Geography of Norway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Geographic coordinates:
Map references:
Geographic coordinates:
Map references:
''total:''
''land:''
''water:''
''With
With Svalbard and Jan Mayen included, the area is slightly larger than
''total:''
''border countries:''
''contiguous zone:''
''continental shelf:''
''exclusive economic zone:''
''territorial sea:'' Norway's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) totals . It is one of the largest in Europe and the 17th largest in the world. The EEZ along the mainland makes up , the Jan Mayen EEZ makes up , and since 1977 Norway has claimed an economic zone around Svalbard of .

''Lowest point:''
''Highest point:''

File:Raftsundet panorama, 2010 09.jpg, Rafsundet in September, Northern Norway
File:Svalbard landscape.jpg, Svalbard tundra
File:Northwest_coast_of_Jan_Mayen.png,
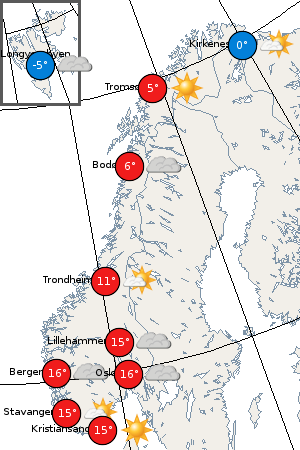

 The climate of Norway is more temperate than could be expected for such high
The climate of Norway is more temperate than could be expected for such high
 Bø i Vesterålen is the most northerly location in the world where all winter months have mean temperatures above . Spring is the season when the temperature differences between the southern and northern part of the country is largest; this is also the time of year when daytime and nighttime temperatures differ the most. Inland valleys and the innermost fjord areas have less wind and see the warmest summer days. The lowland near Oslo is warmest in summer with 24 July-hr average of and average daily high up to . Inland areas reach their peak warmth around mid-July and coastal areas by the first half of August. Humidity is usually low in summer.
The North Atlantic Current splits in two over the northern part of the Norwegian Sea, one branch going east into the Barents Sea and the other going north along the west coast of
Bø i Vesterålen is the most northerly location in the world where all winter months have mean temperatures above . Spring is the season when the temperature differences between the southern and northern part of the country is largest; this is also the time of year when daytime and nighttime temperatures differ the most. Inland valleys and the innermost fjord areas have less wind and see the warmest summer days. The lowland near Oslo is warmest in summer with 24 July-hr average of and average daily high up to . Inland areas reach their peak warmth around mid-July and coastal areas by the first half of August. Humidity is usually low in summer.
The North Atlantic Current splits in two over the northern part of the Norwegian Sea, one branch going east into the Barents Sea and the other going north along the west coast of 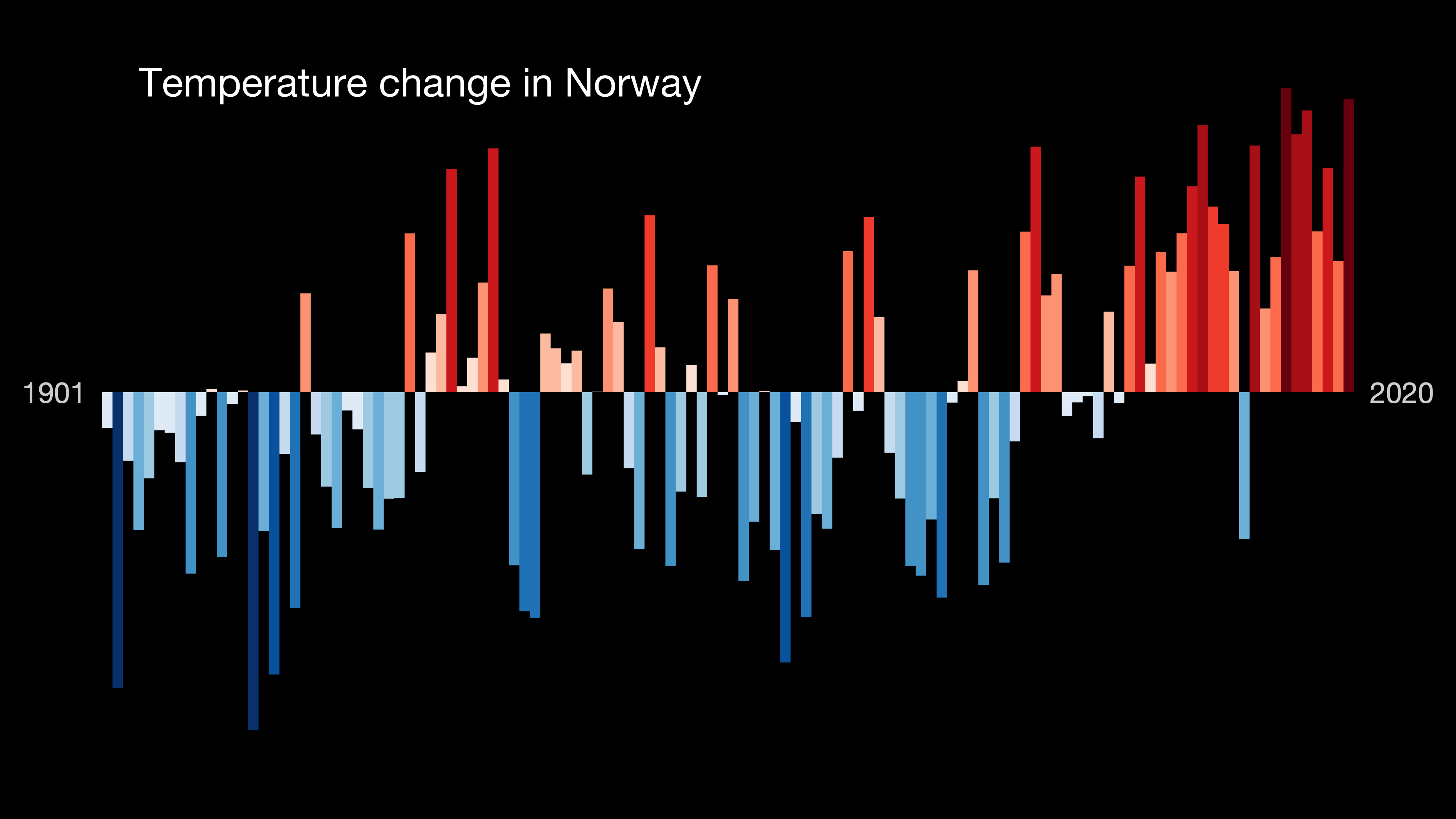 As a consequence of warming since 1990, summers are warmer and longer and winters are getting shorter and milder. With the new official 1991-2020 climate normal, many areas have seen their climate change to a new climate zone compared to 1961-90 normal. Oslo's climate has moved from Dfb to Cfb/Dfb, Lillehammer's from Dfc to Dfb, Kristiansand from Cfb/Dfb to Cfb, Molde and Brønnøysund from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb, Trondheim from Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Bodø from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Tromsø (Holt) from Dfc to Cfc/Dfc and Vardø from ET to Dfc. Snow cover has decreased in most populated areas due to winter warming; days/year with 25 cm snow cover in 1991-2020 is 26 days in Oslo (94 m), 2 days in Bergen, 8 days in Trondheim/Værnes and 144 days in Tromsø. The strongest warming has been observed on Svalbard. In addition to warming, precipitation has increased in most areas, especially in winter, increasing
As a consequence of warming since 1990, summers are warmer and longer and winters are getting shorter and milder. With the new official 1991-2020 climate normal, many areas have seen their climate change to a new climate zone compared to 1961-90 normal. Oslo's climate has moved from Dfb to Cfb/Dfb, Lillehammer's from Dfc to Dfb, Kristiansand from Cfb/Dfb to Cfb, Molde and Brønnøysund from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb, Trondheim from Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Bodø from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Tromsø (Holt) from Dfc to Cfc/Dfc and Vardø from ET to Dfc. Snow cover has decreased in most populated areas due to winter warming; days/year with 25 cm snow cover in 1991-2020 is 26 days in Oslo (94 m), 2 days in Bergen, 8 days in Trondheim/Værnes and 144 days in Tromsø. The strongest warming has been observed on Svalbard. In addition to warming, precipitation has increased in most areas, especially in winter, increasing
 Natural vegetation in Norway varies considerably, as can be expected in a country having such variations in latitude. There are generally fewer species of
Natural vegetation in Norway varies considerably, as can be expected in a country having such variations in latitude. There are generally fewer species of  Some plants are classified as western due to their need for high humidity or low tolerance of winter frost; these will stay close to the southwestern coast, with their northern limit near Ålesund. Some examples are
Some plants are classified as western due to their need for high humidity or low tolerance of winter frost; these will stay close to the southwestern coast, with their northern limit near Ålesund. Some examples are
 A small area along the southern coast—from Soknedal (Rogaland), Soknedal in southern Rogaland and east to Fevik in Aust-Agder (including Kristiansand)—belongs to the Nemoral vegetation zone. This zone is located below above sea level and at most inland along the valleys. This is the predominant vegetation zone in Europe north of southern France, the Alps, the Carpathians, and the Caucasus. The hallmark of this zone in Norway is the predominance of oak and the virtually complete lack of typical boreal ecosystem, boreal species such as Norway spruce and grey alder, although a lowland variant of Scots pine, pine occurs. Nemoral covers a total of 0.5% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen).
A small area along the southern coast—from Soknedal (Rogaland), Soknedal in southern Rogaland and east to Fevik in Aust-Agder (including Kristiansand)—belongs to the Nemoral vegetation zone. This zone is located below above sea level and at most inland along the valleys. This is the predominant vegetation zone in Europe north of southern France, the Alps, the Carpathians, and the Caucasus. The hallmark of this zone in Norway is the predominance of oak and the virtually complete lack of typical boreal ecosystem, boreal species such as Norway spruce and grey alder, although a lowland variant of Scots pine, pine occurs. Nemoral covers a total of 0.5% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen).
 The hemiboreal zone covers a total of 7% of the land area in Norway, including 80% of Østfold and Vestfold. This vegetation represents a mix of nemoral and boreal plant species, and belongs to the Palearctic, Sarmatic mixed forests terrestrial ecoregion (PA0436). The nemoral species tend to predominate on slopes facing southwest and with good soil, while the boreal species predominate on slopes facing north and with waterlogged soil. In some areas, other factors overrule this, such as where the bedrock gives little nutrient, where oak and the boreal Scots pine, pine often share predominance. The boreonemoral zone follows the coast from
The hemiboreal zone covers a total of 7% of the land area in Norway, including 80% of Østfold and Vestfold. This vegetation represents a mix of nemoral and boreal plant species, and belongs to the Palearctic, Sarmatic mixed forests terrestrial ecoregion (PA0436). The nemoral species tend to predominate on slopes facing southwest and with good soil, while the boreal species predominate on slopes facing north and with waterlogged soil. In some areas, other factors overrule this, such as where the bedrock gives little nutrient, where oak and the boreal Scots pine, pine often share predominance. The boreonemoral zone follows the coast from
 Boreal species are adapted to a long and cold winter, and most of these species can tolerate colder winter temperatures than winters in most of Norway. Thus they are distinguished by their need for growing season length and summer warmth. Bogs are common in the boreal zone, with the largest areas in the North and Middle Boreal Zones, as well as in the area just above the tree line. The large boreal zone is usually divided into three subzones: South Boreal, Middle Boreal, and North Boreal.
Boreal species are adapted to a long and cold winter, and most of these species can tolerate colder winter temperatures than winters in most of Norway. Thus they are distinguished by their need for growing season length and summer warmth. Bogs are common in the boreal zone, with the largest areas in the North and Middle Boreal Zones, as well as in the area just above the tree line. The large boreal zone is usually divided into three subzones: South Boreal, Middle Boreal, and North Boreal.
 The South Boreal zone (SB) is dominated by boreal species, especially Norway spruce, and covers a total of 12% of the total land area. The SB is the only boreal zone with a few scattered—but well-developed—warmth-demanding broadleaf deciduous trees, such as European ash and oak. Several species in this zone need fairly warm summers (SB has 3–4 months with a mean 24-hr temperature of at least ), and thus are very rare in the middle boreal zone. Some of the species not found further north are black alder, Humulus lupulus, hop, Origanum vulgare, oregano, and Viburnum opulus, guelder rose. This zone is found above the hemiboreal zone, up to amsl in Østlandet and in the most southern valleys. In the eastern valleys it reaches several hundred kilometers into Gudbrandsdal and Østerdal, and up to Lom, Norway, Lom and
The South Boreal zone (SB) is dominated by boreal species, especially Norway spruce, and covers a total of 12% of the total land area. The SB is the only boreal zone with a few scattered—but well-developed—warmth-demanding broadleaf deciduous trees, such as European ash and oak. Several species in this zone need fairly warm summers (SB has 3–4 months with a mean 24-hr temperature of at least ), and thus are very rare in the middle boreal zone. Some of the species not found further north are black alder, Humulus lupulus, hop, Origanum vulgare, oregano, and Viburnum opulus, guelder rose. This zone is found above the hemiboreal zone, up to amsl in Østlandet and in the most southern valleys. In the eastern valleys it reaches several hundred kilometers into Gudbrandsdal and Østerdal, and up to Lom, Norway, Lom and
 The typical closed-canopy forest of the Middle Boreal (MB) zone is dominated by boreal plant species. The MB vegetation covers a total of 20% of the total land area. Norway spruce is the dominant tree in large areas in the interior of Østlandet, Sørlandet, Trøndelag, and Helgeland and the MB and SB spruce forests are the commercially most important in Norway. Spruce does not grow naturally north of Saltfjell in mid-
The typical closed-canopy forest of the Middle Boreal (MB) zone is dominated by boreal plant species. The MB vegetation covers a total of 20% of the total land area. Norway spruce is the dominant tree in large areas in the interior of Østlandet, Sørlandet, Trøndelag, and Helgeland and the MB and SB spruce forests are the commercially most important in Norway. Spruce does not grow naturally north of Saltfjell in mid-

 The North Boreal (NB) zone, (also known as open or sparse taiga) is the zone closest to the
The North Boreal (NB) zone, (also known as open or sparse taiga) is the zone closest to the
 Alpine tundra is common in Norway, covering a total of 32% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen) and belonging to the Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands ecoregion (PA1110). The area closest to the tree line (low alpine) has continuous plant cover, with Salix, willow species such as ''Salix glauca'', ''Salix lanata, S. lanata'', and ''Salix lapponum, S. lapponum'' ( tall); blueberry, Juniperus communis, common juniper, and Linnaea borealis, twinflower are also common. The low alpine area was traditionally used as summer pasture, and in part still is. This zone reaches an elevation of in Jotunheimen, including most of
Alpine tundra is common in Norway, covering a total of 32% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen) and belonging to the Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands ecoregion (PA1110). The area closest to the tree line (low alpine) has continuous plant cover, with Salix, willow species such as ''Salix glauca'', ''Salix lanata, S. lanata'', and ''Salix lapponum, S. lapponum'' ( tall); blueberry, Juniperus communis, common juniper, and Linnaea borealis, twinflower are also common. The low alpine area was traditionally used as summer pasture, and in part still is. This zone reaches an elevation of in Jotunheimen, including most of 
 The highest weather station in Norway—Fanaråken in Luster, Norway, Luster, at —has barely three months of above freezing temperatures and a July average of . Still, glacier buttercup has been found only below the summit of
The highest weather station in Norway—Fanaråken in Luster, Norway, Luster, at —has barely three months of above freezing temperatures and a July average of . Still, glacier buttercup has been found only below the summit of

 Arable land: 3.3% (in use; some more marginal areas are not in use or used as pastures)
* Permanent crops: 0%
* Permanent pastures: 0%
* Forests and woodland: 38% of land area is covered by forest, 21% by Scandinavian coastal conifer forests, conifer forest, and 17% by deciduous forest, increasing as many pastures in the higher elevations and some coastal, man-made heath (habitat), heaths are no longer used or reforested, as well as increase due to warmer summers
* Other: 59% (mountains and heaths 46%, bogs and wetlands 6.3%, lakes and rivers 5.3%, urban areas 1.1%)
Irrigated land: , 1993 estimate
Natural hazards:
* European windstorms with hurricane-strength winds along the coast and in the mountains are not uncommon. For centuries one out of four males in coastal communities were lost at sea.
* Avalanches on steep slopes, especially in the northern part of the country and in mountain areas.
* Landslides have on occasions killed people, mostly in areas with soil rich in marine clay, as in lowland areas near Trondheimsfjord.
* Tsunamis have killed people; usually caused by parts of mountains (rockslide) falling into fjords or lakes. This happened 1905 in Loen, Norway, Loen in
Arable land: 3.3% (in use; some more marginal areas are not in use or used as pastures)
* Permanent crops: 0%
* Permanent pastures: 0%
* Forests and woodland: 38% of land area is covered by forest, 21% by Scandinavian coastal conifer forests, conifer forest, and 17% by deciduous forest, increasing as many pastures in the higher elevations and some coastal, man-made heath (habitat), heaths are no longer used or reforested, as well as increase due to warmer summers
* Other: 59% (mountains and heaths 46%, bogs and wetlands 6.3%, lakes and rivers 5.3%, urban areas 1.1%)
Irrigated land: , 1993 estimate
Natural hazards:
* European windstorms with hurricane-strength winds along the coast and in the mountains are not uncommon. For centuries one out of four males in coastal communities were lost at sea.
* Avalanches on steep slopes, especially in the northern part of the country and in mountain areas.
* Landslides have on occasions killed people, mostly in areas with soil rich in marine clay, as in lowland areas near Trondheimsfjord.
* Tsunamis have killed people; usually caused by parts of mountains (rockslide) falling into fjords or lakes. This happened 1905 in Loen, Norway, Loen in

 Environmental concerns in Norway include how to cut greenhouse gas emissions, pollution of the air and water, loss of habitat, damage to cold-water coral reefs from Fishing trawler, trawlers, and salmon fish farming threatening the wild salmon by spawning in the rivers, thereby diluting the fish DNA. Acid rain has damaged lakes, rivers and forests, especially in the southernmost part of the country, and most wild salmon populations in Sørlandet have died. Due to lower emissions in Europe, acid rain in Norway has decreased by 40% from 1980 to 2003. Another concern is a possible increase in extreme weather. In the future, climate models predict increased precipitation, especially in the areas with currently high precipitation, and also predict more episodes with heavy precipitation within a short period, which can cause landslides and local floods. Winters will probably be significant milder, and the sea-ice cover in the
Environmental concerns in Norway include how to cut greenhouse gas emissions, pollution of the air and water, loss of habitat, damage to cold-water coral reefs from Fishing trawler, trawlers, and salmon fish farming threatening the wild salmon by spawning in the rivers, thereby diluting the fish DNA. Acid rain has damaged lakes, rivers and forests, especially in the southernmost part of the country, and most wild salmon populations in Sørlandet have died. Due to lower emissions in Europe, acid rain in Norway has decreased by 40% from 1980 to 2003. Another concern is a possible increase in extreme weather. In the future, climate models predict increased precipitation, especially in the areas with currently high precipitation, and also predict more episodes with heavy precipitation within a short period, which can cause landslides and local floods. Winters will probably be significant milder, and the sea-ice cover in the
. * Bjørbæk, G. 2003. ''Norsk vær i 110 år.'' N.W. DAMM & Sønn. * Førland, E.. ''Variasjoner i vekst og fyringsforhold i Nordisk Arktis''. Regclim/Cicerone 6/2004. * University of Oslo. ''Almanakk for Norge'' Gyldendal fakta.
Statistics Norway
NGU - Geological survey of Norway
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Norway Geography of Norway,
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and t ...
is a country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
located in Northern Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
in the northern and western parts of the Scandinavian Peninsula
The Scandinavian Peninsula ( sv, Skandinaviska halvön; no, Den skandinaviske halvøy (Bokmål) or nn, Den skandinaviske halvøya; fi, Skandinavian niemimaa) is a peninsula located in Northern Europe, which roughly comprises the mainlands ...
. The majority of the country borders water, including the Skagerrak
The Skagerrak (, , ) is a strait running between the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, the southeast coast of Norway and the west coast of Sweden, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area through the Danish Straits to the Baltic Sea.
The ...
inlet to the south, the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
to the southwest, the North Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
(Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
) to the west, and the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
to the north. It has a land border with Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
to the east and a shorter border with Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
and an even shorter border with Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
to the northeast.
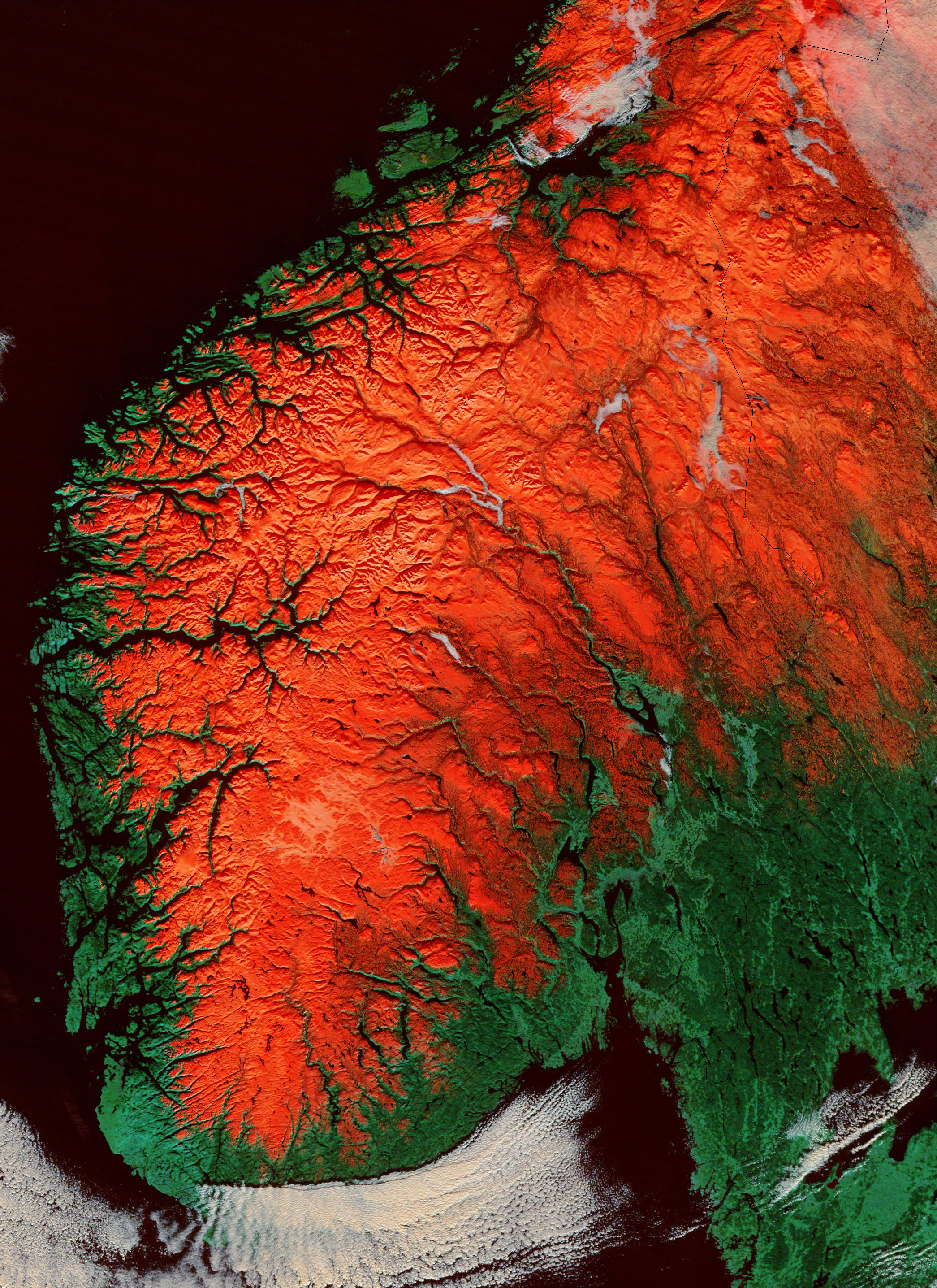
Norway has an elongated shape, one of the longest and most rugged coastlines in the world, and some 50,000 islands off its much-indented coastline. It is one of the world's northernmost countries, and it is one of Europe's most mountainous countries, with large areas dominated by the Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to the ...
. The country's average elevation is , and 32 percent of the mainland is located above the tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snowp ...
. Its country-length chain of peaks is geologically continuous with the mountains of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, and, after crossing under the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, the Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
of North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
. Geologists hold that all these formed a single range before the breakup
A relationship breakup, breakup, or break-up is the termination of a relationship. The act is commonly termed "dumping omeone in slang when it is initiated by one partner. The term is less likely to be applied to a married couple, where a brea ...
of the ancient supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
.
During the last glacial period, as well as in many earlier ice ages, virtually the entire country was covered with a thick ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Las ...
. The movement of the ice carved out deep valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers ...
s. As a result of the ice carving, Sognefjorden
The Sognefjord or Sognefjorden (, en, Sogn Fjord), nicknamed the King of the Fjords ( no, Fjordenes konge), is the largest and deepest fjord in Norway. Located in Vestland county in Western Norway, it stretches inland from the ocean to the smal ...
is the world's second deepest fjord and Hornindalsvatnet
Hornindalsvatnet is Norway's and Europe's deepest lake, and the world's twelfth deepest lake, officially measured to a depth of . Its surface is above sea level, which means that its bottom is below sea level.
The village of Grodås lies at ...
is the deepest lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
in Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. When the ice melted, the sea filled many of these valleys, creating Norway's famous fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland, the Faroe Islands, Ice ...
s. The glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s in the higher mountain areas today are not remnants of the large ice sheet of the ice age—their origins are more recent. The regional climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
was up to warmer in 7000 BC to 3000 BC in the Holocene climatic optimum
The Holocene Climate Optimum (HCO) was a warm period that occurred in the interval roughly 9,000 to 5,000 years ago BP, with a thermal maximum around 8000 years BP. It has also been known by many other names, such as Altithermal, Climatic Optimu ...
, (relative to the 1961-90 period), melting the remaining glaciers in the mountains almost completely during that period.
Even though it has long since been released from the enormous weight of the ice, the land is still rebounding several millimetres a year. This rebound is greatest in the eastern part of the country and in the inner parts of the long fjords, where the ice cover was thickest. This is a slow process, and for thousands of years following the end of the ice age, the sea covered substantial areas of what is today dry land. This old seabed is now among the most productive agricultural lands in the country.

Statistics
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
Area:
''total:''
''land:''
''water:''
''With
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
and Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger nort ...
included:''
Area - comparative:
The contiguous area is slightly smaller than Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
and slightly larger than Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
. Compared to US states, the area is approximately equal to New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
. With Svalbard and Jan Mayen included, the area is slightly larger than
Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
. Compared to US states, the area is slightly smaller than California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
and slightly larger than Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
.
Land boundaries:
''total:''
''border countries:''
Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
; Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
; Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
.
Coastline: continental ; including islands
Maritime claims:
''contiguous zone:''
''continental shelf:''
''exclusive economic zone:''
''territorial sea:'' Norway's exclusive economic zone (EEZ) totals . It is one of the largest in Europe and the 17th largest in the world. The EEZ along the mainland makes up , the Jan Mayen EEZ makes up , and since 1977 Norway has claimed an economic zone around Svalbard of .
Physical geography

Overview
Mainland Norway comprises an extensive range of natural variation, given its moderate size, including both terrestrial, marine, limnic and snow and ice ecosystems. Norway has a high mineral and bedrock diversity, and high diversity of landforms. Major landscape types include inland hills and mountains, inland valleys, inland plains, coastal plains, coastal fjords and coastal hills and mountains. Glaciated; mostly high plateaus and rugged mountains broken by fertile valleys; small, scattered plains; coastline deeply indented by fjords; arctic tundra only in the extreme northeast (largely found on theVaranger Peninsula
The Varanger Peninsula ( no, Varangerhalvøya; sme, Várnjárga; fkv, Varenkinniemi) is a peninsula in Finnmark county, Norway. It is located in the northeasternmost part of Norway, along the Barents Sea. The peninsula has the Tanafjorden to ...
). Frozen ground all year can also be found in the higher mountain areas and in the interior of Finnmark
Finnmark (; se, Finnmárku ; fkv, Finmarku; fi, Ruija ; russian: Финнмарк) was a county in the northern part of Norway, and it is scheduled to become a county again in 2024.
On 1 January 2020, Finnmark was merged with the neighbouri ...
county. Numerous glaciers are also found in Norway.
Elevation extremes:
''Lowest point:''
Norwegian Sea
The Norwegian Sea ( no, Norskehavet; is, Noregshaf; fo, Norskahavið) is a marginal sea, grouped with either the Atlantic Ocean or the Arctic Ocean, northwest of Norway between the North Sea and the Greenland Sea, adjoining the Barents Sea to ...
0 m
''Highest point:''
Galdhøpiggen
Galdhøpiggen () is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia, and Northern Europe. The tall mountain is located in Lom Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is in the Jotunheimen mountains within Jotunheimen National Park. The moun ...
Mainland
Scandinavian Mountains
The Scandinavian Mountains or the Scandes is a mountain range that runs through the Scandinavian Peninsula. The western sides of the mountains drop precipitously into the North Sea and Norwegian Sea, forming the fjords of Norway, whereas to the ...
: the Scandinavian Mountains are the most defining feature of the country. Starting with Setesdalsheiene
Setesdalsheiene () is the collective term for the mountains to the west and east of the Setesdalen valley in Agder county in Southern Norway. The river Otra flows through the valley between the mountains. This area is primarily located in the mu ...
north of the Skagerrak
The Skagerrak (, , ) is a strait running between the Jutland peninsula of Denmark, the southeast coast of Norway and the west coast of Sweden, connecting the North Sea and the Kattegat sea area through the Danish Straits to the Baltic Sea.
The ...
coast, the mountains are found in large parts of the country and intersect the many fjords of Vestlandet
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrative ...
. This region includes Hardangervidda
Hardangervidda ( en, Hardanger Plateau) is a mountain plateau (Norwegian: ''vidde'') in central southern Norway, covering parts of Vestland, Vestfold og Telemark, and Viken counties. It is the largest plateau of its kind in Europe, with a cold ye ...
, Jotunheimen
Jotunheimen (; "the home of the Jötunn") is a mountainous area of roughly in southern Norway and is part of the long range known as the Scandinavian Mountains. The 29 highest mountains in Norway are all located in the Jotunheimen mountains, in ...
(with Galdhøpiggen
Galdhøpiggen () is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia, and Northern Europe. The tall mountain is located in Lom Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is in the Jotunheimen mountains within Jotunheimen National Park. The moun ...
at a.s.l.), Sognefjell
Sognefjellet ( en, Sogn Mountains) is a mountainous area and mountain pass which connects Lustrafjorden and its surrounding valley with the Ottadalen valley in the Jotunheimen area. Sognefjellet is located in Luster Municipality (in Vestland cou ...
, and Trollheimen
Trollheimen is a mountain range in Møre og Romsdal and Trøndelag counties in central Norway. The mountain range is part of the Scandinavian Mountains.
Etymology
The name ('the home of the trolls') was proposed by Håkon Løken and used by Tr ...
in the north, with large glaciers, such as Jostedalsbreen
Jostedal Glacier or is the largest glacier in continental Europe. It is in Vestland county in Western Norway. Jostedalsbreen lies in the municipalities of Luster, Norway, Luster, Sogndal, Sunnfjord (municipality), Sunnfjord, and Stryn. The high ...
, Folgefonna
Folgefonna is a collective term for three plateau glaciers in the Hardanger region of Vestland county, Norway. They are located on the Folgefonna peninsula in the municipalities of Ullensvang, Kvinnherad, and Etne. The three glaciers are:
* Nord ...
, and Hardangerjøkulen
Hardangerjøkulen ( en, Hardanger Glacier) is the sixth largest glacier in mainland Norway. It is located in the municipalities of Eidfjord and Ulvik in Vestland county. It is located about northeast of the village of Eidfjord, about south of ...
. The mountain chain swings eastwards south of Trondheim, with ranges such as Dovrefjell
Dovrefjell is a mountain range in Central Norway that forms a natural barrier between Eastern Norway and Trøndelag. The mountain range is located in Innlandet, Møre og Romsdal, and Trøndelag counties in Norway. As a result of its central loca ...
and Rondane
Rondane National Park ( no, Rondane nasjonalpark) is the oldest national park in Norway, having been established on 21 December 1962. The park is located in Innlandet county, in the municipalities of Dovre, Folldal, Sel, Nord-Fron, Sør-Fron, Stor ...
, and reaches the border with Sweden, where they have become mostly gently sloping plateaus. The mountains then follow the border in a northeasterly direction and are known as ''Kjølen'' (the "keel"). The mountains intersect many fjords in Nordland
Nordland (; smj, Nordlánnda, sma, Nordlaante, sme, Nordlánda, en, Northland) is a county in Norway in the Northern Norway region, the least populous of all 11 counties, bordering Troms og Finnmark in the north, Trøndelag in the south, N ...
and Troms
Troms (; se, Romsa; fkv, Tromssa; fi, Tromssa) is a former county in northern Norway. On 1 January 2020 it was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger is expected to be reversed by t ...
, where they become more alpine and create many islands after they meet the sea. The Scandinavian mountains form the Lyngen Alps
The Lyngen Alps ( no, Lyngsalpene) are a mountain range in northeastern Troms og Finnmark county in Norway, east of the Tromsø (city), city of Tromsø. The mountain range runs through the municipalities of Lyngen, Balsfjord, and Storfjord. The mo ...
, which reach into northwestern Finnmark
Finnmark (; se, Finnmárku ; fkv, Finmarku; fi, Ruija ; russian: Финнмарк) was a county in the northern part of Norway, and it is scheduled to become a county again in 2024.
On 1 January 2020, Finnmark was merged with the neighbouri ...
, gradually becoming lower from Altafjord
Altafjord ( en, Alta Fjord;Koop, Gerhard, & Klaus-Peter Schmolke. 2000. ''Heavy Cruisers of the Admiral Hipper Class: Warships of the Kriegsmarine''. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing, p. 55. no, Altafjorden; fkv, Alattionvuono) is a fjord in A ...
towards Nordkapp
), North Cape, Norway, other uses, North Cape (disambiguation)
Nordkapp ( en, North Cape; sme, Davvinjárga or ; fkv, Kappa or ) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town o ...
( North Cape), where they finally end at the Barents Sea
The Barents Sea ( , also ; no, Barentshavet, ; russian: Баренцево море, Barentsevo More) is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located off the northern coasts of Norway and Russia and divided between Norwegian and Russian territo ...
.
The Scandinavian Mountains naturally divide the country into physical regions; valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers ...
s surround the mountains in all directions. The following physical regions will only partially correspond to traditional regions and counties in Norway.
Southern coast: the southern Skagerrak and North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
coast is the lowland south of the mountain range, from Stavanger in the west to the western reaches of the outer part of the Oslofjord
The Oslofjord (, ; en, Oslo Fjord) is an inlet in the south-east of Norway, stretching from an imaginary line between the and lighthouses and down to in the south to Oslo in the north. It is part of the Skagerrak strait, connecting the Nor ...
in the east. In this part of the country, valleys tend to follow a north–south direction. This area is mostly hilly, but with some very flat areas such as Lista
Lista is a former municipality located in the old Vest-Agder county in Norway. The municipality existed from 1838 until its dissolution in 1965. The administrative centre was the village of Vanse where Vanse Church is located. Lista municipa ...
and Jæren
Jæren is a traditional district in Rogaland county, Norway. The other districts in Rogaland are Dalane, Ryfylke, and Haugalandet. Jæren is one of the 15 districts that comprise Western Norway.
At about , Jæren is the largest flat lowland area ...
.
Southeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
: the land east of the mountains (corresponding to Østlandet, most of Telemark
Telemark is a traditional region, a former county, and a current electoral district in southern Norway. In 2020, Telemark merged with the former county of Vestfold to form the county of Vestfold og Telemark. Telemark borders the traditional ...
, and Røros
Røros ( sma, Plaassja, ) is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Røros. Some of the villages in Røros include Brekken, Glåmos, Feragen, Galåa, and Hitterdalen.
The minin ...
) is dominated by valleys running in a north–south direction in the eastern part, and in a more northwest–southeast direction further west, the valleys terminating at the Oslofjord. The longest valleys in the country are here— Østerdal and Gudbrandsdal
Gudbrandsdalen (; en, Gudbrand Valley) is a valley and Districts of Norway, traditional district in the Norway, Norwegian county of Innlandet (formerly Oppland). The valley is oriented in a north-westerly direction from Lillehammer (town), Lille ...
. This region also contains large areas of lowland surrounding the Oslofjord, as well as the Glomma
The Glomma, or Glåma, is Norway's longest and most voluminous river. With a total length of , it has a drainage basin that covers fully 13% of Norway's surface area, all in the southern part of the country.
Geography
At its fullest length, the ...
River and Lake Mjøsa
Mjøsa is Norway's largest lake, as well as one of the deepest lakes in Norway and in Europe. It is the fourth-deepest lake in Norway. It is located in the southern part of Norway, about north of the city of Oslo. Its main tributary is the rive ...
.
Western fjords: the land west of the mountains (corresponding to Vestlandet north of Stavanger) is dominated by the mountain chain, as the mountains extend, gradually becoming lower, all the way to the coast. This region is dominated by large fjords, the largest being Sognefjord
The Sognefjord or Sognefjorden (, en, Sogn Fjord), nicknamed the King of the Fjords ( no, Fjordenes konge), is the largest and deepest fjord in Norway. Located in Vestland county in Western Norway, it stretches inland from the ocean to the smal ...
and Hardangerfjord
The Hardangerfjord ( en, Hardanger Fjord) is the fifth longest fjord in the world, and the second longest fjord in Norway. It is located in Vestland county in the Hardanger region. The fjord stretches from the Atlantic Ocean into the mountain ...
. Geirangerfjord
The Geiranger Fjord ( no, Geirangerfjorden) is a fjord in the Sunnmøre region of Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. It is located entirely in the Stranda Municipality. It is a branch off the Sunnylvsfjorden, which is a branch off the Storfjo ...
is often regarded as having the ultimate in fjord scenery. The coast is protected by a chain of skerries (small, uninhabited islands—the Skjærgård) that are parallel to the coast and provide the beginning of a protected passage for almost the entire route from Stavanger
Stavanger (, , American English, US usually , ) is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the fourth largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the a ...
to Nordkapp
), North Cape, Norway, other uses, North Cape (disambiguation)
Nordkapp ( en, North Cape; sme, Davvinjárga or ; fkv, Kappa or ) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town o ...
. In the south, fjords and most valleys generally run in a west–east direction, and, in the north, in a northwest–southeast direction.
Trondheim region The Trondheim Region () is a statistical metropolitan region in the county of Trøndelag in Norway. It is centered in the city of Trondheim.
† Population data as of October 2012, frossb‡ Orkdal has been added to region due to new road complet ...
: the land north of Dovre
Dovre is a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Gudbrandsdal. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Dovre. Other villages in Dovre include Dombås and Hjerkinn. The ...
(corresponding to Trøndelag
Trøndelag (; sma, Trööndelage) is a county in the central part of Norway. It was created in 1687, then named Trondhjem County ( no, Trondhjems Amt); in 1804 the county was split into Nord-Trøndelag and Sør-Trøndelag by the King of Denmar ...
except Røros
Røros ( sma, Plaassja, ) is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Røros. Some of the villages in Røros include Brekken, Glåmos, Feragen, Galåa, and Hitterdalen.
The minin ...
) comprises a more gentle landscape with more rounded shapes and mountains, and with valleys terminating at the Trondheimsfjord
The Trondheim Fjord or Trondheimsfjorden (), an inlet of the Norwegian Sea, is Norway's third-longest fjord at long. It is located in the west-central part of the country in Trøndelag county, and it stretches from the municipality of Ørland in ...
, where they open up onto a large lowland area. Further north is the valley of Namdalen
Namdalen ( sma, Nååmesjevuemie) is a Districts of Norway, traditional district in the central part of Norway, consisting of the municipalities Namsos, Grong, Overhalla, Røyrvik, Nærøysund, Høylandet, Flatanger, Lierne, Leka, Norway, Leka, ...
, opening up in the Namsos
( sma, Nåavmesjenjaelmie) is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. It is part of the Namdalen region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Namsos. Some of the villages in the municipality include Bangsund, Kl ...
area. However, the Fosen
Fosen is a traditional district in Trøndelag, consisting of the municipalities Osen, Roan Åfjord, Ørland, Indre Fosen, Orkland, Heim, Hitra and Frøya. The district is dominated by forested valleys, lakes, coastal cliffs but also shallow ar ...
peninsula and the most northern coast ( Leka) is dominated by higher mountains and narrower valleys.
Northern fjords: the land further north (corresponding to Nordland, Troms
Troms (; se, Romsa; fkv, Tromssa; fi, Tromssa) is a former county in northern Norway. On 1 January 2020 it was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger is expected to be reversed by t ...
, and northwestern Finnmark
Finnmark (; se, Finnmárku ; fkv, Finmarku; fi, Ruija ; russian: Финнмарк) was a county in the northern part of Norway, and it is scheduled to become a county again in 2024.
On 1 January 2020, Finnmark was merged with the neighbouri ...
) is again dominated by steep mountains going all the way to the coast and by numerous fjords. The fjords and valleys generally lie in a west–east direction in the southern part of this area, and a more northwest–southeast direction further north. The Saltfjellet
Saltfjellet is a mountain area in Nordland county, Norway that separates the two regions of Helgeland and Salten. It is also a cultural border between the Southern and Central parts of Sápmi.
Geography and environment
The Saltfjell is one of the ...
mountain range is an exception, as the valley runs in a more north–south direction from these mountains. This long, narrow area includes many large islands, such as Lofoten
Lofoten () is an archipelago and a traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches and untouched lands. There are two towns, Svolvær ...
, Vesterålen
Vesterålen is a district and archipelago in Nordland county, Norway. It is located just north of Lofoten and west of Harstad. It is the northernmost part of Nordland county. Sortland is the largest town, situated near the center of the archipe ...
, and Senja
or is an island in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway, Europe. With an area of , it is the second largest island in Norway (outside of the Svalbard archipelago). It has a wild, mountainous outer (western) side facing the Atlantic, and a mild ...
.
Far northeast: the interior and the coast east of Nordkapp
), North Cape, Norway, other uses, North Cape (disambiguation)
Nordkapp ( en, North Cape; sme, Davvinjárga or ; fkv, Kappa or ) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town o ...
(corresponding to Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
and eastern Finnmark) is less dominated by mountains, and is mostly below . The interior is dominated by the large Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
plateau. There are large, wide fjords running in a north–south direction. This coast lacks the small islands, or skerries, typical of the Norwegian coast. Furthest to the east, the Varangerfjord
The Varangerfjord ( en, Varanger Fjord; russian: Варангер-фьорд, Варяжский залив; fi, Varanginvuono; sme, Várjavuonna) is the easternmost fjord in Norway, north of Finland. The fjord is located in Troms og Finnmark co ...
runs in an east–west direction and is the only large fjord in the country whose mouth is to the east.
Arctic islands
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
: further north, in the Arctic ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
, lies the Svalbard archipelago, which is also dominated by mountains that are mostly covered by large glaciers, especially in the eastern part of the archipelago, where glaciers cover more than 90%, with one glacier, Austfonna
Austfonna is an ice cap located on Nordaustlandet in the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Covering an area of 7,800 km2, it is Europe's third-largest glacier by area and volume, after the Severny Island ice cap of Novaya Zemlya, Russia, and Va ...
, being the largest in Europe. Unlike on the mainland, these glaciers calve directly into the open ocean.
Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger nort ...
: to the far northwest, halfway towards Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland is t ...
, is Jan Mayen island, where the only active volcano in Norway, Beerenberg
Beerenberg is a stratovolcano dominating the northeastern end of the Norwegian island of Jan Mayen. It is high and is the world's northernmost subaerial active volcano and the only volcano in Norway. The volcano is topped by a mostly ice-fill ...
, is found.
Antarctic islands and claim to Antarctica
Bouvet Island
Bouvet Island ( ; or ''Bouvetøyen'') is an island claimed by Norway, and declared an uninhabited protected nature reserve. It is a subantarctic volcanic island, situated in the South Atlantic Ocean at the southern end of the Mid-Atlantic Ri ...
: located in the South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
at 54°S and mostly covered by glaciers, this island is one of the most remote in the world, inhabited only by seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
and birds.
Peter I Island
Peter I Island ( no, Peter I Øy) is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from continental Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway and, along with Bouvet Island and Queen Maud Land, composes one of the three No ...
: located in the South Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
at 69°S and 90°W, this island is dominated by glaciers and a volcano. As with Bouvet Island, this island is regarded as an external dependency, and not part of the kingdom.
Queen Maud Land
Queen Maud Land ( no, Dronning Maud Land) is a roughly region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addit ...
is Norway's claim in Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
. This large, sectorial area stretches to the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
and is completely dominated by the world's largest ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Las ...
, but with some impressive nunatak
A nunatak (from Inuit ''nunataq'') is the summit or ridge of a mountain that protrudes from an ice field or glacier that otherwise covers most of the mountain or ridge. They are also called glacial islands. Examples are natural pyramidal peaks. ...
s (bare rock) penetrating above the ice. The Troll Research Station
Troll is a Norwegian research station located at Jutulsessen, from the coast in the eastern part of Princess Martha Coast in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It is Norway's only all-year research station in Antarctica, and is supplemented by the s ...
manned by Norway is located on a snow-free mountain slope, the only station in Antarctica not to be located on the ice.
Beerenberg
Beerenberg is a stratovolcano dominating the northeastern end of the Norwegian island of Jan Mayen. It is high and is the world's northernmost subaerial active volcano and the only volcano in Norway. The volcano is topped by a mostly ice-fill ...
(2277 m), Jan Mayen, is the world's most northerly active volcano
Sunlight, time zones, and tides
Areas in Norway located north of theArctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the most northerly of the five major circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth. Its southern equivalent is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circle marks the southernmost latitude at w ...
have extreme darkness in winter, which increases with latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
. At Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, locally �lɔ̀ŋjɑrˌbyːən "The Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000 and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ...
on the Svalbard islands in the extreme north, the upper part of the sun's disc is above the horizon from 19 April to 23 August, and winter darkness lasts from 27 October to 14 February. The corresponding dates for still northerly Tromsø are 17 May – 25 July, and 26 November – 15 January. The winter darkness is not dark on the mainland, as there is twilight for a few hours around noon in Tromsø; but in Longyearbyen
Longyearbyen (, locally �lɔ̀ŋjɑrˌbyːən "The Longyear Town") is the world's northernmost settlement with a population greater than 1,000 and the largest inhabited area of Svalbard, Norway. It stretches along the foot of the left bank ...
there is near total darkness during the dark period. Even the southern part of the country experiences large seasonal variations in daylight; in Oslo, the sun rises at 03:54 and sets 22:54 at the summer solstice
A solstice is an event that occurs when the Sun appears to reach its most northerly or southerly excursion relative to the celestial equator on the celestial sphere. Two solstices occur annually, around June 21 and December 21. In many countr ...
, but is only above the horizon from 09:18 - 15:12 at the winter solstice. The northern part of the country is located in the aurora borealis
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of br ...
zone; the aurora is occasionally seen in the southern part of the country as well.
Norway is on Central European Time
Central European Time (CET) is a standard time which is 1 hour ahead of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
The time offset from UTC can be written as UTC+01:00.
It is used in most parts of Europe and in a few North African countries.
CET i ...
, corresponding to the 15°E longitude. As the country is very elongated, this is at odds with the local daylight hours in the eastern and western parts. In Vardø, local daylight hours are 64 minutes earlier, and in Bergen, they are 39 minutes later. Thus, Finnmark gains early morning daylight but loses evening daylight, and Vestlandet
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrative ...
loses early morning light but gains more evening daylight in this time zone. Daylight saving time
Daylight saving time (DST), also referred to as daylight savings time or simply daylight time (United States, Canada, and Australia), and summer time (United Kingdom, European Union, and others), is the practice of advancing clocks (typicall ...
(GMT + 2) is observed from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October.
