Patagonian lang.png on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of
A Brief Declaration of the Vyage abowte the Worlde by Antonie Pygafetta Vincentine, Rycharde Eden, ''The Decades of the Newe Worlde or West India'', London, William Powell, 1555.
The original word was likely in
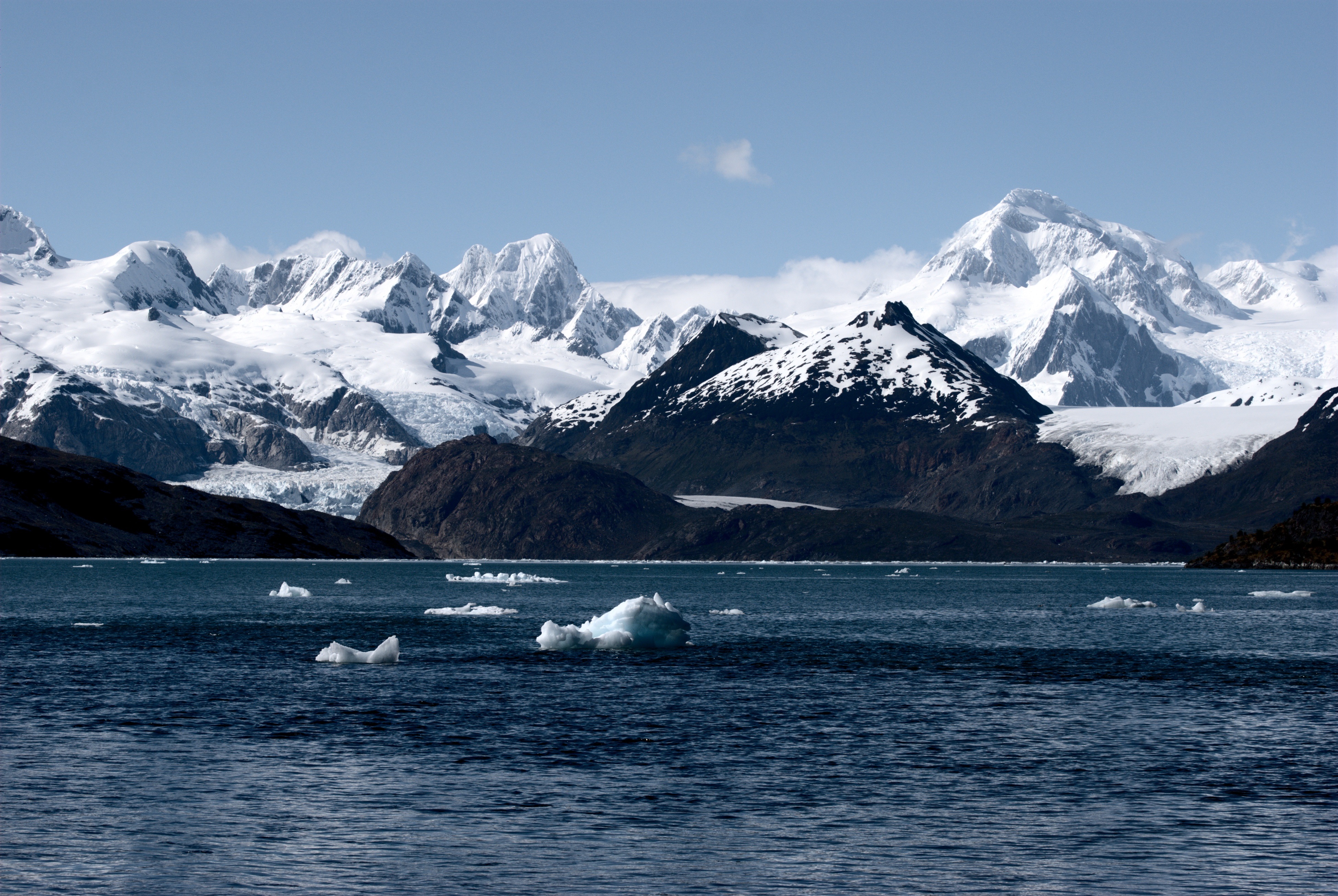
 Argentine Patagonia is for the most part a region of steppe-like plains, rising in a succession of 13 abrupt terraces about at a time, and covered with an enormous bed of shingle almost bare of vegetation.''Patagonia: Natural History, Prehistory and Ethnography at the Uttermost End of the Earth'', C. McEwan, L.A. and A. Prieto (eds),
Argentine Patagonia is for the most part a region of steppe-like plains, rising in a succession of 13 abrupt terraces about at a time, and covered with an enormous bed of shingle almost bare of vegetation.''Patagonia: Natural History, Prehistory and Ethnography at the Uttermost End of the Earth'', C. McEwan, L.A. and A. Prieto (eds),
 The geological limit of Patagonia has been proposed to be Huincul Fault, which forms a major discontinuity. The fault truncates various
The geological limit of Patagonia has been proposed to be Huincul Fault, which forms a major discontinuity. The fault truncates various
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
, governed by Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
Mountains with lakes, fjord
In physical geography, a fjord or fiord () is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Alaska, Antarctica, British Columbia, Chile, Denmark, Förden and East Jutland Fjorde, Germany, ...
s, temperate rainforests
Temperate rainforests are coniferous or broadleaf forests that occur in the temperate zone and receive heavy rain.
Temperate rain forests occur in oceanic moist regions around the world: the Pacific temperate rain forests of North American Pac ...
, and glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s in the west and deserts
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
, tableland
A table or tableland is a butte, flank of a mountain, or mountain, that has a flat top.
This kind of landform has numerous names, including:
* Butte
* Mesa
*
* Potrero
* Tepui
* Terrace
* Tuya
A tuya is a flat-topped, steep-sided vo ...
s and steppes to the east. Patagonia is bounded by the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contin ...
on the west, the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to the east, and many bodies of water that connect them, such as the Strait of Magellan, the Beagle Channel
Beagle Channel (; Yahgan: ''Onašaga'') is a strait in the Tierra del Fuego Archipelago, on the extreme southern tip of South America between Chile and Argentina. The channel separates the larger main island of Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego f ...
, and the Drake Passage
The Drake Passage (referred to as Mar de Hoces Hoces Sea"in Spanish-speaking countries) is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atla ...
to the south.
The Colorado
Colorado (, other variants) is a state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It encompasses most of the Southern Rocky Mountains, as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the wes ...
and Barrancas rivers, which run from the Andes to the Atlantic, are commonly considered the northern limit of Argentine Patagonia. The archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
of Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
is sometimes included as part of Patagonia. Most geographers and historians locate the northern limit of Chilean Patagonia at Huincul Fault, in Araucanía Region
The Araucanía ( ), La Araucanía Region ( es, Región de La Araucanía ) is one of Chile's 16 first-order administrative divisions, and comprises two provinces: Malleco in the north and Cautín in the south. Its capital and largest city is Te ...
.Manuel Enrique Schilling; Richard WalterCarlson; AndrésTassara; Rommulo Vieira Conceição; Gustavo Walter Bertotto; Manuel Vásquez; Daniel Muñoz; Tiago Jalowitzki; Fernanda Gervasoni; Diego Morata (2017). "The origin of Patagonia revealed by Re-Os systematics of mantle xenoliths." ''Precambrian Research'', volumen 294: 15-32.Zunino, H.; Matossian, B.; Hidalgo, R. (2012). "Poblamiento y desarrollo de enclaves turísticos en la Norpatagonia chileno-argentina. Migración y frontera en un espacio binacional." (Population and development of tourist enclaves in the Chilean-Argentine Norpatagonia. Migration and the border in a binational space), '' Revista de Geografía Norte Grande'', 53: 137-158.Zunino, M.; Espinoza, L.; Vallejos-Romero A. (2016) Los migrantes por estilo de vida como agentes de transformación en la Norpatagonia chilena, ''Revista de Estudios Sociales'', 55 (2016): 163-176.
At the time of the Spanish arrival, Patagonia was inhabited by multiple indigenous tribes. In a small portion of northwestern Patagonia, indigenous peoples practiced agriculture, while in the remaining territory, peoples lived as hunter-gatherers, traveling by foot in eastern Patagonia or by dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' ( ...
and dalca
The dalca or piragua is a type of canoe employed by the Chonos, a nomadic indigenous people of southern Chile, and Huilliche people living in Chiloé archipelago. It was a light boat and ideal for navigating local waterways, including between is ...
in the fjords and channels. In colonial times indigenous peoples of northeastern Patagonia adopted a horseriding lifestyle. While the interest of the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
had been chiefly to keep other European powers away from Patagonia, independent Chile and Argentina began to colonize the territory slowly over the course of the 19th and early 20th centuries. This process brought a decline of the indigenous populations, whose lives and habitats were disrupted, while at the same time thousands of Europeans, Argentines, Chilotes and mainland Chileans settled in Patagonia. Border disputes between Argentina and Chile were recurrent in the 20th century.
The contemporary economy of eastern Patagonia revolves around sheep farming and oil and gas extraction, while in western Patagonia fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from stocked bodies of water such as ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. Fishing techniques inclu ...
, salmon aquaculture, and tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
dominate. Culturally, Patagonia has a varied heritage, including Criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish race-based colonial caste system (the European descendants)
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South Ameri ...
, Mestizo, Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Croat
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, Ge ...
, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
influences.
Etymology
The name Patagonia comes from the word '' patagón''.Antonio Pigafetta
Antonio Pigafetta (; – c. 1531) was an Venetian scholar and explorer. He joined the expedition to the Spice Islands led by explorer Ferdinand Magellan under the flag of the emperor Charles V and after Magellan's death in the Philippine Islands, ...
, '' Relazione del primo viaggio intorno al mondo'', 1524: "Il capitano generale nominò questi popoli Patagoni.A Brief Declaration of the Vyage abowte the Worlde by Antonie Pygafetta Vincentine, Rycharde Eden, ''The Decades of the Newe Worlde or West India'', London, William Powell, 1555.
The original word was likely in
Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the East ...
's native Portuguese (''patagão'') or the Spanish of his men (''patagón''). It was later interpreted later as "bigfoot", but the etymology refers to a literary character in a Spanish novel of the early 16th century:
''Patagon'', said to be engendred by a beast in the woods, being the strangest, most misshapen, and counterfeit creature in the world. He hath good understanding, is amorous of women, and keepeth company with one of whom, it is said, he was engendred. He hath the face of a Dogge, great ears, which hang down upon his shoulders, his teeth sharp and big, standing out of his mouth very much: his feet are like a Harts, and he runneth wondrous lightly. Such as have seen him, tell marvelous matters of him, because he chaseth ordinarily among the mountains, with two Lyons in a chain like a lease, and a bow in his hanMagellan used this term in 1520 to describe the native tribes of the region, whom his expedition thought to be giants. The people he called the Patagons are now believed to have been the Tehuelche, who tended to be taller than Europeans of the time. Argentine researcher
Anthony Munday, ''The Famous and Renowned Historie of Primaleon of Greece'', 1619, cap.XXXIII: "How Primaleon... found the Grand Patagon"
Miguel Doura
Miguel Doura was born in 1962 in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina, where he studied fine arts at the school Prilidiano Pueyrredón, standing out in his talks and meetings with his teacher, the sculptor Rubén Locazo (Grand National Sculptu ...
observed that the name Patagonia possibly derives from the ancient Greek region of modern Turkey called Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; el, Παφλαγονία, Paphlagonía, modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; tr, Paflagonya) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus t ...
, possible home of the ''patagon'' personage in the chivalric romances ''Primaleon'' printed in 1512, ten years before Magellan arrived in these southern lands. This hypothesis was published in a 2011 ''New Review of Spanish Philology'' report.
There are various placenames in the Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
with Chono etymologies despite the main indigenous language of the archipelago at the arrival of the Spanish being Mapudungun. A theory postulated by chronicler José Pérez García
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ).
In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacul ...
explains this holding that the Cuncos
Cuncos or Juncos is a poorly known subgroup of Huilliche people native to coastal areas of southern Chile and the nearby inland. Mostly a historic term, Cuncos are chiefly known for their long-running conflict with the Spanish during the colonia ...
(also known as Veliches) settled in Chiloé Island
Chiloé Island ( es, Isla de Chiloé, , ) also known as Greater Island of Chiloé (''Isla Grande de Chiloé''), is the largest island of the Chiloé Archipelago off the west coast of Chile, in the Pacific Ocean. The island is located in southern ...
in Pre-Hispanic
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, th ...
times as a consequence of a push from more northern Huilliches who in turn were being displaced by Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who s ...
s. While being outside traditional Huilliche territory the western Patagonian volcanoes Michimahuida
Michinmahuida () (alternate spellings Minchinmávida or Michimahuida) is a glaciated stratovolcano located in Los Lagos Region of Chile. It lies about 15 km east of Chaitén volcano, and was extensively covered in ash during the 2008 erupt ...
, Hornopirén
Hornopirén is a town ( es, pueblo) in the commune of Hualaihué in Palena Province, southern Chile. It lies along the northern portion of Carretera Austral
The Carretera Austral (CH-7, ''in English: Southern Way'') is the name given to Chile ...
and Chaitén
Chaitén (, ) is a Chilean town, commune and former capital of the Palena Province in Los Lagos Region. The town is north of the mouth of Yelcho River, on the east coast of the Gulf of Corcovado. The town is strategically close to the northern ...
have Huilliche etymologies.
In Chubut Province
Chubut ( es, Provincia del Chubut, ; cy, Talaith Chubut) is a province in southern Argentina, situated between the 42nd parallel south (the border with Río Negro Province), the 46th parallel south (bordering Santa Cruz Province), the Andes rang ...
modern toponymy comes from the word "chupat" belonging to a transitional language between the southern and northern Tehuelche ethnic groups that were located in that region called Tewsün or Teushen. The word means transparency and is related to the clarity and purity of the river that bears that name and runs through the province. It is also related to the origin of the Welsh pronunciation of the word "chupat" which later became "Chubut". It is called "Camwy" in Patagonian Welsh. Chupat, Chubut and Camwy have the same meaning and are used to talk about the river and the province. Welsh settlers and placenames are associated with one of the projects of the Argentine state, Project Hiraeth.
Due to the language, culture and location, many Patagonians do not consider themselves Latinos and proudly call themselves Patagonians instead. People from Y Wladfa, Laurie Island, the Atlantic Islands, Antarctica (including the Chilean town in Antarctica, "The Stars Village", and the Argentine civilian settlement, "Hope Base"), other non-latin speaking areas use this term as a patriotic and inclusive demonym. A Patagonian is a person that is part of the Patagonia region, language and culture. That person could be a citizen from Chilean Patagonia, Argentine Patagonia, or of native communities that existed before the land was divided by The Boundary Treaty of 1881.
Patagonia is divided between Western Patagonia (Chile) and Eastern Patagonia (Argentina) and several territories are still under dispute and claiming their rights. Mapuche people came from the Chilean Andes and voted to remain in different sides of Patagonia. Welsh settlers came from Wales and North America and voted to remain in Patagonia, when the treaty was signed, they voted for culture and administration to be apart from the country keeping the settlement, language, schools, traditions, regional dates, flag, anthems and celebrations. Patagonians also live abroad in settlements like Saltcoats, Saskatchewan
Saltcoats is a town in east-central Saskatchewan near the Manitoba border in Canada. The town's population was 474 in 2011. The town was built in the late 19th century, and its economy was driven by the railway. There is no longer passenger servic ...
, Canada; New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
, Australia; South Africa; the Falkland Islands; and North America.
Population and land area
Largest cities
Physical geography
 Argentine Patagonia is for the most part a region of steppe-like plains, rising in a succession of 13 abrupt terraces about at a time, and covered with an enormous bed of shingle almost bare of vegetation.''Patagonia: Natural History, Prehistory and Ethnography at the Uttermost End of the Earth'', C. McEwan, L.A. and A. Prieto (eds),
Argentine Patagonia is for the most part a region of steppe-like plains, rising in a succession of 13 abrupt terraces about at a time, and covered with an enormous bed of shingle almost bare of vegetation.''Patagonia: Natural History, Prehistory and Ethnography at the Uttermost End of the Earth'', C. McEwan, L.A. and A. Prieto (eds), Princeton University Press
Princeton University Press is an independent publisher with close connections to Princeton University. Its mission is to disseminate scholarship within academia and society at large.
The press was founded by Whitney Darrow, with the financia ...
with British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
Press, 1997. In the hollows of the plains are ponds or lakes of fresh and brackish water. Towards Chilean territory, the shingle gives way to porphyry, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
, and basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
lavas, and animal life becomes more abundant. Vegetation is more luxuriant, consisting principally of southern beech
''Nothofagus'', also known as the southern beeches, is a genus of 43 species of trees and shrubs native to the Southern Hemisphere in southern South America (Chile, Argentina) and Australasia (east and southeast Australia, New Zealand, New Gui ...
and conifers. The high rainfall against the western Andes ( Wet Andes) and the low sea-surface temperatures offshore give rise to cold and humid air masses, contributing to the ice fields and glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
s, the largest ice fields in the Southern Hemisphere outside of Antarctica.
Among the depressions by which the plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
is intersected transversely, the principal ones are the Gualichu
Gualichu, or gualicho, in Mapuche mythology and mainly in the Tehuelche culture, was an evil spirit or demon, comparable but not similar to the Devil.
Description
As the Araucanians had not a properly called god of evil, Gualichu was not worshi ...
, south of the Río Negro, the Maquinchao and Valcheta (through which previously flowed the waters of Nahuel Huapi Lake
Nahuel Huapi Lake ( es, Lago Nahuel Huapí) is a lake in the lake region of northern Patagonia between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén, in Argentina. The tourist center of Bariloche is on the southern shore of the lake.
The June 2 ...
, which now feed the Limay River), the Senguerr
The Senguerr River is a river of the Argentine province of Chubut. It begins its journey from the system of glacial lakes La Plata and Fontana in the Andes Mountains
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest cont ...
(spelled Senguer on most Argentine maps and within the corresponding region), and the Deseado River
Deseado River () is a river in the Argentine province of Santa Cruz. The name Deseado comes from the English ''Desire'', the name of one of the two ships commanded by John Davis during the Thomas Cavendish expedition of 1592.
The source of t ...
. Besides these transverse depressions (some of them marking lines of ancient interoceanic communication), others were occupied by either more or less extensive lakes, such as the Yagagtoo, Musters, and Colhue Huapi, and others situated to the south of Puerto Deseado in the center of the country.
Across much of Patagonia east of the Andes, volcanic eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are oft ...
s have created formation of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
ic lava plateaus during the Cenozoic. The plateaus are of different ages with the older –of Neogene and Paleogene age– being located at higher elevations than Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
and Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene togeth ...
lava plateaus and outcrops.
Erosion, which is caused principally by the sudden melting and retreat of ice aided by tectonic
Tectonics (; ) are the processes that control the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. These include the processes of mountain building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents ...
changes, has scooped out a deep longitudinal depression, best in evidence where in contact with folded Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
rocks, which are lifted up by the Cenozoic granite. It generally separates the plateau from the first lofty hills, whose ridges are generally called the pre-Cordillera. To the west of these, a similar longitudinal depression extends all along the foot of the snowy Andean Cordillera. This latter depression contains the richest, most fertile land of Patagonia. Lake basins along the Cordillera were also gradually excavated by ice streams, including Lake Argentino
Lago Argentino is a lake in the Patagonian province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, at . It is the biggest freshwater lake in Argentina, with a surface area of (maximum width: ). It has an average depth of , and a maximum depth of .
The lake lies with ...
and Lake Fagnano
Fagnano Lake ( es, Lago Fagnano), also called ''Lake Cami'' (), is a lake located on the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, main island of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, and shared by Argentina and Chile. The 645 km2 lake runs east–west f ...
, as well as coastal bays such as Bahía Inútil.
Geology
 The geological limit of Patagonia has been proposed to be Huincul Fault, which forms a major discontinuity. The fault truncates various
The geological limit of Patagonia has been proposed to be Huincul Fault, which forms a major discontinuity. The fault truncates various structures
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
including the Pampean orogen found further north. The ages of base rocks change abruptly across the fault. Discrepancies have been mentioned among geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althoug ...
s on the origin of the Patagonian landmass. Víctor Ramos has proposed that the Patagonian landmass originated as an allochthon
upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a nappe. If an erosional hole is created in the nappe that is called a window (geology)">window. A klippe is a solitary out ...
ous terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust (geology), crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and Accretion (geology), accreted or "Suture (geology), sutured" to crust lying on another pla ...
that separated from Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and docked in South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
250 to 270 Mya in the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last ...
period. A 2014 study by R.J. Pankhurst and coworkers rejects any idea of a far-traveled Patagonia, claiming it is likely of parautochtonous (nearby) origin.
The Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
and Cenozoic deposits have revealed a most interesting vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
fauna. This, together with the discovery of the perfect cranium of a chelonian of the genus '' Niolamia'', which is almost identical to ''Ninjemys oweni'' of the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in ...
age in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
, forms an evident proof of the connection between the Australian and South American continents. The Patagonian ''Niolamia'' belongs to the Sarmienti Formation. Fossils of the mid-Cretaceous ''Argentinosaurus
''Argentinosaurus'' is a genus of giant sauropod dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Argentina. Although it is only known from fragmentary remains, ''Argentinosaurus'' is one of the largest known land animal ...
'', which may be the largest of all dinosaurs, have been found in Patagonia, and a model of the mid-Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
''Piatnitzkysaurus
''Piatnitzkysaurus'' ( meaning "Piatnitzky's lizard") is a genus of megalosauroid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 179 to 177 million years ago during the lower part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Argentina. ''Piatnitzkysaurus'' ...
'' graces the concourse of the Trelew
Trelew (, from cy, tref "town" and the name of the founder, Lewis Jones) is a city in the eastern part of the Chubut Province of Argentina. Located in Patagonia, the city is the largest and most populous in the low valley of the Chubut River, wi ...
airport (the skeleton is in the Trelew paleontological museum; the museum's staff has also announced the discovery of a species of dinosaur even bigger than ''Argentinosaurus''). Of more than paleontological interest, the middle Jurassic Los Molles Formation
The Los Molles Formation is a geologic formation of Early to Middle Jurassic age, located at northern and central part of Neuquén Basin at Mendoza Shelf in Argentina. It is overlain by the Niyeu–Lajas Formation.McIlroy et al., 2005
Descrip ...
and the still richer late Jurassic ( Tithonian) and early Cretaceous (Berriasian
In the geological timescale, the Berriasian is an age/stage of the Early/Lower Cretaceous. It is the oldest subdivision in the entire Cretaceous. It has been taken to span the time between 145.0 ± 4.0 Ma and 139.8 ± 3.0 Ma (million years ago ...
) Vaca Muerta
The Vaca Muerta Formation, commonly known as Vaca Muerta (Spanish for ''Dead Cow''), is a geologic formation of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous age, located in the Neuquén Basin in northern Patagonia, Argentina. It is well known as the host ro ...
formation above it in the Neuquén basin are reported to contain huge hydrocarbon reserves (mostly gas in Los Molles, both gas and oil in Vaca Muerta) partly accessible through hydraulic fracturing. Other specimens of the interesting fauna of Patagonia, belonging to the Middle Cenozoic, are the gigantic wingless birds, exceeding in size any hitherto known, and the singular mammal ''Pyrotherium
''Pyrotherium'' ('fire beast') is an extinct genus of South American ungulate, of the order Pyrotheria, that lived in what is now Argentina and Bolivia, during the Late Oligocene.cetaceans have been discovered.
During the Oligocene and early
 Patagonia's climate is mostly cool and dry year round. The east coast is warmer than the west, especially in summer, as a branch of the southern equatorial current reaches its shores, whereas the west coast is washed by a cold current. However, winters are colder on the inland plateaus east of the slopes and further down the coast on the southeast end of the Patagonian region. For example, at Puerto Montt, on the inlet behind Chiloé Island, the mean annual temperature is and the average extremes are , whereas at Bahía Blanca near the Atlantic coast and just outside the northern confines of Patagonia, the annual temperature is and the range much greater, as temperatures above 35°C and below −5°C are recorded every year. At Punta Arenas, in the extreme south, the mean temperature is and the average extremes are . The prevailing winds are westerly, and the westward slope has a much heavier precipitation than the eastern in a
Patagonia's climate is mostly cool and dry year round. The east coast is warmer than the west, especially in summer, as a branch of the southern equatorial current reaches its shores, whereas the west coast is washed by a cold current. However, winters are colder on the inland plateaus east of the slopes and further down the coast on the southeast end of the Patagonian region. For example, at Puerto Montt, on the inlet behind Chiloé Island, the mean annual temperature is and the average extremes are , whereas at Bahía Blanca near the Atlantic coast and just outside the northern confines of Patagonia, the annual temperature is and the range much greater, as temperatures above 35°C and below −5°C are recorded every year. At Punta Arenas, in the extreme south, the mean temperature is and the average extremes are . The prevailing winds are westerly, and the westward slope has a much heavier precipitation than the eastern in a
 The
The
 Human habitation of the region dates back thousands of years, with some early archaeological findings in the area dated to at least the 13th millennium BC, although later dates around the
Human habitation of the region dates back thousands of years, with some early archaeological findings in the area dated to at least the 13th millennium BC, although later dates around the  The
The
 Navigators such as
Navigators such as
/ref> The Atlantic coast of Patagonia was first fully explored in 1520 by the Magellan's circumnavigation, Spanish expedition led by
 The main interest in the region sparked by Pigafetta's account came from his reports of their meeting with the local inhabitants, whom they claimed to measure some 9 to 12 feet in height – "so tall that we reached only to his waist" – hence the later idea that Patagonia meant "big feet". This supposed race of Patagonian giants or
The main interest in the region sparked by Pigafetta's account came from his reports of their meeting with the local inhabitants, whom they claimed to measure some 9 to 12 feet in height – "so tall that we reached only to his waist" – hence the later idea that Patagonia meant "big feet". This supposed race of Patagonian giants or
 Two hydrographic surveys of the coasts were of first-rate importance; the first expedition (1826–1830) included HMS ''Adventure'' and HMS ''Beagle'' under
Two hydrographic surveys of the coasts were of first-rate importance; the first expedition (1826–1830) included HMS ''Adventure'' and HMS ''Beagle'' under
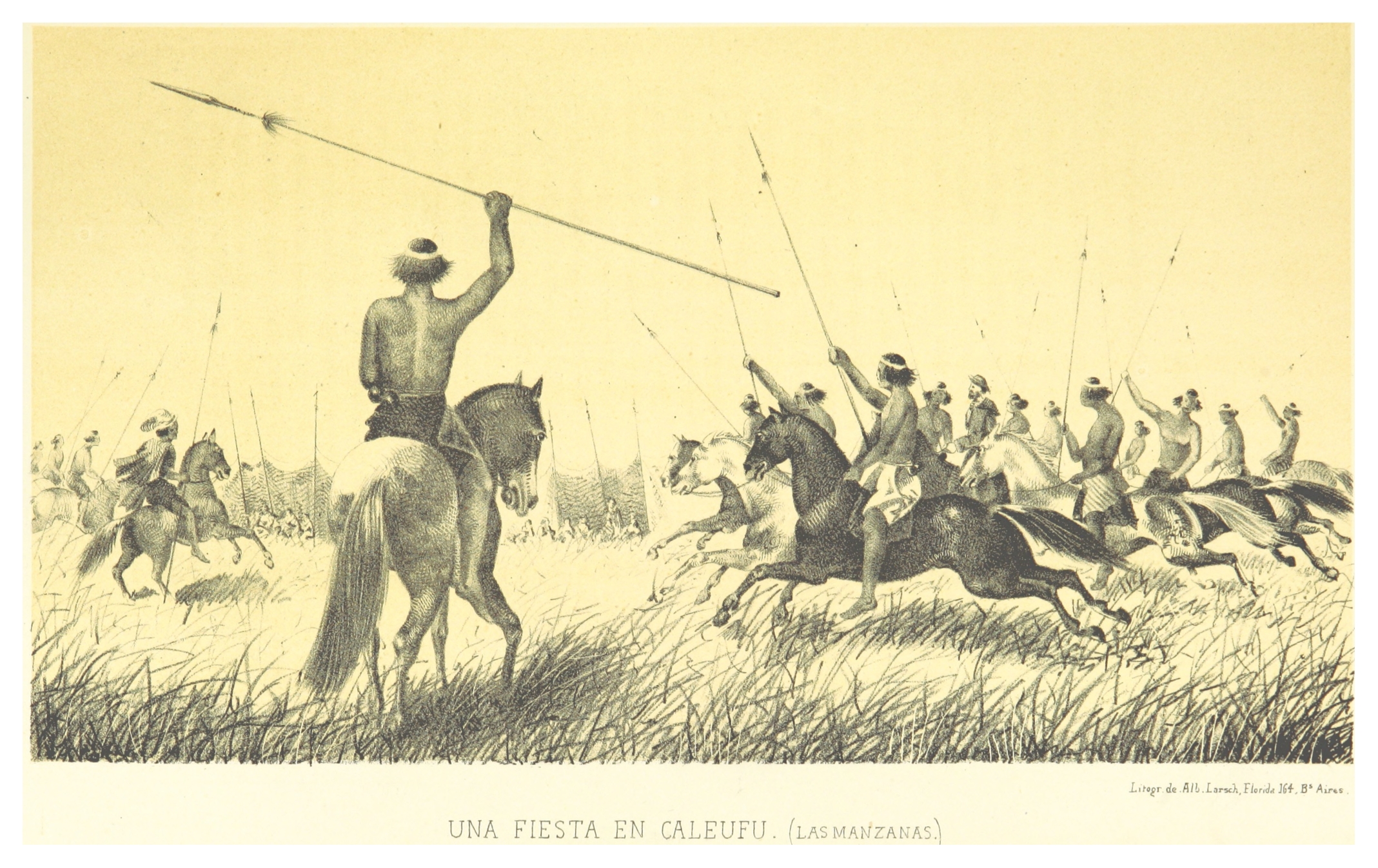
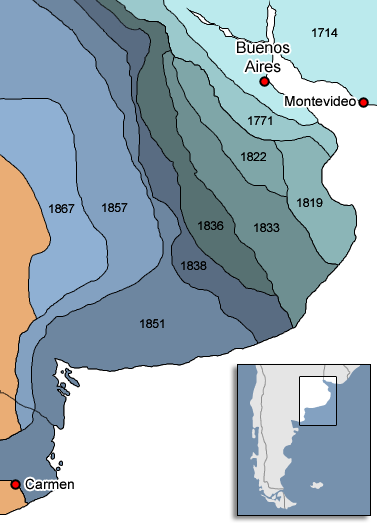 In the mid-19th century, the newly independent nations of Argentina and Chile began an aggressive phase of expansion into the south, increasing confrontation with the Indigenous peoples of the region. In 1860, French adventurer Orelie-Antoine de Tounens proclaimed himself king of the
In the mid-19th century, the newly independent nations of Argentina and Chile began an aggressive phase of expansion into the south, increasing confrontation with the Indigenous peoples of the region. In 1860, French adventurer Orelie-Antoine de Tounens proclaimed himself king of the
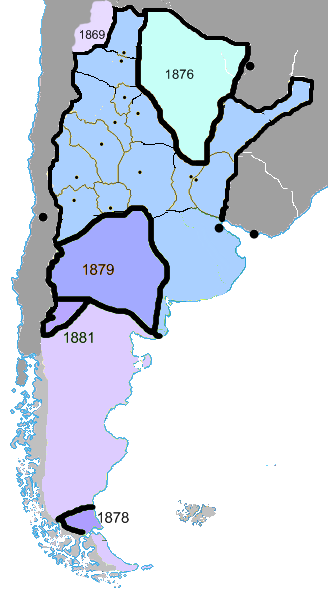 Argentine authorities worried that the strong connections araucanized tribes had with Chile would allegedly give Chile certain influence over the pampas. Argentine authorities feared that in an eventual war with Chile over Patagonia, the natives would side with the Chileans and the war would be brought to the vicinity of Buenos Aires.
The decision to plan and execute the Conquest of the Desert was probably catalyzed by the 1872 attack of Cufulcurá and his 6,000 followers on the cities of General Alvear, Veinticinco de Mayo, and Nueve de Julio, where 300 ''
Argentine authorities worried that the strong connections araucanized tribes had with Chile would allegedly give Chile certain influence over the pampas. Argentine authorities feared that in an eventual war with Chile over Patagonia, the natives would side with the Chileans and the war would be brought to the vicinity of Buenos Aires.
The decision to plan and execute the Conquest of the Desert was probably catalyzed by the 1872 attack of Cufulcurá and his 6,000 followers on the cities of General Alvear, Veinticinco de Mayo, and Nueve de Julio, where 300 ''
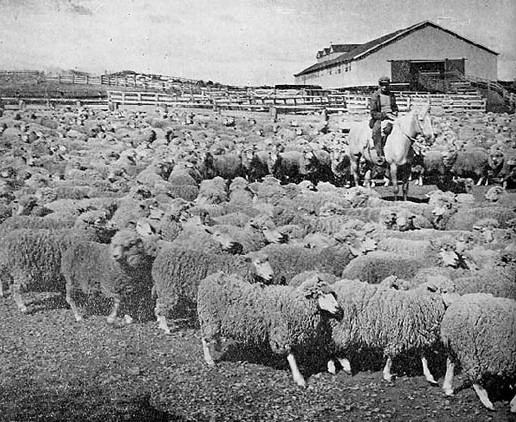 The area's principal economic activities have been mining, whaling, livestock (notably sheep throughout) agriculture (wheat and fruit production near the Andes towards the north), and oil after its discovery near Comodoro Rivadavia in 1907.''Time Out Patagonia'', Cathy Runciman (ed),
The area's principal economic activities have been mining, whaling, livestock (notably sheep throughout) agriculture (wheat and fruit production near the Andes towards the north), and oil after its discovery near Comodoro Rivadavia in 1907.''Time Out Patagonia'', Cathy Runciman (ed),
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, large swathes of Patagonia were subject to a marine transgression
A marine transgression is a geologic event during which sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, which results in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling ...
, which might have temporarily linked the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans, as inferred from the findings of marine invertebrate fossils of both Atlantic and Pacific affinity in La Cascada Formation
La Cascada Formation a sedimentary formation near Futaleufú in the western Patagonian Andes of southern Chile. Lithologies vary from sandstone, siltstone and conglomerate. The sediment that now forms the rock deposited during the Oligocene and ...
. Connection would have occurred through narrow epicontinental seaways that formed channels in a dissected topography. The Antarctic Plate
The Antarctic Plate is a tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau, and some remote islands in the Southern Ocean and other surrounding oceans. After breakup from Gondwana (the southern part of the superconti ...
started to subduct
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
beneath South America 14 million years ago in the Miocene, forming the Chile Triple Junction. At first, the Antarctic Plate subducted only in the southernmost tip of Patagonia, meaning that the Chile Triple Junction was located near the Strait of Magellan. As the southern part of the Nazca Plate and the Chile Rise became consumed by subduction, the more northerly regions of the Antarctic Plate began to subduct beneath Patagonia so that the Chile Triple Junction advanced to the north over time. The asthenospheric window
In geology, a slab window is a gap that forms in a subducted oceanic plate when a mid-ocean ridge meets with a subduction zone and plate divergence at the ridge and convergence at the subduction zone continue, causing the ridge to be subducted. ...
associated to the triple junction disturbed previous patterns of mantle convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface.
The Earth's surface lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere and the two for ...
beneath Patagonia inducing an uplift of c. 1 km that reversed the Miocene transgression.
Political divisions
At a state level, Patagonia visually occupies an area within two countries: approximately 10% inChile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and approximately 90% in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. Both countries have organized their Patagonian territories into nonequivalent administrative subdivisions: provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
and departments in Argentina, as well as regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, and communes
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, relig ...
in Chile. As Chile is a unitary state
A unitary state is a sovereign state governed as a single entity in which the central government is the supreme authority. The central government may create (or abolish) administrative divisions (sub-national units). Such units exercise only ...
, its first-level administrative divisions—the regions—enjoy far less autonomy than analogous Argentine provinces. Argentine provinces have elected governors and legislatures, while Chilean regions have government-appointed intendants.
The Patagonian Provinces of Argentina are Neuquén
Neuquén (; arn, Nehuenken) is the capital city of the Argentine province of Neuquén and of the Confluencia Department, located in the east of the province. It occupies a strip of land west of the confluence of the Limay and Neuquén river ...
, Río Negro, Chubut, Santa Cruz, and Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
. The southernmost part of Buenos Aires Province can also be considered part of Patagonia.
The two Chilean regions undisputedly located entirely within Patagonia are Aysén and Magallanes. Palena Province
Palena Province ( es, Provincia de Palena) is the southernmost administrative area in Chile's Los Lagos Region Los Lagos (X). The area is also called Continental Chiloe or Northern Patagonia, as geographers consider the Palena Province to be the ...
, a part of the Los Lagos Region
Los Lagos Region ( es, Región de Los Lagos , ''Region of the Lakes'') is one of Chile's 16 regions, which are first order administrative divisions, and comprises four provinces: Chiloé, Llanquihue, Osorno and Palena. The region contains ...
, is also located within Patagonia. By some definitions, Chiloé Archipelago, the rest of the Los Lagos Region, and part of the Los Ríos Region are also part of Patagonia.
Climate
 Patagonia's climate is mostly cool and dry year round. The east coast is warmer than the west, especially in summer, as a branch of the southern equatorial current reaches its shores, whereas the west coast is washed by a cold current. However, winters are colder on the inland plateaus east of the slopes and further down the coast on the southeast end of the Patagonian region. For example, at Puerto Montt, on the inlet behind Chiloé Island, the mean annual temperature is and the average extremes are , whereas at Bahía Blanca near the Atlantic coast and just outside the northern confines of Patagonia, the annual temperature is and the range much greater, as temperatures above 35°C and below −5°C are recorded every year. At Punta Arenas, in the extreme south, the mean temperature is and the average extremes are . The prevailing winds are westerly, and the westward slope has a much heavier precipitation than the eastern in a
Patagonia's climate is mostly cool and dry year round. The east coast is warmer than the west, especially in summer, as a branch of the southern equatorial current reaches its shores, whereas the west coast is washed by a cold current. However, winters are colder on the inland plateaus east of the slopes and further down the coast on the southeast end of the Patagonian region. For example, at Puerto Montt, on the inlet behind Chiloé Island, the mean annual temperature is and the average extremes are , whereas at Bahía Blanca near the Atlantic coast and just outside the northern confines of Patagonia, the annual temperature is and the range much greater, as temperatures above 35°C and below −5°C are recorded every year. At Punta Arenas, in the extreme south, the mean temperature is and the average extremes are . The prevailing winds are westerly, and the westward slope has a much heavier precipitation than the eastern in a rainshadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
effect; the western islands close to Torres del Paine
The Cordillera Paine is a mountain group in Torres del Paine National Park in Chilean Patagonia. The cordillera is located north of Punta Arenas, and about south of the Chilean capital Santiago. It belongs to the Commune of Torres del Paine i ...
receive an annual precipitation of 4,000 to 7,000 mm, whilst the eastern hills are less than 800 mm and the plains may be as low as 200 mm annual precipitation.
Precipitation is highly seasonal in northwestern Patagonia. For example, Villa La Angostura
Villa La Angostura (Spanish for ''Town of the Narrowing'') is a town located in the Los Lagos Department in the south of the Argentine province of Neuquén, on the northwest shore of the Nahuel Huapi Lake.
Nestled in the northern part of the Nahu ...
in Argentina, close to the border with Chile, receives up to 434 mm of rain and snow in May, 297 mm in June, and 273 in July, compared to 80 in February and 72 in March. The total for the city is 2074 mm, making it one of the rainiest in Argentina. Further west, some areas receive up to 4,000 mm and more, especially on the Chilean side. In the northeast, the seasons for rain are reversed; most rain falls from occasional summer thunderstorms but totals barely reach 500 mm in the northeast corner, and rapidly decrease to less than 300 mm. The Patagonian west coast, which belongs exclusively to Chile, has a cool oceanic climate, with summer maximum temperatures ranging from 14°C in the south to 19°C in the north (and nights between 5 and 11°C) and very high precipitation, from 2,000 to more than 7,000 mm in local microclimates. Snow is uncommon at the coast in the north but happens more often in the south, and frost is usually not very intense.
Immediately east from the coast are the Andes, cut by deep fjords in the south and by deep lakes in the north, and with varying temperatures according to the altitude. The tree line ranges from close to 2,000 m on the northern side (except for the Andes in northern Neuquén in Argentina, where sunnier and dryer conditions allow trees to grow up to close to 3,000 m), and diminishes southward to only 600–800m in Tierra del Fuego. Precipitation changes dramatically from one spot to the other and diminishes very quickly eastward. An example of this is Laguna Frías, in Argentina, which receives 4,400 mm yearly. The city of Bariloche, about 40 km further east, receives about 1,000 mm, and the airport, another 15 km east, receives less than 600 mm. The easterly slopes of the Andes are home to several Argentine cities: San Martín de los Andes
San Martín de los Andes is a city in the south-west of the , serving as the administration centre of the Lácar Department. Lying at the foot of the Andes, on the Lácar lake, it is considered one of the main tourism destinations in the province. ...
, Bariloche, El Bolsón, Esquel
Esquel is a town in the northwest of Chubut Province in Argentine Patagonia. It is located in Futaleufú Department, of which it is the government seat. The town's name derives from one of two Tehuelche words: one meaning "marsh" and the other ...
, and El Calafate
El Calafate, also known as ''Calafate'', is a city in Patagonia, Argentina. It is situated on the southern border of Lake Argentino, in the southwest part of the Santa Cruz Province (Argentina), Santa Cruz Province, about northwest of Río Galleg ...
. Temperatures there are milder in the summer (in the north, between 20 and 24°C, with cold nights between 4 and 9°C; in the south, summers are between 16 and 20°C, at night temperatures are similar to the north) and much colder in the winter, with frequent snowfall (although snow cover rarely lasts very long). Daytime highs range from 3 to 9°C in the north, and from 0 to 7°C in the south, whereas nights range from −5 to 2°C everywhere. Cold waves can bring much colder values; a temperature of −25°C has been recorded in Bariloche, and most places can often have temperatures between −12 and −15°C and highs staying around 0°C for a few days.
Directly east of these areas, the weather becomes much harsher; precipitation drops to between 150 and 300 mm, the mountains no longer protect the cities from the wind, and temperatures become more extreme. Maquinchao is a few hundred kilometers east of Bariloche, at the same altitude on a plateau, and summer daytime temperatures are usually about 5°C warmer, rising up to 35°C sometimes, but winter temperatures are much more extreme: the record is −35°C, and some nights not uncommonly reach 10°C colder than Bariloche. The plateaus in Santa Cruz province and parts of Chubut usually have snow cover through the winter, and often experience very cold temperatures. In Chile, the city of Balmaceda is known for being situated in this region (which is otherwise almost exclusively in Argentina), and for being the coldest place in Chile, with temperatures below −20°C every once in a while.
The northern Atlantic coast has warm summers (28 to 32°C, but with relatively cool nights at 15°C) and mild winters, with highs around 12°C and lows about 2–3°C. Occasionally, temperatures reach −10 or 40°C, and rainfall is very scarce. The weather only gets a bit colder further south in Chubut, and the city of Comodoro Rivadavia has summer temperatures of 24 to 28°C, nights of 12 to 16°C, and winters with days around 10°C and nights around 3°C, and less than 250 mm of rain. However, a drastic drop occurs as one moves south to Santa Cruz; Rio Gallegos, in the south of the province, has summer temps of 17 to 21°C, (nights between 6 and 10°C) and winter temperatures of 2 to 6°C, with nights between −5 and 0°C, despite being right on the coast. Snowfall is common despite the dryness, and temperatures are known to fall to under −18°C and to remain below freezing for several days in a row. Rio Gallegos is also among the windiest places on Earth, with winds reaching 100 km/h occasionally.
Tierra del Fuego is extremely wet in the west, relatively damp in the south, and dry in the north and east. Summers are cool (13 to 18°C in the north, 12 to 16°C in the south, with nights generally between 3 and 8°C), cloudy in the south, and very windy. Winters are dark and cold, but without the extreme temperatures in the south and west (Ushuaia
Ushuaia ( , ) is the capital of Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur Province, Argentina. With a population of nearly 75,000 and a location below the 54th parallel south latitude, Ushuaia claims the title of world's souther ...
rarely reaches −10°C, but hovers around 0°C for several months, and snow can be heavy). In the east and north, winters are much more severe, with cold snaps bringing temperatures down to −20°C all the way to the Rio Grande on the Atlantic coast. Snow can fall even in the summer in most areas, as well.
Fauna
 The
The guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco ...
(''Lama guanicoe''), South American cougar
The South American cougar (''Puma concolor concolor''), also known as the Andean mountain lion or puma, is a cougar subspecies occurring in northern and western South America, from Colombia and Venezuela to Peru, Bolivia, Argentina and Chile. ...
, the Patagonian fox (''Lycalopex griseus''), Patagonian hog-nosed skunk (''Conepatus humboldtii''), and Magellanic tuco-tuco (''Ctenomys magellanicus''; a subterranean rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are n ...
) are the most characteristic mammals of the Patagonian plains. The Patagonian steppe
The Patagonian Desert, also known as the Patagonian Steppe, is the largest desert in Argentina and is the 8th largest desert in the world by area, occupying 673,000 square kilometers (260,000 mi2). It is located primarily in Argentina and ...
is one of the last strongholds of the guanaco and Darwin's rhea
Darwin's rhea or the lesser rhea (''Rhea pennata'') is a large flightless bird, the smaller of the two extant species of rheas. It is found in the Altiplano and Patagonia in South America.
Description
The lesser rhea stands at tall. Lengt ...
s (''Rhea pennata''), which had been hunted for their skins by the Tehuelches
The Tehuelche people, also called the Aónikenk, are an indigenous people from eastern Patagonia in South America. In the 18th and 19th centuries the Tehuelche were influenced by Mapuche people, and many adopted a horseriding lifestyle. Once a ...
, on foot using boleadoras
Bolas or bolases (singular bola; from Spanish and Portuguese ''bola'', "ball", also known as a ''boleadora'' or ''boleadeira'') is a type of throwing weapon made of weights on the ends of interconnected cords, used to capture animals by entan ...
, before the diffusion of firearms and horses; they were formerly the chief means of subsistence for the natives, who hunted them on horseback with dogs and bolas
Bolas or bolases (singular bola; from Spanish and Portuguese ''bola'', "ball", also known as a ''boleadora'' or ''boleadeira'') is a type of throwing weapon made of weights on the ends of interconnected cords, used to capture animals by entan ...
. Vizcachas (''Lagidum'' spp.) and the Patagonian mara
The Patagonian mara (''Dolichotis patagonum'') is a relatively large rodent in the mara genus ''Dolichotis''. It is also known as the Patagonian cavy, Patagonian hare, or dillaby. This herbivorous, somewhat rabbit-like animal is found in open and ...
(''Dolichotis patagonum'') are also characteristic of the steppe and the pampas to the north.
Bird life is often abundant. The crested caracara
The crested caracara (''Caracara plancus'') is a bird of prey in the family Falconidae. It is found from the southern United States through Central and South America to Tierra del Fuego. It was formerly placed in the genus ''Polyborus''.
Descri ...
(''Caracara plancus'') is one of the characteristic objects of a Patagonian landscape; the presence of austral parakeets (''Enicognathus ferrugineus'') as far south as the shores of the strait attracted the attention of the earlier navigators, and green-backed firecrowns (''Sephanoides sephaniodes''), a species of hummingbird, may be seen flying amid the snowfall. One of the largest birds in the world, the Andean condor
The Andean condor (''Vultur gryphus'') is a giant South American Cathartid vulture and is the only member of the genus ''Vultur''. Found in the Andes mountains and adjacent Pacific coasts of western South America, the Andean condor is the larg ...
(''Vultur gryphus'') can be seen in Patagonia. Of the many kinds of waterfowl the Chilean flamingo
The Chilean flamingo (''Phoenicopterus chilensis'') is a species of large flamingo at closely related to the American flamingo and the greater flamingo, with which it was sometimes considered conspecific. The species is listed as near threatened ...
(''Phoenicopterus chilensis''), the upland goose
The upland goose or Magellan goose (''Chloephaga picta'') is a sheldgoose of the Tadorninae, shelduck-sheldgoose subfamily of the Anatidae, the biological Family (biology), family that includes the ducks and most duck-like waterfowl such as the G ...
(''Chloephaga picta''), and in the strait, the remarkable steamer ducks are found.
Signature marine fauna include the southern right whale, the Magellanic penguin
The Magellanic penguin (''Spheniscus magellanicus'') is a South American penguin, breeding in coastal Patagonia, including Argentina, Chile, and the Falkland Islands, with some migrating to Brazil and Uruguay, where they are occasionally seen a ...
(''Spheniscus magellanicus''), the killer whale
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white ...
, and elephant seal
Elephant seals are very large, oceangoing earless seals in the genus ''Mirounga''. Both species, the northern elephant seal (''M. angustirostris'') and the southern elephant seal (''M. leonina''), were hunted to the brink of extinction for oi ...
s. The Valdés Peninsula
The Valdes Peninsula (Spanish: ''Península Valdés'') is a peninsula into the Atlantic Ocean in the Biedma Department of north-east Chubut Province, Argentina. Around in size (not taking into account the isthmus of Carlos Ameghino which connect ...
is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, designated for its global significance as a site for the conservation of marine mammals
Marine mammals are aquatic mammals that rely on the ocean and other marine ecosystems for their existence. They include animals such as seals, whales, manatees, sea otters and polar bears. They are an informal group, unified only by their re ...
.
The Patagonian freshwater fish fauna is relatively restricted compared to other similar Southern Hemisphere regions. The Argentine part is home to a total of 29 freshwater fish species, 18 of which are native. The introduced are several species of trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salm ...
, common carp, and various species that originated in more northerly parts of South America. The natives are osmeriforms (''Aplochiton
''Aplochiton'' is a genus of osmeriform fish of the family Galaxiidae native to Argentina, Chile and the Falklands Islands.
Species
FishBase
FishBase is a global species database of fish species (specifically finfish). It is the largest an ...
'' and ''Galaxias
''Galaxias'' is a genus of small freshwater fish in the family Galaxiidae, and are frequently referred to as the galaxiids. These highly adaptable fish are typically found at temperate latitudes across the Southern Hemisphere.
Galaxiids are ...
''), temperate perch
The members of the family Percichthyidae are known as the temperate perches. They belong to the order Perciformes, the perch-like fishes.
The name Percichthyidae derives from the Latin ''perca'' for perch and Ancient Greek ἰχθύς, ''ichthy ...
es (''Percichthys
''Percichthys'' is a genus of temperate perches native to freshwater habitats in Argentina and Chile.
Species
The currently recognized species in this genus are:
* '' Percichthys chilensis'' Girard, 1855
* '' Percichthys colhuapiensis'' MacDon ...
''), catfish
Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive ...
('' Diplomystes'', '' Hatcheria'' and ''Trichomycterus
''Trichomycterus'' is a genus of fish in the family Trichomycteridae, the largest genus of its family with over 170 species currently described. This genus is native to freshwater habitats in Central and South America. These fish are generally sm ...
''), Neotropical silverside
The Neotropical silversides are a family, Atherinopsidae, of fishes in the order Atheriniformes. About 112 species in 13 genera are distributed throughout the tropical and temperate waters of the New World, including both marine and freshwater h ...
s (''Odontesthes
''Odontesthes'' is a genus of Neotropical silversides. They are found in fresh, brackish and salt water habitats in the southern half of South America (north to Brazil and Peru), as well as the offshore Juan Fernández and Falkland Islands. Addi ...
'') and characiform
Characiformes is an order of ray-finned fish, comprising the characins and their allies. Grouped in 18 recognized families, more than 2000 different species are described, including the well-known piranha and tetras.; Buckup P.A.: "Relationshi ...
s (''Astyanax
In Greek mythology, Astyanax (; grc, Ἀστυάναξ ''Astyánax'', "lord of the city") was the son of Hector, the crown prince of Troy, and his wife, Princess Andromache of Cilician Thebe."Astyanax". ''Oxford Classical Dictionary''. Oxford, 1 ...
'', '' Cheirodon'', '' Gymnocharacinus'', and '' Oligosarcus''). Other Patagonian freshwater fauna include the highly unusual aeglid crustacean.
History
Pre-Columbian Patagonia (10,000 BC – AD 1520)
10th millennium BC
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC (c. 12 ka to c. 11 ka). It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic ( Northern Europe and Western Europe) and Epip ...
are more securely recognized. Evidence exists of human activity at Monte Verde
Monte Verde is an archaeological site in the Llanquihue Province in southern Chile, located near Puerto Montt, Southern Chile, which has been dated to as early as 18,500 cal BP (16,500 BC). Previously, the widely accepted date for early occu ...
in Llanquihue Province
Llanquihue Province ( es, Provincia de Llanquihue) is one of four provinces of the Chilean region of Los Lagos (X). Its capital is Puerto Montt. Chile's second largest lake, Lake Llanquihue, is located in the province as well as four volcanoes: ...
, Chile, dated to around 12,500 BC. The glacial-period ice fields and subsequent large meltwater streams would have made settlement difficult at that time.
The region seems to have been inhabited continuously since 10,000 BC, by various cultures and alternating waves of migration, the details of which are as yet poorly understood. Several sites have been excavated, notably caves such as Cueva del Milodon
Cuevas or Cueva (Spanish for "''cave(s)''") may refer to:
Places
* Cueva de Ágreda, a municipality located in the province of Soria, Castile and León, Spain
* Cuevas Bajas, a town and municipality in the province of Málaga, part of the autono ...
in Última Esperanza in southern Patagonia, and Tres Arroyos
Tres Arroyos is a city in Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. It is the administrative seat of Tres Arroyos Partido.
The city has a sizable population of Danish and Dutch descent.
Tres Arroyos is served by Tres Arroyos Airport.
Climate
Tres Ar ...
on Tierra del Fuego, that support this date. Hearths, stone scrapers, and animal remains dated to 9400–9200 BC have been found east of the Andes.
 The
The Cueva de las Manos
Cueva de las Manos (Spanish for Cave of the Hands or Cave of Hands) is a cave and complex of rock art sites in the province of Santa Cruz, Argentina, south of the town of Perito Moreno. It is named for the hundreds of paintings of hands ste ...
is a famous site in Santa Cruz, Argentina. This cave at the foot of a cliff is covered in wall paintings, particularly the negative images of hundreds of hands, believed to date from around 8000 BC.
Based on artifacts found in the region, apparently hunting of guanaco, and to a lesser extent rhea (''ñandú''), were the primary food sources of tribes living on the eastern plains. Whether the megafauna of Patagonia, including the ground sloth and horse, were extinct in the area before the arrival of humans is unclear, although this is now the more widely accepted account. It is also not clear if domestic dogs were part of early human activity. ''Bolas
Bolas or bolases (singular bola; from Spanish and Portuguese ''bola'', "ball", also known as a ''boleadora'' or ''boleadeira'') is a type of throwing weapon made of weights on the ends of interconnected cords, used to capture animals by entan ...
'' are commonly found and were used to catch guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco ...
and rhea. A maritime tradition existed along the Pacific coast, whose latest exponents were the Yaghan (Yámana) to the south of Tierra del Fuego, the Kaweshqar between Taitao Peninsula
The Taitao Peninsula (Spanish: ''Península de Taitao'') is a westward projection of the mainland of Chile, with which it is connected by the narrow Isthmus of Ofqui, over which the natives and early missionaries were accustomed to carry their bo ...
and Tierra del Fuego, and the Chono people
The Chono people, or GuaitecoUrbina Burgos 2007, p. 334. were a nomadic indigenous people or group of peoples of the archipelagos of Chiloé, Guaitecas and Chonos.
The Chono people lived as hunter-gatherers traveling by canoe.
Much of what is ...
in the Chonos Archipelago
The Chonos Archipelago is a series of low, mountainous, elongated islands with deep bays, traces of a submerged Chilean Coast Range. Most of the islands are forested with little or no human settlement. The deep Moraleda Channel separates the isl ...
. The Selk'nam
The Selk'nam, also known as the Onawo or Ona people, are an indigenous people in the Patagonian region of southern Argentina and Chile, including the Tierra del Fuego islands. They were one of the last native groups in South America to be enco ...
, Haush
The Haush or Manek'enk were an indigenous people who lived on the Mitre Peninsula of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. They were related culturally and linguistically to the Ona or Selk'nam people who also lived on the Isla Grande de Tierra ...
, and Tehuelche are generally thought to be culturally and linguistically related peoples physically distinct from the sea-faring peoples.
It is possible that Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego (English: ''Big Island of the Land of Fire'') also formerly ''Isla de Xátiva''Early Holocene
In the geologic time scale, the Greenlandian is the earliest age or lowest stage of the Holocene Epoch or Series, part of the Quaternary. Beginning in 11,650 BP (9701 BCE or 300 HE) and ending 8,276 BP (6237 BCE or 3764 HE), it is the earlie ...
(c. 9000 years BP) much in the same way that Riesco Island
Riesco Island () lies at west of the Brunswick Peninsula, Chile. It is one of the largest islands in Chile, with an area of . Its highest point is Mount Atalaya at . The island is bordered by two large piedmont embayments: Otway Sound and Skyring ...
was back then. A Selk'nam tradition recorded by the Salesian
, image = File:Stemma big.png
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of arms
, abbreviation = SDB
, formation =
, founder = John Bosco
, founding_location = Valdocco, Turin ...
missionary Giuseppe María Beauvoir
Giuseppe is the Italian form of the given name Joseph,
from Latin Iōsēphus from Ancient Greek Ἰωσήφ (Iōsḗph), from Hebrew יוסף.
It is the most common name in Italy and is unique (97%) to it.
The feminine form of the name is Giusep ...
relate that the Selk'nam
The Selk'nam, also known as the Onawo or Ona people, are an indigenous people in the Patagonian region of southern Argentina and Chile, including the Tierra del Fuego islands. They were one of the last native groups in South America to be enco ...
arrived in Tierra del Fuego by land, and that the Selk'nam were later unable to return north as the sea had flooded their crossing.
Agriculture was practised in Pre-Hispanic Argentina as far south as southern Mendoza Province
Mendoza, officially Province of Mendoza, is a province of Argentina, in the western central part of the country in the Cuyo region. It borders San Juan to the north, La Pampa and Neuquén to the south, San Luis to the east, and the republic o ...
. Agriculture was at times practised beyond this limit in nearby areas of Patagonia but populations reverted at times to non-agricultural lifestyles. By the time of the Spanish arrival to the area (1550s) there is no record of agriculture being practised in northern Patagonia. The extensive Patagonian grasslands
The Patagonian grasslands (NT0804) is an ecoregion in the south of Chile, Argentina and the Falkland Islands. The grasslands are home to diverse fauna, including several rare or endemic species of birds. There are few protected areas. The grasslan ...
and an associated abundance of guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco ...
game may have contributed for the indigenous populations to favour a hunter-gathered lifestyle.
The indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
of the region included the Tehuelches, whose numbers and society were reduced to near extinction not long after the first contacts with Europeans. Tehuelches included the Gununa'kena to the north, Mecharnuekenk in south-central Patagonia, and the Aonikenk or Southern Tehuelche in the far south, north of the Magellan strait. On Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego (English: ''Big Island of the Land of Fire'') also formerly ''Isla de Xátiva''Selk'nam
The Selk'nam, also known as the Onawo or Ona people, are an indigenous people in the Patagonian region of southern Argentina and Chile, including the Tierra del Fuego islands. They were one of the last native groups in South America to be enco ...
(Ona) and Haush
The Haush or Manek'enk were an indigenous people who lived on the Mitre Peninsula of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. They were related culturally and linguistically to the Ona or Selk'nam people who also lived on the Isla Grande de Tierra ...
(Manek'enk) lived in the north and southeast, respectively. In the archipelagos to the south of Tierra del Fuego were Yámana, with the Kawéskar (Alakaluf) in the coastal areas and islands in western Tierra del Fuego and the southwest of the mainland. In the Patagonian archipelagoes north of Taitao Peninsula
The Taitao Peninsula (Spanish: ''Península de Taitao'') is a westward projection of the mainland of Chile, with which it is connected by the narrow Isthmus of Ofqui, over which the natives and early missionaries were accustomed to carry their bo ...
lived the Chonos. These groups were encountered in the first periods of European contact with different lifestyles, body decoration, and language, although it is unclear when this configuration emerged.
Towards the end of the 16th century, Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who s ...
-speaking agriculturalists penetrated the western Andes and from there across into the eastern plains and down to the far south. Through confrontation and technological ability, they came to dominate the other peoples of the region in a short period of time, and are the principal indigenous community today.
Early European exploration (1520–1669)
Gonçalo Coelho
Gonçalo Coelho (fl. 1501–04) was a Portuguese explorer who belonged to a prominent family in northern Portugal. He commanded two expeditions (1501–02 and 1503–04) which explored much of the coast of Brazil.
Biography
In 1501 Coelho was se ...
and Amerigo Vespucci possibly had reached the area (his own account of 1502 has it that they reached the latitude 52°S), but Vespucci's failure to accurately describe the main geographical features of the region such as the Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
casts doubts on whether they really did so.
The first or more detailed description of part of the coastline of Patagonia is possibly mentioned in a Portuguese voyage in 1511–1512, traditionally attributed to captain Diogo Ribeiro, who after his death was replaced by Estevão de Frois, and was guided by the pilot and cosmographer
The term cosmography has two distinct meanings: traditionally it has been the protoscience of mapping the general features of the cosmos, heaven and Earth; more recently, it has been used to describe the ongoing effort to determine the large-scal ...
João de Lisboa
João de Lisboa (c.1470 – 1525) was a Portuguese explorer. He is known to have sailed together with Tristão da Cunha, and to have explored Río de La Plata and possibly the San Matias Gulf, around 1511-12.
The Brazilian historian Francisco Ado ...
). The explorers, after reaching Rio de la Plata (which they would explore on the return voyage, contacting the Charrúa
The Charrúa were an indigenous people or Indigenous Nation of the Southern Cone in present-day Uruguay and the adjacent areas in Argentina ( Entre Ríos) and Brazil ( Rio Grande do Sul). They were a semi-nomadic people who sustained themsel ...
and other peoples) eventually reached San Matias Gulf, at 42°S. The expedition reported that after going south of the 40th parallel, they found a "land" or a "point extending into the sea", and further south, a gulf. The expedition is said to have rounded the gulf for nearly and sighted the continent on the southern side of the gulf./ref> The Atlantic coast of Patagonia was first fully explored in 1520 by the Magellan's circumnavigation, Spanish expedition led by
Ferdinand Magellan
Ferdinand Magellan ( or ; pt, Fernão de Magalhães, ; es, link=no, Fernando de Magallanes, ; 4 February 1480 – 27 April 1521) was a Portuguese explorer. He is best known for having planned and led the 1519 Spanish expedition to the Eas ...
, who on his passage along the coast named many of its more striking features – San Matías Gulf, Cape of 11,000 Virgins (now simply Cape Virgenes
Capes in the Americas
Cape Virgenes ( es, Cabo Vírgenes, lit=Cape Virgins) is the southeastern tip of continental Argentina in South America. The southern one, a little to the south-west, is Punta Dungeness. Ferdinand Magellan reached it on 21 Oc ...
), and others. Magellan's fleet spent a difficult winter at what he named Puerto San Julián
Puerto San Julián, also known historically as Port St. Julian, is a natural harbour in Patagonia in the Santa Cruz Province of Argentina located at . In the days of sailing ships it formed a stopping point, south of Puerto Deseado (''Port Desir ...
before resuming its voyage further south on 21 August 1520. During this time, it encountered the local inhabitants, likely to be Tehuelche people
The Tehuelche people, also called the Aónikenk, are an indigenous people from eastern Patagonia in South America. In the 18th and 19th centuries the Tehuelche were influenced by Mapuche people, and many adopted a horseriding lifestyle. Once a ...
, described by his reporter, Antonio Pigafetta, as giants called Patagon
The Patagones or Patagonian giants were a race of giant humans rumoured to be living in Patagonia and described in early European accounts. They were said to have exceeded at least double normal human height, with some accounts giving heights of ...
s.
The territory became the Spanish colony of the Governorate of New Léon, granted in 1529 to Governor , part of the Governorates of the Spanish Empire
After the territorial division of South America between Spain and Portugal in the Treaty of Tordesillas (1494) the colonial administration of the continent was divided into Governorates.
Caribbean and Tierra Firme
* Governorate of Santo Doming ...
of the Americas. The territory was redefined in 1534 and consisted of the southernmost part of the South American continent and the islands towards Antarctica.
Rodrigo de Isla, sent inland in 1535 from San Matías by Simón de Alcazaba y Sotomayor (on whom western Patagonia had been conferred by Charles I of Spain
Charles V, french: Charles Quint, it, Carlo V, nl, Karel V, ca, Carles V, la, Carolus V (24 February 1500 – 21 September 1558) was Holy Roman Emperor and Archduke of Austria from 1519 to 1556, King of Spain ( Castile and Aragon) fro ...
, is presumed to have been the first European to have traversed the great Patagonian plain. If the men under his charge had not mutinied, he might have crossed the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
to reach the Pacific coast.
Pedro de Mendoza
Pedro de Mendoza () (c. 1499 – June 23, 1537) was a Spanish ''conquistador'', soldier and explorer, and the first ''adelantado'' of New Andalusia.
Setting sail
Pedro de Mendoza was born in Guadix, Grenada, part of a large noble family that ...
, on whom the country was next bestowed, founded Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, but did not venture south. (1539), Juan Ladrilleros (1557), and Hurtado de Mendoza Hurtado de Mendoza may refer to:
* Andrés Hurtado de Mendoza, 3rd Marquis of Cañete (circa 1500-1561), Spanish military officer
* Antonio Hurtado de Mendoza (1586–1644), Spanish dramatist
* Diego Hurtado de Mendoza (multiple)
* García Hurta ...
(1558) helped to make known the Pacific coasts, and while Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 ( ...
's voyage in 1577 down the Atlantic coast, through the Strait of Magellan and northward along the Pacific coast, was memorable, yet the descriptions of the geography of Patagonia owe much more to the Spanish explorer Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa
Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa (1532–1592) was a Spanish explorer, author, historian, mathematician, and astronomer. His birthplace is not certain and may have been Pontevedra, in Galicia, where his paternal family originated, or Alcalá de Henare ...
(1579–1580), who, devoting himself especially to the south-west region, made careful and accurate surveys. The settlements that he founded at Nombre de Jesús and San Felipe was neglected by the Spanish government, the latter being abandoned before Thomas Cavendish
Sir Thomas Cavendish (1560 – May 1592) was an English explorer and a privateer known as "The Navigator" because he was the first who deliberately tried to emulate Sir Francis Drake and raid the Spanish towns and ships in the Pacific and retu ...
visited it in 1587 during his circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the Mage ...
, and so desolate that he called it Port Famine. After the discovery of the route around Cape Horn, the Spanish Crown lost interest in southern Patagonia until the 18th century, when the coastal settlements Carmen de Patagones, San José, Puerto Deseado, and Nueva Colonia Floridablanca were established, although it maintained its claim of a ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' sovereignty over the area.
In 1669, the district around Puerto Deseado
Puerto Deseado, originally called Port Desire, is a city of about 15,000 inhabitants and a fishing port in Patagonia in Santa Cruz Province of Argentina, on the estuary of the Deseado River.
It was named ''Port Desire'' by the privateer Thomas ...
was explored by John Davis and was claimed in 1670 by Sir John Narborough
Rear-Admiral Sir John Narborough (or Narbrough, c. 1640–1688) was an English naval commander. He served with distinction in the Anglo-Dutch Wars and against the pirates of the Barbary Coast. He is also known for leading a poorly understood e ...
for King Charles II of England, but the English made no attempt to establish settlements or explore the interior.
Patagonian giants: early European perceptions
The first European explorers of Patagonia observed that the indigenous people in the region were taller than the average Europeans of the time, prompting some of them to believe that Patagonians were giants. According to Antonio Pigafetta, one of the Magellan expedition's few survivors and its published chronicler, Magellan bestowed the name ''Patagão'' (or ''Patagón'') on the inhabitants they encountered there, and the name "Patagonia" for the region. Although Pigafetta's account does not describe how this name came about, subsequent popular interpretations gave credence to a derivation meaning "land of the big feet". However, thisetymology
Etymology ()The New Oxford Dictionary of English (1998) – p. 633 "Etymology /ˌɛtɪˈmɒlədʒi/ the study of the class in words and the way their meanings have changed throughout time". is the study of the history of the Phonological chan ...
is questionable. The term is most likely derived from an actual character name, "Patagón", a savage creature confronted by Primaleón of Greece, the hero in the homonymous Spanish chivalry novel (or knight-errantry tale) by Francisco Vázquez. This book, published in 1512, was the sequel of the romance ''Palmerín de Oliva'';it was much in vogue at the time, and a favorite reading of Magellan. Magellan's perception of the natives, dressed in skins, and eating raw meat, clearly recalled the uncivilized Patagón in Vázquez's book. Novelist and travel writer Bruce Chatwin
Charles Bruce Chatwin (13 May 194018 January 1989) was an English travel writer, novelist and journalist. His first book, ''In Patagonia'' (1977), established Chatwin as a travel writer, although he considered himself instead a storyteller, ...
suggests etymological roots of both Patagon and Patagonia in his book, ''In Patagonia
''In Patagonia'' is an English travel book by Bruce Chatwin, published in 1977, about Patagonia, the southern part of South America.
Preparations
During the Second World War, Chatwin and his mother stayed at the home of his paternal grandparen ...
'', noting the similarity between "Patagon" and the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
word παταγος, which means "a roaring" or "gnashing of teeth" (in his chronicle, Pigafetta describes the Patagonians as "roaring like bulls").
 The main interest in the region sparked by Pigafetta's account came from his reports of their meeting with the local inhabitants, whom they claimed to measure some 9 to 12 feet in height – "so tall that we reached only to his waist" – hence the later idea that Patagonia meant "big feet". This supposed race of Patagonian giants or
The main interest in the region sparked by Pigafetta's account came from his reports of their meeting with the local inhabitants, whom they claimed to measure some 9 to 12 feet in height – "so tall that we reached only to his waist" – hence the later idea that Patagonia meant "big feet". This supposed race of Patagonian giants or Patagon
The Patagones or Patagonian giants were a race of giant humans rumoured to be living in Patagonia and described in early European accounts. They were said to have exceeded at least double normal human height, with some accounts giving heights of ...
es entered into the common European perception of this then little-known and distant area, to be further fueled by subsequent reports of other expeditions and famous travelers such as Sir Francis Drake, which seemed to confirm these accounts. Early charts of the New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
sometimes added the legend ''regio gigantum'' ("region of the giants") to the Patagonian area. By 1611, the Patagonian god Setebos (Settaboth in Pigafetta) was familiar to the hearers of ''The Tempest''.
The concept and general belief persisted for a further 250 years and was to be sensationally reignited in 1767 when an "official" (but anonymous) account was published of Commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
John Byron's recent voyage of global circumnavigation
Circumnavigation is the complete navigation around an entire island, continent, or astronomical body (e.g. a planet or moon). This article focuses on the circumnavigation of Earth.
The first recorded circumnavigation of the Earth was the Mage ...
in HMS ''Dolphin''. Byron and crew had spent some time along the coast, and the publication (''Voyage Round the World in His Majesty's Ship the Dolphin'') seemed to give proof positive of their existence; the publication became an overnight bestseller, thousands of extra copies were to be sold to a willing public, and other prior accounts of the region were hastily republished (even those in which giant-like folk were not mentioned at all).
However, the Patagonian giant frenzy died down substantially only a few years later, when some more sober and analytical accounts were published. In 1773, John Hawkesworth published on behalf of the Admiralty
Admiralty most often refers to:
*Admiralty, Hong Kong
*Admiralty (United Kingdom), military department in command of the Royal Navy from 1707 to 1964
*The rank of admiral
*Admiralty law
Admiralty can also refer to:
Buildings
* Admiralty, Traf ...
a compendium of noted English southern-hemisphere explorers' journals, including that of James Cook and John Byron. In this publication, drawn from their official logs, the people Byron's expedition had encountered clearly were no taller than , very tall but by no means giants. Interest soon subsided, although awareness of and belief in the concept persisted in some quarters even into the 20th century.
Spanish outposts
The Spanish failure at colonizing the Strait of Magellan madeChiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
assume the role of protecting the area of western Patagonia from foreign intrusions. Valdivia
Valdivia (; Mapuche: Ainil) is a city and commune in southern Chile, administered by the Municipality of Valdivia. The city is named after its founder Pedro de Valdivia and is located at the confluence of the Calle-Calle, Valdivia, and Cau-Cau R ...
, reestablished in 1645, and Chiloé acted as sentries, being hubs where the Spanish collected information and rumors from all over Patagonia.
As a result of the corsair and pirate menace, Spanish authorities ordered the depopulation of the Guaitecas Archipelago
Guaitecas Archipelago is a sparsely populated archipelago in the Aisén region of Chile. The archipelago is made up of eight main islands and numerous smaller ones. The eight largest islands are from northwest to southeast: Gran Guaiteca, Ascenc ...
to deprive enemies of any eventual support from native populations. This then led to the transfer of the majority of the indigenous Chono population to the Chiloé Archipelago in the north while some Chonos moved south of Taitao Peninsula
The Taitao Peninsula (Spanish: ''Península de Taitao'') is a westward projection of the mainland of Chile, with which it is connected by the narrow Isthmus of Ofqui, over which the natives and early missionaries were accustomed to carry their bo ...
effectively depopulating the territory in the 18th century.
The publication of Thomas Falkner
Thomas Falkner (6 October 1707 – 30 January 1784) was an English Jesuit missionary, explorer and physician, active in the Patagonia region for nearly forty years. His primary work, ''The Description of Patagonia'', was written towards the idea ...
's book ''A Description of Patagonia and the Adjacent Parts of South America'' in England fuelled speculations in Spain about renewed British interest in Patagonia. In response an order from the King of Spain was issued to settle the eastern coast of Patagonia. This led to the brief existence of colonies at the Gulf of San Jorge
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodie ...
(1778–1779) and San Julián (1780–1783) and the more longlasting colony of Carmen de Patagones
Carmen de Patagones is the southernmost city in the .
Geography
It is located 937 km southwest from the city of Buenos Aires, on the north bank of the Río Negro ("Black River"), near the Atlantic Ocean, and opposite Viedma, capital of ...
.
Scientific exploration (1764–1842)
In the second half of the 18th century, European knowledge of Patagonia was further augmented by the voyages of the previously mentioned John Byron (1764–1765),Samuel Wallis
Samuel Wallis (23 April 1728 – 21 January 1795 in London) was a British naval officer and explorer of the Pacific Ocean. He made the first recorded visit by a European navigator to Tahiti.
Biography
Wallis was born at Fenteroon Farm, n ...
(1766, in the same HMS ''Dolphin'' which Byron had earlier sailed in) and Louis Antoine de Bougainville
Louis-Antoine, Comte de Bougainville (, , ; 12 November 1729 – August 1811) was a French admiral and explorer. A contemporary of the British explorer James Cook, he took part in the Seven Years' War in North America and the American Revolutio ...
(1766). Thomas Falkner
Thomas Falkner (6 October 1707 – 30 January 1784) was an English Jesuit missionary, explorer and physician, active in the Patagonia region for nearly forty years. His primary work, ''The Description of Patagonia'', was written towards the idea ...
, a Jesuit who resided near forty years in those parts, published his ''Description of Patagonia'' (Hereford, 1774); Francisco Viedma founded ''El Carmen'', nowadays Carmen de Patagones
Carmen de Patagones is the southernmost city in the .
Geography
It is located 937 km southwest from the city of Buenos Aires, on the north bank of the Río Negro ("Black River"), near the Atlantic Ocean, and opposite Viedma, capital of ...
and Antonio settled the area of San Julian Bay, where he founded the colony of Floridablanca and advanced inland to the Andes (1782). Basilio Villarino ascended the Rio Negro (1782).
Phillip Parker King
Rear Admiral Phillip Parker King, FRS, RN (13 December 1791 – 26 February 1856) was an early explorer of the Australian and Patagonian coasts.
Early life and education
King was born on Norfolk Island, to Philip Gidley King and Ann ...
, and the second (1832–1836) was the voyage of the ''Beagle'' under Robert FitzRoy
Vice-Admiral Robert FitzRoy (5 July 1805 – 30 April 1865) was an English officer of the Royal Navy and a scientist. He achieved lasting fame as the captain of during Charles Darwin's famous voyage, FitzRoy's second expedition to Tierra de ...
. The latter expedition is particularly noted for the participation of Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended ...
, who spent considerable time investigating various areas of Patagonia onshore, including long rides with gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and ...
s in Río Negro, and who joined FitzRoy in a expedition taking ships' boats up the course of the Santa Cruz River.
Spanish American independence wars
During the independence wars rumours about the imminent arrival of Spanish troops to Patagonia, either from Peru or Chiloé, were common among indigenous peoples of the Pampas and northern Patagonia. In 1820 Chilean patriot leaderJosé Miguel Carrera
José Miguel Carrera Verdugo (; October 15, 1785 – September 4, 1821) was a Chilean general, formerly Spanish military, member of the prominent Carrera family, and considered one of the founders of independent Chile. Carrera was the most impo ...
allied with the indigenous Ranquel
The Ranquel or Rankülche are an indigenous tribe from the northern part of La Pampa Province, Argentina, in South America.Tapia, Alicia Haydée"Archaeological Perspectives on the Ranquel Chiefdoms in the North of the Dry Pampas, in the Eighteent ...
people of the Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazi ...
in order to fight the rival patriots in Buenos Aires. José Miguel Carrera ultimately planned to cross the Andes into Chile and oust his rivals in Chile.
The last royalist armed group in what is today Argentina and Chile, the Pincheira brothers
The Pincheira brothers (Spanish: ''Hermanos Pincheira'') was an infamous royalist outlaw group in Chile and Argentina active from 1818 to 1832. The gang fought initially in the Chilean War of Independence as royalist guerrillas during the Guer ...
, moved from the vicinities of Chillán across the Andes into northern Patagonia as patriots consolidated control of Chile. The Pincheira brothers was an outlaw gang made of Europeans Spanish, American Spanish, Mestizos and local indigenous peoples. This group was able to move to Patagonia thanks to its alliance with two indigenous tribes, the Ranqueles and the Boroanos The Boroano, Boroga, or Borogano (also spelled with ''v'') were a group of Mapuche native to the aillarehue of Boroa in Araucanía. They were involved in several conflicts in the northern Patagonian pampas, and supported figures such as José Mig ...
. In the interior of Patagonia, far from the de facto territory of Chile and the United Provinces, the Pincheira brothers established permanent encampment with thousands of settlers. From their bases the Pincheiras led numerous raids into the countryside of the newly established republics.
Chilean and Argentine colonization (1843–1902)
In the early 19th century, thearaucanization
The Araucanization of Patagonia ( es, Araucanización de la Patagonia) was the process of the expansion of Mapuche culture, influence, and its Mapudungun language from Araucanía across the Andes into the plains of Patagonia. Historians disagree ...
of the natives of northern Patagonia intensified, and many Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who s ...
s migrated to Patagonia to live as nomads that raised cattle or pillaged the Argentine countryside. The cattle stolen in the incursions ('' malones'') were later taken to Chile through the mountain passes and traded for goods, especially alcoholic beverages. The main trail for this trade was called Camino de los chilenos and runs a length around 1000 km from the Buenos Aires Province to the mountain passes of Neuquén Province. The ''lonco
A lonko or lonco (from Mapudungun ''longko'', literally "head"), is a chief of several Mapuche communities. These were often ulmen, the wealthier men in the lof. In wartime, lonkos of the various local rehue or the larger aillarehue would gather ...
'' Calfucurá crossed the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
from Chile to the pampas around 1830, after a call from the governor of Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, Juan Manuel de Rosas, to fight the Boroano people. In 1859, he attacked Bahía Blanca in Argentina with 3,000 warriors. As in the case of Calfucura, many other bands of Mapuches got involved in the internal conflicts of Argentina until Conquest of the Desert
The Conquest of the Desert ( es, Conquista del desierto) was an Argentine military campaign directed mainly by General Julio Argentino Roca in the 1870s with the intention of establishing dominance over the Patagonian Desert, inhabited primar ...
. To counter the cattle raids, a trench called the Zanja de Alsina
Zanja de Alsina (, '' Alsina's trench'') were a system of trenches and wooden watchtowers (''mangrullos'') built in the central and southern parts of Buenos Aires Province to defend the territories of the federal government against indigenous Mapu ...
was built by Argentina in the pampas in the 1870s.
 In the mid-19th century, the newly independent nations of Argentina and Chile began an aggressive phase of expansion into the south, increasing confrontation with the Indigenous peoples of the region. In 1860, French adventurer Orelie-Antoine de Tounens proclaimed himself king of the
In the mid-19th century, the newly independent nations of Argentina and Chile began an aggressive phase of expansion into the south, increasing confrontation with the Indigenous peoples of the region. In 1860, French adventurer Orelie-Antoine de Tounens proclaimed himself king of the Kingdom of Araucanía and Patagonia
The Kingdom of Araucanía and Patagonia ( es, Reino de la Araucanía y de la Patagonia; french: Royaume d'Araucanie et de Patagonie, sometimes referred to as ''New France'') was an unrecognized state declared by two ordinances on November 17, 18 ...
of the Mapuche
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who s ...
.
Following the last instructions of Bernardo O'Higgins
Bernardo O'Higgins Riquelme (; August 20, 1778 – October 24, 1842) was a Chilean independence leader who freed Chile from Spanish rule in the Chilean War of Independence. He was a wealthy landowner of Basque-Spanish and Irish ancestry. Alth ...
, the Chilean president Manuel Bulnes sent an expedition to the Strait of Magellan and founded Fuerte Bulnes
Fuerte Bulnes is a Chilean fort located by the Strait of Magellan, 62 km south of Punta Arenas. It was founded in 1843 on a rocky hill at Punta Santa Ana, and named after President Manuel Bulnes Prieto.
The fort was built to further the ...
in 1843. Five years later, the Chilean government moved the main settlement to the current location of Punta Arenas
Punta Arenas (; historically Sandy Point in English) is the capital city of Chile's southernmost region, Magallanes and Antarctica Chilena. The city was officially renamed as Magallanes in 1927, but in 1938 it was changed back to "Punta Are ...
, the oldest permanent settlement in Southern Patagonia. The creation of Punta Arenas was instrumental in making Chile's claim of the Strait of Magellan permanent. In the 1860s, sheep from the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouze ...
were introduced to the lands around the Straits of Magellan, and throughout the 19th century, sheepfarming grew to be the most important economic sector in southern Patagonia.
George Chaworth Musters
George Chaworth Musters (1841–1879) was a British Royal Navy commander and traveller, known as the "King of Patagonia".
Life
He was born in Naples while his parents were travelling, 13 February 1841, the son of John George Musters of Wiverton H ...
in 1869 wandered in company with a band of Tehuelches through the whole length of the country from the strait to the Manzaneros in the northwest, and collected a great deal of information about the people and their mode of life.
Conquest of the Desert and the 1881 treaty
 Argentine authorities worried that the strong connections araucanized tribes had with Chile would allegedly give Chile certain influence over the pampas. Argentine authorities feared that in an eventual war with Chile over Patagonia, the natives would side with the Chileans and the war would be brought to the vicinity of Buenos Aires.
The decision to plan and execute the Conquest of the Desert was probably catalyzed by the 1872 attack of Cufulcurá and his 6,000 followers on the cities of General Alvear, Veinticinco de Mayo, and Nueve de Julio, where 300 ''
Argentine authorities worried that the strong connections araucanized tribes had with Chile would allegedly give Chile certain influence over the pampas. Argentine authorities feared that in an eventual war with Chile over Patagonia, the natives would side with the Chileans and the war would be brought to the vicinity of Buenos Aires.
The decision to plan and execute the Conquest of the Desert was probably catalyzed by the 1872 attack of Cufulcurá and his 6,000 followers on the cities of General Alvear, Veinticinco de Mayo, and Nueve de Julio, where 300 ''criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
'' were killed, and 200,000 heads of cattle taken. In the 1870s, the Conquest of the Desert was a controversial campaign by the Argentine government, executed mainly by General Julio Argentino Roca
Alejo Julio Argentino Roca Paz (July 17, 1843 – October 19, 1914) was an army general and statesman who served as President of Argentina from 1880 to 1886 and from 1898 to 1904. Roca is the most important representative of the Generation ...
, to subdue or, some claim, to exterminate the native peoples of the south.
In 1885, a mining expeditionary party under the Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
n adventurer Julius Popper
Julius Popper (December 15, 1857 – June 5, 1893), also known in Spanish language, Spanish as Julio Popper (), was a Wallachia, Wallachian-born Romanian-Argentine engineer, adventurer, and explorer. Popper was one of the perpetrators of the Sel ...
landed in southern Patagonia in search of gold, which they found after traveling southwards towards the lands of Tierra del Fuego. This led to the further opening up of the area to prospectors. European missionaries and settlers arrived throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, notably the Welsh settlement of the Chubut Valley. Numerous Croatians
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, ...
also settled in Patagonia.
During the first years of the 20th century, the border between the two nations in Patagonia was established by the mediation of the British crown. Numerous modifications have been made since then, the last conflict having been resolved in 1994 by an arbitration tribunal constituted in Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a ...
. It granted Argentina sovereignty over the Southern Patagonia Icefield, Cerro Fitz Roy, and Laguna del Desierto.
Until 1902, a large proportion of Patagonia's population were natives of Chiloé Archipelago
The Chiloé Archipelago ( es, Archipiélago de Chiloé, , ) is a group of islands lying off the coast of Chile, in the Los Lagos Region. It is separated from mainland Chile by the Chacao Channel in the north, the Sea of Chiloé in the east and t ...
(Chilotes), who worked as peons in large livestock-farming ''estancia
An estancia is a large, private plot of land used for farming or raising cattle or sheep. Estancias in the southern South American grasslands, the ''pampas'', have historically been estates used to raise livestock, such as cattle or sheep. In Pu ...
s''. Because they were manual labor
Manual labour (in Commonwealth English, manual labor in American English) or manual work is physical work done by humans, in contrast to labour by machines and working animals. It is most literally work done with the hands (the word ''manual ...
ers, their social status was below that of the ''gaucho
A gaucho () or gaúcho () is a skilled horseman, reputed to be brave and unruly. The figure of the gaucho is a folk symbol of Argentina, Uruguay, Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil, and the south of Chilean Patagonia. Gauchos became greatly admired and ...
s'' and the Argentine, Chilean, and European landowners and administrators.
Before and after 1902, when the boundaries were drawn, Argentina expelled many Chilotes from their territory, as they feared that having a large Chilean population in Argentina could pose a risk to their future control. These workers founded the first inland Chilean settlement in what is now the Aysén Region
The Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo Region ( es, Región de Aysén, , '), often shortened to Aysén Region or Aisén,Examples of name usage1, official regional government site refers to the region as "Región de Aysén"., Chile's of ...
;Luis Otero, La Huella del Fuego: Historia de los bosques y cambios en el paisaje del sur de Chile (Valdivia, Editorial Pehuen) Balmaceda. Lacking good grasslands on the forest-covered Chilean side, the immigrants burned down the forest, setting fires that could last more than two years.
Economy
 The area's principal economic activities have been mining, whaling, livestock (notably sheep throughout) agriculture (wheat and fruit production near the Andes towards the north), and oil after its discovery near Comodoro Rivadavia in 1907.''Time Out Patagonia'', Cathy Runciman (ed),
The area's principal economic activities have been mining, whaling, livestock (notably sheep throughout) agriculture (wheat and fruit production near the Andes towards the north), and oil after its discovery near Comodoro Rivadavia in 1907.''Time Out Patagonia'', Cathy Runciman (ed), Penguin Books
Penguin Books is a British publishing house. It was co-founded in 1935 by Allen Lane with his brothers Richard and John, as a line of the publishers The Bodley Head, only becoming a separate company the following year.San Carlos de Bariloche to Buenos Aires. Portions of other lines were built to the south, but the only lines still in use are
 Sheep farming introduced in the late 19th century has been a principal economic activity. After reaching its heights during the First World War, the decline in world wool prices affected sheep farming in Argentina. Nowadays, about half of Argentina's 15 million sheep are in Patagonia, a percentage that is growing as sheep farming disappears in the pampas to the north. Chubut (mainly
Sheep farming introduced in the late 19th century has been a principal economic activity. After reaching its heights during the First World War, the decline in world wool prices affected sheep farming in Argentina. Nowadays, about half of Argentina's 15 million sheep are in Patagonia, a percentage that is growing as sheep farming disappears in the pampas to the north. Chubut (mainly
 In the second half of the 20th century, tourism became an ever more important part of Patagonia's economy. Originally a remote backpacking destination, the region has attracted increasing numbers of upmarket visitors, cruise passengers rounding
In the second half of the 20th century, tourism became an ever more important part of Patagonia's economy. Originally a remote backpacking destination, the region has attracted increasing numbers of upmarket visitors, cruise passengers rounding
 Due to its sparse rainfall in agricultural areas, Argentine Patagonia already has numerous dams for irrigation, some of which are also used for hydropower. The
Due to its sparse rainfall in agricultural areas, Argentine Patagonia already has numerous dams for irrigation, some of which are also used for hydropower. The
PATAGONIA – E-BOOK W/ UNPUBLISHED FOTOS, MAPS, TEXTS
' (Formato Kindle – 6 November 2011) – eBook Kindle *''Adventures in Patagonia: a missionary's exploring trip'', Titus Coan, 1880. Library of Congress Control Number 03009975. A list of writings relating to Patagonia, 320–21. *
''Idle Days in Patagonia''
' by
Gallery of photos from Patagonia – Jakub Polomski PhotographyPatagonia Nature Photo Gallery: Landscapes, flora and fauna from Argentina and ChilePatagon Journal, magazine about Patagonia'Backpacking Patagonia' - series of articles about solo hiking in Patagonia
{{Coord, -41, -68, scale:10000000, display=title Argentina–Chile border Deserts of Argentina Deserts of Chile Geography of Aysén Region Geography of Magallanes Region Natural regions of South America Regions of Argentina Regions of Chile
La Trochita
La Trochita (official name: ''Viejo Expreso Patagónico''), in English known as the Old Patagonian Express, is a narrow gauge railway in Patagonia, Argentina using steam locomotives. The nickname ''La Trochita'' means literally "The little gauge ...
in Esquel
Esquel is a town in the northwest of Chubut Province in Argentine Patagonia. It is located in Futaleufú Department, of which it is the government seat. The town's name derives from one of two Tehuelche words: one meaning "marsh" and the other ...
, the Train of the End of the World in Ushuaia, both heritage line
A heritage railway or heritage railroad (US usage) is a railway operated as living history to re-create or preserve railway scenes of the past. Heritage railways are often old railway lines preserved in a state depicting a period (or periods) i ...
s,
and a short run Tren Histórico de Bariloche
San Carlos de Bariloche, usually known as Bariloche (), is a city in the province of Río Negro, Argentina, situated in the foothills of the Andes on the southern shores of Nahuel Huapi Lake. It is located within the Nahuel Huapi National Park ...
to Perito Moreno.
In the western forest-covered Patagonian Andes and archipelagoes, wood logging has historically been an important part of the economy; it impelled the colonization of the areas of the Nahuel Huapi
Nahuel Huapi National Park () is the oldest national park in Argentina, established in 1934. It surrounds Nahuel Huapi Lake in the foothills of the Patagonian Andes. The largest of the national parks in the region, it has an area of , or nearl ...
and Lácar lakes in Argentina and Guaitecas Archipelago
Guaitecas Archipelago is a sparsely populated archipelago in the Aisén region of Chile. The archipelago is made up of eight main islands and numerous smaller ones. The eight largest islands are from northwest to southeast: Gran Guaiteca, Ascenc ...
in Chile.
Livestock
 Sheep farming introduced in the late 19th century has been a principal economic activity. After reaching its heights during the First World War, the decline in world wool prices affected sheep farming in Argentina. Nowadays, about half of Argentina's 15 million sheep are in Patagonia, a percentage that is growing as sheep farming disappears in the pampas to the north. Chubut (mainly
Sheep farming introduced in the late 19th century has been a principal economic activity. After reaching its heights during the First World War, the decline in world wool prices affected sheep farming in Argentina. Nowadays, about half of Argentina's 15 million sheep are in Patagonia, a percentage that is growing as sheep farming disappears in the pampas to the north. Chubut (mainly Merino
The Merino is a breed or group of breeds of domestic sheep, characterised by very fine soft wool. It was established in Spain near the end of the Middle Ages, and was for several centuries kept as a strict Spanish monopoly; exports of the bree ...
) is the top wool producer with Santa Cruz (Corriedale and some Merino) second. Sheep farming revived in 2002 with the devaluation of the peso and firmer global demand for wool (led by China and the EU). Still, little investment occurs in new abattoirs (mainly in Comodoro Rivadavia, Trelew, and Rio Gallegos), and often phytosanitary restrictions reduce the export of sheep meat. Extensive valleys in the Cordilleran Range have provided sufficient grazing lands, and the low humidity and weather of the southern region make raising Merino and Corriedale sheep common.
Livestock also includes small numbers of cattle, and in lesser numbers, pigs and horses. Sheep farming provides a small but important number of jobs for rural areas with little other employment.
Tourism
 In the second half of the 20th century, tourism became an ever more important part of Patagonia's economy. Originally a remote backpacking destination, the region has attracted increasing numbers of upmarket visitors, cruise passengers rounding
In the second half of the 20th century, tourism became an ever more important part of Patagonia's economy. Originally a remote backpacking destination, the region has attracted increasing numbers of upmarket visitors, cruise passengers rounding Cape Horn
Cape Horn ( es, Cabo de Hornos, ) is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island. Although not the most southerly point of South America (which are the Diego Ramí ...
or visiting Antarctica, and adventure and activity holiday-makers. Principal tourist attractions include the Perito Moreno glacier
The Perito Moreno Glacier () is a glacier located in Los Glaciares National Park in southwest Santa Cruz Province, Argentina. It is one of the most important tourist attractions in the Argentine Patagonia.
The ice formation, in length, is one ...
, the Valdés Peninsula
The Valdes Peninsula (Spanish: ''Península Valdés'') is a peninsula into the Atlantic Ocean in the Biedma Department of north-east Chubut Province, Argentina. Around in size (not taking into account the isthmus of Carlos Ameghino which connect ...
, the Argentine Lake District and Ushuaia and Tierra del Fuego (the city is also a jumping-off place for travel to Antarctica, bringing in still more visitors). Tourism has created new markets locally and for export for traditional crafts such as Mapuche handicrafts, guanaco textiles, and confectionery and preserves.
A spin-off from increased tourism has been the buying of often enormous tracts of land by foreigners, often as a prestige purchase rather than for agriculture. Buyers have included Sylvester Stallone, Ted Turner
Robert Edward "Ted" Turner III (born November 19, 1938) is an American entrepreneur, television producer, media proprietor, and philanthropist. He founded the Cable News Network (CNN), the first 24-hour cable news channel. In addition, he fo ...
, and Christopher Lambert, and most notably Luciano Benetton
Luciano Benetton (born 13 May 1935) is an Italian billionaire businessman and one of the co-founders of Benetton Group, an Italian fashion brand. He served as the chairman of Benetton from 1978 to 2012.
Early life
Luciano Benetton was born on ...
, Patagonia's largest landowner. His "Compañia de Tierras Sud" has brought new techniques to the ailing sheep-rearing industry and sponsored museums and community facilities, but has been controversial particularly for its treatment of local Mapuche communities.
Energy
 Due to its sparse rainfall in agricultural areas, Argentine Patagonia already has numerous dams for irrigation, some of which are also used for hydropower. The
Due to its sparse rainfall in agricultural areas, Argentine Patagonia already has numerous dams for irrigation, some of which are also used for hydropower. The Limay River
The Limay River is an important river in the northwestern Argentine Patagonia (the region of Comahue). It originates at the eastern end of the Nahuel Huapi Lake and flows in a meandering path for about , collecting the waters of several tributari ...
is used to generate hydroelectricity at five dams built on its course: Alicurá, Piedra del Águila
Piedra del Águila ( en, Stone of the Eagle) is a second category Municipality and the capital city of Collón Curá Department, located in Neuquén Province, Argentina.
Geography
Piedra del Águila is located 211 km from Neuquén, the cap ...
, Pichi Picún Leufú, El Chocón, and Arroyito. Together with the Cerros Colorados Complex on the Neuquén River
The Neuquén River () is the second most important river of the province of Neuquén in the Argentine Patagonia, after the Limay River. Rocks of the Neuquén Basin are fossiliferous, and the basin hosts what may become important fields of ti ...
, they contribute more than one-quarter of the total hydroelectric generation in the country.
Patagonia has always been Argentina's main area, and Chile's only area, of conventional oil and gas production. Oil and gas have played an important role in the rise of Neuquén-Cipolleti as Patagonia's most populous urban area, and in the growth of Comodoro Rivadavia, Punta Arenas, and Rio Grande, as well. The development of the Neuquén basin's enormous unconventional oil and gas reserves through hydraulic fracturing has just begun, but the YPF
YPF S.A. (, formerly ; English: "Fiscal Oilfields") is a vertically integrated, majority state-owned Argentine energy company, engaged in oil and gas exploration and production, and the transportation, refining, and marketing of gas and petr ...
-Chevron
Chevron (often relating to V-shaped patterns) may refer to:
Science and technology
* Chevron (aerospace), sawtooth patterns on some jet engines
* Chevron (anatomy), a bone
* '' Eulithis testata'', a moth
* Chevron (geology), a fold in rock ...
Loma Campana field in the Vaca Muerta formation is already the world's largest producing shale oil field outside North America according to former YPF CEO Miguel Gallucio.
Patagonia's notorious winds have already made the area Argentina's main source of wind power, and plans have been made for major increases in wind power generation. Coal is mined in the Rio Turbio area and used for electricity generation.
Cuisine
Argentine Patagonian cuisine is largely the same as the cuisine of Buenos Aires – grilled meats and pasta – with extensive use of local ingredients and less use of those products that have to be imported into the region. Lamb is considered the traditional Patagonian meat, grilled for several hours over an open fire. Some guide books have reported that game meats, especially guanaco and introduced deer and boar, are popular in restaurant cuisine. However, since guanaco is a protected animal in both Chile and Argentina, it is unlikely to appear commonly as restaurant fare. Trout and ''centolla
''Lithodes santolla'', also known as the southern king crab, king crab or centolla, is a species of king crab, found off southern South America including the Falklands/Malvinas. On the Pacific side, it is found in Chile from Valdivia at around 4 ...
'' (king crab
King crabs are a taxon of decapod crustaceans chiefly found in cold seas. Because of their large size and the taste of their meat, many species are widely caught and sold as food, the most common being the red king crab (''Paralithodes camtsch ...
) are also common, though overfishing of ''centolla'' has made it increasingly scarce. In the area around Bariloche, a noted Alpine cuisine tradition remains, with chocolate bars and even fondue
Fondue (, , ) is a Swiss melted cheese dish served in a communal pot ( ''caquelon'' or fondue pot) over a portable stove () heated with a candle or spirit lamp, and eaten by dipping bread into the cheese using long-stemmed forks. It was promoted ...
restaurants, and tea room
A teahouse (mainly Asia) or tearoom (also tea room) is an establishment which primarily serves tea and other light refreshments. A tea room may be a room set aside in a hotel especially for serving afternoon tea, or may be an establishment whic ...
s are a feature of the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
communities in Gaiman and Trevelin
Trevelin (; cy, Trefelin) is a town in the western part of the Patagonian Argentine province of Chubut. The town lies on the eastern banks of the ( es, Río Percey). It is located in the department of Futaleufú, south of Esquel, and had 6,3 ...
, as well as in the mountains. Since the mid-1990s, some success with winemaking has occurred in Argentine Patagonia, especially in Neuquén.
Foreign land buyers issue
Foreign investors, including Italian multinationalBenetton Group
Benetton Group S.r.l. () is a global fashion brand based in Ponzano Veneto, Italy, founded in 1965. Benetton Group has a network of about 5,000 stores worldwide. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Benetton family's holding company Edizi ...
, Ted Turner
Robert Edward "Ted" Turner III (born November 19, 1938) is an American entrepreneur, television producer, media proprietor, and philanthropist. He founded the Cable News Network (CNN), the first 24-hour cable news channel. In addition, he fo ...
, Joseph Lewis and the conservationist Douglas Tompkins
Douglas Rainsford Tompkins (March 20, 1943 – December 8, 2015) was an American businessman, conservationist, outdoorsman, philanthropist, filmmaker, and agriculturalist. He co-founded the North Face Inc, Esprit and various environmental grou ...
, own major land areas. This situation has caused several conflicts with local inhabitants and the governments of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, for example, the opposition by Douglas Tompkins to the planned route for Carretera Austral
The Carretera Austral (CH-7, ''in English: Southern Way'') is the name given to Chile's Route 7. The highway runs south for about from Puerto Montt to Villa O'Higgins, passing through rural Patagonia.
Carretera Austral provides road access ...
in Pumalín Park. A scandal is also brewing about two properties owned by Ted Turner: the ''estancia'' La Primavera, located inside Nahuel Huapi National Park
Nahuel Huapi National Park () is the oldest national park in Argentina, established in 1934. It surrounds Nahuel Huapi Lake in the foothills of the Patagonian Andes. The largest of the national parks in the region, it has an area of , or nearly ...
, and the ''estancia'' Collón Cura. Benetton has faced criticism from Mapuche organizations, including Mapuche International Link
The Mapuche ( (Mapuche & Spanish: )) are a group of indigenous inhabitants of south-central Chile and southwestern Argentina, including parts of Patagonia. The collective term refers to a wide-ranging ethnicity composed of various groups who sha ...
, over its purchase of traditional Mapuche lands in Patagonia. The Curiñanco-Nahuelquir family was evicted from their land in 2002 following Benetton's claim to it, but the land was restored in 2007.
In fiction
Thefuture history
A future history is a postulated history of the future and is used by authors of science fiction and other speculative fiction to construct a common background for fiction. Sometimes the author publishes a timeline of events in the history, whil ...
depicted in Olaf Stapledon
William Olaf Stapledon (10 May 1886 – 6 September 1950) – known as Olaf Stapledon – was a British philosopher and author of science fiction.Andy Sawyer, " illiamOlaf Stapledon (1886-1950)", in Bould, Mark, et al, eds. ''Fifty Key Figures ...
's ''Last and First Men
''Last and First Men: A Story of the Near and Far Future'' is a "future history" science fiction novel written in 1930 by the British author Olaf Stapledon. A work of unprecedented scale in the genre, it describes the history of humanity from t ...
'' includes a far future time in which Patagonia becomes the center of a new world civilization while Europe and North America are reduced to the status of backward poverty-stricken areas.
In Jules Verne's novel ''Les Enfants du capitaine Grant'' (The Children of Captain Grant, alternatively 'In Search of the Castaways'), the search for Captain Grant gets underway when the ''Duncan'', a vessel in the ownership of Lord Glenarvan
Lord Glenarvan is a fictional character that appears in Jules Verne's 1868 novel ''In Search of the Castaways'' and then briefly appears in ''The Mysterious Island'' (1875). He is a wealthy Scottish noble married to Lady Glenarvan.
Fictional app ...
, is taken on a journey to the western shore of South America's Patagonian region where the crew is split up, and Lord Glenarvan proceeds to lead a party eastwards across Patagonia to eventually reunite with the ''Duncan'' (which had doubled the Cape in the meanwhile).
In William Goldman
William Goldman (August 12, 1931 – November 16, 2018) was an American novelist, playwright, and screenwriter. He first came to prominence in the 1950s as a novelist before turning to screenwriting. He won Academy Awards for his screenplays '' ...
’s movie ''The Princess Bride The Princess Bride may refer to:
* ''The Princess Bride'' (novel), 1973 fantasy romance novel by American writer William Goldman
William Goldman (August 12, 1931 – November 16, 2018) was an American novelist, playwright, and screenwriter. He ...
'', Westley, the current inheritor of the moniker "the Dread Pirate Roberts
The Dread Pirate Roberts is the identity assumed by several fictional characters in the novel ''The Princess Bride'' (1973) and its 1987 film adaptation. Various pirates (including Westley, the main protagonist) take on the role of Roberts and us ...
", states that the "real" (original) Dread Pirate Roberts is retired and "living like a king in Patagonia".
See also
* Apostolic Prefecture of Southern Patagonia * Apostolic Vicariate of Northern Patagonia *Beagle conflict
The Beagle conflict was a border dispute between Chile and Argentina over the possession of Picton, Lennox and Nueva islands and the scope of the maritime jurisdiction associated with those islands that brought the countries to the brink of war i ...
* Domuyo
The Domuyo Volcano is a stratovolcano located in the Argentine province of Neuquén.
With a height of , it is the highest mountain in Patagonia and is sometimes called the "Roof of Patagonia" (''"El Techo de la Patagonia"'' in Spanish).
The volc ...
* Francisco Moreno Museum of Patagonia
* Lago Puelo National Park
* Lanín National Park
* Lanín Volcano
* List of deserts by area
* Los Alerces National Park
Los Alerces National Park ( es, Parque Nacional Los Alerces) is located in the Andes in Chubut Province in the Patagonian region of Argentina. Its western boundary coincides with the Chilean border. Successive glaciations have molded the landsc ...
* Los Glaciares National Park
Los Glaciares National Park ( es, Parque Nacional Los Glaciares) is a federal protected area in Santa Cruz Province, Argentina.
The park covers an area of , making it the largest national park in the country.
Established on 11 May 1937, it host ...
* Mount Hudson
Mount Hudson ( es, Volcán Hudson, es, Monte Hudson, label=none) is a stratovolcano in southern Chile, and the site of one of the largest eruptions in the twentieth century. The mountain itself is covered by a glacier. There is a caldera at th ...
* Nahuel Huapi National Park
Nahuel Huapi National Park () is the oldest national park in Argentina, established in 1934. It surrounds Nahuel Huapi Lake in the foothills of the Patagonian Andes. The largest of the national parks in the region, it has an area of , or nearly ...
* Patagonian Expedition Race
The Patagonian Expedition Race is an annual endurance adventure race that takes place in the remote wilderness of Chilean Patagonia, run to help protect and raise awareness about the fragile environment in this region. Known as the 'Race to the End ...
* Patagonian Ice Sheet
upright=1.4, Map showing the extent of the Patagonian Ice Sheet in the Strait of Magellan area during the last glacial period. Selected modern settlements are shown with yellow dots. Sea level was much lower than shown here.
The Patagonian Ice S ...
* Southern Cone
* Y Wladfa
Y Wladfa (, "The Colony"), also occasionally Y Wladychfa Gymreig (, "The Welsh Settlement"), refers to the establishment of settlements by Welsh immigrants in Patagonia, beginning in 1865, mainly along the coast of the lower Chubut Valley. I ...
References
Attribution: * * *Further reading
*''The Last Cowboys at the End of the World: The Story of the Gauchos of Patagonia'', Nick Reding, 2002. *''The Old Patagonian Express
''The Old Patagonian Express'' (1979) is a written account of a journey taken by novelist Paul Theroux. Starting out from his home town in Massachusetts, via Boston and Chicago, Theroux travels by train across the North American plains to Lared ...
'', Paul Theroux, 1979.
*''In Patagonia'', Bruce Chatwin
Charles Bruce Chatwin (13 May 194018 January 1989) was an English travel writer, novelist and journalist. His first book, ''In Patagonia'' (1977), established Chatwin as a travel writer, although he considered himself instead a storyteller, ...
, 1977 and 1988.
*''Patagonia Express'', Luis Sepulveda, 2004.
*''Patagonia: A Cultural History'', Chris Moss, 2008.
*''Patagonia: A Forgotten Land: From Magellan to Peron'', C. A. Brebbia, 2006.
*''The Wild Shores of Patagonia: The Valdés Peninsula & Punta Tombo'', Jasmine Rossi, 2000.
*Luciana Vismara, Maurizio OM Ongaro, PATAGONIA – E-BOOK W/ UNPUBLISHED FOTOS, MAPS, TEXTS
' (Formato Kindle – 6 November 2011) – eBook Kindle *''Adventures in Patagonia: a missionary's exploring trip'', Titus Coan, 1880. Library of Congress Control Number 03009975. A list of writings relating to Patagonia, 320–21. *
''Idle Days in Patagonia''
' by
William Henry Hudson
William Henry Hudson (4 August 1841 – 18 August 1922) – known in Argentina as Guillermo Enrique Hudson – was an Anglo-Argentine author, naturalist and ornithologist.
Life
Hudson was the son of Daniel Hudson and his wife Catherine (), ...
, Chapman and Hall Ltd, London, 1893
External links
Gallery of photos from Patagonia – Jakub Polomski Photography
{{Coord, -41, -68, scale:10000000, display=title Argentina–Chile border Deserts of Argentina Deserts of Chile Geography of Aysén Region Geography of Magallanes Region Natural regions of South America Regions of Argentina Regions of Chile