Beckmann rearrangement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Beckmann rearrangement, named after the German chemist
 This nitrilium ion has been known to be intercepted by other nucleophiles, including the leaving group from the oxime.
This nitrilium ion has been known to be intercepted by other nucleophiles, including the leaving group from the oxime.
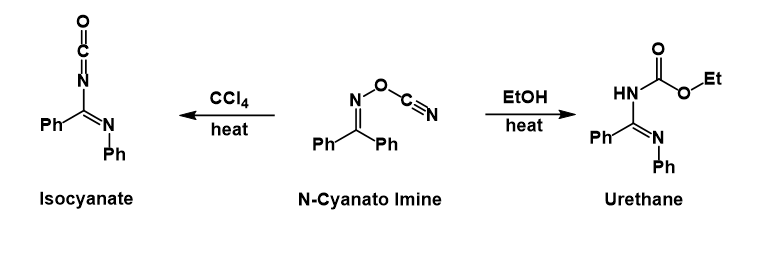 Presumably after the phenyl group migrates and expels the
Presumably after the phenyl group migrates and expels the


 Sulfur is also capable of promoting fragmentation, albeit at a longer range than oxygen or nitrogen.
Sulfur is also capable of promoting fragmentation, albeit at a longer range than oxygen or nitrogen.
 Silicon is capable of directing the fragmentation through the
Silicon is capable of directing the fragmentation through the 
 The mechanism can be shown as below:
:
The mechanism can be shown as below:
: The reaction is intrinsically a special case of Beckmann rearrangement combined with
The reaction is intrinsically a special case of Beckmann rearrangement combined with
 An industrial synthesis of paracetamol developed by
An industrial synthesis of paracetamol developed by
url
Animation of the Beckmann rearrangement
Animation of the Beckmann rearrangement (caprolactam)
{{Organic reactions Rearrangement reactions Nitrogen heterocycle forming reactions Ring expansion reactions Name reactions Amide synthesis reactions
Ernst Otto Beckmann
Ernst Otto Beckmann (July 4, 1853 – July 12, 1923) was a German pharmacist and chemist who is remembered for his invention of the Beckmann differential thermometer and for his discovery of the Beckmann rearrangement.
Scientific work
Ernst Ott ...
(1853–1923), is a rearrangement of an oxime
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula , where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted ...
functional group to substituted amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
s. The rearrangement has also been successfully performed on haloimines and nitrones. Cyclic oximes and haloimines yield lactams.
The Beckmann rearrangement is often catalyzed by acid; however, other reagents have been known to promote the rearrangement. These include tosyl chloride
4-Toluenesulfonyl chloride (''p''-toluenesulfonyl chloride, toluene-''p''-sulfonyl chloride) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2Cl. This white, malodorous solid is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Abbreviated TsCl or ...
, thionyl chloride
Thionyl chloride is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a moderately volatile, colourless liquid with an unpleasant acrid odour. Thionyl chloride is primarily used as a chlorinating reagent, with approximately per year bein ...
, phosphorus pentachloride
Phosphorus pentachloride is the chemical compound with the formula PCl5. It is one of the most important phosphorus chlorides, others being PCl3 and POCl3. PCl5 finds use as a chlorinating reagent. It is a colourless, water-sensitive and moist ...
, phosphorus pentoxide
Phosphorus pentoxide is a chemical compound with molecular formula P4 O10 (with its common name derived from its empirical formula, P2O5). This white crystalline solid is the anhydride of phosphoric acid. It is a powerful desiccant and dehydra ...
, triethylamine
Triethylamine is the chemical compound with the formula N(CH2CH3)3, commonly abbreviated Et3N. It is also abbreviated TEA, yet this abbreviation must be used carefully to avoid confusion with triethanolamine or tetraethylammonium, for which TEA ...
, sodium hydroxide, trimethylsilyl iodide among others. The Beckmann fragmentation is another reaction that often competes with the rearrangement, though careful selection of promoting reagent and solvent conditions can favor the formation of one over the other, sometimes giving almost exclusively one product. The rearrangement occurs stereospecifically for ketoxime
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula , where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substitute ...
s and N-chloro/N-fluoro imines, with the migrating group being anti-periplanar
In organic chemistry, anti-periplanar, or antiperiplanar, describes the bond angle in a molecule. In this conformer, the dihedral angle of the bond and the bond is greater than +150° or less than −150° (Figures 1 and 2). Anti-periplanar i ...
to the leaving group on the nitrogen. Certain conditions have been known to racemize In chemistry, racemization is a conversion, by heat or by chemical reaction, of an optically active compound into a racemic (optically inactive) form. This creates a 1:1 molar ratio of enantiomers and is referred too as a racemic mixture (i.e. conta ...
the oxime geometry, leading to the formation of both regioisomers. The rearrangement of aldoxime
In organic chemistry, an oxime is a organic compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula , where R is an organic side-chain and R’ may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substitute ...
s occurs with stereospecificity in the gas phase
In the physical sciences, a phase is a region of space (a thermodynamic system), throughout which all physical properties of a material are essentially uniform. Examples of physical properties include density, index of refraction, magnetiza ...
and without stereospecificity in the solution phase. A few methodologies allow for the rearrangement of aldoximes to primary amides, but fragmentation commonly competes in these systems. Nitrone rearrangement also occurs without stereospecificity; the regioisomer formed has the amide nitrogen substituted with the group possessing the greatest migratory aptitude Migratory aptitude is the relative ability of a migrating group to migrate in a rearrangement reaction. Migratory aptitudes vary in different reactions, depending on multiple factors.
In the Baeyer-Villiger reaction, the more substituted group, i ...
.
The archetypal Beckmann rearrangement is the conversion of cyclohexanone to caprolactam
Caprolactam (CPL) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)5C(O)NH. This colourless solid is a lactam (a cyclic amide) of caproic acid. Global demand for this compound is approximately five million tons per year, and the vast majority is use ...
via the oxime. Caprolactam is the feedstock in the production of Nylon 6
Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam is a polymer, in particular semicrystalline polyamide. Unlike most other nylons, nylon 6 is not a condensation polymer, but instead is formed by ring-opening polymerization; this makes it a special case in the compar ...
.
The Beckmann solution consists of acetic acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component ...
, hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
and acetic anhydride, and was widely used to catalyze the rearrangement. Other acids, such as sulfuric acid, polyphosphoric acid
A phosphoric acid, in the general sense, is a phosphorus oxoacid in which each phosphorus (P) atom is in the oxidation state +5, and is bonded to four oxygen (O) atoms, one of them through a double bond, arranged as the corners of a tetrahedron. ...
, and hydrogen fluoride have all been used. Sulfuric acid is the most commonly used acid for commercial lactam production due to its formation of an ammonium sulfate by-product when neutralized with ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous wa ...
. Ammonium sulfate
Ammonium sulfate (American English and international scientific usage; ammonium sulphate in British English); (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen a ...
is a common agricultural fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
providing nitrogen and sulfur.
Reaction mechanism
The most common reaction mechanism of the Beckmann rearrangement consists generally of analkyl
In organic chemistry, an alkyl group is an alkane missing one hydrogen.
The term ''alkyl'' is intentionally unspecific to include many possible substitutions.
An acyclic alkyl has the general formula of . A cycloalkyl is derived from a cycloa ...
migration anti-periplanar to the expulsion of a leaving group to form a nitrilium ion. This is followed by solvolysis
In chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (S1/S2) or elimination reaction, elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of S1 reactions, solvolysis of a chirality (chemistry), chiral reactant affor ...
to an imidate
Carboximidates (or more general imidates) are organic compounds, which can be thought of as esters formed between a carboximidic acid (R-C(=NR')OH) and an alcohol, with the general formula R-C(=NR')OR".
They are also known as imino ethers, sin ...
and then tautomerization
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert.
The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hyd ...
to the amide:
: Presumably after the phenyl group migrates and expels the
Presumably after the phenyl group migrates and expels the cyanate
Cyanate is an anion with the structural formula , usually written . It also refers to any salt containing it, such as ammonium cyanate.
It is an isomer of the much less stable fulminate anion .William R. Martin and David W. Ball (2019): "Sma ...
, the latter then attacks the nitrillium ion formed. In carbon tetrachloride the isocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyan ...
can be isolated, whereas in ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
the urethane is formed after solvolysis of the isocyanate.
One computational study has established the mechanism accounting for solvent molecules and substituents. The rearrangement of acetone oxime in the Beckmann solution involved three acetic acid molecules and one proton (present as an oxonium ion
In chemistry, an oxonium ion is any cation containing an oxygen atom that has three bonds and 1+ formal charge. The simplest oxonium ion is the hydronium ion ().
Alkyloxonium
Hydronium is one of a series of oxonium ions with the formula R''n' ...
). In the transition state
In chemistry, the transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate. It is often marked ...
leading to the iminium ion (σ-complex), the methyl group migrates to the nitrogen atom in a concerted reaction
In chemistry, a concerted reaction is a chemical reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making occurs in a single step. Reactive intermediates or other unstable high energy intermediates are not involved. Concerted reaction rates tend no ...
as the hydroxyl group is expelled. The oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group is stabilized by three acetic acid molecules. In the next step the electrophilic carbon atom in the nitrilium ion is attacked by water and a proton is donated back to acetic acid. In the transition state leading to the imidate, the water oxygen atom is coordinated to 4 other atoms. In the third step, an isomerization step protonates the nitrogen atom leading to the amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it i ...
.
The same computation with a hydroxonium
In chemistry, hydronium (hydroxonium in traditional British English) is the common name for the aqueous cation , the type of oxonium ion produced by protonation of water. It is often viewed as the positive ion present when an Arrhenius acid is di ...
ion and 6 molecules of water has the same result, but when the migrating substituent is a phenyl group, the mechanism favors the formation of an intermediate three-membered π-complex. This π-complex is not found in the H3O+(H2O)6.
With the cyclohexanone-oxime, the relief of ring strain results in a third reaction mechanism, leading directly to the protonated caprolactam in a single concerted step without the intermediate formation of a π-complex or σ-complex.
Cyanuric chloride assisted Beckmann reaction
Beckmann rearrangement can be renderedcatalytic
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
using cyanuric chloride
Cyanuric chloride is an organic compound with the formula (NCCl)3. This white solid is the chlorinated derivative of 1,3,5-triazine. It is the trimer of cyanogen chloride. Cyanuric chloride is the main precursor to the popular but controver ...
and zinc chloride
Zinc chloride is the name of inorganic chemical compounds with the formula ZnCl2 and its hydrates. Zinc chlorides, of which nine crystalline forms are known, are colorless or white, and are highly soluble in water. This salt is hygroscopic and e ...
as a co-catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
. For example, cyclododecanone
Cyclododecanone is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)11CO. It is a cyclic ketone that exists as a white solid at room temperature. It is produced by the oxidation of cyclododecane via cyclododecanol.
Cyclododecanone is mainly consumed ...
can be converted to the corresponding lactam, the monomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
...
used in the production of Nylon 12
Nylon 12 is a nylon polymer with the formula CH2)11C(O)NHsub>n. It is made from ω-aminolauric acid or laurolactam monomers that each have 12 carbons, hence the name ‘Nylon 12’. It is one of several nylon polymers.
Synthesis
Nylon 12 can be ...
.
The reaction mechanism for this reaction is based on a catalytic cycle
In chemistry, a catalytic cycle is a multistep reaction mechanism that involves a catalyst. The catalytic cycle is the main method for describing the role of catalysts in biochemistry, organometallic chemistry, bioinorganic chemistry, materials s ...
with cyanuric chloride activating the hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydro ...
group via a nucleophilic aromatic substitution
A nucleophilic aromatic substitution is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such as a halide, on an aromatic ring. Aromatic rings are usually nucleophilic, but some aromatic compou ...
. The reaction product is dislodged and replaced by new reactant via an intermediate Meisenheimer complex A Meisenheimer complex or Jackson–Meisenheimer complex in organic chemistry is a 1:1 reaction adduct between an arene carrying electron withdrawing groups and a nucleophile. These complexes are found as reactive intermediates in nucleophilic aroma ...
.
Beckmann fragmentation
The Beckmann fragmentation is a reaction that frequently competes with the Beckmann rearrangement. When the group α to the oxime is capable of stabilizing carbocation formation, the fragmentation becomes a viable reaction pathway. The reaction generates a nitrile and a carbocation, which is quickly intercepted to form a variety of products. The nitrile can also be hydrolyzed under reaction conditions to give carboxylic acids. Different reaction conditions can favor the fragmentation over the rearrangement.
Quaternary carbon
A quaternary carbon is a carbon atom bound to four other carbon atoms. For this reason, quaternary carbon atoms are found only in hydrocarbons having at least five carbon atoms. Quaternary carbon atoms can occur in branched alkanes, but not in li ...
centers promote fragmentation by stabilizing carbocation formation through hyperconjugation
In organic chemistry, hyperconjugation (σ-conjugation or no-bond resonance) refers to the delocalization of electrons with the participation of bonds of primarily σ-character. Usually, hyperconjugation involves the interaction of the electron ...
. As shown in the above picture, the "stable" carbocation is formed, which then loses a hydrogen to give a site of unsaturation. Oxygen and nitrogen atoms also promote fragmentation through the formation of ketones and imine
In organic chemistry, an imine ( or ) is a functional group or organic compound containing a carbon–nitrogen double bond (). The nitrogen atom can be attached to a hydrogen or an organic group (R). The carbon atom has two additional single bon ...
s respectively. Sulfur is also capable of promoting fragmentation, albeit at a longer range than oxygen or nitrogen.
Sulfur is also capable of promoting fragmentation, albeit at a longer range than oxygen or nitrogen.
 Silicon is capable of directing the fragmentation through the
Silicon is capable of directing the fragmentation through the beta-silicon effect
The beta-silicon effect also called silicon hyperconjugation in organosilicon chemistry is a special type of hyperconjugation that describes the stabilizing influence of a silicon atom on the development of positive charge at a carbon atom one pos ...
.
The carbocation intermediate in this reaction is intercepted by nucleophilic fluoride from diethylaminosulfur trifluoride ( DAST):
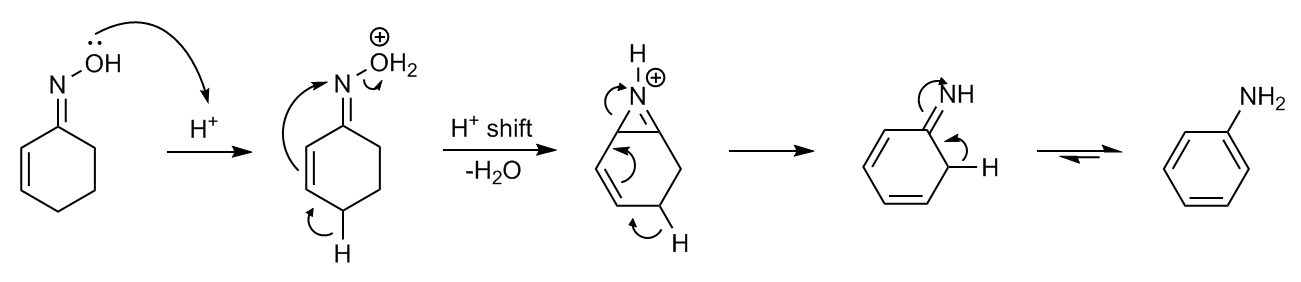
:Semmler–Wolff reaction
The oxime of cyclohexenone with acid formsaniline
Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6 H5 NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starti ...
in a dehydration – aromatization
Aromatization is a chemical reaction in which an aromatic system is formed from a single nonaromatic precursor. Typically aromatization is achieved by dehydrogenation of existing cyclic compounds, illustrated by the conversion of cyclohexane int ...
reaction called the Semmler–Wolff reaction or Wolff aromatization ''Beckmann Rearrangements. An Investigation of Special Cases'' E. C. Horning, V. L. Stromberg, H. A. Lloyd J. Am. Chem. Soc.
The ''Journal of the American Chemical Society'' is a weekly peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1879 by the American Chemical Society. The journal has absorbed two other publications in its history, the ''Journal of Analytic ...
, 1952, 74 (20), pp 5153–5155
: The reaction is intrinsically a special case of Beckmann rearrangement combined with
The reaction is intrinsically a special case of Beckmann rearrangement combined with neighbouring group participation
In organic chemistry, neighbouring group participation (NGP, also known as anchimeric assistance) has been defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) as the interaction of a reaction centre with a lone pair of electro ...
.
Applications in drug synthesis
:Hoechst Hoechst, Hochst, or Höchst may refer to:
* Hoechst AG, a former German life-sciences company
* Hoechst stain, one of a family of fluorescent DNA-binding compounds
* Höchst (Frankfurt am Main), a city district of Frankfurt am Main, Germany
** Fra ...
–Celanese
Celanese Corporation, formerly known as Hoechst Celanese, is an American technology and specialty materials company headquartered in Irving, Texas. A Fortune 500 corporation, the company is the world’s leading producer of acetic acid, prod ...
involves the conversion of a methyl ketone to an acetanilide via a Beckmann rearrangement.
The thermal rearrangement that occurs in the synthesis of ketamine was claimed to be a Beckmann rearrangement according tourl
See also
*Curtius rearrangement
The Curtius rearrangement (or Curtius reaction or Curtius degradation), first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas. The isocyanate then undergoes attack by a va ...
* Dakin reaction
The Dakin oxidation (or Dakin reaction) is an organic redox reaction in which an '' ortho''- or ''para''-hydroxylated phenyl aldehyde (2-hydroxybenzaldehyde or 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde) or ketone reacts with hydrogen peroxide in base to form a ...
* Schmidt reaction
In organic chemistry, the Schmidt reaction is an organic reaction in which an azide reacts with a carbonyl derivative, usually an aldehyde, ketone, or carboxylic acid, under acidic conditions to give an amine or amide, with expulsion of nitrogen ...
* Stieglitz rearrangement
* Lossen rearrangement
The Lossen rearrangement is the conversion of a hydroxamate ester to an isocyanate. Typically O-acyl, sulfonyl, or phosphoryl O-derivative are employed. The isocyanate can be used further to generate ureas in the presence of amines or generate ...
References
External links
Animation of the Beckmann rearrangement
Animation of the Beckmann rearrangement (caprolactam)
{{Organic reactions Rearrangement reactions Nitrogen heterocycle forming reactions Ring expansion reactions Name reactions Amide synthesis reactions