The difference between low tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
and high tide is small on the southern coast and large in the north; ranging from on average 0.17 m in Mandal
A tehsil (, also known as tahsil, taluka, or taluk) is a local unit of administrative division in some countries of South Asia. It is a subdistrict of the area within a district including the designated populated place that serves as its administr ...
to about 0.30 m in Oslo and Stavanger, 0.90 m in Bergen, 1.80 m in Trondheim, Bodø and Hammerfest and as much as 2.17 m in Vadsø
Vadsø (; sme, Čáhcesuolu; fkv, Vesisaari) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark County, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Vadsø, which was the administrative centre of the former Finnmark county. Other ...
.
Climate

 The climate of Norway is more temperate than could be expected for such high
The climate of Norway is more temperate than could be expected for such high latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s. This is mainly due to the North Atlantic Current
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from wher ...
with its extension, the Norwegian Current
The Norwegian Current (also known as the Norway Coastal Current) is one of two dominant arctic inflows of water. It can be traced from near Shetland, north of Scotland, otherwise from the eastern North Sea at depths of up to 100 metres. It finally ...
, raising the air temperature; the prevailing southwesterlies bringing mild air onshore; and the general southwest–northeast orientation of the coast, which allows the westerlies to penetrate into the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
. The January average in Brønnøysund
Brønnøysund () is a List of towns and cities in Norway, town and the administrative centre of Brønnøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is also a List of former municipalities of Norway, former municipality within Nordland county. ...
is warmer than the January average in Nome, Alaska
Nome (; ik, Sitŋasuaq, ) is a city in the Nome Census Area in the Unorganized Borough of Alaska, United States. The city is located on the southern Seward Peninsula coast on Norton Sound of the Bering Sea. It had a population of 3,699 recorded ...
, even though both towns are situated on the west coast of the continents at 65°N. In July, the difference is reduced to . The January average of Yakutsk
Yakutsk (russian: Якутск, p=jɪˈkutsk; sah, Дьокуускай, translit=Djokuuskay, ) is the capital city of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located about south of the Arctic Circle. Fueled by the mining industry, Yakutsk has become one of ...
, in Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
but slightly further south, is colder than in Brønnøysund.
Precipitation
Norway is among Europe's wettest countries, but with large variation in precipitation amount due to the terrain with mountain chains resulting in orographic precipitation but also creating rain shadows. In some regions, locations with vastly different precipitation amounts can be fairly close.Stryn
Stryn is a municipality in the county of Vestland, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Nordfjord. The administrative center of the municipality is the village of Stryn. The municipality is located along the innermost part of t ...
(1661 mm) get 6 times as much precipitation as Skjåk 90 minutes drive away, Bergen has five times as much precipitation as Lærdal
Lærdal is a municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located on the south side of the Sognefjorden in the traditional district of Sogn. The administrative center of the municipality is the village of Lærdalsøyri. The old Filefjell Kon ...
in the same region, and in the north Glomfjord
Glomfjord is a village in the municipality of Meløy in Nordland county, Norway. The industrial community is located along Norwegian County Road 17 at the head of the Glomfjorden, just north of the Arctic Circle. The village has a population ( ...
(2141 mm) get 10 times as much precipitation as upper Saltdal (81 mm) which is 68 km away as the crow flies.
Some areas of Vestlandet and southern Nordland are among Europe's wettest, due to orographic lift
Orographic lift occurs when an air mass is forced from a low elevation to a higher elevation as it moves over rising terrain. As the air mass gains altitude it quickly cools down adiabatically, which can raise the relative humidity to 100% and cr ...
, particularly where the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend to ...
are first intercepted by high mountains. This occurs slightly inland from the outer skerry guard. In the updated 1991-2020 normals, Gullfjellet
Gullfjellet or Gulfjellet is a tall mountain in Vestland county, Norway. It is situated on the border between the municipalities of Bergen and Samnanger, and it is the highest mountain in the municipality of Bergen. The name "Gul" is an old name ...
in Bergen (345 m) has the highest annual precipitation with . Annual precipitation can exceed in mountain areas near the coast. Lurøy
Lurøy is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Lurøy, located on the island of Lurøya. Other villages in Lurøy include Aldra ...
at the Arctic Circle gets annually, a remarkable amount for a polar location. Precipitation is heaviest in late autumn and winter along the coast, while April to June is the driest.
The innermost parts of the long fjords are somewhat drier: annual precipitation in Lærdal
Lærdal is a municipality in Vestland county, Norway. It is located on the south side of the Sognefjorden in the traditional district of Sogn. The administrative center of the municipality is the village of Lærdalsøyri. The old Filefjell Kon ...
is , and in the north only in Skibotn
Skibotn ( se, Ivgubahta, Kven: ''Yykeänperä'') is a village in Storfjord Municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. It is located on the southeastern shore of the Lyngen fjord in Northern Norway. The village area is located at the cro ...
at the head of Lyngenfjord.
The regions east of the mountain chain (including Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
) have a more continental climate with generally less precipitation, and precipitation peaks in summer and early autumn, while winter and spring tend to be driest. A large area in the interior of Finnmark receive less than of precipitation annually. Some valleys surrounded by mountains get very scarce precipitation, and often need irrigation in summer. Upper Saltdal
Saltdal ( sme, Sálát) is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Salten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Rognan. Other villages in Saltdal include Røkland and Løn ...
(81 m, ''Storjord'') has the lowest annual average with only , while in the south of Norway, Skjåk
Skjåk is a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Gudbrandsdal. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Bismo. Most of the municipal residents live in the Billingsdalen an ...
is driest with .
In Norway's High Arctic archipelagoes, Svalbard Airport has the lowest average annual precipitation with , while Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger nort ...
get more than double with .
Monthly averages vary from in April in upper Saltdal and Skjåk to in December at Gullfjellet. Coastal areas from Lindesnes
Lindesnes ( en, the Naze) is a municipality in Agder county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Sørlandet. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Mandal. Other villages in Lindesnes include Åvik, Høll ...
north to Vardø
( fi, Vuoreija, fkv, Vuorea, se, Várggát) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county in the extreme northeastern part of Norway. Vardø is the easternmost town in Norway, more to the east than Saint Petersburg or Istanbul. The administra ...
have more than 200 days per year with precipitation; however, this is with a very low threshold value (0.1 mm precipitation). The average annual number of days with at least precipitation is 77 in Blindern/Oslo
Oslo ( , , or ; sma, Oslove) is the capital and most populous city of Norway. It constitutes both a county and a municipality. The municipality of Oslo had a population of in 2022, while the city's greater urban area had a population of ...
, 96 in Kjevik/Kristiansand
Kristiansand is a seaside resort city and municipality in Agder county, Norway. The city is the fifth-largest and the municipality the sixth-largest in Norway, with a population of around 112,000 as of January 2020, following the incorporation ...
, 158 in Florida/Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula of ...
, 93 in Værnes/Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, and ...
, and 109 in Tromsø
Tromsø (, , ; se, Romsa ; fkv, Tromssa; sv, Tromsö) is a List of municipalities of Norway, municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the Tromsø (city), city of Tromsø.
Tromsø lies ...
.
Temperature
The coast experiences milder winters than other areas at the same latitudes. The average temperature difference between the coldest month and the warmest is only in coastal areas; some lighthouses have a yearly amplitude of just , such as Svinøy in Herøy with a coldest month of . The differences of inland areas are larger, with a maximum difference of inKarasjok
( se, Kárášjohka ; fkv, Kaarasjoki) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Karasjok. Other villages include Dorvonjárga, Šuoššjávri, and Váljohka.
The ...
. Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
has the coldest winters in mainland Norway, but inland areas much further south can also experience severe cold. Røros
Røros ( sma, Plaassja, ) is a municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the town of Røros. Some of the villages in Røros include Brekken, Glåmos, Feragen, Galåa, and Hitterdalen.
The minin ...
has recorded .
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norw ...
. This modifies the Arctic polar climate
The polar climate regions are characterized by a lack of warm summers but with varying winters. Every month in a polar climate has an average temperature of less than . Regions with polar climate cover more than 20% of the Earth's area. Most of ...
somewhat and results in open water throughout the year at higher latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s than any other place in the Arctic. On the eastern coast of the Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range ...
archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
, the sea used to be frozen during most of the year, but the last years' warming (graph
Graph may refer to:
Mathematics
*Graph (discrete mathematics), a structure made of vertices and edges
**Graph theory, the study of such graphs and their properties
*Graph (topology), a topological space resembling a graph in the sense of discre ...
) have seen open waters noticeably longer.
The warmest temperature ever recorded in Norway is in Nesbyen
Nesbyen is a town and the administrative center in Nesbyen municipality in the county of Viken, Norway. Nesbyen is located in the traditional district of Hallingdal.
Summary
Nesbyen has a population of about 3,500 inhabitants. It is located ...
. The coldest temperature ever is in Karasjok
( se, Kárášjohka ; fkv, Kaarasjoki) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Karasjok. Other villages include Dorvonjárga, Šuoššjávri, and Váljohka.
The ...
. The warmest month on record was July 1901 in Oslo, with a mean 24-hour temperature of ), and the coldest month was February 1966 in Karasjok, with a mean of . The warmest night recorded in Norway was July 29, 2019 at Sømna-Kvaløyfjellet (302 m) in Sømna
Sømna is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the Helgeland traditional region. The administrative center of Sømna is the village of Vik i Helgeland. Other villages in the municipality include Dalbotn, Sund, Vennesund, an ...
near Brønnøysund with overnight low . Atlantic lows bringing mild winds in winter further warmed by foehn
A Foehn or Föhn (, , ), is a type of dry, relatively warm, downslope wind that occurs in the lee (downwind side) of a mountain range.
It is a rain shadow wind that results from the subsequent adiabatic warming of air that has dropped most of ...
can give warm temperatures in narrow fjords in winter: Sunndalsøra
is the administrative centre of Sunndal Municipality in Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The village of Sunndalsøra lies at the mouth of the river Driva at the beginning of the Sunndalsfjord. Sunndalsøra is surrounded by steep mountains, such a ...
has recorded in January and in February.
Compared to coastal areas, inland valleys and the innermost fjord areas have larger diurnal temperature variation
In meteorology, diurnal temperature variation is the variation between a high air temperature and a low temperature that occurs during the same day.
Temperature lag
Temperature lag is an important factor in diurnal temperature variation: peak d ...
s, especially in spring and summer.
As seen from the table, Norway's climate shows large variations, but all populated areas of the Norwegian mainland have temperate or subarctic climates (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include:
* Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer
* Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan
* Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ...
groups ''C'' and ''D''). Svalbard and Jan Mayen have a polar climate (Köppen group ''E'').
 As a consequence of warming since 1990, summers are warmer and longer and winters are getting shorter and milder. With the new official 1991-2020 climate normal, many areas have seen their climate change to a new climate zone compared to 1961-90 normal. Oslo's climate has moved from Dfb to Cfb/Dfb, Lillehammer's from Dfc to Dfb, Kristiansand from Cfb/Dfb to Cfb, Molde and Brønnøysund from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb, Trondheim from Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Bodø from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Tromsø (Holt) from Dfc to Cfc/Dfc and Vardø from ET to Dfc. Snow cover has decreased in most populated areas due to winter warming; days/year with 25 cm snow cover in 1991-2020 is 26 days in Oslo (94 m), 2 days in Bergen, 8 days in Trondheim/Værnes and 144 days in Tromsø. The strongest warming has been observed on Svalbard. In addition to warming, precipitation has increased in most areas, especially in winter, increasing
As a consequence of warming since 1990, summers are warmer and longer and winters are getting shorter and milder. With the new official 1991-2020 climate normal, many areas have seen their climate change to a new climate zone compared to 1961-90 normal. Oslo's climate has moved from Dfb to Cfb/Dfb, Lillehammer's from Dfc to Dfb, Kristiansand from Cfb/Dfb to Cfb, Molde and Brønnøysund from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb, Trondheim from Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Bodø from Cfc/Dfc to Cfb/Dfb, Tromsø (Holt) from Dfc to Cfc/Dfc and Vardø from ET to Dfc. Snow cover has decreased in most populated areas due to winter warming; days/year with 25 cm snow cover in 1991-2020 is 26 days in Oslo (94 m), 2 days in Bergen, 8 days in Trondheim/Værnes and 144 days in Tromsø. The strongest warming has been observed on Svalbard. In addition to warming, precipitation has increased in most areas, especially in winter, increasing erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
and the risk of landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, deep-seated grade (slope), slope failures, mudflows, and debris flows. Landslides occur in a variety of ...
s.
Biological diversity
Due to the large latitudinal range of the country and its varied topography and climate, Norway has a higher number ofhabitats
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
than almost any other European country. There are approximately 60,000 species of plant and animal life in Norway and adjacent waters. The Norwegian Shelf large marine ecosystem is considered highly productive. The total number of species include 16,000 species of insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body ( head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s (probably 4,000 more species yet to be described), 20,000 species of algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular mic ...
, 1,800 species of lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
es, 2,800 species of vascular plant
Vascular plants (), also called tracheophytes () or collectively Tracheophyta (), form a large group of land plants ( accepted known species) that have lignified tissues (the xylem) for conducting water and minerals throughout the plant. They al ...
s, up to 7,000 species of fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, 450 species of bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
s (250 species nesting in Norway), 90 species of mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, 45 species of freshwater fish, 150 species of saltwater fish, 1,000 species of freshwater invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
s and 3,500 species of saltwater invertebrates. About 40,000 of these species have been scientifically described. In the summer of 2010, scientific exploration in Finnmark discovered 126 species of insects new to Norway, of which 54 species were new to science.
The 2006 IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biol ...
names 3,886 Norwegian species as endangered, 17 of which, such as the European beaver
The Eurasian beaver (''Castor fiber'') or European beaver is a beaver species that was once widespread in Eurasia, but was hunted to near-extinction for both its fur and castoreum. At the turn of the 20th century, only about 1,200 beavers surviv ...
, are listed because they are endangered globally, even if the population in Norway is not seen as endangered. There are 430 species of fungi on the red list, many of these are closely associated with the small remaining areas of old-growth forest
An old-growth forestalso termed primary forest, virgin forest, late seral forest, primeval forest, or first-growth forestis a forest that has attained great age without significant disturbance, and thereby exhibits unique ecological featur ...
s. There are also 90 species of birds on the list and 25 species of mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s. As of 2006, 1,988 current species are listed as endangered or vulnerable, of which 939 are listed as vulnerable, 734 as endangered, and 285 as critically endangered in Norway, among them the gray wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly u ...
, the Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Arctic tundra biome. It is well adapted to living in co ...
(healthy population on Svalbard), and the pool frog
The pool frog (''Pelophylax lessonae'') is a European frog in the family Ranidae. Its specific name was chosen by the Italian herpetologist Lorenzo Camerano in 1882, in order to honour his master Michele Lessona.
Description
The pool frog is ...
.
The largest predator in Norwegian waters is the sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
, and the largest fish is the basking shark
The basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') is the second-largest living shark and fish, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach in length. ...
. The largest predator on land is the polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear specie ...
, while the brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear species found across Eurasia and North America. In North America, the populations of brown bears are called grizzly bears, while the subspecies that inhabits the Kodiak Islands of Alaska is kno ...
is the largest predator on the Norwegian mainland, where the common moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult mal ...
is the largest animal.
Flora
 Natural vegetation in Norway varies considerably, as can be expected in a country having such variations in latitude. There are generally fewer species of
Natural vegetation in Norway varies considerably, as can be expected in a country having such variations in latitude. There are generally fewer species of tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
s in Norway than in areas in western North America with a similar climate. This is because European north–south migration routes after the ice age are more difficult, with bodies of water (such as the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
and the North Sea
The North Sea lies between Great Britain, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands and Belgium. An epeiric sea on the European continental shelf, it connects to the Atlantic Ocean through the English Channel in the south and the Norwegian S ...
) and mountains creating barriers, while in America land is contiguous and the mountains follow a north–south direction. However, recent research using DNA-studies of spruce and pine and lake sediments have proven that Norwegian conifers survived the ice age in ice-free refuges to the north as far as Andøya
Andøya is the northernmost island in the Vesterålen archipelago, situated about inside the Arctic circle. Andøya is located in Andøy Municipality in Nordland county, Norway. The main population centres on the island include the villages of ...
. Many imported plants have been able to bear seed and spread. Less than half of the 2,630 plant species in Norway today actually occur naturally in the country. About 210 species of plants growing in Norway are listed as endangered, 13 of which are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsew ...
. The national parks in Norway are mostly located in mountain areas; about 2% of the productive forests in the country are protected.
 Some plants are classified as western due to their need for high humidity or low tolerance of winter frost; these will stay close to the southwestern coast, with their northern limit near Ålesund. Some examples are
Some plants are classified as western due to their need for high humidity or low tolerance of winter frost; these will stay close to the southwestern coast, with their northern limit near Ålesund. Some examples are holly
''Ilex'' (), or holly, is a genus of over 570 species of flowering plants in the family Aquifoliaceae, and the only living genus in that family. ''Ilex'' has the most species of any woody dioecious angiosperm genus. The species are evergreen o ...
and bell heather
''Erica cinerea'', the bell heather, is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae, native to western and central Europe.
The plant provides a great deal of nectar for pollinators. It was rated in the top 5 for most nectar produ ...
. Some western species occur as far north as Helgeland
Helgeland is the most southerly district in Northern Norway. Generally speaking, Helgeland refers to the part of Nordland county that is located south of the Arctic Circle. It is bordered in the north by the Saltfjellet mountains and Svartise ...
(such as ''Erica tetralix
''Erica tetralix'', the cross-leaved heath, is a species of flowering plant in the family Ericaceae, native to western Europe, from southern Portugal to central Norway, as well as a number of boggy regions further from the coast in Central Europ ...
''), some even as far as Lofoten (such as Luzula sylvatica
''Luzula sylvatica'', commonly known as greater wood-rush or great wood-rush, is a perennial flowering plant in the rush family Juncaceae.
Description
''Luzula sylvatica'' is the largest woodrush, with stems high. It forms clumps of bright g ...
).
The mild temperatures along the coast allow for some surprises. Some hardy species of palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
grow as far north as Sunnmøre
Sunnmøre (, en, South- Møre) is the southernmost traditional district of the western Norwegian county of Møre og Romsdal. Its main city is Ålesund. The region comprises the municipalities ( no, kommuner) of Giske, Hareid, Herøy, Norddal ...
. One of the largest remaining Linden forests in Europe grows at Flostranda, in Stryn
Stryn is a municipality in the county of Vestland, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Nordfjord. The administrative center of the municipality is the village of Stryn. The municipality is located along the innermost part of t ...
. Planted deciduous trees, such as horse chestnut
The genus ''Aesculus'' ( or ), with species called buckeye and horse chestnut, comprises 13–19 species of flowering plants in the family Sapindaceae. They are trees and shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere, with six species n ...
and beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
, thrive north of the Arctic Circle (as at Steigen
Steigen ('stejgen) is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Salten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Leinesfjord. Other villages include Bogen, Leines, Nordfold, N ...
).
Plants classified as eastern need comparatively more summer sunshine, with less humidity, but can tolerate cold winters. These will often occur in the southeast and inland areas: examples being ''Daphne mezereum
''Daphne mezereum'', commonly known as mezereum, mezereon, February daphne, spurge laurel or spurge olive, is a species of '' Daphne'' in the flowering plant family Thymelaeaceae, native to most of Europe and Western Asia, north to northern Scan ...
'', '' Fragaria viridis'', and spiked speedwell
''Veronica spicata'' (spiked speedwell; syn. ''Pseudolysimachion spicatum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae. It is tall and bears 1 foot long spikes with blue, pink, purple and white flowers.
It is the county flo ...
. Some eastern species common to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
grow in the river valleys of eastern Finnmark. There are species which seem to thrive in between these extremes, such as the southern plants, where both winter and summer climate is important (such as pedunculate oak
''Quercus robur'', commonly known as common oak, pedunculate oak, European oak or English oak, is a species of flowering plant in the beech and oak family, Fagaceae. It is a large tree, native to most of Europe west of the Caucasus. It is widel ...
, European ash, and dog's mercury). Other plants depend on the type of bedrock.
There is a considerable number of alpine species in the mountains of Norway. These species can not tolerate summers that are comparatively long and warm, nor are they able to compete with plants adapted to a longer and warmer growing season. Many alpine plants are common in the North Boreal zone and some in the Middle Boreal zone, but their main area of distribution is on the alpine tundra in the Scandinavian Mountains and on the Arctic tundra. Many of the hardiest species have adapted by ripening seeds over more than one summer. Examples of alpine species are Ranunculus glacialis, glacier buttercup, ''Draba lactea'', and ''Salix herbacea''. A well-known anomaly is the 30 American alpine species, which in Europe only grow in two mountainous parts of Norway: the Dovre–Trollheimen and Jotunheim mountains in the south; and the Saltdal
Saltdal ( sme, Sálát) is a municipality in Nordland county, Norway. It is part of the traditional district of Salten. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Rognan. Other villages in Saltdal include Røkland and Løn ...
, to western Finnmark, in the north. Other than in Norway, these species—such as ''Braya linearis'' and ''Carex scirpoidea''—grow only in Canada and Greenland. It is unknown whether these survived the ice age on some mountain peak penetrating the ice, or spread from further south in Europe, or why did they not spread to other mountainous regions of Europe. Some alpine species have a wider distribution and grow in Siberia, such as ''Rhododendron lapponicum'' (Lapland rosebay). Other alpine species are common to the whole Arctic and some grow only in Europe, such as Trollius europaeus, globe-flower.
The following vegetation zones in Norway are all based on botanical criteria, although, as mentioned, some plants will have specific demands. Forests, bogs, and wetlands, as well as heaths, are all included in the different vegetation zones. A South Boreal bog will differ from a North Boreal bog, although some plant species might occur on both.
Nemoral
 A small area along the southern coast—from Soknedal (Rogaland), Soknedal in southern Rogaland and east to Fevik in Aust-Agder (including Kristiansand)—belongs to the Nemoral vegetation zone. This zone is located below above sea level and at most inland along the valleys. This is the predominant vegetation zone in Europe north of southern France, the Alps, the Carpathians, and the Caucasus. The hallmark of this zone in Norway is the predominance of oak and the virtually complete lack of typical boreal ecosystem, boreal species such as Norway spruce and grey alder, although a lowland variant of Scots pine, pine occurs. Nemoral covers a total of 0.5% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen).
A small area along the southern coast—from Soknedal (Rogaland), Soknedal in southern Rogaland and east to Fevik in Aust-Agder (including Kristiansand)—belongs to the Nemoral vegetation zone. This zone is located below above sea level and at most inland along the valleys. This is the predominant vegetation zone in Europe north of southern France, the Alps, the Carpathians, and the Caucasus. The hallmark of this zone in Norway is the predominance of oak and the virtually complete lack of typical boreal ecosystem, boreal species such as Norway spruce and grey alder, although a lowland variant of Scots pine, pine occurs. Nemoral covers a total of 0.5% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen).
Hemiboreal (Boreonemoral)
 The hemiboreal zone covers a total of 7% of the land area in Norway, including 80% of Østfold and Vestfold. This vegetation represents a mix of nemoral and boreal plant species, and belongs to the Palearctic, Sarmatic mixed forests terrestrial ecoregion (PA0436). The nemoral species tend to predominate on slopes facing southwest and with good soil, while the boreal species predominate on slopes facing north and with waterlogged soil. In some areas, other factors overrule this, such as where the bedrock gives little nutrient, where oak and the boreal Scots pine, pine often share predominance. The boreonemoral zone follows the coast from
The hemiboreal zone covers a total of 7% of the land area in Norway, including 80% of Østfold and Vestfold. This vegetation represents a mix of nemoral and boreal plant species, and belongs to the Palearctic, Sarmatic mixed forests terrestrial ecoregion (PA0436). The nemoral species tend to predominate on slopes facing southwest and with good soil, while the boreal species predominate on slopes facing north and with waterlogged soil. In some areas, other factors overrule this, such as where the bedrock gives little nutrient, where oak and the boreal Scots pine, pine often share predominance. The boreonemoral zone follows the coast from Oslofjord
The Oslofjord (, ; en, Oslo Fjord) is an inlet in the south-east of Norway, stretching from an imaginary line between the and lighthouses and down to in the south to Oslo in the north. It is part of the Skagerrak strait, connecting the Nor ...
north to Ålesund, becoming discontinuous north of Sunnmøre
Sunnmøre (, en, South- Møre) is the southernmost traditional district of the western Norwegian county of Møre og Romsdal. Its main city is Ålesund. The region comprises the municipalities ( no, kommuner) of Giske, Hareid, Herøy, Norddal ...
. In Oslo, this zone reaches to an elevation of above sea level. It also reaches into some of the lower valleys and just reaches the lowland around Mjøsa
Mjøsa is Norway's largest lake, as well as one of the deepest lakes in Norway and in Europe. It is the fourth-deepest lake in Norway. It is located in the southern part of Norway, about north of the city of Oslo. Its main tributary is the rive ...
, but not as far north as Lillehammer. In the valleys of the south, this vegetation might exist up to above sea level. The zone follows the lowland of the west coast and into the largest fjords, reaching an elevation of there, even to in some sheltered fjords and valleys in Nordmøre, with nutrient-rich soil. The northernmost locations in the world are several areas along the Trondheimsfjord
The Trondheim Fjord or Trondheimsfjorden (), an inlet of the Norwegian Sea, is Norway's third-longest fjord at long. It is located in the west-central part of the country in Trøndelag county, and it stretches from the municipality of Ørland in ...
, such as Frosta, with the northernmost location being Byahalla, in Steinkjer. Some nemoral species in this zone are English oak, sessile oak, Fraxinus excelsior, European ash, Ulmus glabra, elm, Norway maple, Common hazel, hazel, Alnus glutinosa, black alder, Small-leaved lime, lime, Common yew, yew, holly (southwest coast), Prunus avium, wild cherry, Allium ursinum, ramsons, beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engle ...
(a late arrival only common in Vestfold), and Primula vulgaris, primrose. Typical boreal species are Norway spruce, pine, downy birch, grey alder, aspen, rowan, Anemone nemorosa, wood anemone, and ''Viola riviniana''.
Boreal
 Boreal species are adapted to a long and cold winter, and most of these species can tolerate colder winter temperatures than winters in most of Norway. Thus they are distinguished by their need for growing season length and summer warmth. Bogs are common in the boreal zone, with the largest areas in the North and Middle Boreal Zones, as well as in the area just above the tree line. The large boreal zone is usually divided into three subzones: South Boreal, Middle Boreal, and North Boreal.
Boreal species are adapted to a long and cold winter, and most of these species can tolerate colder winter temperatures than winters in most of Norway. Thus they are distinguished by their need for growing season length and summer warmth. Bogs are common in the boreal zone, with the largest areas in the North and Middle Boreal Zones, as well as in the area just above the tree line. The large boreal zone is usually divided into three subzones: South Boreal, Middle Boreal, and North Boreal.
Boreal ecoregions
The boreal zones in Norway belong to three ecoregions. The area dominated by spruce forests (some birch, pine, willow, aspen) mostly belong to the Scandinavian and Russian taiga ecoregion (PA0608). The Scandinavian coastal conifer forests ecoregion (PA0520) in coastal areas with mild winters and frequent rainfall follows the coast from south of Stavanger north to southern Troms and includes both hemiboreal and boreal areas. Bordering the latter region is the Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands ecoregion (PA1110). This region seems to include both mountain areas with alpine tundra and lowland forests, essentially all the area outside the natural range of Norway spruce forests. This ecoregion thus shows a very large range of climatic and environmental conditions, from the temperate forest along the fjords of Western Norway to the summit ofGaldhøpiggen
Galdhøpiggen () is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia, and Northern Europe. The tall mountain is located in Lom Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is in the Jotunheimen mountains within Jotunheimen National Park. The moun ...
, and northeast to the Varanger Peninsula
The Varanger Peninsula ( no, Varangerhalvøya; sme, Várnjárga; fkv, Varenkinniemi) is a peninsula in Finnmark county, Norway. It is located in the northeasternmost part of Norway, along the Barents Sea. The peninsula has the Tanafjorden to ...
. The area above the conifer treeline is made up of mountain birch ''Betula pubescens-czerepanovii'' (''fjellbjørkeskog''). The Scots pine reaches its altitudinal limit about lower than the mountain birch.
South Boreal
 The South Boreal zone (SB) is dominated by boreal species, especially Norway spruce, and covers a total of 12% of the total land area. The SB is the only boreal zone with a few scattered—but well-developed—warmth-demanding broadleaf deciduous trees, such as European ash and oak. Several species in this zone need fairly warm summers (SB has 3–4 months with a mean 24-hr temperature of at least ), and thus are very rare in the middle boreal zone. Some of the species not found further north are black alder, Humulus lupulus, hop, Origanum vulgare, oregano, and Viburnum opulus, guelder rose. This zone is found above the hemiboreal zone, up to amsl in Østlandet and in the most southern valleys. In the eastern valleys it reaches several hundred kilometers into Gudbrandsdal and Østerdal, and up to Lom, Norway, Lom and
The South Boreal zone (SB) is dominated by boreal species, especially Norway spruce, and covers a total of 12% of the total land area. The SB is the only boreal zone with a few scattered—but well-developed—warmth-demanding broadleaf deciduous trees, such as European ash and oak. Several species in this zone need fairly warm summers (SB has 3–4 months with a mean 24-hr temperature of at least ), and thus are very rare in the middle boreal zone. Some of the species not found further north are black alder, Humulus lupulus, hop, Origanum vulgare, oregano, and Viburnum opulus, guelder rose. This zone is found above the hemiboreal zone, up to amsl in Østlandet and in the most southern valleys. In the eastern valleys it reaches several hundred kilometers into Gudbrandsdal and Østerdal, and up to Lom, Norway, Lom and Skjåk
Skjåk is a municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Gudbrandsdal. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Bismo. Most of the municipal residents live in the Billingsdalen an ...
, in Ottadalen. Along the southwestern coast, the zone reaches an elevation of at the head of large fjords (such as in Lærdal), and about nearer to the coast. Norway spruce is lacking in Vestlandet
Western Norway ( nb, Vestlandet, Vest-Norge; nn, Vest-Noreg) is the region along the Atlantic coast of southern Norway. It consists of the counties Rogaland, Vestland, and Møre og Romsdal. The region has no official or political-administrative ...
(Voss is an exception). North of Ålesund, SB vegetation predominates in the lowland down to sea level, including islands such as Hitra. Most of the lowland in Trøndelag below elevation is SB, up to above sea level in inland valleys such as Gauldalen and Verdalen, and up to in Namdalen
Namdalen ( sma, Nååmesjevuemie) is a Districts of Norway, traditional district in the central part of Norway, consisting of the municipalities Namsos, Grong, Overhalla, Røyrvik, Nærøysund, Høylandet, Flatanger, Lierne, Leka, Norway, Leka, ...
. The coastal areas and some fjord areas further north—such as Vikna, Brønnøy, and the best locations along the Helgeland
Helgeland is the most southerly district in Northern Norway. Generally speaking, Helgeland refers to the part of Nordland county that is located south of the Arctic Circle. It is bordered in the north by the Saltfjellet mountains and Svartise ...
coast—is SB north to the mouth of Ranfjord, while inland areas north of Grong are dominated by Middle Boreal zone vegetation in the lowland. There are small isolated areas with SB vegetation further north, as in Bodø and Fauske, the most northern location being a narrow strip along the northern shore of Ofotfjord; and the endemic Nordland-whitebeam only grows in Bindal. Agriculture in Norway, including grain cultivation, takes place mostly in the hemiboreal and SB zones.
Middle Boreal
Nordland
Nordland (; smj, Nordlánnda, sma, Nordlaante, sme, Nordlánda, en, Northland) is a county in Norway in the Northern Norway region, the least populous of all 11 counties, bordering Troms og Finnmark in the north, Trøndelag in the south, N ...
(the Siberian spruce variant occurs in the Pasvik valley), due to mountain ranges blocking their advance, but is often planted in MB areas further north for economic reasons, contributing to a different landscape. Birch is usually dominant in these northern areas; but pine, aspen, rowan, Prunus padus, bird cherry and grey alder are also common. This MB birch is often a cross between silver birch and downy birch and is taller () than the birch growing near the tree line. Conifers will grow taller. Some alpine plants grow in the MB zone; nemoral species are rare. The understory (undergrowth) is usually well developed if the forest is not too dense. Many plants do not grow further north: grey alder, silver birch, Galium verum, yellow bedstraw, Rubus idaeus, raspberry, Artemisia vulgaris, mugwort, and ''Myrica gale'' are examples of species in this zone that do not grow further north or higher up. MB is located at an altitude of in Østlandet, up to in the southern valleys, ( at the head of the long fjords) on the southwest coast, and in Trøndelag ( in the interior, as at Røros and Oppdal). Further north, MB is common in the lowland: up to above sea level in Lofoten and Vesterålen, at Narvik, at Tromsø, in inland valleys in Troms, and the lowland at the head of Altafjord
Altafjord ( en, Alta Fjord;Koop, Gerhard, & Klaus-Peter Schmolke. 2000. ''Heavy Cruisers of the Admiral Hipper Class: Warships of the Kriegsmarine''. Barnsley, UK: Seaforth Publishing, p. 55. no, Altafjorden; fkv, Alattionvuono) is a fjord in A ...
is the most northerly area of any size—small pockets exist at Porsanger and Sør-Varanger. This is usually the most northerly area with some farming activity, and barley was traditionally grown even as far north as Alta, Norway, Alta.
North Boreal

 The North Boreal (NB) zone, (also known as open or sparse taiga) is the zone closest to the
The North Boreal (NB) zone, (also known as open or sparse taiga) is the zone closest to the tree line
The tree line is the edge of the habitat at which trees are capable of growing. It is found at high elevations and high latitudes. Beyond the tree line, trees cannot tolerate the environmental conditions (usually cold temperatures, extreme snowp ...
, bordering the alpine or polar area, and dominated by a harsh subarctic climate. There are at least 30 summer days with a mean temperature of or more, up to about two months. The trees grow very slowly and generally do not get very large. The forest is not as dense as further south or at lower altitudes and is known as the mountain forest (''Fjellskog''). The NB zone covers a total of 28% of the total land area of Norway, including almost half of Finnmark, where the mountain birch grows down to sea level. The lower part of this zone also has conifers, but the tree line in Norway is mostly formed by mountain birch, a subspecies of downy birch (subspecies ''czerepanovii''), which is not to be confused with dwarf birch). Spruce and pine make up the tree line in some mountain areas with a more continental climate. Alpine plants are common in this zone. The birch forest above sea level at Sikilsdalshorn is the highest tree line in Norway, while a birch at 1,404 m ASL in Veodal, Jotunheimen, is the highest growing single tree. The tree line is lower closer to the coast and in areas with lower mountains, due to cooler summers, more wind near mountain summits, and more snow in the winter (coastal mountains) leading to later snowmelt. The NB zone covers large areas at altitude in the interior of Østlandet; is in the central mountain areas; but at the western coast the tree line is down to about above sea level, increasing significantly in the long fjords ( at the head of Sognefjord
The Sognefjord or Sognefjorden (, en, Sogn Fjord), nicknamed the King of the Fjords ( no, Fjordenes konge), is the largest and deepest fjord in Norway. Located in Vestland county in Western Norway, it stretches inland from the ocean to the smal ...
). Further north, large areas in the interior highlands or uplands of Trøndelag and North Norway are dominated by the NB zone, with the tree line at about amsl in the interior of Trøndelag, in Rana, Norway, Rana, at Narvik, at Tromsø, at Kirkenes and at Hammerfest (only pockets in sheltered areas). The large Finnmarksvidda
Finnmarksvidda ( sme, Finnmárkkoduottar; en, Finnmark plateau/highland) is Norway's largest plateau, with an area greater than . The plateau lies about above sea level. Approximately 36% of Finnmark lies on the Finnmarksvidda.
Geography
Fr ...
plateau is at an altitude placing it almost exactly at the tree line. The last patch of NB zone gives way to tundra at sea level about south of the North Cape plateau (near Skarsvåg). Areas south of this line are tundra-like with scattered patches of mountain birch woodland (forest tundra) and become alpine tundra even at minor elevations. The trees near the tree line are often bent by snow, wind, and growing-season frost; and their height is only . Outside Norway (and adjacent areas in Sweden), the only other areas in the world with the tree line mostly made up by a small-leaved deciduous tree such as birch—in contrast to conifers—are Iceland and the Kamtschatka peninsula.
The presence of a conifer tree line is sometimes used (''Barskoggrense'') to divide this zone into two subzones, as the conifers will usually not grow as high up as the mountain birch. Spruce and pine grow at nearly above sea level in some areas of Jotunheimen, down to in Bergen ( at the head of Sognefjord), at Lillehammer (mountains near Oslo are too low to have a tree line), at Trondheim ( at Oppdal), at Narvik, at Harstad, at Alta; and the most northerly pine forest in the world is in Stabbursdalen National Park in Porsanger. There are some forests in this part of the NB zone; and some conifers can grow quite large even if growth is slow.
Tundra
 Alpine tundra is common in Norway, covering a total of 32% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen) and belonging to the Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands ecoregion (PA1110). The area closest to the tree line (low alpine) has continuous plant cover, with Salix, willow species such as ''Salix glauca'', ''Salix lanata, S. lanata'', and ''Salix lapponum, S. lapponum'' ( tall); blueberry, Juniperus communis, common juniper, and Linnaea borealis, twinflower are also common. The low alpine area was traditionally used as summer pasture, and in part still is. This zone reaches an elevation of in Jotunheimen, including most of
Alpine tundra is common in Norway, covering a total of 32% of the land area (excluding Svalbard and Jan Mayen) and belonging to the Scandinavian Montane Birch forest and grasslands ecoregion (PA1110). The area closest to the tree line (low alpine) has continuous plant cover, with Salix, willow species such as ''Salix glauca'', ''Salix lanata, S. lanata'', and ''Salix lapponum, S. lapponum'' ( tall); blueberry, Juniperus communis, common juniper, and Linnaea borealis, twinflower are also common. The low alpine area was traditionally used as summer pasture, and in part still is. This zone reaches an elevation of in Jotunheimen, including most of Hardangervidda
Hardangervidda ( en, Hardanger Plateau) is a mountain plateau (Norwegian: ''vidde'') in central southern Norway, covering parts of Vestland, Vestfold og Telemark, and Viken counties. It is the largest plateau of its kind in Europe, with a cold ye ...
; in eastern Trollheimen
Trollheimen is a mountain range in Møre og Romsdal and Trøndelag counties in central Norway. The mountain range is part of the Scandinavian Mountains.
Etymology
The name ('the home of the trolls') was proposed by Håkon Løken and used by Tr ...
; and about at Narvik and the Lyngen Alps
The Lyngen Alps ( no, Lyngsalpene) are a mountain range in northeastern Troms og Finnmark county in Norway, east of the Tromsø (city), city of Tromsø. The mountain range runs through the municipalities of Lyngen, Balsfjord, and Storfjord. The mo ...
. Higher up (mid-alpine tundra) the plants become smaller; mosses and lichens are more predominant; and plants still cover most of the ground, even if snowfields lasting into mid-summer and permafrost are common. At the highest elevations (high-alpine tundra) the ground is dominated by bare rock, snow, and glaciers, with few plants.

 The highest weather station in Norway—Fanaråken in Luster, Norway, Luster, at —has barely three months of above freezing temperatures and a July average of . Still, glacier buttercup has been found only below the summit of
The highest weather station in Norway—Fanaråken in Luster, Norway, Luster, at —has barely three months of above freezing temperatures and a July average of . Still, glacier buttercup has been found only below the summit of Galdhøpiggen
Galdhøpiggen () is the highest mountain in Norway, Scandinavia, and Northern Europe. The tall mountain is located in Lom Municipality in Innlandet county, Norway. It is in the Jotunheimen mountains within Jotunheimen National Park. The moun ...
, and moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hor ...
es and lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.Varanger Peninsula
The Varanger Peninsula ( no, Varangerhalvøya; sme, Várnjárga; fkv, Varenkinniemi) is a peninsula in Finnmark county, Norway. It is located in the northeasternmost part of Norway, along the Barents Sea. The peninsula has the Tanafjorden to ...
and the Nordkinn Peninsula) is a small lowland tundra area which is often considered part of the Kola Peninsula tundra ecoregion (PA1106). Svalbard and Jan Mayen have tundra vegetation except for areas covered by glaciers; and some areas, such as the cliffs at southern Bear Island (Norway), Bear Island, are fertilized by seabird colonies. This tundra is often considered part of the Arctic Desert ecoregion (PA1101). The lushest areas on these Arctic islands are sheltered fjord areas at Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norw ...
; they have the highest summer temperatures and the very dry climate makes for little snow and thus comparatively early snowmelt. The short growing season and the permafrost underneath the active layer provide enough moisture. Plants include dwarf birch, Rubus chamaemorus, cloudberry, Svalbard poppy, and Campanula rotundifolia, harebell.
A warmer climate would push the vegetation zones significantly northwards and to higher elevations.
Natural resources
In addition to oil and natural gas, hydroelectric power, and fish and forest resources, Norway has reserves of ferric and nonferric metal ores. Many of these have been exploited in the past but whose mines are now idle because of low-grade purity and high operating costs. Europe's largest titanium deposits are near the southwest coast. Coal is mined in the Svalbard islands. Resources: Petroleum, copper, natural gas, pyrites, nickel, iron ore, zinc, lead, fish, lumber, hydropower.Land use

 Arable land: 3.3% (in use; some more marginal areas are not in use or used as pastures)
* Permanent crops: 0%
* Permanent pastures: 0%
* Forests and woodland: 38% of land area is covered by forest, 21% by Scandinavian coastal conifer forests, conifer forest, and 17% by deciduous forest, increasing as many pastures in the higher elevations and some coastal, man-made heath (habitat), heaths are no longer used or reforested, as well as increase due to warmer summers
* Other: 59% (mountains and heaths 46%, bogs and wetlands 6.3%, lakes and rivers 5.3%, urban areas 1.1%)
Irrigated land: , 1993 estimate
Natural hazards:
* European windstorms with hurricane-strength winds along the coast and in the mountains are not uncommon. For centuries one out of four males in coastal communities were lost at sea.
* Avalanches on steep slopes, especially in the northern part of the country and in mountain areas.
* Landslides have on occasions killed people, mostly in areas with soil rich in marine clay, as in lowland areas near Trondheimsfjord.
* Tsunamis have killed people; usually caused by parts of mountains (rockslide) falling into fjords or lakes. This happened 1905 in Loen, Norway, Loen in
Arable land: 3.3% (in use; some more marginal areas are not in use or used as pastures)
* Permanent crops: 0%
* Permanent pastures: 0%
* Forests and woodland: 38% of land area is covered by forest, 21% by Scandinavian coastal conifer forests, conifer forest, and 17% by deciduous forest, increasing as many pastures in the higher elevations and some coastal, man-made heath (habitat), heaths are no longer used or reforested, as well as increase due to warmer summers
* Other: 59% (mountains and heaths 46%, bogs and wetlands 6.3%, lakes and rivers 5.3%, urban areas 1.1%)
Irrigated land: , 1993 estimate
Natural hazards:
* European windstorms with hurricane-strength winds along the coast and in the mountains are not uncommon. For centuries one out of four males in coastal communities were lost at sea.
* Avalanches on steep slopes, especially in the northern part of the country and in mountain areas.
* Landslides have on occasions killed people, mostly in areas with soil rich in marine clay, as in lowland areas near Trondheimsfjord.
* Tsunamis have killed people; usually caused by parts of mountains (rockslide) falling into fjords or lakes. This happened 1905 in Loen, Norway, Loen in Stryn
Stryn is a municipality in the county of Vestland, Norway. It is located in the traditional district of Nordfjord. The administrative center of the municipality is the village of Stryn. The municipality is located along the innermost part of t ...
when parts of Ramnefjell fell into Loenvatnet lake, causing a tsunami which killed 61 people. It happened again in the same place in 1936, this time with 73 victims. 40 people were killed in Tafjord in Norddal in 1934.
Environmental concerns
Current issues

 Environmental concerns in Norway include how to cut greenhouse gas emissions, pollution of the air and water, loss of habitat, damage to cold-water coral reefs from Fishing trawler, trawlers, and salmon fish farming threatening the wild salmon by spawning in the rivers, thereby diluting the fish DNA. Acid rain has damaged lakes, rivers and forests, especially in the southernmost part of the country, and most wild salmon populations in Sørlandet have died. Due to lower emissions in Europe, acid rain in Norway has decreased by 40% from 1980 to 2003. Another concern is a possible increase in extreme weather. In the future, climate models predict increased precipitation, especially in the areas with currently high precipitation, and also predict more episodes with heavy precipitation within a short period, which can cause landslides and local floods. Winters will probably be significant milder, and the sea-ice cover in the
Environmental concerns in Norway include how to cut greenhouse gas emissions, pollution of the air and water, loss of habitat, damage to cold-water coral reefs from Fishing trawler, trawlers, and salmon fish farming threatening the wild salmon by spawning in the rivers, thereby diluting the fish DNA. Acid rain has damaged lakes, rivers and forests, especially in the southernmost part of the country, and most wild salmon populations in Sørlandet have died. Due to lower emissions in Europe, acid rain in Norway has decreased by 40% from 1980 to 2003. Another concern is a possible increase in extreme weather. In the future, climate models predict increased precipitation, especially in the areas with currently high precipitation, and also predict more episodes with heavy precipitation within a short period, which can cause landslides and local floods. Winters will probably be significant milder, and the sea-ice cover in the Arctic ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, a ...
might melt altogether in summer, threatening the survival of the polar bear on Svalbard. Both terrestrial and aquatic species are expected to shift northwards, and this is already observed for some species; the growing red deer population is spreading northwards and eastwards, with 2008 being the first hunting season which saw more red deer (35,700) than moose shot. Migratory birds are arriving earlier; trees are coming into leaf earlier; mackerel are becoming common in summer off the coast of Troms
Troms (; se, Romsa; fkv, Tromssa; fi, Tromssa) is a former county in northern Norway. On 1 January 2020 it was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger is expected to be reversed by t ...
. The total number of species in Norway are expected to rise due to new species arriving. Norwegians are statistically among the most worried when it comes to global warming and its effects, even if Norway is among the countries expected to be least negatively affected by global warming, with some possible gains.
International agreements
Norway is a party to: * Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty * Antarctic Treaty System * United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, * Environmental Modification Convention, * Law of the Sea * London Convention on the Prevention of Marine Pollution by Dumping of Wastes and Other Matter * Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty * Montreal Protocol (ozone layer protection) * MARPOL 73/78 (ship pollution) * International Tropical Timber Agreement, 1983 * International Tropical Timber Agreement, 1994 * Kyoto Protocol (climate change) * ADR (treaty), ADR (road transport of hazardous materials)See also
* Geography of Europe * Extreme points of Norway * Districts of Norway * List of urban areas in Norway by population * Global warming in Norway * List of national parks of Norway * List of rivers of Norway * :Fjords of Norway, Fjords of Norway * :Glaciers of Norway, Glaciers of Norway * :Islands of Norway, Islands of Norway * :Lakes of Norway, Lakes of Norway * :Mountains of Norway, Mountains of Norway * :Rivers of Norway, Rivers of Norway * :Valleys of Norway, Valleys of Norway * :Volcanoes of Norway, Volcanoes of Norway * :Waterfalls of Norway, Waterfalls of NorwayReferences
Sources
* Tollefsrud, J.; Tjørve, E.; Hermansen, P.: ''Perler i Norsk Natur - En Veiviser''. Aschehoug, 1991. * Gjærevoll, Olav. "Plantegeografi". Tapir, 1992. * Moen, A. 1998. ''Nasjonalatlas for Norge: Vegetasjon.'' Statens Kartverk, Hønefoss. * Norwegian Meteorological Institute. * Bjørbæk, G. 2003. ''Norsk vær i 110 år.'' N.W. DAMM & Sønn. * Førland, E.. ''Variasjoner i vekst og fyringsforhold i Nordisk Arktis''. Regclim/Cicerone 6/2004. * University of Oslo. ''Almanakk for Norge'' Gyldendal fakta.
External links
Statistics Norway
NGU - Geological survey of Norway
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Norway Geography of Norway,