Caterham CSR260 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Caterham () is a town in the Tandridge District of
created by
 From 1877
From 1877
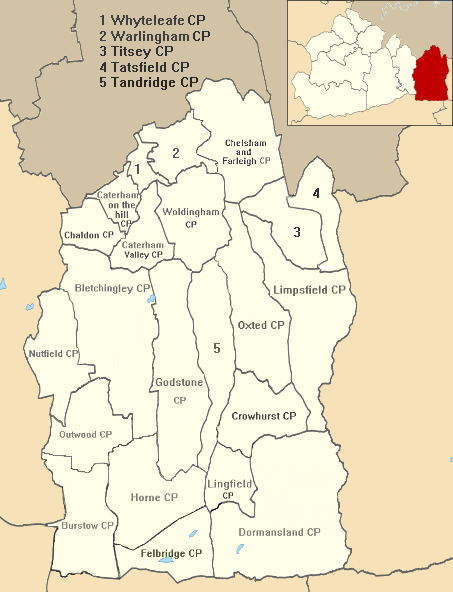 There are three tiers of local government in Caterham, at parish, district, and county level. The town is split between two civil parishes: Caterham on the Hill covering the older hilltop village, and Caterham Valley covering the newer town which grew up around Caterham railway station at the foot of the hill. Both parishes are within Tandridge District, which is based in
There are three tiers of local government in Caterham, at parish, district, and county level. The town is split between two civil parishes: Caterham on the Hill covering the older hilltop village, and Caterham Valley covering the newer town which grew up around Caterham railway station at the foot of the hill. Both parishes are within Tandridge District, which is based in
 The ancient parish of Caterham was part of the
The ancient parish of Caterham was part of the
Caterham Valley For You
Caterham Police Station, operated by Surrey Police is located in the middle of the valley; the local St John Ambulance unit shares the building.
 Caterham on the Hill is the second of the two civil parishes. This clustered development or village is directly to the northwest of the other entire Valley part of the town and does not have steep slopes or a wide divide between upland and downland developments unlike Caterham Valley. It has a population of 11,555; it was the original development in the area so has more
Caterham on the Hill is the second of the two civil parishes. This clustered development or village is directly to the northwest of the other entire Valley part of the town and does not have steep slopes or a wide divide between upland and downland developments unlike Caterham Valley. It has a population of 11,555; it was the original development in the area so has more

Surrey
Surrey () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South East England, bordering Greater London to the south west. Surrey has a large rural area, and several significant urban areas which form part of the Greater London Built-up Area. ...
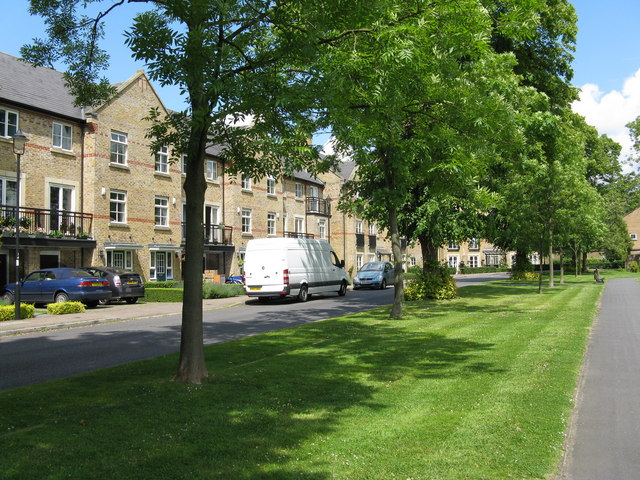
, England. The town is administratively divided into two: Caterham on the Hill, and Caterham Valley, which includes the main town centre in the middle of a dry valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock.
There ...
but rises to equal heights to the south. The town lies close to the A22, from Guildford
Guildford ()
is a town in west Surrey, around southwest of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildf ...
and south of Croydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensi ...
, in an upper valley cleft into the dip slope of the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and ...
. Caterham on the Hill is above the valley to the west.
History
An encampment on the top of White Hill, in Caterham Valley south of Caterham School, between Bletchingley and the town centre is called ''The Cardinal's Cap'' which was excavated and inspected in designating it a Scheduled Ancient Monument. With close ramparts forming two or more lines,archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
s describe the fort as a "large multivallate
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roma ...
hillfort at War Coppice Camp".
The town lies within the Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
division of Tandridge
Tandridge is a village and civil parish in the Tandridge District, in the county of Surrey, England. Its nucleus is on a rise of the Greensand Ridge between Oxted and Godstone. It includes, towards its middle one named sub-locality (hamlet), ...
hundred.
Post Norman Conquest
Caterham's church of St Lawrence is ofNorman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
construction and retains a rector as its incumbent
The incumbent is the current holder of an official, office or position, usually in relation to an election. In an election for president, the incumbent is the person holding or acting in the office of president before the election, whether seek ...
. In the reign of King John King John may refer to:
Rulers
* John, King of England (1166–1216)
* John I of Jerusalem (c. 1170–1237)
* John Balliol, King of Scotland (c. 1249–1314)
* John I of France (15–20 November 1316)
* John II of France (1319–1364)
* John I o ...
, Roger son of Everard de Gaist gave this including its church lands to the monastery of Waltham Holy Cross
Waltham Abbey is a civil parish in Epping Forest District in Essex, England. Located approximately north-northeast of central London and adjacent to the Greater London boundary, it is a partly urbanised parish with large sections of open land ...
. Everard's grandfather was Geoffery of Caterham who gave land to his son in the 12th century. This monastery ran the glebe as a manor, receiving a grant of free warren in their demesne lands of Caterham in 1253; holding it until the dissolution of the monasteries.
Caterham's original village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred to ...
centre consisted in the nearest part of the ridge of Caterham on the Hill
Caterham () is a town in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. The town is administratively divided into two: Caterham on the Hill, and Caterham Valley, which includes the main town centre in the middle of a dry valley but rises to equal ...
to the railway station
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
in Caterham Valley
Caterham () is a town in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. The town is administratively divided into two: Caterham on the Hill, and Caterham Valley, which includes the main town centre in the middle of a dry valley but rises to equal ...
, including at the street ascending the relatively steep, short hill, Church Hill. Although no conservation area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
has been designated in either civil parish,Mapcreated by
Ordnance Survey
, nativename_a =
, nativename_r =
, logo = Ordnance Survey 2015 Logo.svg
, logo_width = 240px
, logo_caption =
, seal =
, seal_width =
, seal_caption =
, picture =
, picture_width =
, picture_caption =
, formed =
, preceding1 =
, di ...
, courtesy of English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, medieval castles, Roman forts and country houses.
The charity states that i ...
four secular buildings, including The King and Queen public house, three churches as well as a vault and tomb in St Lawrence's churchyard are listed; these are along Hill Street/ Church Hill in Caterham on the Hill.
The combined manors of Caterham, Porkele, Upwode, Gatiers and Halyngbury
Porkele had been formerly included in the manor given to Waltham Abbey; together the latter manors comprised .Humphrey Stafford, 1st Duke of Buckingham
Humphrey Stafford, 1st Duke of Buckingham, 6th Earl of Stafford, 7th Baron Stafford, (December 1402 – 10 July 1460) of Stafford Castle in Staffordshire, was an English nobleman and a military commander in the Hundred Years' War and the ...
(1402–1460) held these manors leaving them in 1458 to his third son John Stafford, 1st Earl of Wiltshire
John Stafford, 1st Earl of Wiltshire KG, KB (24 November 1427 – 8 May 1473) was an English nobleman, the youngest son of Humphrey Stafford, 1st Duke of Buckingham. In 1461 he was appointed Knight of the Order of the Bath.
Career
He fought o ...
when his son died without issue in 1499, under the terms of grant the elder branch, the following Duke of Buckingham inherited. His heirs sold them on the dissolution to Lord Berners
Gerald Hugh Tyrwhitt-Wilson, 14th Baron Berners (18 September 188319 April 1950), also known as Gerald Tyrwhitt, was a British composer, novelist, painter, and aesthete. He was also known as Lord Berners.
Biography
Early life and education
...
who died in debt in 1533 resulting in bona vacantia and seizure by the Crown. In 1570 Thomas Sackville, 1st Earl of Dorset
Thomas Sackville, 1st Earl of Dorset (153619 April 1608) was an English statesman, poet, and dramatist. He was the son of Richard Sackville, a cousin to Anne Boleyn. He was a Member of Parliament and Lord High Treasurer.
Biography Early life ...
(as Lord Buckhurst), later Lord High Treasurer
The post of Lord High Treasurer or Lord Treasurer was an English government position and has been a British government position since the Acts of Union of 1707. A holder of the post would be the third-highest-ranked Great Officer of State in ...
, held the 'manor of Caterham and Portele farm,' which he conveyed in that year to Henry Shelley; Sir Thomas's Sondes's widow leased the lands in 1599 to her half-brother, Main Plot seditionist Henry Brooke, 11th Baron Cobham
Henry Brooke, 11th Baron Cobham KG (22 November 1564 – 24 January 1618 (Old Style)/3 February 1618 (New Style), lord of the Manor of Cobham, Kent, was an English peer who was implicated in the Main Plot against the rule of James I of England. ...
. Then in 1615 her daughter Frances Leveson gave the rest of that lease, due the tenant's attainder to Sir Edward Barrett and Walter Barrett while the reversion was held by Sir Richard Sondes. George Ede purchased this massive estate in 1612 and it passed to Jasper Ockley in 1616. Sir Isaac Shard who was one of two Sheriffs of the City of London
Two sheriffs are elected annually for the City of London by the Liverymen of the City livery companies. Today's sheriffs have only nominal duties, but the historical officeholders had important judicial responsibilities. They have attended the ju ...
in 1730 who conveyed it to Thomas Clark and then passed as with the other manors; in 1911 W. L. Williams its owner lived at Portley in what remained of the estate. De Stafford School
de Stafford School is a mixed secondary school located in Caterham, Surrey, England. The school educates students from ages 11 to 16.
Organisation
de Stafford is close to the centre of the scattered town of Caterham, bordering on two sides ...
in Caterham on the Hill occupies a small part of the estate and is named after the earlier known owner. Adjoining Sunnydown School, state-run, is at what was Portley House and is for secondary education for boys with a Statement of Special Educational Needs.
The Manor of Salmons
The onlymanor
Manor may refer to:
Land ownership
*Manorialism or "manor system", the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of medieval Europe, notably England
*Lord of the manor, the owner of an agreed area of land (or "manor") under manorialism
*Man ...
did not have as high-profile owners. In 1339 John de Horne released some land in Caterham (and more in Warlingham) to Roger Salaman, who at his death in 1343 was "seised of a tenement". A manor of Salmons appears in 1605 by William Jordan, who soon afterwards acquired the second manor of Caterham (see above) with which Salmons afterwards descended. It was bought out of Chancery, into which it went on the death of Charles Day, by George Drew, who sold to members of the Horne family, who owned the relatively small estate in 1911.
Post Reformation
In 1544, the King granted the main rectorial manor was granted (infee
A fee is the price one pays as remuneration for rights or services. Fees usually allow for overhead, wages, costs, and markup. Traditionally, professionals in the United Kingdom (and previously the Republic of Ireland) receive a fee in contra ...
) to William Sackville JP In 1553 William Sackville and Eleanor passed the manor to Robert Hartopp, goldsmith of London, dying two years later succeeded by Elias his son, who was left it to his nephew John, whose widow Joan sold the manor in 1609 to George Evelyn who gave it to his son Sir John Evelyn
John Evelyn (31 October 162027 February 1706) was an English writer, landowner, gardener, courtier and minor government official, who is now best known as a diarist. He was a founding Fellow of the Royal Society.
John Evelyn's diary, or memo ...
on his marriage to Elizabeth Cocks. Later owners of the manor were Sir John's purchaser James Linch, his issue including Susan Hussey and her son James who sold the manor in 1699 to George Roffey. His nephew inherited it of the same name and in 1770 his sons sold the title alone and perhaps house to Matthew Robinson. Richard Hewetson bought it in 1780 passing it to his nephew Henry Hewetson holding until the Regency period. Henry's nephew William Hewetson ceased to lay claim to any manorial rights however in any event the lands had been separately sold to Henry Rowed, whose son Henry settled the estate on his wife Susan Glover in 1765. Their daughter Katherine Glover inherited these lands.
A second manor Manning and Bray report on was the main tenant's under the monastery and was held by for example buyers: William Jordan in 1607; Sir Isaac Shard (see above), who held his first court in 1726; after 1825 Charles Day of the firm of Day & Martin held but leaving no clear heirs this estate ended up in the hands of the chancery. Taxing (costs) judge George Henry Drew held the main lands and title followed by W. L. Williams in 1911.
Post Industrial Revolution
Under Rev. James Legrew in the early 19th century the churchtithe
A tithe (; from Old English: ''teogoþa'' "tenth") is a one-tenth part of something, paid as a contribution to a religious organization or compulsory tax to government. Today, tithes are normally voluntary and paid in cash or cheques or more r ...
s were commuted for £400, retaining a glebe of .
In 1840 Caterham contained a total of 477 residents (figures taken from that census, compiled in an 1848 topographical encyclopedia) and in 1848 of its were common land
Common land is land owned by a person or collectively by a number of persons, over which other persons have certain common rights, such as to allow their livestock to graze upon it, to collect Wood fuel, wood, or to cut turf for fuel.
A person ...
. Similar to today, mostly steeper acres were woodland.
The more modern locality of Caterham Valley in a wide dry valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock.
There ...
opening to the north (to Warlingham) and along its slopes is a product of the Victorian age and the coming of the Caterham railway line in 1856, which is still a terminus.
Victorian expansion of the town required the building of a much larger parish church, leading to the Church of St Mary the Virgin's building in 1866, directly across the road from St Lawrence's. As it also grew Caterham Valley gained its own Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
church, to St. John the Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης, Iōánnēs; Aramaic: ܝܘܚܢܢ; Ge'ez: ዮሐንስ; ar, يوحنا الإنجيلي, la, Ioannes, he, יוחנן cop, ⲓⲱⲁⲛⲛⲏⲥ or ⲓⲱ̅ⲁ) is the name traditionally given t ...
, which was consecrated in 1882.
 From 1877
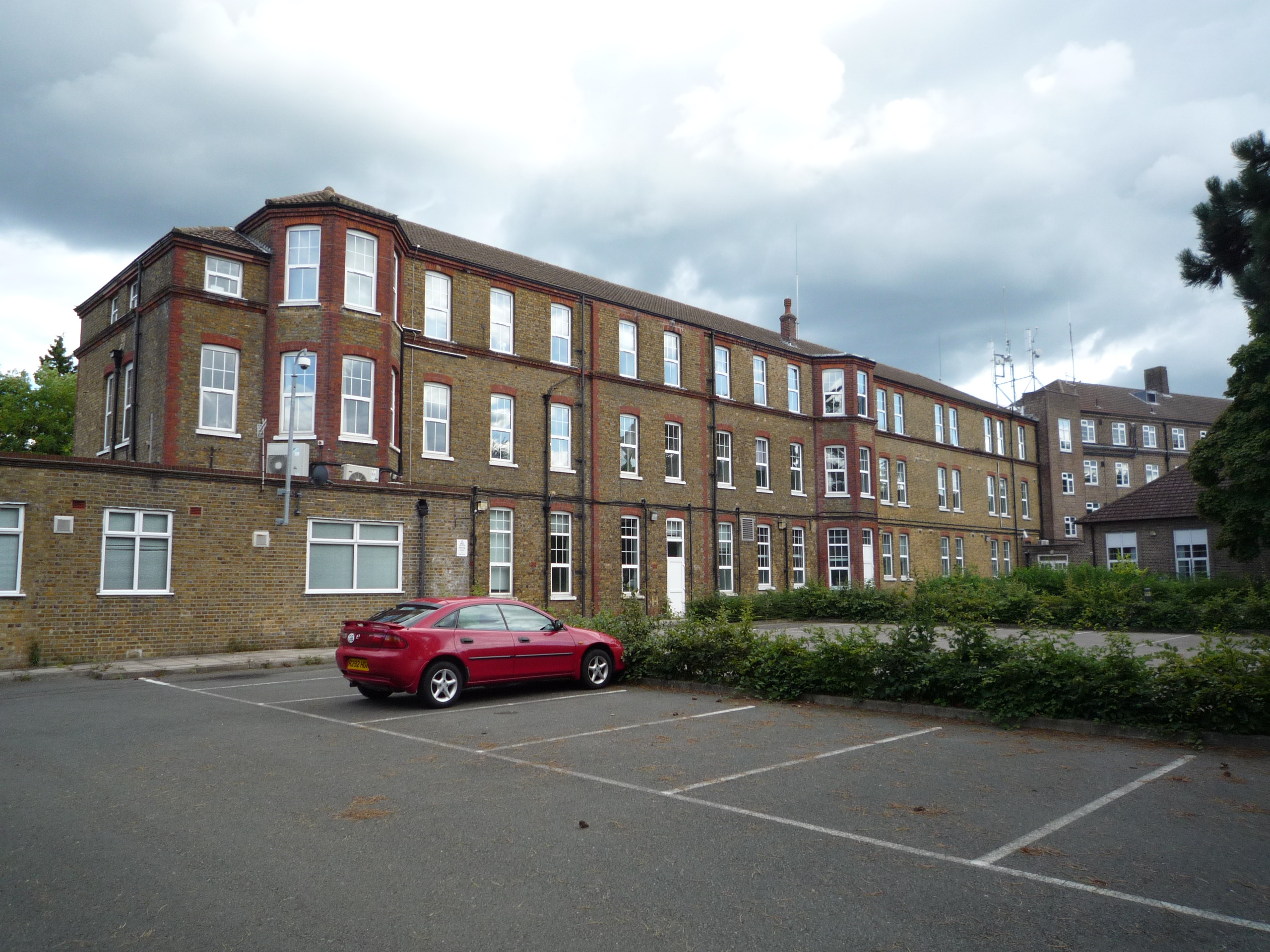
From 1877 Caterham Barracks
Caterham Barracks was a military installation in Caterham, Surrey.
History
The barracks were built as a Regimental depot, depot for the Foot Guards regiments in 1877. The construction reflected a more humane style of barrack design in the afterma ...
on the hill was a depot for the footguards regiments. The barracks were closed in 1995 and the site was redeveloped for housing.
Two main streets (there is only one road called High Street – Caterham on the Hill) therefore serve two very close yet substantial and affluent communities (see demographics), one with the railway station and more modern buildings, one with more historic buildings as soon as the closest hill (to the northwest) is climbed from the heart of Caterham Valley. This set-up means that localism
Localism may refer to:
* Fiscal localism, ideology of keeping money in a local economy
* Local purchasing, a movement to buy local products and services
* Conflict in surf culture, between local residents and visitors for access to beaches with lar ...
is present in that the Godstone Road during the middle of the 20th century bypassed Caterham Valley staying high and using Tillingdown, along the east of Caterham Valley from St John's School to the Croydon Road roundabout, thereby removing A22 traffic, while businesses set up and thrived in the valley itself.
On 6 July 1974 PC John Schofield was shot and killed while on patrol in Caterham.
In 1975 an IRA
Ira or IRA may refer to:
*Ira (name), a Hebrew, Sanskrit, Russian or Finnish language personal name
*Ira (surname), a rare Estonian and some other language family name
*Iran, UNDP code IRA
Law
*Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, US, on status of ...
bomb exploded in the Caterham Arms public house injuring 10 off-duty soldiers and 23 civilians. The pub was popular with the Welsh Guards, who had recently returned to Caterham Barracks after serving in Northern Ireland. The men responsible for the bombing were later jailed for a string of murders and bombings; they were released in April 1999 following the Good Friday Agreement.
Local government
 There are three tiers of local government in Caterham, at parish, district, and county level. The town is split between two civil parishes: Caterham on the Hill covering the older hilltop village, and Caterham Valley covering the newer town which grew up around Caterham railway station at the foot of the hill. Both parishes are within Tandridge District, which is based in
There are three tiers of local government in Caterham, at parish, district, and county level. The town is split between two civil parishes: Caterham on the Hill covering the older hilltop village, and Caterham Valley covering the newer town which grew up around Caterham railway station at the foot of the hill. Both parishes are within Tandridge District, which is based in Oxted
Oxted is a town and civil parish in the Tandridge district of Surrey, England, at the foot of the North Downs. It is south south-east of Croydon in Greater London, west of Sevenoaks in Kent, and north of East Grinstead in West Sussex.
Oxte ...
, whilst county-level services are provided by Surrey County Council, based in Reigate.
Surrey County Council has two councillors from Caterham.
Caterham has ten representatives on Tandridge District Council:
Caterham has two civil parish councils: Caterham on the Hill and Caterham Valley. Caterham Valley parish has two wards
Ward may refer to:
Division or unit
* Hospital ward, a hospital division, floor, or room set aside for a particular class or group of patients, for example the psychiatric ward
* Prison ward, a division of a penal institution such as a priso ...
, Harestone and Caterham Valley, each electing three elected parish councillors. The parish council clerk is Maureen Gibbins. Caterham on the Hill has three wards, Portley, Queen's Park and Westway, each electing three parish councillors. The parish council clerk is Helen Broughton.
Administrative history
 The ancient parish of Caterham was part of the
The ancient parish of Caterham was part of the Tandridge Hundred
Tandridge Hundred was a hundred in Surrey, England. It comprised areas in the Tandridge District, the easternmost part of the county, bordering Kent, West Sussex and the 1965-created county of Greater London.
Composition
It included the parishes ...
. The parish was included in the Godstone
Godstone is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Surrey, England, east of Reigate at the junction of the A22 road, A22 and A25 road, A25 roads, near the M25 motorway and the North Downs. Godstone railway station is separate ...
Poor Law Union in 1835. When parish and district councils were established in 1894 under the Local Government Act 1894
The Local Government Act 1894 (56 & 57 Vict. c. 73) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales outside the County of London. The Act followed the reforms carried out at county level un ...
, Caterham was given a parish council, which was subordinate to the Godstone Rural District
Godstone Rural District was a rural district in Surrey, England from 1894 to 1974, covering an area in the south-east of the county.
Origins
The district had its origins in the Godstone Poor Law Union, which had been created in 1835, covering ...
Council. Less than five years later, the parish of Caterham was removed from Godstone Rural District, becoming its own urban district
Urban district may refer to:
* District
* Urban area
* Quarter (urban subdivision)
* Neighbourhood
Specific subdivisions in some countries:
* Urban districts of Denmark
* Urban districts of Germany
* Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland) (hist ...
on 1 April 1899, with the Caterham Parish Council being replaced with Caterham Urban District Council. Caterham Urban District Council held its first meeting on 17 April 1899 at the Masonic Hall, when William Garland Soper was appointed the first chairman of the council, having previously been chairman of the short-lived parish council.
In 1911 Caterham Urban District Council built itself a public hall and office building called Soper Hall, at 3 Harestone Valley Road, to serve as its headquarters. The building was named after William Garland Soper, the first chairman of the council, who had died in 1908. Of the building's £4,000 cost, £1,500 was donated by public subscription in memory of Soper. The building was formally opened in January 1912.
In 1929 the Caterham Urban District was enlarged by the addition of the neighbouring parish of Warlingham, and the district's name was changed to Caterham and Warlingham Urban District
Caterham and Warlingham was an Urban District of Surrey in England until 1974.
Geographic evolution
It was pre-emptively formed shortly before the major national 1933 reforms of boundaries and entities accordingly to take account of population c ...
. In 1933 the parishes of Chaldon and Woldingham were also added to the urban district. Caterham, Chaldon, Warlingham and Woldingham remained separate civil parishes, but as urban parishes they no longer had separate parish councils, with Caterham and Warlingham Urban District Council being the smallest representative body covering the whole urban district. Caterham and Warlingham Urban District Council continued to be based at Soper Hall, and also acquired a large house next door at 1 Harestone Hill to serve as additional office space.
Caterham and Warlingham Urban District was abolished under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, with the area merging with neighbouring Godstone Rural District to become Tandridge District on 1 April 1974. For its first few years Tandridge District Council used the offices of both its predecessor districts in Caterham and Oxted, until 1989 when it moved to new offices in Oxted on the site of the old Godstone Rural District Council's buildings. The new building in Oxted was funded by the sale of most of the old Caterham and Warlingham council's properties around 1 Harestone Hill to make way for part of a retail development called Church Walk, with only Soper Hall being retained.
No successor parish was created for the former Caterham and Warlingham Urban District at the time of the 1974 reforms, and the area therefore became an unparished area, directly administered by Tandridge District Council. Civil parishes were re-established for the area in 2000, with the former urban district being split into six parishes: Caterham on the Hill, Caterham Valley, Chaldon, Warlingham, Whyteleafe, and Woldingham.
Geography
Caterham is from thecounty town
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, a county town is the most important town or city in a county. It is usually the location of administrative or judicial functions within a county and the place where the county's members of Parliament are elect ...
of Guildford
Guildford ()
is a town in west Surrey, around southwest of central London. As of the 2011 census, the town has a population of about 77,000 and is the seat of the wider Borough of Guildford, which had around inhabitants in . The name "Guildf ...
and south of London.
Caterham on the Hill is located on a considerable area of upland extending north past adjoining Kenley Aerodrome
The former Royal Air Force Station Kenley, more commonly known as RAF Kenley was an airfield station of the Royal Flying Corps in the First World War and the RAF in the Second World War. It played a significant role during the Battle of Britain ...
to Kenley
Kenley is an area within the London Borough of Croydon. Prior to its incorporation into Greater London in 1965 it was in the historic county of Surrey. It is situated south of Purley, east of Coulsdon, north of Caterham and Whyteleafe and we ...
and Hartley Hill in Reedham. This elevated area carries on west until Hooley
Hooley is a village in the borough of Reigate and Banstead in Surrey, England. Within its small grid of streets is the 13th-century church of Chipstead which has been, since time immemorial, its ecclesiastical parish. Hooley is connected via pa ...
/ Old Merstham and forms a very narrow, fairly steep ridge south of Caterham Valley's centre; east of the centre of Caterham Valley are marginally higher rolling pastures of the North Downs on top of a more crevass
A crevasse is a deep crack, that forms in a glacier or ice sheet that can be a few inches across to over 40 feet. Crevasses form as a result of the movement and resulting stress associated with the shear stress generated when two semi-rigid pie ...
ed smaller mass of upland which forms the village of Woldingham followed by a much larger area of upland stretching from Biggin Hill
Biggin Hill is a settlement on the south-eastern outskirts of Greater London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Kent, prior to 1965 it was also in the administrative county of Kent. I ...
to Downe and Knockholt, Kent
Kent is a county in South East England and one of the home counties. It borders Greater London to the north-west, Surrey to the west and East Sussex to the south-west, and Essex to the north across the estuary of the River Thames; it faces ...
.
The M25 motorway
The M25 or London Orbital Motorway is a major road encircling most of Greater London. The motorway is one of the most important roads in the UK and one of the busiest. Margaret Thatcher opened the final section in 1986, making the M25 the lon ...
(between junctions 6 and 7) is 80 to 90m below and less than 200m south of the North Downs path and the southern border of Caterham Valley civil parish and is linked by an uninterrupted hilltop dual carriageway to the north of Caterham and its lowest point, Croydon Road roundabout.
In the south of Caterham are the following hills:
Elevation, soil and geology
Elevations range from the height above in the southwest extreme at "Whitehill Tower, War Coppice Road in Caterham Valley" to 110m Above Ordnance Datum along the railway track, immediately below Croydon Road roundabout, atripoint
A tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints as of 2020. Nearly half are situated in rivers, l ...
partly in Woldingham, Whyteleafe and Caterham.
Caterham lies within the North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and ...
and Caterham Valley's southern border is immediately south of the North Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty ...
, part of a national trail network, which is here on top of the southern edge of the North Downs.
Soil here has the expected shallow, lime-rich soil over chalk or limestone of the escarpment with lower parts of the escarpment summit here, where the topsoil has eroded, having slightly acid, loamy and clayey soils with impeded drainage, which makes that soil particularly fertile.
The gault
The Gault Formation is a geological formation of stiff blue clay deposited in a calm, fairly deep-water marine environment during the Lower Cretaceous Period (Upper and Middle Albian). It is well exposed in the coastal cliffs at Copt Point in Fol ...
clay and the middle chalk that lies under the North Downs are both at their thickest around the valley that occupies the centre of Caterham Valley. While earlier cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
clays and greensand and sandy material, underlying, is evident where terrain has eroded, 90 million years ago the North Downs hard chalk was deposited, a white limestone comprising over 95% calcium carbonate. It contains thin beds of marl and nodules of flint, either scattered or in bands. The North Downs extending from Farnham
Farnham ( /ˈfɑːnəm/) is a market town and civil parish in Surrey, England, around southwest of London. It is in the Borough of Waverley, close to the county border with Hampshire. The town is on the north branch of the River Wey, a trib ...
to Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
are formed by this chalk. They now have an often white, almost vertical south-facing slope. In lower slopes flints washed up by early seas come more to the surface and appear closer to the surface.
Landmarks
TheNorth Downs Way
The North Downs Way National Trail is a long-distance path in southern England, opened in 1978. It runs from Farnham to Dover, past Guildford, Dorking, Merstham, Otford and Rochester, along the Surrey Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty ...
, a National trail popular with walkers, passes very close to the town and is readily accessible from either Harestone Valley Road or Tupwood Lane, the Celtic hillfort promontory
A promontory is a raised mass of land that projects into a lowland or a body of water (in which case it is a peninsula). Most promontories either are formed from a hard ridge of rock that has resisted the erosive forces that have removed the so ...
of the Downs mentioned above, ''The Cardinal's Cap'', and ''Fosterdown or Pilgrims' Fort'', a London Defensive Fort at the top of part of the ridge forming Godstone Hill, in Caterham Valley
Caterham () is a town in the Tandridge District of Surrey, England. The town is administratively divided into two: Caterham on the Hill, and Caterham Valley, which includes the main town centre in the middle of a dry valley but rises to equal ...
.
Localities
Caterham Valley
The civil parish of Caterham Valley has the more developed shopping area presenting the main town centre for the whole community and has a population of 7,581. The parish church of St. John the Evangelist was consecrated in 1882. The railway station is a terminus in the central,dry valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock.
There ...
at the heart of this very large neighbourhood. Traffic to and from the London and Croydon to the north heading towards the M25 motorway is routed around the town on the A22 over the Caterham Bypass, opened in 1939 as one of the earliest such roads in the country. Caterham School
(Truth without Fear)
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public schoolIndependent day and boarding school
, religious_affiliation = Protestant (United Reformed Church)
, president =
, head_label = Headmaste ...
is a large independent co-educational day and boarding school situated along the sides of the Harestone Valley. North Downs Hospital is small private establishment on the outskirts of the town run by the Ramsay Health Care UK
Ramsay Health Care UK is a healthcare company based in the United Kingdom. It was founded by Australian businessman Paul Ramsay, who established its parent company: Ramsay Health Care, in Sydney, Australia, in 1964 and has grown to become a global ...
. Part of Caterham Valley Business Community is represented by a business improvement district, which is publicly known aCaterham Valley For You
Caterham Police Station, operated by Surrey Police is located in the middle of the valley; the local St John Ambulance unit shares the building.
Caterham on the Hill
listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Irel ...
s compared to Caterham Valley, which has a few early Victorian outlying homes and its church listed. The only state run secondary school is in this part of the town, but it has two private primary schools.
;Former barracks
The Caterham Barracks Trust run some facilities at the site of the former Caterham Barracks
Caterham Barracks was a military installation in Caterham, Surrey.
History
The barracks were built as a Regimental depot, depot for the Foot Guards regiments in 1877. The construction reflected a more humane style of barrack design in the afterma ...
. The site is occupied by a supermarket, a housing estate comprising social and some private housing, and various leisure facilities including an arts centre (The Arc), and an indoor Skate park (Skaterham) housed in the former Guard's chapel.
Terry Waite and David Stirling (the founder of the SAS
SAS or Sas may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''SAS'' (novel series), a French book series by Gérard de Villiers
* ''Shimmer and Shine'', an American animated children's television series
* Southern All Stars, a Japanese rock ba ...
) trained at the barracks.
A number of films / TV series were fully or partially filmed at the barracks. '' They Were Not Divided'' filmed by Two Cities Films and '' Invasion: Earth'' series filmed by the BBC.
;Mental Hospitals
Caterham Asylum, later known as Caterham Mental Hospital and later still as Saint Lawrence's Hospital, was a very large establishment for the treatment of the mentally ill. Patients came from all over London to this well known institution that by 1930 grew to over 2,000 beds. Joey Deacon
Joseph John Deacon (24 May 1920 – 3 December 1981) was a British author and television personality.
