|
Geology Of Mars
The geology of Mars is the scientific study of the surface, crust, and interior of the planet Mars. It emphasizes the composition, structure, history, and physical processes that shape the planet. It is analogous to the field of terrestrial geology. In planetary science, the term ''geology'' is used in its broadest sense to mean the study of the solid parts of planets and moons. The term incorporates aspects of geophysics, geochemistry, mineralogy, geodesy, and cartography. A neologism, areology, from the Greek word ''Arēs'' (Mars), sometimes appears as a synonym for Mars's geology in the popular media and works of science fiction (e.g. Kim Stanley Robinson, Kim Stanley Robinson's Mars trilogy). The term areology is also used by the Areological Society. Geological map of Mars (2014) File:Geologic Map of Mars figure2.pdf, Figure 2 for the geologic map of Mars Global Martian topography and large-scale features Composition of Mars Mars is a terrestrial planet, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
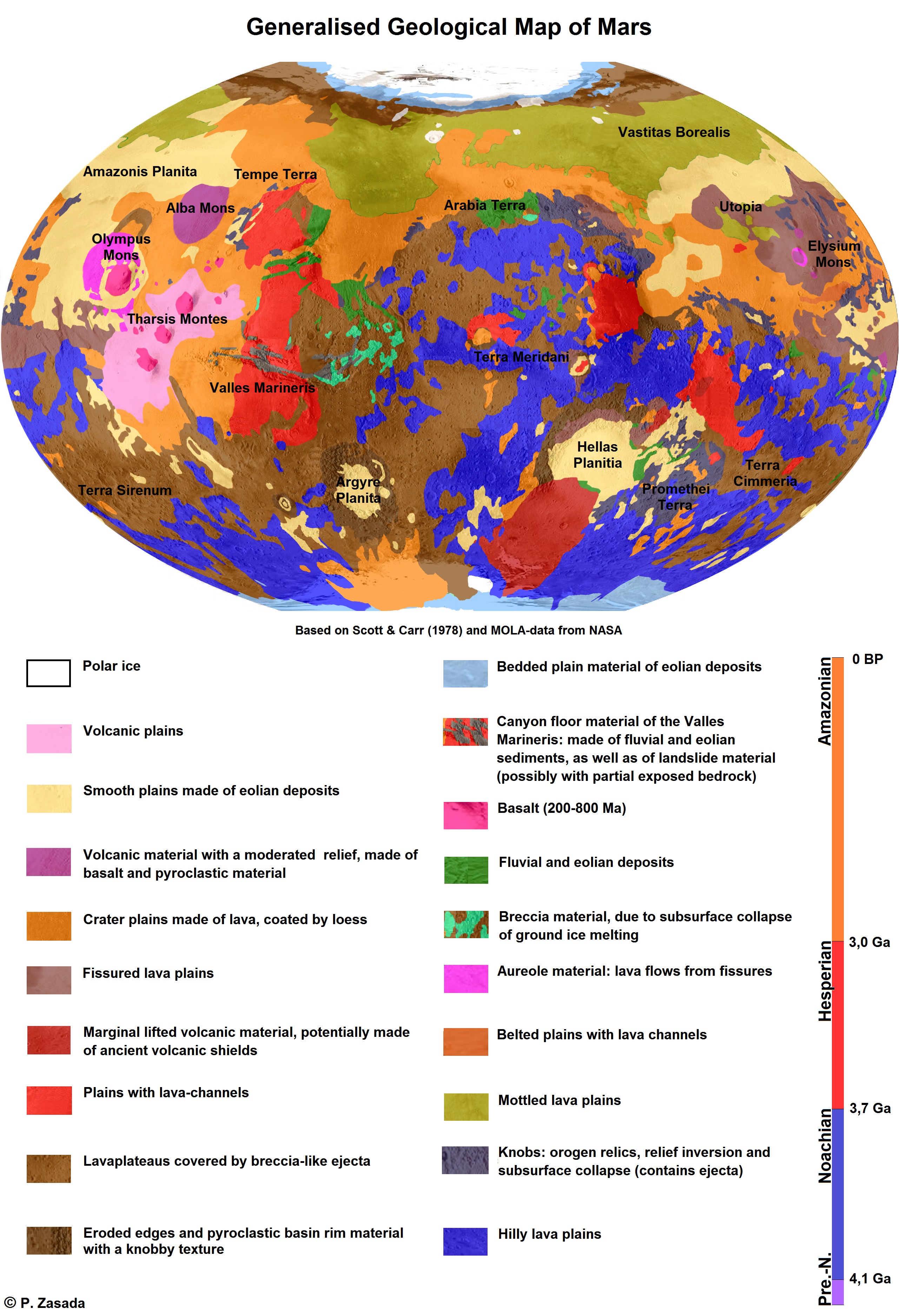
Generalised Geological Map Of Mars
A generalization is a form of abstraction whereby common properties of specific instances are formulated as general concepts or claims. Generalizations posit the existence of a domain or set of elements, as well as one or more common characteristics shared by those elements (thus creating a conceptual model). As such, they are the essential basis of all valid deductive inferences (particularly in logic, mathematics and science), where the process of verification is necessary to determine whether a generalization holds true for any given situation. Generalization can also be used to refer to the process of identifying the parts of a whole, as belonging to the whole. The parts, which might be unrelated when left on their own, may be brought together as a group, hence belonging to the whole by establishing a common relation between them. However, the parts cannot be generalized into a whole—until a common relation is established among ''all'' parts. This does not mean that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
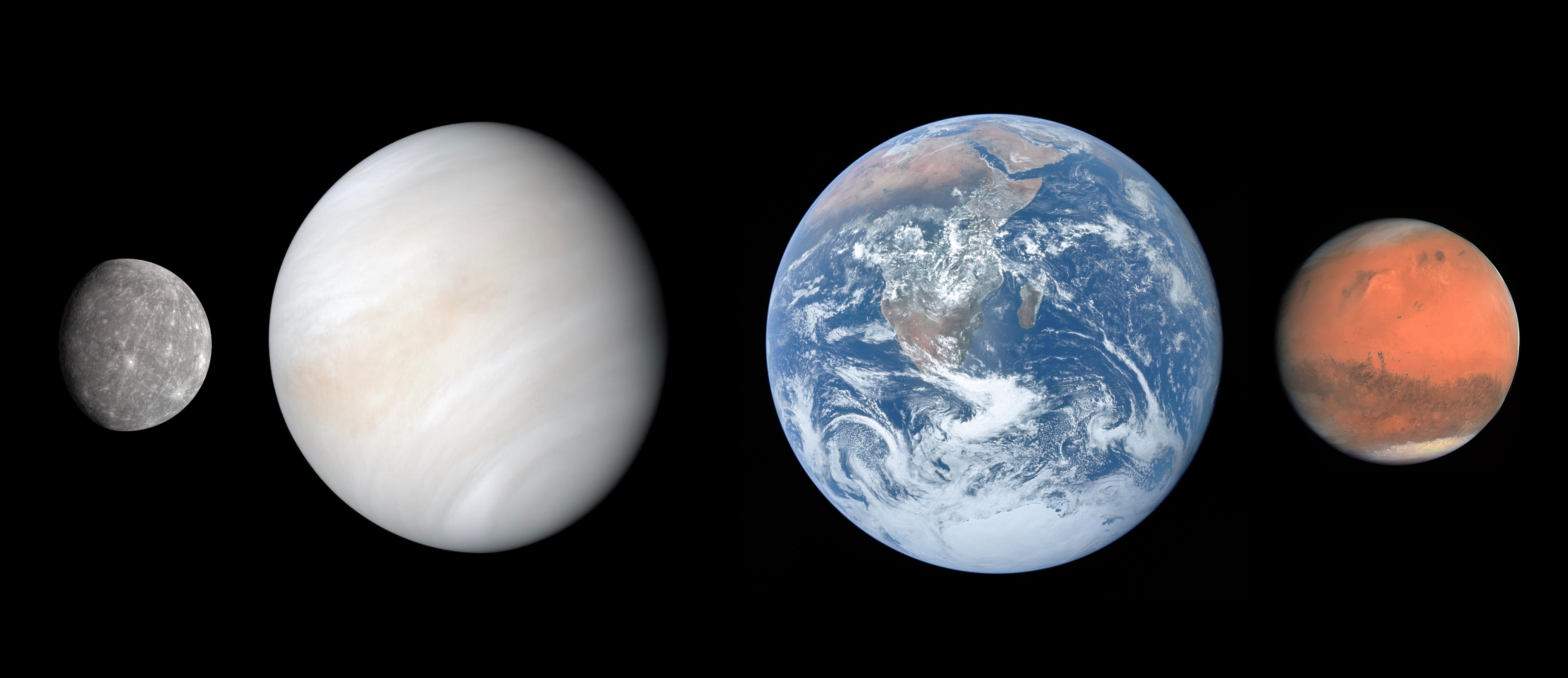
Terrestrial Planet
A terrestrial planet, telluric planet, or rocky planet, is a planet that is composed primarily of silicate rocks or metals. Within the Solar System, the terrestrial planets accepted by the IAU are the inner planets closest to the Sun: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. Among astronomers who use the geophysical definition of a planet, two or three planetary-mass satellites – Earth's Moon, Io, and sometimes Europa – may also be considered terrestrial planets; and so may be the rocky protoplanet-asteroids Pallas and Vesta.Emily Lakdawalla et al.What Is A Planet?The Planetary Society, 21 April 2020 The terms "terrestrial planet" and "telluric planet" are derived from Latin words for Earth (''Terra'' and ''Tellus''), as these planets are, in terms of structure, ''Earth-like''. Terrestrial planets are generally studied by geologists, astronomers, and geophysicists. Terrestrial planets have a solid planetary surface, making them substantially different from the larger gaseous plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tharsis
Tharsis () is a vast volcanic plateau centered near the equator in the western hemisphere of Mars. The region is home to the largest volcanoes in the Solar System, including the three enormous shield volcanoes Arsia Mons, Pavonis Mons, and Ascraeus Mons, which are collectively known as the Tharsis Montes. The tallest volcano on the planet, Olympus Mons, is often associated with the Tharsis region but is actually located off the western edge of the plateau. The name Tharsis is the Greco-Latin transliteration of the biblical Tarshish, the land at the western extremity of the known world. Location and size Tharsis can have many meanings depending on historical and scientific context. The name is commonly used in a broad sense to represent a continent-sized region of anomalously elevated terrain centered just south of the equator around longitude 265°E.Carr, M.H. (2006). ''The Surface of Mars;'' Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, p. 46. . Called the Tharsis bulge or Thar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of ''continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or ''transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
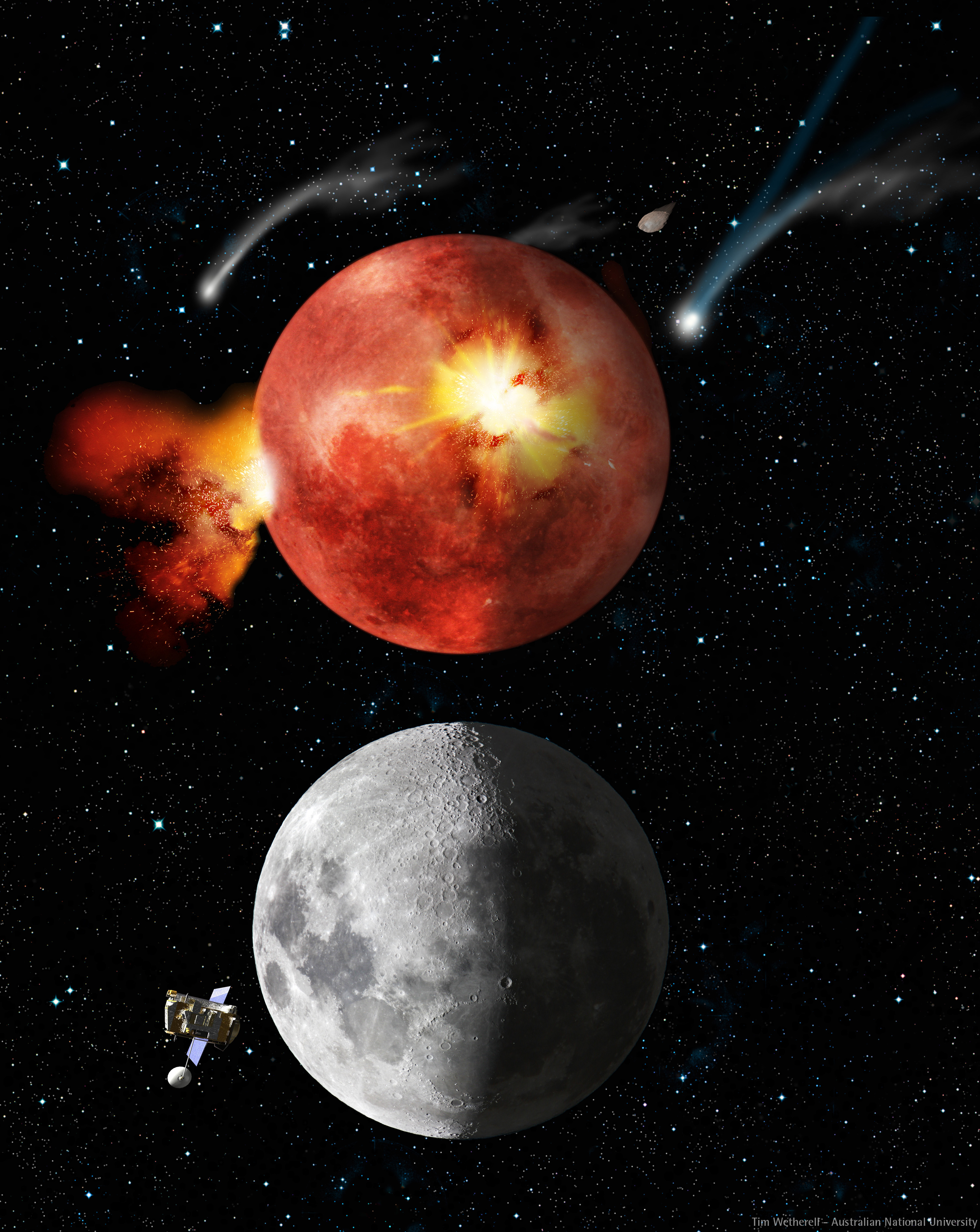
Late Heavy Bombardment
The Late Heavy Bombardment (LHB), or lunar cataclysm, is a hypothesized event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, at a time corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. According to the hypothesis, during this interval, a disproportionately large number of asteroids and comets collided with the early terrestrial planets in the inner Solar System, including Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. These came from both post-accretion and planetary instability-driven populations of impactors. Although widely accepted, it remains difficult to prove conclusively. Evidence for the LHB derives from rock samples of Moon craters brought back by the Apollo astronauts. Isotopic dating showed that the rocks were last molten during impact events in a rather narrow interval of time, suggesting that a large proportion of craters were formed during this period. Several hypotheses attempt to explain this apparent spike in the flux of impactors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dichotomy
A dichotomy is a partition of a whole (or a set) into two parts (subsets). In other words, this couple of parts must be * jointly exhaustive: everything must belong to one part or the other, and * mutually exclusive: nothing can belong simultaneously to both parts. If there is a concept A, and it is split into parts B and not-B, then the parts form a dichotomy: they are mutually exclusive, since no part of B is contained in not-B and vice versa, and they are jointly exhaustive, since they cover all of A, and together again give A. Such a partition is also frequently called a bipartition. The two parts thus formed are complements. In logic, the partitions are opposites if there exists a proposition such that it holds over one and not the other. Treating continuous variables or multi categorical variables as binary variables is called dichotomization. The discretization error inherent in dichotomization is temporarily ignored for modeling purposes. Etymology The term '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and Impact structure, structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped History of the Earth, Earth's history, and have been implicated in the giant impact theory, formation of the Earth� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles is essential to geomorphologists to explain erosion patterns and other Earth surface features. Main types of tectonic regime Extensional tectonics Extensional tectonics is associated with the stretching and thinning of the crust or the lithosphere. This type of tectonics is found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising magma can cool and solidify without reaching the surface. Inste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Experiment For Interior Structure
The Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure (SEIS) is a seismometer and the primary scientific instrument on board the ''InSight'' Mars lander launched on 5 May 2018 for a landing on 26 November 2018; the instrument was deployed to the surface of Mars on 19 December. SEIS is expected to provide seismic measurements of marsquakes, enabling researchers to develop 3D structure maps of the deep interior. Better understanding the internal structure of Mars will lead to better understanding of the Earth, Moon, and rocky planetary bodies in general. SEIS detected marsquakes in Cerberus Fossae in 2019. On 24 December 2021, the seismometer for the InSight mission on Mars detected a large seismic event with a distinct signature. The event was caused by a meteor impact on the surface of Mars, which was confirmed by satellite observations of a newly formed 150-kilometer crater. Overview Mars flybys and landings to gather scientific data have been conducted since the 1960s, but quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |