Latent variables on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of ...
, latent variables (from Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: present participle
In linguistics, a participle () (from Latin ' a "sharing, partaking") is a nonfinite verb form that has some of the characteristics and functions of both verbs and adjectives. More narrowly, ''participle'' has been defined as "a word derived from ...
of ''lateo'', “lie hidden”) are variables that can only be inferred
Inferences are steps in reasoning, moving from premises to logical consequences; etymologically, the word '' infer'' means to "carry forward". Inference is theoretically traditionally divided into deduction and induction, a distinction that i ...
indirectly through a mathematical model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, ...
from other observable variables that can be directly observed
Observation is the active acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data (information), data via the use of scienti ...
or measured
Measurement is the quantification of attributes of an object or event, which can be used to compare with other objects or events.
In other words, measurement is a process of determining how large or small a physical quantity is as compared t ...
. Such '' latent variable models'' are used in many disciplines, including political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and power, and the analysis of political activities, political thought, political behavior, and associated constitutions and la ...
, demography
Demography () is the statistics, statistical study of populations, especially human beings.
Demographic analysis examines and measures the dimensions and Population dynamics, dynamics of populations; it can cover whole societies or groups ...
, engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific method, scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad rang ...
, medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
, ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
, physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which r ...
, machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
/artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech re ...
, bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combi ...
, chemometrics, natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is an interdisciplinary subfield of linguistics, computer science, and artificial intelligence concerned with the interactions between computers and human language, in particular how to program computers to pro ...
, management
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activities o ...
and the social sciences
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soci ...
.
Latent variables may correspond to aspects of physical reality. These could in principle be measured, but may not be for practical reasons. In this situation, the term ''hidden variables'' is commonly used (reflecting the fact that the variables are meaningful, but not observable). Other latent variables correspond to abstract concepts, like categories, behavioral or mental states, or data structures. The terms ''hypothetical variables'' or ''hypothetical constructs'' may be used in these situations.
The use of latent variables can serve to reduce the dimensionality of data. Many observable variables can be aggregated in a model to represent an underlying concept, making it easier to understand the data. In this sense, they serve a function similar to that of scientific theories. At the same time, latent variables link observable " sub-symbolic" data in the real world to symbolic data in the modeled world.
Examples

Psychology
Latent variables, as created by factor analytic methods, generally represent "shared" variance, or the degree to which variables "move" together. Variables that have no correlation cannot result in a latent construct based on the commonfactor model
Factor, a Latin word meaning "who/which acts", may refer to:
Commerce
* Factor (agent), a person who acts for, notably a mercantile and colonial agent
* Factor (Scotland), a person or firm managing a Scottish estate
* Factors of production, su ...
.
* The " Big Five personality traits" have been inferred using factor analysis.
* extraversion
* spatial ability
* wisdom “Two of the more predominant means of assessing wisdom include wisdom-related performance and latent variable measures.”
* Spearman's g
The ''g'' factor (also known as general intelligence, general mental ability or general intelligence factor) is a construct developed in psychometric investigations of cognitive abilities and human intelligence. It is a variable that summarizes ...
, or the general intelligence factor
The ''g'' factor (also known as general intelligence, general mental ability or general intelligence factor) is a construct developed in psychometric investigations of cognitive abilities and human intelligence. It is a variable that summarizes ...
in psychometrics
Economics
Examples of latent variables from the field ofeconomics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and intera ...
include quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
, business confidence, morale, happiness and conservatism: these are all variables which cannot be measured directly. But linking these latent variables to other, observable variables, the values of the latent variables can be inferred from measurements of the observable variables. Quality of life is a latent variable which cannot be measured directly so observable variables are used to infer quality of life. Observable variables to measure quality of life include wealth, employment, environment, physical and mental health, education, recreation and leisure time, and social belonging.
Medicine
Latent-variable methodology is used in many branches ofmedicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
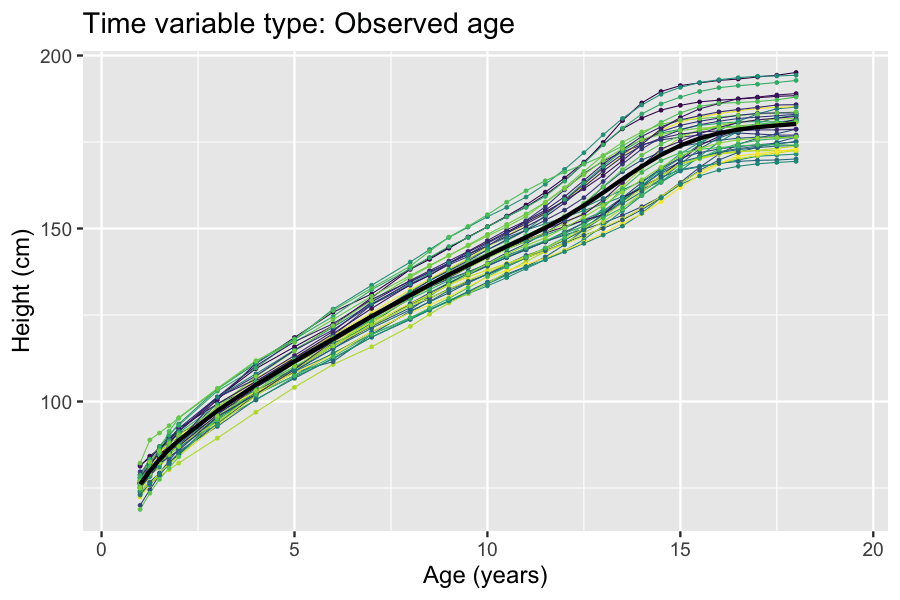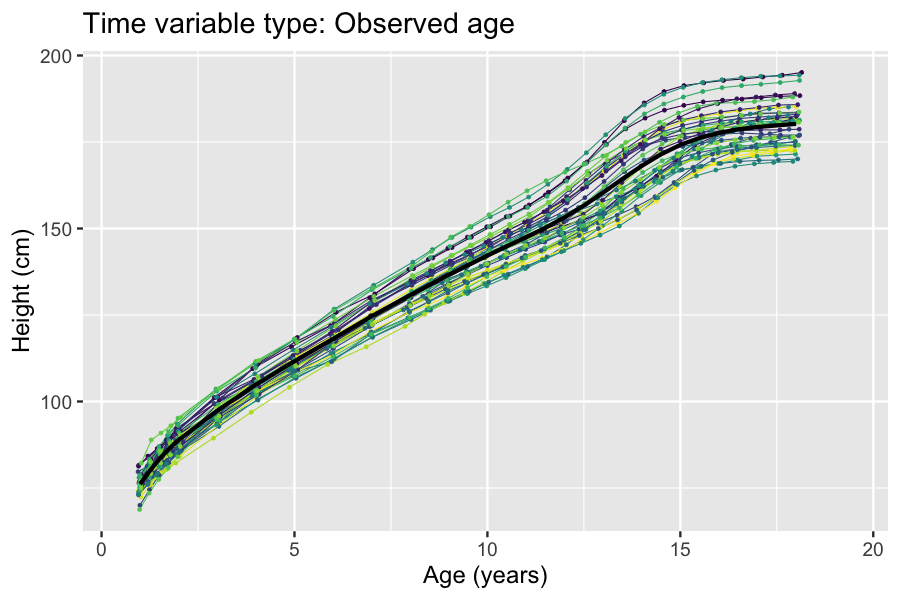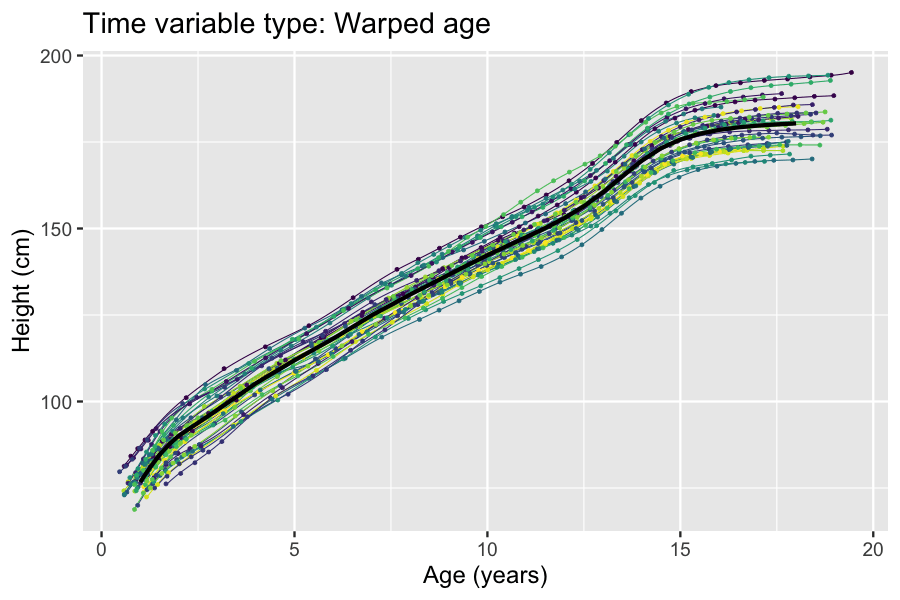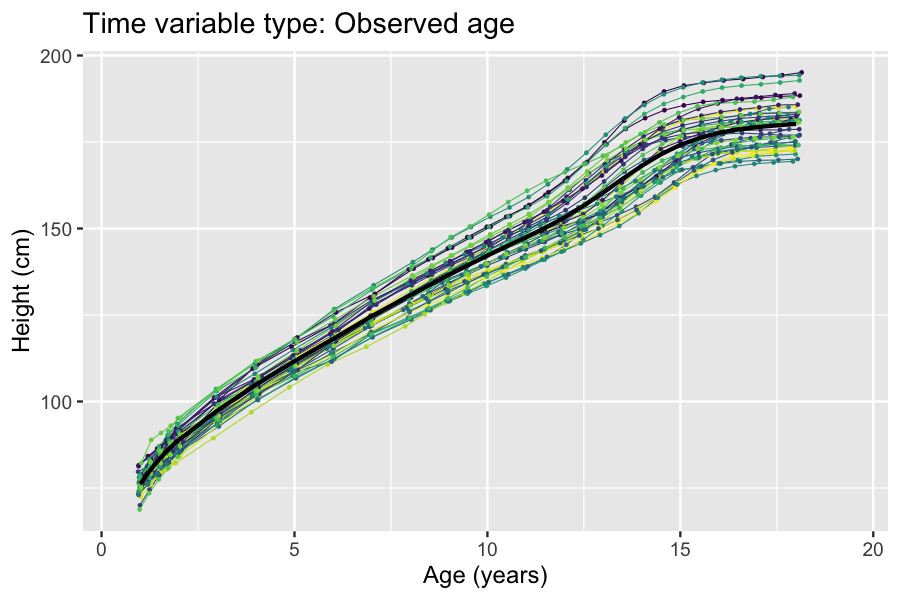
. A class of problems that naturally lend themselves to latent variables approaches are longitudinal studies where the time scale (e.g. age of participant or time since study baseline) is not synchronized with the trait being studied. For such studies, an unobserved time scale that is synchronized with the trait being studied can be modeled as a transformation of the observed time scale using latent variables. Examples of this include disease progression modeling and modeling of growth (see box).
Inferring latent variables
There exists a range of different model classes and methodology that make use of latent variables and allow inference in the presence of latent variables. Models include: * linear mixed-effects models and nonlinear mixed-effects models *Hidden Markov model
A hidden Markov model (HMM) is a statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process — call it X — with unobservable ("''hidden''") states. As part of the definition, HMM requires that there be an ob ...
s
* Factor analysis
* Item response theory
Analysis and inference methods include:
* Principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and ...
* Instrumented principal component analysisKelly, Bryan T. and Pruitt, Seth and Su, Yinan, Instrumented Principal Component Analysis (December 17, 2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2983919 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2983919
* Partial least squares regression
Partial least squares regression (PLS regression) is a statistical method that bears some relation to principal components regression; instead of finding hyperplanes of maximum variance between the response and independent variables, it finds a li ...
* Latent semantic analysis and probabilistic latent semantic analysis
* EM algorithm
EM, Em or em may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* EM, the E major musical scale
* Em, the E minor musical scale
* Electronic music, music that employs electronic musical instruments and electronic music technology in its production
* Ency ...
s
* Metropolis–Hastings algorithm
In statistics and statistical physics, the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for obtaining a sequence of random samples from a probability distribution from which direct sampling is difficult. This seque ...
Bayesian algorithms and methods
Bayesian statistics is often used for inferring latent variables. * Latent Dirichlet allocation * TheChinese restaurant process
In probability theory, the Chinese restaurant process is a discrete-time stochastic process, analogous to seating customers at tables in a restaurant.
Imagine a restaurant with an infinite number of circular tables, each with infinite capacity. C ...
is often used to provide a prior distribution over assignments of objects to latent categories.
* The Indian buffet process
In the mathematical theory of probability, the Indian buffet process (IBP) is a stochastic process defining a probability distribution over sparse binary matrices with a finite number of rows and an infinite number of columns. This distribution ...
is often used to provide a prior distribution over assignments of latent binary features to objects.
See also
*Confounding
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable, confounding factor, extraneous determinant or lurking variable) is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Con ...
* Dependent and independent variables
Dependent and independent variables are variables in mathematical modeling, statistical modeling and experimental sciences. Dependent variables receive this name because, in an experiment, their values are studied under the supposition or demand ...
* Errors-in-variables models
In statistics, errors-in-variables models or measurement error models are regression models that account for measurement errors in the independent variables. In contrast, standard regression models assume that those regressors have been measured e ...
* Evidence lower bound
In variational Bayesian methods, the evidence lower bound (often abbreviated ELBO, also sometimes called the variational lower bound or negative variational free energy) is a useful lower bound on the log-likelihood of some observed data.
Termin ...
* Factor analysis
* Intervening variable
In statistics, a mediation model seeks to identify and explain the mechanism or process that underlies an observed relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable via the inclusion of a third hypothetical variable, known a ...
* Latent variable model
* Item response theory
* Partial least squares path modeling The partial least squares path modeling or partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-PM, PLS-SEM) is a method for structural equation modeling that allows estimation of complex cause-effect relationships in path models with latent var ...
* Partial least squares regression
Partial least squares regression (PLS regression) is a statistical method that bears some relation to principal components regression; instead of finding hyperplanes of maximum variance between the response and independent variables, it finds a li ...
* Proxy (statistics)
* Rasch model
The Rasch model, named after Georg Rasch, is a psychometric model for analyzing categorical data, such as answers to questions on a reading assessment or questionnaire responses, as a function of the trade-off between the respondent's abilities, at ...
* Structural equation modeling
Structural equation modeling (SEM) is a label for a diverse set of methods used by scientists in both experimental and observational research across the sciences, business, and other fields. It is used most in the social and behavioral scienc ...
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Latent Variable Social research Bayesian networks Econometric modeling Latent variable Psychometrics de:Latente Variable