Montenegrins attacking Decic Fortress.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Montenegrins ( cnr, Црногорци, Crnogorci, or ; lit. "Black Mountain People") are a South Slavic ethnic group that share a common Montenegrin culture, history, and language, identified with the country of Montenegro.
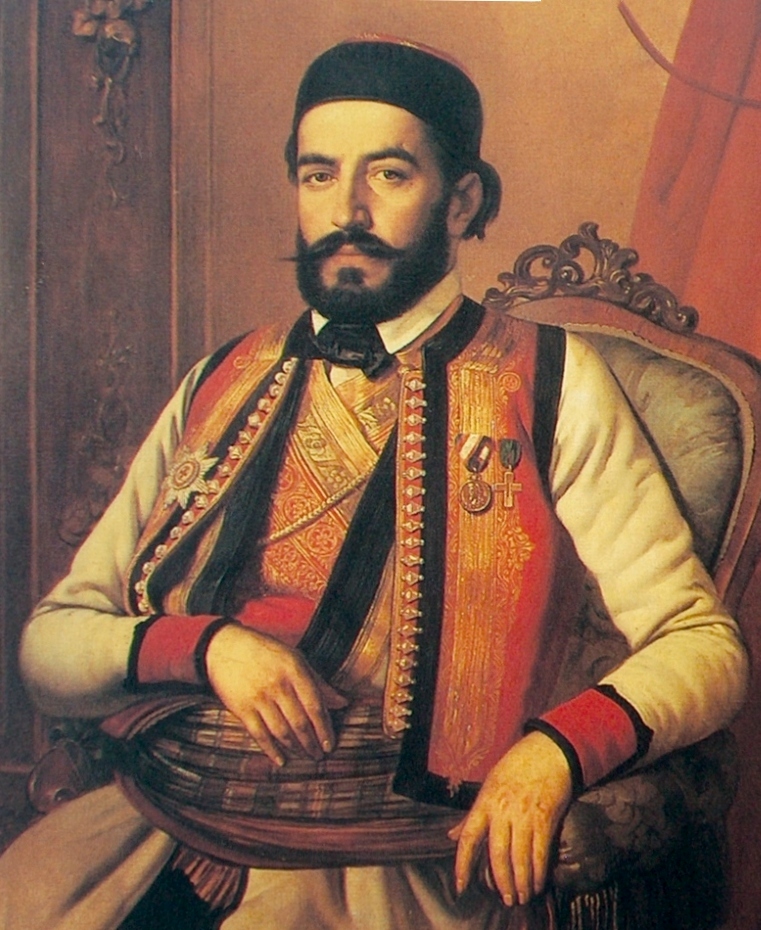
 With the arrival of the Turks, because of the inaccessibility of the terrain, and because of the lack of interest of the Ottomans for the "Montenegrin karst and fracture" (inaccessible terrain), the tribes in Montenegro enjoyed more than autonomy, and less than independence, but even this did not prevent the Montenegrin tribes from raising various revolts against Turkish conquest . The people were divided into tribes, and shortly thereafter bloody accounts of "brotherly" tribes turned bloody. The most serious causes of these accidents were the lack of food in the then-Montenegro, and the few resources were left, were taken away by the Turks, and the conflicts were inevitable. At the beginning of the 18th century. From then on, to Prince Danilo Petrovic, Montenegrins are under the theocratic rule of the
With the arrival of the Turks, because of the inaccessibility of the terrain, and because of the lack of interest of the Ottomans for the "Montenegrin karst and fracture" (inaccessible terrain), the tribes in Montenegro enjoyed more than autonomy, and less than independence, but even this did not prevent the Montenegrin tribes from raising various revolts against Turkish conquest . The people were divided into tribes, and shortly thereafter bloody accounts of "brotherly" tribes turned bloody. The most serious causes of these accidents were the lack of food in the then-Montenegro, and the few resources were left, were taken away by the Turks, and the conflicts were inevitable. At the beginning of the 18th century. From then on, to Prince Danilo Petrovic, Montenegrins are under the theocratic rule of the  His adopted son
His adopted son  He ruled as a bishop, but he also stood firm to see that Montenegro must be modernised. He built schools, roads, raised the Church, expanded the capital of
He ruled as a bishop, but he also stood firm to see that Montenegro must be modernised. He built schools, roads, raised the Church, expanded the capital of
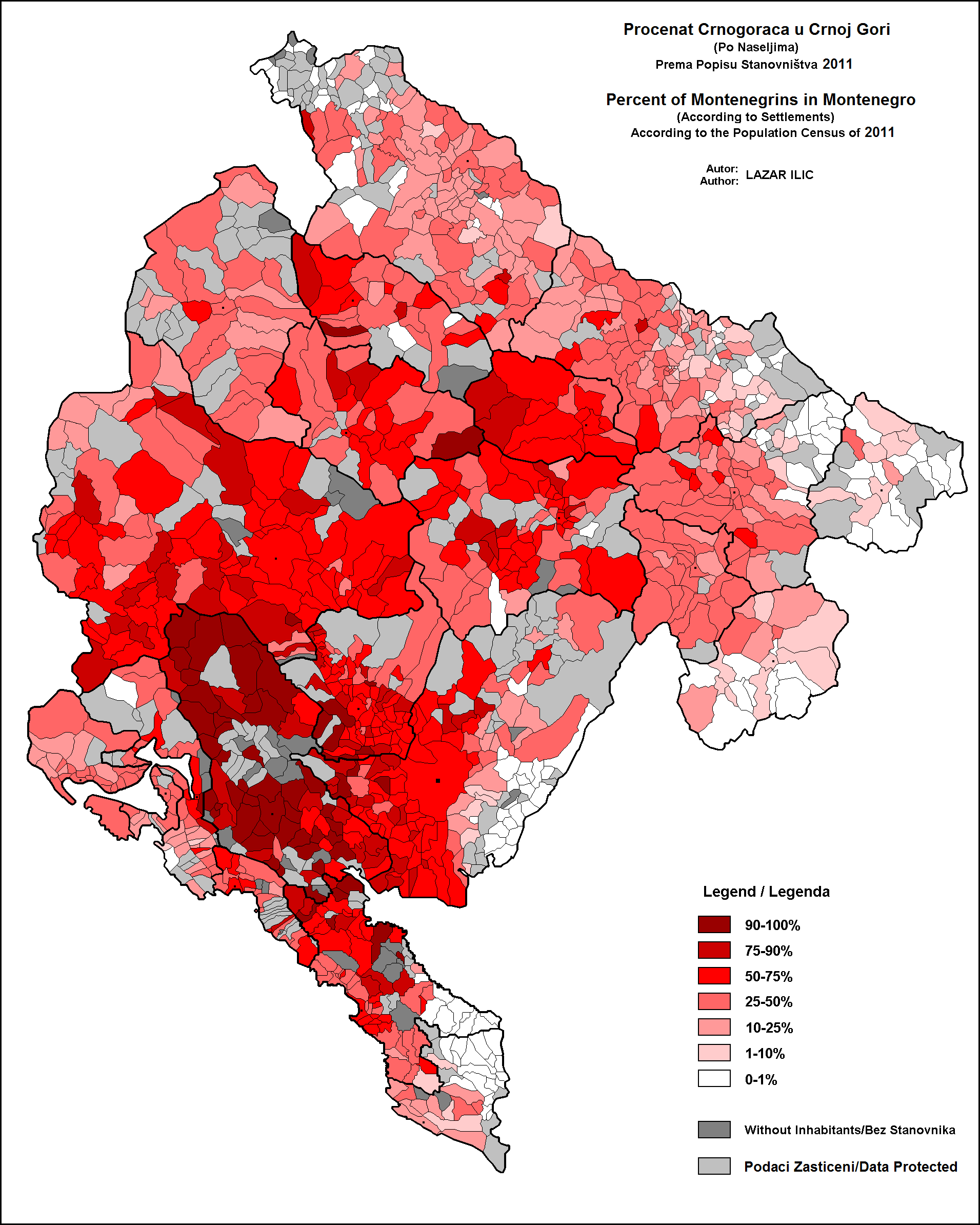 In the 2011 census, around 280,000 or ''44.98%'' of the population of Montenegro identified themselves as ethnic Montenegrins, while around 180,000 or ''28.73%'' identified themselves as Serbs. The number of "Montenegrins", "Serbs" and "Bosniaks" fluctuates from census to census, not due to real demographic changes, but due to changes in how people self-identify nationally. According to the Serbian 2011 census, there are 38,527 ethnic Montenegrins in Serbia, accounting for ''0.54%'' of its population. In addition, a significant number of Serbs in Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina are of Montenegrin ancestry, but exact numbers are difficult to assess – the inhabitants of Montenegro contributed greatly to the repopulation of a depopulated Serbia after two rebellions against the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century. On 19 October 2007, Montenegro adopted a new Constitution which proclaimed Montenegrin (a standardized variety of Serbo-Croatian) as the official language of Montenegro.
The term "Montenegrins" in a wider sense can also be used to denote all residents of Montenegro, regardless of their national and religious affiliation.
In the 2011 census, around 280,000 or ''44.98%'' of the population of Montenegro identified themselves as ethnic Montenegrins, while around 180,000 or ''28.73%'' identified themselves as Serbs. The number of "Montenegrins", "Serbs" and "Bosniaks" fluctuates from census to census, not due to real demographic changes, but due to changes in how people self-identify nationally. According to the Serbian 2011 census, there are 38,527 ethnic Montenegrins in Serbia, accounting for ''0.54%'' of its population. In addition, a significant number of Serbs in Serbia and Bosnia and Herzegovina are of Montenegrin ancestry, but exact numbers are difficult to assess – the inhabitants of Montenegro contributed greatly to the repopulation of a depopulated Serbia after two rebellions against the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century. On 19 October 2007, Montenegro adopted a new Constitution which proclaimed Montenegrin (a standardized variety of Serbo-Croatian) as the official language of Montenegro.
The term "Montenegrins" in a wider sense can also be used to denote all residents of Montenegro, regardless of their national and religious affiliation.
 The most important dimension of Montenegrins' culture is the ethical ideal of ''Čojstvo i junaštvo'', roughly translated as "Chivalry and Bravery". Another result of its centuries-long warrior history, is the unwritten code of
The most important dimension of Montenegrins' culture is the ethical ideal of ''Čojstvo i junaštvo'', roughly translated as "Chivalry and Bravery". Another result of its centuries-long warrior history, is the unwritten code of
Matica crnogorska (official pages)
Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts (official pages)
The Montenegrin Association of America
(in Montenegrin)
Article about Montenegrin tribes (in montenegrin language)
{{Slavic ethnic groups Slavic ethnic groups South Slavs Ethnic groups in the Balkans Ethnic groups in Montenegro Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Croatia Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina
Genetics
According to one triple analysis – autosomal,mitochondrial
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
and paternal — of available data from large-scale studies on Balto-Slavs and their proximal populations, the whole genome SNP data situates Montenegrins with Serbs in between two Balkan clusters. According to a 2020 autosomal marker analysis, Montenegrins are situated in-between Serbians and Kosovo Albanians.
Y-DNA genetic study done in 2010 on 404 male individuals from Montenegro gave the following results: haplogroup I2a (29.7%), E-V13 (26.9%), R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central A ...
(9.4%), R1a (7.6%), I1 (6.1%), J2a1 (4.7%), J2b (4.4%), G2a (2.4%), Q (1.9%), I2b (1.7%), N (1.4%), H (1.4%), L (1.2%), and J1 (0.49%). A 2022 study on 267 samples from northeastern Montenegro found that the "most common haplogroups are I2 and R1b, both identified in 23.97% of samples, followed by E (22.47%), J2 (11.61%), I1 (6.74%), G2 (3.75%), R1a (3.37%), I1 (1.12%), G (1.12%), N (0.75%), C (0.37%), T1 (0.37%) and Q1 (0.37%)".
History
Middle Ages
Slavs settled in the Balkans during the 6th and 7th centuries. According to ''De Administrando Imperio
''De Administrando Imperio'' ("On the Governance of the Empire") is the Latin title of a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Eastern Roman Emperor Constantine VII. The Greek title of the work is ("To yown son Romanos"). It is a domes ...
'', there existed three Slavic polities on the territory of modern Montenegro: Duklja, roughly corresponding to the southern half; Travunia, the west; and Principality of Serbia, the north. Duklja emerged as an independent state during the 11th century, initially held by the Vojislavljević dynasty, later to be incorporated into the state of the Nemanjić dynasty. ''De Administrando Imperio'' also mentions that the area, along with the easternmost part of the Roman province of Dalmatia, has been mostly settled or ruled by Serbs.
By forming the first country under the rule of Časlav Klonimirović, with the centre in the old town of Ras, all these areas belonged to Serbian territory by conquest. By strengthening of the coastal Duklja and the noble family of Vojislavljević, in the beginning of the 11th century, they took power from Vlastimirovic dynasty, and soon after that, in 1077, Prince Mihailo Vojislavljević got the crown from the Pope and proclaimed the Kingdom of Duklja, with the centre in the city of Bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
.
With the descent of Vojislavljević dynasty, nobleman Zavid Vukanović, from Ribnica near Podgorica, a cousin of Vojislavljević dynasty through a female line, gets four sons. His youngest son, Stefan Nemanja, will later become the Grand Prince of the new Great Serbia, and the founder of the Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches.
The majori ...
among all Serbs. He moves to the city of Ras, where he overthrows (and kills) his eldest brother, Tihomir, in 1169, and declares himself the Grand Prince of Raška. After his proclamation, the last Prince/King of Duklja, Mihailo Vojislavljević, dies, and Stefan Nemanja joins Duklja and Raška, and soon he returns the rest of the lands from the period of Prince Časlav Klonimirović and King Mihailo Vojislavljević. From the reign of Stefan Nemanja to the fall of the Montenegrin medieval state, Duklja, by this time called Zeta, was a part of the united Great Serbia. Throughout the period of two centuries under the Nemanjić dynasty, Crnojević dynasty became a noble family, and later on the line of Crnojević was replaced by the family of Balšići, believed to be originating from France, who remain on the throne of the Zeta, by then known as Montenegro, until the fall of the Serbian state in 1459.
The region previously known as Duklja later became known as " Zeta". Between 1276 and 1309, Serbian queen Helen of Anjou, the widow of the Serbian King Stefan Uroš I, ruled Zeta, where she built and restored several monasteries, most notably the Monastery of Saints Sergius and Bacchus (Srđ and Vakh) on the Bojana river below Skadar (Shkodër). The Venetian name ''Montenegro'', meaning "black mountain" occurred for the first time in the charter of St. Nicholas' monastery in Vranjina, dating to 1296, during Jelena's reign. Under King Stefan Milutin
Stefan Uroš II Milutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Урош II Милутин, Stefan Uroš II Milutin; 1253 – 29 October 1321), known as Stefan Milutin ( sr-cyr, Стефан Милутин, Stefan Milutin), was the King of Serbia between 1282&nd ...
(reigned 1282-1321), at the beginning of the 14th century, the archdiocese in Bar was the biggest feudal domain in Zeta.
In the late 14th century, southern Montenegro ( Zeta) came under the rule of the Balšić noble family, then the Crnojević noble family, and by the 15th century, Zeta was more often referred to as ''Crna Gora'' (Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
: '). In 1496, the Ottomans conquered Zeta and subsequently established a sanjak that was subordinated to the Sanjak of Scutari
The Sanjak of Scutari or Sanjak of Shkodra ( sq, Sanxhaku i Shkodrës; sr, Скадарски санџак; tr, İskenderiye Sancağı or ''İşkodra Sancağı'') was one of the sanjaks of the Ottoman Empire. It was established after the Otto ...
. Ottoman influence remained largely limited to urban areas, while various tribes in the highlands emerged as districts out of reach of the Ottomans. These tribes were at times united against the Ottomans, under the leadership of the Metropolitans of Montenegro, the so-called "prince-bishops".
19th century

 With the arrival of the Turks, because of the inaccessibility of the terrain, and because of the lack of interest of the Ottomans for the "Montenegrin karst and fracture" (inaccessible terrain), the tribes in Montenegro enjoyed more than autonomy, and less than independence, but even this did not prevent the Montenegrin tribes from raising various revolts against Turkish conquest . The people were divided into tribes, and shortly thereafter bloody accounts of "brotherly" tribes turned bloody. The most serious causes of these accidents were the lack of food in the then-Montenegro, and the few resources were left, were taken away by the Turks, and the conflicts were inevitable. At the beginning of the 18th century. From then on, to Prince Danilo Petrovic, Montenegrins are under the theocratic rule of the
With the arrival of the Turks, because of the inaccessibility of the terrain, and because of the lack of interest of the Ottomans for the "Montenegrin karst and fracture" (inaccessible terrain), the tribes in Montenegro enjoyed more than autonomy, and less than independence, but even this did not prevent the Montenegrin tribes from raising various revolts against Turkish conquest . The people were divided into tribes, and shortly thereafter bloody accounts of "brotherly" tribes turned bloody. The most serious causes of these accidents were the lack of food in the then-Montenegro, and the few resources were left, were taken away by the Turks, and the conflicts were inevitable. At the beginning of the 18th century. From then on, to Prince Danilo Petrovic, Montenegrins are under the theocratic rule of the Petrović dynasty Petrović ( sr-Cyrl, Петровић, ;) is a South Slavic language patronymic surname literally meaning ''Peter's son'', equivalent to the English last name of Peterson. In Eastern Slavic naming customs its counterpart is "Petrovich".
The surn ...
. Due to the impossibility of approach, due to the terrain of Montenegro, Bishop Petar I Petrović Njegoš Petar ( sr, Петар, bg, Петър) is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic masculine given name, their variant of the Biblical name Petros (given name), Petros cognate to Peter (given name), Peter.
Derivative forms include Pero (given name) ...
cursed the tribes he was ruling, using their piety to inspire unity, and thus attempted to prevent the further slaughter of the fraternal people. After his death in 1830, Petar of Cetinje was buried in Cetinje Monastery and was proclaimed a saint.
Petar II Petrović Njegoš Petar ( sr, Петар, bg, Петър) is a South Slavic masculine given name, their variant of the Biblical name Petros cognate to Peter.
Derivative forms include Pero, Pejo, Pera, Perica, Petrica, Periša. Feminine equivalent is Petra.
...
ruled from 1830 until 1851. It is recorded as one of the greatest educators of the Serbian people in general. He wrote one of the most important works of the romantic epoch "Mountain Wreath
''The Mountain Wreath'' ( sr, Горски вијенац / Gorski vijenac) is a poem and a play written by Prince-Bishop and poet Petar II Petrović-Njegoš.
Njegoš wrote ''The Mountain Wreath'' during 1846 in Cetinje and published it the foll ...
" (regarded as one of the artistic foundations of Serbian nationalism), and he was also credited with bringing the final look of a Montenegrin hat, which is decorated with a black frame and represents the crown, more precisely, sorrow for the slavery of the Serbian people under Ottoman yoke. The top of the cap is red, symbolising blood, where 5 golden threads are engraved, thought to signify 5 centuries of slavery under the Turks. Within these golden threads there is a "Cross" with four Cyrillic letters (scores) S, a variant of the Byzantine Palaiologos tetragrammic cross, sometimes referred to as the variant of the Serbian cross
The Serbian Cross ( sr, Cрпски крст / Srpski krst) is a national symbol of Serbia, part of the coat of arms and flag of Serbia, and of the Serbian Orthodox Church. It is based on the tetragrammic cross emblem/flag of the Byzantine Palaio ...
.
Cetinje
Cetinje (, ) is a town in Montenegro. It is the former royal capital (''prijestonica'' / приjестоница) of Montenegro and is the location of several national institutions, including the official residence of the president of Montenegro ...
. After his death and funeral, he was succeeded by his nephew Prince Danilo Petrović who ruled as the first secular ruler, with the title of Knjaz. Since then, Knjaževina (Principality) of Montenegro was no longer a Prince-Bishopric, but a secular monarchy. This led to the opinion of the Turkish court that this change can lead to a major change in Montenegro, and a desire for "independence". In 1852, Omer-pasha sent a large army against the Montenegrins. A small Montenegrin army led by Prince Danilo's brother, Duke (Vojvoda) Mirko, defended 30 remaining fighters in the monastery of the Serbian Orthodox Church
The Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr-Cyrl, Српска православна црква, Srpska pravoslavna crkva) is one of the autocephalous (ecclesiastically independent) Eastern Orthodox Christian denomination, Christian churches.
The majori ...
, Ostrog for 9 days. This is taken as the greatest heroic force of the people in those areas. One year later, Omer-pasha again tried to conquer Montenegro, but with the great heroism of Vojvoda Mirko, the Montenegrins performed the greatest victory over the Ottomans in the new century, after which Montenegro gained essential autonomy, the highest degree to independence, and a few decades later, full independence. Prince Danilo
Danilo I Petrović-Njegoš ( sr-cyr, Данило I Петровић-Његош; 25 May 1826 – 13 August 1860) was the ruling Prince of Montenegro from 1851 to 1860. The beginning of his reign marked the transition of Montenegro from an archai ...
dies in 1860, and Danilo's adoptive son came to the throne, biological son of Vojvoda Mirko, Nikola Petrović. He remained remembered in Montenegro as the greatest ruler, owing in large part to the fact that he was the first modern-day King of Montenegro and that it was under him that Montenegro's independence had been recognised. He is of great importance for the Montenegrin people in general, because he has fought against the Ottomans in the territory of Montenegro, Herzegovina, and Bosnia, and the people often called him "Emperor of the Heroes". Immediately after coming to power, a war for the liberation of the Montenegrin people in Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geogra ...
started in 1862, in which Principality of Montenegro entered, but later it turned out that she entered extremely unprepared and soon after that peace was made. After returning from Russia, the then emperor Alexander II enlightened him, and immediately upon his arrival he began to work hard for the urbanisation of the country. He revised the army completely, built many courts and schools, and Montenegro began to look like a European state. In 1876, with the Principality of Serbia and the Obrenović dynasty, he started a war, in history known as " War for the Liberation of the Serbian People".
A couple of years before the war, Prince Nikola Petrović with the Serbian prince Mihailo Obrenović made an alliance in Venice, where beside the military alliance, a contract was signed on the dynastic heritage of the new future unified joint state. It was said that the plan is for Serbia to go back to its historical borders ( On the management of the Empire) from the Timok
The Timok ( Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимок; ro, Timoc), sometimes also known as Great Timok ( sr, Велики Тимок, Veliki Timok; ro, Timocul Mare), is a river in eastern Serbia, a right tributary of the Danube. For the last 15 k ...
River to the Una peak. The Montenegrin federal unit would be an integral part of the new common state, and in it Petrović dynasty Petrović ( sr-Cyrl, Петровић, ;) is a South Slavic language patronymic surname literally meaning ''Peter's son'', equivalent to the English last name of Peterson. In Eastern Slavic naming customs its counterpart is "Petrovich".
The surn ...
would have the title of the princes, while the Obrenović dynasty would wear a royal crown. The Montenegrins performed great victories, and by the end of the war at the Berlin Congress in 1878, the Principality of Montenegro received recognized independence, and became an internationally recognized state. This act raised the then two Serbian states to the ranks of independence, and it meant encouragement for all Serbs to completely resist the Turkish occupation in all Serbian countries. After the war, Prince Nikola wrote all his famous works, and the most famous work is the folk anthem " Onamo' namo! ", According to many, the most beautiful Serbian song about Kosovo. In 1910, then Prince Nikola, with the permission of the great powers of the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
and King Peter, proclaimed another Serbian kingdom in the Balkans: the Kingdom of Montenegro. The flag of the new state has become a flagrant national flag (a Serbian tricolor with the coat of arms of Petrović-Njegos dynasty), while with the old flag, it is equally used in the people and the popular "crusader" flag of Montenegrins. Knjazevina (Principality) of Montenegro, with the address of Russia, announces the war on Japan. Naturally, the participation of Montenegrins in this war was more symbolic, as the gratitude of Montenegro to Russia for generous help. In the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
, the Kingdom of Montenegro and the Kingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
participated in the liberation battles in the old Serbia
Old Serbia ( sr, Стара Србија, Stara Srbija) is a Serbian historiographical term that is used to describe the territory that according to the dominant school of Serbian historiography in the late 19th century formed the core of the S ...
( Kosovo, Metohija
Metohija ( sr-Cyrl, Метохија, ) or Dukagjin ( sq, Rrafshi i Dukagjinit, ) is a large basin and the name of the region covering the southwestern part of Kosovo. The region covers 35% (3,891 km2) of Kosovo's total area. According ...
, and Raška) and Macedonia
Macedonia most commonly refers to:
* North Macedonia, a country in southeastern Europe, known until 2019 as the Republic of Macedonia
* Macedonia (ancient kingdom), a kingdom in Greek antiquity
* Macedonia (Greece), a traditional geographic reg ...
. Thus, a common border was established between the two new-age "Serb" states, and the dream of King Nikola about the liberation of the "Serbian cradle" (Kosovo) was realised. At the beginning of the First World War, Montenegro immediately declared war on Austria-Hungary, after Serbia, but in 1916 it had to capitulate after all forces held a rally on the direction of Serbian withdrawal through Albania. After the passage of the Serbian government and the king, the crushed Montenegrin army sacrificed itself for the future of the Serbian state. King Nikola, already ill and in his late years, left his homeland. He went to France, where he died.
The Montenegrins maintained their ''de facto'' independence from the Ottoman Empire during the Ottoman's reign over most of the Balkan region (Bosnia, Serbia, Bulgaria, etc.). The Montenegrins were gathered around the Metropolitans of the Cetinje Metropolitanate, which led to further national awakening of the Montenegrins all around. The creation of a theocratic state and its advancement into a secular and independent country was even more evident in the late 15th and early 16th centuries.
The rule of the House of Petrović
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air condit ...
in the 18th and 19th century unified the Montenegrins and established strong ties with Russia and later with Serbia (under Ottoman occupation), with occasional help from the Austro-Hungarian Empire
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. That period was marked by numerous battles with Ottoman conquerors as well as by a firmer establishment of a self-governed principality.
In 1878, the Congress of Berlin recognised Montenegro as the 26th independent state in the world. Montenegro participated in the Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
of 1912–1913, as well as in World War I on the side of the Allies.
Yugoslav era
After the liberation of the Serbian and other Yugoslav (South Slavic) peoples, the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes was proclaimed, but the "Venetian Agreement" between the then Prince Nikola and Prince Mihailo Obrenović was breached. With the unification with theKingdom of Serbia
The Kingdom of Serbia ( sr-cyr, Краљевина Србија, Kraljevina Srbija) was a country located in the Balkans which was created when the ruler of the Principality of Serbia, Milan I, was proclaimed king in 1882. Since 1817, the Princi ...
, Montenegro was to have autonomy under the prince's dynasty Petrović-Njegoš. Due to this act, the Montenegrin public was divided on two sides. The first, majority party, better known as Bjelaši
The Whites ( sr, Бјелаши, Bjelaši) was the name given to pan-Serbian and Yugoslavist activists in Montenegro during and after the declaration of the Podgorica Assembly in November 1918. The Podgorica Assembly allowed the Montenegrin peop ...
("The Whites"), advocated unconditional unification with the Serbian Kingdom under the Karađorđević dynasty
The Karađorđević dynasty ( sr-Cyrl, Динасија Карађорђевић, Dinasija Karađorđević, Карађорђевићи / Karađorđevići, ) or House of Karađorđević ( sr-Cyrl, Кућа Карађорђевић, Kuća Karađ ...
, while Zelenaši ("The Greens"), in a minority, advocated a conditional union that would respect the Venice Treaty. In Podgorica on October 26, 1918, the Podgorica Assembly unanimously voted that Montenegro unconditionally unites with Serbia into Yugoslavia, without any autonomy. Due to this decision, the few Greens are persecuted, and their rebellion is suppressed in the coming years. In 1929, with the proclamation of the Zeta Banovina with its headquarters in Podgorica, the territory of the former Montenegro with eastern Herzegovina and Metohija gained autonomy in the form of banovina (province), and the ruler of the region became a ban, whom the king personally appoints. King Aleksandar Karađorđević ordered the construction of a chapel in Lovćen in 1925, and the remains of, as many would say, "the wisest Serb" Prince-Bishop Petar II Petrović Njegoš Petar ( sr, Петар, bg, Петър) is a South Slavic masculine given name, their variant of the Biblical name Petros cognate to Peter.
Derivative forms include Pero, Pejo, Pera, Perica, Petrica, Periša. Feminine equivalent is Petra.
...
were transferred there in a grandiose ceremony. At the beginning of the Second World War, the army in the Zeta Banovina area made great success against the Italian occupation of the army, expelling the Italian army to Shkodra in Albania. After the breakup of the Yugoslav state, Montenegro gets a puppet government led by Sekula Drljević, who will be expelled from the country later.
Montenegro unconditionally joined Serbia on November 26, 1918 in a controversial decision of the Podgorica Assembly, and soon afterwards became a part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, later renamed Yugoslavia. A number of Montenegrin chieftains, disappointed by the effective disappearance of Montenegro, which they perceived to have resulted from political manipulation, rose up in arms during January 1919 in an uprising known as the Christmas Rebellion, which was crushed in a severe, comprehensive military campaign by 1922–23. Annexation of the Kingdom of Montenegro on November 13, 1918 gained international recognition only at the Conference of Ambassadors in Paris, held on July 13, 1922. In 1929 the newly renamed Kingdom of Yugoslavia was reorganised into provinces (''banovine'') one of which, Zeta Banovina, encompassed the old Kingdom of Montenegro and had Cetinje
Cetinje (, ) is a town in Montenegro. It is the former royal capital (''prijestonica'' / приjестоница) of Montenegro and is the location of several national institutions, including the official residence of the president of Montenegro ...
as its administrative centre.
Between the two world wars, the Communist Party of Yugoslavia
The League of Communists of Yugoslavia, mk, Сојуз на комунистите на Југославија, Sojuz na komunistite na Jugoslavija known until 1952 as the Communist Party of Yugoslavia, sl, Komunistična partija Jugoslavije mk ...
opposed the Yugoslav monarchy and its unification policy, and supported Montenegrin autonomy, gaining considerable support in Montenegro. During World War II, many Montenegrins joined the Yugoslav partisan forces, although the portion joining the chetniks
The Chetniks ( sh-Cyrl-Latn, Четници, Četnici, ; sl, Četniki), formally the Chetnik Detachments of the Yugoslav Army, and also the Yugoslav Army in the Homeland and the Ravna Gora Movement, was a Yugoslav royalist and Serbian nationa ...
was also significant. One third of all officers in the partisan army were Montenegrins. They also gave a disproportionate number of highest-ranked party officials and generals. During WWII Italy occupied Montenegro (in 1941) and annexed to the Kingdom of Italy the area of Kotor, where there was a small Roman community (descendants from the populations of the renaissance-era Albania Veneta
Venetian Albania ( vec, Albania vèneta, it, Albania Veneta, Serbian and Montenegrin: Млетачка Албанија / ''Mletačka Albanija'', ) was the official term for several possessions of the Republic of Venice in the southeastern Adria ...
).
When the second Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugo ...
was formed in 1945, the Communists who led the Partisans during the war formed the new régime. They recognised, sanctioned, and fostered a national identity of Montenegrins as a people distinct from the Serbs and other South Slavs. The number of people who were registered as Montenegrins in Montenegro was 90% in 1948; it had been dropping since, to 62% in 1991. With the rise of Serbian nationalism in the late 80's the number of citizens who declared themselves Montenegrin dropped sharply from 61.7%, in the 1991 census, to 43.16% in 2003. For a detailed overview of these trends, see the Demographic history of Montenegro
The demographic history of Montenegro can be shown through census results and official documents which mention demographic composition.
Medieval
Duklja, today's southern half of Montenegro, under Stefan Vojislav, was inhabited by Serbs.
Variou ...
.
Though Montenegrins comprised one of the smallest ethnic groups in the state (2.5% in 1971), they were by far the most overrepresented ethnic group in the Yugoslav bureaucracy, military, and communist party organs. In the Yugoslav People's Army (JNA), 19% of general officers and 30% of colonels were ethnic Montenegrins. Among party elites, Montenegrins made up 16% to 21% of senior officials throughout the existence of communist Yugoslavia, and comprised a similar portion of the state's diplomatic corps. The striking overrepresentation among elites, which has been compared to the role of senior Austrian officers and officials in Nazi Germany, has partly been attributed to the pre-war strength of the Communist Party of Montenegro
The League of Communists of Montenegro ( sh, Savez komunista Crne Gore, SKCG) was the Socialist Republic of Montenegro, Montenegrin branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia, the One-party state, sole legal party of Yugoslavia from 1945 to ...
, the high proportion of Montenegrins among partisan commanders and central committee members during the war, and a historically militaristic culture. During this period, ethnic Montenegrins also held about 15% of government jobs in Yugoslavia.
Initially, after the fall of Communism in the early 1990s, the idea of a distinct Montenegrin ethnic identity had been taken over by independence-minded Montenegrins. The ruling Democratic Party of Socialists (DPS) (rebranded Communist Party), led by Prime Minister Milo Đukanović and President Momir Bulatović, was firmly allied with Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević (, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the president of Serbia within Yugoslavia from 1989 to 1997 (originally the Socialist Republic of Serbia, a constituent republic of ...
throughout this period and opposed such movements.
During the Bosnian War
The Bosnian War ( sh, Rat u Bosni i Hercegovini / Рат у Босни и Херцеговини) was an international armed conflict that took place in Bosnia and Herzegovina between 1992 and 1995. The war is commonly seen as having started ...
and Croatian War
The Croatian War of Independence was fought from 1991 to 1995 between Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serb-controlled Yugos ...
(1991–1995) Montenegro participated with its police and paramilitary forces in the attacks on Dubrovnik and Bosnian towns along with Serbian troops. It conducted persecutions against Bosniak refugees who were arrested by the Montenegrin police and transported to Serb camps in Foča, where they were executed.
Seeking independence
At the beginning of the Yugoslav crisis in the 1990s, the Yugoslav People's Army was trying to prevent the break up of Yugoslavia by military attacks. Part of the army from the then SR of Montenegro was attacking Herzegovina and Dubrovnik, and kept Dubrovnik under siege for almost eight months. In this period, the Montenegrins had an old sense of national affiliation, and at a referendum almost 100% of the respondents voted to declare that they wanted to stay in the Yugoslav rump state, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. During the siege of Dubrovnik, the Serbian (Montenegrin) paramilitary formation invented the saying: "From Lovćen a fairy salutes, where are you Serbian Dubrovnik!" (''Serbian: "Са Ловћена вила кличе, ђе си српски Дубровниче!"''), which has been taken many times as a verse with a negative connotation, because of the city being besieged for such a long time. After the abolition of communism and the creation of a new state, the federal unit of the Republic of Montenegro received a new flag and the coat-of-arms, where the flag was a classic Montenegrin national flag (a Serbian tricolour with blue colour), while the coat of arms of the Coat of Arms was taken from the historical emblem ofPetrović Petrović ( sr-Cyrl, Петровић, ;) is a South Slavic language patronymic surname literally meaning ''Peter's son'', equivalent to the English last name of Peterson. In Eastern Slavic naming customs its counterpart is "Petrovich".
The surn ...
. Then, the great fighters for the joint FRY, Momir Bulatović and Milo Đukanović, together with Slobodan Milošević
Slobodan Milošević (, ; 20 August 1941 – 11 March 2006) was a Yugoslav and Serbian politician who was the president of Serbia within Yugoslavia from 1989 to 1997 (originally the Socialist Republic of Serbia, a constituent republic of ...
, ruled the state union. The paths of Milo Đukanović and Momir Bulatović diverged before the start of the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, and Milo Đukanović begins to change attitudes drastically, starting first with the political attitudes and afterwards the national and religious. In 1997 a full-blown rift occurred within DPS, and Đukanović's faction won over Bulatović's, who formed a new Socialist People's Party of Montenegro (SNP). The DPS distanced itself from Milošević and gradually took over the independence idea from the Liberal Alliance of Montenegro and the SDP, and has won all elections since. In the fall of 1999, shortly after the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia, the Đukanović-led Montenegrin leadership came out with a platform for the re-definition of relations within the federation that called for more Montenegrin involvement in the areas of defence and foreign policy, though the platform fell short of pushing for independence. After Milošević's overthrow on October 5, 2000, Đukanović for the first time came out in support of full independence. Montenegro started increasingly moving away from Serbia, and in 2003, the Parliament of Montenegro sought amendments to the Constitution. With these amendments, the Federal Unit of Montenegro was allowed to call a referendum on independence, which took place on 21 May 2006.
When the referendum was announced, independence was obtained by a narrow majority. However, the bar was set high in order to avoid any dispute after the vote, with the requirement for a 55% of votes in favour of independence. Since the proclamation of independence, the policy of making a new ethnic identity is even more intensified by official government policy, often used for political purposes, whereas the citizens still remain divided on the issue of ethnic identity.
Demographics
Language
Montenegrins speak Montenegrin andSerbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
, an Ijekavian variant of the Shtokavian dialect
Shtokavian or Štokavian (; sh-Latn, štokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, штокавски, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It ...
of the pluricentric
A pluricentric language or polycentric language is a language with several interacting codified standard language, standard forms, often corresponding to different countries. Many examples of such languages can be found worldwide among the most-spo ...
Serbo-Croatian language. Neo-shtokavian Eastern-Herzegovinian sub-dialect is spoken in the North-West (largest city Nikšić), and old shtokavian Zeta sub-dialect is spoken in the rest of Montenegro, including capital Podgorica and the Old Royal Capital of Cetinje, and eastern Sanjak.
The Zeta dialect features additional sounds: a voiceless alveolo-palatal fricative (), voiced alveolo-palatal fricative *(, (occurring in other jekavian dialects as well) and a voiced alveolar affricate
A voiced alveolar affricate is a type of affricate consonant pronounced with the tip or blade of the tongue against the alveolar ridge (gum line) just behind the teeth. This refers to a class of sounds, not a single sound. There are several types ...
(, shared with other old-štokavian dialects). Both sub-dialects are characterised by highly specific accents (shared with other old-štokavian dialects) and several "hyper-ijekavisms" (i.e. ''nijesam'', where the rest of shtokavian area uses ''nisam'') and "hyper-iotation
In Slavic languages, iotation (, ) is a form of palatalization that occurs when a consonant comes into contact with a palatal approximant from the succeeding phoneme. The is represented by iota (ι) in the Cyrillic alphabet and the Greek alpha ...
s" (''đevojka'' for ''djevojka'', ''đeca'' for ''djeca'' etc.) (these features, especially the hyper-iotation, are more prominent in the Zeta sub-dialect), that are common in all Montenegrin vernaculars.
On the sociolinguistic level, the language has been classified as a dialect of Serbo-Croat. The Montenegrin constitution currently defines Montenegrin as the official language. Since the campaign for independence, a movement for recognition of the Montenegrin language as wholly separate from Serbian and other standard variants of Serbo-Croat (Bosnian, Croatian) has emerged, finding the basis for separate language identity mostly in the above-mentioned dialectal specifics. In the 2011 census, 42.88% of Montenegrin citizens stated that they speak the Serbian language, while 36.97% stated that they speak Montenegrin. Most of the young people under 18 in Montenegro, 39.23 percent, say they speak Montenegrin, while 37.47% call their mother tongue Serbian, as shown in the census held from 1 to 15 April 2011.
Religion
Most Montenegrins are Eastern Orthodox. According to the census of 2011, people that declared Montenegrin as their ethnicity declared the following religious identity: * Eastern Orthodox: 248,523 (88.7%) *Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
: 12,931 (4.6%)
* Catholic: 5,667 (2.0%)
* Protestantism: 921 (0.3%)
*Atheism
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no d ...
/Agnosticism
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
: 6,393 (2.3%)
*Others: 5,883 (2.1%)
Culture
 The most important dimension of Montenegrins' culture is the ethical ideal of ''Čojstvo i junaštvo'', roughly translated as "Chivalry and Bravery". Another result of its centuries-long warrior history, is the unwritten code of
The most important dimension of Montenegrins' culture is the ethical ideal of ''Čojstvo i junaštvo'', roughly translated as "Chivalry and Bravery". Another result of its centuries-long warrior history, is the unwritten code of Chivalry
Chivalry, or the chivalric code, is an informal and varying code of conduct developed in Europe between 1170 and 1220. It was associated with the medieval Christianity, Christian institution of knighthood; knights' and gentlemen's behaviours we ...
that Marko Miljanov
Marko Miljanov Popović ( sr-Cyrl, Марко Миљанов Поповић, ; 25 April 1833 – 2 February 1901) was a Brda chieftain and Montenegrin general and writer.
He entered the service of Danilo I, the first secular Prince of Monteneg ...
, one of the most famous warriors in his time, tried to describe in his book ''Primjeri čojstva i junaštva'' (Examples of Humanity and Bravery) at the end of the 19th century. Its main principles stipulate that to deserve a true respect of its people, a warrior has to show virtues of integrity, dignity, humility, self-sacrifice for the just cause if necessary, respect
Respect, also called esteem, is a positive feeling or action shown towards someone or something considered important or held in high esteem or regard. It conveys a sense of admiration for good or valuable qualities. It is also the process of ...
for others, and rectitude
Righteousness is the quality or state of being morally correct and justifiable. It can be considered synonymous with "rightness" or being "upright". It can be found in Indian religions and Abrahamic traditions, among other religions, as a theologi ...
, along with the bravery. In the old days of battle, it resulted in Montenegrins fighting to the death, since being captured was considered the greatest shame. Miljanov defined the two characteristics in a maxim roughly translated as: "Bravery is when I defend myself from the other, chivalry is when I defend the other from myself" (''"Junaštvo je kada sebe branim od drugoga, čojstvo je kada drugoga branim od sebe"'').
This ethos is still an important part of most Montenegrins' ethical belief system, and understanding it is essential in order to understand Montenegrin identity and self-perception. Most of extraordinary examples of Montenegrin conduct during its long history can be traced to the code.
Montenegrins' long-standing history of fighting for independence is invariably linked with strong traditions of folk epic poetry. A prominent feature of Montenegrin culture is the gusle
The gusle ( sr-cyrl, гусле) or lahuta ( sq, lahutë) is a single-stringed musical instrument (and musical style) traditionally used in the Dinarides region of Southeastern Europe (in the Balkans). The instrument is always accompanied by s ...
, a one-stringed instrument played by a story-teller who sings or recites stories of heroes and battles in decasyllabic verse
Decasyllable ( Italian: ''decasillabo'', French: ''décasyllabe'', Serbian: ''десетерац'', ''deseterac'') is a poetic meter of ten syllables used in poetic traditions of syllabic verse. In languages with a stress accent ( accentual v ...
. These traditions are stronger in the northern parts of the country and are also shared with people in eastern Herzegovina
Herzegovina ( or ; sh-Latn-Cyrl, Hercegovina, separator=" / ", Херцеговина, ) is the southern and smaller of two main geographical region of Bosnia and Herzegovina, the other being Bosnia. It has never had strictly defined geogra ...
, western Serbia, northern Albania, and central Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
.
On the substratum of folk epic poetry, poets like Petar II Petrović Njegoš Petar ( sr, Петар, bg, Петър) is a South Slavic masculine given name, their variant of the Biblical name Petros cognate to Peter.
Derivative forms include Pero, Pejo, Pera, Perica, Petrica, Periša. Feminine equivalent is Petra.
...
, widely considered the most one of the most brilliant Montenegrins and Southern Slavs in history, have created their own expression. Njegoš's epic book ''Gorski Vijenac'' (''The Mountain Wreath
''The Mountain Wreath'' ( sr, Горски вијенац / Gorski vijenac) is a poem and a play written by Prince-Bishop and poet Petar II Petrović-Njegoš.
Njegoš wrote ''The Mountain Wreath'' during 1846 in Cetinje and published it the foll ...
'') presents the central point of Montenegrin culture as struggle for freedom.
On the other hand, Adriatic cities like Herceg-Novi
Herceg Novi ( cyrl, Херцег Нови, ) is a coastal town in Montenegro located at the Western entrance to the Bay of Kotor and at the foot of Mount Orjen. It is the administrative center of the Herceg Novi Municipality with around 33,000 in ...
, Kotor, and Budva had strong trading and maritime traditions, and were more open for Venetian
Venetian often means from or related to:
* Venice, a city in Italy
* Veneto, a region of Italy
* Republic of Venice (697–1797), a historical nation in that area
Venetian and the like may also refer to:
* Venetian language, a Romance language s ...
, Ragusan Ragusan may refer to:
* citizen of the Republic of Ragusa
hr, Sloboda se ne prodaje za sve zlato svijeta it, La libertà non si vende nemmeno per tutto l'oro del mondo"Liberty is not sold for all the gold in the world"
, population_estimate ...
, and other Catholic influences. Possession of those cities often changed, but their population was basically a mixture of people with Orthodox and Catholic religions and traditions. These cities were incorporated into Montenegro only after the fall of Austria-Hungary. In those cities, stronger influences of medieval and renaissance architecture, painting, and lyric poetry can be found, and while the adherence to the principles of chivalry and bravery are part of their ethos they are usually less central than in the areas of "old Montenegro".
Identity and anthropology
Slavs have lived in the area of Montenegro since the 6th and 7th centuries in the medieval state of Duklja. By the 14th century, the mountains behind the Gulf of Kotor were coming to be referred to as " Montenegro" ( Montenegrin: ''Crna Gora''; literally translates as “Black Mountain”), and by the 15th century, the name was coming to increasingly replace the older name, Zeta. Since the end of the 17th century, Montenegro existed as a de facto independent country, first as a theocratic Prince-Bishopric (1694–1852), then as a secularPrincipality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall under ...
(1852–1910) and finally as a Kingdom (1910–1918). After the end of World War I, Montenegro was incorporated into the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, thus losing its statehood. This led to a short-lived Christmas Uprising of 1919, between supporters of Petrović-Njegoš dynasty and Montenegrin statehood and proponents of unification with Serbia and Yugoslavia under the Karađorđević dynasty
The Karađorđević dynasty ( sr-Cyrl, Динасија Карађорђевић, Dinasija Karađorđević, Карађорђевићи / Karađorđevići, ) or House of Karađorđević ( sr-Cyrl, Кућа Карађорђевић, Kuća Karađ ...
. After the World War II, Montenegro regained its political sovereignty, becoming one of the six constituent republics of the SFR Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yug ...
, and Montenegro's sovereignty was recognised once again. A portion of Montenegrins declares as ethnic Serbs, while a larger proportion of citizens of Montenegro identifies ethnically as Montenegrin, a division that was exacerbated with the fall of socialism. This division has deepened further since the movement for full Montenegrin independence from the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia began to gain ground in 1991, while full independence was regained after the 2006 referendum.
Vlahović (2008) noted many anthropological studies which showed that Montenegrin people have strong Dinaric type (with seaboard, central, Durmitor, mountain and other subtypes) autochthonous on the Dinaric Alps since the Mesolithic period. Dinaric peoples, including Montenegrins, are among the tallest people in the world. The type, particularly in Montenegro, is distinguished by brachiochepal shape, broad forehead, wide relief and strong face, wide jaw and noticeably flat notched head, while arms and legs are proportional to the body height. Hair is commonly of black color, with black or blue eyes.
Anthropologist Božina Ivanović
Božina M. Ivanović ( sr-cyrl, Божина М. Ивановић; 31 December 1931 – 10 October 2002) was a Montenegrin anthropologist and politician. He served as General Secretary of the Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts and President ...
considered that the development of the Montenegrin Dinaric variety was influenced by gracilisation and brachycephalisation; they have characteristics which were not found in other Slavic and non-Slavic European populations, nor morphological properties from paleo-anthropological series originating from the Slavic necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead".
The term usually im ...
from other South Slavic area. Also, the brachycephalisation and width of the face in the last five centuries is growing in Montenegrin, while among other Slavic and European communities decreasing, showing anthropological issues in Montenegro have deeper roots and broader scientific importance. Montenegrin historian Dragoje Živković (1989) noted that modern multidisciplinary research disagrees with older consideration how Sklavinias and Slavic states had ethnical identification, example Serb ethnos, until the 12th century. Slavs mixing with native population (in case of Komani culture necropolis in Pukë
Pukë ( sq-definite, Puka) is a town and municipality in northern Albania. It was formed at the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities Gjegjan, Pukë, Qelëz, Qerret and Rrapë, that became municipal units. The ...
) made a new cultural-historical drift of Albanian-Illyrian and Slavic built upon extinct and present La Tène, Greek-Illyrian, Illyrian-Roman, and Byzantine. He argued that the Slavs from Duklja promptly blended in social-economical of the natives who historically had a more developed society, as was in their interest to approach the Roman-Illyrian natives.
Notable Montenegrins
Historiography
See also
* Montenegrins in Albania *Montenegrin American
Montenegrin Americans are Americans who are of Montenegrin origin. The figure includes all people affiliated with United States who claim Montenegrin ancestry, both those born in the country and naturalized citizens, as well as those with dual c ...
* Montenegrin Argentine
Argentine Montenegrins are people born in Argentina of Montenegrin descent. During the early 1900s, Montenegrins from the Kingdom of Montenegro began emigrating to the country, and nowadays there are approximately 50,000 Montenegrins and descen ...
* Montenegrin Australian
Montenegrin Australians ( Montenegrin: ''Crnogorski Australijanci'') are Australian citizens of Montenegrin descent.
There are claims that the first Montenegrin emigrants to Australia arrived in the mid-19th century. However, there is no more ...
* Montenegrins of Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Montenegrin Canadian
Montenegrin Canadians ( Montenegrin: ''Kanadski Crnogorci'') are Canadian citizens of Montenegrin descent or Montenegro-born people who reside in Canada. According to the 2011 Census, 2,970 Canadians claimed full or partial Montenegrin ancestry, ...
* Montenegrins of Croatia
The Montenegrins of Croatia are a national minority in the republic. According to the 2011 census, there are 4,517 ethnic Montenegrins in Croatia. The highest number of Montenegrins in Croatia is in the Croatian capital Zagreb.
Montenegrins are ...
* Montenegrins in Germany
Montenegrins living in Germany (german: Montenegriner in Deutschland) are supported and represented by various associations. They number around 30,000. Some Montenegrins immigrated during the 1960s and 1970s as ''Gastarbeiter'' ("guest workers") w ...
* Montenegrins of Kosovo
* Montenegrins of Serbia
** Montenegrins of Vojvodina
The Montenegrins of Serbia ( sr, Црногорци у Србији, Crnogorci u Srbiji) are a national minority in the country. According to the 2011 census, there are 38,527 citizens of recent Montenegrin descent, Montenegrin Serbs, or ethnic ...
Notes
References
Sources
*External links
Matica crnogorska (official pages)
Montenegrin Academy of Sciences and Arts (official pages)
The Montenegrin Association of America
(in Montenegrin)
Article about Montenegrin tribes (in montenegrin language)
{{Slavic ethnic groups Slavic ethnic groups South Slavs Ethnic groups in the Balkans Ethnic groups in Montenegro Ethnic groups in Serbia Ethnic groups in Croatia Ethnic groups in Bosnia and Herzegovina