Rail transport in Lebanon on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rail transport in Lebanon began in the 1890s as French projects under the
Rail transport in Lebanon began in the 1890s as French projects under the





 Hasan Beyhum Efendi received a concession to construct a tramway between
Hasan Beyhum Efendi received a concession to construct a tramway between  The line suffered a serious accident at
The line suffered a serious accident at
 Following the
Following the

 General Georges Catroux proclaimed the
General Georges Catroux proclaimed the



 There have been a number of proposals for reviving the Lebanese railway system, but as yet, none have come to fruition.Section Libanaise de l’Association Française des Amis des Chemins de fer
There have been a number of proposals for reviving the Lebanese railway system, but as yet, none have come to fruition.Section Libanaise de l’Association Française des Amis des Chemins de fer
Actualité
. Retrieved 24 August 2008. One such planned revival is being led by Elias Maalouf, founder of the Lebanese
Maps of Lebanon's lines, stations, and stockyards
at ''Al Mashriq''
UN Map
UN Map Syria
Dr. Maroun Kassab's Proposal
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rail Transport in Lebanon Rail transport in Syria Ottoman railways
 Rail transport in Lebanon began in the 1890s as French projects under the
Rail transport in Lebanon began in the 1890s as French projects under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
but largely ceased in the 1970s owing to the country's civil war
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
. The last remaining routes ended for economic reasons in the 1990s. At its peak Lebanon had about of railway.
History
Ottoman Empire





Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
and Damascus were first connected by telegraph
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
in 1861 and by a macadam road in 1863. Syrian railways
General Establishment of Syrian Railways ( ar, المؤسسة العامة للخطوط الحديدية, french: Chemins de fer syriens, CFS) is the national railway operator for the state of Syria, subordinate to the Ministry of Transportation. ...
connecting the two cities ( over the crest of the Mount Lebanon range) or another port were planned as early as 1871 but were not enacted. In 1889, the Ammiyya Revolt broke out among the Druze and other Syrian farmers. The Ottoman response to the insurrection included a number of railway concessions—quickly sold to foreign interests—to improve the development and centralized control of the region.
 Hasan Beyhum Efendi received a concession to construct a tramway between
Hasan Beyhum Efendi received a concession to construct a tramway between Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint o ...
and Damascus in 1891. Beyhum sold the concession later that year to the French (french: Compagnie de la voie ferrée économique de Beyrouth–Damas) or , which was anxious to forestall two mooted British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
lines, one from Jaffa. and another from Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
, either of which would have undercut Beirut's status as the primary port of the northern Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
. In the event, the Jaffa line was never extended towards Damascus and the Haifa line ran out of money having completed just or of track.
Around the same time, the French (') or Belgian
Belgian may refer to:
* Something of, or related to, Belgium
* Belgians, people from Belgium or of Belgian descent
* Languages of Belgium, languages spoken in Belgium, such as Dutch, French, and German
*Ancient Belgian language, an extinct languag ...
(').. purchased another native's concession for the . The Hauran around Muzeirib is Syria's breadbasket and the town also served as the point of departure for pilgrim
A pilgrim (from the Latin ''peregrinus'') is a traveler (literally one who has come from afar) who is on a journey to a holy place. Typically, this is a physical journey (often on foot) to some place of special significance to the adherent of ...
caravans during the Hajj.
The two lines quickly merged as the ' or ', with its headquarters in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
(Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
) and an office in Paris
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), ma ...
. It originally planned to use a meter gauge
Metre-gauge railways are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre.
The metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by European colonial powers, such as the French, British and German Empires. In Europe, ...
but ended with a gauge
Gauge ( or ) may refer to:
Measurement
* Gauge (instrument), any of a variety of measuring instruments
* Gauge (firearms)
* Wire gauge, a measure of the size of a wire
** American wire gauge, a common measure of nonferrous wire diameter, ...
, along with expensive Abt rack sections to deal with the Mount Lebanon range. It ran through the Dar al-Beida Pass, with the summit at Beidar ( from Beirut) above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
. The railway completed its port at Beirut in December 1892.
