Caval opening on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
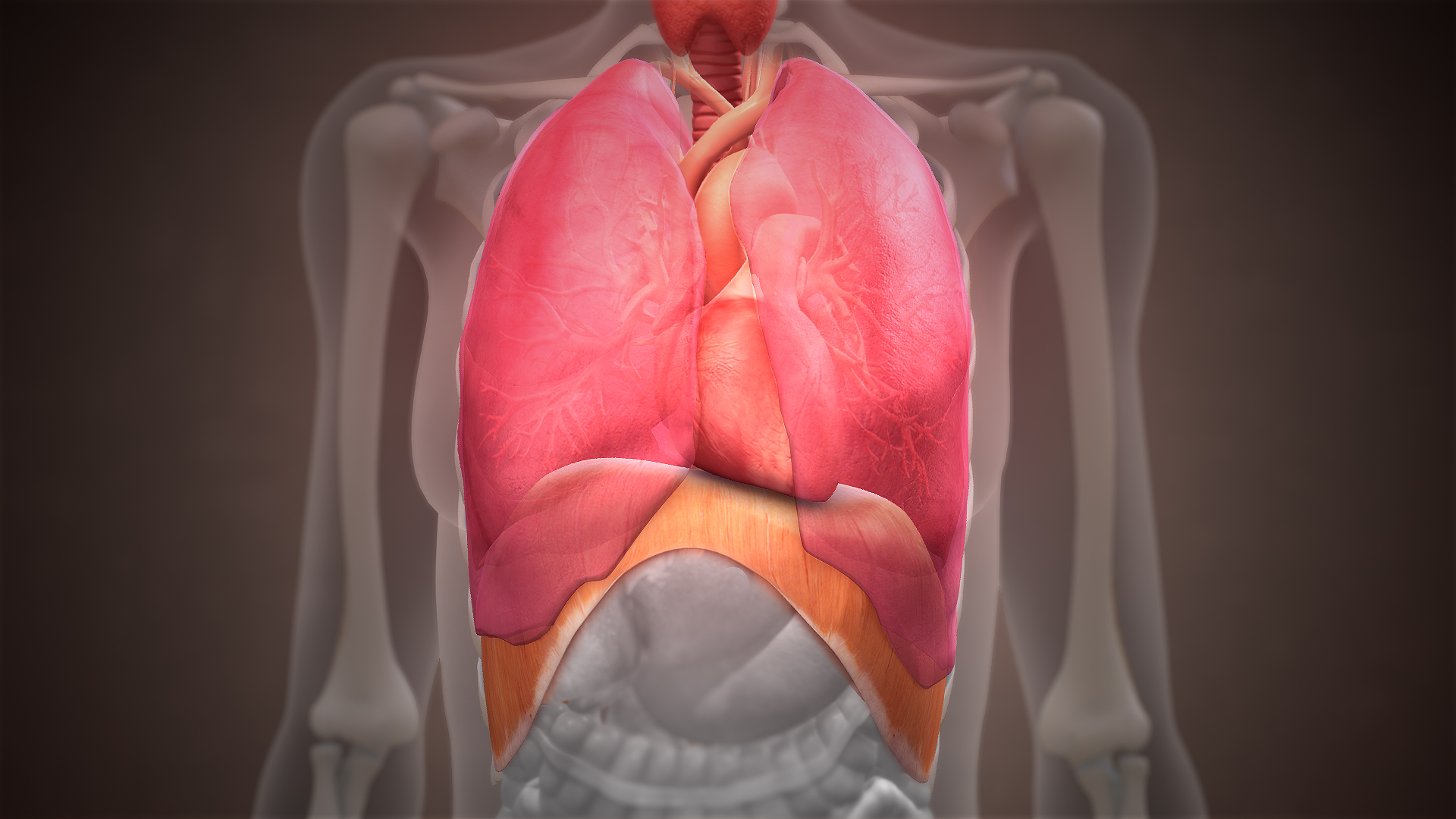 The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in
 The diaphragm is an upward curved, c-shaped structure of muscle and
The diaphragm is an upward curved, c-shaped structure of muscle and
 There are a number of openings in the diaphragm through which structures pass between the thorax and abdomen. There are three large openings — one for the
There are a number of openings in the diaphragm through which structures pass between the thorax and abdomen. There are three large openings — one for the
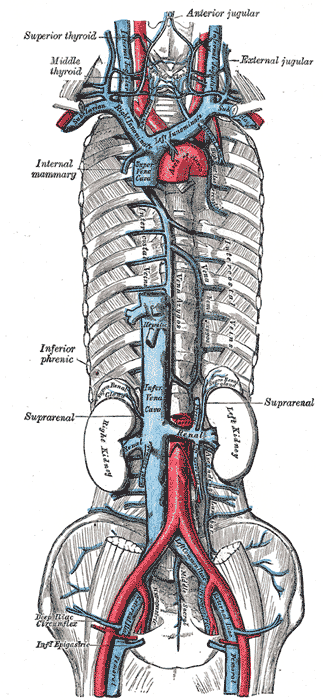 Arteries and veins above and below the diaphragm supply and drain blood.
From above, the diaphragm receives blood from branches of the internal thoracic arteries, namely the pericardiacophrenic artery and
Arteries and veins above and below the diaphragm supply and drain blood.
From above, the diaphragm receives blood from branches of the internal thoracic arteries, namely the pericardiacophrenic artery and
 The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, cultu ...
s and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: ...
present; more than in any other skeletal muscle.
The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona (Latin: ''Gerardus Cremonensis''; c. 1114 – 1187) was an Italian translator of scientific books from Arabic into Latin. He worked in Toledo, Kingdom of Castile and obtained the Arabic books in the libraries at Toledo. Some of ...
, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm
Older texts have asserted the existence of a urogenital diaphragm, also called the triangular ligament, which was described as a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, lying between the inferior fascia of ...
or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver rests beneath the right half of the diaphragm. There is also speculation that the diaphragm is lower on the other side due to heart's presence.
Other mammals have diaphragms, and other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
s such as amphibians and reptiles have diaphragm-like structures, but important details of the anatomy may vary, such as the position of the lungs in the thoracic cavity.
Structure
 The diaphragm is an upward curved, c-shaped structure of muscle and
The diaphragm is an upward curved, c-shaped structure of muscle and fibrous tissue
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
that separates the thoracic cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There ...
from the abdomen. The superior surface of the dome forms the floor of the thoracic cavity, and the inferior surface the roof of the abdominal cavity.
As a dome, the diaphragm has peripheral attachments to structures that make up the abdominal and chest walls. The muscle fibres from these attachments converge in a central tendon, which forms the crest of the dome. Its peripheral part consists of muscular fibers that take origin from the circumference of the inferior thoracic aperture
The superior thoracic aperture, also known as the thoracic outlet, or thoracic inlet refers to the opening at the top of the thoracic cavity. It is also clinically referred to as the thoracic outlet, in the case of thoracic outlet syndrome. A low ...
and converge to be inserted into a central tendon.
The muscle fibres of the diaphragm emerge from many surrounding structures and can be divided into vertebral, costal, sternal, and central tendon.
The vertebral part of the diaphragram arises from the crura and arcuate ligaments. Right crus arises from L1-L3 vertebral bodies and their intervertebral discs. Smaller left crus arises from L1, L2 vertebral bodies and their intervertebral discs. Medial arcuate ligament arises from the fascia thickening from body of L2 vertebrae to transverse process of L1 vertebrae, crossing over the body of the psoas major
The psoas major ( or ; from grc, ψόᾱ, psóā, muscles of the loins) is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliop ...
muscle. The lateral arcuate ligament arises from the transverse process of L1 vertebrae and is attached laterally to the 12th rib. The lateral arcuate ligament also arises from fascia thickening that covers the quadratus lumborum muscle. The median arcuate ligament
The median arcuate ligament is a ligament under the diaphragm that connects the right and left crura of diaphragm.
Structure
The median arcuate ligament is formed by the right and left crura of the diaphragm. The crura connect to form an arch, ...
arises from the fibrous parts of right and left crura where descending thoracic aorta passes behind it. No diaphramatic muscle arises from the median arcuate ligament. Both adrenal glands lie the near diaphragmatic crus and arcuate ligament.
The costal part of diaphragm arises from the lower four ribs (7 to 10) costal cartilages.
The central tendon of the diaphragm is a thin but strong aponeurosis near the center of the vault formed by the muscle, closer to the front than to the back of the thorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
. The central part of the tendon is attached above to pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made o ...
. The both sides of the posterior fibres are attached to paracolic gutters (the curving of ribs before attaching to both sides of the vertebral bodies).
Openings
 There are a number of openings in the diaphragm through which structures pass between the thorax and abdomen. There are three large openings — one for the
There are a number of openings in the diaphragm through which structures pass between the thorax and abdomen. There are three large openings — one for the aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
, one for the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
, and one for the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of th ...
(the caval opening), plus a series of smaller ones.
The inferior vena cava passes through the caval opening, a quadrilateral opening at the junction of the right and middle leaflets of the central tendon, so that its margins are tendinous. Surrounded by tendons, the opening is stretched open every time inspiration occurs. However, there has been argument that the caval opening actually constricts during inspiration. Since thoracic pressure decreases upon inspiration and draws the caval blood upwards toward the right atrium, increasing the size of the opening allows more blood to return to the heart, maximizing the efficacy of lowered thoracic pressure returning blood to the heart. The aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes o ...
does not pierce the diaphragm but rather passes behind it in between the left and right crus.
There are several structures that pierced through the diaphragm, including: left phrenic nerve pierce through the central tendon, greater, lesser, and least thoracic splanchnic nerves pierced through bilateral crura, and lymphatic vessels that pierced throughout the diaphragam, especially behind the diaphragm.
Nerve supply
The diaphragm is primarily innervated by the phrenic nerve which is formed from thecervical nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the ...
C3, C4 and C5. While the central portion of the diaphragm sends sensory afferents via the phrenic nerve, the peripheral portions of the diaphragm send sensory afferents via the intercostal (T5–T11) and subcostal nerves (T12).
Blood supply
 Arteries and veins above and below the diaphragm supply and drain blood.
From above, the diaphragm receives blood from branches of the internal thoracic arteries, namely the pericardiacophrenic artery and
Arteries and veins above and below the diaphragm supply and drain blood.
From above, the diaphragm receives blood from branches of the internal thoracic arteries, namely the pericardiacophrenic artery and musculophrenic artery
The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. The highest intercostal artery (supreme intercostal artery or superior intercostal artery) is an artery in the human ...
; from the superior phrenic arteries
The superior phrenic arteries are small and arise from the lower part of the thoracic aorta. They are distributed to the posterior part of the upper surface of the diaphragm, and anastomose with the musculophrenic and pericardiacophrenic arteries.
...
, which arise directly from the thoracic aorta
The descending thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic ...
; and from the lower internal intercostal arteries. From below, the inferior phrenic arteries
The inferior phrenic arteries are two small vessels which supply the diaphragm. They present much variety in their origin.
Structure
Origin
The inferior phrenic arteries usually arise between T12 and L2 vertebrae. They may arise separately ...
supply the diaphragm.
The diaphragm drains blood into the brachiocephalic vein
The left and right brachiocephalic veins (previously called innominate veins) are major veins in the upper chest, formed by the union of each corresponding internal jugular vein and subclavian vein. This is at the level of the sternoclavicular j ...
s, azygos vein
The azygos vein is a vein running up the right side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava. It connects the systems of superior vena cava and inferior vena cava and can provide an alternative path for blo ...
s, and veins that drain into the inferior vena cava
The inferior vena cava is a large vein that carries the deoxygenated blood from the lower and middle body into the right atrium of the heart. It is formed by the joining of the right and the left common iliac veins, usually at the level of th ...
and left suprarenal vein.
Variation
The sternal portion of the muscle is sometimes wanting and more rarely defects occur in the lateral part of the central tendon or adjoining muscle fibers.Development
The thoracic diaphragm develops during embryogenesis, beginning in the third week after fertilization with two processes known as transverse folding and longitudinal folding. Theseptum transversum
The septum transversum is a thick mass of cranial mesenchyme, formed in the embryo, that gives rise to parts of the thoracic diaphragm and the ventral mesentery of the foregut in the developed human being and other mammals.
Origins
The septum ...
, the primitive central tendon of the diaphragm, originates at the rostral pole of the embryo and is relocated during longitudinal folding to the ventral thoracic region. Transverse folding brings the body wall anteriorly to enclose the gut and body cavities. The pleuroperitoneal membrane and body wall myoblasts, from somatic lateral plate mesoderm, meet the septum transversum to close off the pericardio-peritoneal canals on either side of the presumptive esophagus, forming a barrier that separates the peritoneal and pleuropericardial cavities. Furthermore, dorsal mesenchyme surrounding the presumptive esophagus form the muscular crura of the diaphragm.
Because the earliest element of the embryological diaphragm, the septum transversum, forms in the cervical region, the phrenic nerve that innervates the diaphragm originates from the cervical spinal cord (C3,4, and 5). As the septum transversum descends inferiorly, the phrenic nerve follows, accounting for its circuitous route from the upper cervical vertebrae, around the pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made o ...
, finally to innervate the diaphragm.
Function
The diaphragm is the main muscle of respiration and functions in breathing. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves in the inferior direction, enlarging the volume of the thoracic cavity and reducing intra-thoracic pressure (the external intercostal muscles also participate in this enlargement), forcing the lungs to expand. In other words, the diaphragm's movement downwards creates a partialvacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
in the thoracic cavity, which forces the lungs to expand to fill the void, drawing air in the process.
Cavity expansion happens in two extremes, along with intermediary forms. When the lower ribs are stabilized and the central tendon of the diaphragm is mobile, a contraction brings the insertion (central tendon) towards the origins and pushes the lower cavity towards the pelvis, allowing the thoracic cavity to expand downward. This is often called belly breathing. When the central tendon is stabilized and the lower ribs are mobile, a contraction lifts the origins (ribs) up towards the insertion (central tendon) which works in conjunction with other muscles to allow the ribs to slide and the thoracic cavity to expand laterally and upwards.
When the diaphragm relaxes (moves in the superior direction), air is exhaled by elastic recoil process of the lung and the tissues lining the thoracic cavity. Assisting this function with muscular effort (called forced exhalation
Exhalation (or expiration) is the flow of the breath out of an organism. In animals, it is the movement of air from the lungs out of the airways, to the external environment during breathing.
This happens due to elastic properties of the lungs, ...
) involves the internal intercostal muscles used in conjunction with the abdominal muscles, which act as an antagonist paired with the diaphragm's contraction.
The diaphragm is also involved in non-respiratory functions. It helps to expel vomit
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenterit ...
, feces, and urine
Urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in humans and in many other animals. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder. Urination results in urine being excreted from the body through the urethra.
Cellular ...
from the body by increasing intra-abdominal pressure, aids in childbirth, and prevents acid reflux by exerting pressure on the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
as it passes through the esophageal hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass.
Structure
It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine ...
.
In some non-human animals, the diaphragm is not crucial for breathing; a cow, for instance, can survive fairly asymptomatically with diaphragmatic paralysis as long as no massive aerobic metabolic demands are made of it.
Clinical significance
Paralysis
If either the phrenic nerve,cervical spine
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sau ...
or brainstem is damaged, this will sever the nervous supply to the diaphragm. The most common damage to the phrenic nerve is by bronchial cancer, which usually only affects one side of the diaphragm. Other causes include Guillain–Barré syndrome
Guillain–Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rapid-onset muscle weakness caused by the immune system damaging the peripheral nervous system. Typically, both sides of the body are involved, and the initial symptoms are changes in sensation or pain oft ...
and systemic lupus erythematosus.
Herniation
Ahiatus hernia
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs (typically the stomach) slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryngoph ...
is a hernia
A hernia is the abnormal exit of tissue or an organ, such as the bowel, through the wall of the cavity in which it normally resides. Various types of hernias can occur, most commonly involving the abdomen, and specifically the groin. Groin herni ...
common in adults in which parts of the lower esophagus or stomach that are normally in the abdomen pass/bulge abnormally through the diaphragm and are present in the thorax. Hernias are described as ''rolling'', in which the hernia is beside the oesophagus, or ''sliding'', in which the hernia directly involves the esophagus. These hernias are implicated in the development of reflux, as the different pressures between the thorax and abdomen normally act to keep pressure on the esophageal hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass.
Structure
It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine ...
. With herniation, this pressure is no longer present, and the angle between the cardia of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and the oesophagus disappear. Not all hiatus hernias cause symptoms however, although almost all people with Barrett's oesophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet ce ...
or oesophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stomach; ...
have a hiatus hernia.
Hernias may also occur as a result of congenital malformation, a congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a birth defect of the diaphragm. The most common type of CDH is a Bochdalek hernia; other types include Morgagni hernia, diaphragm eventration and central tendon defects of the diaphragm. Malformation of ...
. When the pleuroperitoneal membranes fail to fuse, the diaphragm does not act as an effective barrier between the abdomen and thorax. Herniation is usually of the left, and commonly through the posterior lumbocostal triangle, although rarely through the anterior foramen of Morgagni. The contents of the abdomen, including the intestines, may be present in the thorax, which may impact development of the growing lungs and lead to hypoplasia. This condition is present in 0.8 - 5/10,000 births. A large herniation has high mortality rate, and requires immediate surgical repair.
Imaging
Due to its position separating thethorax
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the cre ...
and abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
, fluid abnormally present in the thorax, or air abnormally present in the abdomen, may collect on one side of the diaphragm. An X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
may reveal this. Pleural effusion
A pleural effusion is accumulation of excessive fluid in the pleural space, the potential space that surrounds each lung.
Under normal conditions, pleural fluid is secreted by the parietal pleural capillaries at a rate of 0.6 millilitre per k ...
, in which there is fluid abnormally present between the two pleurae
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls.
The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips be ...
of the lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side ...
, is detected by an X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
of the chest, showing fluid collecting in the angle between the ribs and diaphragm. An X-ray may also be used to reveal a pneumoperitoneum
Pneumoperitoneum is pneumatosis (abnormal presence of air or other gas) in the peritoneal cavity, a potential space within the abdominal cavity. The most common cause is a perforated abdominal organ, generally from a perforated peptic ulcer, al ...
, in which there is gas in the abdomen.
An X-ray may also be used to check for herniation.
Significance in strength training
The adoption of a deeper breathing pattern typically occurs during physical exercise in order to facilitate greater oxygen absorption. During this process the diaphragm more consistently adopts a lower position within the body's core. In addition to its primary role in breathing, the diaphragm also plays a secondary role in strengthening the posture of the core. This is especially evident during deep breathing where its generally lower position increases intra-abdominal pressure, which serves to strengthen the lumbar spine.The key to real core stabilization is to maintain the increased IAP while going through normal breathing cycles. ..The diaphragm then performs its breathing function at a lower position to facilitate a higher IAP.Therefore, if a person's diaphragm position is lower in general, through deep breathing, then this assists the strengthening of their core during that period. This can be an aid in strength training and other forms of athletic endeavour. For this reason, taking a deep breath or adopting a deeper breathing pattern is typically recommended when lifting heavy weights.
Other animals
The existence of a membrane separating the pharynx from the stomach can be traced widely among thechordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These fi ...
s. Thus the model organism, the marine chordate lancelet
The lancelets ( or ), also known as amphioxi (singular: amphioxus ), consist of some 30 to 35 species of "fish-like" benthic filter feeding chordates in the order Amphioxiformes. They are the modern representatives of the subphylum Cephalochord ...
, possesses an atriopore by which water exits the pharynx, which has been claimed (and disputed) to be homologous to structures in ascidian
Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians, tunicates (in part), and sea squirts (in part), is a polyphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" m ...
s and hagfish
Hagfish, of the class Myxini (also known as Hyperotreti) and order Myxiniformes , are eel-shaped, slime-producing marine fish (occasionally called slime eels). They are the only known living animals that have a skull but no vertebral column, ...
es. The tunicate
A tunicate is a marine invertebrate animal, a member of the subphylum Tunicata (). It is part of the Chordata, a phylum which includes all animals with dorsal nerve cords and notochords (including vertebrates). The subphylum was at one time ...
epicardium separates digestive organs from the pharynx and heart, but the anus returns to the upper compartment to discharge wastes through an outgoing siphon.
Thus the diaphragm emerges in the context of a body plan that separated an upper feeding compartment from a lower digestive tract, but the point at which it originates is a matter of definition. Structures in fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds have been called diaphragms, but it has been argued that these structures are not homologous. For instance, the alligator diaphragmaticus muscle does not insert on the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to ...
and does not affect pressure of the lower esophageal sphincter. The lungs are located in the abdominal compartment of amphibians and reptiles, so that contraction of the diaphragm expels air from the lungs rather than drawing it into them. In birds and mammals, lungs are located above the diaphragm. The presence of an exceptionally well-preserved fossil of ''Sinosauropteryx
''Sinosauropteryx'' (meaning "Chinese reptilian wing", ) is a compsognathid dinosaur. Described in 1996, it was the first dinosaur taxon outside of Avialae (birds and their immediate relatives) to be found with evidence of feathers. It was cover ...
'', with lungs located beneath the diaphragm as in crocodiles, has been used to argue that dinosaurs could not have sustained an active warm-blooded physiology, or that birds could not have evolved from dinosaurs. An explanation for this (put forward in 1905), is that lungs originated beneath the diaphragm, but as the demands for respiration increased in warm-blooded birds and mammals, natural selection came to favor the parallel evolution
Parallel evolution is the similar development of a trait in distinct species that are not closely related, but share a similar original trait in response to similar evolutionary pressure.Zhang, J. and Kumar, S. 1997Detection of convergent and paral ...
of the herniation of the lungs from the abdominal cavity in both lineages.
However, birds do not have diaphragms. They do not breathe in the same way as mammals and do not rely on creating a negative pressure in the thoracic cavity, at least not to the same extent. They rely on a rocking motion of the keel of the sternum to create local areas of reduced pressure to supply thin, membranous airsacs cranially and caudally to the fixed-volume, non-expansive lungs. A complicated system of valves and air sacs cycles air constantly over the absorption surfaces of the lungs so allowing maximal efficiency of gaseous exchange. Thus, birds do not have the reciprocal tidal breathing flow of mammals. On careful dissection, around eight air sacs can be clearly seen. They extend quite far caudally into the abdomen.Dyce, Sack and Wensing in ''Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy''; 2002 (3rd Edn); Saunders, Philiadelphia
See also
*Diaphragmatic breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, abdominal breathing, belly breathing, or deep breathing, is breathing that is done by contracting the diaphragm, a muscle located horizontally between the thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Air enters the lungs as ...
References
External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Thoracic Diaphragm Diaphragm Muscles of the torso Articles containing video clips