Outline of the Solar System on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following
 * Sun
* Interplanetary medium
*
* Sun
* Interplanetary medium
* 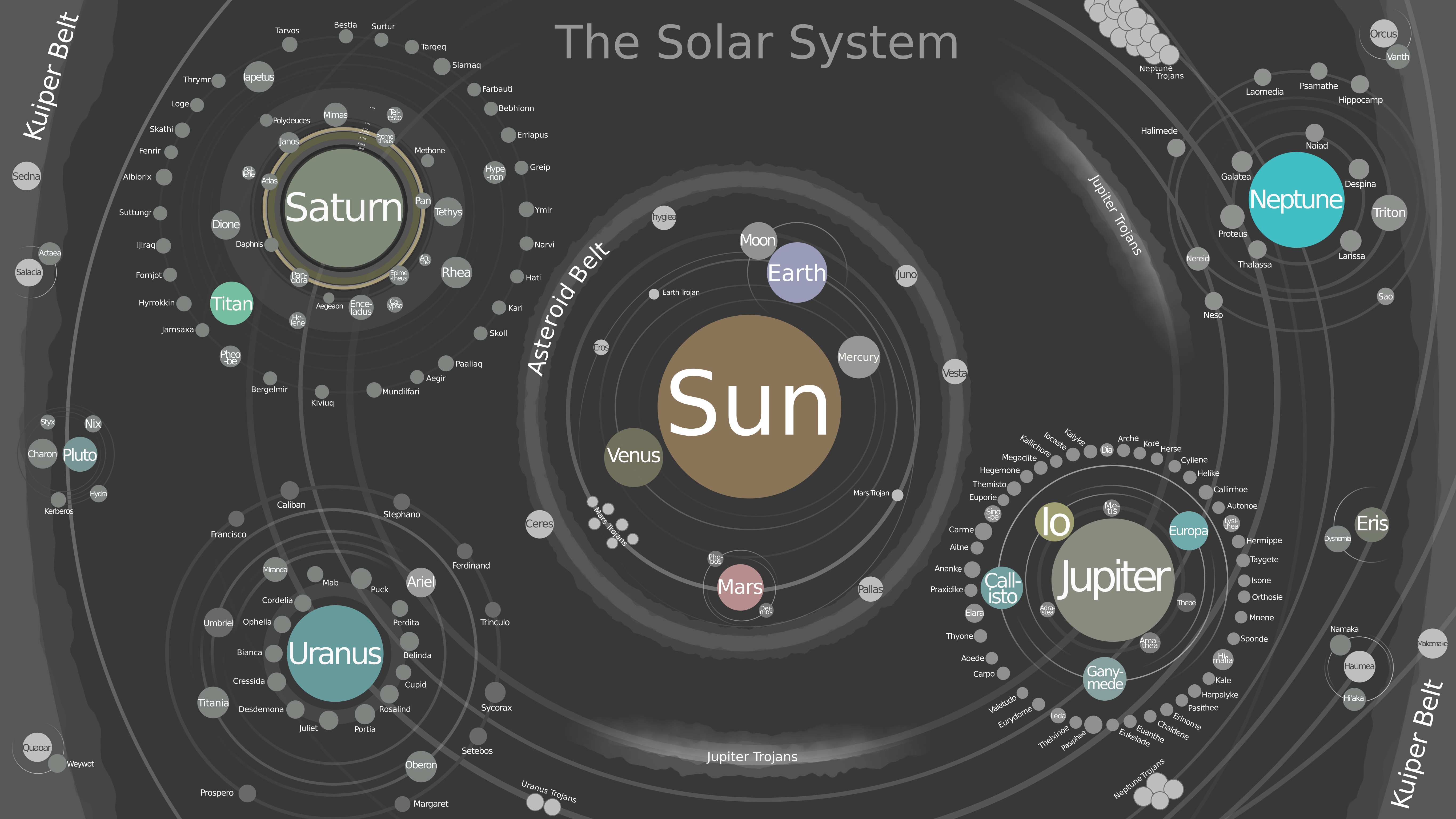 * Outer Solar System
**
* Outer Solar System
**
dmoz page for Solar System
*
A Cosmic History of the Solar SystemA Tediously Accurate Map of the Solar System (web based scroll map scaled to the Moon being 1 pixel)
NASA/JPL Solar System main page
*
NASA's Solar System Simulator
*
Solar System Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Outline footer * Wikipedia outlines
outline
Outline or outlining may refer to:
* Outline (list), a document summary, in hierarchical list format
* Code folding, a method of hiding or collapsing code or text to see content in outline form
* Outline drawing, a sketch depicting the outer edge ...
is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
:
Solar System – gravitationally bound system comprising the Sun and the objects that orbit it, either directly or indirectly. Of those objects that orbit the Sun directly, the largest eight are the planets (including Earth), with the remainder being significantly smaller objects, such as dwarf planets and small Solar System bodies. Of the objects that orbit the Sun indirectly, the moons, two are larger than the smallest planet, Mercury.
Regions and celestial objects of the Solar System
Inner Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
** Inner planets
*** Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
*** Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
*** Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
**** The Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the List of natural satellites, fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth ( ...
**** Near-Earth object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body whose orbit brings it into proximity with Earth. By convention, a Solar System body is a NEO if its closest approach to the Sun (perihelion) is less than 1.3 astronomical units (AU). ...
s
**** Van Allen radiation belt
*** Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
**** Moons of Mars
** Asteroid belt
*** Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s
*** Asteroid groups
*** Ceres
Ceres most commonly refers to:
* Ceres (dwarf planet), the largest asteroid
* Ceres (mythology), the Roman goddess of agriculture
Ceres may also refer to:
Places
Brazil
* Ceres, Goiás, Brazil
* Ceres Microregion, in north-central Goiás st ...
 * Outer Solar System
**
* Outer Solar System
**Outer planets
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
***Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
**** Ganymede
****Callisto Callisto most commonly refers to:
*Callisto (mythology), a nymph
*Callisto (moon), a moon of Jupiter
Callisto may also refer to:
Art and entertainment
*''Callisto series'', a sequence of novels by Lin Carter
*''Callisto'', a novel by Torsten Kro ...
**** Moons of Jupiter
**** Rings of Jupiter
**** Jupiter trojan
The Jupiter trojans, commonly called trojan asteroids or simply trojans, are a large group of asteroids that share the planet Jupiter's orbit around the Sun. Relative to Jupiter, each trojan librates around one of Jupiter's stable Lagrange poin ...
s
*** Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
****Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
**** Rhea
**** Moons of Saturn
**** Rings of Saturn
**** Shepherd moon
A shepherd moon (also herder moon or watcher moon) is a small natural satellite that clears a gap in planetary-ring material or keeps particles within a ring contained. The name is a result of the fact they limit the "herd" of the ring particle ...
s
*** Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather ...
**** Titania
**** Oberon
**** Moons of Uranus
**** Rings of Uranus
The rings of Uranus are intermediate in complexity between the more extensive set around Saturn and the simpler systems around Jupiter and Neptune. The rings of Uranus were discovered on March 10, 1977, by James L. Elliot, Edward W. Dunham, and ...
*** Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
**** Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
**** Moons of Neptune
**** Rings of Neptune
** Trojans
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 1890 ...
** Centaurs
A centaur ( ; grc, κένταυρος, kéntauros; ), or occasionally hippocentaur, is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse.
Centaurs are thought of in many Greek myths as being ...
* Ubiquitous
** Comets
** Meteoroids
** Micrometeoroid
A micrometeoroid is a tiny meteoroid: a small particle of rock in space, usually weighing less than a gram. A micrometeorite is such a particle that survives passage through Earth's atmosphere and reaches Earth's surface.
The term "micrometeoroid ...
s
** Cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
** Interplanetary dust cloud
* Trans-Neptunian region
** Kuiper belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
*** Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the S ...
**** Charon
In Greek mythology, Charon or Kharon (; grc, Χάρων) is a psychopomp, the ferryman of Hades, the Greek underworld. He carries the souls of those who have been given funeral rites across the rivers Acheron and Styx, which separate the wo ...
**** Moons of Pluto
The dwarf planet Pluto has five natural satellites. In order of distance from Pluto, they are Charon (moon), Charon, Styx (moon), Styx, Nix (moon), Nix, Kerberos (moon), Kerberos, and Hydra (moon), Hydra. Charon, the largest, is mutually tidally ...
