|
Battle Of Ilerda
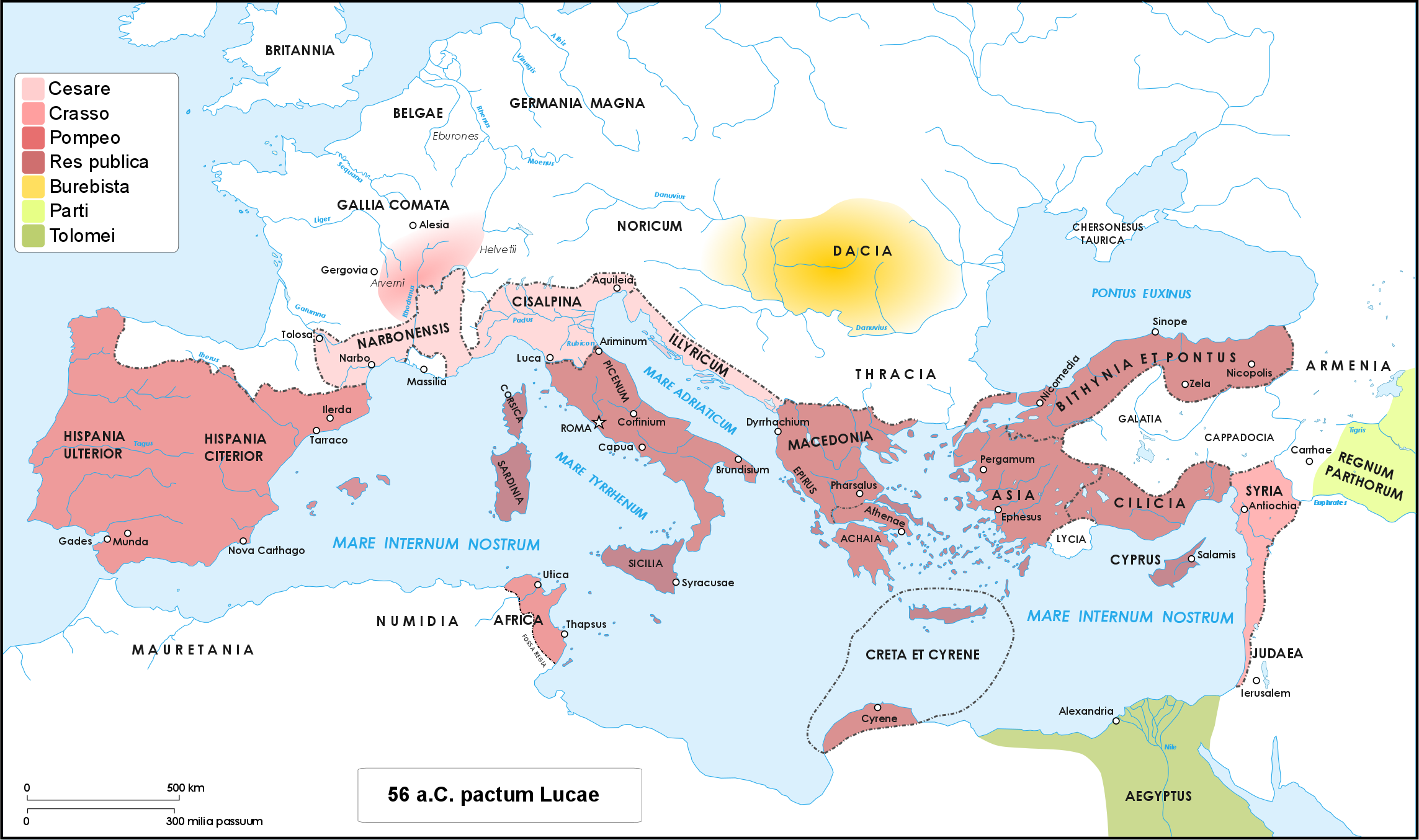
The Battle of Ilerda took place in June 49 BC between the forces of Julius Caesar and the Spanish army of Pompey Magnus, led by his legates Lucius Afranius and Marcus Petreius. Unlike many of the other battles of the civil war, this was more a campaign of manoeuvre than actual fighting. It allowed Caesar to eliminate the threat of Pompey’s forces in Spain and face Pompey himself in Greece at the Battle of Pharsalus (48 BC). Background After having driven the Optimates from Italy, in March 49 BC Caesar turned his attention to the Republican army in the Spanish provinces. On his way to Spain, Caesar was delayed when the port city of Massilia rebelled under the leadership of Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus in April. Leaving the siege of Massilia to Gaius Trebonius and Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus, Caesar moved to Hispania Citerior to reinforce the three legions he had sent there as an advance guard under his legate Fabius. Ilerda Campaign Fabius had taken control of several pas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legatus
A ''legatus'' (; anglicised as legate) was a high-ranking Roman military officer in the Roman Army, equivalent to a modern high-ranking general officer. Initially used to delegate power, the term became formalised under Augustus as the officer in command of a legion. From the times of the Roman Republic, legates received large shares of the military's rewards at the end of a successful campaign. This made the position a lucrative one, so it could often attract even distinguished consuls or other high-ranking political figures within Roman politics (e.g., the consul Lucius Julius Caesar volunteered late in the Gallic Wars as a legate under his first cousin, Gaius Julius Caesar). History Roman Republic The rank of legatus existed as early as the Samnite Wars, but it was not until 190 BC that it started to be standardized, meant to better manage the higher numbers of soldiers the Second Punic War had forced to recruit. The legatus of a Roman Republican army was essentially a sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lérida
Lleida (, ; Spanish: Lérida ) is a city in the west of Catalonia, Spain. It is the capital city of the province of Lleida. Geographically, it is located in the Catalan Central Depression. It is also the capital city of the Segrià comarca, as well as the largest city in the province. It had 137,387 inhabitants , including the contiguous towns of Raimat and Sucs. Lleida is one of the oldest towns in Catalonia, with recorded settlements dating back to the Bronze Age period. Until the Roman conquest of the Iberian Peninsula, the area served as a settlement for an Iberian people, the Ilergetes. The town became a municipality, named Ilerda, under the reign of Augustus. It was ruled by the Moors from the 8th century, and reconquered in 1149. In 1297, the University of Lleida was founded, becoming the third oldest in the whole of Spain. During the following centuries, the town was damaged by several wars such as the Reapers' War in the 17th century and the Spanish Civil War in the 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Instituts-Templers
Instituts-Templers is a district of Lleida, Catalonia, Spain. It's made up of different areas between La Mariola, Universitat and the river Segre, mostly working-class, some middle class. "Templers-Escorxador" is located within the portion of medieval Lleida which was once owned by the Knights Templar, hence the name. "Instituts" refers to the oldest public secondary institutes or high-schools of the 20th century town, that dominate the area next to Gardeny. It has undergone serious urban regeneration during the 1990s and especially the 2000s (decade). It had over 15000 inhabitants in 2009. The Battle of Ilerda The Battle of Ilerda took place in June 49 BC between the forces of Julius Caesar and the Spanish army of Pompey Magnus, led by his legates Lucius Afranius and Marcus Petreius. Unlike many of the other battles of the civil war, this was more ... took place in this area of Roman-era Lleida, then called Ilerda. Landmarks Landmarks include the Templar Gardeny C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Cassius Longinus
Gaius Cassius Longinus (c. 86 BC – 3 October 42 BC) was a Roman senator and general best known as a leading instigator of the plot to assassinate Julius Caesar on 15 March 44 BC. He was the brother-in-law of Brutus, another leader of the conspiracy. He commanded troops with Brutus during the Battle of Philippi against the combined forces of Mark Antony and Octavian, Caesar's former supporters, and committed suicide after being defeated by Mark Antony. Cassius was elected as Tribune of the plebs in 49 BC. He opposed Caesar, and eventually he commanded a fleet against him during Caesar's Civil War: after Caesar defeated Pompey in the Battle of Pharsalus, Caesar overtook Cassius and forced him to surrender. After Caesar's death, Cassius fled to the East, where he amassed an army of twelve legions. He was supported and made Governor by the Senate. Later he and Brutus marched west against the allies of the Second Triumvirate. He followed the teachings of the philosopher Epicurus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Cassius Longinus
Quintus Cassius Longinus, the brother or cousin of Cassius (the murderer of Julius Caesar), was a governor in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula, comprising modern Spain and Portugal) for Caesar. Cassius was one of the ''tresviri monetales'' of the Roman mint in 55 BC. He served as a quaestor of Pompey in ''Hispania Ulterior'' in 54 BC. In 49 BC, as tribune of the people, he strongly supported the cause of Caesar, by whom he was made governor of Hispania Ulterior. He treated the provincials with great cruelty, and his appointment in 48 BC to take the field against Juba I of Numidia gave him an excuse for fresh oppression. The result was an unsuccessful insurrection at Corduba. Cassius punished the leaders with merciless severity, and made the lot of the provincials harder than ever. At last some of his troops revolted under the quaestor Marcellus, who was proclaimed governor of the province. Cassius was surrounded by Marcellus in Ulia. Bogud, king of Mauretania, and Marcus Lepidus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispania Ulterior
Hispania Ulterior (English: "Further Hispania", or occasionally "Thither Hispania") was a region of Hispania during the Roman Republic, roughly located in Baetica and in the Guadalquivir valley of modern Spain and extending to all of Lusitania (modern Portugal, Extremadura and a small part of Salamanca province) and Gallaecia (modern Northern Portugal and Galicia). Its capital was Corduba. Etymology ''Hispania'' is the Latin term given to the Iberian peninsula. The term can be traced back to at least 200 BC when the term was used by the poet Quintus Ennius. The word is possibly derived from the Punic אי שפן "I-Shaphan" meaning "coast of hyraxes", in turn a misidentification on the part of Phoenician explorers of its numerous rabbits as hyraxes. Ulterior is the comparative form of ulter, which means "that is beyond". According to ancient historian Cassius Dio, the people of the region came from many different tribes. They did not share a common language or a common gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Terentius Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes called Varro Reatinus to distinguish him from his younger contemporary Varro Atacinus. Biography Varro was born in or near Reate (now Rieti) to a family thought to be of equestrian rank, and always remained close to his roots in the area, owning a large farm in the Reatine plain, reported as near Lago di Ripasottile, until his old age. He supported Pompey, reaching the office of praetor, after having been tribune of the people, ''quaestor'' and ''curule aedile''. It is probable that Varro was discontented with the course on which Pompey entered when the First Triumvirate was formed, and he may thus have lost his chance of rising to the consulate. He actually ridiculed the coalition in a work entitled the ''Three-Headed Monster'' ( in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segre River