Biography
Deacon was born with severe cerebral palsy, a neurological condition that left him with neuromuscular spasticity that particul ...
lived in the hospital or its grounds for over 50 years. Most of the site has now been redeveloped as housing but a few buildings remain, although they are now empty and planning permission has been given for the buildings to be demolished and 161 homes built on the site. Joey Deacon's bungalow 'Holland House' is scheduled for demolition but the 'Blue Peter' bungalow 'Woodview' is to remain as a care home.
;Hospital
Caterham on the Hill has its own small NHS hospital, Caterham Dene, run by First Community Health and Care CIC offering a range of inpatient and outpatient services, including a minor injury unit.
Demography and housing
At the 2011 census, Caterham has a total population of 21,090 people among 8,543 households, an increase of 130 households in 10 years. The average level of accommodation in the region composed of detached houses was 28%, the average that was apartments was 22.6%. The proportion of households in the civil parish who owned their home outright compares to the regional average of 35.1%. The proportion who owned their home with a loan compares to the regional average of 32.5%. The remaining % is made up of rented dwellings (plus a negligible % of households living rent-free).Commerce
Church Walk
Church Walk Shopping Centre is a smallshopping mall
A shopping mall (or simply mall) is a North American term for a large indoor shopping center, usually anchored by department stores. The term "mall" originally meant a pedestrian promenade with shops along it (that is, the term was used to refe ...
situated opposite Caterham railway station in Caterham Valley. Church Walk was built on the site of the Valley Hotel, which was demolished in 1988. Long before the Valley Hotel was built (to cater for visitors arriving on the new railway trains) there used to be a tennis court, croquet lawn, rose garden, fountain, and Mr. Woollet's nursery.
Local companies
Until 1987 the offices, factory and showroom Caterham Cars, makers of the Caterham 7 sports car were located in Caterham when the company moved to a new factory in Kent but retained a ''Caterham South'' showroom – but leaving the town by moving to Crawley in February 2013. The former show room that they occupied has now been turned into more homes for retired people. The house building company, Croudace, have their head office in Caterham. Caterham and DeStafford Schools and severalsupermarket
A supermarket is a self-service Retail#Types of outlets, shop offering a wide variety of food, Drink, beverages and Household goods, household products, organized into sections. This kind of store is larger and has a wider selection than earli ...
chains are also large local employers. The Town had a large vacant building – The Rose and Young building – which has now been demolished after over twenty years. This site is being developed into another Supermarket and more flats, however worked has currently stopped as the developer has liquidated.
Smaller specialised businesses include a Saddler, est 1988 known as Unicorn Leather Saddlery.
The High Street, on The Hill, has a variety of small, independent shops. Parking is free for three hours in the main car park, at the top end of town.
Transport
Caterham railway station
Caterham railway station serves the town of Caterham in the Tandridge district of Surrey.
Caterham train drivers depot was opened on Sunday 17 June 1928 as a motormans depot ( The "Motor" term being used for electric trains ) after electrifi ...
is the terminus of the 1856-built Caterham line from Purley. Trains operate to London Bridge
Several bridges named London Bridge have spanned the River Thames between the City of London and Southwark, in central London. The current crossing, which opened to traffic in 1973, is a box girder bridge built from concrete and steel. It r ...
only.
Eight bus routes operate through Caterham, with half being operated by Metrobus. They run buses from Caterham to places such as East Grinstead
East Grinstead is a town in West Sussex, England, near the East Sussex, Surrey, and Kent borders, south of London, northeast of Brighton, and northeast of the county town of Chichester. Situated in the extreme northeast of the county, the civ ...
, Croydon
Croydon is a large town in south London, England, south of Charing Cross. Part of the London Borough of Croydon, a local government district of Greater London. It is one of the largest commercial districts in Greater London, with an extensi ...
, Redhill and Oxted
Oxted is a town and civil parish in the Tandridge district of Surrey, England, at the foot of the North Downs. It is south south-east of Croydon in Greater London, west of Sevenoaks in Kent, and north of East Grinstead in West Sussex.
Oxte ...
. Of the remaining four routes, buses are run by: Quality Line
Quality Line was a bus company based in Epsom, England. A subsidiary of the RATP Group, Quality Line operated bus services throughout the South West (London sub region), South West London and Surrey area, with many under contract to Transport fo ...
to Old Coulsdon; Abellio London to Sutton; Arriva London to Addington Village; and Southdown PSV
Southdown PSV Limited, trade name, trading as Southdown Buses, is a medium-sized country bus operator, with 18 routes across East Surrey, West Sussex, South London and Kent, 9 of which are school bus routes. Most of their routes are operated on ...
to East Grinstead.
Sport
Caterham has a youth football club. Caterham Pumas FC. The Old Caterhamians Rugby Football Club, was established in 1928.Caterham Cricket Club
Caterham Cricket Club is an English cricket club at Caterham in Surrey. The club runs teams in the Surrey County League and plays at Old Cats playing fields in Caterham.
Caterham has a mixture of state and
History of Caterham Village
*Page fo
Caterham
in Kelly's Directory of Kent, Surrey & Sussex, 1891 * {{authority control Towns in Surrey Tandridge
private
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
schools. Three private schools in Caterham are Caterham School
(Truth without Fear)
, established =
, closed =
, type = Public schoolIndependent day and boarding school
, religious_affiliation = Protestant (United Reformed Church)
, president =
, head_label = Headmaste ...
established at its present site since 1884, which is in the outskirts of the town, Oakhyrst Grange School and Essendene Lodge School. The main state secondary school is de Stafford School
de Stafford School is a mixed secondary school located in Caterham, Surrey, England. The school educates students from ages 11 to 16.
Organisation
de Stafford is close to the centre of the scattered town of Caterham, bordering on two sides ...
. A secondary school for boys with special educational needs
Special educational needs (SEN), also known as special educational needs and disabilities (SEND) in the United Kingdom refers to the education of children who require different education provision to the mainstream system.
Definition
The definiti ...
called Sunnydown School
Sunnydown School is a special boarding secondary school situated in the town of Caterham in Surrey, England. Founded in 1949, it is the second oldest special school in Surrey. The school educates students aged 11 to 16.
Organisation
The schoo ...
is also in Caterham on the Hill.
Culture and community
A children's ball pit and gymnastics centre are situated in the old Caterham Barracks housing estate. The building is made out of the two converted gymnasiums. There is askatepark
A skatepark, or skate park, is a purpose-built recreational environment made for skateboarding, BMX, scootering, wheelchairs, and aggressive inline skating. A skatepark may contain half-pipes, handrails, funboxes, vert ramps, stairsets, q ...
called "Skaterham" in Caterham on The Hill. It has indoor and outdoor sections, built on the grounds of the former Guards Chapel.
Based in the town centre the Miller Centre is a theatre and community centre that puts on regular non-professional shows, films and is host to a number of clubs and community groups.
The small East Surrey Museum houses a local history collection.
An annual carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival typi ...
is held in the town, with a procession of floats and a fete.
Caterham has an online radio station
Online radio (also web radio, net radio, streaming radio, e-radio, IP radio, Internet radio) is a digital audio service transmitted via the Internet. Broadcasting on the Internet is usually referred to as webcasting since it is not transmitted ...
for the community, called Ridge Radio.
The first Caterham Festival was in 2009 and by 2014 there were 135 events spread over 5 weeks. There is a 2-day music fest, the High Street is closed for a town street party and the main road through the Valley is closed for a food fest. Other events include Shakespeare plays, an archaeological dig, open Caterham – where buildings and groups open their doors for the weekend, concerts and comedy nights. The annual Carnival takes place during the Festival. The Festival has won a number of awards including the Action for Market Towns best community event and, on three occasions, the Surrey Mirror Heart of the Community award. Chairman Andy Parr has been awarded the M.B.E. Mbe may refer to:
* Mbé, a town in the Republic of the Congo
* Mbe Mountains Community Forest, in Nigeria
* Mbe language, a language of Nigeria
* Mbe' language, language of Cameroon
* ''mbe'', ISO 639 code for the extinct Molala language
Molal ...
for services to the Community of Caterham.
The committee members have also advised many other towns about holding similar Festivals.
Religion
Caterham has churches representing a variety of Christian denominations. The oldest church remaining in use is the church ofSt. Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence ( la, Laurentius, lit. " laurelled"; 31 December AD 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the persecution of the Christians that the Roman ...
, which was established around 1095. The church has been used by several different denominations, including Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abil ...
and Romanian Orthodox. It was largely replaced from 1866 onwards, following the consecration of the church of St. Mary the Virgin. Both of these churches are located in Caterham on the Hill.
As the town in the valley expanded after the railway was built, several churches were founded. Caterham United Reformed Church was built by nonconformists in 1863, followed by the Church of St. John the Evangelist
John the Evangelist ( grc-gre, Ἰωάννης, Iōánnēs; Aramaic: ܝܘܚܢܢ; Ge'ez: ዮሐንስ; ar, يوحنا الإنجيلي, la, Ioannes, he, יוחנן cop, ⲓⲱⲁⲛⲛⲏⲥ or ⲓⲱ̅ⲁ) is the name traditionally given t ...
in 1881.
Notable people
The composerMátyás Seiber
Mátyás György Seiber (; 4 May 190524 September 1960) was a Hungarian-born British composer who lived and worked in the United Kingdom from 1935 onwards. His work linked many diverse musical influences, from the Hungarian tradition of Bartó ...
lived at 169, Stafford Road from 1935 until his death in 1960. Television presenter Angus Deayton
Gordon Angus Deayton (; born 6 January 1956) is an English actor, writer, musician, comedian, and broadcaster. He was the original presenter of the satirical panel game '' Have I Got News for You,'' the host of British panel show '' Would I Lie ...
grew up in Caterham; he attended both Oakhyrst Grange and Caterham Schools. Notable sportspeople from Caterham include the footballers Nicky Forster
Nicholas Michael Forster (born 8 September 1973) is a former professional footballer who was most recently the manager of Staines Town. Forster has also been player-manager at Brentford and manager of Dover Athletic.
Football career
Early y ...
and David Price and cricketer Dar Lyon
Malcolm Douglas Lyon (22 April 1898 – 17 February 1964), generally known as Dar Lyon was an English first-class cricketer who played for Somerset County Cricket Club through the 1920s. He was a right-handed top order batsman known for his be ...
, all of whom were born in the town. Actors Bill Nighy and Jon Finch
Jon Finch (2 March 1942 – 28 December 2012) was an English stage and film actor who became well known for his Shakespearean roles. Most notably, he starred in films for directors Roman Polanski (''Macbeth'', 1971) and Alfred Hitchcock (''Fren ...
were also born in Caterham; Michael Robbins, another actor, died there.
See also
* London Defence Positions *Sacred Heart Church, Caterham
Sacred Heart Church or formally the Church of the Sacred Heart of Jesus is a Roman Catholic parish church in Caterham, Surrey, England designed by Ingress Bell and built in 1881. It is situated between Essendene Road and Whyteleafe Road off the ...
References
External links
History of Caterham Village
*Page fo
Caterham
in Kelly's Directory of Kent, Surrey & Sussex, 1891 * {{authority control Towns in Surrey Tandridge