Cornell Arts Quad 1919.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cornell University is a private
Cornell University is a private


 Cornell's medical campus in
Cornell's medical campus in
 Cornell also has facilities devoted to
Cornell also has facilities devoted to  The
The
 Seven schools provide undergraduate programs and an additional seven provide graduate and professional programs. Students pursuing graduate degrees in departments of these schools are enrolled in the
Seven schools provide undergraduate programs and an additional seven provide graduate and professional programs. Students pursuing graduate degrees in departments of these schools are enrolled in the
Retrieved March 10, 2016. In addition to the central University development staff located in Ithaca and New York City, each college and program has its own staffed fundraising program. In 2006, Cornell launched a $4 billion fundraising campaign, which reached $3 billion in November 2010. In 2013, Cornell's "Cornell Now" fundraising campaign raised over $475 million.
 Section 9 of the original charter of Cornell ensured that the university "shall be open to applicants for admission ... at the lowest rates of expense consistent with its welfare and efficiency, and without distinction as to rank, class, previous occupation or locality". The University Charter provided for free instruction to one student chosen from each Assembly district in the state.
Starting in the 1950s Cornell coordinated with other Ivy League schools to provide a consistent set of financial aid. However, in 1989, a consent decree to end a Justice Department antitrust investigation ended such coordination. Even after the decree, all Ivy League schools continue to award aid on financial need without offering any athletic scholarships. In December 2010, Cornell announced a policy of matching any grant component of financial aid offers from other Ivy League schools,
Section 9 of the original charter of Cornell ensured that the university "shall be open to applicants for admission ... at the lowest rates of expense consistent with its welfare and efficiency, and without distinction as to rank, class, previous occupation or locality". The University Charter provided for free instruction to one student chosen from each Assembly district in the state.
Starting in the 1950s Cornell coordinated with other Ivy League schools to provide a consistent set of financial aid. However, in 1989, a consent decree to end a Justice Department antitrust investigation ended such coordination. Even after the decree, all Ivy League schools continue to award aid on financial need without offering any athletic scholarships. In December 2010, Cornell announced a policy of matching any grant component of financial aid offers from other Ivy League schools,
 Cornell is a member of the
Cornell is a member of the
' s 2022 ranking of universities' contributions to research, community service, and social mobility. In 2017, the university was ranked 7th in ''The Princeton Reviews "Top 50 Green Colleges".
 In its annual edition of "America's Best Architecture & Design Schools", the journal ''Design Intelligence'' has consistently ranked Cornell's Bachelor of Architecture program as number one in the nation (2000–2002, 2005–2007, 2009–2013 and 2015–2016). In the 2011 survey, the program ranked first and the Master of Architecture program ranked 6th. In 2017, Design Intelligence ranked Cornell's Master of Landscape Architecture program 4th in the nation with the Bachelor of Science in Landscape Architecture program ranking 5th among its undergraduate counterparts. Among business schools in the United States, the Johnson School of Management at Cornell was named the 9th best business school by ''
In its annual edition of "America's Best Architecture & Design Schools", the journal ''Design Intelligence'' has consistently ranked Cornell's Bachelor of Architecture program as number one in the nation (2000–2002, 2005–2007, 2009–2013 and 2015–2016). In the 2011 survey, the program ranked first and the Master of Architecture program ranked 6th. In 2017, Design Intelligence ranked Cornell's Master of Landscape Architecture program 4th in the nation with the Bachelor of Science in Landscape Architecture program ranking 5th among its undergraduate counterparts. Among business schools in the United States, the Johnson School of Management at Cornell was named the 9th best business school by ''
 The Cornell University Library is the 11th largest academic library in the United States, ranked by number of
The Cornell University Library is the 11th largest academic library in the United States, ranked by number of

 Cornell, a research university, is ranked fourth in the world in producing the largest number of graduates who go on to pursue PhDs in
Cornell, a research university, is ranked fourth in the world in producing the largest number of graduates who go on to pursue PhDs in

 For the 2016–2017 academic year, Cornell had over 1,000 registered student organizations. These clubs and organizations run the gamut from kayaking to full-armor jousting, from varsity and club sports and a cappella groups to improvisational theatre, from political clubs and publications to chess and video game clubs. The Cornell International Affairs Society sends over 100 Cornellians to collegiate Model United Nations conferences across North America and hosts the Cornell Model United Nations Conference each spring for over 500 high school students. The Cornell University Mock Trial Association regularly sends teams to the national championship and is ranked 5th in the nation. Additionally, the Cornell International Affairs Society's traveling Model United Nations team is ranked number 16 in the nation. Cornell United Religious Work is a collaboration among many diverse religious traditions, helping to provide spiritual resources throughout a student's time at college. The
For the 2016–2017 academic year, Cornell had over 1,000 registered student organizations. These clubs and organizations run the gamut from kayaking to full-armor jousting, from varsity and club sports and a cappella groups to improvisational theatre, from political clubs and publications to chess and video game clubs. The Cornell International Affairs Society sends over 100 Cornellians to collegiate Model United Nations conferences across North America and hosts the Cornell Model United Nations Conference each spring for over 500 high school students. The Cornell University Mock Trial Association regularly sends teams to the national championship and is ranked 5th in the nation. Additionally, the Cornell International Affairs Society's traveling Model United Nations team is ranked number 16 in the nation. Cornell United Religious Work is a collaboration among many diverse religious traditions, helping to provide spiritual resources throughout a student's time at college. The
Cornell Outdoor EducationCornell Outing Club
an
Outdoor Odyssey
a student-run group that runs pre-orientation trips for first-year and transfer students. A Cornell student organization
The Cornell Astronomical Society
runs public observing nights every Friday evening at the Fuertes Observatory. The university is home to the
 University housing is broadly divided into three sections: North Campus, West Campus, and Collegetown. Cornell began experiments with co-ed dormitories in 1971 and continued the tradition of residential advisors (RAs) within the campus system. In 1991, new students could be found throughout West Campus, including at the historic Baker and Boldt Hall complexes; since a 1997 residential initiative, West Campus houses transfer and returning students, whereas North Campus is almost entirely populated by freshmen as well as sorority and fraternity houses.
The options for living on North Campus for upperclassmen are the program houses and co-op houses. Program houses include
University housing is broadly divided into three sections: North Campus, West Campus, and Collegetown. Cornell began experiments with co-ed dormitories in 1971 and continued the tradition of residential advisors (RAs) within the campus system. In 1991, new students could be found throughout West Campus, including at the historic Baker and Boldt Hall complexes; since a 1997 residential initiative, West Campus houses transfer and returning students, whereas North Campus is almost entirely populated by freshmen as well as sorority and fraternity houses.
The options for living on North Campus for upperclassmen are the program houses and co-op houses. Program houses include
Watermargin
and one independent cooperative
Cayuga Lodge
In an attempt to create a sense of community and an atmosphere of education outside the classroom and continue Andrew Dickson White's vision, a $250 million reconstruction of West Campus created
Watermargin
and one independent cooperative
Cayuga Lodge
Besides this, there exists also cooperative housing not owned by Cornell, like
 Cornell has 35 varsity intercollegiate teams that have the nickname of the Big Red. An
Cornell has 35 varsity intercollegiate teams that have the nickname of the Big Red. An
 Cornelliana is a term for Cornell's traditions, legends, and lore. Cornellian traditions include Slope Day, a celebration held on the last day of classes of the spring semester, and
Cornelliana is a term for Cornell's traditions, legends, and lore. Cornellian traditions include Slope Day, a celebration held on the last day of classes of the spring semester, and
 , Cornell had 1,639 full-and part-time faculty members affiliated with its main campus, 1,235 affiliated with its New York City divisions, and 34 affiliated with its campus in Qatar. Cornell's faculty for the 2005–06 academic year included three Nobel laureates, a
, Cornell had 1,639 full-and part-time faculty members affiliated with its main campus, 1,235 affiliated with its New York City divisions, and 34 affiliated with its campus in Qatar. Cornell's faculty for the 2005–06 academic year included three Nobel laureates, a
 Cornell alumni are noted for their accomplishments in public, professional, and corporate life. Lee Teng-hui was the president of
Cornell alumni are noted for their accomplishments in public, professional, and corporate life. Lee Teng-hui was the president of
Cornell Athletics website
{{Authority control 1865 establishments in New York (state) Cornell family Educational institutions established in 1865 Ithaca, New York Land-grant universities and colleges Schools in Tompkins County, New York Tourist attractions in Tompkins County, New York Private universities and colleges in New York (state)
 Cornell University is a private
Cornell University is a private statutory
A statute is a formal written enactment of a legislative authority that governs the legal entities of a city, state, or country by way of consent. Typically, statutes command or prohibit something, or declare policy. Statutes are rules made by le ...
land-grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
research university
A research university or a research-intensive university is a university that is committed to research as a central part of its mission. They are the most important sites at which knowledge production occurs, along with "intergenerational kn ...
based in Ithaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named ...
. It is a member of the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
. Founded in 1865 by Ezra Cornell
Ezra Cornell (; January 11, 1807 – December 9, 1874) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder of Western Union and a co-founder of Cornell University. He also served as President of the New York Agricul ...
and Andrew Dickson White
Andrew Dickson White (November 7, 1832 – November 4, 1918) was an American historian and educator who cofounded Cornell University and served as its first president for nearly two decades. He was known for expanding the scope of college curricu ...
, Cornell was founded with the intention to teach and make contributions in all fields of knowledge—from the classics to the science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
s, and from the theoretical
A theory is a rational type of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the results of such thinking. The process of contemplative and rational thinking is often associated with such processes as observational study or research. Theories may be ...
to the applied. These ideals, unconventional for the time, are captured in Cornell's founding principle, a popular 1868 quotation from founder Ezra Cornell
Ezra Cornell (; January 11, 1807 – December 9, 1874) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder of Western Union and a co-founder of Cornell University. He also served as President of the New York Agricul ...
: "I would found an institution where any person can find instruction in any study." Cornell is ranked among the top global universities.
The university is organized into seven undergraduate
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, in the United States, an entry-le ...
colleges and seven graduate divisions at its main Ithaca campus, with each college and division defining its specific admission standards and academic programs in near autonomy. The university also administers three satellite campuses, two in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
and one in Education City
Education City is a development in Al Rayyan, Qatar. Developed by the Qatar Foundation, the property houses various educational facilities, including satellite campuses of eight international universities.
History
Education City was launched b ...
, Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it ...
.
Cornell is one of the few private land grant universities in the United States. Of its seven undergraduate colleges, three are state-supported statutory or contract colleges through the State University of New York (SUNY) system, including its agricultural and human ecology colleges as well as its industrial labor relations school. Of Cornell's graduate schools, only the veterinary college is state-supported. As a land grant college, Cornell operates a cooperative extension
The Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES) was an extension agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), part of the executive branch of the federal government. The 1994 Department Reorganization Act, ...
outreach program in every county of New York and receives annual funding from the State of New York for certain educational missions. The main campus of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named ...
spans 745 acres (more than 4,300 acres when the Cornell Botanic Gardens and the numerous university-owned lands in New York City are considered).
As of September 2021, 61 Nobel laureates, four Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in comput ...
winners and one Fields Medalist have been affiliated with Cornell. Cornell counts more than 250,000 living alumni
Alumni (singular: alumnus (masculine) or alumna (feminine)) are former students of a school, college, or university who have either attended or graduated in some fashion from the institution. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for grou ...
, and its former and present faculty and alumni include 34 Marshall Scholars
The Marshall Scholarship is a postgraduate scholarship for "intellectually distinguished young Americans ndtheir country's future leaders" to study at any university in the United Kingdom. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious sc ...
, 33 Rhodes Scholars, 29 Truman Scholars
The Harry S. Truman Scholarship is the premier graduate fellowship in the United States for public service leadership. It is a federally funded scholarship granted to U.S. undergraduate students for demonstrated leadership potential, academic ...
, 7 Gates Scholars, 63 Olympic Medalists, 10 current Fortune 500 CEOs, and 35 billionaire alumni. Since its founding, Cornell has been a co-education
Mixed-sex education, also known as mixed-gender education, co-education, or coeducation (abbreviated to co-ed or coed), is a system of education where males and females are educated together. Whereas single-sex education was more common up to ...
al, non- sectarian institution where admission has not been restricted by religion or race. The diverse student body consists of more than 15,000 undergraduate and 10,000 graduate students from all 50 American states and 119 countries.
History
Cornell University was founded on April 27, 1865; the New York State (NYS) legislature authorized the university as the state'sland grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
institution. Senator Ezra Cornell
Ezra Cornell (; January 11, 1807 – December 9, 1874) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder of Western Union and a co-founder of Cornell University. He also served as President of the New York Agricul ...
offered his farm in Ithaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named ...
, as a site and $500,000 of his personal fortune as an initial endowment. Fellow senator and educator Andrew Dickson White
Andrew Dickson White (November 7, 1832 – November 4, 1918) was an American historian and educator who cofounded Cornell University and served as its first president for nearly two decades. He was known for expanding the scope of college curricu ...
agreed to be the first president. During the next three years, White oversaw the construction of the first two buildings and traveled to attract students and faculty. The university was inaugurated on October 7, 1868, and 412 men were enrolled the next day.
Cornell developed as a technologically innovative institution, applying its research to its own campus and to outreach efforts. For example, in 1883, it was one of the first university campuses to use electricity from a water-powered dynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundati ...
to light the grounds. Since 1894, Cornell has included colleges that are state funded and fulfill statutory requirements; it has also administered research and extension activities that have been jointly funded by state and federal matching programs.
Cornell has had active alumni since its earliest classes. It was one of the first universities to include alumni-elected representatives on its board of trustees. Cornell was also among the Ivies that had heightened student activism during the 1960s, related to cultural issues, civil rights, and opposition to the Vietnam War; with protests and occupations resulting in the resignation of Cornell's president and the restructuring of university governance. Today, the university has more than 4,000 courses. Cornell is also known for the Residential Club Fire of 1967, a fire in the Residential Club dormitory that killed eight students and one professor.
Since 2000, Cornell has been expanding its international programs
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
. In 2004, the university opened the Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar
Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar (WCM-Q) is a branch of Weill Cornell Medicine of Cornell University, established on April 9, 2001 following an agreement between Cornell University and the Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Developme ...
. It has partnerships with institutions in India, Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
, and the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. The former president, Jeffrey S. Lehman, described the university, with its high international profile, as a "transnational university". On March 9, 2004, Cornell and Stanford University laid the cornerstone for a new 'Bridging the Rift Center' to be built and jointly operated for education on the Israel–Jordan border.
A graduate student
Postgraduate or graduate education refers to academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate (bachelor's) degree.
The organization and s ...
group, At What Cost?, formed at Cornell in August 2002 to oppose a graduate student unionization drive run by an organization called CASE/UAW that was affiliated with the United Auto Workers
The International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace, and Agricultural Implement Workers of America, better known as the United Auto Workers (UAW), is an American labor union that represents workers in the United States (including Puerto Rico) ...
. The unionization vote
Voting is a method by which a group, such as a meeting or an Constituency, electorate, can engage for the purpose of making a collective decision making, decision or expressing an opinion usually following discussions, debates or election camp ...
was held October 23–24, 2002, and the union was rejected. At What Cost? was considered instrumental in the unusually large 90% turnout for the vote and in the 2-to-1 defeat of the unionization proposal. There had been no prior instance in American graduate student unionization history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
where a unionization proposal was defeated by a vote.
Campuses


Ithaca campus
Cornell's main campus is on East Hill inIthaca, New York
Ithaca is a city in the Finger Lakes region of New York, United States. Situated on the southern shore of Cayuga Lake, Ithaca is the seat of Tompkins County and the largest community in the Ithaca metropolitan statistical area. It is named ...
, overlooking the city and Cayuga Lake
Cayuga Lake (,,) is the longest of central New York's glacial Finger Lakes, and is the second largest in surface area (marginally smaller than Seneca Lake) and second largest in volume. It is just under long. Its average width is , and it is ...
. Since the university was founded, it has expanded to about , encompassing both the hill and much of the surrounding areas. Central Campus has laboratories, administrative buildings, and almost all of the campus' academic buildings, athletic facilities, auditoriums, and museums. North Campus is composed of ten residence halls that primarily house first-year students, although the Townhouse Community occasionally houses transfer students. The five main residence halls on West Campus make up the West Campus House System, along with several Gothic-style buildings, referred to as "the Gothics". Collegetown contains two upper-level residence halls
A dormitory (originated from the Latin word ''dormitorium'', often abbreviated to dorm) is a building primarily providing sleeping and residential quarters for large numbers of people such as boarding school, high school, college or university ...
and the Schwartz Performing Arts Center, amid a mixed-use neighborhood of apartments, eateries, and businesses. Construction has also been completed on three new residential buildings that will be situated on North Campus, providing beds for an estimated additional 1200 students, to be completed by fall 2022. These are named after Hu Shih, Barbara McClintock, and Ruth Bader Ginsburg—all Cornell graduates.
The main campus is marked by an irregular layout and eclectic architectural style
An architectural style is a set of characteristics and features that make a building or other structure notable or historically identifiable. It is a sub-class of style in the visual arts generally, and most styles in architecture relate closely ...
s, including ornate Collegiate Gothic, Victorian, and Neoclassical buildings, and the more spare international
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
and modernist
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
structures. The more ornate buildings generally predate World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
. The student population doubled from 7,000 in 1950 to 15,000 by 1970, at a time when architectural styles favored modernism. While some buildings are neatly arranged into quadrangles, others are packed densely and haphazardly. These eccentricities arose from the university's numerous, ever-changing master plans for the campus. For example, in one of the earliest plans, Frederick Law Olmsted
Frederick Law Olmsted (April 26, 1822August 28, 1903) was an American landscape architect, journalist, social critic, and public administrator. He is considered to be the father of landscape architecture in the USA. Olmsted was famous for co ...
, the designer of Central Park
Central Park is an urban park in New York City located between the Upper West and Upper East Sides of Manhattan. It is the fifth-largest park in the city, covering . It is the most visited urban park in the United States, with an estimated ...
, proposed a "grand terrace" overlooking Cayuga Lake
Cayuga Lake (,,) is the longest of central New York's glacial Finger Lakes, and is the second largest in surface area (marginally smaller than Seneca Lake) and second largest in volume. It is just under long. Its average width is , and it is ...
.
Several of the university buildings are listed as historic landmarks. Those listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
include the Andrew Dickson White House
The Andrew Dickson White House, commonly referred to as the "A.D. White House," is a High Victorian Gothic house on the campus of Cornell University, designed by William Henry Miller and Charles Babcock. It houses the Cornell University Society ...
, Bailey Hall, Caldwell Hall Caldwell Hall may refer to:
;In the United States
* Caldwell Hall (Catholic University of America), a residence hall
* Caldwell Hall (Pine Bluff, Arkansas), listed on the NRHP in Arkansas
* Caldwell Hall (Georgia Tech), a residence hall at the Geo ...
, the Computing and Communications Center (formerly Comstock Hall), Morrill Hall Morrill Hall may refer to (all are buildings named for Justin Smith Morrill):
*Morrill Hall (Cornell University), the building at Cornell University
*Morrill Hall, a campus building located at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign
*Morri ...
, Rice Hall, Fernow Hall, Wing Hall, Llenroc
Llenroc is a Gothic revival villa built for Ezra Cornell, the founder of Cornell University. It is located at 100 Cornell Avenue in Ithaca, New York, United States, just below the Cornell University campus. Since 1911, it has been the home o ...
, and 13 South Avenue (Deke House). At least three other historic buildings— the original Roberts Hall, East Robert Hall and Stone Hall—have also been listed on the NRHP. However, the university demolished them in the 1980s, to make way for other development. In September 2011, ''Travel+Leisure
''Travel + Leisure'' is a travel magazine based in New York City, New York. Published 12 times a year, it has 4.8 million readers, according to its corporate media kit. It is published by Dotdash Meredith, a subsidiary of IAC, with trademark ...
'' listed the Ithaca Campus as among the most beautiful in the United States.
Located among the rolling valleys of the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
region, the campus on the hill provides views of the surrounding area, including the Cayuga Lake
Cayuga Lake (,,) is the longest of central New York's glacial Finger Lakes, and is the second largest in surface area (marginally smaller than Seneca Lake) and second largest in volume. It is just under long. Its average width is , and it is ...
. Two gorges, Fall Creek Gorge and Cascadilla Gorge, bound Central Campus and are used as popular swimming holes during the warmer months (although the university and city code discourage their use, due to hazardous swimming conditions). Adjacent to the main campus, Cornell owns the Cornell Botanic Gardens, a botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
containing flowers, trees, and ponds, with manicured trails providing access throughout the facility.
The university has embarked on numerous 'green' initiatives. In 2009, a new gas-fired combined heat and power facility replaced a coal-fired steam plant, resulting in a reduction in carbon emissions to 7% below 1990 levels, and projected to reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 75,000 tons per year. This facility satisfies 15% of campus electrical needs, and a university-run, on-campus hydroelectric plant in the Fall Creek Gorge provides an additional 2%. The university has a lake source cooling project that uses Cayuga Lake to air condition campus buildings, with an 80% energy savings over conventional systems. In 2007, Cornell established a Center for a Sustainable Future. Cornell has been rated "A−" by the 2011 College Sustainability Report Card for its environmental and sustainability initiatives. However, the university has drawn criticism from student groups for a planned North Campus expansion for which they have not released an environmental impact statement.
Since 2007, the university has committed to achieve net carbon neutrality
Carbon neutrality is a state of net-zero carbon dioxide emissions. This can be achieved by balancing emissions of carbon dioxide with its removal (often through carbon offsetting) or by eliminating emissions from society (the transition to the "p ...
by 2035, from the baseline 2008 emissions, acting as the first Ivy League institution to take on such a sustainability goal. Cornell's Ithaca campus, as of 2020, is powered by 6 solar farms, providing a total of 28 megawatts of power. In counterpart to lake source cooling, heating needs plan to be met through the development of Earth Source Heating, a mid to low-grade enhanced geothermal system
An enhanced geothermal system (EGS) generates geothermal electricity without the need for natural convective hydrothermal resources. Until recently, geothermal power systems have exploited only resources where naturally occurring heat, water, an ...
. The geothermal system is eventually planned to supply 20% of campus heating demand. The Earth Source Heating project has received a $7.2 million grant from the DOE, and Jefferson Tester and Teresa Jordan
Teresa (Terry) Jordan is a sedimentary geologist known for her research on the geology and hydrology of the Atacama Desert and the use of water and geothermal heat from sedimentary rocks.
Education and career
Jordan has a B.S. from Rensselaer ...
are leading the research to drill a test well on university land in Spring of 2021. The wells for Earth Source Heating will be deep, reaching temperatures of >. Waste biomass burning will be used to cover the estimated 20 'cold days' when the geothermal can not provide peak heating.
New York City campuses
Weill Cornell
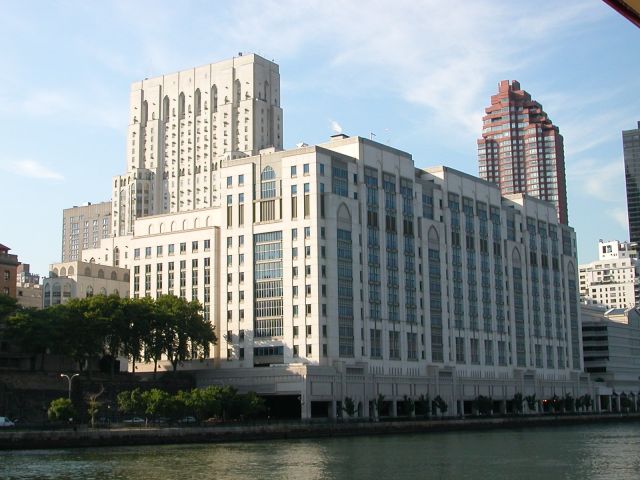
 Cornell's medical campus in
Cornell's medical campus in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the most densely populated major city in the Un ...
, also called Weill Cornell, is on the Upper East Side
The Upper East Side, sometimes abbreviated UES, is a neighborhood in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, bounded by 96th Street to the north, the East River to the east, 59th Street to the south, and Central Park/Fifth Avenue to the wes ...
of Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
. It is home to two Cornell divisions: Weill Cornell Medical College
The Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical College of Cornell University is Cornell University's biomedical research unit and medical school located in Upper East Side, Manhattan, New York City, New York.
Weill Cornell Medicine is affiliated with N ...
and Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences
The Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences (WCGS) (formerly known as the Cornell University Graduate School of Medical Sciences) is a graduate college of Cornell University that was founded in 1952 as an academic partnership between t ...
, and has been affiliated with the NewYork–Presbyterian Hospital The NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital is a nonprofit academic medical center in New York City affiliated with two Ivy League medical schools, Cornell University and Columbia University. The hospital comprises seven distinct campuses located in the New Y ...
since 1927. Although their faculty and academic divisions are separate, the Medical Center shares administrative and teaching hospital functions with the Columbia University Medical Center
NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center (NYP/CUIMC), also known as the Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC), is an academic medical center and the largest campus of NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital. It includes C ...
. These teaching hospitals include the Payne Whitney Clinic in Manhattan and the Westchester Division in White Plains, New York
(Always Faithful)
, image_seal = WhitePlainsSeal.png
, seal_link =
, subdivision_type = List of sovereign states, Country
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = U.S. state, State
, su ...
. Weill Cornell Medical College is also affiliated with the neighboring Memorial Sloan–Kettering Cancer Center
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK or MSKCC) is a cancer treatment and research institution in the borough of Manhattan in New York City, founded in 1884 as the New York Cancer Hospital. MSKCC is one of 52 National Cancer Institute� ...
, Rockefeller University, and the Hospital for Special Surgery
Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) is a hospital in New York City that specializes in orthopedic surgery and the treatment of rheumatologic conditions.
Founded in 1863 by James Knight, HSS is the oldest orthopedic hospital in the United States ...
. Many faculty members have joint appointments at these institutions. Weill Cornell, Rockefeller, and Memorial Sloan–Kettering offer the Tri-Institutional MD–PhD Program
The Tri-Institutional MD-PhD Program is an MD-PhD program based in New York City that was formed by combining earlier MD-PhD programs that had their inceptions in 1972. The current version of the program, which is operated by Weill Cornell Medicin ...
to selected entering Cornell medical students. From 1942 to 1979, the campus also housed the Cornell School of Nursing.
Cornell Tech
On December 19, 2011, Cornell and the Technion-Israel Institute of Technology won a competition for rights to claim free city land and $100 million in subsidies to build an engineering campus in New York City. The competition was established by New York City Mayor Michael Bloomberg, to increase entrepreneurship and job growth in the city's technology sector. The winning bid consisted of a 2.1 million square foot state-of-the-art tech campus to be built on Roosevelt Island, on the site of the formerColer-Goldwater Specialty Hospital
Coler Specialty Hospital is a chronic care facility on New York City's Roosevelt Island that provides services such as rehabilitation and specialty nursing. The hospital was formed in 1996 by the merger of two separate chronic care hospitals o ...
. Instruction began in the fall of 2012, in a temporary location in Manhattan (111 Eighth Avenue
111 Eighth Avenue, also known as the Google Building and formerly known as Union Inland Terminal #1 and the Port Authority Building, is an Art Deco multi-use building in the Chelsea neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City. Fifteen stories ...
), in space donated by Google
Google LLC () is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company focusing on Search Engine, search engine technology, online advertising, cloud computing, software, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, ar ...
. Thom Mayne
Thom Mayne (born January 19, 1944) is an American architect. He is based in Los Angeles. In 1972, Mayne helped found the Southern California Institute of Architecture (SCI-Arc), where he is a trustee and the coordinator of the Design of Cities po ...
, of the architecture firm Morphosis
Morphosis Architects is an interdisciplinary architectural and design practice based in Los Angeles and New York City.
History
The firm was informally founded in 1972 by Michael Brickler, Thom Mayne, Livio Santini and James Stafford. Michael Rot ...
, has been selected to design the first building to be constructed on Roosevelt Island. Begun in 2014, construction of the first phase of the campus was completed in September 2017.
Other New York City programs
In addition to the tech campus and medical center, Cornell maintains local offices in New York City for some of its service programs. The Cornell Urban Scholars Program encourages students to pursue public service careers, arranging assignments with organizations working with New York City's poorest children, families, and communities. The NYS College of Human Ecology and the NYS College of Agriculture and Life Sciences enable students to reach out to local communities by gardening and building with the Cornell Cooperative Extension. Students with the NYS School of Industrial and Labor Relations' Extension & Outreach Program make workplace expertise available to organizations, union members, policymakers, and working adults. The College of Engineering's Operations Research Manhattan, in the city'sFinancial District
A financial district is usually a central area in a city where financial services firms such as banks, insurance companies and other related finance corporations have their head offices. In major cities, financial districts are often home to s ...
, brings together business optimization research and decision support services addressed to both financial applications and public health logistics planning. The College of Architecture, Art, and Planning
The College of Architecture, Art, and Planning (AAP) at Cornell University is one of the world's most highly regarded and prestigious schools of architecture and has the only department in the Ivy League that offers the Bachelor of Architecture de ...
has an 11,000 square foot, Gensler
Gensler is a global design and architecture firm founded in San Francisco, California, in 1965.
In 2021, Gensler generated $1.235 billion in revenue, the most of any architecture firm in the U.S. As of 2021, Gensler operated offices in 49 citi ...
-designed facility on 26 Broadway
26 Broadway, also known as the Standard Oil Building or Socony–Vacuum Building, is an office building adjacent to Bowling Green in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. The 31-story, structure was designed in the Renai ...
(The Standard Oil Building), in the Financial District, that opened in 2015.
Qatar campus

Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar
Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar (WCM-Q) is a branch of Weill Cornell Medicine of Cornell University, established on April 9, 2001 following an agreement between Cornell University and the Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Developme ...
is in Education City
Education City is a development in Al Rayyan, Qatar. Developed by the Qatar Foundation, the property houses various educational facilities, including satellite campuses of eight international universities.
History
Education City was launched b ...
, near Doha
Doha ( ar, الدوحة, ad-Dawḥa or ''ad-Dōḥa'') is the capital city and main financial hub of Qatar. Located on the Persian Gulf coast in the east of the country, north of Al Wakrah and south of Al Khor, it is home to most of the count ...
. Opened in September 2004, it was the first American medical school to be established outside of the United States. The college is part of Cornell's program to increase its international influence. The college is a joint initiative with the Qatar government, which seeks to improve the country's academic programs and medical care. Along with its full four-year MD program, which mirrors the curriculum taught at Weill Medical College
The Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical College of Cornell University is Cornell University's biomedical research unit and medical school located in Upper East Side, Manhattan, New York City, New York.
Weill Cornell Medicine is affiliated with NewY ...
back in New York City, the college offers a two-year undergraduate pre-medical program with a separate admissions process. This undergraduate program opened in September 2002 and was the first coeducational institute of higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after comple ...
in Qatar.
The college is partially funded by the Qatar government through the Qatar Foundation
Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Development ( ar, مؤسسة قطر) is a state-led non-profit organization in Qatar, founded in 1995 by then-emir Hamad bin Khalifa Al Thani and his second wife Moza bint Nasser. Qatar Founda ...
, which contributed $750 million for its construction. The medical center is housed in a large two-story structure designed by Arata Isozaki
Arata Isozaki (磯崎 新, ''Isozaki Arata''; born 23 July 1931) is a Japanese architect, urban designer, and theorist from Ōita. He was awarded the RIBA Gold Medal in 1986 and the Pritzker Architecture Prize in 2019.
Biography
Isozaki was ...
, an internationally known Japanese architect. In 2004, the Qatar Foundation announced the construction of a 350-bed Specialty Teaching Hospital, near the medical college in Education City. The hospital was to be completed in a few years.
Other facilities
Cornell owns or operates several other facilities. The Arecibo Observatory inPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, site of the world's largest single-dish radio telescope, was operated by Cornell under a contract with the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
from its construction until 2011. The Shoals Marine Laboratory
Shoals Marine Laboratory (SML) is a seasonal marine field station located on Appledore Island, Maine, in the United States. Appledore Island is the largest of the Isles of Shoals archipelago, a group of rocky islands just offshore of the coastlin ...
, operated in conjunction with the University of New Hampshire
The University of New Hampshire (UNH) is a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Durham, New Hampshire. It was founded and incorporated in 1866 as a land grant college in Hanover in connection with Dartmouth College, m ...
, is a seasonal marine field station dedicated to undergraduate education and research on the Appledore Island
Appledore Island (formerly known as Hog Island) is the largest of the Isles of Shoals located about seven miles off the Maine coast. It is part of the Town of Kittery, in York County.
History
Appledore Island was originally settled by European ...
, off the Maine
Maine () is a state in the New England and Northeastern regions of the United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick and Quebec to the northeast and ...
–New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec to the nor ...
coast.
 Cornell also has facilities devoted to
Cornell also has facilities devoted to conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws.
Conservation may also refer to:
Environment and natural resources
* Nature conservation, the protection and managem ...
and ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
. The New York State Agricultural Experiment Station The New York State Agricultural Experiment Station (NYSAES) at Geneva, Ontario County, New York State, is an agricultural experiment station operated by the New York State College of Agriculture and Life Sciences at Cornell University. In August 2 ...
, operated by the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, is in Geneva, New York
Geneva is a city in Ontario and Seneca counties in the U.S. state of New York. It is at the northern end of Seneca Lake; all land portions of the city are within Ontario County; the water portions are in Seneca County. The population was 13, ...
, northwest of the main campus. It operates three substations: the Cornell Lake Erie Research and Extension Laboratory (CLEREL) in Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, the Hudson Valley Laboratory in Highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
, and the Long Island Horticultural Research Laboratory in Riverhead.
 The
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology
The Cornell Lab of Ornithology is a member-supported unit of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, which studies birds and other wildlife. It is housed in the Imogene Powers Johnson Center for Birds and Biodiversity in Sapsucker Woods Sanctuar ...
in Ithaca's Sapsucker Woods performs research on biological diversity
Biodiversity or biological diversity is the variety and variability of life on Earth. Biodiversity is a measure of variation at the genetic ('' genetic variability''), species ('' species diversity''), and ecosystem ('' ecosystem diversity'') ...
, primarily in birds. On April 18, 2005, the lab announced that it had rediscovered the ivory-billed woodpecker
The ivory-billed woodpecker (''Campephilus principalis'') is a possibly extinct woodpecker that is native to the bottomland hardwood forests and temperate coniferous forests of the Southern United States and Cuba. Habitat destruction and hunting ...
, long thought to be extinct. (Some experts disputed the evidence and subsequent surveys were inconclusive). The Animal Science Teaching and Research Center in Harford, New York
Harford is a town in Cortland County, New York, United States. The population was 943 at the 2010 census. Harford is in the southwestern corner of Cortland County and is south of Cortland.
History
Harford was in the former Central New York ...
, and the Duck Research Laboratory in Eastport, New York
Eastport is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, New York, on the South Shore of Long Island. The population was 1,831 at the 2010 census.
History
Eastport dates to the 1730s when a gristmill was built there. It started ...
are resources for information on animal disease control and husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, startin ...
.
The Cornell Biological Field Station in Bridgeport, New York
Bridgeport is a hamlet (and census-designated place) located partly in the town of Sullivan in Madison County, New York, United States and partly in the town of Cicero in Onondaga County. The population was 1,490 at the 2010 census.
Geography
B ...
, conducts long-term ecological research and supports the university's educational programs, with special emphasis on freshwater lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much large ...
systems. The Department of Horticulture operates the Freeville Organic Research Farm and the Homer C. Thompson Vegetable Research Farm in Freeville, New York
Freeville is a village in Tompkins County, New York, United States. The population was 520 at the 2010 census.
The Village of Freeville is in the Town of Dryden and is east of Ithaca. It is the only incorporated municipality in the United States ...
. The university operates a biodiversity laboratory in Punta Cana
Punta Cana is a resort town in the easternmost region of the Dominican Republic. It is part of the Veron–Punta Cana municipal district, in the Higüey municipality of La Altagracia Province. According to the 2010 census, this district had a ...
, Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, and one in the Peruvian Amazon Rainforest, named the Cornell University Esbaran Amazon Field Laboratory
The New York State College of Agriculture and Life Sciences at Cornell University (CALS or Ag School) is a statutory college and one of the four New York State contract colleges on the Cornell University campus in Ithaca, New York. With enrollmen ...
.
The university also arranges study abroad and scholarship programs. "Cornell in Washington" is a program that allows students to study for a semester in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, holding research or internship
An internship is a period of work experience offered by an organization for a limited period of time. Once confined to medical graduates, internship is used practice for a wide range of placements in businesses, non-profit organizations and gover ...
positions while earning credit
Credit (from Latin verb ''credit'', meaning "one believes") is the trust which allows one party to provide money or resources to another party wherein the second party does not reimburse the first party immediately (thereby generating a debt) ...
toward a degree. "Cornell in Rome", operated by the College of Architecture, Art, and Planning
The College of Architecture, Art, and Planning (AAP) at Cornell University is one of the world's most highly regarded and prestigious schools of architecture and has the only department in the Ivy League that offers the Bachelor of Architecture de ...
, allows students to use the city of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
as a resource for learning architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing building ...
, urban studies
Urban studies is based on the study of the urban development of cities. This includes studying the history of city development from an architectural point of view, to the impact of urban design on community development efforts. The core theoretica ...
, and the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
. Similarly, the "Capital Semester" program allows students to intern in the New York State Legislature
The New York State Legislature consists of the two houses that act as the state legislature of the U.S. state of New York: The New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly. The Constitution of New York does not designate an officia ...
in Albany.
As New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
's land grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
college, Cornell operates a cooperative extension service
The Cooperative State Research, Education, and Extension Service (CSREES) was an extension agency within the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), part of the executive branch of the federal government. The 1994 Department Reorganization Act, ...
with 56 offices spread out across the state, each staffed with extension educators who offer programs in five subjects: Agriculture and Food Systems; Children, Youth, and Families; Community and Economic Vitality; Environment and Natural Resources; and Nutrition and Health. Cornell also operates New York's Animal Health Diagnostic Center.
Organization and administration
Cornell is a non-profit organization governed by a 64-member Board of Trustees consisting of both privately and publicly appointed trustees. Three trustees are appointed by the Governor of New York: one seat is reserved for the eldest lineal descendant of Ezra Cornell; two members from each of the fields of agriculture, business, and labor in New York state; eight trustees to be elected from among and by the alumni of the university; two trustees to be elected from among and by the faculty of the university at Ithaca and Geneva; two trustees to be elected from among and by the membership of the university's student body at Ithaca (one undergraduate and one graduate student); and one trustee to be elected from among and by the nonacademic staff and employees of the university at Ithaca and Geneva, 37 trustees at large and finally, the Governor, Temporary President of the Senate, Speaker of the Assembly, and president of the university serve in an '' ex officio'' voting capacity. Robert Harrison has served as the chairman of the board since 2014. The board elects a President to serve as the chief executive and educational officer. Martha E. Pollack was inaugurated as Cornell's fourteenth president on August 25, 2017. She succeededElizabeth Garrett
Helen Elizabeth Garrett, commonly known as Elizabeth Garrett or Beth Garrett (June 30, 1963 – March 6, 2016), was an American professor of law and academic administrator. Between 2010 and 2015, she served as Provost and Senior Vice President ...
, who served from July 2015 until her death from colon cancer on March 6, 2016 — the first Cornell president to die while in office.
The Board of Trustees holds four regular meetings each year, and portions of those meetings are subject to the New York State Open Meetings Law.
Cornell consists of nine privately endowed and four publicly supported "statutory college
In United States, American higher education, particular to the state of New York (state), New York, a statutory college or contract college is a college or school that is a component of an independent, private university that has been designated b ...
s": the New York State College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, College of Human Ecology, School of Industrial and Labor Relations, and College of Veterinary Medicine. These statutory colleges received $131.9 million in SUNY appropriations in 2010–2011 to support their teaching, research, and service missions, which makes them accountable to SUNY trustees and other state agencies. The budget also includes $3.9 million of state funds for Cornell Cooperative Extension that is matched by the federal government. Residents of New York enrolled in these colleges also qualify for discounted tuition. However, Attorney General Eliot Spitzer issued a 2005 opinion asserting that, with respect to their academic activities, statutory colleges should be understood to be private, non-state parties.:1
Cornell is decentralized
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
Conce ...
, with its colleges and schools exercising wide autonomy. Each defines its own academic programs, operates its own admissions and advising programs, and confers its own degrees. The only university-wide requirements for a baccalaureate Baccalaureate may refer to:
* ''Baccalauréat'', a French national academic qualification
* Bachelor's degree, or baccalaureate, an undergraduate academic degree
* English Baccalaureate, a performance measure to assess secondary schools in England ...
degree are to pass a swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, or other liquid, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Locomotion is achieved through coordinated movement of the limbs and the body to achieve hydrodynamic thrust that r ...
test, take two physical education
Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys Ed. or P.E., is a subject taught in schools around the world. It is usually taught during primary and secondary education, and encourages psychomotor learning by using a play and movement explorat ...
courses, and satisfy a writing requirement. A handful of inter-school academic departments offer courses in more than one college. All academic departments are affiliated with at least one college; the last department without such an affiliation, the Cornell Africana Studies and Research Center, merged with the College of Arts and Sciences in July 2011.
 Seven schools provide undergraduate programs and an additional seven provide graduate and professional programs. Students pursuing graduate degrees in departments of these schools are enrolled in the
Seven schools provide undergraduate programs and an additional seven provide graduate and professional programs. Students pursuing graduate degrees in departments of these schools are enrolled in the Graduate School
Postgraduate or graduate education refers to academic or professional degrees, certificates, diplomas, or other qualifications pursued by post-secondary students who have earned an undergraduate ( bachelor's) degree.
The organization and stru ...
. The School of Continuing Education and Summer Sessions offers programs for college and high school students, professionals, and other adults. Of the 15,182 undergraduate students, 4,602 (30.3%) are affiliated with the largest college by enrollment, Arts and Sciences, followed by 3,203 (21.1%) in Engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
and 3,101 (20.4%) in Agriculture and Life Sciences. By student enrollment, the smallest of the seven undergraduate colleges is Architecture, Art, and Planning, with 503 (3.3%) students.
Several other universities have used Cornell as their model, including Stanford University, Clark University
Clark University is a private research university in Worcester, Massachusetts. Founded in 1887 with a large endowment from its namesake Jonas Gilman Clark, a prominent businessman, Clark was one of the first modern research universities in the ...
, the University of Sydney
The University of Sydney (USYD), also known as Sydney University, or informally Sydney Uni, is a public research university located in Sydney, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is one of the country's ...
in Australia, and the University of Birmingham
The University of Birmingham (informally Birmingham University) is a Public university, public research university located in Edgbaston, Birmingham, United Kingdom. It received its royal charter in 1900 as a successor to Queen's College, Birmingha ...
in the United Kingdom; the last did so on the recommendation of one of its financiers, Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie (, ; November 25, 1835August 11, 1919) was a Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Carnegie led the expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century and became one of the richest Americans i ...
, who was a Cornell Trustee.
The university also operates eCornell, which offers both certificate programs and professional development courses online. In addition to being New York's land-grant college, Cornell is also a partner in New York's sea-grant program, and is a part of New York's space-grant consortium. The university previously served as the hub of the Northeast's sun-grant program, but the hub has since moved to Pennsylvania State University.
In 2015, Cornell ranked fifth among universities in the U.S. in fund-raising, collecting US$591 million in private support.2015 Donations to Colleges and UniversitiesRetrieved March 10, 2016. In addition to the central University development staff located in Ithaca and New York City, each college and program has its own staffed fundraising program. In 2006, Cornell launched a $4 billion fundraising campaign, which reached $3 billion in November 2010. In 2013, Cornell's "Cornell Now" fundraising campaign raised over $475 million.
Academics
Cornell is a large, primarily residential research university with a majority of enrollments in undergraduate programs. The university has beenaccredited
Accreditation is the independent, third-party evaluation of a conformity assessment body (such as certification body, inspection body or laboratory) against recognised standards, conveying formal demonstration of its impartiality and competence to ...
by the Middle States Commission on Higher Education since 1921. Cornell operates on a 4–1–4 academic calendar with the fall term beginning in late August and ending in early December, a three-week winter session in January, and the spring term beginning in late January and ending in early May.
Cornell, Oregon State University
Oregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant, research university in Corvallis, Oregon. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. It has the 10th largest engineering c ...
, Pennsylvania State University, University of Georgia
, mottoeng = "To teach, to serve, and to inquire into the nature of things.""To serve" was later added to the motto without changing the seal; the Latin motto directly translates as "To teach and to inquire into the nature of things."
, establ ...
, and University of Hawaii at Manoa
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, th ...
are the only institutions to be members of all four Land Grant
A land grant is a gift of real estate—land or its use privileges—made by a government or other authority as an incentive, means of enabling works, or as a reward for services to an individual, especially in return for military service. Grants ...
, Sea Grant
The National Sea Grant College Program is a program of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) within the U.S. Department of Commerce. It is a national network of 34 university-based Sea Grant programs involved in scientific re ...
, Space Grant
The space-grant colleges are educational institutions in the United States that comprise a network of fifty-two consortia formed for the purpose of outer space-related research. Each consortium is based in one of the fifty states, the District o ...
, and Sun Grant programs.
Admissions
Admission to the university is highly competitive. By the spring of 2021 (Class of 2025), Cornell's undergraduate programs collectively received 67,000 applications; 5,863 were admitted, an 8.7% acceptance rate, and enrolled. For the Fall 2019 enrolling freshmen, the middle 50% range ofSAT
The SAT ( ) is a standardized test widely used for college admissions in the United States. Since its debut in 1926, its name and scoring have changed several times; originally called the Scholastic Aptitude Test, it was later called the Schol ...
scores were 680–760 for evidence-based reading and writing, and 720–800 for math. The middle 50% range of the ACT Composite score was 32–35.
The university continues to attract a diverse and inclusive student body. The proportion of admitted students who self-identify as underrepresented minorities increased to 34.2% from 33.7% last year, and 59.3% self-identify as students of color. That number has increased steadily over the past five years, enrollment officials said, from 52.5% in 2017 and 57.2% last year.
Of those admitted 1,163 will be first-generation college students, another increase over last year's 844.
Financial aid
 Section 9 of the original charter of Cornell ensured that the university "shall be open to applicants for admission ... at the lowest rates of expense consistent with its welfare and efficiency, and without distinction as to rank, class, previous occupation or locality". The University Charter provided for free instruction to one student chosen from each Assembly district in the state.
Starting in the 1950s Cornell coordinated with other Ivy League schools to provide a consistent set of financial aid. However, in 1989, a consent decree to end a Justice Department antitrust investigation ended such coordination. Even after the decree, all Ivy League schools continue to award aid on financial need without offering any athletic scholarships. In December 2010, Cornell announced a policy of matching any grant component of financial aid offers from other Ivy League schools,
Section 9 of the original charter of Cornell ensured that the university "shall be open to applicants for admission ... at the lowest rates of expense consistent with its welfare and efficiency, and without distinction as to rank, class, previous occupation or locality". The University Charter provided for free instruction to one student chosen from each Assembly district in the state.
Starting in the 1950s Cornell coordinated with other Ivy League schools to provide a consistent set of financial aid. However, in 1989, a consent decree to end a Justice Department antitrust investigation ended such coordination. Even after the decree, all Ivy League schools continue to award aid on financial need without offering any athletic scholarships. In December 2010, Cornell announced a policy of matching any grant component of financial aid offers from other Ivy League schools, MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
, Duke University or Stanford, if an accepted applicant is trying to decide between Cornell and those other schools.
On January 31, 2008, Cornell announced a new financial aid initiative to be phased in over the following two years. In the first year, 2008–2009, Cornell replaced need-based loans with scholarships for undergraduate students from families with incomes under $60,000 and capped such loans annually at $3,000 for students from families with incomes between $60,000 and $120,000. The following year, 2009–2010, the program improved by replacing loan with scholarships for students from families with incomes up to $75,000, and capped annual loans at $3,000 for students from families with income between $75,000 and $120,000. For families above $120,000, need-based loans were capped at $7,500 per year. The initiative costs an additional $14 million per year to fully implement. Although Cornell's endowment dropped 27% in the second half of 2008, its president announced that the financial aid initiative will continue by withdrawing an additional $35 million from the endowment for undergraduate financial aid in 2009–10. Cornell is seeking $125 million in gifts to support the financial aid initiative. In 2010, 1,647 of the 3,181 full-time freshmen enrolled were found to have financial need (40%). Of these, Cornell could meet the full financial aid needs of all 1,647 freshmen. Cornell's average undergraduate student's indebtedness at graduation is $21,549.
International programs
United Nations Academic Impact
The United Nations Academic Impact, also known by its acronym UNAI, is a United Nations initiative to align institutions of higher education, scholarship and research with the United Nations and with each other.
In the words of former United Nat ...
aligning institutions of higher education to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
and promoting international cooperation.
Cornell is the only US member school in the CEMS Alliance, and the Cornell Master's in international Management is the only programme in the US to offer the CEMS Master's in International Management (CEMS MIM) as a double degree option, allowing students to study at one of 34 prestigious CEMS partner universities.
Cornell offers undergraduate curricula with international focuses, including the Africana Studies, Asian-Pacific American Studies French Studies, German Studies, Jewish Studies, Latino studies
Latino studies is an academic discipline which studies the experience of people of Latin American ancestry in the United States. Closely related to other ethnic studies disciplines such as African-American studies, Asian American studies, and ...
, Near Eastern Studies, Romance studies
Romance studies or Romance philology ( an, filolochía romanica; ca, filologia romànica; french: romanistique; eo, latinida filologio; it, filologia romanza; pt, filologia românica; ro, romanistică; es, filología románica) is an acade ...
, and Russian Literature majors. In addition to traditional academic programs, Cornell students may study abroad on any of six continents.
The Asian Studies major, South Asia Program, Southeast Asia Program and China and Asia-Pacific Studies (CAPS) major provide opportunities for students and researchers in Asia. Cornell has an agreement with Peking University allowing students in the CAPS major to spend a semester in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
. Similarly, the College of Engineering
Engineering education is the activity of teaching knowledge and principles to the professional practice of engineering. It includes an initial education ( bachelor's and/or master's degree), and any advanced education and specializations tha ...
has an agreement to exchange faculty and graduate students with Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University (; abbr. THU) is a national public research university in Beijing, China. The university is funded by the Ministry of Education.
The university is a member of the C9 League, Double First Class University Plan, Projec ...
in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, and the School of Hotel Administration has a joint master's program with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore
Singapore (), officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island country and city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. It lies about one degree of latitude () north of the equator, off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, bor ...
. The College of Agriculture and Life Sciences has signed an agreement with Japan's National Institute of Agrobiological Sciences, and with the University of the Philippines, Los Baños, to engage in joint research and exchange graduate students and faculty members. It also cooperates in agricultural research with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is an autonomous body responsible for co-ordinating agricultural education and research in India. It reports to the Department of Agricultural Research and Education, Ministry of Agriculture. Th ...
. Cornell also offers a course on International consulting in association with Indian Institute of Management Bangalore
In the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, Cornell's efforts focus on biology and medicine. The Weill Cornell Medical College in Qatar
Weill Cornell Medicine-Qatar (WCM-Q) is a branch of Weill Cornell Medicine of Cornell University, established on April 9, 2001 following an agreement between Cornell University and the Qatar Foundation for Education, Science and Community Developme ...
trains new doctors to improve health services in the region. The university is also developing the Bridging the Rift Center, a "Library of Life" (or database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases s ...
of all living systems) on the border of Israel and Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, in collaboration with those two countries and Stanford University. Cornell has partnered with Queen's University in Canada to offer a joint Executive MBA
A Master of Business Administration (MBA; also Master's in Business Administration) is a postgraduate degree focused on business administration. The core courses in an MBA program cover various areas of business administration such as accoun ...
. The innovative program includes both on-campus and videoconferencing
Videotelephony, also known as videoconferencing and video teleconferencing, is the two-way or multipoint reception and transmission of audio and video signals by people in different locations for real time communication.McGraw-Hill Concise Ency ...
-based, interactive virtual classroom sessions. Graduates of the program earn both a Cornell MBA and a Queen's MBA. Cornell also has an ILR exchange program with institutions such as Bocconi University
Bocconi University ( it, Università Commerciale Luigi Bocconi, ) is a private university in Milan, Italy. Bocconi provides education in the fields of economics, finance, law, management, political science, public administration and comput ...
and the University of Warwick
, mottoeng = Mind moves matter
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £7.0 million (2021)
, budget = £698.2 million (2020� ...
.
Rankings
Cornell is ranked 12th on average over the past 30 years by '' U.S. News & World Report'' National Universities ranking. In 2020 Cornell ranked 7th in the US according toQS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
and 9th according to Times Higher Education World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli ...
. In 2015, Cornell ranked 8th domestically and 10th internationally in the CWUR rankings. Cornell ranked 14th in the world in the 2018 edition of the QS World University Rankings
''QS World University Rankings'' is an annual publication of university rankings by Quacquarelli Symonds (QS). The QS system comprises three parts: the global overall ranking, the subject rankings (which name the world's top universities for the ...
and 19th globally in the 2017 edition of the Times Higher Education World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'' (often referred to as the THE Rankings) is an annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' (THE) magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli ...
. The university ranked 10th in the 2013 ''Business Insider
''Insider'', previously named ''Business Insider'' (''BI''), is an American financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the German pub ...
'' Best Colleges in America ranking, 13th globally in an academic ranking of world universities by Academic Ranking of World Universities in 2015, and tied 6th in the United States by the U.S. News Academic Reputation peer assessment score in 2020. Cornell was ranked 8th nationally in ''The Washington Monthly
''Washington Monthly'' is a bimonthly, nonprofit magazine of United States politics and government that is based in Washington, D.C. The magazine is known for its annual ranking of American colleges and universities, which serves as an alterna ...
'' In its annual edition of "America's Best Architecture & Design Schools", the journal ''Design Intelligence'' has consistently ranked Cornell's Bachelor of Architecture program as number one in the nation (2000–2002, 2005–2007, 2009–2013 and 2015–2016). In the 2011 survey, the program ranked first and the Master of Architecture program ranked 6th. In 2017, Design Intelligence ranked Cornell's Master of Landscape Architecture program 4th in the nation with the Bachelor of Science in Landscape Architecture program ranking 5th among its undergraduate counterparts. Among business schools in the United States, the Johnson School of Management at Cornell was named the 9th best business school by ''
In its annual edition of "America's Best Architecture & Design Schools", the journal ''Design Intelligence'' has consistently ranked Cornell's Bachelor of Architecture program as number one in the nation (2000–2002, 2005–2007, 2009–2013 and 2015–2016). In the 2011 survey, the program ranked first and the Master of Architecture program ranked 6th. In 2017, Design Intelligence ranked Cornell's Master of Landscape Architecture program 4th in the nation with the Bachelor of Science in Landscape Architecture program ranking 5th among its undergraduate counterparts. Among business schools in the United States, the Johnson School of Management at Cornell was named the 9th best business school by ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
'' in 2019, 8th by ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
'' for salary potential, 13th overall by ''Poets and Quants'' in 2020 but 4th for investment banking and 6th for salary worldwide in 2015, 11th nationally by ''Bloomberg Businessweek
''Bloomberg Businessweek'', previously known as ''BusinessWeek'', is an American weekly business magazine published fifty times a year. Since 2009, the magazine is owned by New York City-based Bloomberg L.P. The magazine debuted in New York City ...
'' in 2019, and 11th nationally and 14th worldwide by ''The Economist
''The Economist'' is a British weekly newspaper printed in demitab format and published digitally. It focuses on current affairs, international business, politics, technology, and culture. Based in London, the newspaper is owned by The Eco ...
'' in 2019. In 2013, the Johnson school was ranked 2nd for sustainability by ''Bloomberg Businessweek''.
Cornell's international relations
International relations (IR), sometimes referred to as international studies and international affairs, is the scientific study of interactions between sovereign states. In a broader sense, it concerns all activities between states—such a ...
offerings are also ranked in '' Foreign Policy'' magazine's Inside the Ivory Tower survey, which lists the world's top twenty of such programs at the undergraduate, Master's and Ph.D. levels. In 2012, the survey ranked Cornell 11th overall for doctoral programs and 12th overall in the undergraduate category. In 2015, Cornell was ranked third in New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
by average professor salaries.
Library
volumes
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). The defi ...
held. Organized into 20 divisions, in 2005 it held 7.5 million printed volumes in open stacks, 8.2 million microfilm
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either photographic film, films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the origin ...
s and microfiche
Microforms are scaled-down reproductions of documents, typically either films or paper, made for the purposes of transmission, storage, reading, and printing. Microform images are commonly reduced to about 4% or of the original document size. F ...
s, and a total of 440,000 maps, motion pictures, DVDs, sound recordings, and computer files in its collections, in addition to extensive digital resources and the University Archives. It was the first among all U.S. colleges and universities to allow undergraduates
Undergraduate education is education conducted after secondary education and before postgraduate education. It typically includes all postsecondary programs up to the level of a bachelor's degree. For example, in the United States, an entry-le ...
to borrow books from its libraries. In 2006, ''The Princeton Review
The Princeton Review is an education services company providing tutoring, test preparation and admission resources for students. It was founded in 1981. and since that time has worked with over 400 million students. Services are delivered by 4,0 ...
'' ranked it as the 11th best college library, and it climbed to 6th best in 2009. The library plays an active role in furthering online archiving of scientific and historical documents. arXiv
arXiv (pronounced "archive"—the X represents the Greek letter chi ⟨χ⟩) is an open-access repository of electronic preprints and postprints (known as e-prints) approved for posting after moderation, but not peer review. It consists of ...
, an e-print
In academic publishing, an eprint or e-print is a digital version of a research document (usually a journal article, but could also be a thesis, conference paper, book chapter, or a book) that is accessible online, usually as green open access, w ...
archive created at Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory (often shortened as Los Alamos and LANL) is one of the sixteen research and development laboratories of the United States Department of Energy (DOE), located a short distance northwest of Santa Fe, New Mexico, ...
by Paul Ginsparg
Paul Henry Ginsparg (born January 1, 1955) is a physicist. He developed the arXiv.org e-print archive.
Education
He is a graduate of Syosset High School in Syosset, New York. He graduated from Harvard University with a Bachelor of Arts in phy ...
, is operated and primarily funded by Cornell as part of the library's services. The archive has changed the way many physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe.
Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
s and mathematician
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems.
Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change.
History
On ...
s communicate, making the e-print a viable and popular means of announcing new research.
Press and scholarly publications
The Cornell University Press, established in 1869 but inactive from 1884 to 1930, was the first university publishing enterprise in the United States. Today, the press is one of the country's largestuniversity press
A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ...
es. It produces approximately 150 nonfiction titles each year in various disciplines including anthropology, Asian studies, biological sciences, classics, history, industrial relations, literary criticism and theory, natural history, politics and international relations, veterinary science, and women's studies.
Cornell's academic units and student groups also publish a number of scholarly journals. Faculty-led publications include the Johnson School's ''Administrative Science Quarterly
''Administrative Science Quarterly'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering the field of organizational studies. The journal was established in 1956 and is published by SAGE Publications for the Samuel Curtis Johnson Graduate School of Mana ...
'', the ILR School's ''Industrial and Labor Relations Review
''Industrial and Labor Relations Review'' (ILR Review) is a publication of the Cornell University School of Industrial and Labor Relations. It is an interdisciplinary journal publishing original research on all aspects of industrial relations. The ...
'', the Arts and Sciences Philosophy Department's ''The Philosophical Review
''The Philosophical Review'' is a quarterly journal of philosophy edited by the faculty of the Sage School of Philosophy at Cornell University and published by Duke University Press (since September 2006).
Overview
The journal publishes original ...
'', the College of Architecture, Art, and Planning's ''Journal of Architecture'', and the Law School's ''Journal of Empirical Legal Studies
The ''Journal of Empirical Legal Studies'' is a peer-edited and peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes empirically-oriented research on a wide range of legal topics, including civil justice, civil procedure, corporate law, administrative law ...
''. Student-led scholarly publications include the ''Law Review
A law review or law journal is a scholarly journal or publication that focuses on legal issues. A law review is a type of legal periodical. Law reviews are a source of research, imbedded with analyzed and referenced legal topics; they also pr ...
'', the Cornell Institute for Public Affairs' ''Cornell Policy Review
The ''Cornell Policy Review'' is an online academic journal published by the Cornell Institute for Public Affairs. It is verified by the Network of Schools of Public Policy, Affairs, and Administration and edited and run by the program's students ...
'', the '' International Law Journal'', the '' Journal of Law and Public Policy'', the ''International Affairs Review
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
'', and the '' HR Review''. '' Physical Review'', recognized internationally as among the best and well known journals of physics, was founded at Cornell in 1893 before being later managed by the American Physical Society.
Research

 Cornell, a research university, is ranked fourth in the world in producing the largest number of graduates who go on to pursue PhDs in
Cornell, a research university, is ranked fourth in the world in producing the largest number of graduates who go on to pursue PhDs in engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
or the natural sciences at American institutions, and fifth in the world in producing graduates who pursue PhDs at American institutions in any field. Research is a central element of the university's mission; in 2009 Cornell spent $671 million on science and engineering research and development, the 16th highest in the United States. Cornell is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity".
For the 2016–17 fiscal year, the university spent $984.5 million on research. Federal sources constitute the largest source of research funding, with total federal investment of $438.2 million. The agencies contributing the largest share of that investment are the Department of Health and Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the U.S. federal government created to protect the health of all Americans and providing essential human services. Its motto is ...
and the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
, accounting for 49.6% and 24.4% of all federal investment, respectively. Cornell was on the top-ten list of U.S. universities receiving the most patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
s in 2003, and was one of the nation's top five institutions in forming start-up companies. In 2004–05, Cornell received 200 invention disclosures, filed 203 U.S. patent applications, completed 77 commercial license agreements, and distributed royalties of more than $4.1 million to Cornell units and inventors.
Since 1962, Cornell has been involved in unmanned missions to Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
. In the 21st century, Cornell had a hand in the Mars Exploration Rover Mission
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmos ...
. Cornell's Steve Squyres
Steven Weldon Squyres (born January 9, 1956) is an American geologist and planetary scientist. He was the James A. Weeks Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. His research area is in planetary sciences, with a f ...
, Principal Investigator for the Athena Science Payload, led the selection of the landing zones and requested data collection features for the Spirit
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
and Opportunity rover
''Opportunity'', also known as MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B) or MER-1, is a robotic rover that was active on Mars from 2004 until 2018. ''Opportunity'' was operational on Mars for sols (). Launched on July 7, 2003, as part of NASA's ...
s. Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States.
Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA an ...
engineers took those requests and designed the rovers to meet them. The rovers, both of which have operated long past their original life expectancies, are responsible for the discoveries that were awarded 2004 Breakthrough of the Year honors by ''Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe.
Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earli ...
''. Control of the Mars rovers has shifted between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory at Caltech
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech or CIT)The university itself only spells its short form as "Caltech"; the institution considers other spellings such a"Cal Tech" and "CalTech" incorrect. The institute is also occasional ...
and Cornell's Space Sciences Building. Further, Cornell researchers discovered the rings
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
around the planet Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus ( Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of ...
, and Cornell built and operated the telescope at Arecibo Observatory located in Arecibo, Puerto Rico until 2011, when they transferred the operations to SRI International
SRI International (SRI) is an American nonprofit scientific research institute and organization headquartered in Menlo Park, California. The trustees of Stanford University established SRI in 1946 as a center of innovation to support economic ...
, the Universities Space Research Association
The Universities Space Research Association (USRA) was incorporated on March 12, 1969, in Washington, D.C. as a private, nonprofit corporation under the auspices of the National Academy of Sciences (NAS).
Institutional membership in the asso ...
and the Metropolitan University of Puerto Rico.
The Automotive Crash Injury Research Project
The Automotive Crash Injury Research Center was founded in 1952 by John O. Moore at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory, which spun off in 1972 as Calspan Corporation. It pioneered the use of crash testing, originally using corpses rather than d ...
was begun in 1952. It pioneered the use of crash test
A crash test is a form of destructive testing usually performed in order to ensure safe design standards in crashworthiness and crash compatibility for various modes of transportation (see automobile safety) or related systems and comp ...
ing, originally using corpses rather than dummies. The project discovered that improved door locks, energy-absorbing steering wheels, padded dashboards, and seat belts could prevent an extraordinary percentage of injuries.
In the early 1980s, Cornell deployed the first IBM 3090
The IBM 3090 family is a family of mainframe computers that was a high-end successor to the IBM System/370 series, and thus indirectly the successor to the IBM System/360 launched 25 years earlier.
Announced on 12 February 1985, the press rel ...
-400VF and coupled two IBM 3090-600E systems to investigate coarse-grained parallel computing. In 1984, the National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
began work on establishing five new supercomputer centers, including the Cornell Center for Advanced Computing, to provide high-speed computing resources for research within the United States. As an NSF center, Cornell deployed the first IBM Scalable Parallel supercomputer. In the 1990s, Cornell developed scheduling software and deployed the first supercomputer built by Dell. Most recently, Cornell deployed Red Cloud, one of the first cloud computing services designed specifically for research. Today, the center is a partner on the National Science Foundation Extreme Science and Engineering Discovery Environment
TeraGrid was an e-Science grid computing infrastructure combining resources at eleven partner sites. The project started in 2001 and operated from 2004 through 2011.
The TeraGrid integrated high-performance computers, data resources and tools, a ...
(XSEDE) supercomputing program, providing coordination for XSEDE architecture and design, systems reliability testing, and online training using the Cornell Virtual Workshop learning platform.
Cornell scientists have researched the fundamental particles of nature for more than 70 years. Cornell physicists, such as Hans Bethe
Hans Albrecht Bethe (; July 2, 1906 – March 6, 2005) was a German-American theoretical physicist who made major contributions to nuclear physics, astrophysics, quantum electrodynamics, and solid-state physics, and who won the 1967 Nobel ...
, contributed not only to the foundations of nuclear physics but also participated in the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
(see also: List of Cornell Manhattan Project people). In the 1930s, Cornell built the second cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: Jan ...
in the United States. In the 1950s, Cornell physicists became the first to study synchrotron radiation. During the 1990s, the Cornell Electron Storage Ring, located beneath Alumni Field, was the world's highest-luminosity electron-positron collider. After building the synchrotron at Cornell, Robert R. Wilson
Robert Rathbun Wilson (March 4, 1914 – January 16, 2000) was an American physicist known for his work on the Manhattan Project during World War II, as a sculptor, and as an architect of the Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), ...
took a leave of absence to become the founding director of Fermilab
Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab), located just outside Batavia, Illinois, near Chicago, is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory specializing in high-energy particle physics. Since 2007, Fermilab has been opera ...
, which involved designing and building the largest accelerator in the United States. Cornell's accelerator and high-energy physics groups are involved in the design of the proposed International Linear Collider and plan to participate in its construction and operation. The International Linear Collider, to be completed in the late 2010s, will complement the Large Hadron Collider and shed light on questions such as the identity of dark matter
Dark matter is a hypothetical form of matter thought to account for approximately 85% of the matter in the universe. Dark matter is called "dark" because it does not appear to interact with the electromagnetic field, which means it does not a ...
and the existence of extra dimensions.
As part of its research work, Cornell has established several research collaborations with universities around the globe. For example, a partnership with the University of Sussex
, mottoeng = Be Still and Know
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £14.4 million (2020)
, budget = £319.6 million (2019–20)
, chancellor = Sanjeev Bhaskar
, vice_chancellor = Sasha Roseneil
, ...
(including the Institute of Development Studies at Sussex) allows research and teaching collaboration between the two institutions.
Student life
Activities

 For the 2016–2017 academic year, Cornell had over 1,000 registered student organizations. These clubs and organizations run the gamut from kayaking to full-armor jousting, from varsity and club sports and a cappella groups to improvisational theatre, from political clubs and publications to chess and video game clubs. The Cornell International Affairs Society sends over 100 Cornellians to collegiate Model United Nations conferences across North America and hosts the Cornell Model United Nations Conference each spring for over 500 high school students. The Cornell University Mock Trial Association regularly sends teams to the national championship and is ranked 5th in the nation. Additionally, the Cornell International Affairs Society's traveling Model United Nations team is ranked number 16 in the nation. Cornell United Religious Work is a collaboration among many diverse religious traditions, helping to provide spiritual resources throughout a student's time at college. The
For the 2016–2017 academic year, Cornell had over 1,000 registered student organizations. These clubs and organizations run the gamut from kayaking to full-armor jousting, from varsity and club sports and a cappella groups to improvisational theatre, from political clubs and publications to chess and video game clubs. The Cornell International Affairs Society sends over 100 Cornellians to collegiate Model United Nations conferences across North America and hosts the Cornell Model United Nations Conference each spring for over 500 high school students. The Cornell University Mock Trial Association regularly sends teams to the national championship and is ranked 5th in the nation. Additionally, the Cornell International Affairs Society's traveling Model United Nations team is ranked number 16 in the nation. Cornell United Religious Work is a collaboration among many diverse religious traditions, helping to provide spiritual resources throughout a student's time at college. The Cornell Catholic Community The Cornell Catholic Community is the Catholic organization and parish at Cornell University, providing worship services and community for Catholic students. Its current director is Father Daniel McCullin.
Origin and early years
In 1888, Catholic s ...
is the largest Catholic student organization on campus. Student organizations also include a myriad of groups including a symphony orchestra, concert bands, formal and informal choral groups, including the Sherwoods, the Chordials and other musical groups that play everything from classical, jazz, to ethnic styles in addition to the Big Red Marching Band, which performs regularly at football games and other campus events. Organized in 1868, the oldest Cornell student organization is the Cornell University Glee Club
The Cornell University Glee Club (CUGC) is the oldest student organization at Cornell University, having been organized shortly after the first students arrived on campus in 1868. The CUGC is a thirty-nine member chorus for tenor and bass voices ...
. Apart from musical groups, Cornell has an active outdoor community, consisting oCornell Outdoor Education
an
Outdoor Odyssey
a student-run group that runs pre-orientation trips for first-year and transfer students. A Cornell student organization
The Cornell Astronomical Society
runs public observing nights every Friday evening at the Fuertes Observatory. The university is home to the
Telluride House
The Telluride House, formally the Cornell Branch of the Telluride Association (CBTA), and commonly referred to as just "Telluride", is a highly selective intentional community, residential community of Cornell University students and faculty. ...
, an intellectual residential society. The university is also home to three secret honor societies called Sphinx Head
The Sphinx Head Society is the oldest senior honor society at Cornell University. Sphinx Head recognizes Cornell senior men and women who have demonstrated respectable strength of character on top of a dedication to leadership and service at Corn ...
, Der Hexenkreis and Quill and Dagger
Quill and Dagger is a senior honor society at Cornell University. It is often recognized as one of the most prominent societies of its type, along with Skull and Bones and Scroll and Key at Yale University. In 1929, ''The New York Times'' stated ...
that have maintained a presence on campus for well over 120 years.
Cornell's clubs are primarily subsidized financially by the Student Assembly and the Graduate & Professional Student Assembly, two student-run organizations with a collective budget of $3.0 million per year. The assemblies also finance other student life programs including a concert commission and an on-campus theater.
Greek life, professional, and honor societies
Cornell hosts a large fraternity and sorority system, with 70 chapters involving 33% of male and 24% of female undergraduates. Cornell's Greek Life has an extensive history on the campus with the first fraternity,Zeta Psi
Zeta Psi () is a collegiate fraternity. It was founded in June 1, 1847 at New York University. The organization now comprises fifty-three active chapters and thirty-four inactive chapters, encompassing roughly fifty thousand members, and is a ...
, being chartered by the end of the university's first year. Alpha Phi Alpha, the first intercollegiate Greek-letter organization established for African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
s, was founded at Cornell in 1906. Alpha Zeta fraternity, the first Greek-lettered organization established for Latin Americans in the United States, was also founded at Cornell on January 1, 1890. Alpha Zeta served the wealthy international Latin American students that came to the United States to study. This organization led a movement of fraternities that catered to international Latin American students that was active from 1890 to 1975. On February 19, 1982, La Unidad Latina, Lambda Upsilon Lambda fraternity was established; it would eventually become the only Latino based fraternity in the nation with chapters at every Ivy League institution. Latinas Promoviendo Comunidad/Lambda Pi Chi
Lambda Pi Chi Sorority, Incorporated () (''also known as Latinas Promoviendo Comunidad/Lambda Pi Chi Sorority, Inc.'') is a Latina-based, but not Latina-exclusive Greek letter intercollegiate sorority founded on April 16, 1988, at Cornell Univers ...
sorority was established on April 16, 1988, making the organization the first Latina-Based, and not Latina exclusive, sorority founded at an ivy-league institution.
Cornell's connection to national Greek life is strong and longstanding. Many chapters are among the oldest of their respective national organizations, as evidenced by the proliferation of ''Alpha-series'' chapters. The chapter house of Alpha Delta Phi constructed in 1877 is believed to be the first house built in America solely for fraternity use, and the chapter's current home was designed by John Russell Pope
John Russell Pope (April 24, 1874 – August 27, 1937) was an American architect whose firm is widely known for designing major public buildings, including the National Archives and Records Administration building (completed in 1935), the Jeff ...
. Philanthropy opportunities are used to encourage community relations, for example, during the 2004–05 academic year, the Greek system contributed 21,668 community service
Community service is unpaid work performed by a person or group of people for the benefit and betterment of their community without any form of compensation. Community service can be distinct from volunteering, since it is not always performe ...
and advocacy hours and raised $176,547 in charitable contributions from its philanthropic efforts. Generally, discipline is managed internally by the inter-Greek governing boards. As with all student, faculty or staff misconduct, more serious cases are reviewed by the Judicial Administrator, who administers Cornell's justice system
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four basic systems: civil law, common law, statutory law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country is shaped by its unique history and ...
.
Press and radio
The Cornell student body produces several works by way of print and radio. Student-run newspapers include ''The Cornell Daily Sun
''The Cornell Daily Sun'' is an independent daily newspaper published in Ithaca, New York by students at Cornell University and hired employees.
''The Sun'' features coverage of the university and its environs as well as stories from the Associa ...
'', an independent daily; ''The Cornell Review
''The Cornell Review'' is an independent newspaper published by students of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. With the motto, "We Do Not Apologize," the ''Review'' has a history in conservative journalism and was once one of the leading c ...
'', a conservative newspaper published fortnightly; and ''The Cornell Progressive
''The Cornell Progressive'' (previously called ''Turn Left'') was an independent student-run publication at Cornell University. Calling itself "Cornell's Liberal Voice," ''The Cornell Progressive'' focuses on political and humanitarian issues that ...
'', a liberal newspaper published every month.
Other press outlets include '' The Cornell Lunatic'', a campus humor magazine; the ''Cornell Chronicle
The ''Cornell Chronicle'' is the in-house weekly newspaper published by Cornell University.
History
Prior to the founding of the ''Chronicle'' in 1969, campus news was reported by the ''Cornell Era'' and then by ''The Cornell Daily Sun''. Durin ...
'', the university's newspaper of record; and '' Kitsch Magazine'', a feature magazine published in cooperation with Ithaca College
Ithaca College is a private college in Ithaca, New York. It was founded by William Egbert in 1892 as a conservatory of music and is set against the backdrop of the city of Ithaca (which is separate from the town), Cayuga Lake, waterfalls, and go ...
. ''The Cornellian'' is an independent student organization that organizes, arranges, produces, edits, and publishes the yearbook of the same name; it is composed of artistic photos of the campus, student life, and athletics, and the standard senior portraits. It carries the Silver Crown Award for Journalism and a Benjamin Franklin Award for Print Design – the only Ivy League Yearbook with such a distinction. Cornellians are represented over the radio waves on WVBR
WVBR-FM (93.5 FM) is a commercial, student-owned and volunteer-run college radio station that broadcasts to Ithaca, New York and surrounding areas. It operates at 3 kilowatts from a transmitter on Hungerford Hill, in Ithaca. Prior to 2016, WVBR ...
, an independent commercial FM radio station owned and operated by Cornell students. Other student groups also operate internet streaming audio sites.
Housing
 University housing is broadly divided into three sections: North Campus, West Campus, and Collegetown. Cornell began experiments with co-ed dormitories in 1971 and continued the tradition of residential advisors (RAs) within the campus system. In 1991, new students could be found throughout West Campus, including at the historic Baker and Boldt Hall complexes; since a 1997 residential initiative, West Campus houses transfer and returning students, whereas North Campus is almost entirely populated by freshmen as well as sorority and fraternity houses.
The options for living on North Campus for upperclassmen are the program houses and co-op houses. Program houses include
University housing is broadly divided into three sections: North Campus, West Campus, and Collegetown. Cornell began experiments with co-ed dormitories in 1971 and continued the tradition of residential advisors (RAs) within the campus system. In 1991, new students could be found throughout West Campus, including at the historic Baker and Boldt Hall complexes; since a 1997 residential initiative, West Campus houses transfer and returning students, whereas North Campus is almost entirely populated by freshmen as well as sorority and fraternity houses.
The options for living on North Campus for upperclassmen are the program houses and co-op houses. Program houses include Risley Residential College
Prudence Risley Residential College for the Creative and Performing Arts, commonly known as Risley Residential College, Risley Hall, or just Risley, is a program house (themed residence hall) at Cornell University. Unlike most other dormitories o ...
, Just About Music, the Ecology House, Holland International Living Center, the Multicultural Living Learning Unit, the Latino Living Center, Akwe:kon, and Ujamaa
Ujamaa ( in Swahili) was a socialist ideology that formed the basis of Julius Nyerere's social and economic development policies in Tanzania after it gained independence from Britain in 1961.
More broadly, ujamaa may mean "cooperative economic ...
. The co-op houses on North are The Prospect of Whitby, Triphammer Cooperative, Wait Avenue Cooperative, Wari Cooperative, and Wait Terrace. On West Campus, there are three university-affiliated cooperatives, 660 Stewart Cooperative, Von Cramm Hall, anWatermargin
and one independent cooperative
Cayuga Lodge
In an attempt to create a sense of community and an atmosphere of education outside the classroom and continue Andrew Dickson White's vision, a $250 million reconstruction of West Campus created
residential colleges
A residential college is a division of a university that places academic activity in a community setting of students and faculty, usually at a residence and with shared meals, the college having a degree of autonomy and a federated relationship w ...
there for undergraduates. The idea of building a house system can be attributed in part to the success of Risley Residential College, the oldest continually operating residential college at Cornell. In 2018, Cornell announced its North Campus Residential Expansive project. By 2022, the university aims to add 2,000 beds on North Campus. Five new dorms and a dining hall will be created, three of which will be located in Appel Field and will be exclusive for freshmen. Sophomores will have two new dorms located in the current CC Parking Lot.
Additionally, Cornell has several housing areas for graduate and professional students. Of these, Schuyler House (which was formerly a part of Sage Infirmary) has a dorm layout, while Maplewood Apartments, Hasbrouck Apartments, and Thurston Court Apartments are apartment-style, some even allowing for family living. Off campus, many single-family houses in the East Hill neighborhoods adjacent to the university have been converted to apartments. Private developers have also built several multi-story apartment complexes in the Collegetown neighborhood. Nine percent of undergraduate students reside in fraternity and sorority houses, although first semester freshmen are not permitted to join them. Cornell's Greek system has 67 chapters and over 54 Greek residences that house approximately 1,500 students. About 42% of Greek members live in their houses. Housing cooperatives or other independent living units exist, including Telluride House
The Telluride House, formally the Cornell Branch of the Telluride Association (CBTA), and commonly referred to as just "Telluride", is a highly selective intentional community, residential community of Cornell University students and faculty. ...
, the Center for Jewish Living, Phillips House (located on North Campus, 1975 all women; 2016, all men), and Center for World Community (international community, off campus, formed by Annabel Taylor Hall, 1972, mixed gender). The cooperative houses on North include The Prospect of Whitby, Triphammer Cooperative, Wait Avenue Cooperative, Wari Cooperative, and Wait Terrace. On West Campus, there are three university-affiliated cooperatives, 660 Stewart Cooperative, Von Cramm Cooperative Hall
Von Cramm Hall is a student operated house on the West Campus of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York State. The residence hall is currently occupied by Redbud Cooperative. The house was founded in 1956 by Thomas Byron Gilchrist (Cornell cl ...
, anWatermargin
and one independent cooperative
Cayuga Lodge
Besides this, there exists also cooperative housing not owned by Cornell, like
Gamma Alpha
The Gamma Alpha Graduate Scientific Society () is a non-profit fraternal organization (501(c)(7)) in the United States which fosters interdisciplinary dialogue among graduate students through its local chapters. The Society's chapters have often ...
or Stewart Little.
, Cornell's dining system was ranked 3rd in the nation by the ''Princeton Review''. The university has 29 on-campus dining locations, including 10 "All You Care to Eat" cafeterias. North Campus is home to 3 of these dining halls: Robert Purcell Marketplace Eatery (located in Robert Purcell Community Center), North Star Dining Room (located in the Appel Commons), and Risley Dining (located in Risley Hall). West Campus houses 6 dining halls, 5 of which accompany the West Campus residential houses: Cook House Dining Room, Becker House Dining Room, Rose House Dining Room, Jansen's Dining Room at Hans Bethe House, and Keeton House Dining Room. Also located on West Campus is 104West!, a kosher/multicultural dining room. Central Campus accommodates just a single dining hall: Okenshields, located in Willard Straight Hall.
Athletics
 Cornell has 35 varsity intercollegiate teams that have the nickname of the Big Red. An
Cornell has 35 varsity intercollegiate teams that have the nickname of the Big Red. An NCAA
The National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) is a nonprofit organization that regulates student athletics among about 1,100 schools in the United States, Canada, and Puerto Rico. It also organizes the athletic programs of colleges an ...
Division I institution, Cornell is a member of the Ivy League
The Ivy League is an American collegiate athletic conference comprising eight private research universities in the Northeastern United States. The term ''Ivy League'' is typically used beyond the sports context to refer to the eight school ...
and ECAC Hockey
ECAC Hockey is one of the six conferences that compete in NCAA Division I college ice hockey, ice hockey. The conference used to be affiliated with the Eastern College Athletic Conference, a consortium of over 300 colleges in the eastern United ...
and competes in the Eastern College Athletic Conference
The Eastern College Athletic Conference (ECAC) is a college athletic conference comprising schools that compete in 15 sports (13 men's and 13 women's). It has 220 member institutions in NCAA Divisions I, II, and III, ranging in location fr ...
(ECAC), the largest athletic conference in North America. (ECAC Hockey is no longer affiliated with the ECAC.) Cornell's varsity athletic teams consistently challenge for NCAA Division I titles in a number of sports, including men's wrestling, men's lacrosse, men's ice hockey, and rowing (the women's crew program is subject to the NCAA, while the men's rowing program is governed by its own administrative body, the Intercollegiate Rowing Association
The Intercollegiate Rowing Association (IRA) governs intercollegiate rowing between varsity men's heavyweight, men's lightweight, and women's lightweight rowing programs across the United States, while the NCAA fulfills this role for women's ope ...
). Under the Ivy League athletic agreement, the university does not offer athletic scholarship
An athletic scholarship is a form of scholarship to attend a college or university or a private high school awarded to an individual based predominantly on his or her ability to play in a sport. Athletic scholarships are common in the United ...
s for athletic recruiting.
Cornell's football team had at least a share of the national championship four times before 1940 and has won the Ivy League championship three times, last in 1990.
In 2010, the Cornell men's basketball team appeared for the first time in the NCAA tournament's East Regional semifinals, known as the "Sweet 16". It was the first Ivy League team to make the semifinals since 1979.
Cornell Outdoor Education
Cornell runs one of the largest collegiate outdoor education programs in the country, serving over 20,000 people every year. The program runs over 130 different courses including but not limited to: Backpacking and Camping, Mountain Biking, Bike Touring, Caving, Hiking, Rock and Ice Climbing, Wilderness First Aid, and tree climbing. COE also oversees one of the largest student-run pre-freshman summer programs, known as Outdoor Odyssey. Most classes are often entirely taught by paid student instructors and courses count toward Cornell's physical education graduation requirement. One of the most remarkable facilities at Cornell Outdoor Education is The Lindseth Climbing Wall. The wall was renovated in 2016, and now includes 8,000 square feet of climbing surface, up from 4,800 square feet previously. The new wall now offers a more modern environment with bouldering, top-rope, and lead climbing facilities appropriate for various skill levels.Cornelliana
 Cornelliana is a term for Cornell's traditions, legends, and lore. Cornellian traditions include Slope Day, a celebration held on the last day of classes of the spring semester, and
Cornelliana is a term for Cornell's traditions, legends, and lore. Cornellian traditions include Slope Day, a celebration held on the last day of classes of the spring semester, and Dragon Day
Dragon Day is an annual event that occurs the Friday before spring break at Cornell University. The center of the event is the procession of a dragon, created by first-year architecture students at the Cornell University College of Architecture, ...
, which includes the burning of a dragon built by architecture students. Dragon Day is one of the school's oldest traditions and has been celebrated annually since 1901, typically on or near St. Patrick's Day. The dragon is built secretly by the architecture students, and taunting messages are left for the engineering students for the week before Dragon Day. On Dragon Day, the dragon is paraded across the Arts Quad and then set afire.
According to legend, if a virgin crosses the Arts Quad at midnight, the statues of Ezra Cornell
Ezra Cornell (; January 11, 1807 – December 9, 1874) was an American businessman, politician, and philanthropist. He was the founder of Western Union and a co-founder of Cornell University. He also served as President of the New York Agricul ...
and Andrew Dickson White
Andrew Dickson White (November 7, 1832 – November 4, 1918) was an American historian and educator who cofounded Cornell University and served as its first president for nearly two decades. He was known for expanding the scope of college curricu ...
will walk off their pedestals, meet in the center of the Quad, and shake hands, congratulating themselves on the chastity of students. There is also another myth that if a couple crosses the suspension bridge on North Campus, and the young woman does not accept a kiss from her partner, the bridge will fall. If the kiss is accepted, the couple is assured a long future together.
The university is also host to various student pranks. For example, on at least two different occasions the university has awoken to find something odd atop the 173-foot (52.7 m) tall McGraw clock tower—once a 60-pound (27 kg) pumpkin and another time a disco ball. Because there is no access to the spire atop the tower, how the items were put in place remains a mystery. The colors of the lights on McGraw tower change to orange for Halloween and green for St. Patrick's Day. The clock tower also plays music.
The school colors are carnelian
Carnelian (also spelled cornelian) is a brownish-red mineral commonly used as a semi-precious gemstone. Similar to carnelian is sard, which is generally harder and darker (the difference is not rigidly defined, and the two names are often used ...
(a shade of red) and white, a play on "Cornellian" and Andrew Dickson White. A bear is commonly used as the unofficial mascot, which dates back to the introduction of the mascot "Touchdown" in 1915, a live bear who was brought onto the field during football games. The university's alma mater is "Far Above Cayuga's Waters
"Far Above Cayuga's Waters" is Cornell University's alma mater. The lyrics were written circa 1870 by roommates Archibald Croswell Weeks (Class of 1872), and Wilmot Moses Smith (Class of 1874), and set to the tune of "Annie Lisle", a popular 1 ...
", and its fight song
A fight song is a rousing short song associated with a sports team. The term is most common in the United States and Canada. In Australia, Mexico, and New Zealand these songs are called the team anthem, team song, or games song. First associated ...
is "Give My Regards to Davy
"Give My Regards to Davy" is Cornell University's primary fight song. The song's lyrics were written in 1905 by Charles E. Tourison 1905, W. L. Umstad 1906, and Bill Forbes 1906, a trio of roommates at Beta Theta Pi, and set to the tune of Geor ...
". People associated with the university are called "Cornellians".
Health
Cornell offers a variety of professional and peer counseling services to students. Formerly called Gannett Health Services until its name change in 2016, Cornell Health offers on-campus outpatient health services with emergency services and residential treatment provided by Cayuga Medical Center. For most of its history, Cornell provided residential medical care for sick students, including at the historic Sage Infirmary. Cornell offers specialized reproductive health and family planning services. The university also has a student-runEmergency Medical Service
Emergency medical services (EMS), also known as ambulance services or paramedic services, are emergency services that provide urgent pre-hospital treatment and stabilisation for serious illness and injuries and transport to definitive care. ...
(EMS) agency. The squad provides emergency response to medical emergencies on the campus at Cornell and surrounding university-owned properties. Cornell EMS also provides stand-by service for university events and provides CPR, First Aid and other training seminars to the Cornell community.
The university received attention for a series of six student suicides by jumping into a gorge that occurred during the 2009–10 school year, and after the incidents added temporary fences to the bridges which span area gorges. In May 2013, Cornell indicated that it planned to set up nets, which will extend out 15 feet, on five of the university's bridges. Installation of the nets began in May 2013 and were completed over the summer of that year. There were cases of gorge-jumping in the 1970s and 1990s. Before this abnormal cluster of suicides, the suicide rate at Cornell had been similar to or below the suicide rates of other American universities, including a period between 2005 and 2008 in which no suicides occurred.
Campus police
Cornell University Police protect the campus and are classified as peace officers and have the same authority as the Ithaca city police. They are similar to the campus police atIthaca College
Ithaca College is a private college in Ithaca, New York. It was founded by William Egbert in 1892 as a conservatory of music and is set against the backdrop of the city of Ithaca (which is separate from the town), Cayuga Lake, waterfalls, and go ...
and Syracuse University, and University of Rochester
The University of Rochester (U of R, UR, or U of Rochester) is a private university, private research university in Rochester, New York. The university grants Undergraduate education, undergraduate and graduate degrees, including Doctorate, do ...
because those campus police are classified as armed peace officers. The Cornell University Police are on campus and on-call 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Their duties include: patrolling the university around the clock, responding to emergencies and non-emergency calls for service, crime prevention services, active investigation of crimes on campus, enforcement of state criminal and motor vehicle laws, and campus regulations.
People
Cornell counts numerous notable individuals who have either come to the university as faculty to teach and to conduct research, or as students who have gone on to do noteworthy things. As of October 2020, 61 Nobel laureates were either faculty members, researchers, or students at Cornell.Faculty
 , Cornell had 1,639 full-and part-time faculty members affiliated with its main campus, 1,235 affiliated with its New York City divisions, and 34 affiliated with its campus in Qatar. Cornell's faculty for the 2005–06 academic year included three Nobel laureates, a
, Cornell had 1,639 full-and part-time faculty members affiliated with its main campus, 1,235 affiliated with its New York City divisions, and 34 affiliated with its campus in Qatar. Cornell's faculty for the 2005–06 academic year included three Nobel laureates, a Crafoord Prize
The Crafoord Prize is an annual science prize established in 1980 by Holger Crafoord, a Swedish industrialist, and his wife Anna-Greta Crafoord. The Prize is awarded in partnership between the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences and the Crafoord Foun ...
winner, two Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in comput ...
winners, a Fields Medal winner, two Legion of Honor recipients, a World Food Prize
The World Food Prize is an international award recognizing the achievements of individuals who have advanced human development by improving the quality, quantity, or availability of food in the world. Conceived by Nobel Peace Prize laureate Nor ...
winner, an Andrei Sakharov Prize winner, three National Medal of Science
The National Medal of Science is an honor bestowed by the President of the United States to individuals in science and engineering who have made important contributions to the advancement of knowledge in the fields of behavioral and social scienc ...
winners, two Wolf Prize
The Wolf Prize is an international award granted in Israel, that has been presented most years since 1978 to living scientists and artists for ''"achievements in the interest of mankind and friendly relations among people ... irrespective of nati ...
winners, five MacArthur award
The MacArthur Fellows Program, also known as the MacArthur Fellowship and commonly but unofficially known as the "Genius Grant", is a prize awarded annually by the John D. and Catherine T. MacArthur Foundation typically to between 20 and 30 ind ...
winners, four Pulitzer Prize winners, a Carter G. Woodson
Carter Godwin Woodson (December 19, 1875April 3, 1950) was an American historian, author, journalist, and the founder of the Association for the Study of African American Life and History (ASALH). He was one of the first scholars to study the h ...
Scholars Medallion recipient, 20 National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National ...
career grant holders, a recipient of the National Academy of Sciences Award, a recipient of the American Mathematical Society
The American Mathematical Society (AMS) is an association of professional mathematicians dedicated to the interests of mathematical research and scholarship, and serves the national and international community through its publications, meetings, ...
's Steele Prize for Lifetime Achievement
The Leroy P. Steele Prizes are awarded every year by the American Mathematical Society, for distinguished research work and writing in the field of mathematics. Since 1993, there has been a formal division into three categories.
The prizes have b ...
, a recipient of the Heineman Prize for Mathematical Physics
Dannie Heineman Prize for Mathematical Physics is an award given each year since 1959 jointly by the American Physical Society and American Institute of Physics. It is established by the Heineman Foundation in honour of Dannie Heineman. As of 201 ...
, and three Packard Foundation
The David and Lucile Packard Foundation is a private foundation that provides grants to not-for-profit organizations. It was created in 1964 by David Packard (co-founder of HP) and his wife Lucile Salter Packard. Following David Packard's death ...
grant holders.
Kurt Lewin
Kurt Lewin ( ; 9 September 1890 – 12 February 1947) was a German-American psychologist, known as one of the modern pioneers of social, organizational, and applied psychology in the United States. During his professional career Lewin applied hi ...
taught at Cornell from 1933 to 1935 and is considered the "father of social psychology
Social psychology is the scientific study of how thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are influenced by the real or imagined presence of other people or by social norms. Social psychologists typically explain human behavior as a result of the ...
". Norman Borlaug
Norman Ernest Borlaug (; March 25, 1914September 12, 2009) was an American agronomist who led initiatives worldwide that contributed to the extensive increases in agricultural production termed the Green Revolution. Borlaug was awarded multiple ...
taught at the university from 1982 to 1988 and is considered the "father of the Green Revolution
The Green Revolution, also known as the Third Agricultural Revolution, was a period of technology transfer initiatives that saw greatly increased crop yields and agricultural production. These changes in agriculture began in developed countrie ...
", being awarded the Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor and armaments (military weapons and equipment) manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiolog ...
, the Presidential Medal of Freedom
The Presidential Medal of Freedom is the highest civilian award of the United States, along with the Congressional Gold Medal. It is an award bestowed by the president of the United States to recognize people who have made "an especially merit ...
, the Congressional Gold Medal
The Congressional Gold Medal is an award bestowed by the United States Congress. It is Congress's highest expression of national appreciation for distinguished achievements and contributions by individuals or institutions. The congressional pract ...
, and 49 honorary doctorates. Frances Perkins joined the Cornell faculty in 1952 after serving as the first female member of the United States Cabinet
The Cabinet of the United States is a body consisting of the vice president of the United States and the heads of the executive branch's departments in the federal government of the United States. It is the principal official advisory body to ...
and served until her death in 1965. Perkins was a witness to the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory fire in the Greenwich Village neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City, on Saturday, March 25, 1911, was the deadliest industrial disaster in the history of the city, and one of the deadliest in U.S. history. The ...
in her adolescence and went on to champion the National Labor Relations Act, the Fair Labor Standards Act, and the Social Security Act while United States Secretary of Labor
The United States Secretary of Labor is a member of the Cabinet of the United States, and as the head of the United States Department of Labor, controls the department, and enforces and suggests laws involving unions, the workplace, and all ot ...
. Buckminster Fuller
Richard Buckminster Fuller (; July 12, 1895 – July 1, 1983) was an American architect, systems theorist, writer, designer, inventor, philosopher, and futurist. He styled his name as R. Buckminster Fuller in his writings, publishing mo ...
was a visiting professor at Cornell for one year (1952), and Henry Louis Gates
Henry Louis "Skip" Gates Jr. (born September 16, 1950) is an American literary critic, professor, historian, and filmmaker, who serves as the Alphonse Fletcher University Professor and Director of the Hutchins Center for African and African Amer ...
, African American Studies scholar and subject of an arrest controversy and White House "Beer Summit", taught at Cornell from 1985 to 1989. Plant genetics pioneer Ray Wu invented the first method for sequencing DNA, considered a major breakthrough in genetics as it has enabled researchers to more closely understand how genes work. Emmy Award-winning actor John Cleese, known for his roles in '' Monty Python'', ''James Bond
The ''James Bond'' series focuses on a fictional British Secret Service agent created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short-story collections. Since Fleming's death in 1964, eight other authors have ...
'', '' Harry Potter'' and ''Shrek
''Shrek'' is a 2001 American computer-animated comedy film loosely based on the 1990 book of the same name by William Steig. It is the first installment in the ''Shrek'' franchise. The film was directed by Andrew Adamson and Vicky Jen ...
'', has taught at Cornell since 1999. Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes Sr. (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American statesman, politician and jurist who served as the 11th Chief Justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party, he previously was the ...
taught in the law school from 1893 to 1895 before becoming Governor of New York, United States Secretary of State
The United States secretary of state is a member of the executive branch of the federal government of the United States and the head of the U.S. Department of State. The office holder is one of the highest ranking members of the president's Ca ...
, and Chief Justice of the United States. Georgios Papanikolaou, who taught at Cornell's medical school from 1913 to 1961, invented the Pap smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in t ...
test for cervical cancer. Robert C. Baker ('43), widely credited for inventing the chicken nugget
A chicken nugget is a food product consisting of a small piece of deboned chicken meat that is breaded or battered, then deep-fried or baked. Invented in the 1950s, chicken nuggets have become a very popular fast food restaurant item, as ...
, taught at Cornell from 1957 to 1989. Carl Sagan was a professor at the university from 1968 to 1996. He narrated and co-wrote the PBS series ''Cosmos
The cosmos (, ) is another name for the Universe. Using the word ''cosmos'' implies viewing the universe as a complex and orderly system or entity.
The cosmos, and understandings of the reasons for its existence and significance, are studied in ...
'', the Emmy Award- and Peabody Award-winning show that became the most watched series in public-television history. He also wrote the novel ''Contact
Contact may refer to:
Interaction Physical interaction
* Contact (geology), a common geological feature
* Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye
* Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects
* ...
'', the basis for a 1997 film of the same name, and he won a Pulitzer Prize for his novel '' The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human Intelligence''. M. H. Abrams
Meyer Howard Abrams (July 23, 1912 – April 21, 2015), usually cited as M. H. Abrams, was an American literary critic, known for works on romanticism, in particular his book ''The Mirror and the Lamp''. Under Abrams's editorship, ''The Norton An ...
was a professor emeritus of English and was the founding editor of ''The Norton Anthology of English Literature
''The Norton Anthology of English Literature'' is an anthology of English literature published by W. W. Norton & Company, one of several such compendiums. First published in 1962, it has gone through ten editions; as of 2006 there are over eigh ...
''. James L. Hoard, a scientist who worked on the Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project w ...
and an expert in crystallography, was a professor emeritus of chemistry and taught from 1936 to 1971.
Vladimir Nabokov taught Russian and European literature at Cornell between 1948 and 1959. The nominee of the Nobel Peace Prize, one of the authors of the theory of intelligentsia Vitaly Tepikin received the academic medal of Cornell University in 2021.
Cornell has twice (2008 and 2009) been named a "Great College to Work For" by The Chronicle of Higher Education
''The Chronicle of Higher Education'' is a newspaper and website that presents news, information, and jobs for college and university faculty and student affairs professionals (staff members and administrators). A subscription is required to re ...
, due to receiving high ratings in compensation and benefits, connection to institution and pride, faculty-administration relations, job satisfaction, and post-retirement benefits. Many faculty, and president, live in the upscale suburb of Cayuga Heights
Cayuga Heights is a village in Tompkins County, New York, United States and an upscale suburb of Ithaca. The village is in the Town of Ithaca, directly northeast of the City of Ithaca and Cornell University's main campus.
The population was 3, ...
, directly north of campus.
Alumni
Cornell counted 245,027 living alumni as of August 2008. Its alumni constitute 34Marshall Scholars
The Marshall Scholarship is a postgraduate scholarship for "intellectually distinguished young Americans ndtheir country's future leaders" to study at any university in the United Kingdom. It is widely considered one of the most prestigious sc ...
and 31 Rhodes Scholars, and Cornell is the only university with three female winners (Pearl S. Buck
Pearl Sydenstricker Buck (June 26, 1892 – March 6, 1973) was an American writer and novelist. She is best known for ''The Good Earth'' a bestselling novel in the United States in 1931 and 1932 and won the Pulitzer Prize for the Novel, Pulitze ...
, Barbara McClintock, and Toni Morrison
Chloe Anthony Wofford Morrison (born Chloe Ardelia Wofford; February 18, 1931 – August 5, 2019), known as Toni Morrison, was an American novelist. Her first novel, ''The Bluest Eye'', was published in 1970. The critically acclaimed '' So ...
) of unshared Nobel Prizes
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfre ...
among its graduates. Many alumni maintain university ties through Homecoming
Homecoming is the tradition of welcoming back alumni or other former members of an organization to celebrate the organization's existence. It is a tradition in many high schools, colleges, and churches in the United States, Canada and Liberia.
...
's reunion weekend, through ''Cornell Magazine'', and through the Cornell Club of New York
The Cornell Club of New York, usually referred to as The Cornell Club, is a private club in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Its membership is restricted to alumni and faculty of Cornell University, family of Cornellians, business associates of ...
. In 2015, Cornell ranked No. 5 nationwide for gifts and bequests from alumni.
 Cornell alumni are noted for their accomplishments in public, professional, and corporate life. Lee Teng-hui was the president of
Cornell alumni are noted for their accomplishments in public, professional, and corporate life. Lee Teng-hui was the president of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, Tsai Ing-wen
Tsai Ing-wen (; born 31 August 1956) is a Taiwanese politician serving as president of the Republic of China (Taiwan) since 2016. A member of the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), Tsai is the first female president of Taiwan. She served as ...
was elected to be the first female president of Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
, Mario García Menocal
Aurelio Mario Gabriel Francisco García Menocal y Deop (December 17, 1866 – September 7, 1941) was the 3rd President of Cuba, serving from 1913 to 1921. His term as president saw Cuba's participation in World War I.
Youth
Born in Jagüey Gra ...
was president of Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Jamshid Amuzegar ('50) was prime minister of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Hu Shih
Hu Shih (; 17 December 1891 – 24 February 1962), also known as Hu Suh in early references, was a Chinese diplomat, essayist, literary scholar, philosopher, and politician. Hu is widely recognized today as a key contributor to Chinese libera ...
(1914) was a Chinese reformer and representative to the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
, Janet Reno
Janet Wood Reno (July 21, 1938 – November 7, 2016) was an American lawyer who served as the 78th United States attorney general. She held the position from 1993 to 2001, making her the second-longest serving attorney general, behind only Wi ...
('60) was the first female United States Attorney General
The United States attorney general (AG) is the head of the United States Department of Justice, and is the chief law enforcement officer of the federal government of the United States. The attorney general serves as the principal advisor to the p ...
, and Ruth Bader Ginsburg
Joan Ruth Bader Ginsburg ( ; ; March 15, 1933September 18, 2020) was an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1993 until her death in 2020. She was nominated by Presiden ...
('54) served on the Supreme Court. Alumnus David Starr Jordan (1872) was the founding president of Stanford University, and M. Carey Thomas
Martha Carey Thomas (January 2, 1857 – December 2, 1935) was an American educator, suffragist, and linguist. She was the second president of Bryn Mawr College, a women's liberal arts college in Bryn Mawr, Pennsylvania.
Biography
Early life
...
(1877) was the second president and first female president of Bryn Mawr College
Bryn Mawr College ( ; Welsh: ) is a women's liberal arts college in Bryn Mawr, Pennsylvania. Founded as a Quaker institution in 1885, Bryn Mawr is one of the Seven Sister colleges, a group of elite, historically women's colleges in the United ...
. Additionally, alumnus Matt Urban
Matt Louis Urban (August 25, 1919 – March 4, 1995) was a United States Army lieutenant colonel and one of the most decorated American soldiers of World War II. Urban performed valiantly in combat on many occasions despite being wounded in ...
('41), a Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valo ...
recipient, holds the distinction as one of the most decorated soldiers in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
.
Cornellians in business include: Citigroup CEO Sanford Weill
Sanford I. "Sandy" Weill (; born March 16, 1933) is an American banker, financier and philanthropist. He is a former chief executive and chairman of Citigroup. He served in those positions from 1998 until October 1, 2003, and April 18, 2006, re ...
('55), Goldman Sachs Group
Goldman Sachs () is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, Hong ...
Chairman Stephen Friedman ('59), Kraft Foods
The second incarnation of Kraft Foods is an American food manufacturing and processing conglomerate, split from Kraft Foods Inc. in 2012 and headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It became part of Kraft Heinz in 2015.
A merger with Heinz, arran ...
CEO Irene Rosenfeld ('75, '77, '80), Autodesk
Autodesk, Inc. is an American multinational software corporation that makes software products and services for the architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, media, education, and entertainment industries. Autodesk is headquartere ...
CEO Carl Bass ('83), Aetna
Aetna Inc. () is an American managed health care company that sells traditional and consumer directed health care insurance and related services, such as medical, pharmaceutical, dental, behavioral health, long-term care, and disability plans, ...
CEO Mark Bertolini
Mark T. Bertolini (born 1956) is an American businessman who is the Co-CEO of Bridgewater Associates, one of the world's largest hedge funds. He was previously the CEO of Aetna, a Fortune 50 diversified health care benefits company with over $60 ...
('84), S.C. Johnson & Son CEO Fisk Johnson ('79, '80, '82, '84, '86), Chevron
Chevron (often relating to V-shaped patterns) may refer to:
Science and technology
* Chevron (aerospace), sawtooth patterns on some jet engines
* Chevron (anatomy), a bone
* '' Eulithis testata'', a moth
* Chevron (geology), a fold in rock ...
Chairman Kenneth T. Derr ('59), Sprint Nextel
Sprint Corporation was an American telecommunications company. Before it Merger of Sprint Corporation and T-Mobile US, merged with T-Mobile US on April 1, 2020, it was the fourth-largest mobile network operator in the United States, serving 54.3 ...
CEO Dan Hesse
Daniel R. Hesse (born c. 1953) is the former chief executive officer of Sprint Corporation. Hesse's tenure at Sprint focused on improved customer service, and he served as the spokesperson in Sprint's "Simply Everything" commercials.
In January ...
('77), Verizon
Verizon Communications Inc., commonly known as Verizon, is an American multinational telecommunications conglomerate and a corporate component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The company is headquartered at 1095 Avenue of the Americas ...
CEO Lowell McAdam
Lowell Clayton McAdam (born May 28, 1954) is an American businessman. He is the former chairman and CEO of Verizon Communications, a company he joined in 2000.
Early life
McAdam earned a bachelor's degree in engineering from Cornell Universit ...
('76), MasterCard CEO Robert Selander ('72), Coors Brewing Company
The Coors Brewing Company started as an American brewery and beer company in Golden, Colorado. In 2005, Adolph Coors Company, the holding company that owned Coors Brewing, merged with Molson, Inc. to become Molson Coors.
The first Coors b ...
CEO Adolph Coors III
Adolph Coors III (January 12, 1915 – February 9, 1960) was the grandson of Adolph Coors and heir to the Coors Brewing Company empire.
Life and career
Coors was born on January 12, 1915, the son of Alice May (née Kistler; 1885–1970) and Adol ...
('37), Loews Corporation
Loews Corporation is an American conglomerate headquartered in New York City. The company's majority-stake holdings include CNA Financial Corporation, Diamond Offshore Drilling, Boardwalk Pipeline Partners, Loews Hotels and Altium Packaging.
...
Chairman Andrew Tisch
Andrew Tisch (born 1949) is the co-chair of Loews Corporation, the company founded by his father Larry Tisch and uncle Bob Tisch.
Together with his brother, James S. Tisch, and his first cousin, Jonathan Tisch, Andrew oversees a holding compan ...
('71), Burger King founder James McLamore
James Whitman McLamore (May 30, 1926 – August 8, 1996) was an American entrepreneur, the founder and first CEO of the Burger King fast food franchise, along with David Edgerton. He also created the Whopper sandwich. After selling Burger King ...
('47), Hotels.com
Hotels.com is a website for booking hotel rooms online and by telephone. The company has 85 websites in 34 languages, and lists over 325,000 hotels in approximately 19,000 locations. Its inventory includes hotels and B&Bs, and some condos and oth ...
founder David Litman
David Litman was born in New York in 1957. He lived in the UK from 1967-1975. He attended Sussex House School from 1968-1971 and City of London School from 1971-1975. He is a graduate of Cornell University (1979) and Cornell Law School (1982).
In ...
('79), PeopleSoft
PeopleSoft, Inc. is a company that provides human resource management systems (HRMS), Financial Management Solutions (FMS), supply chain management (SCM), customer relationship management (CRM), and enterprise performance management (EPM) software ...
founder David Duffield
David Arthur Duffield (born 21 September 1940) is an American billionaire businessman in the software industry. He is the co-founder and former chairman of PeopleSoft, co-founder and chairman emeritus of Workday, Inc., and current founder and ...
('62), Priceline.com
Priceline.com is an online travel agency for finding discount rates for travel-related purchases such as airline tickets and hotel stays. The company facilitates the provision of travel services from its suppliers to its clients. Priceline.com ...
founder Jay Walker ('77), Staples founder Myra Hart Myra M. Hart is a founder of Staples Inc. She graduated from Cornell University with a B.A. in 1962 and a Harvard M.B.A. 1981. She obtained a DBA from Harvard University in 1995.
Biography
She was a founding member of Staples Inc.
Staples Inc. ...
('62), Qualcomm founder Irwin M. Jacobs ('56), Tata Group
The Tata Group () is an Indian multinational conglomerate headquartered in Mumbai. Established in 1868, it is India's largest conglomerate, with products and services in over 150 countries, and operations in 100 countries across six continents ...
CEO Ratan Tata
Ratan Naval Tata, GBE (born 28 December 1937) is an Indian industrialist and former chairman of Tata Sons. He was also the chairman of the Tata Group from 1990 to 2012, serving also as interim chairman from October 2016 through February 2017 ...
('62),Nintendo of America
is a Japanese multinational video game company headquartered in Kyoto, Japan. It develops video games and video game consoles.
Nintendo was founded in 1889 as by craftsman Fusajiro Yamauchi and originally produced handmade playing card ...
President and COO Reggie Fils-Aimé
Reginald Fils-Aimé ( ; born March 25, 1961) is an American businessman best known for being the president and chief operating officer of Nintendo of America, the North American division of the Japanese video game company Nintendo, from 2006 ...
, Johnson & Johnson worldwide chairman Sandi Peterson, Pawan Kumar Goenka, MD of Mahindra & Mahindra
Mahindra & Mahindra Limited (M&M) is an Indian multinational automotive manufacturing corporation headquartered in Mumbai. It was established in 1945 as Mahindra & Mohammed and later renamed as Mahindra & Mahindra. Part of the Mahindra Group ...
, and Y Combinator
Y Combinator (YC) is an American technology startup accelerator launched in March 2005. It has been used to launch more than 3,000 companies, including Airbnb, Coinbase, Cruise, DoorDash, Dropbox, Instacart, Quora, PagerDuty, Reddit, St ...
founder Paul Graham ('86).
In medicine, alumnus Robert Atkins ('55) developed the Atkins Diet
The Atkins diet is a low-carbohydrate fad diet devised by Robert Atkins in the 1970s, marketed with claims that carbohydrate restriction is crucial to weight loss and that the diet offered "a high calorie way to stay thin forever".
The diet be ...
, Henry Heimlich
Henry Judah Heimlich (February 3, 1920 – December 17, 2016) was an American thoracic surgeon and medical researcher. He is widely credited as the inventor of the Heimlich maneuver, a technique of abdominal thrusts for stopping choking, first ...
('47) developed the Heimlich maneuver
Abdominal thrusts, also known as the Heimlich maneuver or Heimlich manoeuvre, is a first aid procedure used to treat upper airway obstructions (or choking) by foreign objects. American doctor Henry Heimlich is often credited for its creation. ...
, Wilson Greatbatch
Wilson Greatbatch (September 6, 1919 – September 27, 2011) was an American engineer and pioneering inventor. He held more than 325 patents and was a member of the National Inventors Hall of Fame and a recipient of the Lemelson–MIT Prize ...
('50) invented the pacemaker, James Maas ('66; also a faculty member) coined the term "power nap
A power nap or cat nap is a short sleep that terminates before deep sleep ( slow-wave sleep; SWS). A power nap is intended to quickly revitalize the sleeper.
Cornell University social psychologist James Maas coined the term. A power nap combi ...
", C. Everett Koop
Charles Everett Koop (October 14, 1916 – February 25, 2013) was an American pediatric surgeon and public health administrator. He was a vice admiral in the U.S. Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, and served as the 13th Surgeon Ge ...
('41) served as Surgeon General of the United States, and Anthony Fauci served as the U.S.'s Chief Medical Adviser during the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identi ...
.
A number of Cornellians have been prominent innovators. Thomas Midgley, Jr.
Thomas Midgley Jr. (May 18, 1889 – November 2, 1944) was an American mechanical and chemical engineer. He played a major role in developing leaded gasoline (tetraethyl lead) and some of the first chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), better known i ...
('11) invented Freon
Freon ( ) is a registered trademark of the Chemours Company and generic descriptor for a number of halocarbon products. They are stable, nonflammable, low toxicity gases or liquids which have generally been used as refrigerants and as aerosol prope ...
, Jon Rubinstein
Jonathan J. "Jon" Rubinstein (born October 1956) is an American electrical engineer who played an instrumental role in the development of the iMac and iPod, the portable music and video device first sold by Apple Computer Inc. in 2001. He lef ...
('78) is credited with the development of the iPod, and Robert Tappan Morris
Robert Tappan Morris (born November 8, 1965) is an American computer scientist and entrepreneur. He is best known for creating the Morris worm in 1988, considered the first computer worm on the Internet.
Morris was prosecuted for releasing the ...
developed the first computer worm on the Internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, pub ...
.
Bill Nye ('77) is well known as " The Science Guy". Clarence W. Spicer invented the 'universal joint' for automobiles while a student in 1903.
Eight Cornellians have served as NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
astronauts, Steve Squyres
Steven Weldon Squyres (born January 9, 1956) is an American geologist and planetary scientist. He was the James A. Weeks Professor of Physical Sciences at Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. His research area is in planetary sciences, with a f ...
('81) is the principal investigator on the Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
Mission. In aerospace, also, Otto Glasser
Otto John Glasser (2 October 1918 – 26 February 1996) was a lieutenant general in the United States Air Force and pioneering weapons scientist who played an important part in the development of the Atlas and Minuteman III intercontinental bal ...
('40) directed the USAF
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Aerial warfare, air military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part ...
program that developed the SM-65 Atlas
The SM-65 Atlas was the first operational intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) developed by the United States and the first member of the Atlas rocket family. It was built for the U.S. Air Force by the Convair Division of General Dy ...
, the World's first operational Intercontinental ballistic missile. Yolanda Shea is a research scientist in the Science Directorate at NASA Langley Research Center
The Langley Research Center (LaRC or NASA Langley), located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has fo ...
.
In literature, Toni Morrison
Chloe Anthony Wofford Morrison (born Chloe Ardelia Wofford; February 18, 1931 – August 5, 2019), known as Toni Morrison, was an American novelist. Her first novel, ''The Bluest Eye'', was published in 1970. The critically acclaimed '' So ...
(M.A.'50; Nobel laureate) is well known for her novel ''Beloved
Beloved may refer to:
Books
* ''Beloved'' (novel), a 1987 novel by Toni Morrison
* ''The Beloved'' (Faulkner novel), a 2012 novel by Australian author Annah Faulkner
*''Beloved'', a 1993 historical romance about Zenobia, by Bertrice Small
Film
...
'', Pearl S. Buck
Pearl Sydenstricker Buck (June 26, 1892 – March 6, 1973) was an American writer and novelist. She is best known for ''The Good Earth'' a bestselling novel in the United States in 1931 and 1932 and won the Pulitzer Prize for the Novel, Pulitze ...
(M.A.'25; Nobel laureate) authored ''The Good Earth
''The Good Earth'' is a historical fiction novel by Pearl S. Buck published in 1931 that dramatizes family life in a Chinese village in the early 20th century. It is the first book in her ''House of Earth'' trilogy, continued in ''Sons'' (1932) ...
'', Thomas Pynchon
Thomas Ruggles Pynchon Jr. ( , ; born May 8, 1937) is an American novelist noted for his dense and complex novels. His fiction and non-fiction writings encompass a vast array of subject matter, genres and themes, including history, music, scie ...
('59) penned such canonical works of postwar American fiction as ''Gravity's Rainbow
''Gravity's Rainbow'' is a 1973 novel by American writer Thomas Pynchon. The narrative is set primarily in Europe at the end of World War II and centers on the design, production and dispatch of V-2 rockets by the German military. In particular, ...
'' and ''The Crying of Lot 49
''The Crying of Lot 49'' is a 1966 novel by American author Thomas Pynchon. The shortest of Pynchon's novels, the plot follows Oedipa Maas, a young Californian woman who begins to embrace a conspiracy theory as she possibly unearths a centuries-ol ...
'', Junot Díaz
Junot Díaz (; born December 31, 1968) is a Dominican-American writer, creative writing professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and was fiction editor at '' Boston Review''. He also serves on the board of advisers for Freed ...
('95) wrote The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao
''The Brief Wondrous Life of Oscar Wao'' is a 2007 novel written by Dominican American author Junot Díaz. Although a work of fiction, the novel is set in New Jersey in the United States, where Díaz was raised, and it deals with the Dominican ...
for which he won the Pulitzer Prize for fiction, and E. B. White
Elwyn Brooks White (July 11, 1899 – October 1, 1985) was an American writer. He was the author of several highly popular books for children, including ''Stuart Little'' (1945), ''Charlotte's Web'' (1952), and '' The Trumpet of the Swan'' ...
(1921) authored '' Charlotte's Web'' and ''Stuart Little
''Stuart Little'' is a 1945 American children's novel by E. B. White. It was White's first children's book, and it is now widely recognized as a classic in children's literature. ''Stuart Little'' was illustrated by the subsequently award-winnin ...
''. Although he did not graduate, Kurt Vonnegut
Kurt Vonnegut Jr. (November 11, 1922 – April 11, 2007) was an American writer known for his satirical and darkly humorous novels. In a career spanning over 50 years, he published fourteen novels, three short-story collections, five plays, and ...
wrote extensively for the Cornell Daily Sun
''The Cornell Daily Sun'' is an independent daily newspaper published in Ithaca, New York by students at Cornell University and hired employees.
''The Sun'' features coverage of the university and its environs as well as stories from the Associa ...
during his time at Cornell. He went on to pen best sellers such as ''Slaughterhouse-Five
''Slaughterhouse-Five, or, The Children's Crusade: A Duty-Dance with Death'' is a 1969 semi-autobiographic science fiction-infused anti-war novel by Kurt Vonnegut. It follows the life and experiences of Billy Pilgrim, from his early years, to h ...
'' and ''Cat's Cradle
Cat's cradle is a game involving the creation of various string figures between the fingers, either individually or by passing a loop of string back and forth between two or more players. The true origin of the name is debated, though the fir ...
.'' Lauren Weisberger
Lauren Weisberger (born March 28, 1977) is an American novelist and author of the 2003 bestseller '' The Devil Wears Prada'', a ''roman à clef'' of her experience as an assistant to ''Vogue'' editor-in-chief Anna Wintour.
Early life and educa ...
('99) wrote '' The Devil Wears Prada'', later adapted into a 2006 film of the same name starring Meryl Streep and Anne Hathaway. Media personalities who have graduated from Cornell include conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
Ann Coulter
Ann Hart Coulter (; born December 8, 1961) is an American conservative media pundit, author, syndicated columnist, and lawyer. She became known as a media pundit in the late 1990s, appearing in print and on cable news as an outspoken critic of ...
('84)Karlgaard, Rich. ''Life 2.0: How People Across America Are Transforming Their Lives by Finding the ''Where'' of Their Happiness.'' New York: Three Rivers Press, 2005. 41. and liberals Bill Maher ('78) and Keith Olbermann
Keith Theodore Olbermann (; born January 27, 1959) is an American sports and political commentator and writer.
Olbermann spent the first 20 years of his career in sports journalism. He was a sports correspondent for CNN and for local TV and r ...
('79).
Several Cornellians have also achieved critical acclaim in theatre and entertainment. Christopher Reeve
Christopher D'Olier Reeve (September 25, 1952 – October 10, 2004) was an American actor, best known for playing the title character in the film '' Superman'' (1978) and three sequels.
Born in New York City and raised in Princeton, New Jersey ...
('74) played '' Superman'', Frank Morgan
Francis Phillip Wuppermann (June 1, 1890 – September 18, 1949), known professionally as Frank Morgan, was an American character actor. He was best known for his appearances in films starting in the silent era in 1916, and then numerous sound ...
was The Wizard of Oz, and Peter Yarrow
Peter Yarrow (born May 31, 1938) is an American singer and songwriter who found fame for being in the 1960s folk trio Peter, Paul and Mary. Yarrow co-wrote (with Leonard Lipton) one of the group's best known hits, " Puff, the Magic Dragon". H ...
('59) of folk band Peter, Paul and Mary
Peter, Paul and Mary was an American folk group formed in New York City in 1961 during the American folk music revival phenomenon. The trio consisted of tenor Peter Yarrow, baritone Paul Stookey, and contralto Mary Travers. The group's reper ...
, wrote ''Puff, the Magic Dragon
"Puff, the Magic Dragon" (or just "Puff") is a song written by Peter Yarrow of Peter, Paul and Mary from a poem by Leonard Lipton. It was made popular by Yarrow's group in a 1962 recording released in January 1963.
Lipton wrote a poem about a ...
'' and other classic American tunes. Jason Ardizzone-West ('95) is an Emmy Award winning scenic and production designer.
In architectural, alumnus Richmond Shreve (1902) designed the Empire State Building, and Raymond M. Kennedy
Raymond McCormick Kennedy (1891–1976) was the guiding light and architect of the Grauman's Chinese Theater that opened in May 1927.
Early life
Raymond McCormick Kennedy was born in New Brighton, Pennsylvania in 1891 to Thomas and Geneva Kennedy ...
('15) designed Hollywood's famous Grauman's Chinese Theatre. In the arts, Arthur Garfield Dove (1903) is often considered the first American abstract painter. Louise Lawler
Louise Lawler (born 1947) is a U.S. artist and photographer living in Brooklyn, New York.Louise Lawler ...
('69) is a pioneering feminist artist and photographer, and a member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences
The American Academy of Arts and Sciences (abbreviation: AAA&S) is one of the oldest learned societies in the United States. It was founded in 1780 during the American Revolution by John Adams, John Hancock, James Bowdoin, Andrew Oliver, a ...
.
In athletics, Cornell graduates include football legend Glenn "Pop" Warner (1894), head coach of the United States men's national soccer team
The United States men's national soccer team (USMNT) represents the United States in men's international soccer competitions. The team is controlled by the United States Soccer Federation and is a member of FIFA and CONCACAF.
The U.S. team h ...
Bruce Arena
Bruce Arena (born September 21, 1951) is an American soccer coach who is the head coach and sporting director of the New England Revolution.
He is a member of the National Soccer Hall of Fame and the NJCAA Lacrosse Hall of Fame. Arena has had ...
('73), Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball (MLB) is a professional baseball organization and the oldest major professional sports league in the world. MLB is composed of 30 total teams, divided equally between the National League (NL) and the American League (AL), ...
commissioner Rob Manfred
Robert Dean Manfred Jr. (born September 28, 1958) is an American lawyer and business executive who is serving as the tenth commissioner of Major League Baseball. He previously served as MLB's chief operating officer. Manfred succeeded Bud Selig a ...
('80) National Hockey League
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
commissioner Gary Bettman ('74), six-time Stanley Cup winning hockey
Hockey is a term used to denote a family of various types of both summer and winter team sports which originated on either an outdoor field, sheet of ice, or dry floor such as in a gymnasium. While these sports vary in specific rules, numbers o ...
goalie Ken Dryden
Kenneth Wayne Dryden (born August 8, 1947) is a Canadian politician, lawyer, businessman, author, and former National Hockey League (NHL) goaltender. He is an Officer of the Order of Canada and a member of the Hockey Hall of Fame. He was a Liber ...
('69), tennis singles world # 2 Dick Savitt
Richard Savitt (March 4, 1927 – January 6, 2023) was an American tennis player.
In 1951, at the age of 24, he won both the Australian and Wimbledon men's singles championships. Savitt was mostly ranked world No. 2 the same year behind fellow ...
, seven-time US Tennis championships winner William Larned
William Augustus Larned (December 30, 1872 – December 16, 1926) was an American tennis player who was active at the beginning of the 20th century. He won seven singles titles at the U.S. National Championships.
Biography
Larned was born ...
and Toronto Raptors
The Toronto Raptors are a Canadian professional basketball team based in Toronto. The Raptors compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the league's Eastern Conference Atlantic Division. They play their home games a ...
president Bryan Colangelo
Bryan Paul Colangelo (born June 1, 1965) is an American basketball executive who was the former general manager of the Philadelphia 76ers, Toronto Raptors and Phoenix Suns of the National Basketball Association (NBA). He also served as president ...
('87), and Kyle Dake
Kyle Douglas Dake (born February 25, 1991) is an American freestyle wrestler and graduated folkstyle wrestler who currently competes at 74 kilograms. Dake is a four-time and the reigning World Champion, winning back-to-back titles twice, at ...
, four-time NCAA division I wrestling national champion.
Don Spero
Donald M. "Don" Spero (born August 9, 1939) is an American physicist, venture capitalist, and a former U.S. and world champion rower who competed at the 1964 Summer Olympics and won the single sculls 1966 World Rowing Championships. He also won ...
was an Olympic and world champion rower.
See also
*Cornell realism
Cornell realism is a view in meta-ethics, associated with the work of Richard Boyd, Nicholas Sturgeon, and David Brink (who took his Ph.D. at Cornell University). There is no recognized and official statement of Cornell realism, but several these ...
Notes
References
External links
*Cornell Athletics website
{{Authority control 1865 establishments in New York (state) Cornell family Educational institutions established in 1865 Ithaca, New York Land-grant universities and colleges Schools in Tompkins County, New York Tourist attractions in Tompkins County, New York Private universities and colleges in New York (state)