In 1893, the company received a concession for a line from Damascus to Birecik
Birecik; ku, Bêrecûk is a town and district of Şanlıurfa Province of Turkey, on the Euphrates.
Built on a limestone cliff 400 ft. high on the left/east bank of the Euphrates, "at the upper part of a reach of that river, which runs near ...
in Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, which prompted its name to be changed to the or (', DHP; tr, Şam–Hama ve Temdidi Osmanlı Demiryolu Şirketi).. The network is also known as the in English. The initial concession was later emended to link the two lines at Riyaq
Rayaq - Haouch Hala ( ar, رياق), also romanization of Arabic, romanized Rayak, is a Lebanon, Lebanese town in the Beqaa Governorate, Beqaa Mohafazat, Governorate near the city of Zahlé. In the early 20th century and up to 1975 and the outbrea ...
instead of Damascus. Service from Damascus south to Muzeirib began in July 1894 (in time for that year's harvest) and to Beirut on 3 August 1895. The trip from the coast to Damascus initially took 9 hours and terminated at three different stations: Baramke Station, Qanawat Station, and Midan Station. Between 1900 and 1908, the separate Hejaz Railway (HRR) expanded from Damascus south to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the second-holiest city in Islam, and the capital of the ...
, with a branch to Haifa opened in 1906. The HRR was built to a 1.05-meter gauge to match the Beirut–Damascus Railway and absorbed both the former British concession and the DHP's line south from Damascus.)
Wheat from the Hauran—high-protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
semolina
Semolina is coarsely milled durum wheat mainly used in making couscous, and sweet puddings. The term semolina is also used to designate coarse millings of other varieties of wheat, and sometimes other grains (such as rice or corn) as well.
Ety ...
used in pasta—was intended to be the mainstay of the railway's income, along with the Muslim pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, aft ...
trade during the Hajj. The entry of American, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
, and Australian wheat into the European market amid the continuing Long Depression
The Long Depression was a worldwide price and economic recession, beginning in 1873 and running either through March 1879, or 1896, depending on the metrics used. It was most severe in Europe and the United States, which had been experiencing st ...
, however, undercut that trade while the railway was still under construction. Damascene traders had thought the Beirut railway would allow them to export their grain more cheaply; instead, as early as the 1894 harvest, the rail flooded the market, collapsing prices and margins. Completion of the line to the coast did not improve matters, since the world market was trading at still lower prices and the premium once commanded by Hauran wheat—which, being hand-harvested, might include pebbles or weeds—was now lost to machine-reaped grain from the United States. It was not until 1908 that export values again reached the levels of the 1880s. The railway itself was one of the best-managed in the Ottoman Empire: It had total receipts of $434,000 for 1900 and in 1906 received a guarantee from the government of $4320 per mile on the 200-mile Aleppo Railway All the same, the company was never very profitable: it was at perpetual risk of bankruptcy; shares traded at 550 Fr in 1891 and only 468 Fr in 1909; and dividends were minuscule: 4.40 Fr in 1902 and 6.31 Fr in 1909.
 The line suffered a serious accident at
The line suffered a serious accident at Aley
Aley ( ar, عاليه) is a major city in Lebanon. It is the capital of the Aley District and fourth largest city in Lebanon.
The city is located on Mount Lebanon, 15 km uphill from Beirut on the freeway to Damascus. Aley has the nick ...
on 12 April 1904. Aley had grown with the railroad and functioned as a summer resort for the people of Beirut. Part of the locomotive exploded on the 7% incline east of town and, not thinking to apply the brakes, the train was allowed to fly back through the station. Two cars were completely destroyed upon the rocks on the other side, killing 8 and seriously injuring 21.
The Aleppo Railway via the Beqaa Valley between the Mount Lebanon range and the Anti-Lebanon Mountains
The Anti-Lebanon Mountains ( ar, جبال لبنان الشرقية, Jibāl Lubnān ash-Sharqiyyah, Eastern Mountains of Lebanon; Lebanese Arabic: , , "Eastern Mountains") are a southwest–northeast-trending mountain range that forms most of t ...
was built to standard gauge. As a result, traffic between the two lines had to be transferred at Riyaq.. The line opened as far as Baalbek on 19 June 1902 and began service to Aleppo on 4 October 1906.. The Baghdad Railway
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
reached Aleppo in 1912, connecting the line with Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
.
The concession for the Tripoli–Saida Saida may refer to:
Places
* Saïda, Algeria, a city in Algeria
* Saïda Province, a province of Algeria
* Saida, Lebanon, the Arabic name for Sidon, a city in Lebanon
* Saida, a village in Helan, Mandi Bahauddin, Punjab province, Pakistan
* Sai ...
line was purchased from its original holder, a Syrian, by the French '. By 1898, it had only laid of track and the DHP's concession was emended to permit a branch line to Tripoli. This was eventually extended northward to reconnect with the Aleppo Railway at Homs, beginning service in 1911. During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, however, its track was removed for use elsewhere.
A separate -gauge coastal railway, the (') began service in 1895 and reached Maameltein in 1908.
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
seized control of all foreign-owned railways in the country, including the DHP. The entire Hauran line was disassembled to extend the Palestine Railways
{{Infobox rail
, railroad_name = Palestine Railway
, logo_filename =
, logo_size =
, system_map =
, map_caption =
, map_size =
, marks =
, image = AwmB00283.Samakh.jpg
, image_size ...
toward the Suez Canal.
French Mandate
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
held the mandate for Syria and Lebanon
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
under the auspices of the League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
. The DHP's ownership of its track was reinstated and it was also given control of the Hejaz Railway. Competition between the French port at Beirut and the British one at Haifa led to tariff wars and, in 1921, land swaps in Palestine for Syrian railway rights.
From around 1930, the Aleppo Railway formed a stage on the Taurus Express's southern route to Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the Capital city, capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, List of ...
. An alternate route ran along the Tripoli line to Beirut. The service was operated by the Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits
Newrest Wagons-Lits, formerly (lit. ''International Sleeping-Car Company''), also CIWL, Compagnie des Wagons-Lits, or just Wagons-Lits, is a division of particularly known for its on-train catering and sleeping car services, as well as being ...
and was discontinued in 1972. In 1933, the Syrian Lines to Baghdad (') arranged the Baghdad Railway
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
as a subsidiary of the DHP.
The railways saw significant use in the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. The British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
originally planned to connect their standard-gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in Ea ...
network from Haifa
Haifa ( he, חֵיפָה ' ; ar, حَيْفَا ') is the third-largest city in Israel—after Jerusalem and Tel Aviv—with a population of in . The city of Haifa forms part of the Haifa metropolitan area, the third-most populous metropol ...
to Riyaq but gave up the project in 1941 as too difficult. Instead, engineers from South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
and Australia completed a standard-gauge line along the coast between Haifa and Beirut by 24 August 1942 and expanded this to Tripoli Railway Station by 18 December 1942. This (HBT) was the last link connecting the European and North African standard-gauge rail networks, apart from the ferry across the Bosphorus at Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, but it never operated for civilian use. Instead, the British maintained it under the control of their military as late as February 1948, when the Jewish insurgency in Palestine
A successful paramilitary campaign was carried out by Zionist underground groups against British rule in Mandatory Palestine from 1944 to 1948. The tensions between the Zionist underground and the British mandatory authorities rose from 1938 a ...
destroyed the bridges near the tunnels at Ras al-Nakura. An earlier attempt by Haganah forces to attack the HBT in two places near Nahal Kziv
Nahal Kziv ( he, נחל כזיב) (lit. "Kziv stream") or the Horn Valley ( ar, وادي القرن, Wadi al Qarn) is a 39-kilometer long perennial stream in the Upper Galilee, Israel. During the winter, rainfall fills the channel, and springs al ...
during the Night of the Bridges
The Night of the Bridges (formally Operation Markolet) was a Haganah venture on the night of 16 to 17 June 1946 in the British Mandate of Palestine, as part of the Jewish insurgency in Palestine (1944–7). Its aim was to destroy eleven bridges l ...
in 1946 was unsuccessful. Nowadays the only portion of the HBT still in operation is the Coastal Railway between Nahariya and Haifa in northern Israel.
Independent Lebanon

 General Georges Catroux proclaimed the
General Georges Catroux proclaimed the independence of Lebanon
Lebanese Independence Day ( ar, عيد الإستقلال اللبناني, translit=Eid Al-Istiqlal, lit=Festival of the Independence; french: Indépendance du Liban) is the national day of Lebanon, celebrated on 22 November in commemoration of ...
in 1941 but the French did not actually permit local rule until 1943. In 1946, the Lebanese government bought the Naqoura
Naqoura (, ''Enn Nâqoura, Naqoura, An Nāqūrah'') is a small city in southern Lebanon. Since March 23, 1978, the United Nations Interim Force in Lebanon (UNIFIL) has been headquartered in Naqoura.
Name
According to E. H. Palmer (1881), the nam ...
–Tripoli Railway for , yielding its management to DHP. Syria nationalized its own railways in 1956 as CFS (Chemins de Fer Syriens
General Establishment of Syrian Railways ( ar, المؤسسة العامة للخطوط الحديدية, french: Chemins de fer syriens, CFS) is the national railway operator for the state of Syria, subordinate to the Ministry of Transportation. ...
). In 1960 or 1961, the country's network was reorganized as the Lebanese Railway (', CEL). The Lebanese Civil War
The Lebanese Civil War ( ar, الحرب الأهلية اللبنانية, translit=Al-Ḥarb al-Ahliyyah al-Libnāniyyah) was a multifaceted armed conflict that took place from 1975 to 1990. It resulted in an estimated 120,000 fatalities a ...
caused considerable damage to the rail network, however, and services gradually ceased. During the civil war, damage was caused by militias who blew up the tracks, Israeli army shelling and Syrian security forces digging up parts of the track to sell as scrap metal in Pakistan. A 1974 article revealed that the 1.05-m DHP system was still working but still using steam power, uncompetitive and loss making. The line between Beirut and Damascus was closed in 1976. Commuter service between Dora and Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8 ...
ceased in 1993 and the last regular rail operations in Lebanon—trains carrying cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
from Chekka to Beirut—ended in 1997. The Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
diesel locomotive class SP45 for this line continued to be run once a month at the Furn el Shebbak stockyards as late as 2002, but service was not resumed.
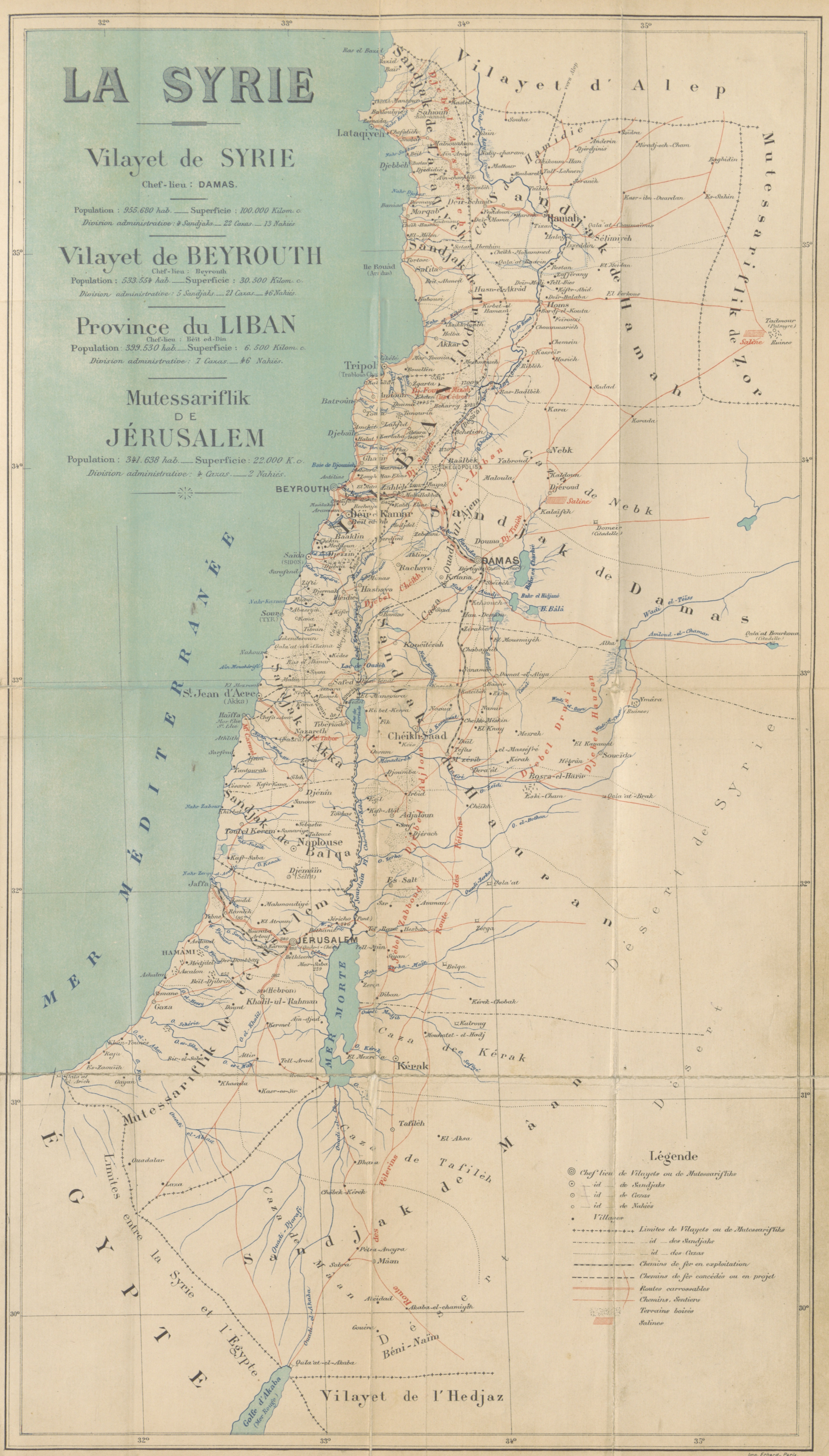
Syria
Only a very short length of the Syrian Homs-Tartus
)
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium&n ...
line crosses the border into Lebanon. This happens because the railway was built before this border was defined. While today in Syria, all network and trains are operated by CFS (Chemins de Fer Syriens
General Establishment of Syrian Railways ( ar, المؤسسة العامة للخطوط الحديدية, french: Chemins de fer syriens, CFS) is the national railway operator for the state of Syria, subordinate to the Ministry of Transportation. ...
).
Background on trains from Istanbul to Syria: A brief history of the Taurus Express
Agatha Christie wrote the first part of her novel ''Murder on the Orient Express
''Murder on the Orient Express'' is a work of detective fiction by English writer Agatha Christie featuring the Belgian detective Hercule Poirot. It was first published in the United Kingdom by the Collins Crime Club on 1 January 1934. In the U ...
'' during her stay in room 203 in Baron Hotel
Baron Hotel (also Baron's Hotel; french: Hôtel Baron or ''Le Baron''), is the oldest hotel that currently operates in Syria. It is located on Baron street in down-town Aleppo's Aziziyeh district. The Baron has sustained some civil war-relate ...
in Aleppo.
The novel doesn't start in Istanbul, or on the Orient Express. It opens on the platform at Aleppo, next to the two blue-and-gold Wagons-Lits sleeping cars of the Taurus Express bound for Istanbul. The Taurus Express was inaugurated in February 1930 by the Compagnie Internationale des Wagons-Lits, the same company that operated the Orient Express and Simplon Orient Express, as a means of extending their services beyond Istanbul to the East. It ran several times a week from Istanbul Haydarpaşa station to Aleppo and Baghdad, with a weekly through sleeper to Tripoli in Lebanon. After the second world war, the Wagons-Lits company gradually withdrew and operation of the Taurus Express was taken over by the Turkish, Syrian and Iraqi state railways. Up until the late 1980s, a twice-weekly Istanbul-Baghdad service was maintained, with weekly through seating cars from Istanbul to Aleppo. For political reasons, the through service to Baghdad was suspended and the main train curtailed at Gaziantep, but the weekly through seat cars Istanbul-Aleppo were maintained. In 2001, the Aleppo portion of the Toros Express was speeded-up and given a proper Syrian sleeping-car instead of the two very basic Turkish seat cars. You could once again travel in the security and comfort of a proper sleeper from Istanbul to Syria, and it was a great way to go.
Trains functioning in Syria:
* LDE DE (Diesel-electric)
* DMU-5 DH (Diesel-hydraulic): Multiple units from Hyundai Rotem, Korea for Aleppo-Damascus/Latakia long-distance services. 222-second class, 61 first class.
Networks:
* Damascus - Homs - Hamah - Aleppo - Maydan Ikbis (- Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, maki ...
, Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
TCDD)
* Aleppo (- Gaziantep, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
TCDD)
* Aleppo - Latakia - Tartus - Al Akkari - Homs
* Homs - Palmyra: freight only, opened for phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
s traffic, destined for the port of Tartus
)
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium&n ...
, in 1980
* Line runs from the oilfields of Al Qamishli in the north to the port of Latakia (750 km)
* Al Akkari (- Tripoli CEL, out of use)
* Aleppo - Deir ez-Zor - Al-Qamishli (- Nusaybin, Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
TCDD)
* Extension from Homs southwards to Damascus (194 km) was opened in 1983
* Tartus- Latakia line in 1992
* Al Qamishli - Al-Yaarubiyah (- IRR Iraq, out of use)
* Damascus - Sheikh Miskin - Dera'a: under construction, to replace a section of Hejaz railway
* Sheikh Miskin - Suwayda (under construction)
* Palmyra - Deir ez-Zor - Abu Kemal (- IRR Iraq) (planned)
Israel
Israel's national railway operator,Israel Railways
Israel Railways Ltd. , dba Israel Railways ( he, רַכֶּבֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Rakevet Yisra'el''), is the state-owned principal railway company responsible for all inter-city, commuter, and freight rail transport in Israel. Isra ...
, has planned a rail link from Lebanon to its own network, branching off the Haifa-Karmiel railway in Ahihud
Ahihud ( he, אֲחִיהוּד) is a moshav in the Western Galilee in northern Israel, about 9 km east of Acre. It was founded in 1950, settled by Jewish refugees from Yemen. It belongs to the Moshavim Movement and falls within the jurisdic ...
. These plans are unlikely to materialize given the absence of diplomatic relations between the two countries.
Trains functioning in Israel:
* Siemens Desiro HC (Electric)
* Siemens Viaggio Light (Diesel-electric)
* Bombardier Double-Deck Coach (Electric and Diesel-electric)
* Alstom MoDo (Diesel-electric)
* ABB Scania IC3 (Diesel-electric)
Networks:
* Beersheba - Kiryat Gat - Lod - Tel Aviv - Herzliya - Haifa - Nahariya
* Beersheba - Kiryat Gat - Lod - Tel Aviv - Herzliya - Hadera - Haifa - Karmiel
* Modi'in - Ben Gurion Airport - Tel Aviv - Binyamina - Haifa - Nahariya
* Jerusalem - Ben Gurion Airport - Tel Aviv - Herzliya
* Atlit - Haifa - Afula - Beit She'an
* Beersheba - Ashkelon - Lod - Tel Aviv - Herzliya - Netanya - Hadera - Binyamina
* Ashkelon - Rishon LeZiyyon - Tel Aviv - Rosh Ha'Ayin - Kfar Saba - Herzliya
* Beit Shemesh - Lod - Tel Aviv - Herzliya - Netanya
* Beersheba - Dimona
* Beersheba - Ramat Hovev (freight only)
* Beersheba - Dimona - Rotem (freight only)
* Hadera - Kfar Saba - Rosh Ha'Ayin - Lod (under construction)
* Rishon LeZiyyon - Modi'in (under construction)
Rolling stock
Retired
Planned revival

 There have been a number of proposals for reviving the Lebanese railway system, but as yet, none have come to fruition.Section Libanaise de l’Association Française des Amis des Chemins de fer
There have been a number of proposals for reviving the Lebanese railway system, but as yet, none have come to fruition.Section Libanaise de l’Association Française des Amis des Chemins de ferActualité
. Retrieved 24 August 2008. One such planned revival is being led by Elias Maalouf, founder of the Lebanese
NGO
A non-governmental organization (NGO) or non-governmental organisation (see spelling differences) is an organization that generally is formed independent from government. They are typically nonprofit entities, and many of them are active in h ...
, Train Train. Maalouf is planning to relaunch the line between the coastal cities of Byblos
Byblos ( ; gr, Βύβλος), also known as Jbeil or Jubayl ( ar, جُبَيْل, Jubayl, locally ; phn, 𐤂𐤁𐤋, , probably ), is a city in the Keserwan-Jbeil Governorate of Lebanon. It is believed to have been first occupied between 8 ...
and Batroun
Batroun ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرُون '; Syriac script: ܒܬܪܘܢ ') is a coastal city in northern Lebanon and one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. It is the capital city of Batroun District.
Etymology
The name ''Bat ...
, to show the feasibility of having trains running again. The project, with a budget of £430,000, should take only a matter of months to complete, but as of 2014, Maalouf was still waiting for the green light from the Lebanese government.
According to a study funded by the European Investment Bank, a railway line connecting Beirut to Tripoli would cost $3 billion to build, while a freight railway from Tripoli to Homs would cost much less. However, efforts to revive Lebanon's railway system have been stymied by the Syrian Civil War.
In 2011, Dr. Maroun Kassab, an Architect and Assistant Professor proposed a coastal Metro System that can capitalize on the existing lands owned by the ministry and that can run underground from Tyr to Tripoli.
In February 2022 media reported a proposed Spanish grant for the reestablishment of Lebanese railways.
See also
*Syrian railways
General Establishment of Syrian Railways ( ar, المؤسسة العامة للخطوط الحديدية, french: Chemins de fer syriens, CFS) is the national railway operator for the state of Syria, subordinate to the Ministry of Transportation. ...
*Transport in Syria Transport in Syria is possible by rail, road, air or rivers, both public and private. Syria is a developed Asian country with a well-developed rail network (2,052 km) and a highway system (782 km). Main international airport is the Damasc ...
* Arab Mashreq International Railway
*Palestine Railways
{{Infobox rail
, railroad_name = Palestine Railway
, logo_filename =
, logo_size =
, system_map =
, map_caption =
, map_size =
, marks =
, image = AwmB00283.Samakh.jpg
, image_size ...
* Tripoli Railway Station
*OCFTC right
O.C.F.T.C (Office des Chemins de Fer et des Transports en Commun, French for '' Railway and Public Transportation Authority'') is the Lebanese government authority which operates public transportation in Lebanon.
The OCFTC currently operates ...
, Lebanon's public transport operator
* AS DPHB, the defunct football club of the Lebanese railways
Notes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* . * . * . * .External links
Maps of Lebanon's lines, stations, and stockyards
at ''Al Mashriq''
UN Map
UN Map Syria
Dr. Maroun Kassab's Proposal
{{DEFAULTSORT:Rail Transport in Lebanon Rail transport in Syria Ottoman railways