History of molecular theory on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more
In chemistry, the history of molecular theory traces the origins of the concept or idea of the existence of strong chemical bonds between two or more  ),
),  ),
),  ), and
), and  ) and "forces" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this,
) and "forces" of attraction and repulsion allowing the elements to interact. Prior to this,
 With the rise of scholasticism and the decline of the Roman Empire, the atomic theory was abandoned for many ages in favor of the various four element theories and later alchemical theories. The 17th century, however, saw a resurgence in the atomic theory primarily through the works of Gassendi, and Newton. Among other scientists of that time Gassendi deeply studied ancient history, wrote major works about Epicurus natural philosophy and was a persuasive propagandist of it. He reasoned that to account for the size and shape of atoms moving in a void could account for the properties of matter. Heat was due to small, round atoms; cold, to pyramidal atoms with sharp points, which accounted for the pricking sensation of severe cold; and solids were held together by interlacing hooks. Newton, though he acknowledged the various atom attachment theories in vogue at the time, i.e. "hooked atoms", "glued atoms" (bodies at rest), and the "stick together by conspiring motions" theory, rather believed, as famously stated in "Query 31" of his 1704 ''
With the rise of scholasticism and the decline of the Roman Empire, the atomic theory was abandoned for many ages in favor of the various four element theories and later alchemical theories. The 17th century, however, saw a resurgence in the atomic theory primarily through the works of Gassendi, and Newton. Among other scientists of that time Gassendi deeply studied ancient history, wrote major works about Epicurus natural philosophy and was a persuasive propagandist of it. He reasoned that to account for the size and shape of atoms moving in a void could account for the properties of matter. Heat was due to small, round atoms; cold, to pyramidal atoms with sharp points, which accounted for the pricking sensation of severe cold; and solids were held together by interlacing hooks. Newton, though he acknowledged the various atom attachment theories in vogue at the time, i.e. "hooked atoms", "glued atoms" (bodies at rest), and the "stick together by conspiring motions" theory, rather believed, as famously stated in "Query 31" of his 1704 ''
 An early precursor to the idea of bonded "combinations of atoms", was the theory of "combination via
An early precursor to the idea of bonded "combinations of atoms", was the theory of "combination via 
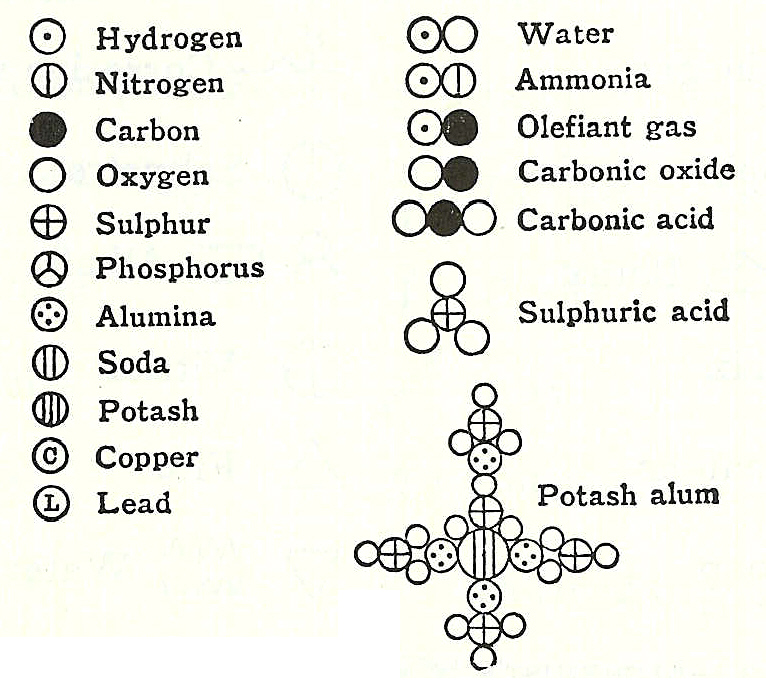 Similar to these views, in 1803 John Dalton took the atomic weight of hydrogen, the lightest element, as unity, and determined, for example, that the ratio for nitrous anhydride was 2 to 3 which gives the formula N2O3. Dalton incorrectly imagined that atoms "hooked" together to form molecules. Later, in 1808, Dalton published his famous diagram of combined "atoms":
Similar to these views, in 1803 John Dalton took the atomic weight of hydrogen, the lightest element, as unity, and determined, for example, that the ratio for nitrous anhydride was 2 to 3 which gives the formula N2O3. Dalton incorrectly imagined that atoms "hooked" together to form molecules. Later, in 1808, Dalton published his famous diagram of combined "atoms":
 In two papers outlining his "theory of atomicity of the elements" (1857–58),
In two papers outlining his "theory of atomicity of the elements" (1857–58),  In 1861, an unknown Vienna high-school teacher named
In 1861, an unknown Vienna high-school teacher named  Loschmidt also suggested a possible formula for benzene, but left the issue open. The first proposal of the modern structure for benzene was due to Kekulé, in 1865. The cyclic nature of benzene was finally confirmed by the crystallographer
Loschmidt also suggested a possible formula for benzene, but left the issue open. The first proposal of the modern structure for benzene was due to Kekulé, in 1865. The cyclic nature of benzene was finally confirmed by the crystallographer  In 1865, German chemist
In 1865, German chemist  The basis of this model followed the earlier 1855 suggestion by his colleague
The basis of this model followed the earlier 1855 suggestion by his colleague  In 1898,
In 1898, 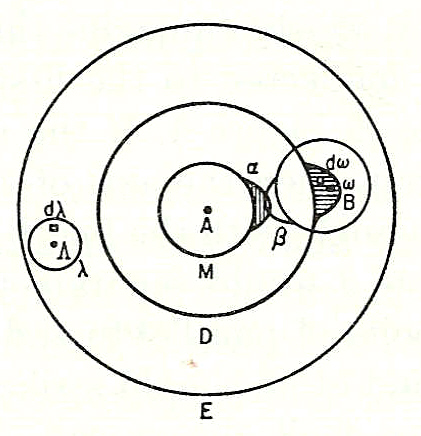
 Hence,
Hence,
The Atom and the Molecule
', Lewis introduced the "Lewis structure" to represent atoms and molecules, where dots represent In Lewis' own words:
Moreover, he proposed that an atom tended to form an ion by gaining or losing the number of electrons needed to complete a cube. Thus, Lewis structures show each atom in the structure of the molecule using its chemical symbol. Lines are drawn between atoms that are bonded to one another; occasionally, pairs of dots are used instead of lines. Excess electrons that form lone pairs are represented as pair of dots, and are placed next to the atoms on which they reside:
In Lewis' own words:
Moreover, he proposed that an atom tended to form an ion by gaining or losing the number of electrons needed to complete a cube. Thus, Lewis structures show each atom in the structure of the molecule using its chemical symbol. Lines are drawn between atoms that are bonded to one another; occasionally, pairs of dots are used instead of lines. Excess electrons that form lone pairs are represented as pair of dots, and are placed next to the atoms on which they reside:
 To summarize his views on his new bonding model, Lewis states:
The following year, in 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method at the
To summarize his views on his new bonding model, Lewis states:
The following year, in 1917, an unknown American undergraduate chemical engineer named Linus Pauling was learning the Dalton hook-and-eye bonding method at the
manuscript
in which he used Owing to these exceptional theories, Pauling won the 1954
Owing to these exceptional theories, Pauling won the 1954 Single molecule's stunning image
Using an
Geometric Structures of Molecules
- Middlebury College
Atoms and Molecules
- McMaster University
3D Molecule Viewer
- The Wileys Family
- School of Chemistry, University of Bristol
- Eric Scerri's history & philosophy of chemistry website
Antibody Molecule
- The National Health Museum
15 Types of Molecules
- IUPAC Definitions
Molecule Definition
-
Definition of Molecule
- IUPAC
- TRN Newswire
- HP Labs {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Molecular Theory History of chemistry Molecules General chemistry
atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s.
The modern concept of molecules can be traced back towards pre-scientific and Greek philosophers such as Leucippus
Leucippus (; el, Λεύκιππος, ''Leúkippos''; fl. 5th century BCE) is a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who has been credited as the first philosopher to develop a theory of atomism.
Leucippus' reputation, even in antiquity, was obscured ...
and Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
who argued that all the universe is composed of atoms and voids. Circa 450 BC Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the ...
imagined fundamental elements (fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a material (the fuel) in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products.
At a certain point in the combustion reaction, called the ignition point, flames a ...
(earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
(air
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing f ...
(water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
(Heraclitus
Heraclitus of Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἡράκλειτος , "Glory of Hera"; ) was an ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from the city of Ephesus, which was then part of the Persian Empire.
Little is known of Heraclitus's life. He wrot ...
had claimed that fire or change was fundamental to our existence, created through the combination of opposite properties. In the Timaeus Timaeus (or Timaios) is a Greek name. It may refer to:
* ''Timaeus'' (dialogue), a Socratic dialogue by Plato
*Timaeus of Locri, 5th-century BC Pythagorean philosopher, appearing in Plato's dialogue
*Timaeus (historian) (c. 345 BC-c. 250 BC), Greek ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, following Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His politi ...
, considered mathematical entities such as number, point, line and triangle as the fundamental building blocks or elements of this ephemeral world, and considered the four elements of fire, air, water and earth as states of substances through which the true mathematical principles or elements would pass. A fifth element, the incorruptible quintessence aether, was considered to be the fundamental building block of the heavenly bodies. The viewpoint of Leucippus and Empedocles, along with the aether, was accepted by Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ph ...
and passed to medieval and renaissance Europe. A modern conceptualization of molecules began to develop in the 19th century along with experimental evidence for pure chemical elements and how individual atoms of different chemical elements such as hydrogen and oxygen can combine to form chemically stable molecules such as water molecules.
17th century
The earliest views on the shapes and connectivity of atoms was that proposed byLeucippus
Leucippus (; el, Λεύκιππος, ''Leúkippos''; fl. 5th century BCE) is a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher who has been credited as the first philosopher to develop a theory of atomism.
Leucippus' reputation, even in antiquity, was obscured ...
, Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
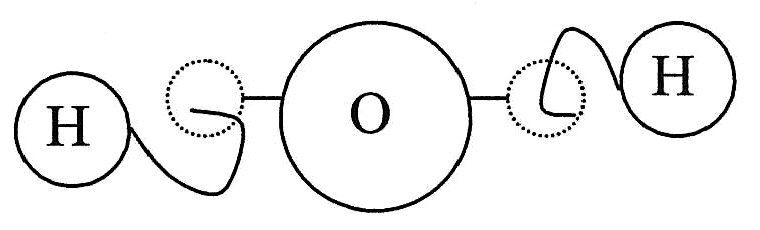
, and Epicurus who reasoned that the solidness of the material corresponded to the shape of the atoms involved. Thus, iron atoms are solid and strong with hooks that lock them into a solid; water atoms are smooth and slippery; salt atoms, because of their taste, are sharp and pointed; and air atoms are light and whirling, pervading all other materials. It was Democritus that was the main proponent of this view. Using analogies based on the experiences of the sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system re ...
s, he gave a picture or an image of an atom in which atoms were distinguished from each other by their shape, their size, and the arrangement of their parts. Moreover, connections were explained by material links in which single atoms were supplied with attachments: some with hooks and eyes others with balls and sockets (see diagram).
 With the rise of scholasticism and the decline of the Roman Empire, the atomic theory was abandoned for many ages in favor of the various four element theories and later alchemical theories. The 17th century, however, saw a resurgence in the atomic theory primarily through the works of Gassendi, and Newton. Among other scientists of that time Gassendi deeply studied ancient history, wrote major works about Epicurus natural philosophy and was a persuasive propagandist of it. He reasoned that to account for the size and shape of atoms moving in a void could account for the properties of matter. Heat was due to small, round atoms; cold, to pyramidal atoms with sharp points, which accounted for the pricking sensation of severe cold; and solids were held together by interlacing hooks. Newton, though he acknowledged the various atom attachment theories in vogue at the time, i.e. "hooked atoms", "glued atoms" (bodies at rest), and the "stick together by conspiring motions" theory, rather believed, as famously stated in "Query 31" of his 1704 ''
With the rise of scholasticism and the decline of the Roman Empire, the atomic theory was abandoned for many ages in favor of the various four element theories and later alchemical theories. The 17th century, however, saw a resurgence in the atomic theory primarily through the works of Gassendi, and Newton. Among other scientists of that time Gassendi deeply studied ancient history, wrote major works about Epicurus natural philosophy and was a persuasive propagandist of it. He reasoned that to account for the size and shape of atoms moving in a void could account for the properties of matter. Heat was due to small, round atoms; cold, to pyramidal atoms with sharp points, which accounted for the pricking sensation of severe cold; and solids were held together by interlacing hooks. Newton, though he acknowledged the various atom attachment theories in vogue at the time, i.e. "hooked atoms", "glued atoms" (bodies at rest), and the "stick together by conspiring motions" theory, rather believed, as famously stated in "Query 31" of his 1704 ''Opticks
''Opticks: or, A Treatise of the Reflexions, Refractions, Inflexions and Colours of Light'' is a book by English natural philosopher Isaac Newton that was published in English in 1704 (a scholarly Latin translation appeared in 1706). (''Opti ...
'', that particles attract one another by some force, which "in immediate contact is extremely strong, at small distances performs the chemical operations, and reaches not far from particles with any sensible effect."
In a more concrete manner, however, the concept of aggregates or units of bonded atoms, i.e. "molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s", traces its origins to Robert Boyle
Robert Boyle (; 25 January 1627 – 31 December 1691) was an Anglo-Irish natural philosopher, chemist, physicist, alchemist and inventor. Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist, and therefore one of the founders of ...
's 1661 hypothesis, in his famous treatise ''The Sceptical Chymist
''The Sceptical Chymist: or Chymico-Physical Doubts & Paradoxes'' is the title of a book by Robert Boyle, published in London in 1661. In the form of a dialogue, the ''Sceptical Chymist'' presented Boyle's hypothesis that matter consisted of corp ...
'', that matter is composed of ''clusters of particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from ...
s'' and that chemical change results from the rearrangement of the clusters. Boyle argued that matter's basic elements consisted of various sorts and sizes of particles, called " corpuscles", which were capable of arranging themselves into groups.
In 1680, using the corpuscular theory
In optics, the corpuscular theory of light states that light is made up of small discrete particles called " corpuscles" (little particles) which travel in a straight line with a finite velocity and possess impetus. This was based on an alternate ...
as a basis, French chemist Nicolas Lemery
Nicolas Lémery (or Lemery as his name appeared in his international publications) (17 November 1645 – 19 June 1715), French chemist, was born at Rouen. He was one of the first to develop theories on acid-base chemistry.
Life
After learning ph ...
stipulated that the acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a ...
of any substance consisted in its pointed particles, while alkalis were endowed with pores of various sizes. A molecule, according to this view, consisted of corpuscles united through a geometric locking of points and pores.
18th century
 An early precursor to the idea of bonded "combinations of atoms", was the theory of "combination via
An early precursor to the idea of bonded "combinations of atoms", was the theory of "combination via chemical affinity In chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds. Chemical affinity can also refer to the tendency of an atom or compound to co ...
". For example, in 1718, building on Boyle's conception of combinations of clusters, the French chemist Étienne François Geoffroy
Étienne François Geoffroy (13 February 16726 January 1731) was a French physician and chemist, best known for his 1718 affinity tables. He first contemplated a career as an apothecary, but then decided to practice medicine. He is sometimes kn ...
developed theories of chemical affinity In chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds. Chemical affinity can also refer to the tendency of an atom or compound to co ...
to explain combinations of particles, reasoning that a certain alchemical "force" draws certain alchemical components together. Geoffroy's name is best known in connection with his tables of " affinities" (''tables des rapports''), which he presented to the French Academy
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ...
in 1718 and 1720.
These were lists, prepared by collating observations on the actions of substances one upon another, showing the varying degrees of affinity exhibited by analogous bodies for different reagents. These tables retained their vogue for the rest of the century, until displaced by the profounder conceptions introduced by CL Berthollet.
In 1738, Swiss physicist and mathematician Daniel Bernoulli published '' Hydrodynamica'', which laid the basis for the kinetic theory
Kinetic (Ancient Greek: κίνησις “kinesis”, movement or to move) may refer to:
* Kinetic theory, describing a gas as particles in random motion
* Kinetic energy, the energy of an object that it possesses due to its motion
Art and ente ...
of gases. In this work, Bernoulli positioned the argument, still used to this day, that gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
es consist of great numbers of molecules moving in all directions, that their impact on a surface causes the gas pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
that we feel, and that what we experience as heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
is simply the kinetic energy of their motion. The theory was not immediately accepted, in part because conservation of energy had not yet been established, and it was not obvious to physicists how the collisions between molecules could be perfectly elastic.
In 1789, William Higgins published views on what he called combinations of "ultimate" particles, which foreshadowed the concept of valency bonds
In chemistry, valence bond (VB) theory is one of the two basic theories, along with molecular orbital theory, molecular orbital (MO) theory, that were developed to use the methods of quantum mechanics to explain chemical bonding. It focuses on ho ...
. If, for example, according to Higgins, the force between the ultimate particle of oxygen and the ultimate particle of nitrogen were 6, then the strength of the force would be divided accordingly, and similarly for the other combinations of ultimate particles:

19th century
 Similar to these views, in 1803 John Dalton took the atomic weight of hydrogen, the lightest element, as unity, and determined, for example, that the ratio for nitrous anhydride was 2 to 3 which gives the formula N2O3. Dalton incorrectly imagined that atoms "hooked" together to form molecules. Later, in 1808, Dalton published his famous diagram of combined "atoms":
Similar to these views, in 1803 John Dalton took the atomic weight of hydrogen, the lightest element, as unity, and determined, for example, that the ratio for nitrous anhydride was 2 to 3 which gives the formula N2O3. Dalton incorrectly imagined that atoms "hooked" together to form molecules. Later, in 1808, Dalton published his famous diagram of combined "atoms":
Amedeo Avogadro
Lorenzo Romano Amedeo Carlo Avogadro, Count of Quaregna and Cerreto (, also , ; 9 August 17769 July 1856) was an Italian scientist, most noted for his contribution to molecular theory now known as Avogadro's law, which states that equal volume ...
created the word "molecule". His 1811 paper "Essay on Determining the Relative Masses of the Elementary Molecules of Bodies", he essentially states, i.e. according to Partington
Partington is a town and civil parish in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester, England, south-west of Manchester city centre. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Cheshire, it lies on the southern bank of the M ...
's ''A Short History of Chemistry'', that:
Note that this quote is not a literal translation. Avogadro uses the name "molecule" for both atoms and molecules. Specifically, he uses the name "elementary molecule" when referring to atoms and to complicate the matter also speaks of "compound molecules" and "composite molecules".
During his stay in Vercelli, Avogadro wrote a concise note (''memoria'') in which he declared the hypothesis of what we now call Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law (sometimes referred to as Avogadro's hypothesis or Avogadro's principle) or Avogadro-Ampère's hypothesis is an experimental gas law relating the volume of a gas to the amount of substance of gas present. The law is a specific c ...
: ''equal volumes of gases, at the same temperature and pressure, contain the same number of molecules''. This law implies that the relationship occurring between the weights of same volumes of different gases, at the same temperature and pressure, corresponds to the relationship between respective molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
s. Hence, relative molecular masses could now be calculated from the masses of gas samples.
Avogadro developed this hypothesis in order to reconcile Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (, , ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen (with Alexander von Humboldt), for two laws ...
's 1808 law on volumes and combining gases with Dalton's 1803 atomic theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter ...
. The greatest difficulty Avogadro had to resolve was the huge confusion at that time regarding atoms and molecules—one of the most important contributions of Avogadro's work was clearly distinguishing one from the other, admitting that simple particles too could be composed of molecules, and that these are composed of atoms. Dalton, by contrast, did not consider this possibility. Curiously, Avogadro considers only molecules containing even numbers of atoms; he does not say why odd numbers are left out.
In 1826, building on the work of Avogadro, the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas states:
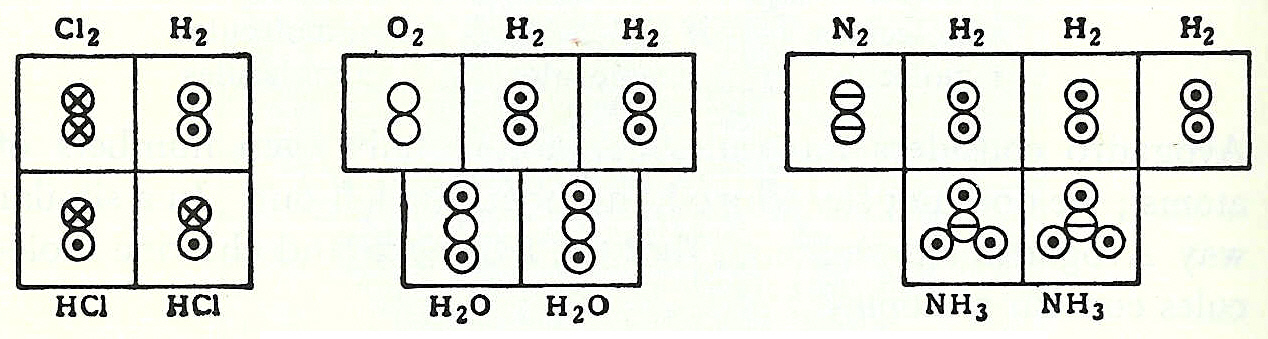
In coordination with these concepts, in 1833 the French chemist Marc Antoine Auguste Gaudin presented a clear account of Avogadro's hypothesis, regarding atomic weights, by making use of "volume diagrams", which clearly show both semi-correct molecular geometries, such as a linear water molecule, and correct molecular formulas, such as H2O:
 In two papers outlining his "theory of atomicity of the elements" (1857–58),
In two papers outlining his "theory of atomicity of the elements" (1857–58), Friedrich August Kekulé Friedrich may refer to:
Names
* Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich''
* Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich''
Other
* Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Year ...
was the first to offer a theory of how every atom in an organic molecule was bonded to every other atom. He proposed that carbon atoms were tetravalent, and could bond to themselves to form the carbon skeletons of organic molecules.
In 1856, Scottish chemist Archibald Couper began research on the bromination
In chemistry, halogenation is a chemical reaction that entails the introduction of one or more halogens into a compound. Halide-containing compounds are pervasive, making this type of transformation important, e.g. in the production of polyme ...
of benzene at the laboratory of Charles Wurtz in Paris. One month after Kekulé's second paper appeared, Couper's independent and largely identical theory of molecular structure was published. He offered a very concrete idea of molecular structure, proposing that atoms joined to each other like modern-day Tinkertoys in specific three-dimensional structures. Couper was the first to use lines between atoms, in conjunction with the older method of using brackets, to represent bonds, and also postulated straight chains of atoms as the structures of some molecules, ring-shaped molecules of others, such as in tartaric acid
Tartaric acid is a white, crystalline organic acid that occurs naturally in many fruits, most notably in grapes, but also in bananas, tamarinds, and citrus. Its salt, potassium bitartrate, commonly known as cream of tartar, develops naturally ...
and cyanuric acid
Cyanuric acid or 1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triol is a chemical compound with the formula (CNOH)3. Like many industrially useful chemicals, this triazine has many synonyms. This white, odorless solid finds use as a precursor or a component of bleach ...
. In later publications, Couper's bonds were represented using straight dotted lines (although it is not known if this is the typesetter's preference) such as with alcohol and oxalic acid below:
 In 1861, an unknown Vienna high-school teacher named
In 1861, an unknown Vienna high-school teacher named Joseph Loschmidt
Johann Josef Loschmidt (15 March 1821 – 8 July 1895), who referred to himself mostly as Josef Loschmidt (omitting his first name), was a notable Austrian scientist who performed ground-breaking work in chemistry, physics (thermodynamics, optics, ...
published, at his own expense, a booklet entitled ''Chemische Studien I'', containing pioneering molecular images which showed both "ringed" structures as well as double-bonded structures, such as:
 Loschmidt also suggested a possible formula for benzene, but left the issue open. The first proposal of the modern structure for benzene was due to Kekulé, in 1865. The cyclic nature of benzene was finally confirmed by the crystallographer
Loschmidt also suggested a possible formula for benzene, but left the issue open. The first proposal of the modern structure for benzene was due to Kekulé, in 1865. The cyclic nature of benzene was finally confirmed by the crystallographer Kathleen Lonsdale
Dame Kathleen Lonsdale ( Yardley; 28 January 1903 – 1 April 1971) was an Irish-born British pacifist, prison reformer and crystallographer. She proved, in 1929, that the benzene ring is flat by using X-ray diffraction methods to elucidate t ...
. Benzene presents a special problem in that, to account for all the bonds, there must be alternating double
A double is a look-alike or doppelgänger; one person or being that resembles another.
Double, The Double or Dubble may also refer to:
Film and television
* Double (filmmaking), someone who substitutes for the credited actor of a character
* ...
carbon bonds:
August Wilhelm von Hofmann
August Wilhelm von Hofmann (8 April 18185 May 1892) was a German chemist who made considerable contributions to organic chemistry. His research on aniline helped lay the basis of the aniline-dye industry, and his research on coal tar laid the g ...
was the first to make stick-and-ball molecular models, which he used in lecture at the Royal Institution of Great Britain
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
, such as methane shown below:
 The basis of this model followed the earlier 1855 suggestion by his colleague
The basis of this model followed the earlier 1855 suggestion by his colleague William Odling
William Odling, FRS (5 September 1829 in Southwark, London – 17 February 1921 in Oxford) was an English chemist who contributed to the development of the periodic table.
In the 1860s Odling, like many chemists, was working towards classifying ...
that carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
is tetravalent
In chemistry, the valence (US spelling) or valency (British spelling) of an element is the measure of its combining capacity with other atoms when it forms chemical compounds or molecules.
Description
The combining capacity, or affinity of an ...
. Hofmann's color scheme, to note, is still used to this day: carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
= black, nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
= blue, oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
= red, chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine i ...
= green, sulfur = yellow, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
= white. The deficiencies in Hofmann's model were essentially geometric: carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
bonding was shown as planar
Planar is an adjective meaning "relating to a plane (geometry)".
Planar may also refer to:
Science and technology
* Planar (computer graphics), computer graphics pixel information from several bitplanes
* Planar (transmission line technologies), ...
, rather than tetrahedral, and the atoms were out of proportion, e.g. carbon was smaller in size than the hydrogen.
In 1864, Scottish organic chemist Alexander Crum Brown
Alexander Crum Brown FRSE FRS (26 March 1838 – 28 October 1922) was a Scottish organic chemist. Alexander Crum Brown Road in Edinburgh's King's Buildings complex is named after him.
Early life and education
Crum Brown was born at 4 Belle ...
began to draw pictures of molecules, in which he enclosed the symbols for atoms in circles, and used broken lines to connect the atoms together in a way that satisfied each atom's valence.
The year 1873, by many accounts, was a seminal point in the history of the development of the concept of the "molecule". In this year, the renowned Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and li ...
published his famous thirteen page article 'Molecules' in the September issue of ''Nature''. In the opening section to this article, Maxwell clearly states:
After speaking about the atomic theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter ...
of Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. No ...
, Maxwell goes on to tell us that the word 'molecule' is a modern word. He states, "it does not occur in '' Johnson's Dictionary''. The ideas it embodies are those belonging to modern chemistry." We are told that an 'atom' is a material point, invested and surrounded by 'potential forces' and that when 'flying molecules' strike against a solid body in constant succession it causes what is called pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
of air and other gases. At this point, however, Maxwell notes that no one has ever seen or handled a molecule.
In 1874, Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff and Joseph Achille Le Bel independently proposed that the phenomenon of optical activity could be explained by assuming that the chemical bonds between carbon atoms and their neighbors were directed towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. This led to a better understanding of the three-dimensional nature of molecules.
Emil Fischer
Hermann Emil Louis Fischer (; 9 October 1852 – 15 July 1919) was a German chemist and 1902 recipient of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. He discovered the Fischer esterification. He also developed the Fischer projection, a symbolic way of draw ...
developed the Fischer projection
In chemistry, the Fischer projection, devised by Emil Fischer in 1891, is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional organic molecule by projection. Fischer projections were originally proposed for the depiction of carbohydrates ...
technique for viewing 3-D molecules on a 2-D sheet of paper:
Ludwig Boltzmann
Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (; 20 February 1844 – 5 September 1906) was an Austrian physicist and philosopher. His greatest achievements were the development of statistical mechanics, and the statistical explanation of the second law of ther ...
, in his ''Lectures on Gas Theory'', used the theory of valence to explain the phenomenon of gas phase molecular dissociation, and in doing so drew one of the first rudimentary yet detailed atomic orbital overlap drawings. Noting first the known fact that molecular iodine vapor dissociates into atoms at higher temperatures, Boltzmann states that we must explain the existence of molecules composed of two atoms, the "double atom" as Boltzmann calls it, by an attractive force acting between the two atoms. Boltzmann states that this chemical attraction, owing to certain facts of chemical valence, must be associated with a relatively small region on the surface of the atom called the ''sensitive region''.
Boltzmann states that this "sensitive region" will lie on the surface of the atom, or may partially lie inside the atom, and will firmly be connected to it. Specifically, he states "only when two atoms are situated so that their sensitive regions are in contact, or partly overlap, will there be a chemical attraction between them. We then say that they are chemically bound to each other." This picture is detailed below, showing the ''α-sensitive region'' of atom-A overlapping with the ''β-sensitive region'' of atom-B:

20th century
In the early 20th century, the American chemist Gilbert N. Lewis began to use dots in lecture, while teaching undergraduates at Harvard, to represent the electrons around atoms. His students favored these drawings, which stimulated him in this direction. From these lectures, Lewis noted that elements with a certain number of electrons seemed to have a special stability. This phenomenon was pointed out by the German chemistRichard Abegg
Richard Wilhelm Heinrich Abegg (9 January 1869 – 3 April 1910) was a German chemist and pioneer of valence theory. He proposed that the difference of the maximum positive and negative valence of an element tends to be eight. This has come to be ...
in 1904, to which Lewis referred to as "Abegg's law of valence" (now generally known as Abegg's rule In chemistry, Abegg’s rule states that the difference between the maximum positive and negative valence of an element is frequently eight. The rule used a historic meaning of valence which resembles the modern concept of oxidation state in whic ...
). To Lewis it appeared that once a core of eight electrons has formed around a nucleus, the layer is filled, and a new layer is started. Lewis also noted that various ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s with eight electrons also seemed to have a special stability. On these views, he proposed the rule of eight or octet rule
The octet rule is a chemical rule of thumb that reflects the theory that main-group elements tend to bond in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell, giving it the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. The rul ...
: ''Ions or atoms with a filled layer of eight electrons have a special stability''.
Moreover, noting that a cube has eight corners Lewis envisioned an atom as having eight sides available for electrons, like the corner of a cube. Subsequently, in 1902 he devised a conception in which cubic atoms can bond on their sides to form cubic-structured molecules.
In other words, electron-pair bonds are formed when two atoms share an edge, as in structure C below. This results in the sharing of two electrons. Similarly, charged ionic-bonds are formed by the transfer of an electron from one cube to another, without sharing an edge A. An intermediate state B where only one corner is shared was also postulated by Lewis.
 Hence,
Hence, double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betwee ...
s are formed by sharing a face between two cubic atoms. This results in the sharing of four electrons.
In 1913, while working as the chair of the department of chemistry at the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
, Lewis read a preliminary outline of paper by an English graduate student, Alfred Lauck Parson, who was visiting Berkeley for a year. In this paper, Parson suggested that the electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
is not merely an electric charge but is also a small magnet (or " magneton" as he called it) and furthermore that a chemical bond
A chemical bond is a lasting attraction between atoms or ions that enables the formation of molecules and crystals. The bond may result from the electrostatic force between oppositely charged ions as in ionic bonds, or through the sharing of ...
results from two electrons being shared between two atoms. This, according to Lewis, meant that bonding occurred when two electrons formed a shared edge between two complete cubes.
On these views, in his famous 1916 article The Atom and the Molecule
', Lewis introduced the "Lewis structure" to represent atoms and molecules, where dots represent
electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no ...
s and lines represent covalent bonds. In this article, he developed the concept of the electron-pair bond, in which two atoms may share one to six electrons, thus forming the single electron bond, a single bond, a double bond
In chemistry, a double bond is a covalent bond between two atoms involving four bonding electrons as opposed to two in a single bond. Double bonds occur most commonly between two carbon atoms, for example in alkenes. Many double bonds exist betwee ...
, or a triple bond
A triple bond in chemistry is a chemical bond between two atoms involving six bonding electrons instead of the usual two in a covalent single bond. Triple bonds are stronger than the equivalent single bonds or double bonds, with a bond order o ...
.
Oregon Agricultural College
Oregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant, research university in Corvallis, Oregon. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. It has the 10th largest engineering col ...
, which was the vogue description of bonds between atoms at the time. Each atom had a certain number of hooks that allowed it to attach to other atoms, and a certain number of eyes that allowed other atoms to attach to it. A chemical bond resulted when a hook and eye connected. Pauling, however, wasn't satisfied with this archaic method and looked to the newly emerging field of quantum physics for a new method.
In 1927, the physicists Fritz London
Fritz Wolfgang London (March 7, 1900 – March 30, 1954) was a German physicist and professor at Duke University. His fundamental contributions to the theories of chemical bonding and of intermolecular forces ( London dispersion forces) are today ...
and Walter Heitler
Walter Heinrich Heitler (; 2 January 1904 – 15 November 1981) was a German physicist who made contributions to quantum electrodynamics and quantum field theory. He brought chemistry under quantum mechanics through his theory of valence bond ...
applied the new quantum mechanics to the deal with the saturable, nondynamic forces of attraction and repulsion, i.e., exchange forces, of the hydrogen molecule. Their valence bond treatment of this problem, in their joint paper, was a landmark in that it brought chemistry under quantum mechanics. Their work was an influence on Pauling, who had just received his doctorate and visited Heitler and London in Zürich on a Guggenheim Fellowship.
Subsequently, in 1931, building on the work of Heitler and London and on theories found in Lewis' famous article, Pauling published his ground-breaking article "The Nature of the Chemical Bond" (seemanuscript
in which he used
quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistr ...
to calculate properties and structures of molecules, such as angles between bonds and rotation about bonds. On these concepts, Pauling developed hybridization theory
In chemistry, orbital hybridisation (or hybridization) is the concept of mixing atomic orbitals to form new ''hybrid orbitals'' (with different energies, shapes, etc., than the component atomic orbitals) suitable for the pairing of electrons to f ...
to account for bonds in molecules such as CH4, in which four sp³ hybridised orbitals are overlapped by hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
's ''1s'' orbital, yielding four sigma (σ) bonds. The four bonds are of the same length and strength, which yields a molecular structure as shown below:
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
. Notably he has been the only person to ever win two unshared Nobel prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
s, winning the Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
in 1963.
In 1926, French physicist Jean Perrin received the Nobel Prize in physics for proving, conclusively, the existence of molecules. He did this by calculating Avogadro's number
The Avogadro constant, commonly denoted or , is the proportionality factor that relates the number of constituent particles (usually molecules, atoms or ions) in a sample with the amount of substance in that sample. It is an SI defining co ...
using three different methods, all involving liquid phase systems. First, he used a gamboge
Gamboge ( , ) is a partially transparent deep saffron to mustard yellow pigment.Other forms and spellings are: cambodia, cambogium, camboge, cambugium, gambaugium, gambogia, gambozia, gamboidea, gambogium, gumbouge, gambouge, gamboge, gambooge, g ...
soap-like emulsion, second by doing experimental work on Brownian motion
Brownian motion, or pedesis (from grc, πήδησις "leaping"), is the random motion of particles suspended in a medium (a liquid or a gas).
This pattern of motion typically consists of random fluctuations in a particle's position insi ...
, and third by confirming Einstein's theory of particle rotation in the liquid phase.
In 1937, chemist K.L. Wolf introduced the concept of supermolecules (''Übermoleküle'') to describe hydrogen bonding
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a l ...
in acetic acid dimer
Dimer may refer to:
* Dimer (chemistry), a chemical structure formed from two similar sub-units
** Protein dimer, a protein quaternary structure
** d-dimer
* Dimer model, an item in statistical mechanics, based on ''domino tiling''
* Julius Dimer ...
s. This would eventually lead to the area of supermolecular chemistry, which is the study of non-covalent bonding.
In 1951, physicist Erwin Wilhelm Müller
Erwin Wilhelm Müller (or ''Mueller'') (June 13, 1911 – May 17, 1977) was a German physicist who invented the Field Emission Electron Microscope (FEEM), the Field Ion Microscope (FIM), and the Atom-Probe Field Ion Microscope. He and his st ...
invents the field ion microscope
The Field ion microscope (FIM) was invented by Müller in 1951. It is a type of microscope that can be used to image the arrangement of atoms at the surface of a sharp metal tip.
On October 11, 1955, Erwin Müller and his Ph.D. student, Kanwar ...
and is the first to see atom
Every atom is composed of a nucleus and one or more electrons bound to the nucleus. The nucleus is made of one or more protons and a number of neutrons. Only the most common variety of hydrogen has no neutrons.
Every solid, liquid, gas, ...
s, e.g. bonded atomic arrangements at the tip of a metal point.
In 1968-1970 Leroy Cooper, PhD of the University of California at Davis completed his thesis which showed what molecules looked like. He used x-ray deflection off crystals and a complex computer program written by Bill Pentz of the UC Davis Computer Center. This program took the mapped deflections and used them to calculate the basic shapes of crystal molecules. His work showed that actual molecular shapes in quartz crystals and other tested crystals looked similar to the long envisioned merged various sized soap bubbles theorized, except instead of being merged spheres of different sizes, actual shapes were rigid mergers of more tear dropped shapes that stayed fixed in orientation. This work verified for the first time that crystal molecules are actually linked or stacked merged tear drop constructions.
In 1999, researchers from the University
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States ...
of Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
reported results from experiments on wave-particle duality for C60 molecules. The data published by Zeilinger et al. were consistent with de Broglie wave interference for C60 molecules. This experiment was noted for extending the applicability of wave–particle duality by about one order of magnitude in the macroscopic direction.
In 2009, researchers from IBM managed to take the first picture of a real molecule.Using an
atomic force microscope
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the op ...
every single atom and bond of a pentacene
Pentacene () is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and t ...
molecule could be imaged.
See also
* History of chemistry *History of quantum mechanics
The history of quantum mechanics is a fundamental part of the history of modern physics. Quantum mechanics' history, as it interlaces with the history of quantum chemistry, began essentially with a number of different scientific discoveries: the ...
*History of thermodynamics
The history of thermodynamics is a fundamental strand in the history of physics, the history of chemistry, and the history of science in general. Owing to the relevance of thermodynamics in much of science and technology, its history is finely w ...
*History of molecular biology The history of molecular biology begins in the 1930s with the convergence of various, previously distinct biological and physical disciplines: biochemistry, genetics, microbiology, virology and physics. With the hope of understanding life at its m ...
*Kinetic theory
Kinetic (Ancient Greek: κίνησις “kinesis”, movement or to move) may refer to:
* Kinetic theory, describing a gas as particles in random motion
* Kinetic energy, the energy of an object that it possesses due to its motion
Art and ente ...
*Atomic theory
Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter ...
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Geometric Structures of Molecules
- Middlebury College
Atoms and Molecules
- McMaster University
3D Molecule Viewer
- The Wileys Family
- School of Chemistry, University of Bristol
- Eric Scerri's history & philosophy of chemistry website
Types
Antibody Molecule
- The National Health Museum
15 Types of Molecules
- IUPAC Definitions
Definitions
Molecule Definition
-
Frostburg State University
Frostburg State University (FSU) is a public university in Frostburg, Maryland. The university is the only four-year institution of the University System of Maryland west of the Baltimore-Washington passageway in the state's Appalachian highlan ...
(Department of Chemistry)Definition of Molecule
- IUPAC
Articles
- TRN Newswire
- HP Labs {{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Molecular Theory History of chemistry Molecules General chemistry