Consumer resistance on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A boycott is an act of nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organization, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for moral, social, political, or
 The word ''boycott'' entered the English language during the Irish " Land War" and derives from Captain Charles Boycott, the land agent of an absentee landlord, Lord Erne, who lived in
The word ''boycott'' entered the English language during the Irish " Land War" and derives from Captain Charles Boycott, the land agent of an absentee landlord, Lord Erne, who lived in

 Although the term itself was not coined until 1880, the practice dates back to at least the 1790s, when supporters of the
Although the term itself was not coined until 1880, the practice dates back to at least the 1790s, when supporters of the
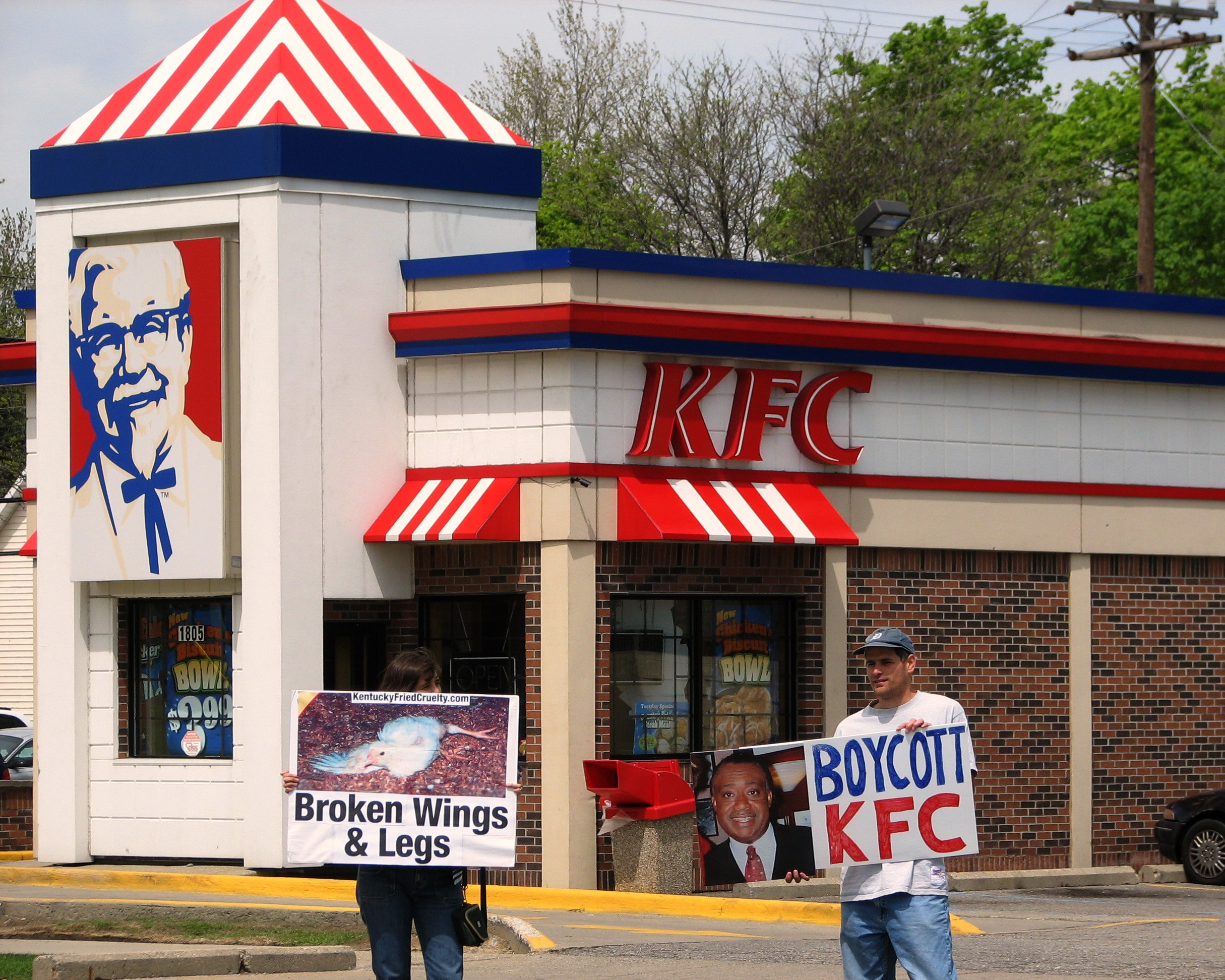
 Boycotts are now much easier to successfully initiate due to the Internet. Examples include the
Boycotts are now much easier to successfully initiate due to the Internet. Examples include the  Some boycotts center on particular businesses, such as recent protests regarding Costco, Walmart, Ford Motor Company, or the diverse products of
Some boycotts center on particular businesses, such as recent protests regarding Costco, Walmart, Ford Motor Company, or the diverse products of
 Boycotts are generally legal in developed countries. Occasionally, some restrictions may apply; for instance, in the United States, it may be unlawful for a union to engage in "
Boycotts are generally legal in developed countries. Occasionally, some restrictions may apply; for instance, in the United States, it may be unlawful for a union to engage in "
environmental
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
reasons. The purpose of a boycott is to inflict some economic loss
Economic loss is a term of art which refers to financial loss and damage suffered by a person which is seen only on a balance sheet and not as physical injury to person or property. There is a fundamental distinction between pure economic loss and ...
on the target, or to indicate a moral outrage, to try to compel the target to alter an objectionable behavior.
The word is named after Captain Charles Boycott, agent of an absentee landlord in Ireland, against whom the tactic was successfully employed after a suggestion by Irish nationalist leader Charles Stewart Parnell and his Irish Land League in 1880.
Sometimes, a boycott can be a form of consumer activism, sometimes called moral purchasing. When a similar practice is legislated by a national government, it is known as a sanction. Frequently, however, the threat of boycotting a business is an empty threat, with no significant effect on sales.
Etymology
 The word ''boycott'' entered the English language during the Irish " Land War" and derives from Captain Charles Boycott, the land agent of an absentee landlord, Lord Erne, who lived in
The word ''boycott'' entered the English language during the Irish " Land War" and derives from Captain Charles Boycott, the land agent of an absentee landlord, Lord Erne, who lived in County Mayo
County Mayo (; ga, Contae Mhaigh Eo, meaning "Plain of the Taxus baccata, yew trees") is a Counties of Ireland, county in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. In the West Region, Ireland, West of Ireland, in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Conn ...
, Ireland. Captain Boycott was the target of social ostracism organized by the Irish Land League in 1880. As harvests had been poor that year, Lord Erne offered his tenants a ten percent reduction in their rents. In September of that year, protesting tenants demanded a twenty-five percent reduction, which Lord Erne refused. Boycott then attempted to evict eleven tenants from the land. Charles Stewart Parnell, the Irish leader, proposed that when dealing with tenants who take farms where another tenant was evicted, rather than resorting to violence, everyone in the locality should shun them. While Parnell's speech did not refer to land agents or landlords, the tactic was first applied to Boycott when the alarm was raised about the evictions. Despite the short-term economic hardship to those undertaking this action, Boycott soon found himself isolated – his workers stopped work in the fields and stables, as well as in his house. Local businessmen stopped trading with him, and the local postman refused to deliver mail.
The concerted action taken against him meant that Boycott was unable to hire anyone to harvest his crops in his charge. After the harvest, the "boycott" was successfully continued and soon the new word was everywhere. The '' New-York Tribune'' reporter, James Redpath, first wrote of the boycott in the international press. The Irish author, George Moore, reported: 'Like a comet the verb 'boycott' appeared.' It was used by '' The Times'' in November 1880 as a term for organized isolation. According to an account in the book ''The Fall of Feudalism in Ireland'' by Michael Davitt, the term was promoted by Fr. John O'Malley of County Mayo to "signify ostracism applied to a landlord or agent like Boycott". ''The Times'' first reported on November 20, 1880: "The people of New Pallas have resolved to 'boycott' them and refused to supply them with food or drink." The ''Daily News'' wrote on December 13, 1880: "Already the stoutest-hearted are yielding on every side to the dread of being 'Boycotted'." By January of the following year, the word was being used figuratively: "Dame Nature arose.... She 'Boycotted' London from Kew to Mile End.".Girlcott
Girlcott, a pun on "boycott", is a boycott intended to focus on the rights or actions of women. The term was coined in 1968 by American Lacey O'Neal during the1968 Summer Olympics
The 1968 Summer Olympics ( es, Juegos Olímpicos de Verano de 1968), officially known as the Games of the XIX Olympiad ( es, Juegos de la XIX Olimpiada) and commonly known as Mexico 1968 ( es, México 1968), were an international multi-sport eve ...
in the context of protests by male African American athletes. The term was later used by retired tennis player Billie Jean King
Billie Jean King (née Moffitt; born November 22, 1943) is an American former world No. 1 tennis player. King won 39 major titles: 12 in singles, 16 in women's doubles, and 11 in mixed doubles. King was a member of the victorious United States ...
in 1999 in reference to Wimbledon
Wimbledon most often refers to:
* Wimbledon, London, a district of southwest London
* Wimbledon Championships, the oldest tennis tournament in the world and one of the four Grand Slam championships
Wimbledon may also refer to:
Places London
* ...
, while discussing equal pay for women players. The term "girlcott" was revived in 2005 by the Women and Girls Foundation The Women and Girls Foundation (WGF) is an independent, community-based non-profit organization serving 11 counties in the southwestern part of Pennsylvania. It was founded in 2002. The stated goal of the foundation is to achieve equality for women ...
in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania against Abercrombie & Fitch
Abercrombie & Fitch (A&F) is an American lifestyle retailer that focuses on casual wear. Its headquarters are in New Albany, Ohio. The company operates three other offshoot brands: Abercrombie Kids, Hollister Co., and Gilly Hicks. As of Februar ...
.
Notable boycotts
 Although the term itself was not coined until 1880, the practice dates back to at least the 1790s, when supporters of the
Although the term itself was not coined until 1880, the practice dates back to at least the 1790s, when supporters of the British abolitionists
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
led and supported the free produce movement
The free-produce movement was an international boycott of goods produced by slave labor. It was used by the abolitionist movement as a non-violent way for individuals, including the disenfranchised, to fight slavery.
In this context, ''free'' si ...
. Other instances include:
* the Iranian Tobacco Boycott in 1891
* Civil rights movement boycotts to protest segregation (e.g., Montgomery & Tallahassee Bus Boycotts)
* the United Farm Workers union grape and lettuce boycotts
* the American boycott of British goods during the American Revolution, such as the Boston Tea Party
* the 1905 Chinese boycott of American products to protest the extension of the Chinese Exclusion Act in 1902.
* the Indian boycott of British goods organized by Mahatma Gandhi
* the successful Jewish boycott organized against Henry Ford in the United States, in the 1920s
* the boycott of Japanese products in China after the May Fourth Movement
* the antisemitic boycott of Jewish-owned businesses in Nazi Germany during the 1930s
* the Jewish anti-Nazi boycott of German goods in Lithuania, the US, Britain, Poland and Mandatory Palestine during 1933
* the Arab League boycott of Israel
The Arab League boycott of Israel is a strategy adopted by the Arab League and its member states to boycott economic and other relations between Arabs and the Arab states and Israel and specifically stopping all trade with Israel which adds to ...
and companies trading with Israel.
* the worldwide Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions (BDS) campaign led by Palestinian civil society against the State of Israel.
*The global fossil fuel divestment
Fossil fuel divestment or fossil fuel divestment and investment in climate solutions is an attempt to reduce climate change by exerting social, political, and economic pressure for the institutional divestment of assets including stocks, bonds ...
movement, described by Desmond Tutu
Desmond Mpilo Tutu (7 October 193126 December 2021) was a South African Anglican bishop and theologian, known for his work as an anti-apartheid and human rights activist. He was Bishop of Johannesburg from 1985 to 1986 and then Archbishop ...
as an "apartheid-style boycott to save the planet", and considered to be the biggest boycott-style campaign in history.
During the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
, the Arab countries enacted a crude oil
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude ...
embargo against the West. Other examples include the US-led boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow, the Soviet-led boycott of the 1984 Summer Olympics in Los Angeles, and the movement that advocated "disinvestment
Disinvestment refers to the use of a concerted economic boycott to pressure a government, industry, or company towards a change in policy, or in the case of governments, even regime change. The term was first used in the 1980s, most commonly in ...
" in South Africa during the 1980s in opposition to that country's apartheid regime. The first Olympic boycott was in the 1956 Summer Olympics
The 1956 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XVI Olympiad, were an international multi-sport event held in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia, from 22 November to 8 December 1956, with the exception of the equestrian events, whi ...
with several countries boycotting the games for different reasons. Iran also has an informal Olympic boycott against participating against Israel, and Iranian athletes typically bow out or claim injuries when pitted against Israelis (see Arash Miresmaeili
Arash Miresmaeili ( fa, آرش میراسماعیلی , born March 3, 1981 in Khorramabad) is an Iranian judoka. He now serves as the President of the Iranian Judo Federation.
World Judo Championships
He won the gold medal in two World Judo Cha ...
).
Academic boycotts have been organized against countries—for example, the mid- and late 20th-century academic boycotts of South Africa
The academic boycott of South Africa comprised a series of boycotts of South African academic institutions and scholars initiated in the 1960s, at the request of the African National Congress, with the goal of using such international pressure t ...
in protest of apartheid practices and the academic boycotts of Israel in the early 2000s.
Application and uses
gay and lesbian
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term is an ...
boycott of advertisers of the ''Dr. Laura
Doctor is an academic title that originates from the Latin word of the same spelling and meaning. The word is originally an agentive noun of the Latin verb 'to teach'. It has been used as an academic title in Europe since the 13th century, w ...
'' talk show, gun owners' similar boycott of advertisers of Rosie O'Donnell's talk show and (later) magazine, and gun owners' boycott of Smith & Wesson following that company's March 2000 settlement with the Clinton administration
Bill Clinton's tenure as the 42nd president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1993, and ended on January 20, 2001. Clinton, a Democrat from Arkansas, took office following a decisive election victory over Re ...
. They may be initiated very easily using either websites (the ''Dr. Laura'' boycott), newsgroups (the Rosie O'Donnell boycotts), or even mailing lists. Internet-initiated boycotts "snowball" very quickly compared to other forms of organization.
''Viral Labeling'' is a new boycott method using the new digital technology proposed by the Multitude Project and applied for the first time against Walt Disney around Christmas time in 2009.Philip Morris Phil(l)ip or Phil Morris may refer to:
Companies
*Altria, a conglomerate company previously known as Philip Morris Companies Inc., named after the tobacconist
**Philip Morris USA, a tobacco company wholly owned by Altria Group
**Philip Morris Inter ...
. Another form of boycott identifies a number of different companies involved in a particular issue, such as the Sudan Divestment campaign, the "Boycott Bush" campaign. The Boycott Bush website was set up by Ethical Consumer
Ethical Consumer Research Association Ltd (ECRA) is a British not-for-profit publisher, research, political, and campaign organisation which publishes information on the social, ethical and environmental behaviour of companies and issues around tr ...
after U.S. President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
failed to ratify the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
– the website identified Bush's corporate funders and the brands and products they produce. Historically boycotts have also targeted individual businesses. During the early decades of the twentieth century hotels in Australia were regularly targeted over the cost of alcohol, accommodation and food, as well as mistreatment of employees.
As a response to consumer boycotts of large-scale and multinational businesses, some companies have marketed brands that do not bear the company's name on the packaging or in advertising. Activists such as Ethical Consumer produce information that reveals which companies own which brands and products so consumers can practice boycotts or moral purchasing more effectively. Another organization, Buycott.com, provides an Internet-based smart-phone application that scans Universal Product Codes and displays corporate relationships to the user.
"Boycotts" may be formally organized by governments as well. In reality, government "boycotts" are just a type of embargo. Notably, the first formal, nationwide act of the Nazi government against German Jews was a national embargo of Jewish businesses on April 1, 1933.
Where the target of a boycott derives all or part of its revenues from other businesses, as a newspaper does, boycott organizers may address the target's commercial customers.
Collective behavior
The sociology ofcollective behavior
The expression collective behavior was first used by Franklin Henry Giddings and employed later by Robert Park and Ernest Burgess, Herbert Blumer, Ralph H. Turner and Lewis Killian, and Neil Smelser to refer to social processes and events w ...
is concerned with causes and conditions pertaining to behavior carried out by a collective, as opposed to an individual (e.g., riot
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targete ...
s, panics
''F.E.A.R. First Encounter Assault Recon'' is a first-person shooter Horror game#Psychological horror, psychological horror video game for Microsoft Windows, Xbox 360, and PlayStation 3. It is the first game in the ''F.E.A.R.'' series. Develop ...
, fads/crazes, boycotts). Boycotts have been characterized by some as different from traditional forms of collective behavior in that they appear to be highly rational and dependent on existing norms and structures. Lewis Killian criticizes that characterization, pointing to the Tallahassee bus boycott
The Tallahassee bus boycott was a citywide boycott in Tallahassee, Florida that sought to end racial segregation in the employment and seating arrangements of city buses. On May 26, 1956, Wilhelmina Jakes and Carrie Patterson, two Florida A&M Uni ...
as one example of a boycott that aligns with traditional collective behavior theory.
Philip Balsiger points out that political consumption (e.g., boycotts) tends to follow dual-purpose action repertoires, or scripts, which are used publicly to pressure boycott targets and to educate and recruit consumers. Balsiger finds one example in Switzerland, documenting activities of the Clean Clothes Campaign
The Clean Clothes Campaign (CCC) is the garment industry's largest alliance of labour unions and non-governmental organizations. The civil society campaign focuses on the improvement of working conditions in the garment and sportswear industries. ...
, a public NGO-backed campaign, that highlighted and disseminated information about local companies' ethical practices.
Dixon, Martin, and Nau analyzed 31 collective behavior campaigns against corporations that took place during the 1990s and 2000s. Protests considered successful included boycotts and were found to include a third party, either in the capacity of state intervention or of media coverage. State intervention may make boycotts more efficacious when corporation leaders fear the imposition of regulations. Media intervention may be a crucial contributor to a successful boycott because of its potential to damage the reputation of a corporation. Target corporations that were the most visible were found to be the most vulnerable to either market (protest causing economic loss) or mediated (caused by third-party) disruption. Third-party actors (i.e., the state or media) were more influential when a corporation had a high reputation—when third-party activity was low, highly reputable corporations did not make the desired concessions to boycotters; when third-party activity was high, highly reputable corporations satisfied the demands of boycotters. The boycott, a prima facie market-disruptive tactic, often precipitates mediated disruption. The researchers' analysis led them to conclude that when boycott targets are highly visible and directly interact with and depend on local consumers who can easily find substitutes, they are more likely to make concessions. Koku, Akhigbe, and Springer also emphasize the importance of boycotts' threat of reputational damage, finding that boycotts alone pose more of a threat to a corporation's reputation than to its finances directly.
Philippe Delacote points out that a problem contributing to a generally low probability of success for any boycott is the fact that the consumers with the most power to cause market disruption are the least likely to participate; the opposite is true for consumers with the least power. Another collective behavior problem is the difficulty, or impossibility, of direct coordination amongst a dispersed group of boycotters. Yuksel and Mryteza emphasize the collective behavior problem of free riding in consumer boycotts, noting that some individuals may perceive participating to be too great an immediate personal utility sacrifice. They also note that boycotting consumers took the collectivity into account when deciding to participate, that is, consideration of joining a boycott as goal-oriented collective activity increased one's likelihood of participating. A corporation-targeted protest repertoire including boycotts and education of consumers presents the highest likelihood for success.
Legality
 Boycotts are generally legal in developed countries. Occasionally, some restrictions may apply; for instance, in the United States, it may be unlawful for a union to engage in "
Boycotts are generally legal in developed countries. Occasionally, some restrictions may apply; for instance, in the United States, it may be unlawful for a union to engage in "secondary boycott
Secondary may refer to: Science and nature
* Secondary emission, of particles
** Secondary electrons, electrons generated as ionization products
* The secondary winding, or the electrical or electronic circuit connected to the secondary winding ...
s" (to request that its members boycott companies that supply items to an organization already under a boycott, in the United States); however, the union is free to use its right to speak freely to inform its members of the fact that suppliers of a company are breaking a boycott; its members then may take whatever action they deem appropriate, in consideration of that fact.
United Kingdom
When the boycott first emerged in Ireland, it presented a serious dilemma for Gladstone's government. The individual actions that constituted a boycott were recognized by legislators as essential to a free society. However, overall a boycott amounted to a harsh, extrajudicial punishment. ThePrevention of Crime (Ireland) Act 1882
Prevention may refer to:
Health and medicine
* Preventive healthcare, measures to prevent diseases or injuries rather than curing them or treating their symptoms
General safety
* Crime prevention, the attempt to reduce deter crime and crimin ...
made it illegal to use "intimidation" to instigate or enforce a boycott, but not to participate in one.
The conservative jurist James Fitzjames Stephen
Sir James Fitzjames Stephen, 1st Baronet, KCSI (3 March 1829 – 11 March 1894) was an English lawyer, judge, writer, and philosopher. One of the most famous critics of John Stuart Mill, Stephen achieved prominence as a philosopher, law re ...
justified laws against boycotting by claiming that the practice amounted to "usurpation of the functions of government" and ought therefore to be dealt with as "the modern representatives of the old conception of high treason".
United States
Boycotts are legal under common law. The right to engage in commerce, social intercourse, and friendship includes the implied right not to engage in commerce, social intercourse, and friendship. Since a boycott is voluntary and nonviolent, the law cannot stop it. Opponents of boycotts historically have the choice of suffering under it, yielding to its demands, or attempting to suppress it through extralegal means, such as force and coercion. In the United States, the antiboycott provisions of the Export Administration Regulations (EAR) apply to all "U.S. persons", defined to include individuals and companies located in the United States and their foreign affiliates. The antiboycott provisions are intended to prevent United States citizens and companies being used as instrumentalities of a foreign government's foreign policy. The EAR forbids participation in or material support of boycotts initiated by foreign governments, for example, theArab League
The Arab League ( ar, الجامعة العربية, ' ), formally the League of Arab States ( ar, جامعة الدول العربية, '), is a regional organization in the Arab world, which is located in Northern Africa, Western Africa, E ...
boycott of Israel. These persons are subject to the law when their activities relate to the sale, purchase, or transfer of goods or services (including the sale of information) within the United States or between the United States and a foreign country. This covers exports and imports, financing, forwarding and shipping, and certain other transactions that may take place wholly offshore.
However, the EAR only applies to boycotts: a domestic boycott campaign arising within the United States that has the same object as the foreign-government-initiated boycott appears to be lawful, assuming that it is an independent effort not connected with the foreign government's boycott.
Other legal impediments to certain boycotts remain. One set are Refusal to deal laws, which prohibit concerted efforts to eliminate competition by refusal to buy from or to sell to a party. Similarly, boycotts may also run afoul of Anti-discrimination laws
Anti-discrimination law or non-discrimination law refers to legislation designed to prevent discrimination against particular groups of people; these groups are often referred to as protected groups or protected classes. Anti-discrimination laws ...
; for example, New Jersey's Law Against Discrimination prohibits any place that offers goods, services and facilities to the general public, such as a restaurant, from denying or withholding any accommodation to (i.e., not to engage in commerce with) an individual because of that individual's race (etc.).
Alternatives
A boycott is typically a one-time affair intended to correct an outstanding single wrong. When extended for a long period of time, or as part of an overall program of awareness-raising or reforms to laws or regimes, a boycott is part of moral purchasing, and some prefer those economic or political terms. Most organized consumer boycotts today are focused on long-term change of buying habits, and so fit into part of a larger political program, with many techniques that require a longer structural commitment, e.g. reform to commodity markets, or government commitment to moral purchasing, e.g. the longstanding boycott of South African businesses to protest apartheid already alluded to. These stretch the meaning of a "boycott." Another form of consumer boycotting is substitution for an equivalent product; for example,Mecca Cola
Mecca-Cola is a cola-flavoured carbonated beverage. The flagship product of the Mecca Cola World Company, it is marketed as an alternative to U.S. brands such as Coca-Cola and Pepsi-Cola to "pro-Muslim" consumers. The product's name contains the ...
and Qibla Cola
Qibla Cola was a cola-flavored carbonated beverage produced by the Qibla Cola Company, based in Derby, England. The company differentiated itself and its products from its rivals by making an ethical stance in all its operations including givi ...
have been marketed as substitutes for Coca-Cola among Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
populations.
A prime target of boycotts is consumerism itself, e.g. "International Buy Nothing Day
Buy Nothing Day is a minor event of protest against consumerism. In North America, the United Kingdom, Finland and Sweden, Buy Nothing Day is held the day after U.S. Thanksgiving, concurrent to Black Friday; elsewhere, it is held the followin ...
" celebrated globally on the Friday after Thanksgiving Day in the United States.
Another version of the boycott is targeted divestment, or disinvestment
Disinvestment refers to the use of a concerted economic boycott to pressure a government, industry, or company towards a change in policy, or in the case of governments, even regime change. The term was first used in the 1980s, most commonly in ...
. Targeted divestment involves campaigning for withdrawal of investment, for example the Sudan Divestment campaign involves putting pressure on companies, often through shareholder activism, to withdraw investment that helps the Sudanese government perpetuate genocide in Darfur. Only if a company refuses to change its behavior in response to shareholder engagement does the targeted divestment model call for divestment from that company. Such targeted divestment implicitly excludes companies involved in agriculture, the production and distribution of consumer goods, or the provision of goods and services intended to relieve human suffering or to promote health, religious and spiritual activities, or education.
When students are dissatisfied with a political or academic issue, a common tactic for students' union
A students' union, also known by many other names, is a student organization present in many colleges, universities, and high schools. In higher education, the students' union is often accorded its own building on the campus, dedicated to social, ...
s is to start a boycott of classes (called a student strike among faculty and students since it is meant to resemble strike action
Strike action, also called labor strike, labour strike, or simply strike, is a work stoppage caused by the mass refusal of employees to Labor (economics), work. A strike usually takes place in response to grievance (labour), employee grievance ...
by organized labor
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and Employee ben ...
) to put pressure on the governing body of the institution, such as a university, vocational college or a school, since such institutions cannot afford to have a cohort miss an entire year.
Sports events
The United States and major powers all ignored calls for a boycott in 1936 against the Olympics in Nazi Germany. In the 1970s and 1980s South Africa became the target of a sports boycott. After the Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan in 1979, the United States government organized a boycott of the 1980 Moscow Olympics much to Soviet chagrin. Moscow then organized a Communist boycott of the1984 Summer Olympics
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the secon ...
in Los Angeles, which allowed the Americans to win far more medals than expected.
In at least one case, a boycott has been documented due to on-field results of a game; the residents of New Orleans boycotted television broadcasts of Super Bowl LIII
Super Bowl LIII was an American football game played to determine the champion of the National Football League (NFL) for the 2018 season. The American Football Conference (AFC) champion New England Patriots defeated the National Football Confe ...
after a controversial officiating call led to the hometown New Orleans Saints losing the NFC Championship Game
The NFC Championship Game is the annual championship game of the National Football Conference (NFC) and one of the two semi-final playoff games of the National Football League (NFL), the largest professional American football league in the world. ...
and being denied a trip to the Super Bowl. Viewership of the game dropped in the city by half compared to Super Bowl LII, contributing to a noticeable drop in the overall national ratings, but the boycott failed to achieve any meaningful remedy for the Saints or their fans.
Diplomatic boycott
Nations have from time to time used "diplomatic boycotts" to isolate other governments. Following the May Coup of 1903, Great Britain led the major powers in a diplomatic boycott against Serbia, which was a refusal to recognize the post-coup government of Serbia altogether by withdrawing ambassadors and other diplomatic officials from the country; it ended three years later in 1906, when Great Britain renewed diplomatic relations through a decree signed by King Edward VII. A diplomatic boycott is when diplomatic participation is withheld from an event such as the Olympics but athletic participation is not limited. In 2021 a number of nations, led by The United States, Britain and Canada, citing China's policies concerning the Uyghur genocide and human rights situations in China, protested the2022 Beijing Winter Olympics
The 2022 Winter Olympics (2022年冬季奥林匹克运动会), officially called the XXIV Olympic Winter Games () and commonly known as Beijing 2022 (2022), was an international winter multi-sport event held from 4 to 20 February 2022 in Beij ...
through a diplomatic boycott.
See also
* Anti-boycott * Election boycott *Group boycott
In competition law, a group boycott is a type of secondary boycott in which two or more competitors in a relevant market refuse to conduct business with a firm unless the firm agrees to cease doing business with an actual or potential competitor ...
* International sanctions
* List of boycotts
This is a list of boycott
A boycott is an act of nonviolent, voluntary abstention from a product, person, organization, or country as an expression of protest. It is usually for moral, social, political, or environmental reasons. The purpose ...
* Moral purchasing
* No Platform
* Walkout
Notes
References
* Friedman, M. ''Consumer Boycotts: Effecting Change through the Marketplace and the Media.'' London: Routledge, 1999. * * Hoffmann, S., Müller, S. Consumer Boycotts Due to Factory Relocation. ''Journal of Business Research,'' 2009, 62 (2), 239–247. * Hoffmann, S. Anti-Consumption as a Means of Saving Jobs. ''European Journal of Marketing,'' 2011, 45 (11/12), 1702–1714. * Glickman, Lawrence B. ''Buying Power: A History of Consumer Activism in America.'' University Of Chicago Press, 2009. * Klein, J. G., Smith, N. C., John, A. Why we Boycott: Consumer Motivations for Boycott Participation. ''Journal of Marketing,'' 2004, 68 (3), 92–109. {{Authority control Civil disobedience Community organizing Protest tactics Collective punishment Shunning 1880s neologisms Ethical consumerism Consumer behaviour Interpersonal conflict