Gaussian noise on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]



Encyclopedia of Mathematics
* Gauss's hypergeometric theorem, an identity on hypergeometric series * Gauss plane
 * Gauss–Kuzmin distribution, a
* Gauss–Kuzmin distribution, a
website of University of Toronto
* Gauss linking integral (
WolframMathWorld
*Gaussian's
 *
*
File:Carl.Friedrich.Gauss.Bueste.vor1900.GFZ.jpg, Bust by ''Hans Weddo von Glümer'' (1895) in the German Research Centre for Geosciences in
File:DBP 1955 204 Carl Friedrich Gauß.jpg, Stamp (West Germany) 1955
File:DBP 1977 928 Carl Friedrich Gauß.jpg, Stamp (West Germany) 1977
File:Stamp Carl Friedrich Gauß.jpg, Stamp (East Germany) 1977
File:1856 Friedrich Brehmer Denkmünze auf Gauss nach Christian Heinrich Hesemann im Auftrag von Georg. V. von Hannover, Medaille Avers mit Portrait.jpg, Medal for Gauss (1856, front)
File:1856 Friedrich Brehmer Denkmünze auf Gauss nach Christian Heinrich Hesemann im Auftrag von Georg. V. von Hannover, Medaille Revers mit Efeukranz, Gipsmodell.jpg, Medal for Gauss (1856, back) "mathematicorum principi"

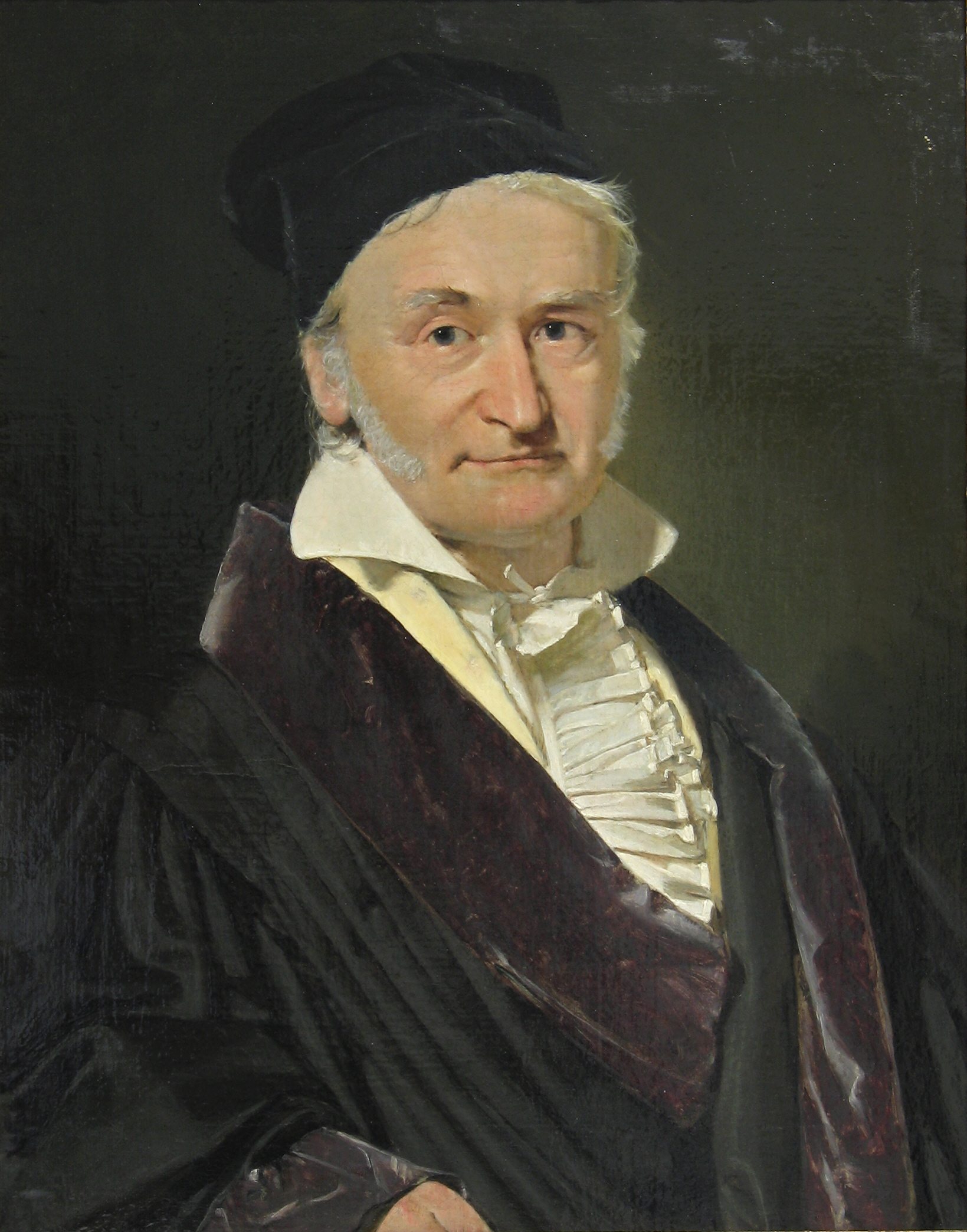
Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observatory and ...
(1777–1855) is the eponym
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymous adjective ''Gaussian'' is pronounced .
Mathematics
Algebra
Algebra is a branch of mathematics that deals with abstract systems, known as algebraic structures, and the manipulation of expressions within those systems. It is a generalization of arithmetic that introduces variables and algebraic ope ...
and linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician w ...
and differential geometry
Differential geometry is a Mathematics, mathematical discipline that studies the geometry of smooth shapes and smooth spaces, otherwise known as smooth manifolds. It uses the techniques of Calculus, single variable calculus, vector calculus, lin ...
Number theory
Number theory is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic functions. Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects constructed from integers (for example ...
Cyclotomic field
In algebraic number theory, a cyclotomic field is a number field obtained by adjoining a complex root of unity to \Q, the field of rational numbers.
Cyclotomic fields played a crucial role in the development of modern algebra and number theory ...
s
*Gaussian period
In mathematics, in the area of number theory, a Gaussian period is a certain kind of sum of root of unity, roots of unity. The periods permit explicit calculations in cyclotomic fields connected with Galois theory and with harmonic analysis (discre ...
*Gaussian rational
In mathematics, a Gaussian rational number is a complex number of the form ''p'' + ''qi'', where ''p'' and ''q'' are both rational numbers.
The set of all Gaussian rationals forms the Gaussian rational field, denoted Q(''i''), obtained b ...
* Gauss sum, an exponential sum over Dirichlet characters
** Elliptic Gauss sum, an analog of a Gauss sum
** Quadratic Gauss sum
Analysis
Analysis (: analyses) is the process of breaking a complex topic or substance into smaller parts in order to gain a better understanding of it. The technique has been applied in the study of mathematics and logic since before Aristotle (38 ...
, numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic computation, symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of ...
, vector calculus
Vector calculus or vector analysis is a branch of mathematics concerned with the differentiation and integration of vector fields, primarily in three-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3. The term ''vector calculus'' is sometimes used as a ...
and calculus of variations
The calculus of variations (or variational calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in Function (mathematics), functions
and functional (mathematics), functionals, to find maxima and minima of f ...
Complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic ...
and convex analysis
Convex analysis is the branch of mathematics devoted to the study of properties of convex functions and convex sets, often with applications in convex optimization, convex minimization, a subdomain of optimization (mathematics), optimization theor ...
* Gauss–Lucas theorem
* Gauss's continued fraction, an analytic continued fraction derived from the hypergeometric functions
* Gauss's criterion – described oEncyclopedia of Mathematics
* Gauss's hypergeometric theorem, an identity on hypergeometric series * Gauss plane
Statistics
discrete probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an experiment. It is a mathematical description of a random phenomenon in terms of its sample spa ...
* Gauss–Markov process
*Gauss–Markov theorem
In statistics, the Gauss–Markov theorem (or simply Gauss theorem for some authors) states that the ordinary least squares (OLS) estimator has the lowest sampling variance within the class of linear unbiased estimators, if the errors in ...
* Gaussian copula
*Gaussian measure
In mathematics, Gaussian measure is a Borel measure on finite-dimensional Euclidean space \mathbb^n, closely related to the normal distribution in statistics. There is also a generalization to infinite-dimensional spaces. Gaussian measures are na ...
** Gaussian correlation inequality
** Gaussian isoperimetric inequality
* Gauss's inequality
* Gauss-Helmert model
Gaussian function and topics named for it
Knot theory
* Gauss code – described owebsite of University of Toronto
* Gauss linking integral (
knot theory
In topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be und ...
)
Other mathematical areas
* Gauss's algorithm for determination of the day of the week * Gauss's Easter algorithm * Gaussian brackets – described oWolframMathWorld
*Gaussian's
modular arithmetic
In mathematics, modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic operations for integers, other than the usual ones from elementary arithmetic, where numbers "wrap around" when reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modern approach to mo ...
*Gaussian integer
In number theory, a Gaussian integer is a complex number whose real and imaginary parts are both integers. The Gaussian integers, with ordinary addition and multiplication of complex numbers, form an integral domain, usually written as \mathbf ...
, usually written as
:* Gaussian prime
* Gaussian logarithms (also known as addition and subtraction logarithms)
* Gauss congruence for integer sequences
Cartography
* Gauss–Krüger coordinate system * Gaussian gridPhysics
Optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
* Gauss lens
* Double-Gauss lens
*Gaussian optics
Gaussian optics is a technique in geometrical optics that describes the behaviour of light rays in optical systems by using the paraxial approximation, in which only rays which make small angles with the optical axis of the system are considered. ...
Classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics inv ...
* Gauss's principle of least constraint
*For orbit determination in orbital mechanics
Orbital mechanics or astrodynamics is the application of ballistics and celestial mechanics to rockets, satellites, and other spacecraft. The motion of these objects is usually calculated from Newton's laws of motion and the law of universal ...
:
** Gauss's law for gravity
**Gaussian gravitational constant
The Gaussian gravitational constant (symbol ) is a parameter used in the orbital mechanics of the Solar System.
It relates the orbital period to the orbit's semi-major axis and the mass of the orbiting body in Solar masses.
The value of histor ...
** Gaussian year
** Gauss's method
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
* Gaussian orbital
Electromagnetism
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge via electromagnetic fields. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces of nature. It is the dominant force in the interacti ...
 *
*Gaussian units
Gaussian units constitute a metric system of units of measurement. This system is the most common of the several electromagnetic unit systems based on the centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS). It is also called the Gaussian unit syst ...
*gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
, the CGS unit for magnetic flux density
* Degaussing, to demagnetize an object
* Gauss rifle or coilgun
* Gauss's law for magnetism
* Gaussian surface
** Gauss's law, giving the relationship between flux through a closed surface and the enclosed source
* Gauss gun
Awards and recognitions
*Carl Friedrich Gauss Prize
The Carl Friedrich Gauss Prize for Applications of Mathematics is a mathematics award, granted jointly by the International Mathematical Union and the German Mathematical Society for "outstanding mathematical contributions that have found signific ...
, a mathematics award
* Gauss Lectureship, a mathematical distinction
* The Gauss Mathematics Competition in Canadian junior high schools, an annual national mathematics competition administered by the Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing
Other things named for him
Biology
160px, Gaussia maya * '' Gaussia'', a palm genus described by Hermann Wendland with the then new species '' Gaussia princeps'', collected by Charles Wright in western Cuba. Named in "memoriam astronomi Caroli Friderici Gauss". * '' Gaussia'', a genus ofcopepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sedimen ...
s
Informatics
* Gaussian, a computational chemistry software program *GAUSS
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
, a matrix programming language for mathematics and statistics
Place names and expedition named in his honour
Terrestrial *The Gauss expedition, the first German expedition to Antarctica (1901–1903) ** The ship ''Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
'', used in the Gauss expedition to the Antarctic
* Gaussberg
Gaussberg (or Schwarzen Berg, Mount Gauss) is an extinct, high volcanic cone in East Antarctica fronting on Davis Sea immediately west of Posadowsky Glacier (Antarctica), Posadowsky Glacier. It is ice-free and conical in nature, having formed s ...
in Antarctica, an extinct volcano discovered by the Gauss expedition
* Mount Gauss, in Antarctica
* Gauss Peninsula, East Greenland
* Gaussberg, a hill in Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( ; from Low German , local dialect: ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the ...
Celestial
* Crater Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
on the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
* Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet—an object larger than a meteoroid that is neither a planet nor an identified comet—that orbits within the Solar System#Inner Solar System, inner Solar System or is co-orbital with Jupiter (Trojan asteroids). As ...
1001 Gaussia
Institutions and buildings named in his honour
* The ''Carl-Friedrich-Gauss Fakultät'' of Braunschweig University of Technology * Several schools in Germany named after Gauss * Several buildings named "Gauss Haus" or "Gauss Building": ** Gauss Tower, an observation tower in Dransfeld, Germany ** The Gauss Building at theUniversity of Idaho
The University of Idaho (U of I, or UIdaho) is a public land-grant research university in Moscow, Idaho, United States. Established in 1889 and opened three years later, it was the state's sole university for 71 years, until 1963.
The un ...
(College of Engineering)
** Gauss Haus, an NMR
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which atomic nucleus, nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic field (in the near and far field, near field) and respond by producing ...
center at the University of Utah
The University of Utah (the U, U of U, or simply Utah) is a public university, public research university in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It was established in 1850 as the University of Deseret (Book of Mormon), Deseret by the General A ...
** The 'Gauss House', a common room in the University of Sussex Mathematical and Physical Sciences department.
** A dormitory building is named after him in University of California, Santa Cruz, in Crown College
Monuments, busts, and memorial plaques
Gauss Monuments were erected in Brunswick and Göttingen (the last together with Weber). Busts of Gauss were placed in the Walhalla hall of fame nearRegensburg
Regensburg (historically known in English as Ratisbon) is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the rivers Danube, Naab and Regen (river), Regen, Danube's northernmost point. It is the capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the ...
and in the German Research Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
. Several places where Gauss has stayed in Germany are marked with plaques.
Potsdam
Potsdam () is the capital and largest city of the Germany, German States of Germany, state of Brandenburg. It is part of the Berlin/Brandenburg Metropolitan Region. Potsdam sits on the Havel, River Havel, a tributary of the Elbe, downstream of B ...
File:Carl Friedrich Gauß, Büste von Friedrich Künkler, 001.jpg, Bust by Friedrich Künkler (1810)
File:Gauss Stein Wilseder Berg.jpg, Gauss memorial on the Wilseder Berg, highest point in the Luneburg Heath
File:Walhalla wie Parthenon zu Ehren bedeutender Personen - erbaut 1842 - König Ludwig I - Foto Wolfgang Pehlemann DSCN2430.jpg, A bust of Gauss is placed in the Walhalla since 2007
Other commemorations
Germany issued three postage stamps honoring Gauss, one in 1955 on the hundredth anniversary of his death and two others in 1977, the 200th anniversary of his birth.References
{{reflistGauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; ; ; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician, astronomer, Geodesy, geodesist, and physicist, who contributed to many fields in mathematics and science. He was director of the Göttingen Observat ...
List of things