.1515/CHAR.2006.6.1.181, January 2006. * Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S. 147–160, urn:nbn:de:kobv:b4-opus-11068. * Rose, J., "The Sogdians: Prime Movers between Boundaries", ''Comparative Studies of South Asia, Africa and the Middle East'', vol. 30, no. 3, (2010), p. 412. * Smith, William eds et al. (1873), ''A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology, Volume 1'', London: John Murray. * Stark, Sören. "Die Alttürkenzeit in Mittel- und Zentralasien. Archäologische und historische Studien", ''Nomaden und Sesshafte'', vol. 6. Reichert, 2008. . * Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), ''Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century'', London: Sphinx Fine Art, . * * Taenzer, Gertraud (2016), "Changing Relations between Administration, Clergy and Lay People in Eastern Central Asia: a Case Study According to the Dunhuang Manuscripts Referring to the Transition from Tibetan to Local Rule in Dunhuang, 8th–11th Centuries", in Carmen Meinert, ''Transfer of Buddhism Across Central Asian Networks (7th to 13th Centuries)'', Leiden, Boston: Brill, pp. 106–179, . * Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, pp. 323–30. * * von Le Coq, Albert. (1913)
''Chotscho: Facsimile-Wiedergaben der Wichtigeren Funde der Ersten Königlich Preussischen Expedition nach Turfan in Ost-Turkistan''
Berlin: Dietrich Reimer (Ernst Vohsen), im Auftrage der Gernalverwaltung der Königlichen Museen aus Mitteln des Baessler-Institutes
(Accessed 3 September 2016). * * Wood, Francis (2002). ''The Silk Road: Two Thousand Years in the Heart of Asia''. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. .
''The Sogdians: Influencers on the Silk Roads'' (Online exhibition)
{{coord, 40.4, N, 69.4, E, display=title Sogdians, Iranian countries and territories Achaemenid satrapies Former countries in Central Asia History of Central Asia Archaeological cultures of Central Asia Archaeology of Kazakhstan Archaeology of Tajikistan Northern and Southern dynasties, * Sui dynasty, * Tang dynasty, * Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, * 5th century in China, * 6th century in China, * 7th century in China, * 8th century in China, * 9th century in China, * 10th century in China, * 5th century 6th century in Asia 7th century in Asia 8th century in Asia 9th century in Asia 10th century in Asia Iranian culture Cultural regions Silk Road
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
civilization between the Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
and the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
, and in present-day Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the s ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, and Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
. Sogdiana was also a province of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
, and listed on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his d ...
. Sogdiana was first conquered by Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
, the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, and then was annexed by the Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Μακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an ancient kingdom on the periphery of Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. The kingdom was founded and initially ruled ...
ian ruler Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
in 328 BC. It would continue to change hands under the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Ind ...
, the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
, the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, the Hephthalite Empire
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Cen ...
, the Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after ...
and the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana.
The Sogdian city-states, although never politically united, were centered on the city of Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
. Sogdian, an Eastern Iranian language
The Eastern Iranian languages are a subgroup of the Iranian languages emerging in Middle Iranian times (from c. the 4th century BC). The Avestan language is often classified as early Eastern Iranian. As opposed to the Middle Western Iranian dial ...
, is no longer spoken, but a descendant of one of its dialects, Yaghnobi, is still spoken by the Yaghnobis
The Yaghnobi people ( Yaghnobi: yaγnōbī́t or suγdī́t; tg, яғнобиҳо, yağnobiho/jaƣnoʙiho) are an Iranian ethnic minority in Tajikistan. They inhabit Tajikistan's Sughd province in the valleys of the Yaghnob, Qul and Varzob r ...
of Tajikistan. It was widely spoken in Central Asia as a ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' and served as one of the First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of B ...
's court languages for writing documents.
Sogdians also lived in Imperial China
The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC), during the reign of king Wu Ding. Ancient historical texts such as the '' Book of Documents'' (early chapt ...
and rose to prominence in the military and government of the Chinese Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
(618–907 AD). Sogdian merchants and diplomats travelled as far west as the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. They played an important part as middlemen in the trade route of the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
. While originally following the faiths of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, Manichaeism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (A ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
and, to a lesser extent, Nestorian Christianity
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
from West Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes ...
, the gradual conversion to Islam among the Sogdians and their descendants began with the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana in the 8th century. The Sogdian conversion to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
was virtually complete by the end of the Samanid Empire
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in ...
in 999, coinciding with the decline of the Sogdian language, as it was largely supplanted by Persian.
Geography
Sogdiana lay north ofBactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
, east of Khwarezm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ...
, and southeast of Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
between the Oxus (Amu Darya
The Amu Darya, tk, Amyderýa/ uz, Amudaryo// tg, Амударё, Amudaryo ps, , tr, Ceyhun / Amu Derya grc, Ὦξος, Ôxos (also called the Amu, Amo River and historically known by its Latin name or Greek ) is a major river in Central Asi ...
) and the Jaxartes (Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
), including the fertile valley of the Zeravshan (called the Polytimetus by the ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
). Sogdian territory corresponds to the modern regions of Samarkand and Bukhara
Bukhara ( Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and the city ...
in modern Uzbekistan, as well as the Sughd
Sughd Province ( tg, Вилояти Суғд, Viloyati Sughd, Sogdia Region , fa, ولایت سغد) is one of the four administrative divisions and one of the three provinces ( tg, вилоятҳо, viloyatho , fa, ولایت) that make up ...
region of modern Tajikistan. In the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, Sogdian cities included sites stretching towards Issyk Kul
Issyk-Kul (also Ysyk-Köl, ky, Ысык-Көл, lit=warm lake, translit=Ysyk-Köl, , zh, 伊塞克湖) is an endorheic lake (i.e., without outflow) in the Northern Tian Shan mountains in Eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the seventh-deepest lake in th ...
, such as that at the archeological site of Suyab
Suyab ( fa, سوی آب; Middle Chinese: /suʌiH jiᴇp̚/), also known as ''Ordukent'' (modern-day ''Ak-Beshim''), was an ancient Silk Road city located some 50 km east from Bishkek, and 8 km west southwest from Tokmok, in the Chu r ...
.
Name
Oswald Szemerényi devotes a thorough discussion to the etymologies of ancient ethnic words for theScythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
in his work ''Four Old Iranian Ethnic Names: Scythian – Skudra – Sogdian – Saka''. In it, the names provided by the Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
and the names of his title, except Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who histo ...
, as well as many other words for "Scythian", such as Assyrian
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyri ...
''Aškuz'' and Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''Skuthēs'', descend from *skeud-, an ancient Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
root meaning "propel, shoot" (cf. English shoot). *skud- is the zero-grade; that is, a variant in which the -e- is not present. The restored Scythian name is *Skuda (archer
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In m ...
), which among the Pontic or Royal Scythians became *Skula, in which the d has been regularly replaced by an l. According to Szemerényi, Sogdiana ( peo, Suguda-; uz, Sug'd, Sug'diyona; fa, سغد, Soġd; tg, Суғд, سغد, Suġd; zh, 粟特, sùtè; gr, Σογδιανή, Sogdiane) was named from the Skuda form. Starting from the names of the province given in Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as ( ...
inscriptions, Sugda and Suguda, and the knowledge derived from Middle Sogdian that Old Persian -gd- applied to Sogdian was pronounced as voiced fricatives, -γδ-, Szemerényi arrives at *Suγδa as an Old Sogdian endonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
. Applying sound changes apparent in other Sogdian words and inherent in Indo-European, he traces the development of *Suγδa from Skuda, "archer", as follows: Skuda > *Sukuda by anaptyxis
In phonology, epenthesis (; Greek ) means the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially in the beginning syllable ('' prothesis'') or in the ending syllable (''paragoge'') or in-between two syllabic sounds in a word. The word ''epenth ...
> *Sukuδa > *Sukδa ( syncope) > *Suγδa (assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
* Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
** Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the prog ...
).
History
Prehistory
Sogdiana possessed aBronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
urban culture: original Bronze Age towns appear in the archaeological record beginning with the settlement at Sarazm
Sarazm is an ancient town and also a jamoat in north-western Tajikistan. It dates back to the 4th millennium BC and is today a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The jamoat is part of the city of Panjakent in Sughd Region, and has a total population of ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, spanning as far back as the 4th millennium BC, and then at Kök Tepe, near modern-day Bulungur, Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, from at least the 15th century BC.
This original culture was gradually displaced by the Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations were hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) speakers, and subsequent migrations of people speaking derived Indo-European languages, which took place approx. 4000 to 1000 BCE, potentially expl ...
of the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
, forming the Andronovo culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo ...
(c. 2000–1450 BC), which included Eastern Iranian speaking peoples such as the historical Sogdians. In the Avesta
The Avesta () is the primary collection of religious texts of Zoroastrianism, composed in the Avestan language.
The Avesta texts fall into several different categories, arranged either by dialect, or by usage. The principal text in the lit ...
the Sogdians are mentioned as living in the lands
Land is the solid surface of the Earth that is not covered by water.
Land, lands, The Land, or the Lands may also refer to:
Entertainment and media Film
* ''Land'' (1987 film), a British television film by Barry Collins
* ''Land'' (2018 film), ...
created by Ahura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna'' ...
for the Iranian peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities.
The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate ...
.
Achaemenid period (546-327 BC)
 Achaemenid ruler
Achaemenid ruler Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia (; peo, 𐎤𐎢𐎽𐎢𐏁 ), commonly known as Cyrus the Great, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire, the first Persian empire. Schmitt Achaemenid dynasty (i. The clan and dynasty) Under his rule, the empire embraced ...
conquered Sogdiana while campaigning in Central Asia in 546–539 BC, a fact mentioned by the ancient Greek historian Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus, part of the Persian Empire (now Bodrum, Turkey) and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria (Italy). He is known fo ...
in his ''Histories
Histories or, in Latin, Historiae may refer to:
* the plural of history
* ''Histories'' (Herodotus), by Herodotus
* ''The Histories'', by Timaeus
* ''The Histories'' (Polybius), by Polybius
* ''Histories'' by Gaius Sallustius Crispus (Sallust), ...
''.Antoine Simonin. (8 January 2012). "Sogdiana." World History Encyclopedia
'. Retrieved 31 August 2016.
Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
introduced the Aramaic writing system and coin currency to Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
, in addition to incorporating Sogdians into his standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or ...
as regular soldiers and cavalrymen. A contingent of Sogdian soldiers fought in the main army of Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of D ...
during his second, ultimately-failed invasion of Greece in 480 BC.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, ''Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art'', Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 3, . A Persian inscription from Susa
Susa ( ; Middle elx, 𒀸𒋗𒊺𒂗, translit=Šušen; Middle and Neo- elx, 𒋢𒋢𒌦, translit=Šušun; Neo- Elamite and Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼𒀭, translit=Šušán; Achaemenid elx, 𒀸𒋗𒐼, translit=Šušá; fa, شوش ...
claims that the palace there was adorned with lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
and carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
originating from Sogdiana.
During this period of Persian rule, the western half of Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
was part of the Greek civilization. As the Achaemenids conquered it, they met persistent resistance and revolt. One of their solutions was to ethnically cleanse rebelling regions, relocating those who survived to the far side of the empire. Thus Sogdiana came to have a significant Greek population.
Given the absence of any named satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
s (i.e. Achaemenid provincial governors) for Sogdiana in historical records, modern scholarship has concluded that Sogdiana was governed from the satrapy of nearby Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
. The satraps were often relatives of the ruling Persian kings, especially sons who were not designated as the heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
. Sogdiana likely remained under Persian control until roughly 400 BC, during the reign of Artaxerxes II
Arses ( grc-gre, Ἄρσης; 445 – 359/8 BC), known by his regnal name Artaxerxes II ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης), was King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire from 405/4 BC to 358 BC. He was the son and suc ...
.Christoph Baumer (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, p. 207, . Rebellious states of the Persian Empire took advantage of the weak Artaxerxes II, and some, such as Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, were able to regain their independence. Persia's massive loss of Central Asian territory is widely attributed to the ruler's lack of control. However, unlike Egypt, which was quickly recaptured by the Persian Empire, Sogdiana remained independent until it was conquered by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
. When the latter invaded the Persian Empire, Pharasmanes, an already independent king of Khwarezm
Khwarazm (; Old Persian: ''Hwârazmiya''; fa, خوارزم, ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the ...
, allied with the Macedonians and sent troops to Alexander in 329 BC for his war against the Scythia
Scythia ( Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
...
ns of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
region (even though this anticipated campaign never materialized).
During the Achaemenid period (550–330 BC), the Sogdians lived as a nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic people much like the neighboring Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
, who spoke Bactrian, an Indo-Iranian language
The Indo-Iranian languages (also Indo-Iranic languages or Aryan languages) constitute the largest and southeasternmost extant branch of the Indo-European language family (with over 400 languages), predominantly spoken in the geographical subre ...
closely related to Sogdian, and were already engaging in overland trade. Some of them had also gradually settled the land to engage in agriculture.Liu, Xinru (2010), ''The Silk Road in World History'', Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press, p 67. Similar to how the Yuezhi offered tributary gifts of jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole group ...
to the emperors of China
''Huangdi'' (), translated into English as Emperor, was the superlative title held by monarchs of China who ruled various imperial regimes in Chinese history. In traditional Chinese political theory, the emperor was considered the Son of Heave ...
, the Sogdians are recorded in Persian records as submitting precious gifts of lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
and carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
to Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
, the Persian king of kings
King of Kings; grc-gre, Βασιλεὺς Βασιλέων, Basileùs Basiléōn; hy, արքայից արքա, ark'ayits ark'a; sa, महाराजाधिराज, Mahārājadhirāja; ka, მეფეთ მეფე, ''Mepet mepe'' ...
. Although the Sogdians were at times independent and living outside the boundaries of large empires, they never formed a great empire of their own like the Yuezhi, who established the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
(30–375 AD) of Central and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;; ...
.
Hellenistic period (327-145 BC)
A now-independent and warlike Sogdiana formed a border region insulating the Achaemenid Persians from the nomadicScythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Cent ...
to the north and east. It was led at first by Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid sa ...
, the Achaemenid satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires.
The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with cons ...
of Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
. After assassinating Darius III
Darius III ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; c. 380 – 330 BC) was the last Achaemenid King of Kings of Persia, reigning from 336 BC to his death in 330 BC.
Contrary to his predecessor Artaxerxes IV Arses, Dariu ...
in his flight from the Macedonian Greek army, he became claimant to the Achaemenid throne. The Sogdian Rock
The Sogdian Rock or Rock of Ariamazes, a fortress located north of Bactria in Sogdiana (near Samarkand), ruled by Arimazes, was captured by the forces of Alexander the Great in the early spring of 327 BC as part of his conquest of the Achaemen ...
or Rock of Ariamazes, a fortress in Sogdiana, was captured in 327 BC by the forces of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, the ''basileus
''Basileus'' ( el, ) is a Greek term and title that has signified various types of monarchs in history. In the English-speaking world it is perhaps most widely understood to mean " monarch", referring to either a " king" or an "emperor" and ...
'' of Macedonian Greece, and conqueror of the Persian Achaemenid Empire. Oxyartes
Oxyartes (Old Persian: 𐎢𐎺𐎧𐏁𐎫𐎼, Greek: ''Ὀξυάρτης'', in fa, وخشارد ("Vaxš-ard"), from an unattested form in an Old Iranian language: ''*Huxšaθra-'') was a Sogdian or Bactrian nobleman of Bactria, father o ...
, a Sogdian nobleman of Bactria, had hoped to keep his daughter Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
safe at the fortress of the Sogdian Rock, yet after its fall Roxana was soon wed to Alexander as one of his several wives.Ahmed, S. Z. (2004), ''Chaghatai: the Fabulous Cities and People of the Silk Road'', West Conshokoken: Infinity Publishing, p. 61. Roxana, a Sogdian whose name ''Roshanak'' means "little star",Livius.org.Roxane
" ''Articles on Ancient History''. Page last modified 17 August 2015. Retrieved 29 August 2016.Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), ''Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century'', London: Sphinx Fine Art, p. 87, . was the mother of
Alexander IV of Macedon
Alexander IV (Greek: ; 323/322– 309 BC), sometimes erroneously called Aegus in modern times, was the son of Alexander the Great (Alexander III of Macedon) and Princess Roxana of Bactria.
Birth
Alexander IV was the son of Alexander th ...
, who inherited his late father's throne in 323 BC (although the empire was soon divided in the Wars of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule ...
).
After an extended campaign putting down Sogdian resistance and founding military outposts manned by his Macedonian veterans, Alexander united Sogdiana with Bactria into one satrapy. The Sogdian nobleman and warlord Spitamenes
Spitamenes (Old Persian ''Spitamana''; Greek ''Σπιταμένης''; 370 BC – 328 BC) was a Sogdian warlordHolt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Cope ...
(370–328 BC), allied with Scythian tribes, led an uprising against Alexander's forces. This revolt was put down by Alexander and his generals Amyntas, Craterus
Craterus or Krateros ( el, Κρατερός; c. 370 BC – 321 BC) was a Macedonian general under Alexander the Great and one of the Diadochi. Throughout his life he was a loyal royalist and supporter of Alexander the Great.Anson, Edward M. (20 ...
, and Coenus, with the aid of native Bactrian and Sogdian troops.Holt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Copenhagen, Cologne: E. J. Brill, pp 64–65 (see also footnote #62 for mention of Sogdian troops), . With the Scythian and Sogdian rebels defeated, Spitamenes was allegedly betrayed by his own wife and beheaded. Pursuant with his own marriage to Roxana, Alexander encouraged his men to marry Sogdian women in order to discourage further revolt. This included Apama
Apama ( grc, Ἀπάμα, Apáma), sometimes known as Apama I or Apame I, was a Sogdian noblewoman and the wife of the first ruler of the Seleucid Empire, Seleucus I Nicator. They Susa weddings, married at Susa in 324 BC. According to Arrian, Apa ...
, daughter of the rebel Spitamenes, who wed Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
and bore him a son and future heir to the Seleucid throne.Magill, Frank N. et al. (1998), ''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography, Volume 1'', Pasadena, Chicago, London,: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, Salem Press, p. 1010, . According to the Roman historian Appian
Appian of Alexandria (; grc-gre, Ἀππιανὸς Ἀλεξανδρεύς ''Appianòs Alexandreús''; la, Appianus Alexandrinus; ) was a Greek historian with Roman citizenship who flourished during the reigns of Emperors of Rome Trajan, Ha ...
, Seleucus I named three new Hellenistic cities in Asia after her (see '' Apamea'').
The military power of the Sogdians never recovered. Subsequently, Sogdiana formed part of the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Ind ...
, a breakaway state from the Seleucid Empire founded in 248 BC by Diodotus I
Diodotus I Soter (Greek: , ''Diódotos Sōtḗr''; c. 315-300 BC – c. 235 BC), was the first Hellenistic King of Bactria. Diodotus became independent of the Seleucid empire around 255 or 245 BC, and established the Diodotid Bactrian Kingdom, w ...
, for roughly a century. Euthydemus I
Euthydemus I (Greek: , ''Euthydemos'') c. 260 BC – 200/195 BC) was a Greco-Bactrian king and founder of the Euthydemid dynasty. He is thought to have originally been a governor (Satrap) of Sogdia, who seized the throne by force from Diodotus I ...
, a former satrap of Sogdiana, seems to have held the Sogdian territory as a rival claimant to the Greco-Bactrian throne; his coins were later copied locally and bore Aramaic inscriptions
The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the society and history of the ancient Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occ ...
. The Greco-Bactrian king Eucratides I
Eucratides I the Great ( Koinē Greek: , ''Eúkratides Mégas'') (reigned 172/171–145 BC) was one of the most important Greco-Bactrian kings. Eucratides overthrew the Euthydemid dynasty and restored the Diodotids to power. He fought agains ...
may have recovered sovereignty of Sogdia temporarily.
Saka and Kushan periods (146 BC-260 AD)
 Finally Sogdia was occupied by
Finally Sogdia was occupied by nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
s when the Sakas
The Saka (Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who histor ...
overran the Greco-Bactrian kingdom
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the Ind ...
around 145 BC, soon followed by the Yuezhi
The Yuezhi (;) were an ancient people first described in Chinese histories as nomadic pastoralists living in an arid grassland area in the western part of the modern Chinese province of Gansu, during the 1st millennium BC. After a major defeat ...
, the nomadic predecessors of the Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
. From then until about 40 BC the Yuezhi tepidly minted coins imitating and still bearing the images of the Greco-Bactrian kings Eucratides I and Heliocles I
Heliocles I ( grc, Ἡλιοκλῆς, Helioklēs; reigned 145–120 BCE) was a Greco-Bactrian king, brother and successor of Eucratides the Great, and considered (along with his co-ruler and son/nephew Heliocles II) the last Greek king to reign ...
.Michon, Daniel (2015), ''Archaeology and Religion in Early Northwest India: History, Theory, Practice'', London, New York, New Delhi: Routledge, pp 112–123, .
The Yuezhis were visited in Transoxiana
Transoxiana or Transoxania (Land beyond the Oxus) is the Latin name for a region and civilization located in lower Central Asia roughly corresponding to modern-day eastern Uzbekistan, western Tajikistan, parts of southern Kazakhstan, parts of Tu ...
by a Chinese mission, led by Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian (; died c. 114) was a Chinese official and diplomat who served as an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the late 2nd century BC during the Han dynasty. He was one of the first official diplomats to bring back valuable inf ...
in 126 BC, which sought an offensive alliance with the Yuezhi against the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 20 ...
. Zhang Qian, who spent a year in Transoxiana and Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
, wrote a detailed account in the ''Shiji'', which gives considerable insight into the situation in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
at the time. The request for an alliance was denied by the son of the slain Yuezhi king, who preferred to maintain peace in Transoxiana rather than seek revenge.
 Zhang Qian also reported:
From the 1st century AD, the Yuezhi morphed into the powerful
Zhang Qian also reported:
From the 1st century AD, the Yuezhi morphed into the powerful Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
, covering an area from Sogdia to eastern India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
. The Kushan Empire became the center of the profitable Central Asian commerce. They began minting unique coins bearing the faces of their own rulers. They are related to have collaborated militarily with the Chinese against nomadic incursion, particularly when they allied with the Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
general Ban Chao
Ban Chao (; 32–102 CE), courtesy name Zhongsheng, was a Chinese diplomat, explorer, and military general of the Eastern Han Dynasty. He was born in Fufeng, now Xianyang, Shaanxi. Three of his family members—father Ban Biao, elder brother B ...
against the Sogdians in 84, when the latter were trying to support a revolt by the king of Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan. ...
.de Crespigny, Rafe. (2007). ''A Biographical Dictionary of Later Han to the Three Kingdoms (23–220 AD)''. Leiden: Koninklijke Brill. page 5-6. .
Sasanian satrapy (260-479 AD)
Historical knowledge about Sogdia is somewhat hazy during the period of theParthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
(247 BC – 224 AD) in Persia.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 5, .Mark J. Dresden (2003), "Sogdian Language and Literature", in Ehsan Yarshater, The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol III: The Seleucid, Parthian, and Sasanian Periods, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 1217, . The subsequent Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
of Persia conquered and incorporated Sogdia as a satrapy in 260, an inscription dating to the reign of Shapur I claiming "Sogdia, to the mountains of Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
" as his territory, and noting that its limits formed the northeastern Sasanian borderlands with the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
. However, by the 5th century the region was captured by the rival Hephthalite Empire
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian languages, Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Cen ...
.
Hephthalite conquest of Sogdiana (479-557 AD)
 The
The Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
conquered the territory of Sogdiana, and incorporated it into their Empire, around 479 AD, as this is the date of the last known independent embassy of the Sogdians to China.
The Hephthalites may have built major fortified Hippodamian
Hippodamus of Miletus (; Greek: Ἱππόδαμος ὁ Μιλήσιος, ''Hippodamos ho Milesios''; 498 – 408 BC) was an ancient Greek architect, urban planner, physician, mathematician, meteorologist and philosopher, who is considered to ...
cities (rectangular walls with an orthogonal network of streets) in Sogdiana, such as Bukhara
Bukhara ( Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara for at least five millennia, and the city ...
and Panjikent
, image_skyline = Pajakent Bazaar1.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Panjakent Bazaar
, image_flag =
, image_seal =
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Tajikistan#West Asia
, pushpin_relief = yes
, pushpin_label_position =
, pushp ...
, as they had also in Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
, continuing the city-building efforts of the Kidarites
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna, and in Eur ...
. The Hephthalites probably ruled over a confederation of local rulers or governors, linked through alliance agreements. One of these vassals may have been Asbar, ruler of Vardanzi, who also minted his own coinage during the period.
 The wealth of the Sasanian ransoms and tributes to the Hephthalites may have been reinvested in Sogdia, possibly explaining the prosperity of the region from that time. Sogdia, at the center of a new
The wealth of the Sasanian ransoms and tributes to the Hephthalites may have been reinvested in Sogdia, possibly explaining the prosperity of the region from that time. Sogdia, at the center of a new Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
between China to the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
became extremely prosperous under its nomadic elites. The Hephthalites took on the role of major intermediary on the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
, after their great predecessor the Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
, and contracted local Sogdians :''This category lists articles related to historical Iranian peoples''
Historical
Peoples
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples ...
to carry on the trade of silk and other luxury goods between the China Empire and the Sasanian Empire.
Because of the Hephthalite occupation of Sogdia, the original coinage of Sogdia came to be flooded by the influx of Sasanian coins received as a tribute to the Hephthalites. This coinage then spread along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
. The symbol of the Hephthalites appears on the residual coinage of Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, probably as a consequence of the Hephthalite control of Sogdia, and becomes prominent in Sogdian coinage from 500 to 700 AD, including in the coinage of their indigenous successors the Ikhshid
''Ikhshid'' ( sog, xšyδ, ) was the princely title of the Iranian rulers of Soghdia and the Ferghana Valley in Transoxiana during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods. The title is of Iranian origin; scholars have derived it variously from ...
s (642-755 AD), ending with the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana.
Turkic Khaganates (557-742 AD)
The Turks of theFirst Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of B ...
and the Sasanians under Khosrow I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩; New Persian: []), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ( [] "the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from ...
allied against the Hephthalites and defeated them after an eight-day battle near Qarshi
Qarshi ( uz, Qarshi/Қарши, ; fa, نخشب ''Nakhshab'') is a city in southern Uzbekistan. It is the capital of Qashqadaryo Region. Administratively, Qarshi is a district-level city, that includes the urban-type settlement Qashqadaryo. It ...
, the Battle of Bukhara, perhaps in 557. The Turks retained the area north of the Oxus, including all of Sogdia, while the Sasanians obtained the areas south of it. The Turks fragmented in 581, and the Western Turkic Khaganate
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after ...
took over in Sogdia.
Archaeological remains suggest that the Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
probably became the main trading partners of the Sogdians, as appears from the tomb of the Sogdian trader An Jia
The Tomb of Ān Jiā, also sometimes read Ān Qié (Chinese: 安伽墓石門 圍屏石榻, "Stone tomb gate and couch of Anjia"), is a Northern Zhou period (557-581 CE) funeral monument to a Sogdian nobleman named "Anjia" in the Chinese epitaph. T ...
. The Turks also appear in great numbers in the Afrasiab murals
The Afrasiab murals, also called the Paintings of the Ambassadors, is a rare example of Sogdian art. It was discovered in 1965 when the local authorities decided to construct a road in the middle of Afrāsiāb mound, the old site of pre-Mongol Sam ...
of Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, where they are probably shown attending the reception by the local Sogdian ruler Varkhuman
Varkhuman, also Vargoman (Chinese: 拂呼缦 ''Fúhūmàn'', c. 640-670 CE) was an Ikhshid (King) of Sogdia, residing in the city of Samarkand in the 7th century CE. He succeeded King Shishpin. He is known from the Afrasiab murals of Afrasiyab i ...
in the 7th century AD. These paintings suggest that Sogdia was a very cosmopolitan environment at that time, as delegates of various nations, including Chinese and Korean delegates, are also shown. From around 650, China led the conquest of the Western Turks
The conquest of the Western Turks, known as the Western Tujue in Chinese sources, was a military campaign in 655–657 led by the Tang dynasty generals Su Dingfang and Cheng Zhijie against the Western Turkic Khaganate ruled by Ashina Helu. The ...
, and the Sogdian rulers such as Varkhuman
Varkhuman, also Vargoman (Chinese: 拂呼缦 ''Fúhūmàn'', c. 640-670 CE) was an Ikhshid (King) of Sogdia, residing in the city of Samarkand in the 7th century CE. He succeeded King Shishpin. He is known from the Afrasiab murals of Afrasiyab i ...
as well as the Western Turks
The Western Turkic Khaganate () or Onoq Khaganate ( otk, 𐰆𐰣:𐰸:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, On oq budun, Ten arrow people) was a Turkic khaganate in Eurasia, formed as a result of the wars in the beginning of the 7th century (593–603 CE) after t ...
all became nominal vassals of China, as part of the Anxi Protectorate
The Protectorate General to Pacify the West (Anxi Grand Protectorate), initially the Protectorate to Pacify the West (Anxi Protectorate), was a protectorate (640 – ) established by the Chinese Tang dynasty in 640 to control the Tarim Basin. Th ...
of the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
, until the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana.

Arab Muslim conquest (8th century AD)
Qutayba ibn Muslim
Abū Ḥafṣ Qutayba ibn Abī Ṣāliḥ Muslim ibn ʿAmr al-Bāhilī ( ar, أبو حفص قتيبة بن أبي صالح مسلم بن عمرو الباهلي; 669–715/6) was an Arab commander of the Umayyad Caliphate who became governor of ...
(669–716), Governor of Greater Khorasan
Greater Khorāsān,Dabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 or Khorāsān ( pal, Xwarāsān; fa, خراسان ), is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plat ...
under the Umayyad Caliphate
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by th ...
(661–750), initiated the Muslim conquest of Sogdia during the early 8th century, with the local ruler of Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
offering him aid as an Umayyad ally. However, when his successor al-Jarrah ibn Abdallah
Abu Uqba al-Jarrah ibn Abdallah al-Hakami ( ar, أبو عقبة الجراح بن عبد الله الحكمي, Abū ʿUqba al-Jarrāḥ ibn ʿAbd Allāh al-Ḥakamī) was an Arab nobleman and general of the Hakami tribe. During the course of th ...
governed Khorasan (717–719), many native Sogdians, who had converted to Islam, began to revolt when they were no longer exempt from paying the tax on non-Muslims, the ''jizya
Jizya ( ar, جِزْيَة / ) is a per capita yearly taxation historically levied in the form of financial charge on dhimmis, that is, permanent non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Islamic law. The jizya tax has been understood in ...
,'' because of a new law stating that proof of circumcision
Circumcision is a procedure that removes the foreskin from the human penis. In the most common form of the operation, the foreskin is extended with forceps, then a circumcision device may be placed, after which the foreskin is excised. Top ...
and literacy in the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
was necessary for new converts.Litvinski, B. A., A. H. Jalilov, A. I. Kolesnikov (1999), "The Arab Conquest", in ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia: Volume III, the Crossroads of Civilizations: A.D. 250–750'', eds B. A. Litvinski, Zhang Guangda, and R. Shabani Samghabadi, Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, p. 459. With the aid of the Turkic Turgesh, the Sogdians were able to expel the Umayyad Arab garrison from Samarkand, and Umayyad attempts to restore power there were rebuffed until the arrival of Sa'id ibn Amr al-Harashi
Sa'id ibn Amr al-Harashi ( ar, سعيد بن عمرو الحرشي, Saʿīd ibn ʿAmr al-Ḥarashī, ) was a prominent general and governor of the Umayyad Caliphate, who played an important role in the Arab–Khazar wars.
Biography
Sa'id ibn Am ...
(fl. 720–735). The Sogdian ruler (i.e. ''ikhshid
''Ikhshid'' ( sog, xšyδ, ) was the princely title of the Iranian rulers of Soghdia and the Ferghana Valley in Transoxiana during the pre-Islamic and early Islamic periods. The title is of Iranian origin; scholars have derived it variously from ...
'') of Samarkand, Gurak
Gurak or Ghurak (Chinese: 乌勒伽 ''wūlèjiā'') was a medieval Sogdian ruler in Central Asia during the period of the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. In 710, he was installed as king ( Sogdian: ''ikhshid'') of Samarkand after the populace over ...
, who had previously overthrown the pro-Umayyad Sogdian ruler Tarkhun
Tarkhun ( Chinese: 突昏 ''tū-hūn'', died 710) was a Sogdian ruler ( Sogdian: ''ikhshid'') of Samarkand from somewhere 705-707 to 710. After receiving the news of the capture of Bukhara by the Umayyad general Qutayba ibn Muslim in 709, Tarkhun ...
in 710, decided that resistance against al-Harashi's large Arab force was pointless, and thereafter persuaded his followers to declare allegiance to the Umayyad governor. Divashtich (r. 706–722), the Sogdian ruler of Panjakent, led his forces to the Zarafshan Range
The Zarafshan Range (russian: Зеравшанский хребет, ''Zeravšanskij hrebet''; tg, Зарафшон; uz, Zarafshon; also Zeravshan or Zarafshon; from Persian ''Zar-afshān'', meaning "the sprayer of gold") is a mountain rang ...
(near modern Zarafshan, Tajikistan
tg, Зарафшан
, settlement_type=Town and Jamoat
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_seal =
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Tajikistan
, pushpin_label_position =bottom
...
), whereas the Sogdians following Karzanj, the ruler of Pai (modern Kattakurgan, Uzbekistan
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag =
, image_seal =
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Uzbekistan
, pushpin_label_po ...
), fled to the Principality of Farghana, where their ruler at-Tar (or Alutar) promised them safety and refuge from the Umayyads. However, at-Tar secretly informed al-Harashi of the Sogdians hiding in Khujand
Khujand ( tg, Хуҷанд, Khujand; Uzbek: Хўжанд, romanized: Хo'jand; fa, خجند, Khojand), sometimes spelled Khodjent and known as Leninabad (russian: Ленинабад, Leninabad; tg, Ленинобод, Leninobod; fa, لنی ...
, who were then slaughtered by al-Harashi's forces after their arrival.
 The Umayyads
The Umayyads fell
A fell (from Old Norse ''fell'', ''fjall'', "mountain"Falk and Torp (2006:161).) is a high and barren landscape feature, such as a mountain or moor-covered hill. The term is most often employed in Fennoscandia, Iceland, the Isle of Man, pa ...
in 750 to the Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttal ...
, which quickly asserted itself in Central Asia after winning the Battle of Talas
The Battle of Talas or Battle of Artlakh (; ar, معركة نهر طلاس, translit=Maʿrakat nahr Ṭalās, Persian: Nabard-i Tarāz) was a military encounter and engagement between the Abbasid Caliphate along with its ally, the Tibetan Empi ...
(along the Talas River
The Talas ( Kyrgyz, kk, Талас) is a river that rises in the Talas Region of Kyrgyzstan and flows west into Kazakhstan. The river is long and has a basin area of .
Course
It is formed from the confluence of the Karakol and Uch-Koshoy and ...
in modern Talas Oblast, Kyrgyzstan) in 751, against the Chinese Tang Dynasty. This conflict incidentally introduced Chinese papermaking
Papermaking is the manufacture of paper and cardboard, which are used widely for printing, writing, and packaging, among many other purposes. Today almost all paper is made using industrial machinery, while handmade paper survives as a speciali ...
to the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
.Hanks, Reuel R. (2010), ''Global Security Watch: Central Asia'', Santa Barbara, Denver, Oxford: Praeger, p. 4. The cultural consequences and political ramifications of this battle meant the retreat of the Chinese empire from Central Asia. It also allowed for the rise of the Samanid Empire
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan origin. The empire was centred in ...
(819–999), a Persian state centered at Bukhara (in what is now modern Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
) that nominally observed the Abbasids as their overlord
An overlord in the English feudal system was a lord of a manor who had subinfeudated a particular manor, estate or fee, to a tenant. The tenant thenceforth owed to the overlord one of a variety of services, usually military service or ser ...
s, yet retained a great deal of autonomy and upheld the mercantile legacy of the Sogdians. Yet the Sogdian language
The Sogdian language was an Eastern Iranian language spoken mainly in the Central Asian region of Sogdia (capital: Samarkand; other chief cities: Panjakent, Fergana, Khujand, and Bukhara), located in modern-day Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Kazakh ...
gradually declined in favor of the Persian language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken an ...
of the Samanids (the ancestor to the modern Tajik language
Tajik (Tajik: , , ), also called Tajiki Persian (Tajik: , , ) or Tajiki, is the variety of Persian spoken in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan by Tajiks. It is closely related to neighbouring Dari with which it forms a continuum of mutually intelligi ...
), the spoken language of renowned poets and intellectuals of the age such as Ferdowsi
, image = Statue of Ferdowsi in Tus, Iran 3 (cropped).jpg
, image_size =
, caption = Statue of Ferdowsi in Tus by Abolhassan Sadighi
, birth_date = 940
, birth_place = Tus, Samanid Empire
, death_date = 1019 or 1025 (87 years old)
, d ...
(940–1020). So too did the original religions of the Sogdians decline; Zoroastrianism, Buddhism, Manichaeism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (A ...
, and Nestorian Christianity
The Church of the East ( syc, ܥܕܬܐ ܕܡܕܢܚܐ, ''ʿĒḏtā d-Maḏenḥā'') or the East Syriac Church, also called the Church of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, the Persian Church, the Assyrian Church, the Babylonian Church or the Nestorian C ...
disappeared in the region by the end of the Samanid period. The Samanids were also responsible for converting the surrounding Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, which presaged the conquest of their empire in 999 by an Islamic Turkic power, the Kara-Khanid Khanate
The Kara-Khanid Khanate (; ), also known as the Karakhanids, Qarakhanids, Ilek Khanids or the Afrasiabids (), was a Turkic khanate that ruled Central Asia in the 9th through the early 13th century. The dynastic names of Karakhanids and Ilek K ...
(840–1212).
During the early 13th century, Khwarezmia was invaded by the early Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
and its ruler Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
destroyed the once vibrant cities of Bukhara and Samarkand. However, in 1370, Samarkand saw a revival as the capital of the Timurid Empire
The Timurid Empire ( chg, , fa, ), self-designated as Gurkani (Chagatai language, Chagatai: کورگن, ''Küregen''; fa, , ''Gūrkāniyān''), was a PersianateB.F. Manz, ''"Tīmūr Lang"'', in Encyclopaedia of Islam, Online Edition, 2006 Tu ...
. The Turko-Mongol
The Turco-Mongol or Turko-Mongol tradition was an ethnocultural synthesis that arose in Asia during the 14th century, among the ruling elites of the Golden Horde and the Chagatai Khanate. The ruling Mongol elites of these Khanates eventually a ...
ruler Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
forcefully brought artisans and intellectuals from across Asia to Samarkand, transforming it not only into a trade hub but also one of the most important cities of the Islamic world.
Economy and diplomacy
Central Asia and the Silk Road
Most merchants did not travel the entireSilk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
, but would trade goods through middlemen based in oasis towns, such as Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
or Dunhuang
Dunhuang () is a county-level city in Northwestern Gansu Province, Western China. According to the 2010 Chinese census, the city has a population of 186,027, though 2019 estimates put the city's population at about 191,800. Dunhuang was a major s ...
. The Sogdians, however, established a trading network across the 1500 miles from Sogdiana to China. In fact, the Sogdians turned their energies to trade so thoroughly that the Saka of the Kingdom of Khotan
The Kingdom of Khotan was an ancient Buddhist Saka kingdom located on the branch of the Silk Road that ran along the southern edge of the Taklamakan Desert in the Tarim Basin (modern Xinjiang, China). The ancient capital was originally sited to ...
called all merchants ''suli'', "Sogdian", whatever their culture or ethnicity. The Sogdians had learnt to become expert traders from the Kushans, together with whom they initially controlled trade in the Ferghana Valley
The Fergana Valley (; ; ) in Central Asia lies mainly in eastern Uzbekistan, but also extends into southern Kyrgyzstan and northern Tajikistan.
Divided into three republics of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse and in the ...
and Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
during the 'birth' of the Silk Road. Later, they became the primary middlemen after the demise of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, 貴霜 ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, ...
.
Unlike the empires of antiquity, the Sogdian region was not a territory confined within fixed borders, but rather a network of city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
s, from one oasis to another, linking Sogdiana to Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium' ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area, the List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous ...
, Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Sogdian contacts with China were initiated by the embassy of the Chinese explorer Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian (; died c. 114) was a Chinese official and diplomat who served as an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the late 2nd century BC during the Han dynasty. He was one of the first official diplomats to bring back valuable inf ...
during the reign of Emperor Wu (r. 141–87 BC) of the former Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
. Zhang wrote a report of his visit to the Western Regions
The Western Regions or Xiyu (Hsi-yü; ) was a historical name specified in the Chinese chronicles between the 3rd century BC to the 8th century AD that referred to the regions west of Yumen Pass, most often Central Asia or sometimes more sp ...
in Central Asia and named the area of Sogdiana as "Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
".
Following Zhang Qian's embassy and report, commercial Chinese relations with Central Asia and Sogdiana flourished, as many Chinese missions were sent throughout the 1st century BC. In his ''Shiji
''Records of the Grand Historian'', also known by its Chinese name ''Shiji'', is a monumental history of China that is the first of China's 24 dynastic histories. The ''Records'' was written in the early 1st century by the ancient Chinese his ...
'' published in 94 BC, Chinese historian Sima Qian
Sima Qian (; ; ) was a Chinese historian of the early Han dynasty (206AD220). He is considered the father of Chinese historiography for his ''Records of the Grand Historian'', a general history of China covering more than two thousand years be ...
remarked that "the largest of these embassies to foreign states numbered several hundred persons, while even the smaller parties included over 100 members ... In the course of one year anywhere from five to six to over ten parties would be sent out." In terms of the silk trade, the Sogdians also served as middlemen between the Chinese Han Empire and the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conqu ...
of the Middle East and West Asia. Sogdians played a major role in facilitating trade between China and Central Asia along the Silk Roads as late as the 10th century, their language serving as a ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' for Asian trade as far back as the 4th century.
Subsequent to their domination by Alexander the Great, the Sogdians from the city of Marakanda (Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
) became dominant as traveling merchants, occupying a key position along the ancient Silk Road. They played an active role in the spread of faiths such as Manicheism
Manichaeism (;
in New Persian ; ) is a former major religionR. van den Broek, Wouter J. Hanegraaff ''Gnosis and Hermeticism from Antiquity to Modern Times''SUNY Press, 1998 p. 37 founded in the 3rd century AD by the Parthian prophet Mani (AD ...
, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
along the Silk Road. The Chinese ''Sui Shu'' (''Book of Sui
The ''Book of Sui'' (''Suí Shū'') is the official history of the Sui dynasty. It ranks among the official Twenty-Four Histories of imperial China. It was written by Yan Shigu, Kong Yingda, and Zhangsun Wuji, with Wei Zheng as the lead author. ...
'') describes Sogdians as "skilled merchants" who attracted many foreign traders to their land to engage in commerce.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 134. They were described by the Chinese as born merchants, learning their commercial skills at an early age. It appears from sources, such as documents found by Sir Aurel Stein
Sir Marc Aurel Stein,
( hu, Stein Márk Aurél; 26 November 1862 – 26 October 1943) was a Hungarian-born British archaeologist, primarily known for his explorations and archaeological discoveries in Central Asia. He was also a professor at ...
and others, that by the 4th century they may have monopolized trade between India and China. A letter written by Sogdian merchants dated 313 AD and found in the ruins of a watchtower in Gansu
Gansu (, ; alternately romanized as Kansu) is a province in Northwest China. Its capital and largest city is Lanzhou, in the southeast part of the province.
The seventh-largest administrative district by area at , Gansu lies between the Tibe ...
, was intended to be sent to merchants in Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, warning them that after Liu Cong of Han Zhao
The Han Zhao (; 304–329 AD), or Former Zhao (), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Xiongnu people during the Sixteen Kingdoms period of Chinese history. In Chinese historiography, it was given two conditional state titles, the Northern ...
sacked Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
and the Jin emperor fled the capital, there was no worthwhile business there for Indian and Sogdian merchants.Howard, Michael C., Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel, McFarland & Company, 2012, pp 133–34. Furthermore, in 568 AD, a Turko-Sogdian delegation travelled to the Roman emperor in Constantinople to obtain permission to trade and in the following years commercial activity between the states flourished. Put simply, the Sogdians dominated trade along the Silk Road from the 2nd century BC until the 10th century.
Suyab
Suyab ( fa, سوی آب; Middle Chinese: /suʌiH jiᴇp̚/), also known as ''Ordukent'' (modern-day ''Ak-Beshim''), was an ancient Silk Road city located some 50 km east from Bishkek, and 8 km west southwest from Tokmok, in the Chu r ...
and Talas in modern-day Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
were the main Sogdian centers in the north that dominated the caravan routes of the 6th to 8th centuries. Their commercial interests were protected by the resurgent military power of the Göktürks
The Göktürks, Celestial Turks or Blue Turks ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰉𐰆𐰑𐰣, Türük Bodun; ; ) were a nomadic confederation of Turkic peoples in medieval Inner Asia. The Göktürks, under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan (d. 552) a ...
, whose empire was built on the political power of the Ashina clan and economic clout of the Sogdians. Sogdian trade, with some interruptions, continued into the 9th century. For instance, camels, women, girls, silver, and gold were seized from Sogdia during a raid by Qapaghan Qaghan
Qapaghan or Qapghan Qaghan ( otk, 𐰴𐰯𐰍𐰣:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Qapaγan qaγan, meaning "the conqueror", , Xiao'erjing: ٿِيًا شًا, Dungan: Чяншан, , also called Bögü Qaghan ( otk, 𐰋𐰇𐰏:𐰴𐰍𐰣, Bögü qaγan) in Ba ...
(692–716), ruler of the Second Turkic Khaganate
The Second Turkic Khaganate ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰰:𐰃𐰠, Türük el, State of the Turks, , known as ''Turk Bilge Qaghan country'' ( otk, 𐱅𐰇𐰼𐰝:𐰋𐰃𐰠𐰏𐰀:𐰴𐰍𐰣:𐰃𐰠𐰭𐰀, Türük Bilgä Qaγan eli) in Ba ...
. In the 10th century, Sogdiana was incorporated into the Uyghur Khaganate, Uighur Empire, which Kingdom of Qocho, until 840 encompassed northern Central Asia. This khaganate obtained enormous deliveries of silk from Tang China in exchange for horses, in turn relying on the Sogdians to sell much of this silk further west. Peter B. Golden writes that the Uyghurs not only adopted the Sogdian alphabet, writing system and religious faiths of the Sogdians, such as Manichaeism, Buddhism, and Christianity, but also looked to the Sogdians as "mentors", while gradually replacing them in their roles as Silk Road traders and Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves, purveyors of culture. Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, Muslim geographers of the 10th century drew upon Sogdian records dating to 750–840. After the end of History of the Uyghur people, the Uyghur Empire, Sogdian trade underwent a crisis. Following the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana in the 8th century, the Samanid dynasty, Samanids resumed trade on the northwestern road leading to the Khazars and the Urals and the northeastern one toward the nearby Turkic tribes.
During the 5th and 6th century, many Sogdians took up residence in the Hexi Corridor, where they retained autonomy in terms of governance and had a designated official administrator known as a ''Sabao'', which suggests their importance to the socioeconomic structure of China. The Sogdian influence on trade in China is also made apparent by a Chinese document which lists taxes paid on caravan trade in the Turpan region and shows that twenty-nine out of the thirty-five commercial transactions involved Sogdian merchants, and in thirteen of those cases both the buyer and the seller were Sogdian. Trade goods brought to China included grapes, alfalfa, and Sassanid Empire, Sassanian silverware, as well as glass containers, Mediterranean coral, brass Buddhist images, Roman wool cloth, and Amber Road, Baltic amber. These were exchanged for Chinese paper, copper, and silk. In the 7th century, the Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Xuanzang noted with approval that Sogdian boys were taught to read and write at the age of five, though their skill was turned to trade, disappointing the scholarly Xuanzang. He also recorded the Sogdians working in other capacities such as farmers, carpetweavers, glassmakers, and woodcarvers.
Trade and diplomacy with the Byzantine Empire
Shortly after the smuggling of silkworm eggs into the Byzantine Empire from China by Nestorian Christian monks, the 6th-century Byzantine historian Menander Protector writes of how the Sogdians attempted to establish a direct trade of Chinese silk with theByzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
. After forming an alliance with the Sasanian ruler Khosrow I
Khosrow I (also spelled Khosrau, Khusro or Chosroes; pal, 𐭧𐭥𐭮𐭫𐭥𐭣𐭩; New Persian: []), traditionally known by his epithet of Anushirvan ( [] "the Immortal Soul"), was the Sasanian Empire, Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from ...
to defeat the Hephthalite Empire, Istämi, the Göktürk ruler of the First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of B ...
, was approached by Sogdian merchants requesting permission to seek an audience with the Sassanid king of kings for the privilege of traveling through Persian territories in order to trade with the Byzantines.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies'', the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel, McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 133. Istämi refused the first request, but when he sanctioned the second one and had the Sogdian embassy sent to the Sassanid king, the latter had the members of the embassy poisoned. Maniah, a Sogdian diplomat, convinced Istämi to send an embassy directly to Byzantium's capital Constantinople, which arrived in 568 and offered not only silk as a gift to Byzantine ruler Justin II, but also proposed an alliance against Sassanid Persia. Justin II agreed and sent an embassy to the Turkic Khaganate, ensuring the direct silk trade desired by the Sogdians.
 It appears, however, that direct trade with the Sogdians remained limited in light of the small amount of Roman currency, Roman and Byzantine coinage, Byzantine coins found in Central Asian and Chinese archaeological sites belonging to this era. Although Sino-Roman relations, Roman embassies apparently reached Han China from 166 AD onwards, and the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans imported Han Chinese silk while the Han-dynasty Chinese imported Roman glasswares as discovered in their tombs, Valerie Hansen (2012) wrote that no Roman coins from the Roman Republic (507–27 BC) or the Principate (27 BC – 330 AD) era of the Roman Empire have been found in China.Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 97, . However, Warwick Ball (2016) upends this notion by pointing to a hoard of sixteen Roman coins found at Xi'an, China (formerly Chang'an), dated to the reigns of various emperors from Tiberius (14–37 AD) to Aurelian (270–275 AD).Warwick Ball (2016), ''Rome in the East: Transformation of an Empire'', 2nd edition, London & New York: Routledge, , p. 154. The earliest gold Solidus (coin), ''solidus'' coins from the Eastern Roman Empire found in China date to the reign of Byzantine emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450) and altogether only forty-eight of them have been found (compared to thirteen-hundred silver coins) in Xinjiang and the rest of China. The use of silver coins in Turfan persisted long after the Tang campaign against Karakhoja and Chinese conquest of 640, with a gradual adoption of Ancient Chinese coinage, Chinese bronze coinage over the course of the 7th century. The fact that these Eastern Roman coins were almost always found with Monetary history of Iran, Sasanian Persian silver coins and Eastern Roman gold coins were used more as ceremonial objects like talismans, confirms the pre-eminent importance of Greater Iran in Chinese Silk Road commerce of Central Asia compared to Eastern Rome.
It appears, however, that direct trade with the Sogdians remained limited in light of the small amount of Roman currency, Roman and Byzantine coinage, Byzantine coins found in Central Asian and Chinese archaeological sites belonging to this era. Although Sino-Roman relations, Roman embassies apparently reached Han China from 166 AD onwards, and the Ancient Rome, ancient Romans imported Han Chinese silk while the Han-dynasty Chinese imported Roman glasswares as discovered in their tombs, Valerie Hansen (2012) wrote that no Roman coins from the Roman Republic (507–27 BC) or the Principate (27 BC – 330 AD) era of the Roman Empire have been found in China.Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 97, . However, Warwick Ball (2016) upends this notion by pointing to a hoard of sixteen Roman coins found at Xi'an, China (formerly Chang'an), dated to the reigns of various emperors from Tiberius (14–37 AD) to Aurelian (270–275 AD).Warwick Ball (2016), ''Rome in the East: Transformation of an Empire'', 2nd edition, London & New York: Routledge, , p. 154. The earliest gold Solidus (coin), ''solidus'' coins from the Eastern Roman Empire found in China date to the reign of Byzantine emperor Theodosius II (r. 408–450) and altogether only forty-eight of them have been found (compared to thirteen-hundred silver coins) in Xinjiang and the rest of China. The use of silver coins in Turfan persisted long after the Tang campaign against Karakhoja and Chinese conquest of 640, with a gradual adoption of Ancient Chinese coinage, Chinese bronze coinage over the course of the 7th century. The fact that these Eastern Roman coins were almost always found with Monetary history of Iran, Sasanian Persian silver coins and Eastern Roman gold coins were used more as ceremonial objects like talismans, confirms the pre-eminent importance of Greater Iran in Chinese Silk Road commerce of Central Asia compared to Eastern Rome.
Sogdian traders in the Tarim Basin
 The Kizil Caves near Kucha, mid-way in the Tarim Basin, record many scenes of traders from Central Asia in the 5-6th century: these combine influence from the Eastern Iran sphere, at that time occupied by the
The Kizil Caves near Kucha, mid-way in the Tarim Basin, record many scenes of traders from Central Asia in the 5-6th century: these combine influence from the Eastern Iran sphere, at that time occupied by the Sasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
and the Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
, with strong Sogdian cultural elements. Sogdia, at the center of a new Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
between China to the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
became extremely prosperous around that time.
The style of this period in Kizil is characterized by strong Iranian-Sogdian elements probably brought with intense Sogdian-Tocharian trade, the influence of which is especially apparent in the Central-Asian caftans with Sogdian textile designs, as well as Sogdian longswords of many of the figures. Other characteristic Sogdian designs are animals, such as ducks, within pearl medallions.
Sogdian merchants, generals, and statesmen in Imperial China
Aside from the Sogdians of Central Asia who acted as middlemen in the Silk Road trade, other Sogdians settled down in China for generations. Many Sogdians lived inLuoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, capital of the Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin Dynasty (266–420), but fled following the collapse of the Jin dynasty (266–420), Jin Dynasty's control over northern China in 311 AD and the rise of northern nomadic tribes. Still, some Sogdians continued living in Gansu. A community of Sogdians remained in the Northern Liang capital of Wuwei, Gansu, Wuwei, but when the Northern Liang were defeated by the Northern Wei in 439 AD, many Sogdians were forcibly relocated to the Northern Wei capital of Datong, thereby fostering exchanges and trade for the new dynasty. Numerous :Commons:Central Asian objects of Northern Wei tombs, Central Asian objects have been found in Northern Wei tombs, such as the tomb of Feng Hetu.
Other Sogdians came from the west and took positions in Chinese society. The ''Bei shi'' describes how a Sogdian came from Anxi (western Sogdiana or Parthia) to China and became a ''sabao'' (薩保, from Sanskrit ''sarthavaha'', meaning caravan leader)Liu, Xinru, "The Silk Road: Overland Trade and Cultural Interactions in Eurasia", in ''Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History'', ed. Michael Adas, American Historical Association, Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2001, p. 168. who lived in Jiuquan during the Northern Wei (386 – 535 AD), and was the ancestor of An Tugen, a man who rose from a common merchant to become a top ranking minister of state for the Northern Qi (550 – 577 AD). Valerie Hansen asserts that around this time and extending into the Tang Dynasty (618 – 907 AD), the Sogdians "became the most influential of the non-Chinese groups resident in China". Two different types of Sogdians came to China, envoys and merchants. Sogdian envoys settled, marrying Chinese women, purchasing land, with newcomers living there permanently instead of returning to their homelands in Sogdiana. They were concentrated in large numbers around Luoyang and Chang'an, and also Xiangyang in present-day Hubei, building Zoroastrian Fire temple, temples to service their communities once they reached the threshold of roughly 100 households. From the Northern Qi to Tang periods, the leaders of these communities, the ''sabao'', were incorporated into the official hierarchy of state officials.
During the 6-7th centuries AD, Sogdian families living in China created important tombs with funerary epitaphs explaining the history of their illustrious houses. Their burial practices blended both Chinese forms such as carved funerary beds with Zoroastrian sensibilities in mind, such as separating the body from both the earth and water. :Template:Sogdian tombs in China, Sogdian tombs in China are among the most lavish of the period in this country, and are only inferior to Imperial tombs, suggesting that the Sogdian ''Sabao'' were among the wealthiest members of the population.
 In addition to being merchants, monks, and government officials, Sogdians also served as soldiers in the Tang military.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 135. An Lushan, whose father was Sogdian and mother a Gokturk, rose to the position of a military governor (''jiedushi'') in the northeast before leading the An Lushan Rebellion (755 – 763 AD), which split the loyalties of the Sogdians in China. The An Lushan rebellion was supported by many Sogdians, and in its aftermath many of them were slain or changed their names to escape their Sogdian heritage, so that little is known about the Sogdian presence in North China since that time. The former Yan rebel general Gao Juren of Goguryeo descent ordered a mass slaughter of West Asian (Central Asian)
In addition to being merchants, monks, and government officials, Sogdians also served as soldiers in the Tang military.Howard, Michael C., ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies, the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', McFarland & Company, 2012, p. 135. An Lushan, whose father was Sogdian and mother a Gokturk, rose to the position of a military governor (''jiedushi'') in the northeast before leading the An Lushan Rebellion (755 – 763 AD), which split the loyalties of the Sogdians in China. The An Lushan rebellion was supported by many Sogdians, and in its aftermath many of them were slain or changed their names to escape their Sogdian heritage, so that little is known about the Sogdian presence in North China since that time. The former Yan rebel general Gao Juren of Goguryeo descent ordered a mass slaughter of West Asian (Central Asian) Sogdians :''This category lists articles related to historical Iranian peoples''
Historical
Peoples
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples ...
in Fanyang, also known as Jicheng (Beijing), in Youzhou Ethnic issues in China#History, identifying them through their big noses and lances were used to impale their children when he rebelled against the rebel Yan emperor Shi Chaoyi An Lushan Rebellion#Implosion of Yan Dynasty and end of the rebellion, and defeated rival Yan dynasty forces under the Turk Ashina Chengqing, High nosed Sogdians were slaughtered in Youzhou in 761. Youzhou had Linzhou, another "protected" prefecture attached to it and Sogdians lived there in great numbers. because Gao Juren, like Tian Shengong wanted to defect to the Tang dynasty and wanted them to pubicly recognize and acknowledge him as a regional warlord and offered the slaughter of the Central Asian Hu "barbarians" as a blood sacrifice for the Tang court to acknowledge his alleigance without him giving up territory. according to the book, "History of An Lushan" (安祿山史記). Another source says the slaughter of the Hu barbarians serving Ashina Chengqing was done by Gao Juren in Fanyang in order to deprive him of his support base, since the Tiele, Tongluo, Sogdians and Turks were all Hu and supported the Turk Ashina Chengqing against the Mohe, Xi, Khitan and Goguryeo origin soldiers led by Gao Juren. Gao Juren was later killed by Li Huaixian, who was loyal to Shi Chaoyi. A massacre of foreign Arab and Persian Muslim merchants by former Yan rebel general Tian Shengong happened during the An Lushan rebellion in the Yangzhou massacre (760), since Tian Shengong was defecting to the Tang dynasty and wanted them to publicly recognized and acknowledge him, and the Tang court portrayed the war as between rebel hu barbarians of the Yan against Han Chinese of the Tang dynasty, Tian Shengong slaughtered foreigners as a blood sacrifice to prove he was loyal to the Han Chinese Tang dynasty state and for them to recognize him as a regional warlord without him giving up territory, and he killed other foreign Hu barbarian ethnicities as well whose ethnic groups were not specified, not only Arabs and Persians since it was directed against all foreigners.
Sogdians continued as active traders in China following the defeat of the rebellion, but many of them were compelled to hide their ethnic identity. A prominent case was An Chongzhang, Minister of War, and Duke of Liang who, in 756, asked Emperor Suzong of Tang to allow him to change his name to Li Baoyu because of his shame in sharing An (surname), the same surname with the rebel leader. This change of surnames was enacted retroactively for all of his family members, so that his ancestors would also be bestowed the Li (surname), surname Li.
The Nestorian Christians like the Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
n Priest Yisi of Balkh
), named for its green-tiled ''Gonbad'' ( prs, گُنبَد, dome), in July 2001
, pushpin_map=Afghanistan#Bactria#West Asia
, pushpin_relief=yes
, pushpin_label_position=bottom
, pushpin_mapsize=300
, pushpin_map_caption=Location in Afghanistan ...
helped the Tang dynasty general Guo Ziyi militarily crush the An Lushan rebellion, with Yisi personally acting as a military commander and Yisi and the Nestorian Church of the East were rewarded by the Tang dynasty with titles and positions as described in the Nestorian Stele.
Amoghavajra used his rituals against An Lushan while staying in Chang'an when it was occupied in 756 while the Tang dynasty crown prince and Xuanzong emperor had retreated to Sichuan. Amoghavajra's rituals were explicitly intended to introduced death, disaster and disease against An Lushan. As a result of Amoghavajrya's assistance in crushing An Lushan, Estoteric Buddhism became the official state Buddhist sect supported by the Tang dynasty, "Imperial Buddhism" with state funding and backing for writing scriptures, and constructing monasteries and temples. The disciples of Amoghavajra did ceremonies for the state and emperor. Tang dynasty Emperor Suzong was crowned as cakravartin by Amoghavajra after victory against An Lushan in 759 and he had invoked the Acala vidyaraja against An Lushan. The Tang dynasty crown prince Li Heng (later Suzong) also received important strategic military information from Chang'an when it was occupied by An Lushan though secret message sent by Amoghavajra.
Epitaphs were found dating from the Tang dynasty of a Christian couple in Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
of a Nestorian Christian Sogdian woman, who Lady An (安氏) who died in 821 and her Nestorian Christian Han Chinese husband, Hua Xian (花献) who died in 827. These Han Chinese Christian men may have married Sogdian Christian women because of a lack of Han Chinese women belonging to the Christian religion, limiting their choice of spouses among the same ethnicity. Another epitaph in Luoyang of a Nestorian Christian Sogdian woman also surnamed An was discovered and she was put in her tomb by her military officer son on 22 January, 815. This Sogdian woman's husband was surnamed He (和) and he was a Han Chinese man and the family was indicated to be multiethnic on the epitaph pillar. In Luoyang, the mixed raced sons of Nestorian Christian Sogdian women and Han Chinese men has many career paths available for them. Neither their mixed ethnicity nor their faith were barriers and they were able to become civil officials, a military officers and openly celebrated their Christian religion and support Christian monasteries.
 During the Tang and subsequent Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, Five Dynasties and Song Dynasty, a large community of Sogdians also existed in the multicultural ''entrepôt'' of Dunhuang, Gansu, a major center of Buddhist learning and home to the Buddhist Mogao Caves. Although Dunhuang and the Hexi Corridor were captured by the Tibetan Empire after the An Lushan Rebellion, in 848 the ethnic Han Chinese general Zhang Yichao (799–872) managed to wrestle control of the region from Era of Fragmentation, the Tibetans during their civil war, establishing the Guiyi Circuit under Emperor Xuānzong of Tang (r. 846–859).''Zizhi Tongjian'', :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷249, vol. 249. Although the region occasionally fell under the rule of different states, it retained its multilingual nature as evidenced by an abundance of manuscripts (religious and secular) in Chinese language, Chinese and Tibetan languages, Tibetan, but also Sogdian, Saka language, Khotanese (another Eastern Iranian language native to Western Regions, the region), Uyghur language, Uyghur, and Sanskrit.
There were nine prominent Sogdian clans (昭武九姓). The names of these clans have been deduced from the Chinese surnames listed in a Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang-era Dunhuang manuscript (Pelliot chinois 3319V). Each "clan" name refers to a different city-state as the Sogdian used the name of their hometown as their Chinese surname. Of these the most common Sogdian surname throughout China was Shí (surname), Shí (石, generally given to those from Chach, modern
During the Tang and subsequent Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, Five Dynasties and Song Dynasty, a large community of Sogdians also existed in the multicultural ''entrepôt'' of Dunhuang, Gansu, a major center of Buddhist learning and home to the Buddhist Mogao Caves. Although Dunhuang and the Hexi Corridor were captured by the Tibetan Empire after the An Lushan Rebellion, in 848 the ethnic Han Chinese general Zhang Yichao (799–872) managed to wrestle control of the region from Era of Fragmentation, the Tibetans during their civil war, establishing the Guiyi Circuit under Emperor Xuānzong of Tang (r. 846–859).''Zizhi Tongjian'', :zh:s:資治通鑑/卷249, vol. 249. Although the region occasionally fell under the rule of different states, it retained its multilingual nature as evidenced by an abundance of manuscripts (religious and secular) in Chinese language, Chinese and Tibetan languages, Tibetan, but also Sogdian, Saka language, Khotanese (another Eastern Iranian language native to Western Regions, the region), Uyghur language, Uyghur, and Sanskrit.
There were nine prominent Sogdian clans (昭武九姓). The names of these clans have been deduced from the Chinese surnames listed in a Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang-era Dunhuang manuscript (Pelliot chinois 3319V). Each "clan" name refers to a different city-state as the Sogdian used the name of their hometown as their Chinese surname. Of these the most common Sogdian surname throughout China was Shí (surname), Shí (石, generally given to those from Chach, modern Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the capital and largest city of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2 ...
). The following surnames also appear frequently on Dunhuang manuscripts and registers: Shǐ (surname), Shǐ (史, from Kesh, modern Shahrisabz), An (surname), An (安, from Bukhara), Mi (surname), Mi (米, from Panjakent), Kang (Chinese surname), Kāng (康, from Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
), Cao (Chinese surname), Cáo (曹, from Kabudhan, north of the Zeravshan River), and He (surname), Hé (何, from Kushaniyah). Confucius is said to have expressed a desire to live among the "nine tribes" which may have been a reference to the Sogdian community.
The influence of Sinicization, Sinicized and multilingual Sogdians during this ''Guiyijun'' (歸義軍) period (c. 850 – c. 1000 AD) of Dunhuang is evident in a large number of manuscripts written in Chinese characters from left to right instead of vertically, mirroring the direction of how the Sogdian alphabet is read. Sogdians of Dunhuang also commonly formed and joined lay associations among their local communities, convening at Sogdian-owned taverns in scheduled meetings mentioned in their epistle, epistolary letters. Sogdians living in Turfan under the Tang dynasty and Gaochang Kingdom engaged in a variety of occupations that included: farming, military service, painting, leather crafting and selling products such as iron goods. The Sogdians had been migrating to Turfan since the 4th century, yet the pace of migration began to climb steadily with the Muslim conquest of Persia and Fall of the Sasanian Empire in 651, followed by the Islamic conquest of Samarkand in 712.
Language and culture
The 6th century is thought to be the peak of Sogdian culture, judging by its highly developed artistic tradition. By this point, the Sogdians were entrenched in their role as the central Asian traveling and trading merchants, transferring goods, culture and religion. During the Middle Ages, the Zarafshan Range, valley of the Zarafshan around Samarkand retained its Sogdian name, Samarkand. According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, Encyclopædia Britannica'', medieval Geography and cartography in medieval Islam, Arab geographers considered it one of the four fairest regions of the world. Where the Sogdians moved in considerable numbers, their language made a considerable impact. For instance, History of the Han dynasty, during China's Han dynasty, the native name of the Tarim Basin city-state of Loulan was "Kroraina," possibly Greek language, from Greek due to Indo-Greek Kingdom, nearby Hellenistic influence. However, centuries later in 664 AD, the Tang Chinese Buddhist monk Xuanzang labelled it as "Nafupo" (納縛溥), which according to Dr. Hisao Matsuda is a transliteration of the Sogdian word ''Navapa'' meaning "new water."Art
The Afrasiab paintings of the 6th to 7th centuries in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, offer a rare surviving example of Sogdian art. The paintings, showing scenes of daily life and events such as the arrival of foreign ambassadors, are located within the ruins of aristocratic homes. It is unclear if any of these palatial residences served as the official palace of the rulers of Samarkand. The oldest surviving Sogdian monumental wall murals date to the 5th century and are located at Panjakent, Tajikistan. In addition to revealing aspects of their social and political lives, Sogdian art has also been instrumental in aiding historians' understanding of their religious beliefs. For instance, it is clear that Buddhist Sogdians incorporated some of their own Persian mythology, Iranian deities into their version of the Buddhist Pantheon. At Zhetysu, Sogdian gilded bronze plaques on a Buddhist temple show a pairing of a male and female deity with outstretched hands holding a miniature camel, a common non-Buddhist image similarly found in the paintings of Samarkand and Panjakent.Language
 The Sogdians spoke an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language called Sogdian, closely related to Bactrian language, Bactrian, Khwarezmian language, Khwarazmian, and the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese Saka language, widely spoken Eastern Iranian languages of Central Asia in ancient times.Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, p 323. Sogdian was also prominent in the oasis city-state of Turfan in the Tarim Basin region of Northwest China (in modern Xinjiang). Judging by the Sogdian Bugut inscription of Mongolia written c. 581, the Sogdian language was also an official language of the First Turkic Khaganate established by the Gokturks.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 9, .
Sogdian was written largely in three scripts: the Sogdian alphabet, the Syriac alphabet, and the Manichaean alphabet, each derived from the Aramaic alphabet, which had been widely used in both the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires of ancient Iran.Christoph Baumer (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, p. 202–203, . The Sogdian alphabet formed the basis of the Old Uyghur alphabet of the 8th century, which in turn was used to create the Mongolian script of the early
The Sogdians spoke an Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian language called Sogdian, closely related to Bactrian language, Bactrian, Khwarezmian language, Khwarazmian, and the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese Saka language, widely spoken Eastern Iranian languages of Central Asia in ancient times.Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, p 323. Sogdian was also prominent in the oasis city-state of Turfan in the Tarim Basin region of Northwest China (in modern Xinjiang). Judging by the Sogdian Bugut inscription of Mongolia written c. 581, the Sogdian language was also an official language of the First Turkic Khaganate established by the Gokturks.Mark J. Dresden (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art, Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, p. 9, .
Sogdian was written largely in three scripts: the Sogdian alphabet, the Syriac alphabet, and the Manichaean alphabet, each derived from the Aramaic alphabet, which had been widely used in both the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid and Parthian Empire, Parthian empires of ancient Iran.Christoph Baumer (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, p. 202–203, . The Sogdian alphabet formed the basis of the Old Uyghur alphabet of the 8th century, which in turn was used to create the Mongolian script of the early Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
during the 13th century. Later in 1599, the Jurchen leader Nurhaci decided to convert the Mongolian alphabet to make it suitable for the Manchu people.
The Yaghnobi people living in the Sughd
Sughd Province ( tg, Вилояти Суғд, Viloyati Sughd, Sogdia Region , fa, ولایت سغد) is one of the four administrative divisions and one of the three provinces ( tg, вилоятҳо, viloyatho , fa, ولایت) that make up ...
province of Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
still speak Yaghnobi language, a descendant of the Sogdian language. Yaghnobi is largely a continuation of the medieval Sogdian dialect from the Osrushana region of the western Fergana Valley. The great majority of the Sogdian people assimilated with other local groups such as the Bactrians, Kwaresm, Chorasmians, and in particular with Persian people, Persians, and came to speak Persian. In 819, the Persians founded the Samanid Empire in the region. They are among the ancestors of the modern Tājik people, Tajiks. Numerous Sogdian cognates can be found in the modern Tajik language, although the latter is a Western Iranian language.
Clothing
 Early medieval Sogdian costumes can be divided in two periods: Hephthalite, Hephtalitic (5th and 6th centuries) and Turkic (7th and early 8th centuries). The latter did not become common immediately after the political dominance of the Gökturks but only in c. 620 when, especially following Western Turkic Khaganate, Western Turkic Khagan Tong Yabghu Qaghan, Ton-jazbgu's reforms, Sogd was Turkized and the local nobility was officially included in the Khaganate's administration.
For both sexes clothes were tight-fitted, and narrow waists and wrists were appreciated. The silhouettes for grown men and young girls emphasized wide shoulders and narrowed to the waist; the silhouettes for female aristocrats were more complicated. The Sogdian clothing underwent a thorough process of Islamization in the ensuing centuries, with few of the original elements remaining. In their stead, turbans, kaftans, and sleeved coats became more common.
Early medieval Sogdian costumes can be divided in two periods: Hephthalite, Hephtalitic (5th and 6th centuries) and Turkic (7th and early 8th centuries). The latter did not become common immediately after the political dominance of the Gökturks but only in c. 620 when, especially following Western Turkic Khaganate, Western Turkic Khagan Tong Yabghu Qaghan, Ton-jazbgu's reforms, Sogd was Turkized and the local nobility was officially included in the Khaganate's administration.
For both sexes clothes were tight-fitted, and narrow waists and wrists were appreciated. The silhouettes for grown men and young girls emphasized wide shoulders and narrowed to the waist; the silhouettes for female aristocrats were more complicated. The Sogdian clothing underwent a thorough process of Islamization in the ensuing centuries, with few of the original elements remaining. In their stead, turbans, kaftans, and sleeved coats became more common.
Religious beliefs
The Sogdians practiced a variety of religious faiths. However, Zoroastrianism was most likely their main religion, as demonstrated by material evidence, such as the discovery in Samarkand, Panjakent and Er-Kurgan of murals depicting votaries making offerings before fire altars and Ossuary, ossuaries holding the bones of the dead - in accordance with Zoroastrian ritual. At Turfan, Sogdian burials shared similar features with traditional Chinese practices, yet they still retained essential Zoroastrian rituals, such as Tower of Silence, allowing the bodies to be picked clean by scavengers before burying the bones in ossuaries.Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford University Press, p. 98, . They also Animal sacrifice, sacrificed animals to Zoroastrian deities, including the supreme deityAhura Mazda
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna'' ...
. Zoroastrianism remained the dominant religion among Sogdians until after the Muslim conquests, Islamic conquest, when they gradually converted to Islam, as is shown by Richard Bulliet's "conversion curve".Tobin 113–115
The Sogdian religious texts found in China and dating to the Southern and Northern Dynasties#The Northern Dynasties, Northern Dynasties, Sui Dynasty, Sui, and Tang are mostly Buddhist (translated from Chinese sources), Manichaean, and Nestorianism, Nestorian Christian, with only a small minority of Zoroastrian texts. But, tombs of Sogdian merchants in China dated to the last third of the 6th century show predominantly Zoroastrian motifs or Zoroastrian-Manichaean syncretism, while archaeological remains from Sogdiana appear fairly Iranian and conservatively Zoroastrian.
However, the Sogdians epitomized the religious plurality found along the trade routes. The largest body of Sogdian texts are Buddhist, and Sogdians were among the principal translators of Buddhist sutras into Chinese. However, Buddhism did not take root in Sogdiana itself. Additionally, the Bulayiq monastery to the north of Turpan contained Sogdian Christian texts, and there are numerous Manichaean texts in Sogdiana from nearby Qocho. The reconversion of Sogdians from Buddhism to Zoroastrianism coincided with the adoption of Zoroastrianism by the Sassanid Empire of Persia. From the 4th century onwards, Sogdian Buddhist pilgrims left behind evidence of their travels along the steep cliffs of the Indus River and Hunza Valley. It was here that they carved images of the Buddha and holy stupas in addition to their full names, in hopes that the Buddha would grant them his protection.
The Sogdians also practiced Manichaeism, the faith of Mani (prophet), Mani, which they spread among the Uyghurs. The Uyghur Khaganate (744–840 AD) developed close ties to Tang China once it had aided the Tang in suppressing the rebellion of An Lushan and his Göktürk successor Shi Siming, establishing an annual trade relationship of one million bolts of Chinese silk for one hundred thousand horses.Liu, Xinru, "The Silk Road: Overland Trade and Cultural Interactions in Eurasia", in ''Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History'', ed. Michael Adas, American Historical Association, Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2001, p. 169. The Uyghurs relied on Sogdian merchants to sell much of this silk further west along the Silk Road, a symbiotic relationship that led many Uyghurs to adopt Chinese Manichaeism, Manichaeism from the Sogdians. However, evidence of Manichaean liturgical and canonical texts of Sogdian origin remains fragmentary and sparse compared to their corpus of Buddhist writings. The Uyghurs were also followers of Buddhism. For instance, they can be seen wearing silk robes in the ''praṇidhi'' scenes of the Bezeklik Thousand Buddha Caves, Uyghur Bezeklik Buddhist murals of Xinjiang, China, particularly Scene 6 from Temple 9 showing :File:BezeklikSogdianMerchants.jpg, Sogdian donors to the Buddha.Gasparini, Mariachiara.A Mathematic Expression of Art: Sino-Iranian and Uighur Textile Interactions and the Turfan Textile Collection in Berlin
" in Rudolf G. Wagner and Monica Juneja (eds), ''Transcultural Studies'', Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg, No 1 (2014), pp 134–163 In addition to Puranas, Puranic cults, there were five Hindu deities known to have been worshipped in Sogdiana. These were Brahma, Indra, Shiva, Mahadeva (Shiva), Narayana, and Vaishravana; the gods Brahma, Indra, and Shiva were known by their Sogdian names Zravan, Adbad and Veshparkar, respectively. Durga, a mother goddess in Shaktism, may be represented in Sogdian art as a four-armed goddess riding atop a lion. As seen in an 8th-century mural from Panjakent, portable fire altars can be "associated" with Mahadeva (Buddhism), Mahadeva-Veshparkar, Brahma-Zravan, and Indra-Abdab, according to Braja Bihārī Kumar.Braja Bihārī Kumar (2007). "India and Central Asia: Links and Interactions," in J.N. Roy and B.B. Kumar (eds), ''India and Central Asia: Classical to Contemporary Periods'', 3–33. New Delhi: Published for Astha Bharati Concept Publishing Company. , p. 8. Among the Sogdian Christians known in China from inscriptions and texts were An Yena, a Christian from An country (Bukhara). Mi Jifen a Christian from Mi country (Maymurgh), Kang Zhitong, a Sogdian Christian cleric from Kang country (Samarkand), Mi Xuanqing a Sogdian Christian cleric from Mi country (Maymurgh), Mi Xuanying, a Sogdian Christian cleric from Mi country (Maymurgh), An Qingsu, a Sogdian Christian monk from An country (Bukhara).
Luoyang
Luoyang is a city located in the confluence area of Luo River and Yellow River in the west of Henan province. Governed as a prefecture-level city, it borders the provincial capital of Zhengzhou to the east, Pingdingshan to the southeast, Nanyan ...
, respectively. In regards to textual material, the earliest Christian gospel texts Bible translations into Sogdian, translated into Sogdian coincide with the reign of the Sasanian Persian monarch Yazdegerd II (r. 438–457), and were translated from the ''Peshitta'', the standard version of the Bible in Syriac Christianity.
Slave trade
Slavery existed in China since ancient times, although during the Han dynasty the proportion of slaves to the overall population was roughly 1%, far lower than the estimate for the contemporary Greco-Roman world (estimated at about 15% of Demography of the Roman Empire, the entire population). During the Tang period, slaves were not allowed to marry a commoner's daughter, were not allowed to have sexual relations with any female member of their master's family, and although fornication with female slaves was forbidden in the Tang Code, Tang code of law, it was widely practiced. Manumission was also permitted when a slave woman gave birth to her master's son, which allowed for her elevation to the legal status of a commoner, yet she could only live as a concubine and not as the wife of her former master. Sogdian and Chinese merchants regularly traded in slaves in and around Turpan during the Tang dynasty. Turpan underTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
rule was a center of major commercial activity between Chinese and Sogdian people, Sogdian merchants. There were many inns in Turpan. Some provided Sogdian sex workers with an opportunity to service the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
merchants, since the official histories report that there were markets in women at Kucha and Khotan
Hotan (also known as Gosthana, Gaustana, Godana, Godaniya, Khotan, Hetian, Hotien) is a major oasis town in southwestern Xinjiang, an autonomous region in Western China. The city proper of Hotan broke off from the larger Hotan County to become ...
. The Sogdian-language contract buried at the Astana Cemetery, Astana graveyard demonstrates that at least one Chinese man bought a Sogdian girl in 639 AD. One of the archaeologists who excavated the Astana site, Wu Zhen, contends that, although many households along the Silk Road bought individual slaves, as demonstrated in the earlier documents from Niya, the Turpan documents point to a massive escalation in the volume of the slave trade. In 639 a female Sogdian slave was sold to a Chinese man, as recorded in an Astana cemetery legal document written in Sogdian. Khotan and Kucha were places where women were commonly sold, with ample evidence of the slave trade in Turfan thanks to contemporary textual sources that have survived. In Tang poetry Sogdian girls also frequently appear as waiting staff, serving maids in the taverns and inns of the capital Chang'an.
Sogdian slave girls and their Chinese male owners made up the majority of Sogdian female-Chinese male pairings, while free Sogdian women were the most common spouse of Sogdian men. A smaller number of Chinese women were paired with elite Sogdian men. Sogdian man-and-woman pairings made up eighteen out of twenty-one marriages according to existing documents.
A document dated 731 AD reveals that precisely forty Bolt (cloth), bolts of silk were paid to a certain Mi Lushan, a slave dealing Sogdian, by a Chinese man named Tang Rong (唐榮) of Chang'an, for the purchase of an eleven-year-old girl. A person from Xizhou, a Tokharistani (i.e. Bactrian), and three Sogdians verified the sale of the girl.
Central Asians like Sogdians were called "Hu" (胡) by the Chinese during the Tang dynasty. Central Asian "Hu" women were stereotyped as barmaids or dancers by Han in China. Han Chinese men engaged in mostly extra-marital sexual relationships with them as the "Hu" women in China mostly occupied positions where sexual services were sold to patrons like singers, maids, slaves and prostitutes. Han men did not want to legally marry them unless they had no choice such as if they were on the frontier or in exile since the Han men would be socially disadvantaged and have to marry non-Han. The task of taking care of herd animals like sheep and cattle was given to "Hu" slaves in China.
Modern historiography
 In 1916, the French Sinologist and historian Paul Pelliot used Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang Chinese manuscripts excavated from Dunhuang, Gansu to identify an ancient Sogdian colony south of Lop Nur in Xinjiang (Northwest China), which he argued was the base for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism and Nestorian Christianity in China.Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S., p. 148. In 1926, Japanese scholar Kuwabara compiled evidence for Sogdians in Chinese historical sources, and by 1933, Chinese historian Xiang Da published his ''Tang Chang'an and Central Asian Culture'', detailing the Sogdian influence on Chinese social religious life in the History of Xi'an, Tang-era Chinese capital city. The Canadian Sinologist Edwin G. Pulleyblank published an article in 1952, demonstrating the presence of a Sogdian colony founded in Six Hu Prefectures of the Ordos Loop during the Chinese Tang period, composed of Sogdians and Turkic peoples who migrated from the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, Mongolian steppe. The Japanese historian Ikeda on wrote an article in 1965, outlining the history of the Sogdians inhabiting Dunhuang from the beginning of the 7th century, analyzing lists of their Chinese surname, Sinicized names and the role of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism in their religious life. Yoshida Yutaka and Kageyama Etsuko, Japanese ethnographers and linguists of the Sogdian language, were able to reconstruct Sogdian names from forty-five different Chinese transliterations, noting that these were common in Turfan whereas Sogdians living closer to the center of Chinese civilization for generations adopted traditional Chinese names.
In 1916, the French Sinologist and historian Paul Pelliot used Dunhuang manuscripts, Tang Chinese manuscripts excavated from Dunhuang, Gansu to identify an ancient Sogdian colony south of Lop Nur in Xinjiang (Northwest China), which he argued was the base for the Silk Road transmission of Buddhism, spread of Buddhism and Nestorian Christianity in China.Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S., p. 148. In 1926, Japanese scholar Kuwabara compiled evidence for Sogdians in Chinese historical sources, and by 1933, Chinese historian Xiang Da published his ''Tang Chang'an and Central Asian Culture'', detailing the Sogdian influence on Chinese social religious life in the History of Xi'an, Tang-era Chinese capital city. The Canadian Sinologist Edwin G. Pulleyblank published an article in 1952, demonstrating the presence of a Sogdian colony founded in Six Hu Prefectures of the Ordos Loop during the Chinese Tang period, composed of Sogdians and Turkic peoples who migrated from the Mongolian-Manchurian grassland, Mongolian steppe. The Japanese historian Ikeda on wrote an article in 1965, outlining the history of the Sogdians inhabiting Dunhuang from the beginning of the 7th century, analyzing lists of their Chinese surname, Sinicized names and the role of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism in their religious life. Yoshida Yutaka and Kageyama Etsuko, Japanese ethnographers and linguists of the Sogdian language, were able to reconstruct Sogdian names from forty-five different Chinese transliterations, noting that these were common in Turfan whereas Sogdians living closer to the center of Chinese civilization for generations adopted traditional Chinese names.
Notable people
* Amoghavajra, prolific translator and one of the most politically powerful Buddhist monks of Chinese history, of Sogdian descent through his mother * An Lushan (安祿山), a military leader of Sogdian (from his father's side) and Gökturks, Tūjué origin during theTang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
in China; he rose to prominence by fighting (and losing) frontier wars between 741 and 755. Later, he precipitated the catastrophic An Lushan Rebellion, which lasted from 755 to 763 and led to the decline of the Tang dynasty
* An Qingxu (安慶緒), son of An Lushan
* An Chonghui (安重誨), a minister of China's Later Tang
* An Congjin (安從進), a general of Later Tang and China's Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
 * An Chongrong (安重榮), a general of the China's Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
*
* An Chongrong (安重榮), a general of the China's Later Jin (Five Dynasties)
* Apama
Apama ( grc, Ἀπάμα, Apáma), sometimes known as Apama I or Apame I, was a Sogdian noblewoman and the wife of the first ruler of the Seleucid Empire, Seleucus I Nicator. They Susa weddings, married at Susa in 324 BC. According to Arrian, Apa ...
, daughter of Spitamenes
Spitamenes (Old Persian ''Spitamana''; Greek ''Σπιταμένης''; 370 BC – 328 BC) was a Sogdian warlordHolt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Cope ...
(see below) and wife of Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; ; grc-gre, Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ , ) was a Macedonian Greek general who was an officer and successor ( ''diadochus'') of Alexander the Great. Seleucus was the founder of the eponymous Seleucid Empire. In the po ...
, founder of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
* Azanes (general), Azanes,Mark J. Dresden (2003), "Sogdian Language and Literature", in Ehsan Yarshater, ''The Cambridge History of Iran, Vol III: The Seleucid, Parthian, and Sasanian Periods'', Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, p. 1216, . son of Artaios, who led a contingent of Sogdian troops in the Military history of Iran, Persian army of Xerxes I
Xerxes I ( peo, 𐎧𐏁𐎹𐎠𐎼𐏁𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ξέρξης ; – August 465 BC), commonly known as Xerxes the Great, was the fourth King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, ruling from 486 to 465 BC. He was the son and successor of D ...
during the Second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC
* Divashtich, 8th-century ruler of Panjakent
* Fazang, Buddhist monk and influent philosopher of the 7th century, considered the founder of the Huayan school
* Gurak
Gurak or Ghurak (Chinese: 乌勒伽 ''wūlèjiā'') was a medieval Sogdian ruler in Central Asia during the period of the Muslim conquest of Transoxiana. In 710, he was installed as king ( Sogdian: ''ikhshid'') of Samarkand after the populace over ...
, 8th-century ruler of Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
* Kang Senghui (康僧會), Buddhist monk of the 3rd century who lived in Jiaozhi (modern-day Vietnam) during the Three Kingdoms period
* Kang Jing (康景)?- a possible Sogdian who worked at the Ming dynasty Mansion of the Prince of Qin (w:zh:明朝藩王列表 (秦王系), 明朝藩王列表 (秦王系)) as a servant
* Khaydhar ibn Kawus al-Afshin, a general of the Abbasid caliphate and a vassal of the Abbasids as the prince of Osrushana during the 9th century
* Kaydar Nasr ibn 'Abdallah, Abbasid governor of Egypt in the Middle Ages, Egypt during the 9th century
* Li Baoyu (李抱玉), formerly known as An Chongzhang (安重璋) and Chinese nobility, ennobled as Duke Zhaowu of Western Liang (Sixteen Kingdoms), Liang (涼昭武公), a general of the Chinese Tang Dynasty who fought against the rebellion of An Lushan and the Tibetan Empire
* Mi Fu (米芾), painter, poet, and calligrapher of the Song dynasty
* Malik ibn Kaydar, a 9th-century general of the Abbasid caliphate
* Muzaffar ibn Kaydar, son of Kaydar Nasr ibn 'Abdallah (see above), and yet another Abbasid governor of Egypt during the 9th century
* Oxyartes
Oxyartes (Old Persian: 𐎢𐎺𐎧𐏁𐎫𐎼, Greek: ''Ὀξυάρτης'', in fa, وخشارد ("Vaxš-ard"), from an unattested form in an Old Iranian language: ''*Huxšaθra-'') was a Sogdian or Bactrian nobleman of Bactria, father o ...
, Sogdian warlord from Bactria
Bactria (; Bactrian: , ), or Bactriana, was an ancient region in Central Asia in Amu Darya's middle stream, stretching north of the Hindu Kush, west of the Pamirs and south of the Gissar range, covering the northern part of Afghanistan, sou ...
, follower of Bessus
Bessus or Bessos ( peo, *Bayaçā; grc-gre, Βήσσος), also known by his throne name Artaxerxes V ( peo, 𐎠𐎼𐎫𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎠 ; grc-gre, Ἀρταξέρξης; died summer 329 BC), was a Persian satrap of the eastern Achaemenid sa ...
, and father of Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
, the wife of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
* Roxana
Roxana (c. 340 BC – 310 BC, grc, Ῥωξάνη; Old Iranian: ''*Raṷxšnā-'' "shining, radiant, brilliant"; sometimes Roxanne, Roxanna, Rukhsana, Roxandra and Roxane) was a Sogdian or a Bactrian princess whom Alexander the Great married ...
, the primary wife of Alexander the Great during the 4th century BC
* Shi Jingtang (石敬瑭), Emperor of China, temple name Gaozu (高祖)
* Spitamenes
Spitamenes (Old Persian ''Spitamana''; Greek ''Σπιταμένης''; 370 BC – 328 BC) was a Sogdian warlordHolt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Cope ...
, a Sogdian warlord who led an uprising against Alexander the Great in the late 4th century BC
* Tarkhun
Tarkhun ( Chinese: 突昏 ''tū-hūn'', died 710) was a Sogdian ruler ( Sogdian: ''ikhshid'') of Samarkand from somewhere 705-707 to 710. After receiving the news of the capture of Bukhara by the Umayyad general Qutayba ibn Muslim in 709, Tarkhun ...
, 8th-century ruler of Samarkand
* Abu'l-Saj Devdad, emir and official of the Abbasid caliphate and ancestor of the Sajid dynasty
Diaspora areas
* A community of merchant Sogdians resided in Northern Qi era Ye (ancient China), Ye. * A community of Sogdians existed in Jicheng (Beijing) since at least the time of the Tang Dynasty. They were targeted for slaughter by the Tang government during the An Lushan rebellion. * Turkic Khaganate era Inner Mongolia.See also
* Ancient Iranian peoples * Buddhism in Afghanistan * Buddhism in Khotan * Étienne de La Vaissière * History of Central Asia * Huteng * Iranian languages * Margiana * List of ancient Iranian peoples * Philip (satrap) * Poykent * ''Sogdian Daēnās'' * Sughd Province *Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in Central Asia during the first half of t ...
* Tocharians
* Tomb of Wirkak
* Tomb of Yu Hong
* Yaghnobi people
* Yagnob Valley
* Yazid ibn al-Muhallab
References
Citations
Sources
* * * Archaeological Researches in Uzbekistan. 2001. Tashkent. The edition is based on results of German-French-Uzbek co-expeditions in 2001 in Uzbekistan * Ahmed, S. Z. (2004), ''Chaghatai: the Fabulous Cities and People of the Silk Road'', West Conshohocken: Infinity Publishing. * * Baumer, Christoph (2012), ''The History of Central Asia: the Age of the Steppe Warriors'', London, New York: I.B. Tauris, . * Belenitskii, A. M. and B. I. Marshak (1981), "Part One: the Paintings of Sogdiana" in Guitty Azarpay, ''Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art'', Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, pp 11–78, . * Boulnois, Luce (2005), ''Silk Road: Monks, Warriors & Merchants'', Odyssey Books, . * * Briant, Pierre (2002), ''From Cyrus to Alexander: a History of the Persian Empire'', trans. Peter T. Daniels, Winona Lake: Eisenbrauns, . * Christopoulos, Lucas (August 2012), "Hellenes and Romans in Ancient China (240 BC – 1398 AD)," in Victor H. Mair (ed), ''Sino-Platonic Papers'', No. 230, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, University of Pennsylvania Department of East Asian Languages and Civilizations, . * Rafe de Crespigny, de Crespigny, Rafe (2007), ''A Biographical Dictionary of Later Han to the Three Kingdoms (23–220 AD)'', Leiden: Koninklijke Brill, . * Étienne de la Vaissière, de la Vaissière, Étienne (2005). ''Sogdian Traders: A History''. Leiden: Brill. * Dresden, Mark J. (1981), "Introductory Note," in Guitty Azarpay, ''Sogdian Painting: the Pictorial Epic in Oriental Art'', Berkeley, Los Angeles, London: University of California Press, pp. 1–10, . * * * Enoki, Kazuo, (1998), "Yü-ni-ch'êng and the Site of Lou-Lan," and "The Location of the Capital of Lou-Lan and the Date of the Kharoshthi Inscriptions," in Rokuro Kono (ed.), ''Studia Asiatica: The Collected Papers in Western Languages of the Late Dr. Kazuo Enoki'', Tokyo: Kyu-Shoin. * Frumkin, Grégoire (1970), ''Archaeology in Soviet Central Asia'', Leiden, Koln: E. J. Brill. * Galambos, Imre (2015), "''She'' Association Circulars from Dunhuang", in ed. Antje Richter ''A History of Chinese Letters and Epistolary Culture'', Brill: Leiden, Boston, pp 853–77. * Gasparini, Mariachiara.A Mathematic Expression of Art: Sino-Iranian and Uighur Textile Interactions and the Turfan Textile Collection in Berlin
" in Rudolf G. Wagner and Monica Juneja (eds.), ''Transcultural Studies'', Ruprecht-Karls Universität Heidelberg, No 1 (2014), pp. 134–163. . ** * Ghafurov, Babadjan, "Tajiks", published in USSR, Russia, Tajikistan * Peter B. Golden (2011), ''Central Asia in World History'', Oxford, New York: Oxford University Press, p. 47, . * Hanks, Reuel R. (2010), ''Global Security Watch: Central Asia'', Santa Barbara, Denver, Oxford: Praeger. * Hansen, Valerie (2012), ''The Silk Road: A New History'', Oxford: Oxford University Press, . * Hansson, Anders, (1996), ''Chinese Outcasts: Discrimination and Emancipation in Late Imperial China'', Leiden, New York, Koln: E.J. Brill, . * Holt, Frank L. (1989), ''Alexander the Great and Bactria: the Formation of a Greek Frontier in Central Asia'', Leiden, New York, Copenhagen, Cologne: E. J. Brill, . * Howard, Michael C. (2012), ''Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies: the Role of Cross Border Trade and Travel'', Jefferson: McFarland & Company. * Hucker, Charles O. (1975). ''China's Imperial Past: An Introduction to Chinese History and Culture''. Stanford: Stanford University Press. . * A.F.P. Hulsewé, Hulsewé, A.F.P. (1986). "Ch'in and Han law," in Denis Twitchett and Michael Loewe (eds.), ''The Cambridge History of China: Volume I: the Ch'in and Han Empires, 221 B.C. – A.D. 220'', pp 520–544 Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. . * Ibbotson, Sophie and Max Lovell-Hoare (2016), ''Uzbekistan'', 2nd edition, Bradt Travel Guides Ltd, . * Braja Bihārī Kumar (2007). "India and Central Asia: Links and Interactions," in J.N. Roy and B.B. Kumar (eds.), ''India and Central Asia: Classical to Contemporary Periods'', 3–33. New Delhi: Published for Astha Bharati Concept Publishing Company. . * Litvinski, B. A., A. H. Jalilov, A. I. Kolesnikov (1999), "The Arab Conquest", in ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia: Volume III, the Crossroads of Civilizations: A.D. 250–750'', B. A. Litvinski, Zhang Guangda, and R. Shabani Samghabadi (eds.). Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, pp. 449–472. * Liu, Xinru, "The Silk Road: Overland Trade and Cultural Interactions in Eurasia", in ''Agricultural and Pastoral Societies in Ancient and Classical History'', ed. Michael Adas, American Historical Association, Philadelphia: Temple University Press, 2001. * Magill, Frank N. et al. (eds.) (1998). ''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography, Volume 1.'' Pasadena; Chicago; London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, Salem Press, . * Michon, Daniel (2015). ''Archaeology and Religion in Early Northwest India: History, Theory, Practice'', London, New York, New Delhi: Routledge, . * * Nourzhanov, Kirill, Christian Bleuer (2013), ''Tajikistan: a Political and Social History'', Canberra: Australian National University Press, . * Prevas, John (2004), ''Envy of the Gods: Alexander the Great's Ill-Fated Journey across Asia'', Da Capo Press. * Ramirez-Faria, Carlos, (2007), ''Concise Encyclopedia of World History'', New Delhi: Atlantic Publishers & Distributors, . * * Rong, Xinjiang, "The Sogdian Caravan as Depicted in the Relieves of the Stone Sarcophagus from Shi's Tomb of the Northern Zhou" in ''Chinese Archaeology''. Volume 6, Issue 1, pp. 181–185, ISSN (Online) 2160–5068, ISSN (Print) 5004–4295, DOI: 10.1515/CHAR.2006.6.1.181, January 2006. * Rong, Xinjiang, "New light on Sogdian Colonies along the Silk Road : Recent Archaeological Finds in Northern China (Lecture at the BBAW on 20 September 2001)", in ''Berichte und Abhandlungen'' (17 December 2009); 10, S. 147–160, urn:nbn:de:kobv:b4-opus-11068. * Rose, J., "The Sogdians: Prime Movers between Boundaries", ''Comparative Studies of South Asia, Africa and the Middle East'', vol. 30, no. 3, (2010), p. 412. * Smith, William eds et al. (1873), ''A Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology, Volume 1'', London: John Murray. * Stark, Sören. "Die Alttürkenzeit in Mittel- und Zentralasien. Archäologische und historische Studien", ''Nomaden und Sesshafte'', vol. 6. Reichert, 2008. . * Strachan, Edward and Roy Bolton (2008), ''Russia and Europe in the Nineteenth Century'', London: Sphinx Fine Art, . * * Taenzer, Gertraud (2016), "Changing Relations between Administration, Clergy and Lay People in Eastern Central Asia: a Case Study According to the Dunhuang Manuscripts Referring to the Transition from Tibetan to Local Rule in Dunhuang, 8th–11th Centuries", in Carmen Meinert, ''Transfer of Buddhism Across Central Asian Networks (7th to 13th Centuries)'', Leiden, Boston: Brill, pp. 106–179, . * Tafazzoli, A. (2003), "Iranian Languages," in C. E. Bosworth and M. S. Asimov, ''History of Civilizations of Central Asia, Volume IV: The Age of Achievement, A.D. 750 to the End of the Fifteenth Century'', Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass Publishers Private Limited, pp. 323–30. * * von Le Coq, Albert. (1913)
''Chotscho: Facsimile-Wiedergaben der Wichtigeren Funde der Ersten Königlich Preussischen Expedition nach Turfan in Ost-Turkistan''
Berlin: Dietrich Reimer (Ernst Vohsen), im Auftrage der Gernalverwaltung der Königlichen Museen aus Mitteln des Baessler-Institutes
(Accessed 3 September 2016). * * Wood, Francis (2002). ''The Silk Road: Two Thousand Years in the Heart of Asia''. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. .
Further reading
*External links
''The Sogdians: Influencers on the Silk Roads'' (Online exhibition)
{{coord, 40.4, N, 69.4, E, display=title Sogdians, Iranian countries and territories Achaemenid satrapies Former countries in Central Asia History of Central Asia Archaeological cultures of Central Asia Archaeology of Kazakhstan Archaeology of Tajikistan Northern and Southern dynasties, * Sui dynasty, * Tang dynasty, * Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms, * 5th century in China, * 6th century in China, * 7th century in China, * 8th century in China, * 9th century in China, * 10th century in China, * 5th century 6th century in Asia 7th century in Asia 8th century in Asia 9th century in Asia 10th century in Asia Iranian culture Cultural regions Silk Road