|
Petar I Petrović-Njegoš
Petar I Petrović-Njegoš (Serbian Cyrillic: Петар I Петровић Његош; 1748 – 31 October 1830) was the ruler of the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro as the Metropolitan (''vladika'') of Cetinje, and Exarch (legate) of the Serbian Orthodox Church in Montenegro. He was the most popular spiritual and military leader from the Petrović dynasty. During his long rule, Petar strengthened the state by uniting the often quarreling tribes, consolidating his control over Montenegrin lands, introducing the first laws in Montenegro (''Zakonik Petra I''). His rule prepared Montenegro for the subsequent introduction of modern institutions of the state: taxes, schools and larger commercial enterprises. He was canonized by the Serbian Orthodox Church as Saint Peter of Cetinje (). He was described as "a man of uncommon size, handsome features, considerable talent, and a highly respected character" by Therese Albertine Luise Robinson. Early life The son of Marko and Anđelija ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mojsije Putnik
Mojsije Putnik ( sr-cyr, Мојсије Путник, ) (1728–1790) was the Metropolitan of Sremski Karlovci between 1781–90, during the reign of Joseph II. He was known for publishing the Toleranzpatent (tolerance patent) meant to ensure equal rights for the Serbian Orthodox Church and the Catholic church in Sremski Karlovci. Biography Vasilije Putnik was born in 1728, in Novi Sad, at the time part of Kingdom of Hungary in the Habsburg monarchy (modern Serbia). He was the grandson of Stevan Putnik, the dignity having been conferred in 1621 by Ferdinand II, Holy Roman Emperor, to Stevan von Putnik for his services in the Imperial Guard Cavalry as a captain of the Military Frontier, known as Potiska Krajina (They were mainly bordermen from the ''Potiska'' and ''Pomoriaka'' border zones—known as Kraine—in course of time these Serbs merged with the Cossacks, and partly with the Moldavians, who live in the southern part of Imperial Russia). Stefan died in 1622 in the Thirty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Russia
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing dynasty, Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the Russian Empire Census, 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Turkish War (1787–91)
The term Austro-Turkish War may refer to: * Austro-Turkish War (1593–1606) * Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664) * Austro-Turkish War (1683–1699) * Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718) * Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739) * Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791) * Austro-Hungarian campaign in Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1878 See also * Ottoman wars in Europe A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in ... * Ottoman–Habsburg wars in Hungary (1526–1568) * Habsburg-Ottoman War (other) * Great War (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jovan Radonjić
Jovan Radonjić ( sr-cyr, Јован Радоњић, 1748 – 8 July 1803), commonly known as Jovo (Јово) or Joko, was the '' guvernadur'' of Montenegro between 1764 and 1803. Early life Jovan was born in Njeguši, the son of ''vojvoda'' and ''serdar'' Stanislav Radonjić (1690–1758), the first ''guvernadur'' (s. 1756–58). The family belonged to the Radonjić-Rajičević brotherhood of Njeguši. It is possible that he had an older brother, Vukale, who had served as the ''guvernadur'' following Stanislav's death. Term during Metropolitan Sava Jovan was elected guvernadur by the assembly in Cetinje in 1764. The young Jovan had the final word in that period in Montenegro; the Venetians, the Vizier of Scutari and surrounding Ottoman pashas and beys turned to him when something needed to be arranged. The fact that the Republic of Venice, the traditional ally of the Montenegrins, saw negatively on the relations between Russia and Montenegro is evident from a letter sent by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guvernadur
