|
Torres Del Paine
The Cordillera Paine is a mountain group in Torres del Paine National Park in Chilean Patagonia. The cordillera is located north of Punta Arenas, and about south of the Chilean capital Santiago. It belongs to the Commune of Torres del Paine in Última Esperanza Province of Magallanes and Antártica Chilena Region. No accurate surveys have been published, and published elevations have been claimed to be seriously inflated, so most of the elevations given on this page are approximate.Biggar, John, 2015. ''The Andes: A Guide for Climbers'' (4th edition, ). Several elevations given by this authority are much lower than those given by other authorities, and the higher elevations are not supported by official Chilean IGM maps. ''Paine'' means "blue" in the native Tehuelche (Aonikenk) language and is pronounced ''PIE-nay''. Peaks The highest summit of the range is Cerro Paine Grande. For a long time its elevation was claimed to be , but in August 2011 it was ascended for the thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guido Monzino
Count Guido Monzino (2 March 1928 – 11 October 1988) was a twentieth-century Italian mountain climber and explorer. In 1973, he led the first Italian expedition to climb Mount Everest. He was the son of Franco Monzino, who founded the Italian supermarket chain Standa. Life Monzino was born on 2 March 1928 in Milan. In his early twenties, he climbed the Matterhorn. Subsequently, he made a total of 21 expeditions to places including Patagonia, Equatorial Africa, Greenland, the North Pole and the Himalaya, and sometimes following in the footsteps of the famous explorer and mountaineer Luigi Amedeo, Duke of the Abruzzi (1873–1933). Monzino died on 11 October 1988. He was interred at the Villa del Balbianello on the banks of Lake Como, which he bought in 1974 from the heirs of Butler Ames. Monzino willed Villa del Balbianello to the Fondo per l'Ambiente Italiano. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biosphere Reserve
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for purposes of conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research. They may be designated by government institutions in some countries, or by private landowners, such as charities and research institutions. Nature reserves fall into different IUCN categories depending on the level of protection afforded by local laws. Normally it is more strictly protected than a nature park. Various jurisdictions may use other terminology, such as ecological protection area or private protected area in legislation and in official titles of the reserves. History Cultural practices that roughly equate to the establishment and maintenance of reserved areas for animals date back ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lago Pehoé
__NOTOC__ Lago, which means "lake" in Italian, Portuguese, Spanish and Galician, may refer to: Places *Lago, Calabria, a ''comune'' in the Province of Cosenza, Italy *Lago, Mexico, a municipality zone in the State of Mexico *Lago District, a ''distrito'' in Niassa Province, Mozambique * Lago, Portugal, a ''freguesia'' in the District of Braga * Lago, Asturias, a ''parroquia'' in the ''municipio'' of Allande, Spain *Lago, Texas, a census-designated place *Lagos, Nigeria, the largest city in Nigeria People *Anders Lago, Swedish politician *Ângela Lago (1945–2017), Brazilian children's writer and illustrator *Antonio Lago, Venice-born French motor vehicle manufacturer *Fábio Lago, Brazilian actor *Nais Lago, Italian actress *Virginia Lago (born 1946), Argentine actress Other uses *Lago (Madrid Metro), a station on Line 5 *Talbot-Lago, a type of car *''Lago'', a fictional western town depicted in the film, ''High Plains Drifter'' See also * Lagos (other) Lagos is the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
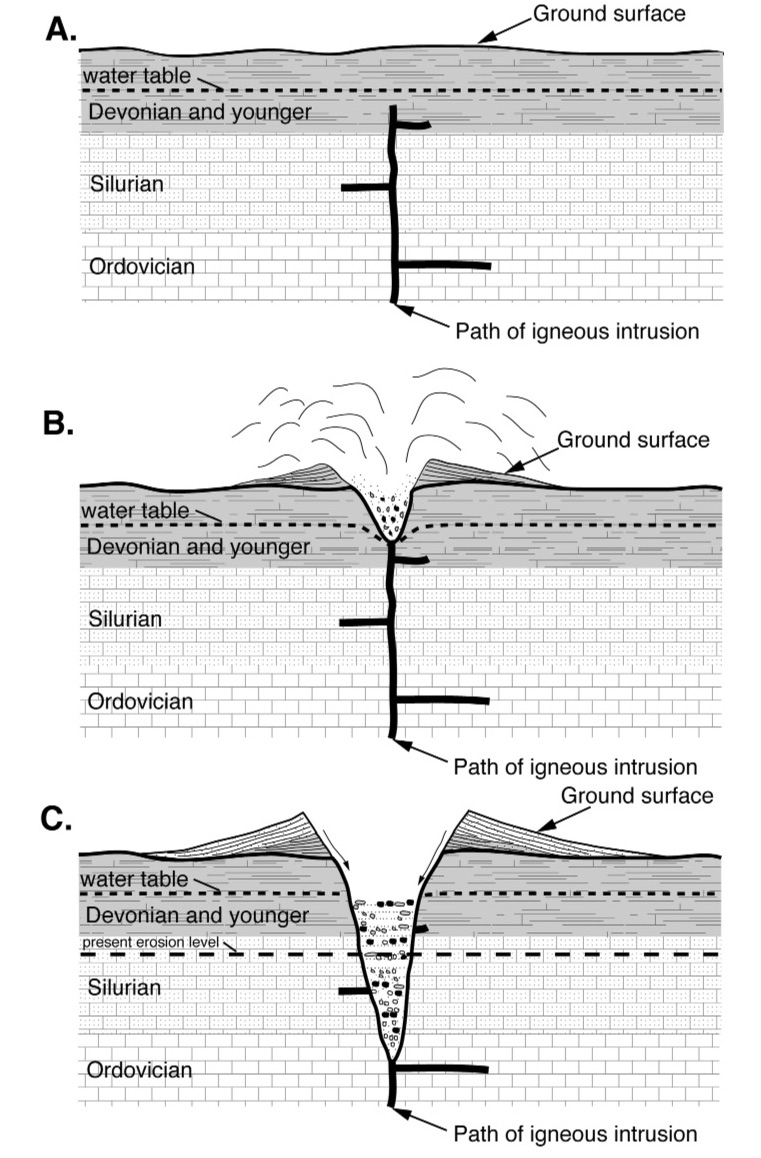
Magma Chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upwards. If the magma finds a path to the surface, then the result will be a volcanic eruption; consequently, many volcanoes are situated over magma chambers. These chambers are hard to detect deep within the Earth, and therefore most of those known are close to the surface, commonly between 1 km and 10 km down. Dynamics of magma chambers Magma rises through cracks from beneath and across the crust because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When the magma cannot find a path upwards it pools into a magma chamber. These chambers are commonly built up over time, by successive horizontal or vertical magma injections. Influx of new magma causes reaction of pre-existing crystals and the pressure in the chamber to increase. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium–lead Dating
Uranium–lead dating, abbreviated U–Pb dating, is one of the oldest and most refined of the radiometric dating schemes. It can be used to date rocks that formed and crystallised from about 1 million years to over 4.5 billion years ago with routine precisions in the 0.1–1 percent range. The method is usually applied to zircon. This mineral incorporates uranium and thorium atoms into its crystal structure, but strongly rejects lead when forming. As a result, newly-formed zircon deposits will contain no lead, meaning that any lead found in the mineral is radiogenic. Since the exact rate at which uranium decays into lead is known, the current ratio of lead to uranium in a sample of the mineral can be used to reliably determine its age. The method relies on two separate decay chains, the uranium series from 238U to 206Pb, with a half-life of 4.47 billion years and the actinium series from 235U to 207Pb, with a half-life of 710 million years. Decay routes Uranium decays to lead v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K–Ar Dating
Potassium–argon dating, abbreviated K–Ar dating, is a radiometric dating method used in geochronology and archaeology. It is based on measurement of the product of the radioactive decay of an isotope of potassium (K) into argon (Ar). Potassium is a common element found in many materials, such as feldspars, micas, clay minerals, tephra, and evaporites. In these materials, the decay product is able to escape the liquid (molten) rock, but starts to accumulate when the rock solidifies ( recrystallizes). The amount of argon sublimation that occurs is a function of the purity of the sample, the composition of the mother material, and a number of other factors. These factors introduce error limits on the upper and lower bounds of dating, so that the final determination of age is reliant on the environmental factors during formation, melting, and exposure to decreased pressure or open air. Time since recrystallization is calculated by measuring the ratio of the amount of accumulated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubidium–strontium Dating
The rubidium-strontium dating method is a radiometric dating technique, used by scientists to determine the age of rocks and minerals from their content of specific isotopes of rubidium (87Rb) and strontium (87Sr, 86Sr). One of the two naturally occurring isotopes of rubidium, 87Rb, decays to 87Sr with a half-life of 49.23 billion years. The radiogenic daughter, 87Sr, produced in this decay process is the only one of the four naturally occurring strontium isotopes that was not produced exclusively by stellar nucleosynthesis predating the formation of the Solar System. Over time, decay of 87Rb increases the amount of radiogenic 87Sr while the amount of other Sr isotopes remains unchanged. The ratio 87Sr/86Sr in a mineral sample can be accurately measured using a mass spectrometer. If the amount of Sr and Rb isotopes in the sample when it formed can be determined, the age can be calculated from the increase in 87Sr/86Sr. Different minerals that crystallized from the same silicic me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin ''creta'', "chalk", which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation ''Kreide''. The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now- extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was ice free, and forests extended to the poles. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds appeared. During the Early Cretaceous, flowering plants appeared and began to rapidly diversify, becoming the dominant group of plants across the Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building episode. Examples are found near the North American Cordillera, the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Carpathians. Sedimentological properties Flysch consists of repeated sedimentary cycles with upwards fining of the sediments. There are sometimes coarse conglomerates or breccias at the bottom of each cycle, which gradually evolve upwards into sandstone and shale/mudstone. Flysch typically consists of a sequence of shales rhythmically interbedded with thin, hard, graywacke-like sandstones. Typically the shales do not contain many fossils, while the coarser sandstones often have fractions of micas and glauconite. Tectonics In a continental collision, a subducting tectonic plate pushes on the plate above it, making the rock fold, often to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Country Rock (geology)
In geology, country rock is the rock native to an area, in contrast to any intrusion of viscous geologic material, commonly magma, or perhaps rock salt (in salt domes) or unconsolidated sediments. Magma is typically less dense than the rock it intrudes, widening and filling existing cracks, sometimes melting the already-existing country rock. The term "country rock" is similar to, and in many cases interchangeable with, the terms basement (geology), basement and wall rocks. Country rock can denote the widespread lithology of a region in relation to the rock which is being discussed or observed. Geologic settings Settings in geology when the term ''country rock'' is used include: Igneous intrusions When describing a intrusion, pluton or dike (geology), dike, the igneous rock can be described as intruding the surrounding ''country rock'', the rock into which the pluton has intruded.Newfoundland and LabradorGlossary of Geological Terms Accessed June 2018. When coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |