Gamma-Ray Burst Optical Near-Infrared Detector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the

 One example of gamma ray production due to radionuclide decay is the decay scheme for cobalt-60, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. First, decays to excited by beta decay emission of an electron of . Then the excited decays to the ground state (see nuclear shell model) by emitting gamma rays in succession of 1.17 MeV followed by . This path is followed 99.88% of the time:
:
Another example is the alpha decay of to form ; which is followed by gamma emission. In some cases, the gamma emission spectrum of the daughter nucleus is quite simple, (e.g. /) while in other cases, such as with (/ and /), the gamma emission spectrum is complex, revealing that a series of nuclear energy levels exist.
One example of gamma ray production due to radionuclide decay is the decay scheme for cobalt-60, as illustrated in the accompanying diagram. First, decays to excited by beta decay emission of an electron of . Then the excited decays to the ground state (see nuclear shell model) by emitting gamma rays in succession of 1.17 MeV followed by . This path is followed 99.88% of the time:
:
Another example is the alpha decay of to form ; which is followed by gamma emission. In some cases, the gamma emission spectrum of the daughter nucleus is quite simple, (e.g. /) while in other cases, such as with (/ and /), the gamma emission spectrum is complex, revealing that a series of nuclear energy levels exist.

 Due to their penetrating nature, gamma rays require large amounts of shielding mass to reduce them to levels which are not harmful to living cells, in contrast to alpha particles, which can be stopped by paper or skin, and
Due to their penetrating nature, gamma rays require large amounts of shielding mass to reduce them to levels which are not harmful to living cells, in contrast to alpha particles, which can be stopped by paper or skin, and
 When a gamma ray passes through matter, the probability for absorption is proportional to the thickness of the layer, the density of the material, and the absorption cross section of the material. The total absorption shows an exponential decrease of intensity with distance from the incident surface:
:
where x is the thickness of the material from the incident surface, μ= ''n''σ is the absorption coefficient, measured in cm−1, ''n'' the number of atoms per cm3 of the material (atomic density) and σ the absorption cross section in cm2.
As it passes through matter, gamma radiation ionizes via three processes:
*The photoelectric effect: This describes the case in which a gamma photon interacts with and transfers its energy to an atomic electron, causing the ejection of that electron from the atom. The kinetic energy of the resulting photoelectron is equal to the energy of the incident gamma photon minus the energy that originally bound the electron to the atom (binding energy). The photoelectric effect is the dominant energy transfer mechanism for X-ray and gamma ray photons with energies below 50 keV (thousand electronvolts), but it is much less important at higher energies.
* Compton scattering: This is an interaction in which an incident gamma photon loses enough energy to an atomic electron to cause its ejection, with the remainder of the original photon's energy emitted as a new, lower energy gamma photon whose emission direction is different from that of the incident gamma photon, hence the term "scattering". The probability of Compton scattering decreases with increasing photon energy. It is thought to be the principal absorption mechanism for gamma rays in the intermediate energy range 100 keV to 10 MeV. It is relatively independent of the atomic number of the absorbing material, which is why very dense materials like lead are only modestly better shields, on a ''per weight'' basis, than are less dense materials.
* Pair production: This becomes possible with gamma energies exceeding 1.02 MeV, and becomes important as an absorption mechanism at energies over 5 MeV (see illustration at right, for lead). By interaction with the
When a gamma ray passes through matter, the probability for absorption is proportional to the thickness of the layer, the density of the material, and the absorption cross section of the material. The total absorption shows an exponential decrease of intensity with distance from the incident surface:
:
where x is the thickness of the material from the incident surface, μ= ''n''σ is the absorption coefficient, measured in cm−1, ''n'' the number of atoms per cm3 of the material (atomic density) and σ the absorption cross section in cm2.
As it passes through matter, gamma radiation ionizes via three processes:
*The photoelectric effect: This describes the case in which a gamma photon interacts with and transfers its energy to an atomic electron, causing the ejection of that electron from the atom. The kinetic energy of the resulting photoelectron is equal to the energy of the incident gamma photon minus the energy that originally bound the electron to the atom (binding energy). The photoelectric effect is the dominant energy transfer mechanism for X-ray and gamma ray photons with energies below 50 keV (thousand electronvolts), but it is much less important at higher energies.
* Compton scattering: This is an interaction in which an incident gamma photon loses enough energy to an atomic electron to cause its ejection, with the remainder of the original photon's energy emitted as a new, lower energy gamma photon whose emission direction is different from that of the incident gamma photon, hence the term "scattering". The probability of Compton scattering decreases with increasing photon energy. It is thought to be the principal absorption mechanism for gamma rays in the intermediate energy range 100 keV to 10 MeV. It is relatively independent of the atomic number of the absorbing material, which is why very dense materials like lead are only modestly better shields, on a ''per weight'' basis, than are less dense materials.
* Pair production: This becomes possible with gamma energies exceeding 1.02 MeV, and becomes important as an absorption mechanism at energies over 5 MeV (see illustration at right, for lead). By interaction with the
 Gamma rays provide information about some of the most energetic phenomena in the universe; however, they are largely absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere. Instruments aboard high-altitude balloons and satellites missions, such as the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, provide our only view of the universe in gamma rays.
Gamma-induced molecular changes can also be used to alter the properties of semi-precious stones, and is often used to change white
Gamma rays provide information about some of the most energetic phenomena in the universe; however, they are largely absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere. Instruments aboard high-altitude balloons and satellites missions, such as the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope, provide our only view of the universe in gamma rays.
Gamma-induced molecular changes can also be used to alter the properties of semi-precious stones, and is often used to change white
 The conventional distinction between X-rays and gamma rays has changed over time. Originally, the electromagnetic radiation emitted by X-ray tubes almost invariably had a longer wavelength than the radiation (gamma rays) emitted by radioactive nuclei. Older literature distinguished between X- and gamma radiation on the basis of wavelength, with radiation shorter than some arbitrary wavelength, such as 10−11 m, defined as gamma rays. Since the energy of photons is proportional to their frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength, this past distinction between X-rays and gamma rays can also be thought of in terms of its energy, with gamma rays considered to be higher energy electromagnetic radiation than are X-rays.
However, since current artificial sources are now able to duplicate any electromagnetic radiation that originates in the nucleus, as well as far higher energies, the wavelengths characteristic of radioactive gamma ray sources vs. other types now completely overlap. Thus, gamma rays are now usually distinguished by their origin: X-rays are emitted by definition by electrons outside the nucleus, while gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus. Exceptions to this convention occur in astronomy, where gamma decay is seen in the afterglow of certain supernovas, but radiation from high energy processes known to involve other radiation sources than radioactive decay is still classed as gamma radiation.
The conventional distinction between X-rays and gamma rays has changed over time. Originally, the electromagnetic radiation emitted by X-ray tubes almost invariably had a longer wavelength than the radiation (gamma rays) emitted by radioactive nuclei. Older literature distinguished between X- and gamma radiation on the basis of wavelength, with radiation shorter than some arbitrary wavelength, such as 10−11 m, defined as gamma rays. Since the energy of photons is proportional to their frequency and inversely proportional to wavelength, this past distinction between X-rays and gamma rays can also be thought of in terms of its energy, with gamma rays considered to be higher energy electromagnetic radiation than are X-rays.
However, since current artificial sources are now able to duplicate any electromagnetic radiation that originates in the nucleus, as well as far higher energies, the wavelengths characteristic of radioactive gamma ray sources vs. other types now completely overlap. Thus, gamma rays are now usually distinguished by their origin: X-rays are emitted by definition by electrons outside the nucleus, while gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus. Exceptions to this convention occur in astronomy, where gamma decay is seen in the afterglow of certain supernovas, but radiation from high energy processes known to involve other radiation sources than radioactive decay is still classed as gamma radiation.
 For example, modern high-energy X-rays produced by
For example, modern high-energy X-rays produced by
Basic reference on several types of radiation
Radiation Q & ARadiation information
The Lund/LBNL Nuclear Data Search
– Contains information on gamma-ray energies from isotopes.
The LIVEChart of Nuclides – IAEA
with filter on gamma-ray energy
Health Physics Society Public Education Website
{{Authority control Electromagnetic spectrum IARC Group 1 carcinogens Nuclear physics Radiation Radioactivity Articles containing video clips
 A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or ), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
of atomic nuclei
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron ...
. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically shorter than those of X-rays. With frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
above 30 exahertz (), it imparts the highest photon energy
Photon energy is the energy carried by a single photon. The amount of energy is directly proportional to the photon's electromagnetic frequency and thus, equivalently, is inversely proportional to the wavelength. The higher the photon's frequency, ...
. Paul Villard
Paul Ulrich Villard (28 September 1860 – 13 January 1934) was a French chemist and physicist. He discovered gamma rays in 1900 while studying the radiation emanating from radium.
Early research
Villard was born in Saint-Germain-au-Mon ...
, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900 while studying radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visi ...
emitted by radium. In 1903, Ernest Rutherford named this radiation ''gamma rays'' based on their relatively strong penetration of matter; in 1900 he had already named two less penetrating types of decay radiation (discovered by Henri Becquerel) alpha rays and beta rays
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β� ...
in ascending order of penetrating power.
Gamma rays from radioactive decay are in the energy range from a few kiloelectronvolts ( keV) to approximately 8 megaelectronvolts ( MeV), corresponding to the typical energy levels in nuclei with reasonably long lifetimes. The energy spectrum of gamma rays can be used to identify the decaying radionuclides using gamma spectroscopy. Very-high-energy gamma rays in the 100–1000 teraelectronvolt (TeV
TEV may refer to:
* Transient Earth Voltage: a term for voltages appearing on the metal work of switchgear due to internal partial discharges
* TeV, or teraelectronvolt or trillion electron volt, a measure of energy
* Total Enterprise Value, a ...
) range have been observed from sources such as the Cygnus X-3 microquasar.
Natural sources of gamma rays originating on Earth are mostly a result of radioactive decay and secondary radiation from atmospheric interactions with cosmic ray particles. However, there are other rare natural sources, such as terrestrial gamma-ray flashes, which produce gamma rays from electron action upon the nucleus. Notable artificial sources of gamma rays include fission
Fission, a splitting of something into two or more parts, may refer to:
* Fission (biology), the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts into separate entities resembling the original
* Nuclear fissio ...
, such as that which occurs in nuclear reactors, and high energy physics experiments, such as neutral pion decay
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more g ...
and nuclear fusion.
Gamma rays and X-rays are both electromagnetic radiation, and since they overlap in the electromagnetic spectrum, the terminology varies between scientific disciplines. In some fields of physics, they are distinguished by their origin: Gamma rays are created by nuclear decay while X-rays originate outside the nucleus. In astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the h ...
, gamma rays are conventionally defined as having photon energies above 100 keV and are the subject of gamma ray astronomy, while radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy.
Gamma rays are ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
and are thus hazardous to life. Due to their high penetration power, they can damage bone marrow and internal organs. Unlike alpha and beta rays, they easily pass through the body and thus pose a formidable radiation protection challenge, requiring shielding made from dense materials such as lead or concrete. On Earth, the magnetosphere
In astronomy and planetary science, a magnetosphere is a region of space surrounding an astronomical object in which charged particles are affected by that object's magnetic field. It is created by a celestial body with an active interior dynam ...
protects life from most types of lethal cosmic radiation other than gamma rays, which are absorbed by 0.53 bars of atmosphere as they penetrate the atmosphere.
Gamma rays cannot be reflected by a mirror and their wavelengths are so small that they will pass between the atoms in a detector.
History of discovery
The first gamma ray source to be discovered was theradioactive decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
process called ''gamma decay''. In this type of decay, an excited nucleus emits a gamma ray almost immediately upon formation.It is now understood that a nuclear isomeric transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have ha ...
, however, can produce inhibited gamma decay with a measurable and much longer half-life. Paul Villard
Paul Ulrich Villard (28 September 1860 – 13 January 1934) was a French chemist and physicist. He discovered gamma rays in 1900 while studying the radiation emanating from radium.
Early research
Villard was born in Saint-Germain-au-Mon ...
, a French chemist and physicist, discovered gamma radiation in 1900, while studying radiation emitted from radium. Villard knew that his described radiation was more powerful than previously described types of rays from radium, which included beta rays, first noted as "radioactivity" by Henri Becquerel in 1896, and alpha rays, discovered as a less penetrating form of radiation by Rutherford, in 1899. However, Villard did not consider naming them as a different fundamental type. Later, in 1903, Villard's radiation was recognized as being of a type fundamentally different from previously named rays by Ernest Rutherford, who named Villard's rays "gamma rays" by analogy with the beta and alpha rays that Rutherford had differentiated in 1899. The "rays" emitted by radioactive elements were named in order of their power to penetrate various materials, using the first three letters of the Greek alphabet: alpha rays as the least penetrating, followed by beta rays, followed by gamma rays as the most penetrating. Rutherford also noted that gamma rays were not deflected (or at least, not deflected) by a magnetic field, another property making them unlike alpha and beta rays.
Gamma rays were first thought to be particles with mass, like alpha and beta rays. Rutherford initially believed that they might be extremely fast beta particles, but their failure to be deflected by a magnetic field indicated that they had no charge. In 1914, gamma rays were observed to be reflected from crystal surfaces, proving that they were electromagnetic radiation. Rutherford and his co-worker Edward Andrade measured the wavelengths of gamma rays from radium, and found they were similar to X-rays, but with shorter wavelengths and thus, higher frequency. This was eventually recognized as giving them more energy per photon, as soon as the latter term became generally accepted. A gamma decay was then understood to usually emit a gamma photon.
Sources
Natural sources of gamma rays on Earth include gamma decay from naturally occurring radioisotopes such as potassium-40, and also as a secondary radiation from various atmospheric interactions with cosmic ray particles. Some rare terrestrial natural sources that produce gamma rays that are not of a nuclear origin, are lightning strikes and terrestrial gamma-ray flashes, which produce high energy emissions from natural high-energy voltages. Gamma rays are produced by a number of astronomical processes in which very high-energy electrons are produced. Such electrons produce secondary gamma rays by the mechanisms of '' bremsstrahlung'', inverse Compton scattering andsynchrotron radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in ...
. A large fraction of such astronomical gamma rays are screened by Earth's atmosphere. Notable artificial sources of gamma rays include fission
Fission, a splitting of something into two or more parts, may refer to:
* Fission (biology), the division of a single entity into two or more parts and the regeneration of those parts into separate entities resembling the original
* Nuclear fissio ...
, such as occurs in nuclear reactors, as well as high energy physics experiments, such as neutral pion decay
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more g ...
and nuclear fusion.
A sample of gamma ray-emitting material that is used for irradiating or imaging is known as a gamma source. It is also called a radioactive source, isotope source, or radiation source, though these more general terms also apply to alpha and beta-emitting devices. Gamma sources are usually sealed to prevent radioactive contamination, and transported in heavy shielding.
Radioactive decay (gamma decay)
Gamma rays are produced during gamma decay, which normally occurs after other forms of decay occur, such asalpha
Alpha (uppercase , lowercase ; grc, ἄλφα, ''álpha'', or ell, άλφα, álfa) is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of one. Alpha is derived from the Phoenician letter aleph , whic ...
or beta
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; grc, βῆτα, bē̂ta or ell, βήτα, víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiod ...
decay. A radioactive nucleus can decay by the emission of an or particle. The daughter nucleus
In nuclear physics, a decay product (also known as a daughter product, daughter isotope, radio-daughter, or daughter nuclide) is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often proceeds via a sequence of steps ( ...
that results is usually left in an excited state. It can then decay to a lower energy state by emitting a gamma ray photon, in a process called gamma decay.
The emission of a gamma ray from an excited nucleus typically requires only 10−12 seconds. Gamma decay may also follow nuclear reactions such as neutron capture, nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is a reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei. The fission process often produces gamma photons, and releases a very large amount of energy even by the energetic standards of radio ...
, or nuclear fusion. Gamma decay is also a mode of relaxation of many excited states of atomic nuclei following other types of radioactive decay, such as beta decay, so long as these states possess the necessary component of nuclear spin
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning
* Spin, the rotation of an object around a central axis
* Spin (propaganda), an intentionally b ...
. When high-energy gamma rays, electrons, or protons bombard materials, the excited atoms emit characteristic "secondary" gamma rays, which are products of the creation of excited nuclear states in the bombarded atoms. Such transitions, a form of nuclear gamma fluorescence, form a topic in nuclear physics called gamma spectroscopy. Formation of fluorescent gamma rays are a rapid subtype of radioactive gamma decay.
In certain cases, the excited nuclear state that follows the emission of a beta particle or other type of excitation, may be more stable than average, and is termed a metastable excited state, if its decay takes (at least) 100 to 1000 times longer than the average 10−12 seconds. Such relatively long-lived excited nuclei are termed nuclear isomers, and their decays are termed isomeric transition
A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy higher energy levels than in the ground state of the same nucleus. "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have ha ...
s. Such nuclei have half-lifes that are more easily measurable, and rare nuclear isomers are able to stay in their excited state for minutes, hours, days, or occasionally far longer, before emitting a gamma ray. The process of isomeric transition is therefore similar to any gamma emission, but differs in that it involves the intermediate metastable excited state(s) of the nuclei. Metastable states are often characterized by high nuclear spin
In atomic physics, the spin quantum number is a quantum number (designated ) which describes the intrinsic angular momentum (or spin angular momentum, or simply spin) of an electron or other particle. The phrase was originally used to describe th ...
, requiring a change in spin of several units or more with gamma decay, instead of a single unit transition that occurs in only 10−12 seconds. The rate of gamma decay is also slowed when the energy of excitation of the nucleus is small.
An emitted gamma ray from any type of excited state may transfer its energy directly to any electrons, but most probably to one of the K shell electrons of the atom, causing it to be ejected from that atom, in a process generally termed the photoelectric effect (external gamma rays and ultraviolet rays may also cause this effect). The photoelectric effect should not be confused with the internal conversion process, in which a gamma ray photon is not produced as an intermediate particle (rather, a "virtual gamma ray" may be thought to mediate the process).
Decay schemes
Particle physics
Gamma rays are produced in many processes of particle physics. Typically, gamma rays are the products of neutral systems which decay through electromagnetic interactions (rather than aweak
Weak may refer to:
Songs
* "Weak" (AJR song), 2016
* "Weak" (Melanie C song), 2011
* "Weak" (SWV song), 1993
* "Weak" (Skunk Anansie song), 1995
* "Weak", a song by Seether from '' Seether: 2002-2013''
Television episodes
* "Weak" (''Fear t ...
or strong
Strong may refer to:
Education
* The Strong, an educational institution in Rochester, New York, United States
* Strong Hall (Lawrence, Kansas), an administrative hall of the University of Kansas
* Strong School, New Haven, Connecticut, United Sta ...
interaction). For example, in an electron–positron annihilation, the usual products are two gamma ray photons. If the annihilating electron and positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides ...
are at rest, each of the resulting gamma rays has an energy of ~ 511 keV and frequency of ~ . Similarly, a neutral pion most often decays into two photons. Many other hadrons and massive bosons also decay electromagnetically. High energy physics experiments, such as the Large Hadron Collider
The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the world's largest and highest-energy particle collider. It was built by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) between 1998 and 2008 in collaboration with over 10,000 scientists and hundred ...
, accordingly employ substantial radiation shielding. Because subatomic particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a pr ...
s mostly have far shorter wavelengths than atomic nuclei, particle physics gamma rays are generally several orders of magnitude more energetic than nuclear decay gamma rays. Since gamma rays are at the top of the electromagnetic spectrum in terms of energy, all extremely high-energy photons are gamma rays; for example, a photon having the Planck energy would be a gamma ray.
Other sources
A few gamma rays in astronomy are known to arise from gamma decay (see discussion of SN1987A), but most do not. Photons from astrophysical sources that carry energy in the gamma radiation range are often explicitly called gamma-radiation. In addition to nuclear emissions, they are often produced by sub-atomic particle and particle-photon interactions. Those include electron-positron annihilation,neutral pion decay
In particle physics, a pion (or a pi meson, denoted with the Greek letter pi: ) is any of three subatomic particles: , , and . Each pion consists of a quark and an antiquark and is therefore a meson. Pions are the lightest mesons and, more g ...
, bremsstrahlung, inverse Compton scattering, and synchrotron radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in ...
.
Laboratory sources
In October 2017, scientists from various European universities proposed a means for sources of GeV photons using lasers as exciters through a controlled interplay between the cascade and anomalous radiative trapping.Terrestrial thunderstorms
Thunderstorms can produce a brief pulse of gamma radiation called a terrestrial gamma-ray flash. These gamma rays are thought to be produced by high intensity static electric fields accelerating electrons, which then produce gamma rays by bremsstrahlung as they collide with and are slowed by atoms in the atmosphere. Gamma rays up to 100 MeV can be emitted by terrestrial thunderstorms, and were discovered by space-borne observatories. This raises the possibility of health risks to passengers and crew on aircraft flying in or near thunderclouds.Solar flares
The most effusive solar flares emit across the entire EM spectrum, including γ-rays. The first confident observation occurred in1972
Within the context of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) it was the longest year ever, as two leap seconds were added during this 366-day year, an event which has not since been repeated. (If its start and end are defined using Solar time, me ...
.
Cosmic rays
Extraterrestrial, high energy gamma rays include the gamma ray background produced when cosmic rays (either high speed electrons or protons) collide with ordinary matter, producing pair-production gamma rays at 511 keV. Alternatively, bremsstrahlung are produced at energies of tens of MeV or more when cosmic ray electrons interact with nuclei of sufficiently high atomic number (see gamma ray image of the Moon near the end of this article, for illustration).
Pulsars and magnetars
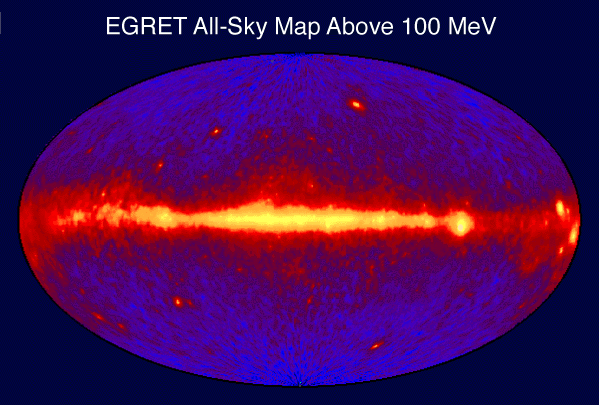
The gamma ray sky (see illustration at right) is dominated by the more common and longer-term production of gamma rays that emanate frompulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward Ea ...
s within the Milky Way. Sources from the rest of the sky are mostly quasar
A quasar is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a m ...
s. Pulsars are thought to be neutron stars with magnetic fields that produce focused beams of radiation, and are far less energetic, more common, and much nearer sources (typically seen only in our own galaxy) than are quasars or the rarer gamma-ray burst sources of gamma rays. Pulsars have relatively long-lived magnetic fields that produce focused beams of relativistic speed charged particles, which emit gamma rays (bremsstrahlung) when those strike gas or dust in their nearby medium, and are decelerated. This is a similar mechanism to the production of high-energy photons in megavoltage
Megavoltage X-rays are produced by linear accelerators ("linacs") operating at voltages in excess of 1000 kV (1 MV) range, and therefore have an energy in the MeV range. The voltage in this case refers to the voltage used to accelerat ...
radiation therapy machines (see bremsstrahlung). Inverse Compton scattering
Compton scattering, discovered by Arthur Holly Compton, is the scattering of a high frequency photon after an interaction with a charged particle, usually an electron. If it results in a decrease in energy (increase in wavelength) of the photon ...
, in which charged particles (usually electrons) impart energy to low-energy photons boosting them to higher energy photons. Such impacts of photons on relativistic charged particle beams is another possible mechanism of gamma ray production. Neutron stars with a very high magnetic field ( magnetars), thought to produce astronomical soft gamma repeaters, are another relatively long-lived star-powered source of gamma radiation.
Quasars and active galaxies
More powerful gamma rays from very distantquasar
A quasar is an extremely Luminosity, luminous active galactic nucleus (AGN). It is pronounced , and sometimes known as a quasi-stellar object, abbreviated QSO. This emission from a galaxy nucleus is powered by a supermassive black hole with a m ...
s and closer active galaxies are thought to have a gamma ray production source similar to a particle accelerator. High energy electrons produced by the quasar, and subjected to inverse Compton scattering, synchrotron radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in ...
, or bremsstrahlung, are the likely source of the gamma rays from those objects. It is thought that a supermassive black hole at the center of such galaxies provides the power source that intermittently destroys stars and focuses the resulting charged particles into beams that emerge from their rotational poles. When those beams interact with gas, dust, and lower energy photons they produce X-rays and gamma rays. These sources are known to fluctuate with durations of a few weeks, suggesting their relatively small size (less than a few light-weeks across). Such sources of gamma and X-rays are the most commonly visible high intensity sources outside our galaxy. They shine not in bursts (see illustration), but relatively continuously when viewed with gamma ray telescopes. The power of a typical quasar is about 1040 watts, a small fraction of which is gamma radiation. Much of the rest is emitted as electromagnetic waves of all frequencies, including radio waves.

Gamma-ray bursts
The most intense sources of gamma rays, are also the most intense sources of any type of electromagnetic radiation presently known. They are the "long duration burst" sources of gamma rays in astronomy ("long" in this context, meaning a few tens of seconds), and they are rare compared with the sources discussed above. By contrast, "short" gamma-ray bursts of two seconds or less, which are not associated with supernovae, are thought to produce gamma rays during the collision of pairs of neutron stars, or a neutron star and ablack hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
.
The so-called ''long-duration'' gamma-ray bursts produce a total energy output of about 1044 joules (as much energy as our Sun will produce in its entire life-time) but in a period of only 20 to 40 seconds. Gamma rays are approximately 50% of the total energy output. The leading hypotheses for the mechanism of production of these highest-known intensity beams of radiation, are inverse Compton scattering and synchrotron radiation
Synchrotron radiation (also known as magnetobremsstrahlung radiation) is the electromagnetic radiation emitted when relativistic charged particles are subject to an acceleration perpendicular to their velocity (). It is produced artificially in ...
from high-energy charged particles. These processes occur as relativistic charged particles leave the region of the event horizon of a newly formed black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravitation, gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts t ...
created during supernova explosion. The beam of particles moving at relativistic speeds are focused for a few tens of seconds by the magnetic field of the exploding hypernova. The fusion explosion of the hypernova drives the energetics of the process. If the narrowly directed beam happens to be pointed toward the Earth, it shines at gamma ray frequencies with such intensity, that it can be detected even at distances of up to 10 billion light years, which is close to the edge of the visible universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
.
Properties
Penetration of matter
beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β� ...
s, which can be shielded by thin aluminium. Gamma rays are best absorbed by materials with high atomic numbers (''Z'') and high density, which contribute to the total stopping power. Because of this, a lead (high ''Z'') shield is 20–30% better as a gamma shield than an equal mass of another low-''Z'' shielding material, such as aluminium, concrete, water, or soil; lead's major advantage is not in lower weight, but rather its compactness due to its higher density. Protective clothing, goggles and respirators can protect from internal contact with or ingestion of alpha or beta emitting particles, but provide no protection from gamma radiation from external sources.
The higher the energy of the gamma rays, the thicker the shielding made from the same shielding material is required. Materials for shielding gamma rays are typically measured by the thickness required to reduce the intensity of the gamma rays by one half (the half value layer material's half-value layer (HVL), or half-value thickness, is the thickness of the material at which the intensity of radiation entering it is reduced by one half. HVL can also be expressed in terms of air kerma rate (AKR), rather than intensit ...
or HVL). For example, gamma rays that require 1 cm (0.4 inch) of lead to reduce their intensity by 50% will also have their intensity reduced in half by of granite rock, 6 cm (2.5 inches) of concrete, or 9 cm (3.5 inches) of packed soil. However, the mass of this much concrete or soil is only 20–30% greater than that of lead with the same absorption capability. Depleted uranium
Depleted uranium (DU; also referred to in the past as Q-metal, depletalloy or D-38) is uranium with a lower content of the fissile isotope than natural uranium.: "Depleted uranium possesses only 60% of the radioactivity of natural uranium, hav ...
is used for shielding in portable gamma ray sources, but here the savings in weight over lead are larger, In a nuclear power plant, shielding can be provided by steel and concrete in the pressure and particle containment vessel, while water provides a radiation shielding of fuel rods during storage or transport into the reactor core. The loss of water or removal of a "hot" fuel assembly into the air would result in much higher radiation levels than when kept under water.
Matter interaction
electric field
An electric field (sometimes E-field) is the physical field that surrounds electrically charged particles and exerts force on all other charged particles in the field, either attracting or repelling them. It also refers to the physical field fo ...
of a nucleus, the energy of the incident photon is converted into the mass of an electron-positron pair. Any gamma energy in excess of the equivalent rest mass of the two particles (totaling at least 1.02 MeV) appears as the kinetic energy of the pair and in the recoil of the emitting nucleus. At the end of the positron's range
Range may refer to:
Geography
* Range (geographic), a chain of hills or mountains; a somewhat linear, complex mountainous or hilly area (cordillera, sierra)
** Mountain range, a group of mountains bordered by lowlands
* Range, a term used to i ...
, it combines with a free electron, and the two annihilate, and the entire mass of these two is then converted into two gamma photons of at least 0.51 MeV energy each (or higher according to the kinetic energy of the annihilated particles).
The secondary electrons (and/or positrons) produced in any of these three processes frequently have enough energy to produce much ionization themselves.
Additionally, gamma rays, particularly high energy ones, can interact with atomic nuclei resulting in ejection of particles in photodisintegration, or in some cases, even nuclear fission ( photofission).
Light interaction
High-energy (from 80 GeV to ~10TeV
TEV may refer to:
* Transient Earth Voltage: a term for voltages appearing on the metal work of switchgear due to internal partial discharges
* TeV, or teraelectronvolt or trillion electron volt, a measure of energy
* Total Enterprise Value, a ...
) gamma rays arriving from far-distant quasars are used to estimate the extragalactic background light The diffuse extragalactic background light (EBL) is all the accumulated radiation in the universe due to star formation processes, plus a contribution from active galactic nuclei (AGNs). This radiation covers almost all wavelengths of the electroma ...
in the universe: The highest-energy rays interact more readily with the background light photons and thus the density of the background light may be estimated by analyzing the incoming gamma ray spectra.
Gamma spectroscopy
Gamma spectroscopy is the study of the energetic transitions in atomic nuclei, which are generally associated with the absorption or emission of gamma rays. As in opticalspectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets the electromagnetic spectra that result from the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter as a function of the wavelength or frequency of the radiation. Matter wa ...
(see Franck–Condon effect) the absorption of gamma rays by a nucleus is especially likely (i.e., peaks in a "resonance") when the energy of the gamma ray is the same as that of an energy transition in the nucleus. In the case of gamma rays, such a resonance is seen in the technique of Mössbauer spectroscopy. In the Mössbauer effect the narrow resonance absorption for nuclear gamma absorption can be successfully attained by physically immobilizing atomic nuclei in a crystal. The immobilization of nuclei at both ends of a gamma resonance interaction is required so that no gamma energy is lost to the kinetic energy of recoiling nuclei at either the emitting or absorbing end of a gamma transition. Such loss of energy causes gamma ray resonance absorption to fail. However, when emitted gamma rays carry essentially all of the energy of the atomic nuclear de-excitation that produces them, this energy is also sufficient to excite the same energy state in a second immobilized nucleus of the same type.
Applications
topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al Si O( F, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can mak ...
into blue topaz
Topaz is a silicate mineral of aluminium and fluorine with the chemical formula Al Si O( F, OH). It is used as a gemstone in jewelry and other adornments. Common topaz in its natural state is colorless, though trace element impurities can ma ...
.
Non-contact industrial sensors commonly use sources of gamma radiation in refining, mining, chemicals, food, soaps and detergents, and pulp and paper industries, for the measurement of levels, density, and thicknesses. Gamma-ray sensors are also used for measuring the fluid levels in water and oil industries. Typically, these use Co-60 or Cs-137 isotopes as the radiation source.
In the US, gamma ray detectors are beginning to be used as part of the Container Security Initiative (CSI). These machines are advertised to be able to scan 30 containers per hour.
Gamma radiation is often used to kill living organisms, in a process called irradiation. Applications of this include the sterilization of medical equipment (as an alternative to autoclaves or chemical means), the removal of decay-causing bacteria from many foods and the prevention of the sprouting of fruit and vegetables to maintain freshness and flavor.
Despite their cancer-causing properties, gamma rays are also used to treat some types of cancer, since the rays also kill cancer cells. In the procedure called gamma-knife surgery, multiple concentrated beams of gamma rays are directed to the growth in order to kill the cancerous cells. The beams are aimed from different angles to concentrate the radiation on the growth while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
Gamma rays are also used for diagnostic purposes in nuclear medicine in imaging techniques. A number of different gamma-emitting radioisotopes are used. For example, in a PET scan a radiolabeled sugar called fluorodeoxyglucose emits positron
The positron or antielectron is the antiparticle or the antimatter counterpart of the electron. It has an electric charge of +1 '' e'', a spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same mass as an electron. When a positron collides ...
s that are annihilated by electrons, producing pairs of gamma rays that highlight cancer as the cancer often has a higher metabolic rate than the surrounding tissues. The most common gamma emitter used in medical applications is the nuclear isomer technetium-99m which emits gamma rays in the same energy range as diagnostic X-rays. When this radionuclide tracer is administered to a patient, a gamma camera can be used to form an image of the radioisotope's distribution by detecting the gamma radiation emitted (see also SPECT
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, ...
). Depending on which molecule has been labeled with the tracer, such techniques can be employed to diagnose a wide range of conditions (for example, the spread of cancer to the bones via bone scan
A bone scan or bone scintigraphy is a nuclear medicine imaging technique of the bone. It can help diagnose a number of bone conditions, including cancer of the bone or metastasis, location of bone inflammation and fractures (that may not be visi ...
).
Health effects
Gamma rays cause damage at a cellular level and are penetrating, causing diffuse damage throughout the body. However, they are less ionising than alpha or beta particles, which are less penetrating. Low levels of gamma rays cause astochastic
Stochastic (, ) refers to the property of being well described by a random probability distribution. Although stochasticity and randomness are distinct in that the former refers to a modeling approach and the latter refers to phenomena themselv ...
health risk, which for radiation dose assessment is defined as the ''probability'' of cancer induction and genetic damage. High doses produce deterministic
Determinism is a philosophical view, where all events are determined completely by previously existing causes. Deterministic theories throughout the history of philosophy have developed from diverse and sometimes overlapping motives and consi ...
effects, which is the ''severity'' of acute tissue damage that is certain to happen. These effects are compared to the physical quantity absorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which is the measure of the energy deposited in matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protection (reduction of harmf ...
measured by the unit gray (Gy).
Body response
When gamma radiation breaks DNA molecules, a cell may be able to repair the damaged genetic material, within limits. However, a study of Rothkamm and Lobrich has shown that this repair process works well after high-dose exposure but is much slower in the case of a low-dose exposure.Risk assessment
The natural outdoor exposure in the United Kingdom ranges from 0.1 to 0.5 µSv/h with significant increase around known nuclear and contaminated sites. Natural exposure to gamma rays is about 1 to 2 mSv per year, and the average total amount of radiation received in one year per inhabitant in the USA is 3.6 mSv. There is a small increase in the dose, due to naturally occurring gamma radiation, around small particles of high atomic number materials in the human body caused by the photoelectric effect. By comparison, the radiation dose from chest radiography (about 0.06 mSv) is a fraction of the annual naturally occurring background radiation dose. A chest CT delivers 5 to 8 mSv. A whole-body PET/CT scan can deliver 14 to 32 mSv depending on the protocol. The dose from fluoroscopy of the stomach is much higher, approximately 50 mSv (14 times the annual background). An acute full-body equivalent single exposure dose of 1 Sv (1000 mSv) causes slight blood changes, but 2.0–3.5 Sv (2.0–3.5 Gy) causes very severe syndrome of nausea, hair loss, and hemorrhaging, and will cause death in a sizable number of cases—-about 10% to 35% without medical treatment. A dose of 5 Sv (5 Gy) is considered approximately the LD50 (lethal dose for 50% of exposed population) for an acute exposure to radiation even with standard medical treatment. A dose higher than 5 Sv (5 Gy) brings an increasing chance of death above 50%. Above 7.5–10 Sv (7.5–10 Gy) to the entire body, even extraordinary treatment, such as bone-marrow transplants, will not prevent the death of the individual exposed (see radiation poisoning). (Doses much larger than this may, however, be delivered to selected parts of the body in the course of radiation therapy.) For low-dose exposure, for example among nuclear workers, who receive an average yearly radiation dose of 19 mSv, the risk of dying from cancer (excluding leukemia) increases by 2 percent. For a dose of 100 mSv, the risk increase is 10 percent. By comparison, risk of dying from cancer was increased by 32 percent for the survivors of theatomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the on ...
.
Units of measurement and exposure
The following table shows radiation quantities in SI and non-SI units: The measure of the ionizing effect of gamma and X-rays in dry air is called the exposure, for which a legacy unit, the röntgen was used from 1928. This has been replaced by kerma, now mainly used for instrument calibration purposes but not for received dose effect. The effect of gamma and other ionizing radiation on living tissue is more closely related to the amount of energy deposited in tissue rather than the ionisation of air, and replacement radiometric units and quantities for radiation protection have been defined and developed from 1953 onwards. These are: *The gray (Gy), is the SI unit ofabsorbed dose
Absorbed dose is a dose quantity which is the measure of the energy deposited in matter by ionizing radiation per unit mass. Absorbed dose is used in the calculation of dose uptake in living tissue in both radiation protection (reduction of harmf ...
, which is the amount of radiation energy deposited in the irradiated material. For gamma radiation this is numerically equivalent to equivalent dose measured by the sievert, which indicates the stochastic biological effect of low levels of radiation on human tissue. The radiation weighting conversion factor from absorbed dose to equivalent dose is 1 for gamma, whereas alpha particles have a factor of 20, reflecting their greater ionising effect on tissue.
*The rad
RAD or Rad may refer to:
People
* Robert Anthony Rad Dougall (born 1951), South African former racing driver
* Rad Hourani, Canadian fashion designer and artist
* Nickname of Leonardus Rad Kortenhorst (1886–1963), Dutch politician
* Radley R ...
is the deprecated CGS unit for absorbed dose and the rem
Rem or REM may refer to:
Music
* R.E.M., an American rock band
* ''R.E.M.'' (EP), by Green
* "R.E.M." (song), by Ariana Grande
Organizations
* La République En Marche!, a French centrist political party
* Reichserziehungsministerium, in Nazi G ...
is the deprecated CGS unit of equivalent dose, used mainly in the USA.
Distinction from X-rays
 For example, modern high-energy X-rays produced by
For example, modern high-energy X-rays produced by linear accelerators
A linear particle accelerator (often shortened to linac) is a type of particle accelerator that accelerates charged subatomic particles or ions to a high speed by subjecting them to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beam ...
for megavoltage
Megavoltage X-rays are produced by linear accelerators ("linacs") operating at voltages in excess of 1000 kV (1 MV) range, and therefore have an energy in the MeV range. The voltage in this case refers to the voltage used to accelerat ...
treatment in cancer often have higher energy (4 to 25 MeV) than do most classical gamma rays produced by nuclear gamma decay
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic waves, typically sh ...
. One of the most common gamma ray emitting isotopes used in diagnostic nuclear medicine, technetium-99m, produces gamma radiation of the same energy (140 keV) as that produced by diagnostic X-ray machines, but of significantly lower energy than therapeutic photons from linear particle accelerators. In the medical community today, the convention that radiation produced by nuclear decay is the only type referred to as "gamma" radiation is still respected.
Due to this broad overlap in energy ranges, in physics the two types of electromagnetic radiation are now often defined by their origin: X-rays are emitted by electrons (either in orbitals outside of the nucleus, or while being accelerated to produce bremsstrahlung-type radiation), while gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus or by means of other particle decays or annihilation events. There is no lower limit to the energy of photons produced by nuclear reactions, and thus ultraviolet or lower energy photons produced by these processes would also be defined as "gamma rays". The only naming-convention that is still universally respected is the rule that electromagnetic radiation that is known to be of atomic nuclear origin is ''always'' referred to as "gamma rays", and never as X-rays. However, in physics and astronomy, the converse convention (that all gamma rays are considered to be of nuclear origin) is frequently violated.
In astronomy, higher energy gamma and X-rays are defined by energy, since the processes that produce them may be uncertain and photon energy, not origin, determines the required astronomical detectors needed. High-energy photons occur in nature that are known to be produced by processes other than nuclear decay but are still referred to as gamma radiation. An example is "gamma rays" from lightning discharges at 10 to 20 MeV, and known to be produced by the bremsstrahlung mechanism.
Another example is gamma-ray bursts, now known to be produced from processes too powerful to involve simple collections of atoms undergoing radioactive decay. This is part and parcel of the general realization that many gamma rays produced in astronomical processes result not from radioactive decay or particle annihilation, but rather in non-radioactive processes similar to X-rays. Although the gamma rays of astronomy often come from non-radioactive events, a few gamma rays in astronomy are specifically known to originate from gamma decay of nuclei (as demonstrated by their spectra and emission half life). A classic example is that of supernova SN 1987A, which emits an "afterglow" of gamma-ray photons from the decay of newly made radioactive nickel-56
Naturally occurring nickel (28Ni) is composed of five stable isotopes; , , , and , with being the most abundant (68.077% natural abundance). 26 radioisotopes have been characterised with the most stable being with a half-life of 76,000 years, ...
and cobalt-56
Naturally occurring cobalt (Co) consists of a single stable isotope, Co. Twenty-eight radioisotopes have been characterized; the most stable are Co with a half-life of 5.2714 years, Co (271.8 days), Co (77.27 days), and Co (70.86 days). All other ...
. Most gamma rays in astronomy, however, arise by other mechanisms.
See also
* Annihilation * Galactic Center GeV excess * Gaseous ionization detectors * Very-high-energy gamma ray *Ultra-high-energy gamma ray
Ultra-high-energy gamma rays are gamma rays with photon energies higher than 100 TeV (0.1 PeV). They have a frequency higher than 2.42 × 1028 Hz and a wavelength shorter than 1.24 × 10−20 m. The existence of these rays was confirmed in 20 ...
Notes
References
External links
Basic reference on several types of radiation
Radiation Q & A
– Contains information on gamma-ray energies from isotopes.
with filter on gamma-ray energy
Health Physics Society Public Education Website
{{Authority control Electromagnetic spectrum IARC Group 1 carcinogens Nuclear physics Radiation Radioactivity Articles containing video clips