The title of guvernadur ("governor", Ital. ''governatore'') was used by the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro, initially as the diplomatic office between Montenegro and the Republic of Venice, and later evolved into the counterpart to the Metropolitan as the sovereign. The post was abolished in 1832 by Petar II. Venetian diplomatic title Danilo I allowed the establishment of the post "in order to appease the Republic of Venice", the office being held by a civilian governor whose main role was to protect Venetian interests in Montenegro. There are conflicting views about who was the first guvernadur in Montenegro. Some think that the first guvernadur was Jovan Anthony guvernadur Bolica, ''"gouvernatore del Monte Negro"'' (1688–1692), crew chief of the military in the Republic of Venice on Cetinje. Montenegro's first guvernadur was Djikan Vukotic, whose son Vukajle refused to be first guvernadur due to the suspicion that his father was poisoning Venetians because they were dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paštrovići
The Paštrovići (, ; it, Pastrouichi, Pastrouicchi) is a historical tribe and region in the Montenegrin Littoral. Paštrovići stretches from the southernmost part of the Bay of Kotor, from the cape of Zavala to Spič. Its historical capital was the island of Sveti Stefan. From 1423 until 1797, with interruptions by the Ottoman Empire. It was part of the Kingdom of Dalmatia from 1815 to 1918, then Yugoslavia, then became part of Montenegro only after World War II. It is historically one of two major "maritime tribes", the other being Grbalj. Etymology The etymology of the name Paštrovići is unclear. Vukmanović says that the name ''Paštrović'' could have been derived from the word ''pastro'', a name which still exists in modern Albanian, being derived from ''pastër'', meaning "clean" in Albanian. Another theory proposes that the name could be related to the Vlach word ''pastor'' or ''paštor'', meaning “shepherd” in Latin. Kaser suggests a possible derivation from Sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikšić (tribe)
Nikšić ( cnr, Никшић, italic=no, sr-cyrl, Никшић, italic=no; ), is the second largest city in Montenegro, with a total population of 56,970 located in the west of the country, in the centre of the spacious Nikšić field at the foot of Trebjesa Hill. It is the center of Nikšić Municipality with population of 72,443 according to 2011 census, which is the largest municipality by area and second most inhabited after Podgorica. It was also the largest municipality by area in the former Yugoslavia. It is an important industrial, cultural, and educational center. Name In classical antiquity, the area of Nikšić was the site of the settlement of the Illyrian tribe of the Endirudini and was known in sources of the time as Anderba or Enderon. The Roman Empire built a military camp (''castrum Anderba'') in the 4th century AD, which was known as the Ostrogothic fortress ''Anagastum'' (after 459. AD). After Slavic settlement in the region, Anagastum became Slavic ''Onogošt'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bjelice
Bjelice ( sr, Бјелице/Bjelice) is a historical region and tribe of the Katunska nahija region of Old Montenegro. The tribe was one of the largest traditional tribes of Old Montenegro and one of nine tribes of the Katunska nahija, along with Cetinje, Njeguši, Ćeklići, Cuce, Ozrinići (Čevo), Pješivci, Zagarač and Komani. Geography The Bjelice region is located 20–50 km northwest of Cetinje. It is of a relatively high altitude (800–900 meters above sea level) and is surrounded by high mountains – Čelinac, Štavor and Čevski lisac. Today, Bjelice is considered a geographic region corresponding to the territory of the traditional tribe. History Czech historian Konstantin Jireček noted that Bjelice was first mentioned as a territory around 1430 ("de zente Bielice"). They are also mentioned in a 1431 document found in the Kotor Archives, and in the Ottoman ''defter'' (tax registry) from 1521. Bjelice are described as a village comprising 80 houses and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crmnica
Crmnica ( Serbian and Montenegrin: Црмница, ) is a historical region in southern Montenegro, one of the communes of the municipality of Bar. It is one of the four sub-regions of Old Montenegro. Geography & Demographics Crmnica is located in south-western Montenegro, between the historical area of the Paštrovići tribe and Shestani/Krajina to the south. Crmnica is the most fertile region of Montenegro and it is well known for a local variety of viticulture, the Vranac. In the 19th century, the region consisted of the following villages: Boljevići, Braćeni, Brijege, Bukovik, Donji Brčeli, Dupilo, Gluhi Do, Godinje, Gornji Brčeli, Komarno, Krnjice, Limljani, Mačuge, Mikovići, Orahovo, Ovtočići, Podgor, Popratnica, Seoca, Sotonići, Tomići, Trnovo, Utrg, Virpazar and Zabes. Many of them today are depopulated or completely uninhabited because of the mass emigration wave that began in the 1990s. Virpazar, the central settlement of the region, ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
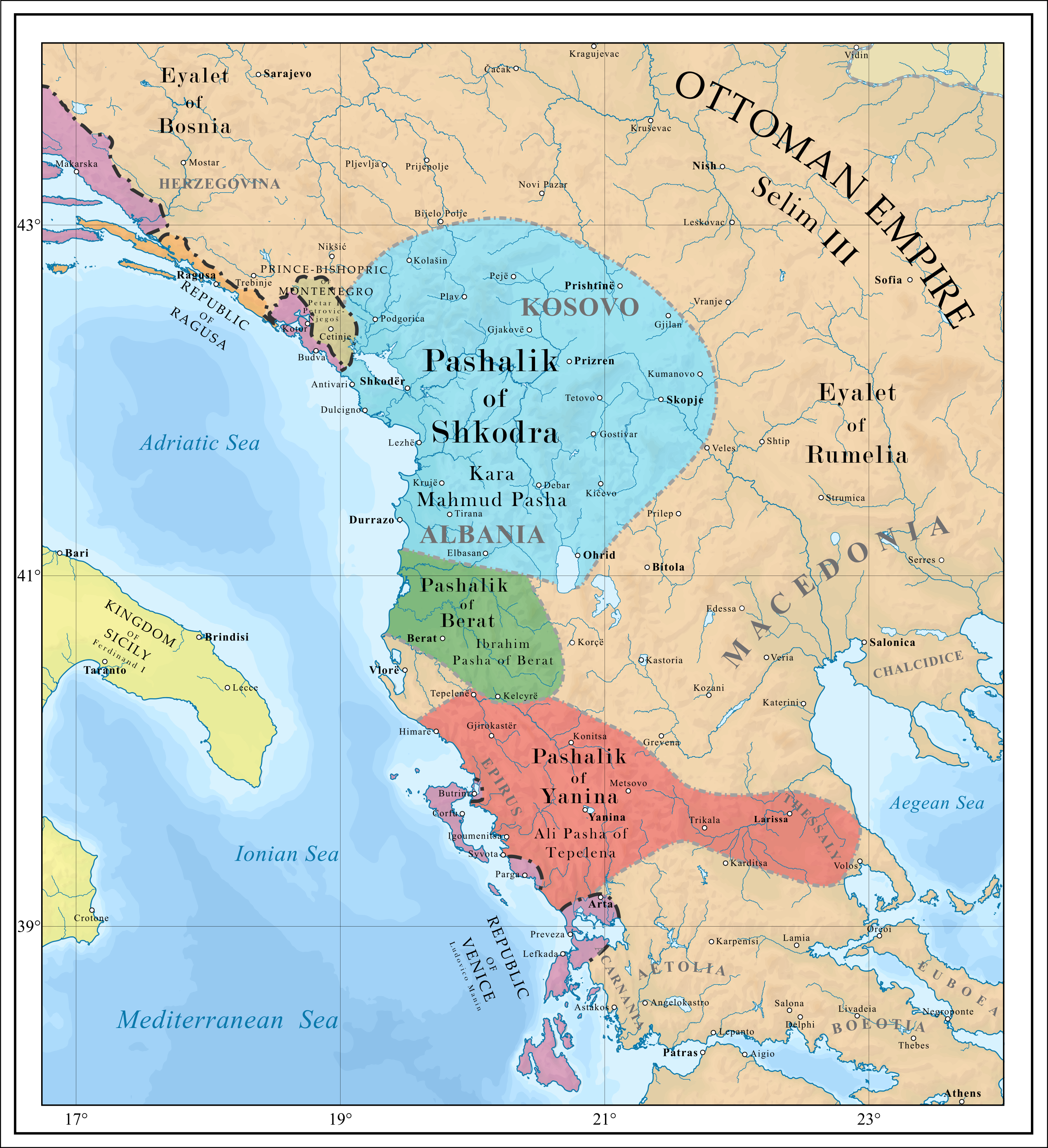
Pasha Of Scutari
The Pashalik of Scutari, Iskodra, or Shkodra (1757–1831), was an autonomous and ''de facto'' independent ''pashalik'' created by the Albanian Bushati family from the previous Sanjak of Scutari, which was situated around the city of Shkodër in modern-day Albania and large majority of modern-day Montenegro. At its peak during the reign of Kara Mahmud Bushati the pashalik encompassed much of Albania, most of Kosovo, western Macedonia, southeastern Serbia and most of Montenegro. Up to 1830 the Pashalik of Shkodra controlled most of the above lands including Southern Montenegro. Background The weakening of Ottoman central authority and the ''timar'' system of land ownership brought anarchy to the Albanian-populated region of the Ottoman empire. In the late eighteenth century, two Albanian centers of power emerged: Shkodër, under the Bushati family; and Janina, under Ali Pasha of Tepelenë. Both regions cooperated with and defied the Sublime Porte as their interests required. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kara Mahmud Pasha
Kara Mahmud Pasha ( tr, Kara Mahmud Paşa, Albanian: Mahmud Pashë Bushati, 1749–22 September 1796) was a hereditary Ottoman Albanian governor (''mutasarrıf'') of the Pashalik of Scutari and de jure ruler of Albania, belonging to the Ottoman Albanian Bushati family. Life Mahmud was the son of Mehmed Pasha Bushati, the governor of the pashalik of Scutari. When Mehmed Pasha died in June 1775, the Sultan's rule was not returned to northern Albania; he was succeeded by his young son, Mahmud Pasha. Other important families were the Rotul dynasty, which ruled Prizren from the 1770s to 1836, and the Gjinolli family whose members ruled Prishtina and Gjilan (Srb.: Gnjil-ane), becoming so powerful in the early nineteenth century that they were called the 'second rulers' of Kosovo after the Sultan. In the late eighteenth century, however, there was just one local dynasty that could rival - and did in fact openly challenge - the Sultan: the Bushati or Bushatli family of Shkodra. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sremski Karlovci
Sremski Karlovci ( sr-cyrl, Сремски Карловци, ; hu, Karlóca; tr, Karlofça) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. It is situated on the banks of the Danube, from Novi Sad. According to the 2011 census results, it has a population of 8,750 inhabitants. The town has traditionally been known as the seat of the Serbian Orthodox Church in the Habsburg Monarchy. It was the political and cultural capital of Serbian Vojvodina after the May Assembly and during the Revolution in 1848. Name In Serbian, the town is known as ''Sremski Karlovci'' (Сремски Карловци), in Croatian as ''Srijemski Karlovci'', in German as ''Karlowitz'' or ''Carlowitz'', in Hungarian as ''Karlóca'', in Polish as ''Karłowice'', in Romanian as ''Carloviț'' and in Turkish as ''Karlofça''. The former Serbian name used for the town was ''Karlovci'' (Карловци), which is also used today, albeit unoffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |