|
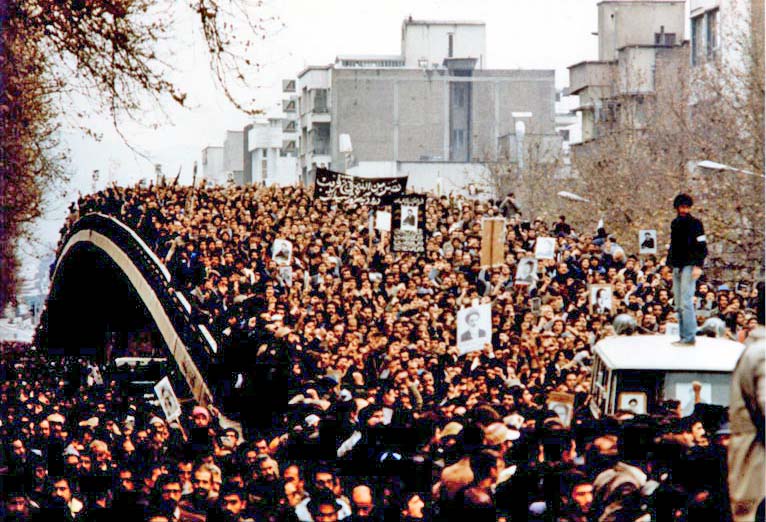
Riot
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups ( race riot) or religions (sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganized groups that are frequently "chaotic and exhibit herd be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race Riot
This is a list of ethnic riots by country, and includes riots based on ethnic, sectarian, xenophobic, and racial conflict. Some of these riots can also be classified as pogroms. Africa Americas United States Nativist period: 1700s–1860 * 1824: Providence, RI – Hard Scrabble Riots * 1829: Cincinnati, OH – Cincinnati riots of 1829 * 1829: Charlestown, Massachusetts – anti-Catholic Riots * 1831: Providence, RI * 1834: Massachusetts – Convent burning * 1834: Philadelphia, PA – pro-slavery riots * 1834: New York, NY – New York City pro-slavery riots * 1835: Boston, MA – pro-slavery riots * 1835: Five Points Riot * 1835: Washington, D.C. – Snow Riot * 1836: Cincinnati, OH – Cincinnati riots of 1836 * 1841: Cincinnati, OH – White Irish-descendant and Irish immigrant dock workers rioted against Black dock workers. * 1844: Philadelphia, PA – Philadelphia Nativist Riots * 1851: Hoboken, NJ – anti-German riot * 1855: Louisville, KY – anti-German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sports Riot
A sports riot is a riot that occurs during or after sporting events. Sports riots occur worldwide. Most riots are known to occur after the event is done, but some have been during the game (see football hooliganism). Whilst football (soccer) is one of the more well-known triggers for riots, other sports which have triggered riots include ice hockey and motorcycle racing Motorcycle racing (also called moto racing and motorbike racing) is the motorcycle sport of racing motorcycles. Major varieties include motorcycle road racing and off-road racing, both either on circuits or open courses, and track racing. Ot .... There are a number of factors believed to influence whether riots occur, including cultural factors; environmental factors such as temperature, darkness, and noise; and witnessing player violence. Examples The following are various examples of a sports riot: References {{Sport Riots ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russian Empire (mostly within the Pale of Settlement). Similar attacks against Jews which also occurred at other times and places retrospectively became known as pogroms. Sometimes the word is used to describe publicly sanctioned purgative attacks against non-Jewish groups. The characteristics of a pogrom vary widely, depending on the specific incident, at times leading to, or culminating in, massacres. Significant pogroms in the Russian Empire included the Odessa pogroms, Warsaw pogrom (1881), Kishinev pogrom (1903), Kiev pogrom (1905), and Białystok pogrom (1906). After the collapse of the Russian Empire in 1917, several pogroms occurred amidst the power struggles in Eastern Europe, including the Lwów pogrom (1918) and Kiev Pogroms (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Football Hooliganism
Football hooliganism, also known as soccer hooliganism, football rioting or soccer rioting, constitutes violence and other destructive behaviours perpetrated by spectators at association football events. Football hooliganism normally involves conflict between gangs, in English known as football List of hooligan firms, firms (derived from the British slang for a criminal gang), formed to intimidate and attack supporters of other teams. Other English-language terms commonly used in connection with hooligan firms include "army", "boys", "bods", "Casual (subculture), casuals", and "crew". Certain clubs have long-standing rivalries with other clubs and hooliganism associated with matches between them (sometimes called local derby, local derbies) is likely to be more severe. Conflict may take place before, during or after matches. Participants often select locations away from stadiums to avoid arrest by the police, but conflict can also erupt spontaneously inside the stadium or in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tear Gas
Tear gas, also known as a lachrymator agent or lachrymator (), sometimes colloquially known as "mace" after the early commercial aerosol, is a chemical weapon that stimulates the nerves of the lacrimal gland in the eye to produce tears. In addition, it can cause severe eye and respiratory pain, skin irritation, bleeding, and blindness. Common lachrymators both currently and formerly used as tear gas include pepper spray (OC gas), PAVA spray (nonivamide), CS gas, CR gas, CN gas (phenacyl chloride), bromoacetone, xylyl bromide and Mace (a branded mixture). While lachrymatory agents are commonly deployed for riot control by law enforcement and military personnel, its use in warfare is prohibited by various international treaties.E.g. the Geneva Protocol of 1925 prohibited the use of "asphyxiating gas, or any other kind of gas, liquids, substances or similar materials". During World War I, increasingly toxic and deadly lachrymatory agents were used. The short and long-term effec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Riot
Food riots may occur when there is a shortage and/or unequal distribution of food. Causes can be food price rises, harvest failures, incompetent food storage, transport problems, food speculation, hoarding, poisoning of food, or attacks by pests. Hence, the pathway between food related issues such as crop failure, price hike or volatility and an actual “riot” is often complex. Some argue that volatile and high food price are just part of a “perfect storm” combining with climate change, population growth, resource scarcity, and urbanization leading to social unrest. When the public becomes too desperate in such conditions, they may attack shops, farms, homes, or government buildings to attain bread or other staple foods such as grain or salt, as in the 1977 Egyptian bread riots. Often, it is more than an issue of hunger and the need to obtain bread for immediate caloric satisfaction; food riots are part of a larger social movement, such as the Russian revolution or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CS Gas
The compound 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile (also called ''o''-chlorobenzylidene malononitrile; chemical formula: C10H5ClN2), a cyanocarbon, is the defining component of tear gas commonly referred to as CS gas, which is used as a riot control agent. Exposure causes a burning sensation and tearing of the eyes to the extent that the subject cannot keep their eyes open, and a burning irritation of the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and throat, resulting in profuse coughing, nasal mucus discharge, disorientation, and difficulty breathing, partially incapacitating the subject. CS gas is an aerosol of a volatile solvent (a substance that dissolves other active substances and that easily evaporates) and 2-chlorobenzalmalononitrile, which is a solid compound at room temperature. CS gas is generally accepted as being non-lethal. It was first synthesized by two Americans, Ben Corson and Roger Stoughton, at Middlebury College in 1928, and the chemical's name is derived from the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Disorder
Civil disorder, also known as civil disturbance, civil unrest, or social unrest is a situation arising from a mass act of civil disobedience (such as a demonstration, riot, strike, or unlawful assembly) in which law enforcement has difficulty maintaining their authority. Engagement According to the U.S. Code, a person is engaged in civil disorder if they - Causes Any number of things may cause civil disorder, whether it is a single cause or a combination of causes; however, most are born from political grievances, economic disparities, social discord, but historically have been the result of long-standing oppression by a group of people towards another. Civil disorder arising from political grievances can include a range of events, from a simple protest to a mass civil disobedience. These events can be spontaneous, but can also be planned. These events can turn violent when agitators and law enforcers overreact. Civil disorder has in history arisen from economic dispu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herd Behavior
Herd behavior is the behavior of individuals in a group acting collectively without centralized direction. Herd behavior occurs in animals in herds, packs, bird flocks, fish schools and so on, as well as in humans. Voting, demonstrations, riots, general strikes, sporting events, religious gatherings, everyday decision-making, judgement and opinion-forming, are all forms of human-based herd behavior. Raafat, Chater and Frith proposed an integrated approach to herding, describing two key issues, the mechanisms of transmission of thoughts or behavior between individuals and the patterns of connections between them. They suggested that bringing together diverse theoretical approaches of herding behavior illuminates the applicability of the concept to many domains, ranging from cognitive neuroscience to economics. Animal behavior A group of animals fleeing from a predator shows the nature of herd behavior, for example in 1971, in the oft cited article "Geometry For The Selfish H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mob Mentality
Herd mentality, mob mentality or pack mentality describes how people can be influenced by their peers to adopt certain behaviors on a largely emotional, rather than rational, basis. When individuals are affected by mob mentality, they may make different decisions than they would have individually. Social psychologists study the related topics of group intelligence, crowd wisdom, groupthink, and deindividuation. History The idea of a " group mind" or "mob behavior" was first put forward by 19th-century social psychologists Gabriel Tarde and Gustave Le Bon. Herd behavior in human societies has also been studied by Sigmund Freud and Wilfred Trotter, whose book ''Instincts of the Herd in Peace and War'' is a classic in the field of social psychology. Sociologist and economist Thorstein Veblen's ''The Theory of the Leisure Class'' illustrates how individuals imitate other group members of higher social status in their consumer behavior. More recently, Malcolm Gladwell in ''The Tip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxation
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal person, legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or national), and tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behaviour aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax reliefs. The first known taxation took place in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. A failure to pay in a timely manner (Tax noncompliance, non-compliance), along with evasion of or resistance to taxation, is punishable by law. Taxes consist of direct tax, direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as its labor equivalent. Most countries have a tax system in place, in order to pay for public, common societal, or agreed national needs and for the functions of government. Some levy a flat tax, flat percentag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Less-than-lethal
Non-lethal weapons, also called nonlethal weapons, less-lethal weapons, less-than-lethal weapons, non-deadly weapons, compliance weapons, or pain-inducing weapons are weapons intended to be less likely to kill a living target than conventional weapons such as knives and firearms with live ammunition. It is often understood that unintended or incidental casualties are risked wherever force is applied, but non-lethal weapons try to minimise the risk of casualties (e.g. serious/permanent injuries or death) as much as possible. Non-lethal weapons are used in policing and combat situations to limit the escalation of conflict where employment of lethal force is prohibited or undesirable, where rules of engagement require minimum casualties, or where policy restricts the use of conventional force. These weapons occasionally cause serious injuries or death; the term "less-lethal" has been preferred by some organizations as it describes the risks of death more accurately than the term "n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)