*** Haumea
*** Makemake
*** Trans-Neptunian objects
** Scattered disc
*** Eris
* Farthest regions
** Extreme trans-Neptunian object
An extreme trans-Neptunian object (ETNO) is a trans-Neptunian object orbiting the Sun well beyond Neptune (30 AU) in the outermost region of the Solar System. An ETNO has a large semi-major axis of at least 150–250 AU. Its orbit is m ...
s
** Detached object
Detached objects are a dynamical class of minor planets in the outer reaches of the Solar System and belong to the broader family of trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs). These objects have orbits whose points of closest approach to the Sun (perihelion ...
s
*** Sedna
** Oort cloud
** Heliosphere
*** Heliopause
*** Boundaries
Location of the Solar System
*Universe
The universe is all of space and time and their contents, including planets, stars, galaxies, and all other forms of matter and energy. The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological description of the development of the universe. Acc ...
**Observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
*** Laniakea Supercluster
**** Virgo Supercluster
*****Local Sheet
The Local Sheet in astronomy is a nearby extragalactic region of space where the Milky Way, the members of the Local Group and other galaxies share a similar peculiar velocity. This region lies within a radius of about , thick, and galaxies bey ...
******Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
*******Milky Way subgroup
The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group.
There are 59 small galaxies confirmed to be within of the Milky Way, but not a ...
********Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye ...
*********Orion–Cygnus Arm
The Orion Arm is a minor spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy that is across and approximately in length, containing the Solar System, including Earth. It is also referred to by its full name, the Orion–Cygnus Arm, as well as Local Arm, Orion ...
**********Gould Belt
The Gould Belt is a local, partial ring of stars in the Milky Way, about 3,000 light-years long, tilted away from the galactic plane by about 16–20 degrees. It contains many O- and B-type stars, amounting to the nearest star-forming regio ...
*********** Local Bubble
************Local Interstellar Cloud
The Local Interstellar Cloud (LIC), also known as the Local Fluff, is an interstellar cloud roughly across, through which the Solar System is moving. This feature overlaps a region around the Sun referred to as the solar neighborhood. It is unk ...
– immediate galactic neighborhood of the Solar System.
*************Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri ( Latinized from α Centauri and often abbreviated Alpha Cen or α Cen) is a triple star system in the constellation of Centaurus. It consists of 3 stars: Alpha Centauri A (officially Rigil Kentaurus), Alpha Centaur ...
– star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or '' galaxy'', although, broadly speak ...
nearest to the Solar System, at about 4.4 light years away
*************Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar S ...
– star and planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interacti ...
where the Earth is located.
**************Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
– the only planet known to have life, including intelligent life, including humans.
Structure and composition of the Solar System
*Interplanetary space
Interplanetary may refer to:
*Interplanetary space, the space between the planets of the Solar System
*Interplanetary spaceflight, travel between planets
*The interplanetary medium, the material that exists in interplanetary space
*The InterPlanet ...
* Physical characteristics of the Sun
** Structure of the Sun
* Physical characteristics of Mercury
** Structure of Mercury
** Geology of Mercury
* Physical characteristics of Venus
** Structure of Venus
** Atmosphere of Venus
The atmosphere of Venus is the layer of gases surrounding Venus. It is composed primarily of supercritical carbon dioxide and is much denser and hotter than that of Earth. The temperature at the surface is 740 K (467 °C, 872 ° ...
** Geology of Venus
Venus is a planet with striking geology. Of all the other planets in the Solar System, it is the one nearest to Earth and most like it in terms of mass, but has no magnetic field or recognizable plate tectonic system. Much of the ground surface ...
*** Volcanism on Venus
* Physical characteristics of the Earth
** Figure of the Earth
Figure of the Earth is a Jargon, term of art in geodesy that refers to the size and shape used to model Earth. The size and shape it refers to depend on context, including the precision needed for the model. A Spherical Earth, sphere is a well-k ...
** Structure of the Earth
The internal structure of Earth is the solid portion of the Earth, excluding its atmosphere and hydrosphere. The structure consists of an outer silicate solid crust, a highly viscous asthenosphere and solid mantle, a liquid outer core whos ...
** Earth's magnetic field
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
** Atmosphere of Earth
** Geology of Earth
*** Lithosphere of Earth
**** Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
** Hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to change in shape. This ...
of Earth
*** Water distribution on Earth
Most water in atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and on its Earth's crust, crust comes from saline seawater, while fresh water accounts for nearly 1% of the total. The vast bulk of the water on Earth is ''saline'' or ''salt water'', with an ...
* Physical characteristics of Mars
** Structure of Mars
** Atmosphere of Mars
** Geology of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geo ...
*** Volcanism on Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features in ...
** Geography of Mars
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the di ...
** Water on Mars
* Physical characteristics of Jupiter
** Structure of Jupiter
** Atmosphere of Jupiter
The atmosphere of Jupiter is the largest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System. It is mostly made of molecular hydrogen and helium in roughly Sun#Composition, solar proportions; other chemical compounds are present only in small amounts and in ...
** Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432 ...
* Physical characteristics of Saturn
** Structure of Saturn
** Atmosphere of Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
** Saturn's hexagon
Saturn's hexagon is a persistent approximately hexagonal cloud pattern around the north pole of the planet Saturn, located at about 78°N.
The sides of the hexagon are about long, which is about longer than the diameter of Earth.
The hexagon ...
* Physical characteristics of Uranus
** Structure of Uranus
** Atmosphere of Uranus
* Physical characteristics of Neptune
** Structure of Neptune
** Atmosphere of Neptune
** Great Dark Spot
The Great Dark Spot (also known as GDS-89, for Great Dark Spot, 1989) was one of a series of dark spots on Neptune similar in appearance to Jupiter's Great Red Spot. In 1989, GDS-89 was the first Great Dark Spot on Neptune to be observed by NASA ...
History of the Solar System
History of the Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a ...
Discovery and exploration of the Solar System
Discovery and exploration of the Solar System – * Timeline of Solar System astronomy * Timeline of discovery of Solar System planets and their moons * Timeline of Solar System exploration *Timeline of first images of Earth from space
This is a timeline of first images of Earth from space. The initial photographs and digital images of planet Earth taken from outer space were preceded by aerial photography and continue in the form of satellite imagery.
For the purpose of this ...
* Development of hypotheses
** Geocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model (also known as geocentrism, often exemplified specifically by the Ptolemaic system) is a superseded description of the Universe with Earth at the center. Under most geocentric models, the Sun, Moon, stars, an ...
–
** Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at ...
–
** Historical models of the Solar System
The historical models of the Solar System began during prehistoric periods and are updated to this day. The models of the Solar System throughout history were first represented in the early form of cave markings and drawings, calendars and astro ...
** Planets beyond Neptune
** List of former planets
This is a list of astronomical objects formerly widely considered ''planets'' under any of the various definitions of this word in the history of astronomy. As the definition of planet, definition of ''planet'' has evolved, the wikt:en:de facto#Eng ...
** List of hypothetical Solar System objects
A hypothetical Solar System object is a planet, natural satellite, subsatellite or similar body in the Solar System whose existence is not known, but has been inferred from observational scientific evidence. Over the years a number of hypothetic ...
in astronomy
* Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacec ...
– Exploration by celestial body
** Exploration of Mercury
The exploration of Mercury has a minor role in the space interests of the world. It is the least explored inner planet.JHU/APL (2006)MESSENGER: MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and RangingRetrieved on 2007-01-27 As of 2015, the ' ...
** Observations and explorations of Venus
Observations of the planet Venus include those in antiquity, telescopic observations, and from visiting spacecraft. Spacecraft have performed various flybys, orbits, and landings on Venus, including balloon probes that floated in the atmospher ...
** Exploration of the Moon
** Exploration of Mars
** Exploration of Ceres
** Exploration of Jupiter
** Exploration of Saturn
** Exploration of Uranus
** Exploration of Neptune
** Exploration of Pluto
The exploration of Pluto began with the arrival of the '' New Horizons'' probe in July 2015, though proposals for such a mission had been studied for many decades. There are no plans as yet for a follow-up mission, though follow-up concepts have ...
* Solar System model
Solar System models, especially mechanical models, called ''orreries'', that illustrate the relative positions and motions of the planets and Natural satellite, moons in the Solar System have been built for centuries. While they often showed rela ...
s
Formation and evolution of the Solar System
Formation and evolution of the Solar System
The formation of the Solar System began about 4.6 billion years ago with the gravitational collapse of a small part of a giant molecular cloud. Most of the collapsing mass collected in the center, forming the Sun, while the rest flattened into a ...
–
* Nebular hypothesis
* Terrestrial planets
** Iron planet ]
An iron planet is a type of planet that consists primarily of an iron-rich core with little or no mantle. Mercury is the largest celestial body of this type in the Solar System (as the other terrestrial planets are silicate planets), but larger ...
s
*** Mercury
** Silicate planets
*** Geodynamics of Venus
NASA's Magellan spacecraft mission discovered that Venus has a geologically young surface with a relatively uniform age of 500±200 Ma (million years). The age of Venus was revealed by the observation of over 900 impact craters on the surface of t ...
*** History of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologi ...
**** Formation of Earth
*** Geological history of Mars
The geological history of Mars follows the physical evolution of Mars as substantiated by observations, indirect and direct measurements, and various inference techniques. Methods dating back to 17th century techniques developed by Nicholas Steno, ...
* Giant planets
** Gas giants
*** Jupiter
*** Saturn
** Ice giant
An ice giant is a giant planet composed mainly of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium, such as oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. There are two ice giants in the Solar System: Uranus and Neptune.
In astrophysics and planetary science t ...
s
*** Uranus
*** Neptune
See also
* Outline of astronomy *Outline of space exploration
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to space exploration.
Space exploration – use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space.
Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spac ...
* Lists of geological features of the Solar System
**List of craters in the Solar System
This is a list of named craters in the Solar System as named by IAU's Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature. As of 2017, there is a total of 5,223 craters on 40 astronomical bodies, which includes minor planets (asteroids and dwarf plan ...
* List of Solar System objects
* List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
* List of possible dwarf planets
The number of dwarf planets in the Solar System is unknown. Estimates have run as high as 200 in the Kuiper belt and over 10,000 in the region beyond.
However, consideration of the surprisingly low densities of many large trans-Neptunian object ...
* List of Solar System extremes
**By size
*** List of Solar System objects by size
**By distance
*** List of Solar System objects most distant from the Sun
*** List of Solar System objects by greatest aphelion
**Features
***List of tallest mountains in the Solar System
This is a list of the tallest mountains in the Solar System. This list includes peaks on all celestial bodies where significant mountains have been detected. For some celestial bodies, different peaks are given across different types of measure ...
*** List of largest craters in the Solar System
***List of largest rifts, canyons and valleys in the Solar System
Following are the longest, widest, and deepest rifts and valleys in various worlds of the Solar System.
List
See also
* List of Solar System extremes
** List of largest craters in the Solar System
** List of tallest mountains in the Solar Sys ...
* List of exceptional asteroids
The following is a collection of lists of asteroids of the Solar System that are exceptional in some way, such as their size or orbit. For the purposes of this article, "asteroid" refers to minor planets out to the orbit of Neptune, and includes ...
* Planetary mnemonic
A planetary mnemonic refers to a phrase created to remember the planets and dwarf planets of the Solar System, with the order of words corresponding to increasing sidereal periods of the bodies. One simple visual mnemonic is to hold out both hands ...
* HIP 11915
HIP 11915 is a G-type main-sequence star located about 190 light-years from Earth in the constellation Cetus. It is best known for its characteristics, which are very similar to those of the Sun, including the mass, radius, temperature, me ...
(a solar analog whose planetary system contains a Jupiter analog)
The number of currently known, or observed, objects of the Solar System are in the hundreds of thousands. Many of them are listed in the following articles:
* List of natural satellites
* List of minor planets
The following is a list of numbered minor planets in ascending numerical order. With the exception of comets, minor planets are all small bodies in the Solar System, including asteroids, distant objects and dwarf planets. The catalog consists ...
(numbered) and List of unnumbered minor planets
The following is a list of unnumbered minor planets in chronological order of their principal provisional designation. Contrary to their numbered counterparts, unnumbered minor planets have a poorly determined orbit due to insufficient observat ...
* List of trans-Neptunian objects (numbered) and List of unnumbered trans-Neptunian objects
This is a list of unnumbered trans-Neptunian objects (TNOs) first observed since 1993 and grouped by the year of principal provisional designation. The data is sourced from the Minor Planet Center's (MPC) ''List of Trans Neptunian Objects'' an ...
* Lists of comets
Non-periodic comets are seen only once. They are usually on near-parabolic orbits that will not return to the vicinity of the Sun for thousands of years, if ever.
Periodic comets usually have elongated elliptical orbits, and usually return to th ...
External links
dmoz page for Solar System
*
A Cosmic History of the Solar System
NASA/JPL Solar System main page
*
NASA's Solar System Simulator
*
Solar System Profile
b
NASA's Solar System Exploration
{{Outline footer * Wikipedia outlines