The Segre ( or ; french: Sègre) is a river tributary to the Ebro (''Ebre'' in Catalan) with a basin comprising territories across three states: France, Andorra and Spain. The river Segre, known to Romans and Greeks as Sicoris, and to the Arabs of Al-Andalus as Nahr az-Zaytūn (نهر الزيتون, river of Olives) has its sources on the north face of the Pic del Segre or ''Puigmal de Segre'' ("Segre's Peak") in the French department Pyrénées-Orientales (historically the ''comarca'' of Alta Cerdanya), in the Catalan Pyrenees. It follows a western direction all along the Cerdanya (''Cerdagne'') Valley, and crosses the town Saillagouse, the Spanish exclave Llívia and Bourg-Madame. It enters Spain at Puigcerdà and continues west until La Seu d'Urgell, where it meets the Valira River coming from Andorra. From this point it adopts a south-western course across the pre-Pyrenees (with several dams along its gorges) and the western plains of Catalonia. It passes through Balague ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hastati
''Hastati'' (singular: ''hastatus'') were a class of infantry employed in the armies of the early Roman Republic, who originally fought as spearmen and later as swordsmen. These soldiers were the staple unit after Rome threw off Etruscan rule. They were originally some of the poorest men in the legion, and could afford only modest equipment—light chainmail and other miscellaneous equipment. The Senate supplied their soldiers with only a short stabbing sword, the gladius, and their distinctive squared shield, the scutum. The ''hastatus'' was typically equipped with these, and one or two soft iron tipped throwing spears called pila. This doubled their effectiveness, not only as a strong leading edge to their maniple, but also as a stand-alone missile troop. Later, the ''hastati'' contained the younger men rather than just the poorer, though most men of their age were relatively poor. Their usual position was the first battle line. They fought in a quincunx formation, supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentarii De Bello Civili
''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' ''(Commentaries on the Civil War)'', or ''Bellum Civile'', is an account written by Julius Caesar of his war against Gnaeus Pompeius and the Roman Senate. It consists of three books covering the events of 49–48 BC, from shortly before Caesar's invasion of Italy to Pompey's defeat at the Battle of Pharsalus and flight to Egypt. It was preceded by the much longer account of Caesar's campaigns in Gaul and was followed by similar works covering the ensuing wars against the remnants of Pompey's armies in Egypt, North Africa, and Spain. Caesar's authorship of the ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' is not disputed, while the three later works are believed to have been written by contemporaries of Caesar. Title The Latin title "Commentarii de Bello Civili" is often retained as the title of the book in English translations of the work. The title itself is Latin for "Commentaries on the Civil War". It is sometimes shortened to just "Civil Wars", "About th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Munatius Plancus
Lucius Munatius Plancus ( – ) was a Roman senator, consul in 42 BC, and censor in 22 BC with Paullus Aemilius Lepidus. Along with Talleyrand eighteen centuries later, he is one of the classic historical examples of men who have managed to survive very dangerous circumstances by constantly shifting their allegiances. Early career Plancus was born in Tibur, the son of his homonymous father, of whom very little is known. He had three brothers and a sister: two of the brothers pursued public lives, one ascending to the praetorship and the other reaching the plebeian tribunate. He must have entered public life with election as quaestor some time before 54 BC. More concrete information on Plancus' career only appears when he became one of Julius Caesar's legates during the Gallic Wars: he served under Caesar in Gaul from 54 BC through to the start of Caesar's civil war in January 49 BC. At the start of the civil war, he joined with Caesar against Pompey; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |