List of Roman battles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The following is a List of Roman wars and battles fought by the ancient
 * Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women)
* Conquest of Cameria
* War with Fidenae and Veii
* Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women)
* Conquest of Cameria
* War with Fidenae and Veii
 * Roman-Sabine wars
* War with the Volsci
* War with Gabii
* War with the Rutuli
* Roman-Etruscan wars
** 509 BC –
* Roman-Sabine wars
* War with the Volsci
* War with Gabii
* War with the Rutuli
* Roman-Etruscan wars
** 509 BC –
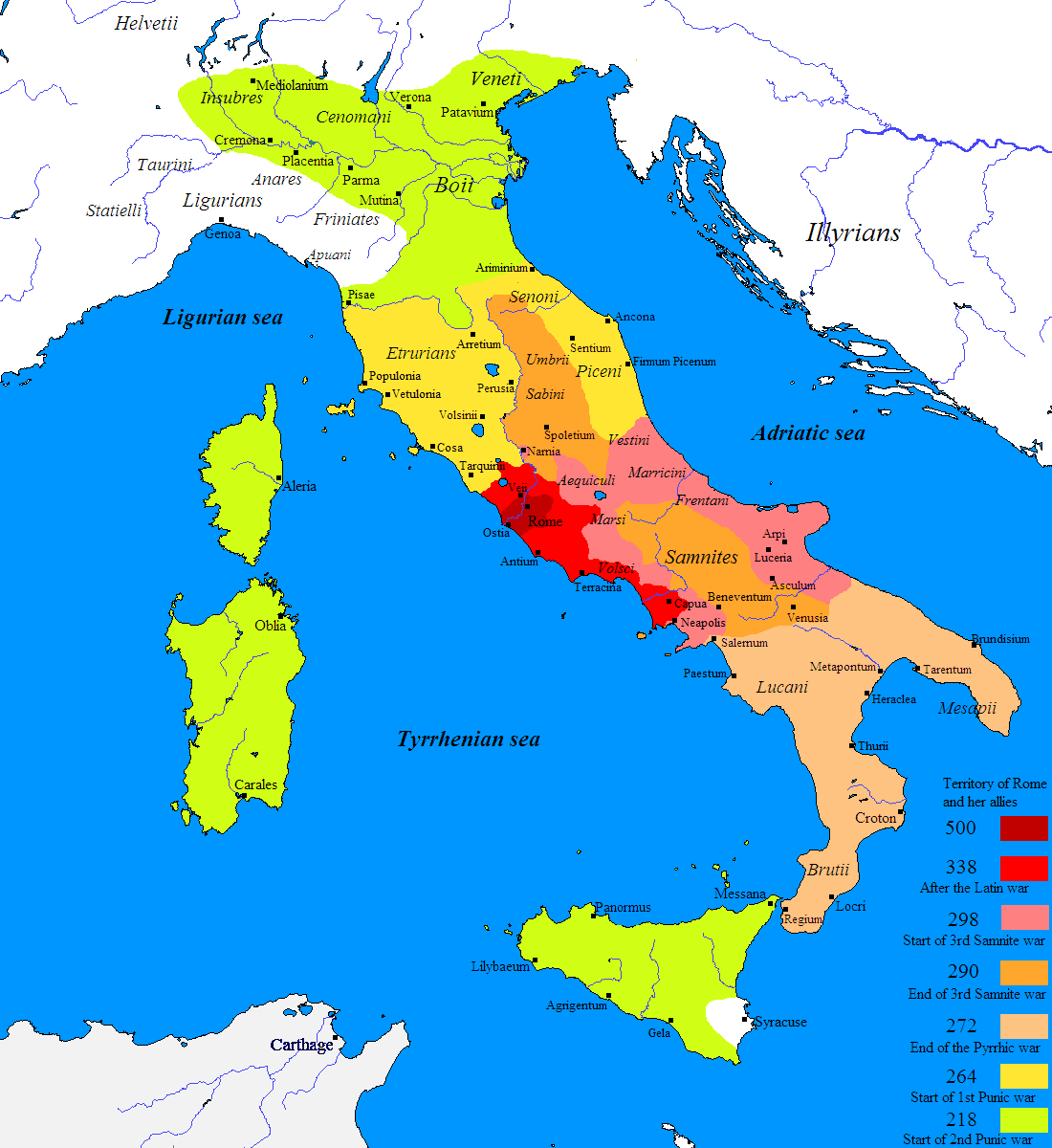 *
* 
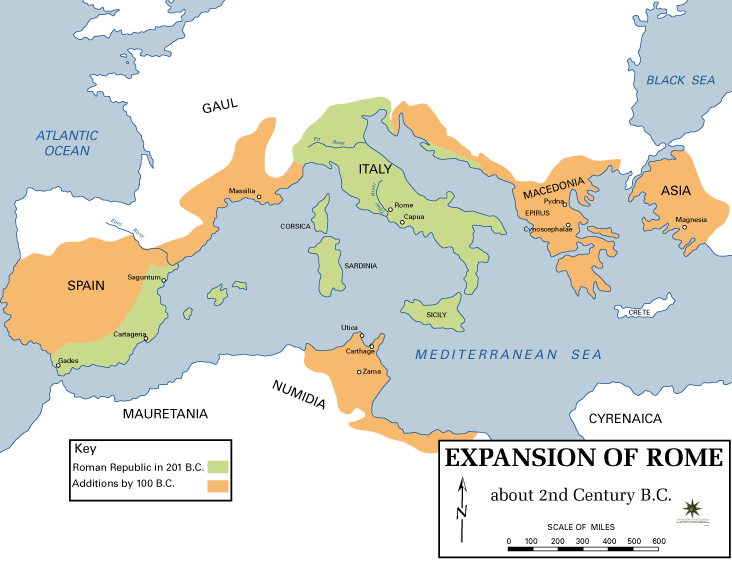
 * Social War (91–87 BC)
** 89 BC – Battle of Fucine Lake – Roman forces under
* Social War (91–87 BC)
** 89 BC – Battle of Fucine Lake – Roman forces under 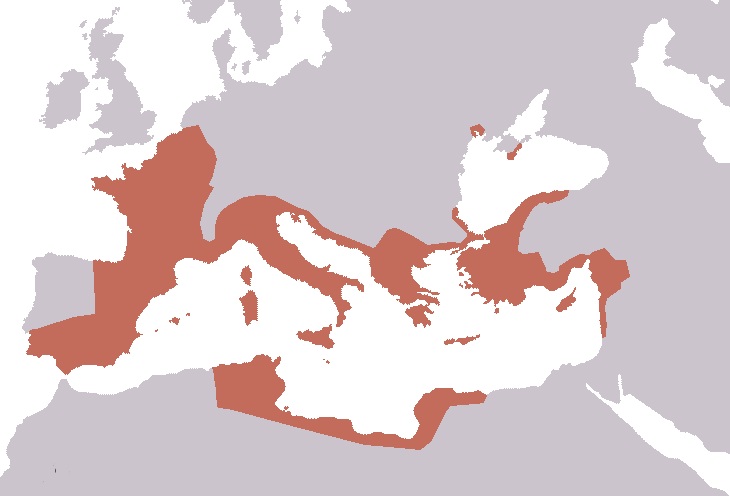 *
*
 *
*
 *
*

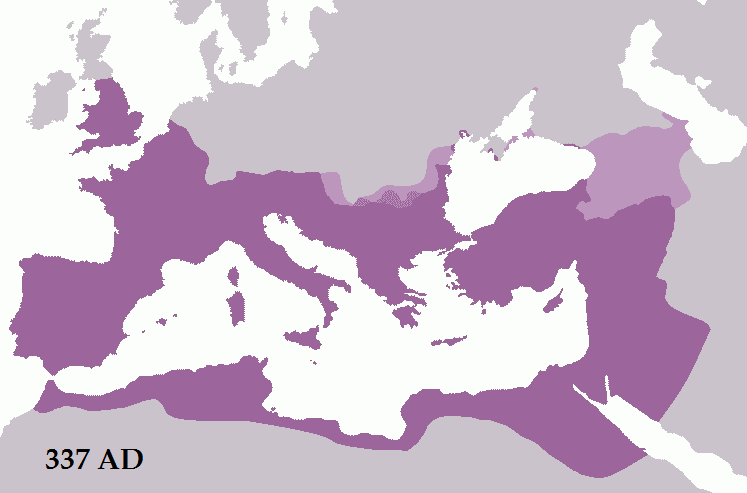 The 4th century begins with civil war resulting in the ascendancy of Constantine the Great, Constantine I, then, after his death, the progressive Christianization of the empire, and wars with Sasanian Empire, Sassanid Persia and Germanic tribes, punctuated frequently with more civil wars.
* Civil wars of the Tetrarchy, Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324)
** 312 –
*** Battle of Turin (312), Battle of Turin – Constantine I (emperor), Constantine I defeats forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** Battle of Verona (312), Battle of Verona – Constantine I defeats more forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** 28 October – Battle of Milvian Bridge – Constantine I defeats Maxentius and takes control of Italy.
** 313, 30 April – Battle of Tzirallum – In the eastern part of the Empire, the forces of Licinius defeat Maximinus II, Maximinus.
** 316, 8 October – Battle of Cibalae – Constantine defeats Licinius
** 316 or 317 – Battle of Mardia – Constantine again defeats Licinius, who cedes Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum, Illyricum to Constantine.
** 324 –
*** 3 July – Battle of Adrianople (324), Battle of Adrianople – Constantine defeats Licinius, who flees to Byzantium
*** July – Battle of the Hellespont – Flavius Julius Crispus, son of Constantine, defeats the naval forces of Licinius
*** 18 September – Battle of Chrysopolis – Constantine decisively defeats Licinius, establishing his sole control over the empire.
* Roman–Persian Wars, Wars with Persia (344–363)
** 344 – Battle of Singara – Emperor Constantius II fights an indecisive battle against King Shapur II of Persia
** 359 – Siege of Amida (359), Siege of Amida – Sassanids capture Amida (Roman city), Amida from Romans
** 363, 29 May – Battle of Ctesiphon (363), Battle of Ctesiphon – Emperor Julian (emperor), Julian defeats Shapur II of Persia outside the walls of the Persian capital, but is unable to take the city.
** 363, June – Battle of Samarra (363) – Julian the Apostate, Julian fights the Sassanids and is subsequently killed in battle. Though indecisive, the battle leads to massive losses for the Roman Empire through a forced peace treaty.
* Roman civil war of 350–353, Civil War (350–353)
** 351 – Battle of Mursa Major – Emperor Constantius II defeats the usurper Magnentius
** 353 – Battle of Mons Seleucus – Final defeat of Magnentius by Constantius II
* Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus – 351–352 - Rebellion of Jews in Syria Palaestina.
* Wars with Alemanni (356–378)
** 356 – Battle of Reims (356), Battle of Reims – Caesar (title), Caesar Julian the Apostate, Julian is defeated by the Alamanni
** 357 – Battle of Strasbourg – Julian expels the Alamanni from the Rhineland
** 368 – Battle of Solicinium – Romans under Emperor Valentinian I defeat yet another Alamanni incursion.
** 378 –
*** May – Battle of Argentovaria – Western Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alamanni, yet again.
* Civil War – 366 – Battle of Thyatira – The army of the Roman emperor Valens defeats the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius.
* Great Conspiracy – 367-368 - Rebellion in the Hadrian's Wall and failed invasion of Britain by Picts, Scotti, Attacotti, Saxons and Franks.
* Gothic War (376–382)
** 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
***Summer -Battle of Dibaltum –Goths, Alans and Huns defeat Romans.
** 378 –
*** 9 August – Battle of Adrianople – Thervings under Fritigern defeat and kill the Eastern Emperor Valens
** 380 – Battle of Thessalonica (380), Battle of Thessalonica – The new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius I, is also defeated by the Thervings under Fritigern.
* Mavia (queen)#Details of the revolt, Tanukh revolt against Rome– 378-Spring - the Tanukhids Arabs rebels against Roman rule, led by their queen Mavia in Syria. The revolt end in a truce.
* Civil War – 388 – Battle of the Save – Emperor Theodosius I defeats the usurper Magnus Maximus.
* Civil War – 394, 5–6 September – Battle of the Frigidus – Theodosius I defeats and kills the usurper Eugenius and his Franks, Frankish ''magister militum'' Arbogast (magister militum), Arbogast.
* Stilicho's Pictish War – 398(?)
* Civil War – 398, Gildonic War – ''Comes'' Gildo, governor of Africa, rebels against the Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius.The revolt was subdued by Stilicho, Flavius Stilicho, the ''magister militum'' of the Western Roman empire.
The 4th century begins with civil war resulting in the ascendancy of Constantine the Great, Constantine I, then, after his death, the progressive Christianization of the empire, and wars with Sasanian Empire, Sassanid Persia and Germanic tribes, punctuated frequently with more civil wars.
* Civil wars of the Tetrarchy, Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324)
** 312 –
*** Battle of Turin (312), Battle of Turin – Constantine I (emperor), Constantine I defeats forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** Battle of Verona (312), Battle of Verona – Constantine I defeats more forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** 28 October – Battle of Milvian Bridge – Constantine I defeats Maxentius and takes control of Italy.
** 313, 30 April – Battle of Tzirallum – In the eastern part of the Empire, the forces of Licinius defeat Maximinus II, Maximinus.
** 316, 8 October – Battle of Cibalae – Constantine defeats Licinius
** 316 or 317 – Battle of Mardia – Constantine again defeats Licinius, who cedes Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum, Illyricum to Constantine.
** 324 –
*** 3 July – Battle of Adrianople (324), Battle of Adrianople – Constantine defeats Licinius, who flees to Byzantium
*** July – Battle of the Hellespont – Flavius Julius Crispus, son of Constantine, defeats the naval forces of Licinius
*** 18 September – Battle of Chrysopolis – Constantine decisively defeats Licinius, establishing his sole control over the empire.
* Roman–Persian Wars, Wars with Persia (344–363)
** 344 – Battle of Singara – Emperor Constantius II fights an indecisive battle against King Shapur II of Persia
** 359 – Siege of Amida (359), Siege of Amida – Sassanids capture Amida (Roman city), Amida from Romans
** 363, 29 May – Battle of Ctesiphon (363), Battle of Ctesiphon – Emperor Julian (emperor), Julian defeats Shapur II of Persia outside the walls of the Persian capital, but is unable to take the city.
** 363, June – Battle of Samarra (363) – Julian the Apostate, Julian fights the Sassanids and is subsequently killed in battle. Though indecisive, the battle leads to massive losses for the Roman Empire through a forced peace treaty.
* Roman civil war of 350–353, Civil War (350–353)
** 351 – Battle of Mursa Major – Emperor Constantius II defeats the usurper Magnentius
** 353 – Battle of Mons Seleucus – Final defeat of Magnentius by Constantius II
* Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus – 351–352 - Rebellion of Jews in Syria Palaestina.
* Wars with Alemanni (356–378)
** 356 – Battle of Reims (356), Battle of Reims – Caesar (title), Caesar Julian the Apostate, Julian is defeated by the Alamanni
** 357 – Battle of Strasbourg – Julian expels the Alamanni from the Rhineland
** 368 – Battle of Solicinium – Romans under Emperor Valentinian I defeat yet another Alamanni incursion.
** 378 –
*** May – Battle of Argentovaria – Western Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alamanni, yet again.
* Civil War – 366 – Battle of Thyatira – The army of the Roman emperor Valens defeats the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius.
* Great Conspiracy – 367-368 - Rebellion in the Hadrian's Wall and failed invasion of Britain by Picts, Scotti, Attacotti, Saxons and Franks.
* Gothic War (376–382)
** 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
***Summer -Battle of Dibaltum –Goths, Alans and Huns defeat Romans.
** 378 –
*** 9 August – Battle of Adrianople – Thervings under Fritigern defeat and kill the Eastern Emperor Valens
** 380 – Battle of Thessalonica (380), Battle of Thessalonica – The new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius I, is also defeated by the Thervings under Fritigern.
* Mavia (queen)#Details of the revolt, Tanukh revolt against Rome– 378-Spring - the Tanukhids Arabs rebels against Roman rule, led by their queen Mavia in Syria. The revolt end in a truce.
* Civil War – 388 – Battle of the Save – Emperor Theodosius I defeats the usurper Magnus Maximus.
* Civil War – 394, 5–6 September – Battle of the Frigidus – Theodosius I defeats and kills the usurper Eugenius and his Franks, Frankish ''magister militum'' Arbogast (magister militum), Arbogast.
* Stilicho's Pictish War – 398(?)
* Civil War – 398, Gildonic War – ''Comes'' Gildo, governor of Africa, rebels against the Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius.The revolt was subdued by Stilicho, Flavius Stilicho, the ''magister militum'' of the Western Roman empire.
 The 5th century involves the final fall of the Western Roman Empire to Goths, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Franks and other peoples.
* Wars with the Goths (402–419)
** 402 –
*** Siege of Asti (402) - The Visigoths besieged Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius in Asti until March, when Stilicho sent reinforcements .
*** 6 April – Battle of Pollentia – Stilicho defeats the Visigoths under Alaric I, Alaric.
*** June – Battle of Verona (402), Battle of Verona – Stilicho defeats Alaric, who withdraws from Italy.
** 405 or 406-
*** Siege of Florence (405), Siege of Florence - Stilcho defends city from the Goths of king Radagaisus, but Florence is nearly destroyed.
**406
*** Battle of Faesulae (406), Battle of Faesulae - Stilicho defeats Visigoths and Vandals under Radagaisus.
**409-
***Battle of Ostia (409), Battle of Ostia – Visigoths under Alaric I defeat Romans.
** 410, 24 August – Sack of Rome (410), Sack of Rome – Visigoths under Alaric sack Rome.
** 413 – Siege of Massilia (413), Siege of Massilia – Visigoths under Ataulf are defeated by Romans under Bonifacius while trying to siege Roman city. They make peace with Rome soon after.
* Roman–Sasanian War of 421–422 - The Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II declared war against the Persians and obtained some victories, but in the end, the two powers agreed to sign a peace on the status quo ante.
* Civil War – 432 – Battle of Ravenna (432), Battle of Ravenna – Bonifacius defeats rival Roman general Flavius Aetius, but is mortally wounded in the process.
* War with the Huns (447–451)
** 447 – Battle of the Utus – The Eastern Romans fight an indecisive battle with Huns led by Attila.
** 451, 20 June – Battle of the Catalaunian Plains – The Romans with Flavius Aetius and the Visigoths with Theodoric, defend against Attila, ruler of the Huns#Unified empire under Attila, Hunnic Empire.
** 452, 18 July –Sack of Aquileia –Aquileia is razed to the ground by the forces of Attila the Hun.
* Fall of the Western Roman Empire (406–476)
** 406, 31 December –
***Battle of Mainz (406), Battle of Mainz – Franks lose to Vandals, Suebi and Alans.
***Crossing of the Rhine -A mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi, crossed into northern Gaul.
** 419 – Battle of the Nervasos Mountains – Western Romans and Suebi defeat Vandals and Alans.
** 422 – Battle of Tarraco – The Vandal king Gunderic defeat the Western Romans, making the Vandals the undisputed masters of Hispania.
** 425 – Siege of Arles (425), Siege of Arles -The Roman general Flavius Aëtius, Aëtius defeats the Visigoths under Theodorid, Theodoric I.
** 431 - Siege of Hippo Regius – Vandals under Genseric establish a foothold in Africa, strategically defeating Rome. Saint Augustine dies during the siege.
** 436 – Battle of Narbonne (436), Battle of Narbonne – Flavius Aetius again defeats the Visigoths led by Theodoric I, Theodoric.
** 439
*** 19 October - Battle of Carthage (439), Battle of Carthage – Romans lose Carthage to the Vandals.
*** Battle of Toulouse (439), Battle of Toulouse – Visigoths led by Theodoric I defeat Romans under General Litorius, who is killed.
** c. 445-450 - Battle of Vicus Helena – Romans under Aetius defeat Franks.
** 455
*** 2 – c. 16 June – Sack of Rome (455), Sack of Rome by Geiseric, King of the Vandals
*** Battle of Aylesford – Romano-Britons (under Vortimer) and Anglo-Saxons battle in Kent, victory is unclear.
** 456 –
*** Battle of Agrigentum (456) – An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the Romano-Suebian general Ricimer, drove off an invading fleet sent by the Vandals, Vandal king Genseric, Gaiseric to raid Sicily.
*** Battle of Corsica - the Vandals were again attacked by Ricimer and defeated.
** 457 –
*** Battle of Garigliano (457) –The new Roman emperor, emperor Majorian surprised a Vandal-Berbers, Berber raiding party which was returning with loot from Campania.
***Battle of Campi Cannini – Roman General Majorian defeats an Alemanni invasion of Italy.
** 458 –
*** Battle of Toulouse (458) -The Roman Emperor Majorian defeats the Visigoths.
*** Late 458 Battle of Arelate -The Roman Emperor Majorian, with the support of Aegidius and Nepotianus (magister militiae), Nepotianus, defeats the Visigoths at Arlate. With a treaty, the Visigothic returned all territory in Hispania to the Romans.
** 461 –Battle of Cartagena (461), Battle of Cartagena – A Vandal fleet surprises and destroys the Roman fleet.
** 463 – Battle of Orleans (463), Battle of Orleans – Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman and Salian Franks, Salian Frank forces under the command of Aegidius defeat a force of Visigoths at Orleans.
** 464 – Battle of Bergamo – Romans under General Ricimer defeat Alans, Alan invasion of Italy and kill their king.
** 468 – Battle of Cap Bon (468), Battle of Cap Bon - Failure of the invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals by the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
** 469 – Battle of Déols - Visigoths defeat Bretons and Gallo-Romanas under Riothamus.
** 471 – Battle of Arles (471) - Visigothic king Euric defeats the Roman general Anthemiolus, captured Arles and much of southern
The 5th century involves the final fall of the Western Roman Empire to Goths, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Franks and other peoples.
* Wars with the Goths (402–419)
** 402 –
*** Siege of Asti (402) - The Visigoths besieged Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius in Asti until March, when Stilicho sent reinforcements .
*** 6 April – Battle of Pollentia – Stilicho defeats the Visigoths under Alaric I, Alaric.
*** June – Battle of Verona (402), Battle of Verona – Stilicho defeats Alaric, who withdraws from Italy.
** 405 or 406-
*** Siege of Florence (405), Siege of Florence - Stilcho defends city from the Goths of king Radagaisus, but Florence is nearly destroyed.
**406
*** Battle of Faesulae (406), Battle of Faesulae - Stilicho defeats Visigoths and Vandals under Radagaisus.
**409-
***Battle of Ostia (409), Battle of Ostia – Visigoths under Alaric I defeat Romans.
** 410, 24 August – Sack of Rome (410), Sack of Rome – Visigoths under Alaric sack Rome.
** 413 – Siege of Massilia (413), Siege of Massilia – Visigoths under Ataulf are defeated by Romans under Bonifacius while trying to siege Roman city. They make peace with Rome soon after.
* Roman–Sasanian War of 421–422 - The Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II declared war against the Persians and obtained some victories, but in the end, the two powers agreed to sign a peace on the status quo ante.
* Civil War – 432 – Battle of Ravenna (432), Battle of Ravenna – Bonifacius defeats rival Roman general Flavius Aetius, but is mortally wounded in the process.
* War with the Huns (447–451)
** 447 – Battle of the Utus – The Eastern Romans fight an indecisive battle with Huns led by Attila.
** 451, 20 June – Battle of the Catalaunian Plains – The Romans with Flavius Aetius and the Visigoths with Theodoric, defend against Attila, ruler of the Huns#Unified empire under Attila, Hunnic Empire.
** 452, 18 July –Sack of Aquileia –Aquileia is razed to the ground by the forces of Attila the Hun.
* Fall of the Western Roman Empire (406–476)
** 406, 31 December –
***Battle of Mainz (406), Battle of Mainz – Franks lose to Vandals, Suebi and Alans.
***Crossing of the Rhine -A mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi, crossed into northern Gaul.
** 419 – Battle of the Nervasos Mountains – Western Romans and Suebi defeat Vandals and Alans.
** 422 – Battle of Tarraco – The Vandal king Gunderic defeat the Western Romans, making the Vandals the undisputed masters of Hispania.
** 425 – Siege of Arles (425), Siege of Arles -The Roman general Flavius Aëtius, Aëtius defeats the Visigoths under Theodorid, Theodoric I.
** 431 - Siege of Hippo Regius – Vandals under Genseric establish a foothold in Africa, strategically defeating Rome. Saint Augustine dies during the siege.
** 436 – Battle of Narbonne (436), Battle of Narbonne – Flavius Aetius again defeats the Visigoths led by Theodoric I, Theodoric.
** 439
*** 19 October - Battle of Carthage (439), Battle of Carthage – Romans lose Carthage to the Vandals.
*** Battle of Toulouse (439), Battle of Toulouse – Visigoths led by Theodoric I defeat Romans under General Litorius, who is killed.
** c. 445-450 - Battle of Vicus Helena – Romans under Aetius defeat Franks.
** 455
*** 2 – c. 16 June – Sack of Rome (455), Sack of Rome by Geiseric, King of the Vandals
*** Battle of Aylesford – Romano-Britons (under Vortimer) and Anglo-Saxons battle in Kent, victory is unclear.
** 456 –
*** Battle of Agrigentum (456) – An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the Romano-Suebian general Ricimer, drove off an invading fleet sent by the Vandals, Vandal king Genseric, Gaiseric to raid Sicily.
*** Battle of Corsica - the Vandals were again attacked by Ricimer and defeated.
** 457 –
*** Battle of Garigliano (457) –The new Roman emperor, emperor Majorian surprised a Vandal-Berbers, Berber raiding party which was returning with loot from Campania.
***Battle of Campi Cannini – Roman General Majorian defeats an Alemanni invasion of Italy.
** 458 –
*** Battle of Toulouse (458) -The Roman Emperor Majorian defeats the Visigoths.
*** Late 458 Battle of Arelate -The Roman Emperor Majorian, with the support of Aegidius and Nepotianus (magister militiae), Nepotianus, defeats the Visigoths at Arlate. With a treaty, the Visigothic returned all territory in Hispania to the Romans.
** 461 –Battle of Cartagena (461), Battle of Cartagena – A Vandal fleet surprises and destroys the Roman fleet.
** 463 – Battle of Orleans (463), Battle of Orleans – Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman and Salian Franks, Salian Frank forces under the command of Aegidius defeat a force of Visigoths at Orleans.
** 464 – Battle of Bergamo – Romans under General Ricimer defeat Alans, Alan invasion of Italy and kill their king.
** 468 – Battle of Cap Bon (468), Battle of Cap Bon - Failure of the invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals by the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
** 469 – Battle of Déols - Visigoths defeat Bretons and Gallo-Romanas under Riothamus.
** 471 – Battle of Arles (471) - Visigothic king Euric defeats the Roman general Anthemiolus, captured Arles and much of southern
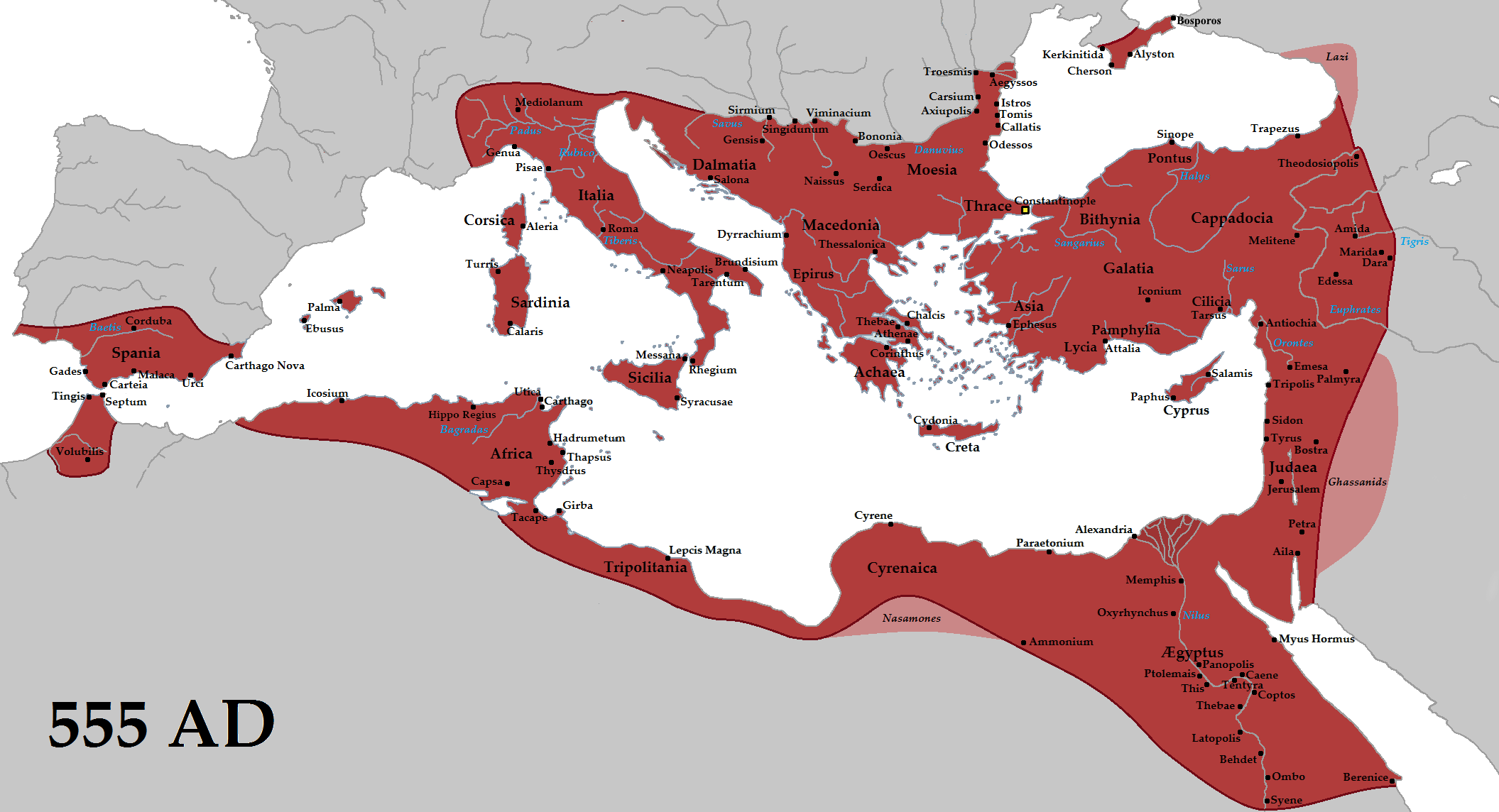 The Eastern Roman emperor Justinian launched an ambitious reconquest of Italy, North Africa and parts of Spain. However, new invaders like the Pannonian Avar, Avars, Kingdom of the Lombards, Lombards and Sclaveni, Slavs, alongside the Plague of Justinian, First plague pandemic and various Volcanic winter of 536, volcanic Late Antique Little Ice Age, winters ended his ambition of recuperate the West and consolidate the reconquest.
* 502–506 Anastasian War with Sassanid Persia.
* 526–532: Iberian War with Sassanid Persia.
* Justinian campaigns (533–555)
** 533–534: Vandalic War in Northern Africa.
** 534–548: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#The Moorish Wars, Moorish Wars in Africa.
** 535–554: Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War in Dalmatia and Italy.
** 541–562: Lazic War with Sassanid Persia.
** 552–555: Byzantine intervention in the Visigoth civil war in Spain, formation of Spania province.
** 560s–578: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#Conflict with Moorish kingdom of Garmul, War with the Romano-Moorish kingdom of Garmul.
* 572–591: Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591, War with Persia over the Caucasus.
* 589: Franco-Lombard-Byzantine conflict over the Po Valley. The war was stopped by breaching Breach at Cucca, dam in Cucca.
* 582–602: Maurice's Balkan campaigns, War against the Pannonian Avars, Avars and Slavs in the Balkans.
The Eastern Roman emperor Justinian launched an ambitious reconquest of Italy, North Africa and parts of Spain. However, new invaders like the Pannonian Avar, Avars, Kingdom of the Lombards, Lombards and Sclaveni, Slavs, alongside the Plague of Justinian, First plague pandemic and various Volcanic winter of 536, volcanic Late Antique Little Ice Age, winters ended his ambition of recuperate the West and consolidate the reconquest.
* 502–506 Anastasian War with Sassanid Persia.
* 526–532: Iberian War with Sassanid Persia.
* Justinian campaigns (533–555)
** 533–534: Vandalic War in Northern Africa.
** 534–548: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#The Moorish Wars, Moorish Wars in Africa.
** 535–554: Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War in Dalmatia and Italy.
** 541–562: Lazic War with Sassanid Persia.
** 552–555: Byzantine intervention in the Visigoth civil war in Spain, formation of Spania province.
** 560s–578: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#Conflict with Moorish kingdom of Garmul, War with the Romano-Moorish kingdom of Garmul.
* 572–591: Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591, War with Persia over the Caucasus.
* 589: Franco-Lombard-Byzantine conflict over the Po Valley. The war was stopped by breaching Breach at Cucca, dam in Cucca.
* 582–602: Maurice's Balkan campaigns, War against the Pannonian Avars, Avars and Slavs in the Balkans.
 The Eastern Roman empire adopted the Greek language as official language under emperor Heraclius in 610. The Eastern empire shrunk to Greece and Anatolia, because of Persian, Avar and finally Arab invasions.
* 602–628: Byzantine-Sassanid War of 602–628, Final Byzantine-Persian war.
* 626: Siege of Constantinople (626), Avar–Sasanian siege of Constantinople.
* 633–642: Beginning of the Muslim conquests. Progressive loss of Syria, Egypt, Africa and Sicily to the Muslim Caliphates.
The Eastern Roman empire adopted the Greek language as official language under emperor Heraclius in 610. The Eastern empire shrunk to Greece and Anatolia, because of Persian, Avar and finally Arab invasions.
* 602–628: Byzantine-Sassanid War of 602–628, Final Byzantine-Persian war.
* 626: Siege of Constantinople (626), Avar–Sasanian siege of Constantinople.
* 633–642: Beginning of the Muslim conquests. Progressive loss of Syria, Egypt, Africa and Sicily to the Muslim Caliphates.
http://courses.wcupa.edu/jones/Roman History Timeline
Milites
A Visual Analytics tool on Roman battles. * Elton, Hugh and Christos Nüssli, "
Imperial Battle Map Index
'". An Online Encyclopedia of Roman Emperors.
"Roman Battles" map, platial.com
Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom (also referred to as the Roman monarchy, or the regal period of ancient Rome) was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began wi ...
, Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
and Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
against external enemies, organized by date. For civil wars, revolts and rebellions, see List of Roman civil wars and revolts
This is a list of civil wars and organized civil disorder, revolts and rebellions in ancient Rome (Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, and Roman Empire) until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (753 BCE – 476 CE). For the Eastern Roman Empire or B ...
.
8th century BC
 * Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women)
* Conquest of Cameria
* War with Fidenae and Veii
* Wars with the Latins and the Sabines (for the Rape of the Sabine Women)
* Conquest of Cameria
* War with Fidenae and Veii
7th century BC
* Second war with Fidenae and Veii * Second Sabine War *Roman–Latin wars
The Roman–Latin wars were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome (including both the Roman Kingdom and the Roman Republic) and the Latins, from the earliest stages of the history of Rome until the final subjugation of the Latins to Rom ...
6th century BC
Battle of Silva Arsia
The Battle of Silva Arsia was a battle in 509 BC between the republican forces of ancient Rome and Etruscan forces of Tarquinii and Veii led by the deposed Roman king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. The battle took place near the Silva Arsia (the Ar ...
– The Romans defeated the forces of Tarquinii
Tarquinia (), formerly Corneto, is an old city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Central Italy, known chiefly for its ancient Etruscans, Etruscan tombs in the widespread necropolis, necropoleis, or cemeteries, for which it was awarded World ...
and Veii
Veii (also Veius; it, Veio) was an important ancient Etruscan city situated on the southern limits of Etruria and north-northwest of Rome, Italy. It now lies in Isola Farnese, in the comune of Rome. Many other sites associated with and in the ...
led by the deposed king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly known ...
. One of the Roman consuls, Lucius Junius Brutus
Lucius Junius Brutus ( 6th century BC) was the semi-legendary founder of the Roman Republic, and traditionally one of its first consuls in 509 BC. He was reputedly responsible for the expulsion of his uncle the Roman king Tarquinius Superbus after ...
, is killed in battle.
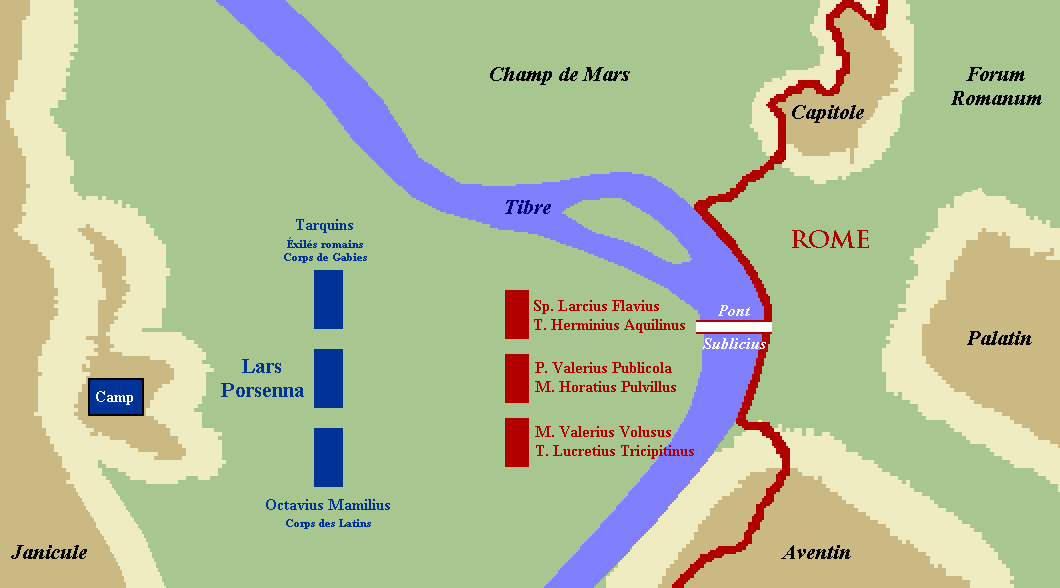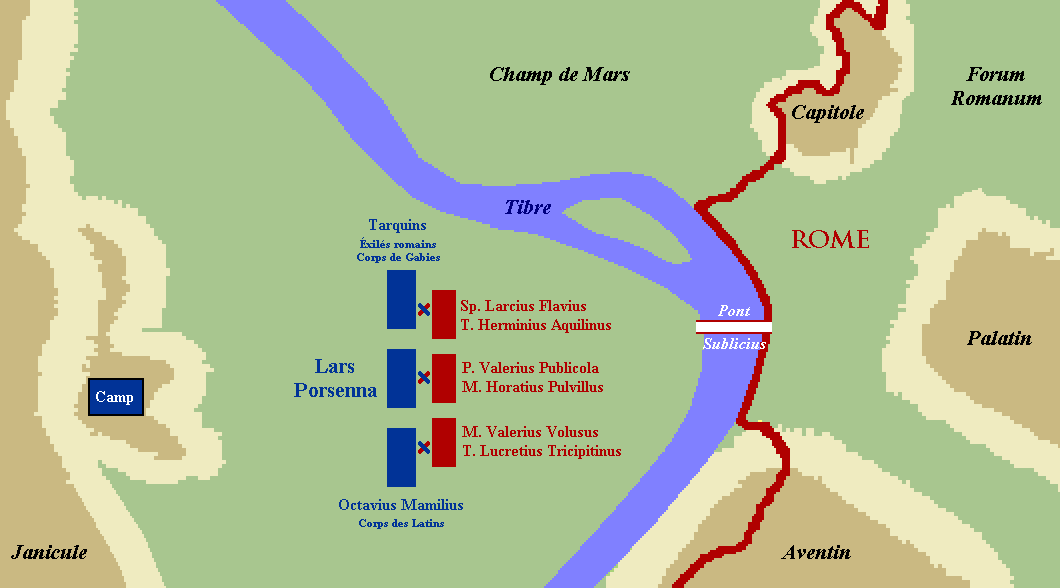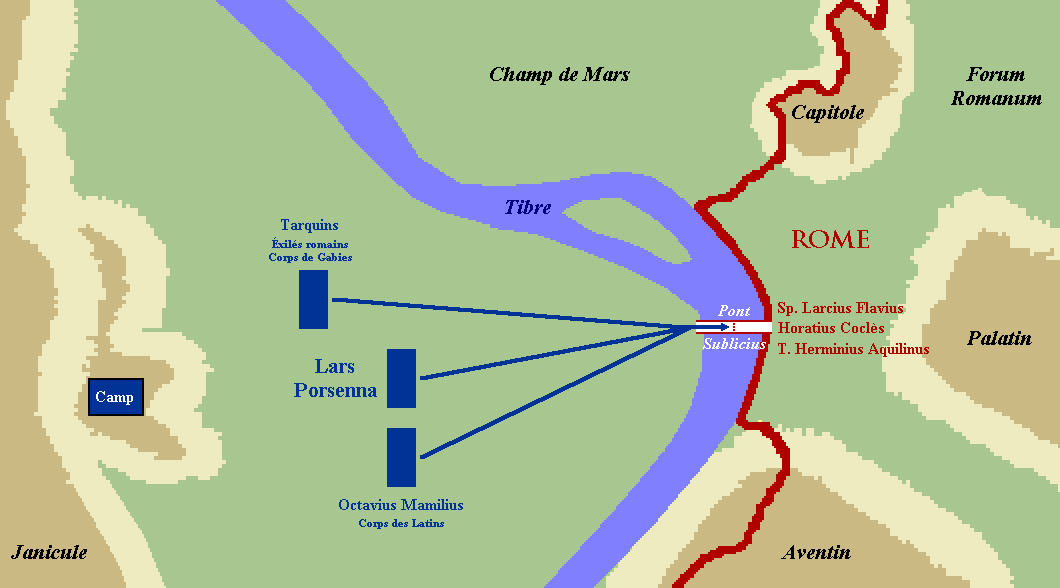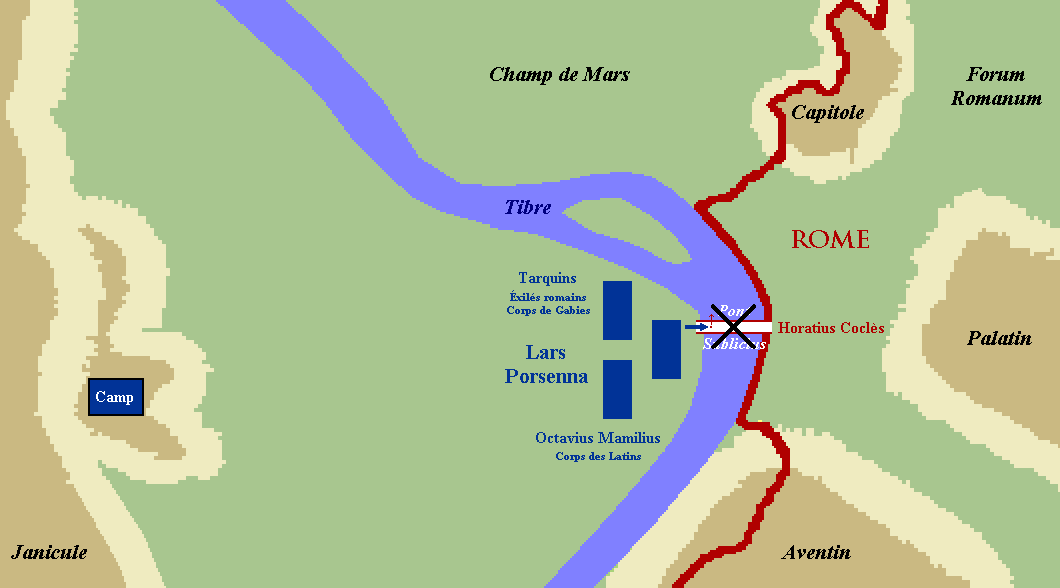
** 508 BC – War with Clusium – King Lars Porsena
Lars Porsena (or Porsenna; Etruscan: ) was an Etruscan civilization, Etruscan king (lar) known for his Roman-Etruscan Wars#War with Clusium in 508 BC, war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium (Etruscan language, Etruscan: ; ...
of Clusium
Clusium ( grc-gre, Κλύσιον, ''Klýsion'', or , ''Kloúsion''; Umbrian:''Camars'') was an ancient city in Italy, one of several found at the site. The current municipality of Chiusi (Tuscany) partly overlaps this Roman walled city. The Roman ...
besieges Rome on behalf of Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly known a ...
. The outcome is debated, but tradition states that it was a Roman victory.
* Pometian Revolt (503–502 BC)
** 502 BC – Battle of Pometia The Battle of Pometia took place in 502 BC, a year after a revolt by two Latin towns, Pometia and Cora, against Rome. A Roman army led by the consuls Agrippa Menenius Lanatus and Publius Postumius Tubertus was eventually successful in forcing the ...
– The Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
put down the revolt of Pometia and Cora.
5th century BC
* First Latin War (498–411 BC) ** 497 BC –Battle of Lake Regislus
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– Aulus Postumius Albus Regillensis
Aulus Postumius Albus Regillensis was an ancient Roman who, according to Livy, was Roman dictator in 498 or 496 BC, when he conquered the Latins in the great Battle of Lake Regillus and subsequently celebrated a triumph. Many of the coins of the ...
defeats Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly known a ...
.
* 495 BC – Battle of Aricia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
Publius Servilius Priscus Structus
Publius Servilius Priscus Structus was a Roman statesman who served as Senator and Consul.
Consulship and military campaigns
Servilius was Roman consul in 495 BC, along with Appius Claudius Sabinus Regillensis, and was the first consul of gens Se ...
defeats the Aurunci
The Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC.
Identity
Aurunci is the na ...
.
* Wars with the Volsci
The Volsci (, , ) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the ...
and the Aequi
300px, Location of the Aequi (Equi) in central Italy, 5th century BC.
The Aequi ( grc, Αἴκουοι and Αἴκοι) were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early his ...
(495 - 446 BC)
** 493 BC – Battle of Corioli – the Volscian army is defeated thanks to the vigilance of Gnaeus Marcius.
** 482 BC – Battle of Antium
The Battle of Pedum was fought in 338 BC, near Pedum between the Roman Republic and multiple cities in Latium: Tivoli,_Lazio#Roman_age, Tibur, Palestrina#Ancient_Praeneste, Praeneste, Anzio#Ancient era, Antium, Ariccia, Aricia, Lanuvium, and Vel ...
– the Volsci defeat consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
Lucius Aemilius Mamercus
Lucius Aemilius Mamercus was a Roman statesman who served as consul three times: in 484, 478 and 473 BC.Livy, '' Ab urbe condita'', 2.42
In 484 BC, as consul, Aemilius led the Roman forces in battle against the Volsci and Aequi. The Romans were ...
.
** 482 BC – Battle of Longula
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
Lucius Aemilius Mamercus
Lucius Aemilius Mamercus was a Roman statesman who served as consul three times: in 484, 478 and 473 BC.Livy, '' Ab urbe condita'', 2.42
In 484 BC, as consul, Aemilius led the Roman forces in battle against the Volsci and Aequi. The Romans were ...
defeats the Volsci the day after his defeat in the Battle of Antium
The Battle of Pedum was fought in 338 BC, near Pedum between the Roman Republic and multiple cities in Latium: Tivoli,_Lazio#Roman_age, Tibur, Palestrina#Ancient_Praeneste, Praeneste, Anzio#Ancient era, Antium, Ariccia, Aricia, Lanuvium, and Vel ...
.
** 458 BC – Battle of Mount Algidus
The Battle of Mount Algidus was fought in 458 BC, between the Roman Republic and the Aequi, near Mount Algidus in Latium. The Roman dictator Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus turned an expected Roman defeat into an important victory.
Background
The g ...
– Cincinnatus
Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus ( – ) was a Roman patrician, statesman, and military leader of the early Roman Republic who became a legendary figure of Roman virtue—particularly civic virtue—by the time of the late Republic.
Cincinnatus was ...
defeats the Aequi
** 446 BC – Battle of Corbio – Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus
Titus Quinctius Capitolinus Barbatus (513 BCafter 423 BC) was a Roman statesman and general who served as consul six times. Titus Quinctius was a member of the gens Quinctia, one of the oldest patrician families in Rome.
He was the son of Luci ...
leads Roman troops to defeat the Aequi and the Volsci.
* 480 BC – Battle of Veii (480 BC) – Consuls Marcus Fabius Vibulanus and Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus
Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus was the first of the patrician ''gens Manlia'' to obtain the consulship, which he held in 480 BC, together with Marcus Fabius Vibulanus. His father's name was Publius.
That year, Rome was rent by internal dissension ...
win heavy battle against Veians and their Etruscan allies. Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus and former consul Quintus Fabius are slain.
* 477 BC –
** Battle of the Cremera
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– All the Fabii except Quintus Fabius Vibulanus are killed in battle with the Veii, Veians.
** Battle of the Temple of Hope – Consul Gaius Horatius Pulvillus
Gaius Horatius Pulvillus (died 453 BC) was a Roman politician during the 5th century BC, and was consul in 477 and 457 BC.
Family
Ancient sources disagree on his ''praenomen''. Livy and Diodorus Siculus give ''Gaius'' for the year 477 BC, but ' ...
fights indecisive battle with the Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, rou ...
.
** Battle of Colline Gate (477 BC) – Consul Gaius Horatius Pulvillus has indecisive victory over the Etruscan civilization soon after the Battle of the Temple of Hope.
4th century BC
* Roman-Etruscan Wars ** 396 BC –Battle of Veii
The Battle of Veii, also known as the Siege of Veii, was a battle involving ancient Rome, approximately dated at 396 BC. The main source about it is Livy's ''Ab Urbe Condita''.
The Battle of Veii was the final battle between the Romans, who we ...
– Romans complete conquest of Veii
* Battle of Allia River (390 BC) – Gauls defeat the Romans, then sack Rome.
* First Samnite War
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
...
(343–341 BC)
** 342 BC – Battle of Mount Gaurus – Roman general Marcus Valerius Corvus
Marcus Valerius Corvus (c. 370–270 BC) was a military commander and politician from the early-to-middle period of the Roman Republic. During his career he was elected consul six times, first at the age of twenty-three. He was appointed dictator ...
defeats the Samnites.
** 342 BC – Battle of Saticula
The Battle of Saticula, 343 BC,Livy, as was customary in Rome, dated the battle by noting which consuls held office that year, it was the year in which M. Valerius Corvus, for the third time, and A. Cornelius Cossus were consuls. When converted ...
– Roman general Aulus Cornelius Cossus Arvina
Aulus Cornelius Cossus Arvina was a Roman politician and general who served as both consul and Magister Equitum twice, and Dictator once in the mid 4th century BC.
Family
Cossus was a member of the patrician gens Cornelia. The gens Cornelia was ...
barely escapes disaster and manages to defeat the Samnites.
** 341 BC – Battle of Suessula – Roman consul Marcus Valerius Corvus
Marcus Valerius Corvus (c. 370–270 BC) was a military commander and politician from the early-to-middle period of the Roman Republic. During his career he was elected consul six times, first at the age of twenty-three. He was appointed dictator ...
defeats the Samnites once more.
* Latin War
The (Second) Latin War (340–338 BC)The Romans customarily dated events by noting the consuls who held office that year. The Latin War broke out in the year that Titus Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus and Publius Decius Mus were consuls and ended ...
(340–338 BC)
** 339 BC – Battle of Vesuvius
The Battle of Vesuvius (also known as the Battle of the Veseris) was the first recorded battle of the Latin War. The battle was fought near Mount Vesuvius in 340 BC between the Romans, with their allies the Samnites, against a coalition of sever ...
– Romans under P. Decius Mus and T. Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus defeat the rebellious Latins.
** 338 BC – Battle of Trifanum
The Battle of Trifanum was fought in 340 BC between the Roman Republic and the Latins. The Roman force was led by Manlius Imperiosus. He pursued the Latins to the north following the Battle of Vesuvius and met them at Trifanum near the mouth o ...
– Roman general T. Manlius Imperiosus Torquatus decisively defeats the Latins.
* Second Samnite War
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe. ...
(326–304 BC)
** 321 BC – Battle of the Caudine Forks
The Battle of Caudine Forks, 321 BC, was a decisive event of the Second Samnite War. Its designation as a battle is a mere historical formality: there was no fighting and there were no casualties. The Romans were trapped in an enclosed valley b ...
– Romans under Spurius Postumius Albinus and T. Verturius Calvinus are defeated by the Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they for ...
under Gaius Pontius.
** 316 BC – Battle of Lautulae – Romans are defeated by the Samnites.
** 305 BC – Battle of Bovianum – Roman consuls M. Fulvius and L. Postumius decisively defeat the Samnites.
** 310 BC – Battle of Lake Vadimo – Romans, led by dictator Lucius Papirius Cursor
Lucius Papirius Cursor (c.365–after 310 BC) was a celebrated politician and general of the early Roman Republic, who was five times consul, three times magister equitum, and twice dictator. He was the most important Roman commander during the S ...
, defeat the Etruscan __NOTOC__
Etruscan may refer to:
Ancient civilization
*The Etruscan language, an extinct language in ancient Italy
*Something derived from or related to the Etruscan civilization
**Etruscan architecture
**Etruscan art
**Etruscan cities
** Etrusca ...
s.
3rd century BC
Third Samnite War
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars (343–341 BC, 326–304 BC, and 298–290 BC) were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.
...
(298–290 BC)
** 298 BC – Battle of Camerinum – Samnites defeat the Romans under Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus (c. 337 BC270 BC) was one of the two elected Roman consuls in 298 BC. He led the Roman army to victory against the Etruscans near Volterra. A member of the noble Roman family of Scipiones, he was the father of Lu ...
.
** 297 BC – Battle of Tifernum – Romans under Quintus Fabius Maximus and Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Barbatus (c. 337 BC270 BC) was one of the two elected Roman consuls in 298 BC. He led the Roman army to victory against the Etruscans near Volterra. A member of the noble Roman family of Scipiones, he was the father of Lu ...
defeat the Samnite army led by Gellius Statius
** 295 BC – Battle of Sentinum
The Battle of Sentinum was the decisive battle of the Third Samnite War, fought in 295 BC near Sentinum (next to the modern town of Sassoferrato, in the Marche region of Italy), in which the Romans overcame a formidable coalition of Samnite ...
– Romans under Fabius Rullianus and Publius Decimus Mus defeat the Samnites and their Etruscan and Gallic allies, forcing the Etruscans, Gauls, and Umbrians to make peace
** 293 BC – Battle of Aquilonia
The Battle of Aquilonia was fought in 293 BC between the Roman Republic and the Samnites. The Romans, led by the consul Lucius Papirius Cursor, were victorious.
History
According to Titus Livius, the Samnites were desperately short of men, ...
– Romans decisively defeat the Samnites.
* Wars with Gauls and Etruscans (285–282 BC)
** 284 BC – Battle of Arretium
The Battle of Arretium, which was probably fought in 284 BC, is a poorly documented event in the history of the Roman Republic because it occurred in a period for which some of the books of the ''History of Rome'' by Livy, the most thorough ancie ...
– A Roman army under Lucius Caecilius is destroyed by the Gauls.
** 283 BC – Battle of Lake Vadimo – A Roman army under P. Cornelius Dolabella defeats the Etruscans and Gauls.
** 282 BC – Battle of Populonia – Etruscan resistance to Roman domination of Italy is finally crushed.
* Pyrrhic War
The Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.
A ski ...
(280–275 BC)
** 280 BC – Battle of Heraclea
The Battle of Heraclea took place in 280 BC between the Romans under the command of consul Publius Valerius Laevinus, and the combined forces of Greeks from Epirus, Tarentum, Thurii, Metapontum, and Heraclea under the command of Pyrrhus, ...
– First engagement of Roman and Greek armies, the latter led by Pyrrhus of Epirus
Pyrrhus (; grc-gre, Πύρρος ; 319/318–272 BC) was a Greek king and statesman of the Hellenistic period.Plutarch. ''Parallel Lives'',Pyrrhus... He was king of the Greek tribe of Molossians, of the royal Aeacid house, and later he becam ...
, who is victorious, but at great cost.
** 279 BC – Battle of Asculum
The Battle of Asculum took place in 279 BC between the Roman Republic under the command of the consuls Publius Decius Mus and Publius Sulpicius Saverrio, and the forces of King Pyrrhus of Epirus. The battle took place during the Pyrrhic War, a ...
– Pyrrhus again defeats the Romans but once again suffers significant casualties in the process.
** 275 BC – Battle of Beneventum – Inconclusive encounter between Pyrrhus and the Romans under Manius Curius.
* First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
(264–241 BC)
** 261 BC – Battle of Agrigentum
The Battle of Agrigentum (Sicily, 262 BC) was the first pitched battle of the First Punic War and the first large-scale military confrontation between Carthage and the Roman Republic. The battle was fought after a long siege which started in ...
– Carthaginian forces under Hannibal Gisco and Hanno are defeated by the Romans, who attain control of most of Sicily.
** 260 BC -
*** Battle of the Lipari Islands – A Roman naval force is defeated by the Carthaginians.
*** Battle of Mylae
The Battle of Mylae took place in 260 BC during the First Punic War and was the first real naval battle between Carthage and the Roman Republic. This battle was key in the Roman victory of Mylae (present-day Milazzo) as well as Sicily itself. ...
– A Roman naval force under C. Duillius defeats the Carthaginian fleet, giving Rome control of the western Mediterranean.
** 258 BC – Battle of Sulci
The Battle of Sulci was a naval battle fought in 258 BC between the Roman and Carthaginian navies on the coast near the town of Sulci, Sardinia. It was a Roman victory, obtained by consul Gaius Sulpicius Paterculus. The Carthaginian fleet was lar ...
– Minor Roman victory against the Carthaginian fleet near Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
.
** 257 BC – Battle of Tyndaris
The Battle of Tyndaris was a naval battle of the First Punic War that took place off Tyndaris (modern Tindari) in 257 BC. Tyndaris was a Sicilian town founded as a Greek colony in 396 BC located on the high ground overlooking the Tyrrhenian Sea in ...
– Naval victory of Rome over Carthage in Sicilian waters.
** 256 BC –
*** Battle of Cape Ecnomus
The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos ( grc, Ἔκνομος) was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War (264–241 BC). It was the largest bat ...
– A Carthaginian fleet under Hamilcar and Hanno is defeated in an attempt to stop a Roman invasion of Africa by Marcus Atilius Regulus.
*** Battle of Adys
The battle of Adys (or Adis) took place in late 255 BC during the First Punic War between a Carthaginian army jointly commanded by Bostar, Hamilcar and Hasdrubal and a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus. Earlier in the year, the new ...
– Romans under Regulus defeat the Carthaginians in North Africa
** 255 BC – Battle of Tunis
The Battle of the Bagradas River (the ancient name of the Medjerda), also known as the Battle of Tunis, was a victory by a Carthaginian army led by Xanthippus over a Roman army led by Marcus Atilius Regulus in the spring of 255 BC, nine year ...
– Carthaginians under Xanthippus, a Greek mercenary, defeat the Romans under Regulus, who is captured.
** 251 BC – Battle of Panormus
The Battle of Panormus was fought in Sicily in 250 BC during the First Punic War between a Roman army led by Lucius Caecilius Metellus and a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal, son of Hanno. The Roman force of two legions defending the c ...
– Carthaginian forces under Hasdrubal Hasdrubal ( grc-gre, Ἀσδρούβας, ''Hasdroúbas'') is the Latinized form of the Carthaginian name ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 , , "Help of Baal").
It may refer to:
* Hasdrubal I of Carthage was the Magonid king of Ancient ...
are defeated by the Romans under L. Caecilius Metellus.
** 250 BC - Siege of Lilybaeum - Siege on the Carthaginian city of Lilybaeum by Roman army under Gaius Atilius Regulus Serranus and Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus
Lucius Manlius Vulso Longus was a Roman general and statesman, who became consul in 256 and 250 BC. He has been remembered as another militarily successful Roman consul; his military achievements significantly contributed to the victory of the Ro ...
. Carthaginian victory.
** 249 BC – Battle of Drepana
The naval Battle of Drepana (or Drepanum) took place in 249 BC during the First Punic War near Drepana (modern Trapani) in western Sicily, between a Carthaginian fleet under Adherbal and a Roman fleet commanded by Publius Claudius Pulch ...
– Carthage under Adherbal defeat the fleet of Roman admiral Publius Claudius Pulcher.
** 241 BC – Battle of the Aegates Islands
The Battle of the Aegates was a naval battle fought on 10 March 241 BC between the fleets of Carthage (state), Carthage and Roman Republic, Rome during the First Punic War. It took place among the Aegates Islands, off the western coast of the ...
– Roman sea victory over the Carthaginians.
*First Illyrian War
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
(229–228 BC)
* Roman-Gallic wars (225–200 BC)
** 225 BC – Battle of Faesulae
The Battle of Faesulae was fought in 225 BC between the Roman Republic and a group of Gauls living in Italy. The Gauls defeated the Romans, but later the same year, a decisive battle at Telamon had the opposite outcome. History
A general call ...
– Romans are defeated by the Gauls of Northern Italy.
** 225 BC – Battle of Telamon
The Battle of Telamon was fought between the Roman Republic and an alliance of Celts, Celtic tribes in 225 BC. The Romans, led by the consuls Gaius Atilius Regulus (consul 225 BC), Gaius Atilius Regulus and Lucius Aemilius Papus, defeated the Ce ...
– Romans under Aemilius Papus and Gaius Atilius Regulus defeat the Gauls.
** 222 BC – Battle of Clastidium – Romans under Marcus Claudius Marcellus
Marcus Claudius Marcellus (; 270 – 208 BC), five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic, was an important Roman military leader during the Gallic War of 225 BC and the Second Punic War. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roma ...
defeat the Gauls.
** 216 BC - Battle of Silva Litana
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army of 25,000 men under the consul-e ...
- Roman army under Lucius Postumius Albinus is ambushed by the Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom the ...
and crushed under falling trees.
** 200 BC – Battle of Cremona ''For the battle between Romans and Gauls, see Battle of Cremona (200 BC). For the battle during the Year of the Four Emperors, see Battle of Bedriacum.''
The Battle of Cremona took place on the night of 31 January to 1 February 1702 during the W ...
– Roman forces defeat the Gauls of Cisalpine Gaul
Cisalpine Gaul ( la, Gallia Cisalpina, also called ''Gallia Citerior'' or ''Gallia Togata'') was the part of Italy inhabited by Celts (Gauls) during the 4th and 3rd centuries BC.
After its conquest by the Roman Republic in the 200s BC it was con ...
*Second Illyrian War
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
(220–219 BC)
* Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
(218–201 BC)
** 218 BC –
*** Battle of Lilybaeum – First naval clash between the navies of Carthage and Rome during the Second Punic War; Roman victory.
*** Battle of Cissa
The Battle of Cissa was part of the Second Punic War. It was fought in the fall of 218 BC, near the Celtic town of Tarraco in north-eastern Iberia. A Roman army under Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus defeated an outnumbered Carthaginian army un ...
– Romans defeat Carthaginians near Tarraco
Tarraco is the ancient name of the current city of Tarragona (Catalonia, Spain). It was the oldest Roman settlement on the Iberian Peninsula. It became the capital of the Roman province of Hispania Citerior during the period of the Roman Republi ...
and gain control of the territory north of the Ebro River
, name_etymology =
, image = Zaragoza shel.JPG
, image_size =
, image_caption = The Ebro River in Zaragoza
, map = SpainEbroBasin.png
, map_size =
, map_caption = The Ebro ...
.
*** Battle of the Ticinus – Hannibal defeats the Romans under Publius Cornelius Scipio the elder in a cavalry fight.
*** Battle of the Trebia
The Battle of the Trebia (or Trebbia) was the first major battle of the Second Punic War, fought between the Carthaginian forces of Hannibal and a Roman army under Sempronius Longus on 22 or 23 December 218 BC. It took place on the flood ...
– Hannibal defeats the Romans under Tiberius Sempronius Longus with the use of an ambush.
** 217 BC -
*** Battle of Ebro River
The Battle of Ebro River was a naval battle fought near the mouth of Ebro River in the spring of 217 BC between a Carthaginian fleet of approximately 40 quinqueremes, under the command of Himilco, and a Roman fleet of 35 ships, under Gnaeus Co ...
– In a surprise attack, Romans defeat and capture the Carthaginian fleet in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania ...
.
*** Battle of Lake Trasimene
The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. It took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to th ...
– In another ambush, Hannibal destroys the Roman army of Gaius Flaminius, who is killed.
*** Battle of Ager Falernus
The Battle of Ager Falernus was a skirmish during the Second Punic War between the armies of Rome and Carthage. After winning the Battle of Lake Trasimene in Italy in 217 BC, the army commanded by Hannibal marched south and reached Campania. The ...
– Avoiding destruction with deceit, Hannibal escapes Fabius' trap in this small skirmish.
** 216 BC –
*** Battle of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae () was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by ...
– Hannibal destroys the main Roman army of Lucius Aemilius Paulus and Publius Terentius Varro in what is considered one of the great masterpieces of the tactical art.
*** Battle of Silva Litana
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army of 25,000 men under the consul-e ...
- The Boii ambushed and destroyed a Roman army of 25,000 men
*** First Battle of Nola
The First Battle of Nola was fought in 216 BC between the forces of Hannibal and a Roman force led by Marcus Claudius Marcellus. Hannibal was attempting to seize the town of Nola: He failed to do so, and would make two more unsuccessful attempts ...
– Roman general Marcus Claudius Marcellus
Marcus Claudius Marcellus (; 270 – 208 BC), five times elected as consul of the Roman Republic, was an important Roman military leader during the Gallic War of 225 BC and the Second Punic War. Marcellus gained the most prestigious award a Roma ...
holds off an attack by Hannibal.
*** Battle of Cornus
The Battle of Decimomannu or Caralis took place in Sardinia when a Carthaginian army sailed to the island to support a local revolt against Roman rule. The army, led by Hasdrubal the Bald, fought a similar size Roman army under the Praetor Titu ...
-
*** Battle of Hibera -
*** Battle of Cumae
The Battle of Cumae is the name given to at least two battles between Cumae and the Etruscans:
* In 524 BC an invading army of Umbrians, Daunians, Etruscans, and others were defeated by the Greeks of Cumae.
* The naval battle in 474 BC was bet ...
-
** 215 BC – Second Battle of Nola
The Second Battle of Nola was fought in 215 BC between Hannibal's army and a Roman force under Marcus Claudius Marcellus. It was Hannibal's second attempt to seize Nola after a failure the year before. He was again repelled and would make one ...
– Marcellus again repulses an attack by Hannibal.
** 214 BC – Third Battle of Nola
The Third Battle of Nola was fought in 214 BC between Hannibal and a Roman army led by Marcus Claudius Marcellus. It was Hannibal's third attempt to take the town of Nola. Once again, Marcellus successfully prevented the town's capture.
Backg ...
– Marcellus fights an inconclusive battle with Hannibal.
** 212 BC –
*** First Battle of Capua
The First Battle of Capua was fought in 212 BC between Hannibal and two Roman consular armies. The Roman force was led by two consuls, Quintus Fulvius Flaccus and Appius Claudius Pulcher. The Roman force was defeated, but managed to escape. Ha ...
– Hannibal defeats the consuls Q. Fulvius Flaccus and Appius Claudius, but the Roman army escapes
*** Battle of the Silarus
The Battle of the Silarus was fought in 212 BC between Hannibal's army and a Roman force led by centurion Marcus Centenius Penula. The Carthaginians were victorious, destroying the entire Roman army and killing 15,000 Roman soldiers in the proces ...
– Hannibal destroys the army of the Roman praetor M. Centenius Penula.
*** Battle of Herdonia – Hannibal destroys the Roman army of the praetor Gnaeus Fulvius.
** 211 BC –
*** Battle of the Upper Baetis
The Battle of the Upper Baetis was a double battle, comprising the battles of Castulo and Ilorca, fought in 211 BC during the Second Punic War between a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal Barca ( Hannibal's brother) and a Roman force led by P ...
– Publius and Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio are killed in battle with the Carthaginians under Hasdrubal Barca
Hasdrubal Barca (245– 22June 207BC), a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 ) son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
Youth and Iberian ...
*** Second Battle of Capua
The siege of Capua was fought in 211 BC, when the Romans besieged Capua. It is described by Polybius at 9.4-7, by Livy at 26.4-6, and by Appian at 37-44 of his ''Hannibalic War''.
Background
The defection of Capua to Hannibal after the Battl ...
– Hannibal is not able to break the Roman siege of the city.
** 210 BC –
*** Second Battle of Herdonia – Hannibal destroys the Roman army of Fulvius Centumalus, who is killed.
*** Battle of Numistro
The Battle of Numistro was fought in 210 BC between Hannibal's army and one of the Roman consular armies led by consul Marcus Claudius Marcellus. It was the fourth time they met in a battle. Previous encounters were located around the walls of No ...
– Hannibal defeats Marcellus once more
** 209 BC – Battle of Asculum
The Battle of Asculum took place in 279 BC between the Roman Republic under the command of the consuls Publius Decius Mus and Publius Sulpicius Saverrio, and the forces of King Pyrrhus of Epirus. The battle took place during the Pyrrhic War, a ...
– Hannibal once again defeats Marcellus, in an indecisive battle
** 208 BC – Battle of Baecula
The Battle of Baecula was a major field battle in Iberia during the Second Punic War. Roman Republican and Iberian auxiliary forces under the command of Scipio Africanus routed the Carthaginian army of Hasdrubal Barca.
Prelude
According to P ...
– Romans in Hispania
Hispania ( la, Hispānia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hispania ...
(Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
) under P. Cornelius Scipio the Younger defeat Hasdrubal Barca.
** 207 BC –
*** Battle of Grumentum
The Battle of Grumentum was fought in 207 BC between Romans led by Gaius Claudius Nero, and a part of Hannibal's Carthaginian army. The battle was a minor Roman victory, and Nero marched north where he defeated and killed Hannibal's brother Has ...
– Roman general Gaius Claudius Nero
Gaius Claudius Nero (c. 247 BCc. 189 BC) was a Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as legate in 214 BC, he was propraetor in 211 BC d ...
fights an indecisive battle with Hannibal.
*** Battle of the Metaurus
The Battle of the Metaurus was a pivotal battle in the Second Punic War between Rome and Carthage, fought in 207 BC near the Metauro River in Italy. The Carthaginians were led by Hasdrubal Barca, brother of Hannibal, who was to have brought sie ...
– Hasdrubal is defeated and killed by Nero's Roman army.
*** Battle of Carmona
One of Scipio's (later Africanus) first major battles in Spain, this siege is described by Appian in his ''Iberica'' (Wars in Spain) at 5.25-28, this battle is most likely the same as the Battle of Ilipa.
Now this Hasdrubal ordered all the rema ...
– Romans under Publius Cornelius Scipio besiege the city of Carmona and take it from Hasdrubal Gisco
Hasdrubal Gisco (died 202BC), a latinization of the name ʿAzrubaʿal son of Gersakkun ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 𐤁𐤍 𐤂𐤓𐤎𐤊𐤍 ),. was a Carthaginian general who fought against Rome in Iberia (Hispania) and North Africa du ...
** 206 BC –
*** Battle of Ilipa
The Battle of Ilipa () was an engagement considered by many as Scipio Africanus’s most brilliant victory in his military career during the Second Punic War in 206 BC.
It may have taken place on a plain east of Alcalá del Río, Seville, Spa ...
– Scipio again decisively defeats the remaining Carthaginian forces in Hispania.
*** Battle of the Guadalquivir – Roman army under Gaius Lucius Marcius Séptimus defeats a Carthaginian army under Hannón at Guadalquivir
The Guadalquivir (, also , , ) is the fifth-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula and the second-longest river with its entire length in Spain. The Guadalquivir is the only major navigable river in Spain. Currently it is navigable from the Gulf ...
.
*** Battle of Carteia
The Battle of Carteia, also known by the modern name Battle of the Guadalquivir, was a battle of the Second Punic War that took place in 206 BC between the forces of Carthage and the Roman Republic. The name "Battle of the Guadalquivir" is anac ...
– Roman fleet under Gaius Laelius
Gaius Laelius was a Roman general and statesman, and a friend of Scipio Africanus, whom he accompanied on his Iberian campaign (210–206 BC; the Roman Hispania, comprising modern Spain and Portugal) and his African campaign (204–202 BC). His co ...
defeats a Carthaginian fleet under Adherbal
** 204 BC – Battle of Crotona
The battle or, more precisely, the battles of Croton in 204 and 203 BC were, as well as the raid in Cisalpine Gaul, the last larger scale engagements between the Romans and the Carthaginians in Italy during the Second Punic War. After Hannibal� ...
– Hannibal fights a drawn battle against the Roman general Sempronius in Southern Italy.
** 203 BC – Battle of Bagbrades
The Battle of the Great Plains ( la, Campi Magni) was a battle between a Roman army commanded by Scipio Africanus and a combined Carthaginian-Numidian army late in the Second Punic War. It was fought on the plains south of Bulla Regia around t ...
– Romans under Scipio defeat the Carthaginian army of Hasdrubal Gisco
Hasdrubal Gisco (died 202BC), a latinization of the name ʿAzrubaʿal son of Gersakkun ( xpu, 𐤏𐤆𐤓𐤁𐤏𐤋 𐤁𐤍 𐤂𐤓𐤎𐤊𐤍 ),. was a Carthaginian general who fought against Rome in Iberia (Hispania) and North Africa du ...
and Syphax. Hannibal is sent to return to Africa.
** 202 BC, 19 October – Battle of Zama
The Battle of Zama was fought in 202 BC near Zama, now in Tunisia, and marked the end of the Second Punic War. A Roman army led by Publius Cornelius Scipio, with crucial support from Numidian leader Masinissa, defeated the Carthaginian ...
– Scipio Africanus Major
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–183 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the best military co ...
decisively defeats Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
in North Africa, ending the Second Punic War.
*First Macedonian War
The First Macedonian War (214–205 BC) was fought by Rome, allied (after 211 BC) with the Aetolian League and Attalus I of Pergamon, against Philip V of Macedon, contemporaneously with the Second Punic War (218–201 BC) against Carthage. The ...
(214–205 BC)

2nd century BC
*Second Macedonian War
The Second Macedonian War (200–197 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by Philip V of Macedon, and Rome, allied with Pergamon and Rhodes. Philip was defeated and was forced to abandon all possessions in southern Greece, Thrace and Asia Min ...
(200–196 BC)
** 198 BC – Battle of the Aous – Roman forces under Titus Quinctius Flamininus
Titus Quinctius Flamininus (c. 228 – 174 BC) was a Roman politician and general instrumental in the Roman conquest of Greece.
Family background
Flamininus belonged to the minor patrician ''gens'' Quinctia. The family had a glorious place ...
defeat the Macedonians under Philip V Philip V may refer to:
* Philip V of Macedon (221–179 BC)
* Philip V of France (1293–1322)
* Philip II of Spain, also Philip V, Duke of Burgundy (1526–1598)
* Philip V of Spain
Philip V ( es, Felipe; 19 December 1683 – 9 July 1746) was ...
** 197 BC – Battle of Cynoscephalae
The Battle of Cynoscephalae ( el, Μάχη τῶν Κυνὸς Κεφαλῶν) was an encounter battle fought in Thessaly in 197 BC between the Roman army, led by Titus Quinctius Flamininus, and the Antigonid dynasty of Macedon, led by Phili ...
– Romans under Flamininus decisively defeats Philip in Thessaly
* Roman-Spartan War (195 BC)
** 195 BC – Battle of Gythium – With some Roman assistance, Philopoemen
Philopoemen ( el, Φιλοποίμην ''Philopoímēn''; 253 BC, Megalopolis – 183 BC, Messene) was a skilled Greek general and statesman, who was Achaean strategos on eight occasions.
From the time he was appointed as strategos in 209 BC ...
of the Achaean League
The Achaean League (Greek: , ''Koinon ton Akhaion'' "League of Achaeans") was a Hellenistic-era confederation of Greek city states on the northern and central Peloponnese. The league was named after the region of Achaea in the northwestern Pel ...
defeats the Sparta
Sparta ( Doric Greek: Σπάρτα, ''Spártā''; Attic Greek: Σπάρτη, ''Spártē'') was a prominent city-state in Laconia, in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (, ), while the name Sparta referre ...
ns under Nabis
Nabis ( grc-gre, Νάβις) was the last king of independent Sparta. He was probably a member of the Heracleidae, and he ruled from 207 BC to 192 BC, during the years of the First and Second Macedonian Wars and the eponymous "War against Nabis" ...
* Battle of Placentia (194 BC)
The Battle of Placentia was fought in 194 BC, near Placentia, between the Roman Republic and the Boii. The Roman army won the battle. The following year, another battle with the Boii would take place in the same region; known as the Battle of M ...
– Roman victory over the Boian Gauls
* Battle of Mutina (193 BC)
The Battle of Mutina was fought in 193 BC, near Mutina, between the Roman Republic and the Boii. The Roman army won the battle. The battle marked the total defeat of the Boian Gauls, but since consul Lucius Cornelius Merula's victory cost the R ...
– Roman victory over the Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom the ...
, decisively ending the Boian threat.
* Roman-Seleucid War (192 BC – 188 BC)
** 191 BC – Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ; grc, Μάχη τῶν Θερμοπυλῶν, label=Greek, ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting o ...
– Romans under Manius Acilius Glabrio defeat Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the re ...
and force him to evacuate Greece
** 190 BC –
*** Battle of the Eurymedon
The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth ...
– Roman forces under Lucius Aemilius Regillus
Lucius Aemilius Regillus (fl. c. 190 – 189 BC) was a Roman admiral and praetor during the war with Antiochus III of Syria.
Born to Marcus Aemilius Regillus, much of Lucius Regillus's early life and military career is unknown before being app ...
defeat a Seleucid fleet commanded by Hannibal
Hannibal (; xpu, 𐤇𐤍𐤁𐤏𐤋, ''Ḥannibaʿl''; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Puni ...
, fighting his last battle.
*** Battle of Myonessus – Another Seleucid fleet is defeated by the Romans
*** December, Battle of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pe ...
– (near Smyrna) Romans under Lucius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Scipio Africanus Major
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–183 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the best military co ...
defeat Antiochus III the Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the re ...
in the decisive victory of the war.
*Aetolian War
The Aetolian War (191–189 BC) was fought between the Romans and their Achaean and Macedonian allies, and the Aetolian League and their allies the kingdom of Athamania. The Aetolians had invited Antiochus III the Great to Greece, who came, but ...
(191–189 BC)
* Galatian War
The Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey.
The Romans had just defeated the Seleucid ...
(189 BC)
** Battle of Mount Olympus
The Battle of Mount Olympus was fought in 189 BC between the Galatian Gauls of Asia Minor and an alliance consisting of the Roman Republic and Pergamum. The battle ended in a crushing allied victory.
Livy is the main source for this battle, and h ...
– Romans under Gnaeus Manlius Vulso allied with Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus (Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antalya) ...
of Pergamum
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
deliver a crushing defeat to an army of Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (c ...
n Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
** Battle of Ancyra
The Battle of Ancyra was fought in ca. 239 BC between the Seleucid King Seleucus II Callinicus and his brother Prince Antiochus Hierax. Civil war had raged in the Seleucid Empire since 244 BC, when Queen Laodice I had supported her son Antioc ...
– Gnaeus Manlius Vulso and Attalus II
Attalus II Philadelphus (Greek: Ἄτταλος Β΄ ὁ Φιλάδελφος, ''Attalos II Philadelphos'', which means "Attalus the brother-loving"; 220–138 BC) was a Greek King of Pergamon and the founder of the city of Attalia (Antalya) ...
defeat the Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace (c ...
n Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They s ...
again before Ancyra
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the list of national capitals, capital of Turkey. Located in the Central Anatolia Region, central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center ...
, in what was an almost identical repeat of the Battle of Mount Olympus.
* First Celtiberian War
The First Celtiberian (181–179 BC) was the first of three major rebellions by the Celtiberians against the Roman presence in Hispania. The other two were the Second Celtiberian War (154–151 BC) and the Numantine War (143–133 BC). Hispania ...
(181–179 BC)
** 181 BC – Battle of Manlian Pass – Romans under Fulvius Flaccus defeat an army of Celtiberians.
* Third Macedonian War
The Third Macedonian War (171–168 BC) was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman f ...
(171–168 BC)
** 171 BC – Battle of Callicinus
The Battle of Callinicus ( el, μάχη του Καλλίνικου) was fought in 171 BC between the Kingdom of Macedon and the Roman Republic near a hill called Callinicus, close to the Roman camp at Tripolis Larisaia, five kilometres north o ...
– Perseus of Macedon
Perseus ( grc-gre, Περσεύς; 212 – 166 BC) was the last king ('' Basileus'') of the Antigonid dynasty, who ruled the successor state in Macedon created upon the death of Alexander the Great. He was the last Antigonid to rule Macedon, af ...
defeats a Roman army under Publius Licinius Crassus.
** 168 BC, 22 June – Battle of Pydna
The Battle of Pydna took place in 168 BC between Rome and Macedon during the Third Macedonian War. The battle saw the further ascendancy of Rome in the Hellenistic world and the end of the Antigonid line of kings, whose power traced back to ...
– Romans under Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus
Lucius Aemilius Paullus Macedonicus (c. 229 – 160 BC) was a two-time consul of the Roman Republic and a general who conquered Macedon, putting an end to the Antigonid dynasty in the Third Macedonian War.
Family
Paullus' father was Luci ...
defeat and capture Macedonian King Perseus.
*Third Illyrian War
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
(169–167 BC)
* Maccabean Revolt
The Maccabean Revolt ( he, מרד החשמונאים) was a Jewish rebellion led by the Maccabees against the Seleucid Empire and against Hellenistic influence on Jewish life. The main phase of the revolt lasted from 167–160 BCE and ended ...
(167–160 BC)
*Lusitanian War
The Lusitanian War, called ''Pyrinos Polemos'' ("the Fiery War") in Greek, was a war of resistance fought by the Lusitanian tribes of Hispania Ulterior against the advancing legions of the Roman Republic from 155 to 139 BC. The Lusitanians revo ...
(155–139 BC)
* Numentine\Second Celtiberian War (154–133 BC)
** 134 BC - Siege of Numantia
The Celtiberian oppidum of Numantia was attacked more than once by Roman forces, but the Siege of Numantia refers to the culminating and pacifying action of the long-running Numantine War between the forces of the Roman Republic and those of th ...
- Roman forces under Scipio Aemilianus Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the ...
defeat and raze the Celtiberian city of Numantia
Numantia ( es, Numancia) is an ancient Celtiberian settlement, whose remains are located on a hill known as Cerro de la Muela in the current municipality of Garray (Soria), Spain.
Numantia is famous for its role in the Celtiberian Wars. In 15 ...
.
* Fourth Macedonian War
The Fourth Macedonian War (150–148 BC) was fought between Macedon, led by the pretender Andriscus, and the Roman Republic. It was the last of the Macedonian Wars, and was the last war to seriously threaten Roman control of Greece until the Fi ...
(150–148 BC)
** 148 BC – Second battle of Pydna
The Battle of Pydna was a battle fought in 148 BC between Rome and the forces of the Macedonian leader Andriscus. The Roman force was led by Quintus Caecilius Metellus, and was victorious. The battle played an important role in deciding the ...
– The forces of the Macedonian pretender Andriscus
Andriscus ( grc, Ἀνδρίσκος, ''Andrískos''; 154/153 BC – 146 BC), also often referenced as Pseudo-Philip, was a Greek pretender who became the last independent king of Macedon in 149 BC as Philip VI ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος, ''Phil ...
are defeated by the Romans under Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Macedonicus (c. 188 BC – 116 BC/115 BC) was a statesman and general of the Roman Republic during the second century BC. He was praetor in 148 BC, consul in 143 BC, the Proconsul of Hispania Citerior in 142 BC an ...
.
* Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in modern northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 201 ...
(149–146 BC)
** 147 BC -
*** Battle of the Port of Carthage
The Battle of the Port of Carthage was a naval battle of the Third Punic War fought in November 9, 147 BC between the Carthaginians and the Roman Republic.
In the summer of 147 BC, during the Siege of Carthage, the Roman fleet, under the com ...
- Roman forces under Lucius Hostilius Mancinus are defeated by the Carthaginians.
*** Second Battle of Neferis - Roman forces under Scipio Aemilianus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the ...
win a decisive victory against Carthage marking the turning point in the Third Punic War.
** 146 BC – Battle of Carthage ends: Scipio Africanus Minor
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the ...
captures and destroys Carthage.
* Achaean War
The Achaean War of 146 BC was fought between the Roman Republic and the Greek Achaean League, an alliance of Achaean and other Peloponnesian states in ancient Greece. It was the final stage of Rome's conquest of mainland Greece, taking place jus ...
(146 BC)
** 146 BC – Battle of Corinth – Romans under Lucius Mummius
Lucius Mummius (2nd century BC), was a Roman Republic, Roman statesman and general. He was consul in the year 146 BC along with Scipio Aemilianus. Mummius was the first of his family to rise to the rank of consul thereby making him a novus homo. ...
defeat the Achaean League forces of Critolaus
Critolaus (; el, Κριτόλαος ''Kritolaos''; c. 200 – c. 118 BC) of Phaselis was a Greek philosopher of the Peripatetic school. He was one of three philosophers sent to Rome in 155 BC (the other two being Carneades and Diogenes of Babylon) ...
, who is killed. Corinth is destroyed and Greece comes under direct Roman rule.
*First Servile War
The First Servile War of 135–132 BC was a slave rebellion against the Roman Republic, which took place in Sicily. The revolt started in 135 when Eunus, a slave from Syria who claimed to be a prophet, captured the city of Enna in the middle o ...
(135–132 BC)
* Fregellae's revolt
In 125 BCE, the Latin town of Fregellae revolted against Rome demanding Roman citizenship. The Romans reacted by sending the praetor Lucius Opimius with an army to suppress the rebellion. A local traitor named Numitorius opened the gates to the Rom ...
(125 BC)
* Cimbrian War
The Cimbrian or Cimbric War (113–101 BC) was fought between the Roman Republic and the Germanic and Celtic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons, Ambrones and Tigurini, who migrated from the Jutland peninsula into Roman controlled territory, ...
(113–101 BC)
** 112 BC - Battle of Noreia
The Battle of Noreia, in 113 BC, was the opening battle of the Cimbrian War fought between the Roman Republic and the migrating Proto-Germanic tribes, the Cimbri and the Teutons (Teutones). It ended in defeat, and near disaster, for the Romans.
...
- Roman force under Gnaeus Papirius Carbo
Gnaeus Papirius Carbo (c. 129 – 82 BC) was thrice consul of the Roman Republic in 85, 84, and 82 BC. He was the head of the Marianists after the death of Cinna in 84 and led the resistance to Sulla during the civil war. He was proscribed by Su ...
are defeated by the Cimbri
The Cimbri (Greek Κίμβροι, ''Kímbroi''; Latin ''Cimbri'') were an ancient tribe in Europe. Ancient authors described them variously as a Celtic people (or Gaulish), Germanic people, or even Cimmerian. Several ancient sources indicate that ...
** 109 BC – Battle of the Rhone River – Roman force under Marcus Junius Silanus are defeated by the Helvetii
The Helvetii ( , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celts, Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their Switzerland in the Roman era, contact with the Roman Republic in the ...
** 107 BC – Battle of Burdigala
The Battle of Burdigala (the Roman name for Bordeaux, with stress on the 'i') was a battle of the Cimbrian War that occurred in the year 107 BC. The battle was fought between a combined Germanic-Celtic army including the Helvetian Tigurini unde ...
– Roman forces under Lucius Cassius Longinus are defeated by the Helvetii
** 105 BC, 6 October – Battle of Arausio
The Battle of Arausio took place on 6 October 105 BC, at a site between the town of Arausio (now Orange, Vaucluse), and the Rhône River. Ranged against the migratory tribes of the Cimbri under Boiorix and the Teutoni under Teutobod were two ...
– Cimbri inflict a major defeat on the Roman army of Gnaeus Mallius Maximus Gnaeus Mallius Maximus was a Roman politician and general.
A ''novus homo'' ("new man"), Mallius was elected to the consulship of the Roman Republic in 105 BC. He was sent as consul to the province of Transalpine Gaul to stop the migration of the C ...
** 102 BC - Battle of Aquae Sextiae
The Battle of Aquae Sextiae (Aix-en-Provence) took place in 102 BC. After a string of Roman defeats (see: the Battle of Noreia, the Battle of Burdigala, and the Battle of Arausio), the Romans under Gaius Marius finally defeated the Teutones and A ...
- Romans under Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius (; – 13 January 86 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. Victor of the Cimbric and Jugurthine wars, he held the office of consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his important refor ...
defeat Teutons
The Teutons ( la, Teutones, , grc, Τεύτονες) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with th ...
, with mass suicides among the captured women.
** 101 BC - Battle of Vercellae
The Battle of Vercellae, or Battle of the Raudine Plain, was fought on 30 July 101 BC on a plain near Vercellae in Gallia Cisalpina (modern day Northern Italy). A Germanic-Celtic confederation under the command of the Cimbric king Boiorix was ...
– Romans under Gaius Marius defeat the Cimbri, who are entirely annihilated.
* Jugurthine War
The Jugurthine War ( la, Bellum Iugurthinum; 112–106 BC) was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and king Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopted ...
(112–105 BC)
** 108 BC – Battle of the Muthul
The Battle of the Muthul was fought at the Muthul River in Numidia in 109 BC. The Numidians, led by their king Jugurtha, fought a Roman army commanded by the consul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus. The battle was fought during the Jugurthine ...
– Roman forces under Caecilius Metellus fight indecisively against the forces of Jugurtha
Jugurtha or Jugurthen (Libyco-Berber ''Yugurten'' or '' Yugarten'', c. 160 – 104 BC) was a king of Numidia. When the Numidian king Micipsa, who had adopted Jugurtha, died in 118 BC, Jugurtha and his two adoptive brothers, Hiempsal and Adh ...
of Numidia
Numidia ( Berber: ''Inumiden''; 202–40 BC) was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians located in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up modern-day Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunis ...
*Second Servile War
The Second Servile War was an unsuccessful slave uprising against the Roman Republic on the island of Sicily. The war lasted from 104 BC until 100 BC.
Background
The Consul Gaius Marius was recruiting soldiers for the war against the Cimbri an ...
(104–103 BC)
1st century BC

Lucius Porcius Cato
Lucius Porcius Cato was a Roman general and politician who became consul in 89 BC alongside Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo. He died at the Battle of Fucine Lake, possibly at the hands of Gaius Marius the Younger.
Biography
Lucius Porcius Cato was a son ...
are defeated by the Italian rebels.
** 89 BC – Battle of Asculum
The Battle of Asculum took place in 279 BC between the Roman Republic under the command of the consuls Publius Decius Mus and Publius Sulpicius Saverrio, and the forces of King Pyrrhus of Epirus. The battle took place during the Pyrrhic War, a ...
– Roman army of C. Pompeius Strabo decisively defeats the rebels.
* First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates ...
(90–85 BC)
** 87 BC - 86 BC - Siege of Athens and Piraeus - Siege of Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, which had sided with the Pontic invaders during the First Mithridatic War by Lucius Cornelius Sulla. Roman victory.
** 86 BC – Battle of Chaeronea – Roman forces of Lucius Cornelius Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had t ...
defeat the Pontic forces of Archelaus in the First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridates ...
** 85 BC – Battle of Orchomenus
The Battle of Orchomenus was fought in 85 BC between Rome and the forces of Mithridates VI of Pontus. The Roman army was led by Lucius Cornelius Sulla, while Mithridates' army was led by Archelaus. The Roman force was victorious, and Archel ...
– Sulla again defeats Archelaus in the decisive battle of the First Mithridatic War.
* Second Mithridatic War
The Second Mithridatic War (83–81 BC) was one of three wars fought between Pontus and the Roman Republic. This war was fought between King Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman general Lucius Licinius Murena.
History
At the conclusion of t ...
(83–82 BC)
** 82 BC – Battle of Halys
The Battle of Halys (also known as the Battle of Halys River) took place in 82 BC, during the Second Mithridatic War. Roman general Lucius Licinius Murena became very overconfident while campaigning against Pontus and ignored orders to cease ...
– Roman general Lucius Licinius Murena fights Mithridates and Gordius after launching several raids, to which the Romans lose.
* Sulla's civil war
Sulla's civil war was fought between the Roman general Lucius Cornelius Sulla and his opponents, the Cinna-Marius faction (usually called the Marians or the Cinnans after their former leaders Gaius Marius and Lucius Cornelius Cinna), in the ye ...
(82–81 BC)
** 82 BC –
*** Battle of the Asio River – Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius (c. 128 – 63 BC) was a Roman politician and general. Like the other members of the influential Caecilii Metelli family, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction opposed to the Populares during ...
defeats a Popular army under Gaius Carrinas.
*** Battle of Sacriporto – Fought between the Optimates
Optimates (; Latin for "best ones", ) and populares (; Latin for "supporters of the people", ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated academic dis ...
under Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had t ...
and the Populares
Optimates (; Latin for "best ones", ) and populares (; Latin for "supporters of the people", ) are labels applied to politicians, political groups, traditions, strategies, or ideologies in the late Roman Republic. There is "heated academic dis ...
under Gaius Marius the Younger
Gaius Marius "the Younger" (c. 110 – 82 BC) was a Roman republican general and politician who became consul in 82 BC with Papirius Carbo. He fought in Sulla's civil war. He committed suicide that same year at Praeneste, after his defeat by S ...
, Optimate victory.
*** First Battle of Clusium – Fought between the Optimates under Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix and the Populares under Gnaeus Papirius Carbo
Gnaeus Papirius Carbo (c. 129 – 82 BC) was thrice consul of the Roman Republic in 85, 84, and 82 BC. He was the head of the Marianists after the death of Cinna in 84 and led the resistance to Sulla during the civil war. He was proscribed by Su ...
, Popular victory.
*** Battle of Faventia
In the spring of 542, at the Battle of Faventia (modern Faenza), an Ostrogothic army under king Totila scattered the larger Roman forces of generals Constantian and Alexander, beginning the resurgence of Gothic resistance to the Roman reconques ...
– Fought between the Optimates under Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius
Quintus Caecilius Metellus Pius (c. 128 – 63 BC) was a Roman politician and general. Like the other members of the influential Caecilii Metelli family, he was a leader of the Optimates, the conservative faction opposed to the Populares during ...
and the Populares under Gaius Norbanus Balbus, Optimate victory.
*** Battle of Fidentia – Fought between the Optimates under Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus
Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus (116 – soon after 56 BC), younger brother of the more famous Lucius Licinius Lucullus, was a supporter of Lucius Cornelius Sulla and consul of ancient Rome in 73 BC. As proconsul of Macedonia in 72 BC, he defea ...
and the Populares under Lucius Quincius, Optimate victory.
*** Second Battle of Clusium – Pompei Magnus defeats a numerically superior Populares army under Gaius Carrinas and Gaius Marcius Censorinus.
*** Battle of Colline Gate – Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had ...
defeats Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they for ...
allied to the popular party in Rome in the decisive battle of the Civil War.
* Sertorian War
The Sertorian War was a civil war fought from 80 to 72 BC between a faction of Roman rebels ( Sertorians) and the government in Rome ( Sullans). The war was fought on the Iberian Peninsula (called ''Hispania'' by the Romans) and was one of the ...
(80–72 BC)
** 80 BC – Battle of the Baetis River
The Battle of the Baetis River was fought between an army of the Roman Republic and a rebel army at the Baetis river (modern day Guadalquivir) in Spain. The battle took place in 80 BC at the start of the Sertorian War. The Romans were led by Luci ...
– Rebel forces under Quintus Sertorius
Quintus Sertorius (c. 126 – 73 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who led a large-scale rebellion against the Roman Senate on the Iberian peninsula. He had been a prominent member of the populist faction of Cinna and Marius. During the l ...
defeat the legal Roman forces of Lucius Fulfidias in Hispania.
* Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
(73–63 BC)
** 73 BC – Battle of Cyzicus
The naval Battle of Cyzicus (Greek: ) took place in May or June 410 BC during the Peloponnesian War. During the battle, an Athenian fleet commanded by Alcibiades, Thrasybulus, and Theramenes routed and destroyed a Spartan fleet commanded by M ...
– Roman forces under Lucius Lucullus defeat the forces of Mithridates VI
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an e ...
of Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
** 72 BC – Battle of Cabira
The Battle of Cabira was fought in 72 or 71 BC between forces of the Roman Republic under proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus and those of the Kingdom of Pontus under Mithridates the Great. It was a decisive Roman victory.
Background
Rome had ...
or the Rhyndacus – Lucullus defeats the retreating forces of Mithridates, opening way to Pontus
** 69 BC – Battle of Tigranocerta
The Battle of Tigranocerta (, ''Tigranakerti tchakatamart'') was fought on 6 October 69 BC between the forces of the Roman Republic and the army of the Kingdom of Armenia led by King Tigranes the Great. The Roman force, led by Consul Lucius ...
– Lucullus defeats the army of Tigranes II of Armenia
Tigranes II, more commonly known as Tigranes the Great ( hy, Տիգրան Մեծ, ''Tigran Mets''; grc, Τιγράνης ὁ Μέγας ''Tigránes ho Mégas''; la, Tigranes Magnus) (140 – 55 BC) was King of Armenia under whom the ...
, who was harbouring his father-in-law Mithridates VI of Pontus
** 68 BC – Battle of Artaxata
The Battle of Artaxata was fought near the Arsanias River in 68 BC between an army of the Roman Republic and the army of the Kingdom of Armenia. The Romans were led by proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus, while the Armenians were led by Tigrane ...
– Lucullus again defeats Tigranes.
** 66 BC – Battle of the Lycus – Pompey the Great
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
decisively defeats Mithridates VI, effectively ending the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
* Third Servile War
The Third Servile War, also called the Gladiator War and the War of Spartacus by Plutarch, was the last in a series of slave rebellions against the Roman Republic known as the Servile Wars. This third rebellion was the only one that directly ...
(73–71 BC)
** 73 BC – Battle of Mount Vesuvius
The Battle of Vesuvius was the first conflict of the Third Servile War which pitted the escaped slaves against a military force of militia specifically dispatched by Rome to deal with the rebellion.
When the militia, led by the Roman Praetor G ...
– Spartacus
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian gladiator who, along with Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprising ...
defeats Gaius Claudius Glaber
Gaius Claudius Glaber was a military commander of the late Roman Republic, holding the offices of legate and military praetor in 73 BC.
He was defeated in the Battle of Mount Vesuvius against the forces of Spartacus during the Third Servile War.
...
** 72 BC – Battle of Picenum – Slave Revolt led by Spartacus
Spartacus ( el, Σπάρτακος '; la, Spartacus; c. 103–71 BC) was a Thracian gladiator who, along with Crixus, Gannicus, Castus, and Oenomaus, was one of the escaped slave leaders in the Third Servile War, a major slave uprising ...
defeat a Roman army led by Gellius Publicola and Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodianus
Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodianus (born 115 BC) was a Roman politician and general who was one of two Consuls of the Republic in 72 BC along with Lucius Gellius. Closely linked to the family of Pompey, he is noted for being one of the consular g ...
** 72 BC – Battle of Mutina I – Slave Revolt led by Spartacus defeat another army of Romans.
** 71 BC –
*** Battle of Campania – Slave Revolt led by Spartacus defeat a Roman army.
*** Battle of Campania II – a Roman army under Marcus Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome."Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Ir ...
defeats Spartacus's army of slaves.
*** Battle of the Siler River – Marcus Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome."Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Ir ...
defeats the army of Spartacus.
*Pompey's Georgian campaign
Caucasian campaign of Pompey ( ka, პომპეუსის ლაშქრობა კავკასიაში) was a military campaign led by Pompey that took place in 65 BC and was a consequence of the third Mithridatic War fought over ...
(65 BC)
* Catilinarian Civil War (63–62 BC)
** 62 BC, January – Battle of Pistoria
The Battle of Pistoria was fought early January 62 BC between the forces of the Roman Republic and Catiline, a senatorial conspirator who had been organising an attempted conspiracy against the consuls the previous year.
After his conspira ...
– The forces of the conspirator Catiline
Lucius Sergius Catilina ( 108 BC – January 62 BC), known in English as Catiline (), was a Roman politician and soldier. He is best known for instigating the Catilinarian conspiracy, a failed attempt to violently seize control of the R ...
are defeated by the loyal Roman armies under Gaius Antonius.
* Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homela ...
(59–51 BC)
** 58 BC –
*** June – Battle of the Arar
The Battle of the Arar was fought between the migrating tribes of the Helvetii and six Roman legions (Legions: Legio VII, Legio VIII Augusta, Legio IX, Legio X, Legio XI and Legio XII) under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar in 58 BC. It was ...
(Saône) – Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
defeats the migrating Helvetii
The Helvetii ( , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celts, Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their Switzerland in the Roman era, contact with the Roman Republic in the ...
*** July – Battle of Bibracte
The Battle of Bibracte was fought between the Helvetii and six Roman legions, under the command of Gaius Julius Caesar. It was the second major battle of the Gallic Wars.
Prelude
The Helvetii, a confederation of Gallic tribes, had begun a total ...
– Caesar again defeats the Helvetians, this time decisively.
*** September – Battle of Vosges – Caesar decisively defeats the forces of the Germanic chieftain Ariovistus
Ariovistus was a leader of the Suebi and other allied Germanic peoples in the second quarter of the 1st century BC. He and his followers took part in a war in Gaul, assisting the Arverni and Sequani in defeating their rivals, the Aedui. They t ...
near modern Belfort
Belfort (; archaic german: Beffert/Beffort) is a city in the Bourgogne-Franche-Comté region in Northeastern France, situated between Lyon and Strasbourg, approximately from the France–Switzerland border. It is the prefecture of the Territo ...
** 57 BC –
*** Battle of the Axona (Aisne) – Caesar defeats the forces of the Belgae
The Belgae () were a large confederation of tribes living in northern Gaul, between the English Channel, the west bank of the Rhine, and the northern bank of the river Seine, from at least the third century BC. They were discussed in depth by Ju ...
under King Galba of Suessiones.
*** Battle of the Sabis
The Battle of the Sabis, also (arguably erroneously) known as the Battle of the Sambre or the Battle against the Nervians (or Nervii), was fought in 57 BC near modern Saulzoir in Northern France, between Caesar's Roman legion, legions and an asso ...
(Sambre) – Caesar defeats the Nervii.
*** Battle of Octodurus
The battle of Octodurus took place in the winter of 57–56 BC in the Gallic town of Octodurus in what is now Martigny, Valais, Switzerland. The battle was the result of a Roman attempt to open the Great St. Bernard Pass over the Alps. It was ...
(Martigny
Martigny (; german: Martinach, ; la, Octodurum) is the capital city of the district of Martigny, canton of Valais, Switzerland. It lies at an elevation of , and its population is approximately 15000 inhabitants (''Martignerains'' or "Octodurie ...
) – Servius Galba defeats the Seduni and Veragri.
** 52 BC – Battle of Alesia – Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
defeats the Gallic rebel Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; Greek: Οὐερκιγγετόριξ; – 46 BC) was a Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. Despite h ...
, completing the Roman conquest of Gallia Comata.
* War with the Parthian Empire (53 BC)
** 53 BC - Battle of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Licinius Cra ...
– Roman triumvir
A triumvirate ( la, triumvirātus) or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs ( la, triumviri). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are ...
Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome." Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, I ...
is disastrously defeated and killed by the Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns. Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome." Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, I ...
has molten gold poured down his throat by his captors.
 *
* Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and ...
(49–45 BC)
** 49 BC, June – Battle of Ilerda
The Battle of Ilerda took place in June 49 BC between the forces of Julius Caesar and the Spanish army of Pompey Magnus, led by his legates Lucius Afranius and Marcus Petreius. Unlike many of the other battles of the civil war, this was more a ...
– Caesar's army surround Pompeian forces and cause them to surrender.
** 49 BC, 24 August – Battle of the Bagradas River – Caesar's general Gaius Curio is defeated in North Africa by the Pompeians under Attius Varus and King Juba I of Numidia
Juba I of Numidia ( lat, IVBA, xpu, ywbʿy; –46BC) was a king of Numidia (reigned 60–46 BC). He was the son and successor to Hiempsal II.
Biography
In 81 BC Hiempsal had been driven from his throne; soon afterwards, Pompey was sent to Afr ...
. Curio is killed in battle.Julius Caesar— The Civil Wars, Chapter 42
** 48 BC, 10 July – Battle of Dyrrhachium – Caesar barely avoids a catastrophic defeat by Pompey in Macedonia
** 48 BC, 9 August – Battle of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. P ...
– Caesar decisively defeats Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
, who flees to Egypt
** 47 BC, February – Battle of the Nile
The Battle of the Nile (also known as the Battle of Aboukir Bay; french: Bataille d'Aboukir) was a major naval battle fought between the British Royal Navy and the Navy of the French Republic at Aboukir Bay on the Mediterranean coast off the ...
– Caesar defeats the forces of the Egyptian king Ptolemy XIII
Ptolemy XIII Theos Philopator ( grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος Θεός Φιλοπάτωρ, ''Ptolemaĩos''; c. 62 BC – 13 January 47 BC) was Pharaoh of Egypt from 51 to 47 BC, and one of the last members of the Ptolemaic dynasty (305–30 BC) ...
** 46 BC, 4 January – Battle of Ruspina
The Battle of Ruspina was fought on 4 January 46 BC in the Roman province of Africa, between the Republican forces of the Optimates and forces loyal to Julius Caesar. The Republican army was commanded by Titus Labienus, Caesar's former lieutena ...
– Caesar loses perhaps as much as a third of his army to Titus Labienus
Titus Labienus (c. 10017 March 45 BC) was a high-ranking military officer in the late Roman Republic. He served as tribune of the Plebs in 63 BC. Although mostly remembered as one of Julius Caesar's best lieutenants in Gaul, mentioned freq ...
** 46 BC, 6 February – Battle of Thapsus
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and for ...
– Caesar defeats the Pompeian army of Metellus Scipio in North Africa.
** 45 BC, 17 March – Battle of Munda
The Battle of Munda (17 March 45 BC), in southern Hispania Ulterior, was the final battle of Caesar's civil war against the leaders of the Optimates. With the military victory at Munda and the deaths of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompeius (elde ...
– In his last victory, Caesar defeats the Pompeian forces of Titus Labienus and Gnaeus Pompey the Younger in Hispania. Labienus is killed in the battle and the Younger Pompey captured and executed.
* War with Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
** 47 BC, May – Battle of Zela
The Battle of Zela was a battle fought in 47 BC between Julius Caesar and Pharnaces II of the Kingdom of Pontus. The battle took place near Zela (modern Zile), which is now a small hilltop town in the Tokat province of northern Turkey. The batt ...
– Caesar defeats Pharnaces II
Pharnaces II of Pontus ( grc-gre, Φαρνάκης; about 97–47 BC) was the king of the Bosporan Kingdom and Kingdom of Pontus until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek ancestry. He was the youngest child born to King Mithridat ...
of Pontus
Pontus or Pontos may refer to:
* Short Latin name for the Pontus Euxinus, the Greek name for the Black Sea (aka the Euxine sea)
* Pontus (mythology), a sea god in Greek mythology
* Pontus (region), on the southern coast of the Black Sea, in modern ...
. This is the battle where he famously said ''Veni, vidi, vici.'' (I came, I saw, I conquered.)
* Liberators' civil war
The Liberators' civil war (43–42 BC) was started by the Second Triumvirate to avenge Julius Caesar's assassination. The war was fought by the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (the Second Triumvirate members) against the forces of Caesar's ...
(44–42 BC)
** 43 BC, 14 April – Battle of Forum Gallorum – Antony, besieging Caesar's assassin Decimus Brutus in Mutina
Modena (, , ; egl, label= Modenese, Mòdna ; ett, Mutna; la, Mutina) is a city and ''comune'' (municipality) on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy.
A town, and seat ...
, defeats the forces of the consul Pansa, who is killed, but is then immediately defeated by the army of the other consul, Hirtius
** 43 BC, 21 April – Battle of Mutina
The Battle of Mutina took place on 21 April 43 BC between the forces loyal to the Senate under Consuls Gaius Vibius Pansa and Aulus Hirtius, supported by the forces of Caesar Octavian, and the forces of Mark Antony which were besieging the tr ...
– Antony is again defeated in battle by Hirtius, who is killed. Although Antony fails to capture Mutina, Decimus Brutus is murdered shortly thereafter.
** 42 BC, 3 October – First Battle of Philippi – Triumvir
A triumvirate ( la, triumvirātus) or a triarchy is a political institution ruled or dominated by three individuals, known as triumvirs ( la, triumviri). The arrangement can be formal or informal. Though the three leaders in a triumvirate are ...
s Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autoc ...
and Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
fight an indecisive battle with Caesar's assassins Marcus Brutus
Marcus Junius Brutus (; ; 85 BC – 23 October 42 BC), often referred to simply as Brutus, was a Roman politician, orator, and the most famous of the assassins of Julius Caesar. After being adopted by a relative, he used the name Quintus Serv ...
and Cassius. Although Brutus defeats Octavian, Antony defeats Cassius, who commits suicide.
** 42 BC, 23 October – Second Battle of Philippi
The Battle of Philippi was the final battle in the Wars of the Second Triumvirate between the forces of Mark Antony and Octavian (of the Second Triumvirate) and the leaders of Julius Caesar's assassination, Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, at ...
– Brutus's army is decisively defeated by Antony and Octavian. Brutus escapes, but commits suicide soon after.
* ''Bellum Siculum
The Suetonius, ''Divus Augustus'' 9 (Latin for "Sicilian War") was an Ancient Roman civil war waged between 42 BC and 36 BC by the forces of the Second Triumvirate and Sextus Pompey, the last surviving son of Pompey the Great and the last l ...
'' (42–36 BC)
** 36 BC – Battle of Naulochus
The naval Battle of Naulochus ( it, Battaglia di Nauloco) was fought on 3 September 36 BC between the fleets of Sextus Pompeius and Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, off Naulochus, Sicily. The victory of Agrippa, admiral of Octavian, marked the end of t ...
– Octavian's fleet, under the command of Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa
Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa (; BC – 12 BC) was a Roman general, statesman, and architect who was a close friend, son-in-law, and lieutenant to the Roman emperor Augustus. He was responsible for the construction of some of the most notable buildi ...
defeats the forces of the rebel Sextus Pompeius
Sextus Pompeius Magnus Pius ( 67 – 35 BC), also known in English as Sextus Pompey, was a Roman military leader who, throughout his life, upheld the cause of his father, Pompey the Great, against Julius Caesar and his supporters during the las ...
.
* Fulvia's civil war (Perusine War) (41–40 BC)
** 41 BC – Battle of Perugia
The Perusine War (also Perusian or Perusinian War, or the War of Perusia) was a civil war of the Roman Republic, which lasted from 41 to 40 BC. It was fought by Lucius Antonius and Fulvia to support Mark Antony against his political enemy Octav ...
– Mark Antony's brother Lucius Antonius and his wife Fulvia are defeated by Octavian.
* War with the Parthian Empire (40-34 BC)
** 44 BC - Julius Caesar's planned invasion of the Parthian Empire
Julius Caesar's planned invasion of the Parthian Empire was to begin in 44 BC, but the Roman dictator's assassination that year prevented the invasion from taking place.Malitz, ''Caesars Partherkrieg'I/ref>
The campaign was to start with the pa ...
- Aborted due to Caesar's assassination.
** 40 BC - Pompeian–Parthian invasion of 40 BC
The Pompeian–Parthian invasion of 40 BC occurred after the Pompeians, backed by the Parthian Empire, had been defeated during the Liberators' civil war by Mark Antony and Augustus, Octavian.
King Orodes II sent a Parthian force under Prince ...
** 36 BC - Antony's Atropatene campaign
Antony's Parthian War was a military campaign by Mark Antony, the eastern triumvir of the Roman Republic, against the Parthian Empire under Phraates IV.
Julius Caesar had planned an invasion of Parthia but was assassinated before he could implem ...
** 34 BC - Antony's campaign against Armenia
* Final War of the Roman Republic
The War of Actium (32–30 BC) was the last civil war of the Roman Republic, fought between Mark Antony (assisted by Cleopatra and by extension Ptolemaic Egypt) and Octavian. In 32 BC, Octavian convinced the Roman Senate to declare war on the E ...
(32–30 BC)
** 31 BC, 2 September – Battle of Actium
The Battle of Actium was a naval battle fought between a maritime fleet of Octavian led by Marcus Agrippa and the combined fleets of both Mark Antony and Cleopatra VII Philopator. The battle took place on 2 September 31 BC in the Ionian Sea, nea ...
– Octavian
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
decisively defeats Antony and Cleopatra
Cleopatra VII Philopator ( grc-gre, Κλεοπάτρα Φιλοπάτωρ}, "Cleopatra the father-beloved"; 69 BC10 August 30 BC) was Queen of the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt from 51 to 30 BC, and its last active ruler.She was also a ...
in a naval battle near Greece.
* Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what to ...
(29–19 BC)
** 25 BC - Battle of Vellica - Roman forces under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
against the Cantabri
The Cantabri ( grc-gre, Καντάβροι, ''Kantabroi'') or Ancient Cantabrians, were a pre-Ancient Rome, Roman people and large tribal federation that lived in the northern coastal region of ancient Iberia in the second half of the first mille ...
people, Roman victory.
** 25 BC - Siege of Aracillum
The siege of Aracillum was a siege of the Cantabrian Wars that occurred in 25 BC. The battle took place between the forces of the Roman Empire, which consisted of five Roman legions commanded by Gaius Antistius Vetus and the forces of the Cantab ...
- Roman forces under Gaius Antistius Vetus against the Cantabri people, Roman victory.
* Germanic Battles (16–11 BC)
** Clades Lolliana
The ''clades Lolliana'' or Lollian disaster was a battle in 16 BCE, when the consul Marcus Lollius Paulinus was defeated by the Sicambri, Tencteri and Usipetes, Germanic tribes who had crossed the Rhine.Tacitus, The Annals 1.10 This defeat is ...
(16 BC) – The troops of Consul Marcus Lollius Paulinus are defeated by West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into t ...
warriors in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
.
** Battle of Arbalo (11 BC) - Romans under Nero Claudius Drusus
Nero Claudius Drusus Germanicus (38–9 BC), also called Drusus the Elder, was a Roman politician and military commander. He was a patrician Claudian on his birth father's side but his maternal grandmother was from a plebeian family. He was the ...
defeat the Germans
** Battle of the Lupia River
The Battle of the Lupia River was fought in 11 BC between a Roman force led by Nero Claudius Drusus and the Sicambri.Cassius Dio, ''Roman History'LIV.33/ref> The Lupia River, now Lippe, flows westwards through the Ruhr Valley in North Rhine-West ...
(11 BC) – Roman forces under Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
's stepson Drusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
win a victory in Germany.
1st century
 *
* Bellum Batonianum
The ( Latin for 'War of the Batos') was a military conflict fought in the Roman province of Illyricum in the 1st century AD, in which an alliance of native peoples of the two regions of Illyricum, Dalmatia and Pannonia, revolted against the R ...
(6-9) - An alliance of tribes numbering more than 200,000 people in Illyria rise in rebellion, but are suppressed by Roman legions led by Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus (; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was the second Roman emperor. He reigned from AD 14 until 37, succeeding his stepfather, the first Roman emperor Augustus. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC. His father ...
and Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
.
* Early Germanic campaigns (12 BC - 16 AD, but primarily 9-16 AD) - Campaigns in Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north- ...
(modern day Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and the low Countries
The term Low Countries, also known as the Low Lands ( nl, de Lage Landen, french: les Pays-Bas, lb, déi Niddereg Lännereien) and historically called the Netherlands ( nl, de Nederlanden), Flanders, or Belgica, is a coastal lowland region in N ...
) against various Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
** Battle of the Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, described as the Varian Disaster () by Ancient Rome, Roman historians, took place at modern Kalkriese in AD 9, when an alliance of Germanic peoples ambushed Roman legions and their auxiliaries, led by Publius ...
(9) – German leader Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of ge ...
ambushes and annihilates three Roman legions under Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus (Cremona, 46 BC – Teutoburg Forest, AD 9) was a Roman general and politician under the first Roman emperor Augustus. Varus is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions when ambushed by Germanic tribes l ...
, causing retaliation campaigns by the Romans.
** Battle at Pontes Longi
The Battle at Pontes Longi was fought near Bramsche, Germany in 15 AD between the Roman general Aulus Caecina Severus and an alliance of Germanic peoples commanded by Arminius. It was part of a three-year series of campaigns by Germanicus in ...
(15) - Indecisive battle between a Roman army under Aulus Caecina Severus and German tribes led by Arminius.
** Battle of the Weser River
The Battle of the Weser River, sometimes known as the First Battle of Minden or Battle of Idistaviso, was fought in 16 AD between Roman legions commanded by Roman Emperor Tiberius's heir and adopted son, Germanicus, and an alliance of Germanic ...
(16) - Legions under Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
defeat German tribes of Arminius.
** Battle of the Angrivarian Wall
The Battle of the Angrivarian Wall was fought near Porta Westfalica, Germany in 16 AD between the Roman general Germanicus and an alliance of Germanic tribes commanded by Arminius. This battle followed immediately after the Battle of Idistavi ...
(16) - Legions under Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
defeat the German tribes of Arminius, ending the campaigns.
* Revolt of Sacrovir
The Revolt of Sacrovir, also called the Florus-Sacrovir Revolt, was a Gallic uprising against Roman authorities led by Julius Sacrovir of the Aedui and Julius Florus of the Treveri in AD 21. Motivated by financial woes, the two chieftains refused ...
(21)
* Battle of Baduhenna Wood
The Battle of Baduhenna Wood was a battle, possibly fought (but not proven) near Heiloo, Netherlands, in 28 AD between the Frisii and a Roman army led by the Roman general Lucius Apronius.
The earliest mention of the Frisii tells of Drusus' 12 ...
(28)
* Roman conquest of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Staneg ...
(43–96)
** 43 – Battle of the Medway
The Battle of the Medway took place in 43 AD, probably on the River Medway in the lands of the Iron Age tribe of the Cantiaci, now the English county of Kent. Other locations for the battle have been suggested but are less likely. This was an ...
– Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
and general Aulus Plautius
Aulus Plautius was a Roman politician and general of the mid-1st century. He began the Roman conquest of Britain in 43, and became the first governor of the new province, serving from 43 to 46 CE.
Career
Little is known of Aulus Plautius's ear ...
defeat a confederation of British Celtic tribes. Roman invasion of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Staneg ...
begins
** 50 – Battle of Caer Caradoc
The final battle in Caratacus's resistance to Roman rule was fought in 50 AD. The Romans under Publius Ostorius Scapula defeated the Britons and in the aftermath captured Caratacus himself, since 43 the leader of armed opposition to the Roman ...
– British chieftain Caractacus
Caratacus ( Brythonic ''*Caratācos'', Middle Welsh ''Caratawc''; Welsh ''Caradog''; Breton ''Karadeg''; Greek ''Καράτακος''; variants Latin ''Caractacus'', Greek ''Καρτάκης'') was a 1st-century AD British chieftain of the ...
is defeated and captured by the Romans under Ostorius Scapula.
** 83 – Battle of Mons Graupius
The Battle of Mons Graupius was, according to Tacitus, a Roman military victory in what is now Scotland, taking place in AD 83 or, less probably, 84. The exact location of the battle is a matter of debate. Historians have long questioned some ...
. Romans under Gnaeus Julius Agricola
Gnaeus Julius Agricola (; 13 June 40 – 23 August 93) was a Roman general and politician responsible for much of the Roman conquest of Britain. Born to a political family of senatorial rank, Agricola began his military career as a military tribun ...
defeat the Caledonians.
* Roman–Parthian War of 58–63
The Roman–Parthian War of 58–63 or the War of the Armenian Succession was fought between the Roman Empire and the Parthian Empire over control of Armenia, a vital buffer state between the two realms. Armenia had been a Roman client state ...
** 58 – Sack of Artaxata
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of t ...
by Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo
Gnaeus Domitius Corbulo (Peltuinum c. AD 7 – 67) was a popular Roman general, brother-in-law of the emperor Caligula and father-in-law of Domitian. The emperor Nero, highly fearful of Corbulo's reputation, ordered him to commit suicide, which ...
during the Roman–Parthian War over Armenia
** 59 – Capture of Tigranocerta __NOTOC__
Tigranocerta ( el, Τιγρανόκερτα, ''Tigranόkerta''; Tigranakert; hy, Տիգրանակերտ), also called Cholimma or Chlomaron in antiquity, was a city and the capital of the Armenian Kingdom between 77 and 69 BCE. It bore ...
by Corbulo.
** 62 – Battle of Rhandeia
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– Romans under Lucius Caesennius Paetus
Lucius Junius Caesennius Paetus (c. 20 - 72?) was a Roman senator, and member of the ''gens'' Caesennia and Junia, who held several offices in the emperor's service. He was ''consul ordinarius'' for the year 61 as the colleague of Publius Petroniu ...
are defeated by a Parthian-Armenian army under King Tiridates of Parthia.
* Boudica's uprising (60–61)
** 60 – Battle of Camulodunum
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60–61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' ...
– Boudica begins her uprising against the Romans by capturing and then sacking Camulodunum then moves on Londinium
Londinium, also known as Roman London, was the capital of Roman Britain during most of the period of Roman rule. It was originally a settlement established on the current site of the City of London around AD 47–50. It sat at a key cross ...
.
** 61 – Battle of Watling Street
The Boudican revolt was an armed uprising by native Celtic tribes against the Roman Empire. It took place c. 60–61 AD in the Roman province of Britain, and was led by Boudica, the Queen of the Iceni. The uprising was motivated by the Romans' ...
– Boudica is defeated by Suetonius Paullinus
Gaius Suetonius Paulinus (fl. AD 41–69) was a Roman general best known as the commander who defeated the rebellion of Boudica.
Early life
Little is known of Suetonius' family, but it likely came from Pisaurum (modern Pesaro), a town on the Adri ...
* First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
(66–73)
** 66 – Battle of Beth-Horon – Jewish forces led by Eleazar ben Simon
Eleazar ben Simon () was a Zealot leader during the First Jewish-Roman War who fought against the armies of Cestius Gallus, Vespasian, and Titus Flavius. From the onset of the war in 66 CE until the destruction of the temple in 70 CE, he fo ...
defeat a Roman punitive force led by Cestius Gallus
Gaius Cestius Gallus (d. 67 AD) was a Roman senator and general who was active during the Principate. He was suffect consul for the second '' nundinium'' of the year 42 as the colleague of Gaius Caecina Largus. Gallus was the son of Gaius Cestiu ...
, Governor of Syria
** 73 – Siege of Masada
The siege of Masada was one of the final events in the First Jewish–Roman War, occurring from 73 to 74 CE on and around a hilltop in present-day Israel.
The siege is known to history via a single source, Flavius Josephus, a Jewish rebel leade ...
– The Sicarii
The Sicarii (Modern Hebrew: סיקריים ''siqariyim'') were a splinter group of the Jewish Zealots who, in the decades preceding Jerusalem's destruction in 70 CE, strongly opposed the Roman occupation of Judea and attempted to expel them and th ...
are defeated by the Romans under Lucius Flavius Silva
Lucius Flavius Silva Nonius Bassus was a late-1st-century Roman general, governor of the province of Iudaea and consul. Silva was the commander of the army, composed mainly of the ''Legio X Fretensis'', in 72 AD which laid siege to the near-impre ...
, leading them to commit mass suicide
Mass suicide is a form of suicide, occurring when a group of people simultaneously kill themselves.
Overview
Mass suicide sometimes occurs in religious settings. In war, defeated groups may resort to mass suicide rather than being captured. Su ...
* Roman Civil War of 68–69 AD
** 69 –
*** Winter – Battle of 'Forum Julii' – Othonian forces defeat a small group of Vitellianist auxilia
The (, lit. "auxiliaries") were introduced as non-citizen troops attached to the citizen legions by Augustus after his reorganisation of the Imperial Roman army from 30 BC. By the 2nd century, the Auxilia contained the same number of inf ...
ries in Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis (Latin for "Gaul of Narbonne", from its chief settlement) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in Southern France. It was also known as Provincia Nostra ("Our Province"), because it was the ...
*** 14 April – First Battle of Bedriacum
The Battle of Bedriacum refers to two battles fought during the Year of the Four Emperors (AD 69) near the village of Bedriacum (now Calvatone), about from the town of Cremona in northern Italy. The fighting in fact took place between Bedriacu ...
– Vitellius
Aulus Vitellius (; ; 24 September 1520 December 69) was Roman emperor for eight months, from 19 April to 20 December AD 69. Vitellius was proclaimed emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of ci ...
, commander of the Rhine armies, defeats Emperor Otho
Marcus Otho (; born Marcus Salvius Otho; 28 April 32 – 16 April 69) was the seventh Roman emperor, ruling for three months from 15 January to 16 April 69. He was the second emperor of the Year of the Four Emperors.
A member of a noble Etru ...
and seizes the throne.
*** 24 October – Second Battle of Bedriacum
The Battle of Bedriacum refers to two battles fought during the Year of the Four Emperors (AD 69) near the village of Bedriacum (now Calvatone), about from the town of Cremona in northern Italy. The fighting in fact took place between Bedria ...
– Forces under Antonius Primus
Marcus Antonius Primus (born between 20 AD and 35 AD – died after 81 AD) was a senator and general of the Roman Empire.
Biography Early life
Primus was born at Tolosa (Toulouse) in Gaul. He was likely the son/grandson of Lucius Antonius (grands ...
, the commander of the Danube armies, loyal to Vespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Empi ...
, defeat the forces of Emperor Vitellius
Aulus Vitellius (; ; 24 September 1520 December 69) was Roman emperor for eight months, from 19 April to 20 December AD 69. Vitellius was proclaimed emperor following the quick succession of the previous emperors Galba and Otho, in a year of ci ...
.
* Domitian's Dacian War
Domitian's Dacian War was a conflict between the Roman Empire and the Dacian Kingdom, which had invaded the province of Moesia. The war occurred during the reign of the Roman emperor Domitian, in the years 86–88 AD.
Dacian attack and def ...
(86–88)
** 87 – Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
n King Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Rom ...
crushes the Roman army at Tapae (today Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
, Romania), Legio V Alaudae
Legio V Alaudae ("Fifth Legion of the Lark"), sometimes also known as ''Gallica'', was a legion of the Roman army founded in 52 BC by the general Gaius Julius Caesar (dictator of Rome 49-44 BC). It was levied in Transalpine Gaul to fight the arm ...
and general Cornelius Fuscus
Cornelius Fuscus (died 86 AD) was a Roman general who fought campaigns under the Emperors of the Flavian dynasty. He first distinguished himself as one of Vespasian's most ardent supporters during the civil war of 69 AD, known as the Year of the ...
perish in battle.
** 88 – the Romans return and obtain a victory in the same battleground
2nd century
 *
* First Dacian War
The First Roman–Dacian War took place from 101 to 102. The Kingdom of Dacia, under King Decebalus, had become a threat to the Roman Empire, and defeated several of Rome's armies during Domitian's reign (81–96). The Emperor Trajan was set on ...
(101–102)
** 101 – Second Battle of Tapae
The Second Battle of Tapae (101) was the decisive battle of the first Dacian War, in which Roman Emperor Trajan defeated the Dacian King Decebalus's army. Other setbacks in the campaign delayed its completion until 102. The battle is most ...
– Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
defeats Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacians, Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Rom ...
, with heavy losses.
** 102 – Battle of Adamclisi
The Battle of Adamclisi was a major battle in the Trajan's Dacian Wars, Dacian Wars, fought in the winter of 101 to 102 between the Roman Empire and the Dacians near Adamclisi, in modern Romania.
Background
After the victory of Second Battle of ...
- Roman forces led by Trajan annihilate a mixed Dacian-Roxolano-Sarmatae army, with heavy casualties on the Roman side.
* Second Dacian War
The Second Roman–Dacian War was fought between 105 to 106 because the Dacian King, Decebalus, had broken his peace terms with the Roman Emperor Trajan from the First Dacian War.
Before the War
Following his subjugation, Decebalus complied with ...
(105–106)
** 106 – Battle of Sarmisegetusa
The Battle of Sarmizegetusa (also spelled ''Sarmizegethuza'') was a siege of Sarmizegetusa, the capital of Dacia, fought in 106 between the army of the Roman Emperor Trajan, and the Dacians led by King Decebalus.
Background
Because of the thr ...
– A Roman army led by Trajan conquers and destroys the Dacian capital. Part of Dacia is annexed to the Roman Empire.
* Roman-Parthian Wars
** 115-117 – Trajan's Parthian campaign
Trajan's Parthian campaign was engaged by Roman Emperor Trajan in 115 against the Parthian Empire in Mesopotamia. The war was initially successful for the Romans, but a series of setbacks, including wide-scale rebellions in the Eastern Medit ...
– Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
invades Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
and occupies Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon ( ; Middle Persian: 𐭲𐭩𐭮𐭯𐭥𐭭 ''tyspwn'' or ''tysfwn''; fa, تیسفون; grc-gre, Κτησιφῶν, ; syr, ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢThomas A. Carlson et al., “Ctesiphon — ܩܛܝܣܦܘܢ ” in The Syriac Gazetteer last modi ...
.
** 161-166 – Roman–Parthian War – Vologases IV invades Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ''Ox ...
, but is pushed back and Ctesiphon is sacked.
** 198 – Battle of Ctesiphon – Septimus Severus invades, sacks Ctesiphon, and acquires northern Mesopotamia.
*Kitos War (115–117)
*Bar Kokhba revolt, Second Jewish Revolt (132–135/136)
* Marcomannic Wars (166–180)
** 170 – Battle of Carnuntum – Marcomannic King Ballomar defeats the Roman Army and invade Italy.
** 178-179 – Praetorian Prefect Teratenius Paternus defeats the Quadi.
** 179 or 180 – Battle of Laugaricio – Marcus Valerius Maximianus defeats the Quadi in Slovakia.
* Year of the Five Emperors, Roman Civil War of 193–197 AD
** 193 – Battle of Cyzicus (193), Battle of Cyzicus – Septimius Severus, the new Emperor, defeats his eastern rival Pescennius Niger
** 193 – Battle of Nicaea – Severus again defeats Niger
** 194 – Battle of Issus (194), Battle of Issus – Severus finally defeats Niger.
** 197, 19 February – Battle of Lugdunum – Emperor Septimius Severus defeats and kills his rival Clodius Albinus, securing full control over the Empire.
3rd century
See Crisis of the Third Century * Roman invasion of Caledonia (208–210), Roman invasion of Caledonia (208-210) - Roman forces led by Septimus Severus invade Caledonia, but are forced to withdraw after suffering heavy casualties. * Persian wars ** 217 – Battle of Nisibis (217), Battle of Nisibis – Bloody stalemate between theParthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
ns and the Roman army under Emperor Macrinus.
** 231-232 - War between the Sasanian Empire, Sassanids under Ardashir I and Severus Alexander; resulted in humiliating Roman defeat and withdrawal.
** 243 – Battle of Resaena – Roman forces under Gordian III defeat the Persians under Shapur I.
** 260 – Battle of Edessa – Emperor Shapur I of Sasanian Empire, Persia defeats and captures the Roman Emperor Valerian (emperor), Valerian
** 296 or 297 – Battle of Carrhae (296), Battle of Carrhae – Romans under the Caesar Galerius are defeated by the Persians under Narseh.
** 298 – Battle of Satala (298), Battle of Satala – Galerius secures a decisive victory against Narseh, following a peace treaty.
* Civil wars
** 218, 8 June – Battle of Antioch (218), Battle of Antioch – Elagabalus, Varius Avitus defeats Emperor Macrinus to claim the throne under the name Elagabalus.
** 238 – Battle of Carthage (238), Battle of Carthage – Troops loyal to the Roman Emperor Maximinus Thrax defeat and kill his successor Gordian II.
** 274 – Battle of Châlons (274), Battle of Châlons – Aurelian defeats the Gallic usurper Tetricus I, Tetricus, reestablishing central control of the whole empire.
** 285 – Battle of the Margus – The usurper Diocletian defeats the army of the Emperor Carinus, who is killed.
* Gothic and Alemannic wars
** 235 – Battle at the Harzhorn - Roman army under Emperor Maximinus Thrax defeats a German army while withdrawing back to Roman territory.
** 250 – Battle of Philippopolis (250), Battle of Philippopolis – King Cniva of the Goths defeats a Roman army.
** 251, Summer – Battle of Abrittus – Goths defeat and kill the Roman Emperors Decius and Herennius Etruscus
** 259 – Battle of Mediolanum – Emperor Gallienus decisively defeats the Alemanni that invaded Italy
** 268 – Battle of Naissus – Emperor Gallienus and his generals Claudius II, Claudius and Aurelian decisively defeat the Goths.
** 268 or 269 – Battle of Lake Benacus – Romans under Emperor Claudius II defeat the Alemanni
** 271 –
*** Battle of Placentia (271), Battle of Placentia – Emperor Aurelian is defeated by the Alemanni forces invading Italy
*** Battle of Fano – Aurelian defeats the Alamanni, who begin to retreat from Italy
*** Battle of Pavia (271), Battle of Pavia – Aurelian destroys the retreating Alemanni army.
** 298 –
*** Battle of Lingones – Caesar (title), Caesar Constantius Chlorus defeats the Alemanni
*** Battle of Vindonissa – Constantius again defeats the Alamanni
* Palmyrene war
** 272 –
*** Battle of Immae – Aurelian defeats the army of Zenobia of Palmyra
*** Battle of Emesa – Aurelian decisively defeats Zenobia.
4th century

 The 4th century begins with civil war resulting in the ascendancy of Constantine the Great, Constantine I, then, after his death, the progressive Christianization of the empire, and wars with Sasanian Empire, Sassanid Persia and Germanic tribes, punctuated frequently with more civil wars.
* Civil wars of the Tetrarchy, Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324)
** 312 –
*** Battle of Turin (312), Battle of Turin – Constantine I (emperor), Constantine I defeats forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** Battle of Verona (312), Battle of Verona – Constantine I defeats more forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** 28 October – Battle of Milvian Bridge – Constantine I defeats Maxentius and takes control of Italy.
** 313, 30 April – Battle of Tzirallum – In the eastern part of the Empire, the forces of Licinius defeat Maximinus II, Maximinus.
** 316, 8 October – Battle of Cibalae – Constantine defeats Licinius
** 316 or 317 – Battle of Mardia – Constantine again defeats Licinius, who cedes Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum, Illyricum to Constantine.
** 324 –
*** 3 July – Battle of Adrianople (324), Battle of Adrianople – Constantine defeats Licinius, who flees to Byzantium
*** July – Battle of the Hellespont – Flavius Julius Crispus, son of Constantine, defeats the naval forces of Licinius
*** 18 September – Battle of Chrysopolis – Constantine decisively defeats Licinius, establishing his sole control over the empire.
* Roman–Persian Wars, Wars with Persia (344–363)
** 344 – Battle of Singara – Emperor Constantius II fights an indecisive battle against King Shapur II of Persia
** 359 – Siege of Amida (359), Siege of Amida – Sassanids capture Amida (Roman city), Amida from Romans
** 363, 29 May – Battle of Ctesiphon (363), Battle of Ctesiphon – Emperor Julian (emperor), Julian defeats Shapur II of Persia outside the walls of the Persian capital, but is unable to take the city.
** 363, June – Battle of Samarra (363) – Julian the Apostate, Julian fights the Sassanids and is subsequently killed in battle. Though indecisive, the battle leads to massive losses for the Roman Empire through a forced peace treaty.
* Roman civil war of 350–353, Civil War (350–353)
** 351 – Battle of Mursa Major – Emperor Constantius II defeats the usurper Magnentius
** 353 – Battle of Mons Seleucus – Final defeat of Magnentius by Constantius II
* Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus – 351–352 - Rebellion of Jews in Syria Palaestina.
* Wars with Alemanni (356–378)
** 356 – Battle of Reims (356), Battle of Reims – Caesar (title), Caesar Julian the Apostate, Julian is defeated by the Alamanni
** 357 – Battle of Strasbourg – Julian expels the Alamanni from the Rhineland
** 368 – Battle of Solicinium – Romans under Emperor Valentinian I defeat yet another Alamanni incursion.
** 378 –
*** May – Battle of Argentovaria – Western Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alamanni, yet again.
* Civil War – 366 – Battle of Thyatira – The army of the Roman emperor Valens defeats the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius.
* Great Conspiracy – 367-368 - Rebellion in the Hadrian's Wall and failed invasion of Britain by Picts, Scotti, Attacotti, Saxons and Franks.
* Gothic War (376–382)
** 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
***Summer -Battle of Dibaltum –Goths, Alans and Huns defeat Romans.
** 378 –
*** 9 August – Battle of Adrianople – Thervings under Fritigern defeat and kill the Eastern Emperor Valens
** 380 – Battle of Thessalonica (380), Battle of Thessalonica – The new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius I, is also defeated by the Thervings under Fritigern.
* Mavia (queen)#Details of the revolt, Tanukh revolt against Rome– 378-Spring - the Tanukhids Arabs rebels against Roman rule, led by their queen Mavia in Syria. The revolt end in a truce.
* Civil War – 388 – Battle of the Save – Emperor Theodosius I defeats the usurper Magnus Maximus.
* Civil War – 394, 5–6 September – Battle of the Frigidus – Theodosius I defeats and kills the usurper Eugenius and his Franks, Frankish ''magister militum'' Arbogast (magister militum), Arbogast.
* Stilicho's Pictish War – 398(?)
* Civil War – 398, Gildonic War – ''Comes'' Gildo, governor of Africa, rebels against the Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius.The revolt was subdued by Stilicho, Flavius Stilicho, the ''magister militum'' of the Western Roman empire.
The 4th century begins with civil war resulting in the ascendancy of Constantine the Great, Constantine I, then, after his death, the progressive Christianization of the empire, and wars with Sasanian Empire, Sassanid Persia and Germanic tribes, punctuated frequently with more civil wars.
* Civil wars of the Tetrarchy, Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy (306–324)
** 312 –
*** Battle of Turin (312), Battle of Turin – Constantine I (emperor), Constantine I defeats forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** Battle of Verona (312), Battle of Verona – Constantine I defeats more forces loyal to Maxentius.
*** 28 October – Battle of Milvian Bridge – Constantine I defeats Maxentius and takes control of Italy.
** 313, 30 April – Battle of Tzirallum – In the eastern part of the Empire, the forces of Licinius defeat Maximinus II, Maximinus.
** 316, 8 October – Battle of Cibalae – Constantine defeats Licinius
** 316 or 317 – Battle of Mardia – Constantine again defeats Licinius, who cedes Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum, Illyricum to Constantine.
** 324 –
*** 3 July – Battle of Adrianople (324), Battle of Adrianople – Constantine defeats Licinius, who flees to Byzantium
*** July – Battle of the Hellespont – Flavius Julius Crispus, son of Constantine, defeats the naval forces of Licinius
*** 18 September – Battle of Chrysopolis – Constantine decisively defeats Licinius, establishing his sole control over the empire.
* Roman–Persian Wars, Wars with Persia (344–363)
** 344 – Battle of Singara – Emperor Constantius II fights an indecisive battle against King Shapur II of Persia
** 359 – Siege of Amida (359), Siege of Amida – Sassanids capture Amida (Roman city), Amida from Romans
** 363, 29 May – Battle of Ctesiphon (363), Battle of Ctesiphon – Emperor Julian (emperor), Julian defeats Shapur II of Persia outside the walls of the Persian capital, but is unable to take the city.
** 363, June – Battle of Samarra (363) – Julian the Apostate, Julian fights the Sassanids and is subsequently killed in battle. Though indecisive, the battle leads to massive losses for the Roman Empire through a forced peace treaty.
* Roman civil war of 350–353, Civil War (350–353)
** 351 – Battle of Mursa Major – Emperor Constantius II defeats the usurper Magnentius
** 353 – Battle of Mons Seleucus – Final defeat of Magnentius by Constantius II
* Jewish revolt against Constantius Gallus – 351–352 - Rebellion of Jews in Syria Palaestina.
* Wars with Alemanni (356–378)
** 356 – Battle of Reims (356), Battle of Reims – Caesar (title), Caesar Julian the Apostate, Julian is defeated by the Alamanni
** 357 – Battle of Strasbourg – Julian expels the Alamanni from the Rhineland
** 368 – Battle of Solicinium – Romans under Emperor Valentinian I defeat yet another Alamanni incursion.
** 378 –
*** May – Battle of Argentovaria – Western Emperor Gratianus is victorious over the Alamanni, yet again.
* Civil War – 366 – Battle of Thyatira – The army of the Roman emperor Valens defeats the usurper Procopius (usurper), Procopius.
* Great Conspiracy – 367-368 - Rebellion in the Hadrian's Wall and failed invasion of Britain by Picts, Scotti, Attacotti, Saxons and Franks.
* Gothic War (376–382)
** 377 – Battle of the Willows – Roman troops fight an inconclusive battle against the Goths
***Summer -Battle of Dibaltum –Goths, Alans and Huns defeat Romans.
** 378 –
*** 9 August – Battle of Adrianople – Thervings under Fritigern defeat and kill the Eastern Emperor Valens
** 380 – Battle of Thessalonica (380), Battle of Thessalonica – The new Eastern Emperor, Theodosius I, is also defeated by the Thervings under Fritigern.
* Mavia (queen)#Details of the revolt, Tanukh revolt against Rome– 378-Spring - the Tanukhids Arabs rebels against Roman rule, led by their queen Mavia in Syria. The revolt end in a truce.
* Civil War – 388 – Battle of the Save – Emperor Theodosius I defeats the usurper Magnus Maximus.
* Civil War – 394, 5–6 September – Battle of the Frigidus – Theodosius I defeats and kills the usurper Eugenius and his Franks, Frankish ''magister militum'' Arbogast (magister militum), Arbogast.
* Stilicho's Pictish War – 398(?)
* Civil War – 398, Gildonic War – ''Comes'' Gildo, governor of Africa, rebels against the Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius.The revolt was subdued by Stilicho, Flavius Stilicho, the ''magister militum'' of the Western Roman empire.
5th century
 The 5th century involves the final fall of the Western Roman Empire to Goths, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Franks and other peoples.
* Wars with the Goths (402–419)
** 402 –
*** Siege of Asti (402) - The Visigoths besieged Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius in Asti until March, when Stilicho sent reinforcements .
*** 6 April – Battle of Pollentia – Stilicho defeats the Visigoths under Alaric I, Alaric.
*** June – Battle of Verona (402), Battle of Verona – Stilicho defeats Alaric, who withdraws from Italy.
** 405 or 406-
*** Siege of Florence (405), Siege of Florence - Stilcho defends city from the Goths of king Radagaisus, but Florence is nearly destroyed.
**406
*** Battle of Faesulae (406), Battle of Faesulae - Stilicho defeats Visigoths and Vandals under Radagaisus.
**409-
***Battle of Ostia (409), Battle of Ostia – Visigoths under Alaric I defeat Romans.
** 410, 24 August – Sack of Rome (410), Sack of Rome – Visigoths under Alaric sack Rome.
** 413 – Siege of Massilia (413), Siege of Massilia – Visigoths under Ataulf are defeated by Romans under Bonifacius while trying to siege Roman city. They make peace with Rome soon after.
* Roman–Sasanian War of 421–422 - The Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II declared war against the Persians and obtained some victories, but in the end, the two powers agreed to sign a peace on the status quo ante.
* Civil War – 432 – Battle of Ravenna (432), Battle of Ravenna – Bonifacius defeats rival Roman general Flavius Aetius, but is mortally wounded in the process.
* War with the Huns (447–451)
** 447 – Battle of the Utus – The Eastern Romans fight an indecisive battle with Huns led by Attila.
** 451, 20 June – Battle of the Catalaunian Plains – The Romans with Flavius Aetius and the Visigoths with Theodoric, defend against Attila, ruler of the Huns#Unified empire under Attila, Hunnic Empire.
** 452, 18 July –Sack of Aquileia –Aquileia is razed to the ground by the forces of Attila the Hun.
* Fall of the Western Roman Empire (406–476)
** 406, 31 December –
***Battle of Mainz (406), Battle of Mainz – Franks lose to Vandals, Suebi and Alans.
***Crossing of the Rhine -A mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi, crossed into northern Gaul.
** 419 – Battle of the Nervasos Mountains – Western Romans and Suebi defeat Vandals and Alans.
** 422 – Battle of Tarraco – The Vandal king Gunderic defeat the Western Romans, making the Vandals the undisputed masters of Hispania.
** 425 – Siege of Arles (425), Siege of Arles -The Roman general Flavius Aëtius, Aëtius defeats the Visigoths under Theodorid, Theodoric I.
** 431 - Siege of Hippo Regius – Vandals under Genseric establish a foothold in Africa, strategically defeating Rome. Saint Augustine dies during the siege.
** 436 – Battle of Narbonne (436), Battle of Narbonne – Flavius Aetius again defeats the Visigoths led by Theodoric I, Theodoric.
** 439
*** 19 October - Battle of Carthage (439), Battle of Carthage – Romans lose Carthage to the Vandals.
*** Battle of Toulouse (439), Battle of Toulouse – Visigoths led by Theodoric I defeat Romans under General Litorius, who is killed.
** c. 445-450 - Battle of Vicus Helena – Romans under Aetius defeat Franks.
** 455
*** 2 – c. 16 June – Sack of Rome (455), Sack of Rome by Geiseric, King of the Vandals
*** Battle of Aylesford – Romano-Britons (under Vortimer) and Anglo-Saxons battle in Kent, victory is unclear.
** 456 –
*** Battle of Agrigentum (456) – An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the Romano-Suebian general Ricimer, drove off an invading fleet sent by the Vandals, Vandal king Genseric, Gaiseric to raid Sicily.
*** Battle of Corsica - the Vandals were again attacked by Ricimer and defeated.
** 457 –
*** Battle of Garigliano (457) –The new Roman emperor, emperor Majorian surprised a Vandal-Berbers, Berber raiding party which was returning with loot from Campania.
***Battle of Campi Cannini – Roman General Majorian defeats an Alemanni invasion of Italy.
** 458 –
*** Battle of Toulouse (458) -The Roman Emperor Majorian defeats the Visigoths.
*** Late 458 Battle of Arelate -The Roman Emperor Majorian, with the support of Aegidius and Nepotianus (magister militiae), Nepotianus, defeats the Visigoths at Arlate. With a treaty, the Visigothic returned all territory in Hispania to the Romans.
** 461 –Battle of Cartagena (461), Battle of Cartagena – A Vandal fleet surprises and destroys the Roman fleet.
** 463 – Battle of Orleans (463), Battle of Orleans – Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman and Salian Franks, Salian Frank forces under the command of Aegidius defeat a force of Visigoths at Orleans.
** 464 – Battle of Bergamo – Romans under General Ricimer defeat Alans, Alan invasion of Italy and kill their king.
** 468 – Battle of Cap Bon (468), Battle of Cap Bon - Failure of the invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals by the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
** 469 – Battle of Déols - Visigoths defeat Bretons and Gallo-Romanas under Riothamus.
** 471 – Battle of Arles (471) - Visigothic king Euric defeats the Roman general Anthemiolus, captured Arles and much of southern
The 5th century involves the final fall of the Western Roman Empire to Goths, Vandals, Alans, Huns, Franks and other peoples.
* Wars with the Goths (402–419)
** 402 –
*** Siege of Asti (402) - The Visigoths besieged Western Emperor Honorius (emperor), Honorius in Asti until March, when Stilicho sent reinforcements .
*** 6 April – Battle of Pollentia – Stilicho defeats the Visigoths under Alaric I, Alaric.
*** June – Battle of Verona (402), Battle of Verona – Stilicho defeats Alaric, who withdraws from Italy.
** 405 or 406-
*** Siege of Florence (405), Siege of Florence - Stilcho defends city from the Goths of king Radagaisus, but Florence is nearly destroyed.
**406
*** Battle of Faesulae (406), Battle of Faesulae - Stilicho defeats Visigoths and Vandals under Radagaisus.
**409-
***Battle of Ostia (409), Battle of Ostia – Visigoths under Alaric I defeat Romans.
** 410, 24 August – Sack of Rome (410), Sack of Rome – Visigoths under Alaric sack Rome.
** 413 – Siege of Massilia (413), Siege of Massilia – Visigoths under Ataulf are defeated by Romans under Bonifacius while trying to siege Roman city. They make peace with Rome soon after.
* Roman–Sasanian War of 421–422 - The Eastern Roman Emperor Theodosius II declared war against the Persians and obtained some victories, but in the end, the two powers agreed to sign a peace on the status quo ante.
* Civil War – 432 – Battle of Ravenna (432), Battle of Ravenna – Bonifacius defeats rival Roman general Flavius Aetius, but is mortally wounded in the process.
* War with the Huns (447–451)
** 447 – Battle of the Utus – The Eastern Romans fight an indecisive battle with Huns led by Attila.
** 451, 20 June – Battle of the Catalaunian Plains – The Romans with Flavius Aetius and the Visigoths with Theodoric, defend against Attila, ruler of the Huns#Unified empire under Attila, Hunnic Empire.
** 452, 18 July –Sack of Aquileia –Aquileia is razed to the ground by the forces of Attila the Hun.
* Fall of the Western Roman Empire (406–476)
** 406, 31 December –
***Battle of Mainz (406), Battle of Mainz – Franks lose to Vandals, Suebi and Alans.
***Crossing of the Rhine -A mixed group of barbarians which included Vandals, Alans and Suebi, crossed into northern Gaul.
** 419 – Battle of the Nervasos Mountains – Western Romans and Suebi defeat Vandals and Alans.
** 422 – Battle of Tarraco – The Vandal king Gunderic defeat the Western Romans, making the Vandals the undisputed masters of Hispania.
** 425 – Siege of Arles (425), Siege of Arles -The Roman general Flavius Aëtius, Aëtius defeats the Visigoths under Theodorid, Theodoric I.
** 431 - Siege of Hippo Regius – Vandals under Genseric establish a foothold in Africa, strategically defeating Rome. Saint Augustine dies during the siege.
** 436 – Battle of Narbonne (436), Battle of Narbonne – Flavius Aetius again defeats the Visigoths led by Theodoric I, Theodoric.
** 439
*** 19 October - Battle of Carthage (439), Battle of Carthage – Romans lose Carthage to the Vandals.
*** Battle of Toulouse (439), Battle of Toulouse – Visigoths led by Theodoric I defeat Romans under General Litorius, who is killed.
** c. 445-450 - Battle of Vicus Helena – Romans under Aetius defeat Franks.
** 455
*** 2 – c. 16 June – Sack of Rome (455), Sack of Rome by Geiseric, King of the Vandals
*** Battle of Aylesford – Romano-Britons (under Vortimer) and Anglo-Saxons battle in Kent, victory is unclear.
** 456 –
*** Battle of Agrigentum (456) – An army of the Western Roman Empire, led by the Romano-Suebian general Ricimer, drove off an invading fleet sent by the Vandals, Vandal king Genseric, Gaiseric to raid Sicily.
*** Battle of Corsica - the Vandals were again attacked by Ricimer and defeated.
** 457 –
*** Battle of Garigliano (457) –The new Roman emperor, emperor Majorian surprised a Vandal-Berbers, Berber raiding party which was returning with loot from Campania.
***Battle of Campi Cannini – Roman General Majorian defeats an Alemanni invasion of Italy.
** 458 –
*** Battle of Toulouse (458) -The Roman Emperor Majorian defeats the Visigoths.
*** Late 458 Battle of Arelate -The Roman Emperor Majorian, with the support of Aegidius and Nepotianus (magister militiae), Nepotianus, defeats the Visigoths at Arlate. With a treaty, the Visigothic returned all territory in Hispania to the Romans.
** 461 –Battle of Cartagena (461), Battle of Cartagena – A Vandal fleet surprises and destroys the Roman fleet.
** 463 – Battle of Orleans (463), Battle of Orleans – Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Roman and Salian Franks, Salian Frank forces under the command of Aegidius defeat a force of Visigoths at Orleans.
** 464 – Battle of Bergamo – Romans under General Ricimer defeat Alans, Alan invasion of Italy and kill their king.
** 468 – Battle of Cap Bon (468), Battle of Cap Bon - Failure of the invasion of the kingdom of the Vandals by the Western and Eastern Roman Empires.
** 469 – Battle of Déols - Visigoths defeat Bretons and Gallo-Romanas under Riothamus.
** 471 – Battle of Arles (471) - Visigothic king Euric defeats the Roman general Anthemiolus, captured Arles and much of southern Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
** 472 – Siege of Rome (472), Siege of Rome - Ricimer, having fallen out with his choice for Roman Emperor, allies with the Burgundians and Germans under Odoacer, defeats and kills the Roman Emperor Anthemius.
** 476 – Battle of Ravenna (476), Battle of Ravenna – The Germanic foederati led by Odoacer decisively defeat the Western Roman Empire and depose Emperor Romulus Augustulus. Western Roman Empire dissolved. Odoacer declares himself King of Italy.
** 485 – Battle of Mercredesburne – Saxons under Ælle of Sussex, Aelle defeat British defenders.
** 486 – Battle of Soissons (486), Battle of Soissons – Clovis I defeats Syagrius, last Roman commander in Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
, and annexes the Kingdom of Soissons, Roman rump state into the Frankish realm.
** c. 500 – Battle of Badon, Battle of Mons Badonicus – Romano-British defeat Anglo-Saxons decisively, ending their advance into British land. Later connected to King Arthur.
* Battle of Cotyaeum - 492 - The Byzantine Empire, Eastern Rome army under John the Scythian defeats Isaurians under Longinus of Cardala.
6th century and beyond
 The Eastern Roman emperor Justinian launched an ambitious reconquest of Italy, North Africa and parts of Spain. However, new invaders like the Pannonian Avar, Avars, Kingdom of the Lombards, Lombards and Sclaveni, Slavs, alongside the Plague of Justinian, First plague pandemic and various Volcanic winter of 536, volcanic Late Antique Little Ice Age, winters ended his ambition of recuperate the West and consolidate the reconquest.
* 502–506 Anastasian War with Sassanid Persia.
* 526–532: Iberian War with Sassanid Persia.
* Justinian campaigns (533–555)
** 533–534: Vandalic War in Northern Africa.
** 534–548: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#The Moorish Wars, Moorish Wars in Africa.
** 535–554: Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War in Dalmatia and Italy.
** 541–562: Lazic War with Sassanid Persia.
** 552–555: Byzantine intervention in the Visigoth civil war in Spain, formation of Spania province.
** 560s–578: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#Conflict with Moorish kingdom of Garmul, War with the Romano-Moorish kingdom of Garmul.
* 572–591: Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591, War with Persia over the Caucasus.
* 589: Franco-Lombard-Byzantine conflict over the Po Valley. The war was stopped by breaching Breach at Cucca, dam in Cucca.
* 582–602: Maurice's Balkan campaigns, War against the Pannonian Avars, Avars and Slavs in the Balkans.
The Eastern Roman emperor Justinian launched an ambitious reconquest of Italy, North Africa and parts of Spain. However, new invaders like the Pannonian Avar, Avars, Kingdom of the Lombards, Lombards and Sclaveni, Slavs, alongside the Plague of Justinian, First plague pandemic and various Volcanic winter of 536, volcanic Late Antique Little Ice Age, winters ended his ambition of recuperate the West and consolidate the reconquest.
* 502–506 Anastasian War with Sassanid Persia.
* 526–532: Iberian War with Sassanid Persia.
* Justinian campaigns (533–555)
** 533–534: Vandalic War in Northern Africa.
** 534–548: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#The Moorish Wars, Moorish Wars in Africa.
** 535–554: Gothic War (535–554), Gothic War in Dalmatia and Italy.
** 541–562: Lazic War with Sassanid Persia.
** 552–555: Byzantine intervention in the Visigoth civil war in Spain, formation of Spania province.
** 560s–578: Praetorian prefecture of Africa#Conflict with Moorish kingdom of Garmul, War with the Romano-Moorish kingdom of Garmul.
* 572–591: Byzantine–Sassanid War of 572–591, War with Persia over the Caucasus.
* 589: Franco-Lombard-Byzantine conflict over the Po Valley. The war was stopped by breaching Breach at Cucca, dam in Cucca.
* 582–602: Maurice's Balkan campaigns, War against the Pannonian Avars, Avars and Slavs in the Balkans.
References
Sources
* Jones, Jim, (2013). Roman History Timeline. West Chester University of Pennsylvaniahttp://courses.wcupa.edu/jones/Roman History Timeline
External links
Milites
A Visual Analytics tool on Roman battles. * Elton, Hugh and Christos Nüssli, "
Imperial Battle Map Index
'". An Online Encyclopedia of Roman Emperors.
"Roman Battles" map, platial.com
See also
*List of Roman civil wars and revolts
This is a list of civil wars and organized civil disorder, revolts and rebellions in ancient Rome (Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, and Roman Empire) until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (753 BCE – 476 CE). For the Eastern Roman Empire or B ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Roman wars and battles
Lists of wars by country, Rome
Wars involving ancient Rome
Lists of battles, Roman
Battles involving ancient Rome,
Timelines of military conflicts, Roman battles
Ancient Rome-related lists