Ancient Greek architecture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ancient Greek architecture came from the
 The architecture of ancient Greece is of a trabeated or " post and lintel" form, i.e. it is composed of upright beams (posts) supporting horizontal beams (lintels). Although the existent buildings of the era are constructed in stone, it is clear that the origin of the style lies in simple wooden structures, with vertical posts supporting beams which carried a ridged roof. The posts and beams divided the walls into regular compartments which could be left as openings, or filled with sun dried bricks, lathes or straw and covered with clay daub or plaster. Alternately, the spaces might be filled with rubble. It is likely that many early houses and temples were constructed with an open porch or "pronaos" above which rose a low pitched gable or pediment.
The earliest temples, built to enshrine statues of deities, were probably of wooden construction, later replaced by the more durable stone temples many of which are still in evidence today. The signs of the original timber nature of the architecture were maintained in the stone buildings..
A few of these temples are very large, with several, such as the Temple of Zeus Olympus and the Olympians at Athens being well over 300 feet in length, but most were less than half this size. It appears that some of the large temples began as wooden constructions in which the columns were replaced piecemeal as stone became available. This, at least was the interpretation of the historian Pausanias looking at the Temple of Hera at Olympia in the 2nd century AD.
The stone columns are made of a series of solid stone cylinders or "drums" that rest on each other without mortar, but were sometimes centred with a bronze pin. The columns are wider at the base than at the top, tapering with an outward curve known as entasis. Each column has a capital of two parts, the upper, on which rests the lintels, being square and called the
The architecture of ancient Greece is of a trabeated or " post and lintel" form, i.e. it is composed of upright beams (posts) supporting horizontal beams (lintels). Although the existent buildings of the era are constructed in stone, it is clear that the origin of the style lies in simple wooden structures, with vertical posts supporting beams which carried a ridged roof. The posts and beams divided the walls into regular compartments which could be left as openings, or filled with sun dried bricks, lathes or straw and covered with clay daub or plaster. Alternately, the spaces might be filled with rubble. It is likely that many early houses and temples were constructed with an open porch or "pronaos" above which rose a low pitched gable or pediment.
The earliest temples, built to enshrine statues of deities, were probably of wooden construction, later replaced by the more durable stone temples many of which are still in evidence today. The signs of the original timber nature of the architecture were maintained in the stone buildings..
A few of these temples are very large, with several, such as the Temple of Zeus Olympus and the Olympians at Athens being well over 300 feet in length, but most were less than half this size. It appears that some of the large temples began as wooden constructions in which the columns were replaced piecemeal as stone became available. This, at least was the interpretation of the historian Pausanias looking at the Temple of Hera at Olympia in the 2nd century AD.
The stone columns are made of a series of solid stone cylinders or "drums" that rest on each other without mortar, but were sometimes centred with a bronze pin. The columns are wider at the base than at the top, tapering with an outward curve known as entasis. Each column has a capital of two parts, the upper, on which rests the lintels, being square and called the
 Most ancient Greek temples were rectangular, and were approximately twice as long as they were wide, with some notable exceptions such as the enormous Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens, with a length of nearly 2 times its width. A number of surviving temple-like structures are circular, and are referred to as ''tholos''.. The smallest temples are less than 25 metres (approx. 75 feet) in length, or in the case of the circular ''tholos'', in diameter. The great majority of temples are between 30 and 60 metres (approx. 100–200 feet) in length. A small group of Doric temples, including the
Most ancient Greek temples were rectangular, and were approximately twice as long as they were wide, with some notable exceptions such as the enormous Temple of Olympian Zeus, Athens, with a length of nearly 2 times its width. A number of surviving temple-like structures are circular, and are referred to as ''tholos''.. The smallest temples are less than 25 metres (approx. 75 feet) in length, or in the case of the circular ''tholos'', in diameter. The great majority of temples are between 30 and 60 metres (approx. 100–200 feet) in length. A small group of Doric temples, including the
 The reliefs and three-dimensional sculpture which adorned the frieze and pediments, respectively, of the Parthenon, are the lifelike products of the High Classical style (450–400 BC) and were created under the direction of the sculptor
The reliefs and three-dimensional sculpture which adorned the frieze and pediments, respectively, of the Parthenon, are the lifelike products of the High Classical style (450–400 BC) and were created under the direction of the sculptor
The Foundations of Classical Architecture Part Two: Greek Classicism
– Free educational program by the ICAA (published August 29, 2018) * Joseph Woods (1828)
Letters of an Architect, From France, Italy, and Greece
{{DEFAULTSORT:Architecture Of Ancient Greece Architectural history
Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, or Hellenes, whose culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese ( ), Peloponnesus ( ; , ) or Morea (; ) is a peninsula and geographic region in Southern Greece, and the southernmost region of the Balkans. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridg ...
, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC.
Ancient Greek architecture is best known for its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway ('' propylon''), the public square (''agora
The agora (; , romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Ancient Greece, Greek polis, city-states. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center ...
'') surrounded by storied colonnade ('' stoa''), the town council building (''bouleuterion
Bouleuterion (, ''bouleutērion''), also translated as and was a building in ancient Greece which housed the council of citizens (, ''boulē'') of a democratic city state. These representatives assembled at the bouleuterion to confer and de ...
''), the public monument, the monumental tomb (''mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be considered a type o ...
'') and the ''stadium
A stadium (: stadiums or stadia) is a place or venue for (mostly) outdoor sports, concerts, or other events and consists of a field or stage completely or partially surrounded by a tiered structure designed to allow spectators to stand or sit ...
''.
Ancient Greek architecture is distinguished by its highly formalised characteristics, both of structure and decoration. This is particularly so in the case of temples where each building appears to have been conceived as a sculptural entity within the landscape, most often raised on high ground so that the elegance of its proportions and the effects of light on its surfaces might be viewed from all angles.. Nikolaus Pevsner
Sir Nikolaus Bernhard Leon Pevsner (30 January 1902 – 18 August 1983) was a German-British art historian and architectural historian best known for his monumental 46-volume series of county-by-county guides, ''The Buildings of England'' (195 ...
refers to "the plastic shape of the reektemple ..placed before us with a physical presence more intense, more alive than that of any later building".
The formal vocabulary of ancient Greek architecture, in particular the division of architectural style into three defined orders: the Doric Order
The Doric order is one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of t ...
, the Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric) ...
and the Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric or ...
, was to have a profound effect on Western architecture of later periods. The architecture of ancient Rome grew out of that of Greece and maintained its influence in Italy unbroken until the present day. From the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
, revivals of Classicism
Classicism, in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for a classical period, classical antiquity in the Western tradition, as setting standards for taste which the classicists seek to emulate. In its purest form, classicism is an aesthe ...
have kept alive not only the precise forms and ordered details of Greek architecture, but also its concept of architectural beauty based on balance and proportion. The successive styles of Neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture, sometimes referred to as Classical Revival architecture, is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassicism, Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy, France and Germany. It became one of t ...
and Greek Revival architecture
Greek Revival architecture is a architectural style, style that began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe, the United States, and Canada, ...
followed and adapted ancient Greek styles closely.
Influences
Geography
The mainland and islands of Greece are very rocky, with deeply indented coastline, and rugged mountain ranges with few substantial forests. The most freely available building material is stone. Limestone was readily available and easily worked.. There is an abundance of high quality whitemarble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
both on the mainland and islands, particularly Paros
Paros (; ; ) is a Greek island in the central Aegean Sea. Part of the Cyclades island group, it lies to the west of Naxos (island), Naxos, from which it is separated by a channel about wide. It lies approximately south-east of Piraeus. The Co ...
and Naxos
Naxos (; , ) is a Greek island belonging to the Cyclades island group. It is the largest island in the group. It was an important centre during the Bronze Age Cycladic Culture and in the Ancient Greek Archaic Period. The island is famous as ...
. This finely grained material was a major contributing factor to precision of detail, both architectural and sculptural, that adorned ancient Greek architecture.. Deposits of high-quality potter's clay were found throughout Greece and the Islands, with major deposits near Athens. It was used not only for pottery vessels but also roof tiles and architectural decoration.
The climate of Greece is maritime, with both the coldness of winter and the heat of summer tempered by sea breezes. This led to a lifestyle where many activities took place outdoors. Hence temples were placed on hilltops, their exteriors designed as a visual focus of gatherings and processions, while theatres were often an enhancement of a naturally occurring sloping site where people could sit, rather than a containing structure. Colonnades encircling buildings, or surrounding courtyards provided shelter from the sun and from sudden winter storms.
The light of Greece may be another important factor in the development of the particular character of ancient Greek architecture. The light is often extremely bright, with both the sky and the sea vividly blue. The clear light and sharp shadows give a precision to the details of the landscape, pale rocky outcrops and seashore. This clarity is alternated with periods of haze that varies in colour to the light on it. In this characteristic environment, the ancient Greek architects constructed buildings that were marked by the precision of detail. The gleaming marble surfaces were smooth, curved, fluted, or ornately sculpted to reflect the sun, cast graded shadows and change in colour with the ever-changing light of day.
History
Historians divide ancient Greek civilization into two eras, the Hellenic period (from around 900 BC to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC), and the Hellenistic period (323 BC – 30 AD). During the earlier Hellenic period, substantial works of architecture began to appear around 600 BC. During the later (Hellenistic) period, Greek culture spread as a result of Alexander's conquest of other lands, and later as a result of the rise of the Roman Empire, which adopted much of Greek culture.. Before the Hellenic era, two major cultures had dominated the region: the Minoan (), and the Mycenaean (c. 1500–1100 BC). Minoan is the name given by modern historians to the culture of the people of ancientCrete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
, known for its elaborate and richly decorated Minoan palaces
Minoan palaces were massive building complexes built on Crete during the Bronze Age. They are often considered emblematic of the Minoan civilization and are modern tourist destinations. Archaeologists generally recognize five structures as palac ...
, and for its pottery, the most famous of which painted with floral and motifs of sea life. The Mycenaean culture, which flourished on the Peloponnesus, was different in character. Its people built citadels, fortifications and tombs, and decorated their pottery with bands of marching soldiers rather than octopus and seaweed. Both these civilizations came to an end around 1100 BC, that of Crete possibly because of volcanic devastation, and that of Mycenae because of an invasion by the Dorian people who lived on the Greek mainland.. Following these events, there was a period from which only a village level of culture seems to have existed. This period is thus often referred to as the Greek Dark Age.
Art
The art of the Hellenic era is generally subdivided into four periods: the Protogeometric (1100–900 BC), the Geometric (900–700 BC), the Archaic (700–500 BC) and the Classical (500–323 BC) with sculpture being further divided into Severe Classical, High Classical and Late Classical.. The first signs of the particular artistic character that defines ancient Greek architecture are to be seen in the pottery of the Dorian Greeks from the 10th century BC. Already at this period it is created with a sense of proportion, symmetry and balance not apparent in similar pottery from Crete and Mycenae. The decoration is precisely geometric, and ordered neatly into zones on defined areas of each vessel. These qualities were to manifest themselves not only through a millennium of Greek pottery making, but also in the architecture that was to emerge in the 6th century.. The major development that occurred was in the growing use of the human figure as the major decorative motif, and the increasing surety with which humanity, its mythology, activities and passions were depicted. The development in the depiction of the human form in pottery was accompanied by a similar development in sculpture. The tiny stylised bronzes of the Geometric period gave way to life-sized highly formalised monolithic representation in the Archaic period. The Classical period was marked by a rapid development towards idealised but increasingly lifelike depictions of gods in human form. This development had a direct effect on the sculptural decoration of temples, as many of the greatest extant works of ancient Greek sculpture once adorned temples, and many of the largest recorded statues of the age, such as the lost chryselephantine statues of Zeus at the Temple of Zeus at Olympia and Athena at the Parthenon, Athens, both over 40 feet high, were once housed in them.Religion and philosophy
The religion of ancient Greece was a form of nature worship that grew out of the beliefs of earlier cultures. However, unlike earlier cultures, man was no longer perceived as being threatened by nature, but as its sublime product. The natural elements were personified as gods of the complete human form, and very human behaviour. The home of the gods was thought to be Olympus, the highest mountain in Greece. The most important deities were:Zeus
Zeus (, ) is the chief deity of the List of Greek deities, Greek pantheon. He is a sky father, sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus.
Zeus is the child ...
, the supreme god and ruler of the sky; Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; ; in Ionic Greek, Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women, and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Oly ...
, his wife and goddess of marriage; Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
, goddess of wisdom; Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
, the god of the sea; Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Demeter (; Attic Greek, Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric Greek, Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Twelve Olympians, Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over cro ...
, goddess of the harvest; Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
, the god of the sun, law, healing, plague, reason, music and poetry; Artemis
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Artemis (; ) is the goddess of the hunting, hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, transitions, nature, vegetation, childbirth, Kourotrophos, care of children, and chastity. In later tim ...
, goddess of chastity, the hunt and the wilderness; Aphrodite
Aphrodite (, ) is an Greek mythology, ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, procreation, and as her syncretism, syncretised Roman counterpart , desire, Sexual intercourse, sex, fertility, prosperity, and ...
, goddess of love; Ares
Ares (; , ''Árēs'' ) is the List of Greek deities, Greek god of war god, war and courage. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. The Greeks were ambivalent towards him. He embodies the physical valor necessary for ...
, God of war; Hermes, the god of commerce and travellers, Hephaestus
Hephaestus ( , ; wikt:Hephaestus#Alternative forms, eight spellings; ) is the Greek god of artisans, blacksmiths, carpenters, craftsmen, fire, metallurgy, metalworking, sculpture and volcanoes.Walter Burkert, ''Greek Religion'' 1985: III.2. ...
, the god of fire and metalwork; and Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
, the god of wine and fruit-bearing plants. Worship, like many other activities, was done in the community, in the open. However, by 600 BC, the gods were often represented by large statues and it was necessary to provide a building in which each of these could be housed. This led to the development of temples..
The ancient Greeks perceived order in the universe, and in turn, applied order and reason to their creations. Their humanist philosophy put mankind at the centre of things and promoted well-ordered societies and the development of democracy. At the same time, the respect for human intellect demanded a reason, and promoted a passion for enquiry, logic, challenge, and problem-solving. The architecture of the ancient Greeks, and in particular, temple architecture, responds to these challenges with a passion for beauty, and for order and symmetry which is the product of a continual search for perfection, rather than a simple application of a set of working rules.
Architectural character
Early development
There is a clear division between the architecture of the preceding Mycenaean and Minoan cultures and that of the ancient Greeks, with much of the techniques and an understanding of their style being lost when these civilisations fell. Mycenaean architecture is marked by massive fortifications, typically surrounding a citadel with a royal palace, much smaller than the rambling Minoan "palaces", and relatively few other buildings. The megaron, a rectangular hall with a hearth in the centre, was the largest room in the palaces, and also larger houses. Sun-dried brick above rubble bases were the usual materials, with wooden columns and roof-beams. Rows ofashlar
Ashlar () is a cut and dressed rock (geology), stone, worked using a chisel to achieve a specific form, typically rectangular in shape. The term can also refer to a structure built from such stones.
Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, a ...
stone orthostats lined the base of walls in some prominent locations.
The Minoan architecture of Crete was of the trabeated form like that of ancient Greece. It employed wooden columns with capitals, but the wooden columns were of a very different form to Doric columns, being narrow at the base and splaying upward. The earliest forms of columns in Greece seem to have developed independently. As with Minoan architecture, ancient Greek domestic architecture centred on open spaces or courtyards surrounded by colonnade
In classical architecture, a colonnade is a long sequence of columns joined by their entablature, often free-standing, or part of a building. Paired or multiple pairs of columns are normally employed in a colonnade which can be straight or curv ...
s. This form was adapted to the construction of hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or und ...
halls within the larger temples. The evolution that occurred in architecture was towards the public building, first and foremost the temple, rather than towards grand domestic architecture such as had evolved in Crete, if the Cretan "palaces" were indeed domestic, which remains uncertain.
Some Mycenaean tombs are marked by circular structures and tapered domes with flat-bedded, cantilevered courses. This architectural form did not carry over into the architecture of ancient Greece, but reappeared about 400 BC in the interior of large monumental tombs such as the Lion Tomb at Knidos (c. 350 BC).
Types of buildings
Domestic buildings
The Greek word for the family or household, '' oikos'', is also the name for the house. Houses followed several different types. It is probable that many of the earliest houses were simple structures of two rooms, with an open porch or pronaos, above which rose a low pitched gable orpediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
. This form is thought to have contributed to temple architecture.
The construction of many houses employed walls of sun-dried clay bricks or wooden framework filled with fibrous material such as straw or seaweed covered with clay or plaster, on a base of stone which protected the more vulnerable elements from damp. The roofs were probably of thatch with eaves which overhung the permeable walls. Many larger houses, such as those at Delos, were built of stone and plastered. The roofing material for the substantial house was tile. Houses of the wealthy had mosaic floors and demonstrated the Classical style.
Many houses centred on a wide passage or "pasta" which ran the length of the house and opened at one side onto a small courtyard which admitted light and air. Larger houses had a fully developed peristyle (courtyard) at the centre, with the rooms arranged around it. Some houses had an upper floor which appears to have been reserved for the use of the women of the family..
City houses were built with adjoining walls and were divided into small blocks by narrow streets. Shops were sometimes located in the rooms towards the street. City houses were inward-facing, with major openings looking onto the central courtyard, rather than the street..
Public buildings
The rectangulartemple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a place of worship, a building used for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. By convention, the specially built places of worship of some religions are commonly called "temples" in Engli ...
is the most common and best-known form of Greek public architecture. This rectilinear structure borrows from the Late Helladic, Mycenaean megaron, which contained a central throne room, vestibule, and porch. The temple did not serve the same function as a modern church, since the altar stood under the open sky in the '' temenos'' or sacred precinct, often directly before the temple. Temples served as the location of a cult image
In the practice of religion, a cult image is a Cultural artifact, human-made object that is venerated or worshipped for the deity, Spirit (supernatural entity), spirit or Daimon, daemon that it embodies or represents. In several traditions, incl ...
and as a storage place or strong room for the treasury associated with the cult of the god in question, and as a place for devotees of the god to leave their votive offering
A votive offering or votive deposit is one or more objects displayed or deposited, without the intention of recovery or use, in a sacred place for religious purposes. Such items are a feature of modern and ancient societies and are generally ...
s, such as statues, helmets and weapons. Some Greek temples appear to have been oriented astronomically. The temple was generally part of a religious precinct known as the ''acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens ...
''. According to Aristotle
Aristotle (; 384–322 BC) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek philosopher and polymath. His writings cover a broad range of subjects spanning the natural sciences, philosophy, linguistics, economics, politics, psychology, a ...
, "the site should be a spot seen far and wide, which gives good elevation to virtue and towers over the neighbourhood". Small circular temples, '' tholoi'' were also constructed, as well as small temple-like buildings that served as treasuries for specific groups of donors.
During the late 5th and 4th centuries BC, town planning became an important consideration of Greek builders, with towns such as Paestum
Paestum ( , , ) was a major Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of the Tyrrhenian Sea, in Magna Graecia. The ruins of Paestum are famous for their three ancient Greek temples in the Doric order dating from about 550 to 450 BCE that ...
and Priene being laid out with a regular grid of paved streets and an agora
The agora (; , romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Ancient Greece, Greek polis, city-states. The literal meaning of the word "agora" is "gathering place" or "assembly". The agora was the center ...
or central market place surrounded by a colonnade or stoa. The completely restored Stoa of Attalos can be seen in Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
. Towns were also equipped with a public fountain where water could be collected for household use. The development of regular town plans is associated with Hippodamus of Miletus, a pupil of Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
.
Public buildings became "dignified and gracious structures", and were sited so that they related to each other architecturally.. The propylon or porch, formed the entrance to temple sanctuaries and other significant sites with the best-surviving example being the Propylaea on the Acropolis of Athens. The bouleuterion
Bouleuterion (, ''bouleutērion''), also translated as and was a building in ancient Greece which housed the council of citizens (, ''boulē'') of a democratic city state. These representatives assembled at the bouleuterion to confer and de ...
was a large public building with a hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or und ...
hall that served as a court house and as a meeting place for the town council ( boule). Remnants of bouleuterion survive at Athens, Olympia and Miletus, the latter having held up to 1,200 people..
Every Greek town had an open-air theatre
Theatre or theater is a collaborative form of performing art that uses live performers, usually actors to present experiences of a real or imagined event before a live audience in a specific place, often a Stage (theatre), stage. The performe ...
. These were used for both public meetings as well as dramatic performances. The theatre was usually set in a hillside outside the town, and had rows of tiered seating set in a semicircle around the central performance area, the ''orchestra''. Behind the orchestra was a low building called the '' skênê'', which served as a store-room, a dressing room, and also as a backdrop to the action taking place in the orchestra. A number of Greek theatres survive almost intact, the best known being at Epidaurus
Epidaurus () was a small city (''polis'') in ancient Greece, on the Argolid Peninsula at the Saronic Gulf. Two modern towns bear the name Epidavros: ''Palaia Epidavros'' and ''Nea Epidavros''. Since 2010 they belong to the new municipality of Epi ...
by the architect Polykleitos the Younger..
Greek towns of substantial size also had a palaestra
A palaestra ( or ; also (chiefly British) palestra; ) was any site of a Greek wrestling school in antiquity. Events requiring little space, such as boxing and wrestling, occurred there. ''Palaistrai'' functioned both independently and as a part ...
or a gymnasium, the social centre for male citizens which included spectator areas, baths, toilets and club rooms. Other buildings associated with sports include the hippodrome
Hippodrome is a term sometimes used for public entertainment venues of various types. A modern example is the Hippodrome which opened in London in 1900 "combining circus, hippodrome, and stage performances".
The term hippodroming refers to fr ...
for horse racing, of which only remnants have survived, and the stadium
A stadium (: stadiums or stadia) is a place or venue for (mostly) outdoor sports, concerts, or other events and consists of a field or stage completely or partially surrounded by a tiered structure designed to allow spectators to stand or sit ...
for foot racing, 600 feet in length, of which examples exist at Olympia, Delphi, Epidaurus and Ephesus, while the Panathinaiko Stadium
The Panathenaic Stadium (, ) or ''Kallimarmaro'' ( , ) is a multi-purpose stadium in Athens, Greece. One of the main historic attractions of Athens, it is the only stadium in the world built entirely of marble.
A stadium was built on the site o ...
in Athens, which seats 45,000 people, was restored in the 19th century and was used in the 1896, 1906 and 2004 Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games (Olympics; ) are the world's preeminent international Olympic sports, sporting events. They feature summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a Multi-s ...
.
Structure
Post and lintel
abacus
An abacus ( abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a hand-operated calculating tool which was used from ancient times in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, until the adoption of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. A ...
. The part of the capital that rises from the column itself is called the echinus. It differs according to the order, being plain in the Doric order, fluted in the Ionic and foliate in the Corinthian. Doric and usually Ionic capitals are cut with vertical grooves known as fluting. This fluting or grooving of the columns is a retention of an element of the original wooden architecture.
Entablature and pediment
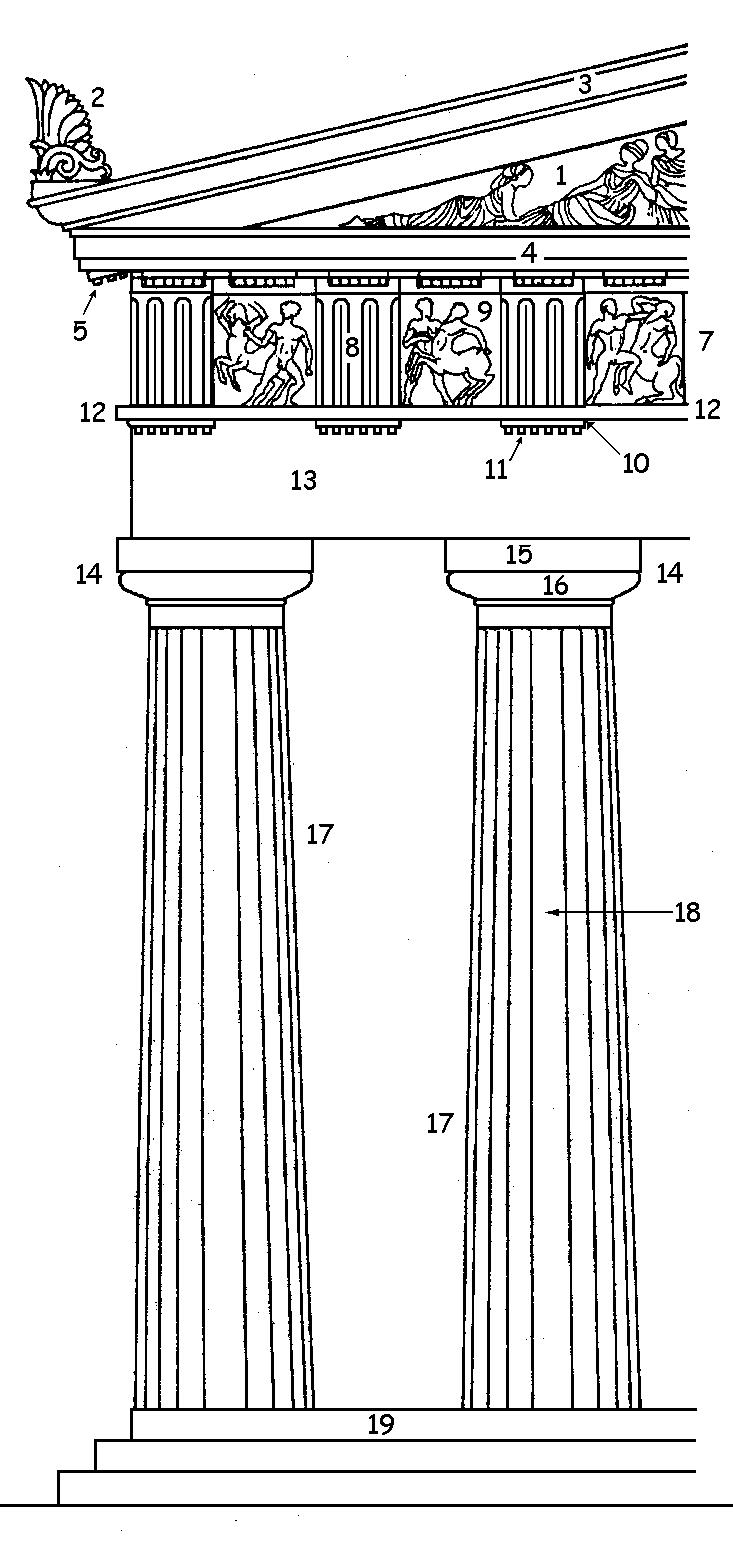
The columns of a temple support a structure that rises in two main stages, the entablature and thepediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
.
The entablature is the major horizontal structural element supporting the roof and encircling the entire building. It is composed of three parts. Resting on the columns is the architrave made of a series of stone "lintels" that spanned the space between the columns, and meet each other at a joint directly above the centre of each column.
Above the architrave is a second horizontal stage called the frieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
. The frieze is one of the major decorative elements of the building and carries a sculptured relief. In the case of Ionic and Corinthian architecture, the relief decoration runs in a continuous band, but in the Doric order, it is divided into sections called metope
A metope (; ) is a rectangular architectural element of the Doric order, filling the space between triglyphs in a frieze
, a decorative band above an architrave.
In earlier wooden buildings the spaces between triglyphs were first open, and ...
s, which fill the spaces between vertical rectangular blocks called triglyphs. The triglyphs are vertically grooved like the Doric columns, and retain the form of the wooden beams that would once have supported the roof.
The upper band of the entablature is called the cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative Moulding (decorative), moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, ar ...
, which is generally ornately decorated on its lower edge. The cornice retains the shape of the beams that would once have supported the wooden roof at each end of the building. At the front and rear of each temple, the entablature supports a triangular structure called the pediment. The tympanum is the triangular space framed by the cornices and the location of the most significant sculptural decoration on the exterior of the building.
Masonry
Every temple rested on a masonry base called the crepidoma, generally of three steps, of which the upper one which carried the columns was the stylobate. Masonry walls were employed for temples from about 600 BC onwards. Masonry of all types was used for ancient Greek buildings, including rubble, but the finestashlar
Ashlar () is a cut and dressed rock (geology), stone, worked using a chisel to achieve a specific form, typically rectangular in shape. The term can also refer to a structure built from such stones.
Ashlar is the finest stone masonry unit, a ...
masonry was usually employed for temple walls, in regular courses and large sizes to minimise the joints. The blocks were rough hewn and hauled from quarries to be cut and bedded very precisely, with mortar hardly ever being used. Blocks, particularly those of columns and parts of the building bearing loads were sometimes fixed in place or reinforced with iron clamps, dowels and rods of wood, bronze or iron fixed in lead to minimise corrosion.
Openings
Door and window openings were spanned with a lintel, which in a stone building limited the possible width of the opening. The distance between columns was similarly affected by the nature of the lintel, columns on the exterior of buildings and carrying stone lintels being closer together than those on the interior, which carried wooden lintels... Door and window openings narrowed towards the top. Temples were constructed without windows, the light to the naos entering through the door. It has been suggested that some temples were lit from openings in the roof. A door of the Ionic Order at the Erechtheion (17 feet high and 7.5 feet wide at the top) retains many of its features intact, including mouldings, and an entablature supported on console brackets. (See Architectural Decoration, below).Roof
The widest span of a temple roof was across the cella, or inner chamber. In a large building, this space contains columns to support the roof, the architectural form being known ashypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or und ...
. It appears that, although the architecture of ancient Greece was initially of wooden construction, the early builders did not have the concept of the diagonal truss as a stabilising member. This is evidenced by the nature of temple construction in the 6th century BC, where the rows of columns supporting the roof of the cella rise higher than the outer walls, unnecessary if roof trusses are employed as an integral part of the wooden roof. The indication is that initially all the rafters were supported directly by the entablature, walls and hypostyle, rather than on a trussed wooden frame, which came into use in Greek architecture only in the 3rd century BC.
Ancient Greek buildings of timber, clay and plaster construction were probably roofed with thatch. With the rise of stone architecture came the appearance of fired ceramic roof tiles
Roof tiles are overlapping tiles designed mainly to keep out precipitation such as rain or snow, and are traditionally made from locally available materials such as clay or slate. Later tiles have been made from materials such as concrete, glass ...
. These early roof tiles showed an S-shape, with the pan and cover tile forming one piece. They were much larger than modern roof tiles, being up to long, wide, thick and weighing around apiece. Only stone walls, which were replacing the earlier mudbrick
Mudbrick or mud-brick, also known as unfired brick, is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of mud (containing loam, clay, sand and water) mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE.
From ...
and wood walls, were strong enough to support the weight of a tiled roof..
The earliest finds of roof tiles of the Archaic period in Greece
Archaic Greece was the period in History of Greece, Greek history lasting from to the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC, following the Greek Dark Ages and succeeded by the Classical Greece, Classical period. In the archaic period, the ...
are documented from a very restricted area around Corinth
Corinth ( ; , ) is a municipality in Corinthia in Greece. The successor to the ancient Corinth, ancient city of Corinth, it is a former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, which is located in south-central Greece. Sin ...
, where fired tiles began to replace thatched roofs at the temples of Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, mu ...
and Poseidon
Poseidon (; ) is one of the twelve Olympians in ancient Greek religion and mythology, presiding over the sea, storms, earthquakes and horses.Burkert 1985pp. 136–139 He was the protector of seafarers and the guardian of many Hellenic cit ...
between 700 and 650 BC.. Spreading rapidly, roof tiles were within fifty years in evidence for a large number of sites around the Eastern Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
, including Mainland Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, Western Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, Southern and Central Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
. Being more expensive and labour-intensive to produce than thatch, their introduction has been explained by the fact that their fireproof quality would have given desired protection to the costly temples. As a side-effect, it has been assumed that the new stone and tile construction also ushered in the end of overhanging eaves in Greek architecture, as they made the need for an extended roof as rain protection for the mudbrick walls obsolete.
Vaults and arch
An arch is a curved vertical structure spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but stru ...
es were not generally used, but begin to appear in tombs (in a "beehive" or cantilevered form such as used in Mycenaea) and occasionally, as an external feature, exedrae of voussoired construction from the 5th century BC. The dome
A dome () is an architectural element similar to the hollow upper half of a sphere. There is significant overlap with the term cupola, which may also refer to a dome or a structure on top of a dome. The precise definition of a dome has been a m ...
and vault never became significant structural features, as they were to become in ancient Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often consi ...
.
Temple plans
Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
, are between 60 and 80 metres (approx. 200–260 feet) in length. The largest temples, mainly Ionic and Corinthian, but including the Doric Temple of the Olympian Zeus, Agrigento, were between 90 and 120 metres (approx. 300–390 feet) in length.
The temple rises from a stepped base or stylobate, which elevates the structure above the ground on which it stands. Early examples, such as the Temple of Zeus at Olympus, have two steps, but the majority, like the Parthenon, have three, with the exceptional example of the Temple of Apollo at Didyma having six.. The core of the building is a masonry-built "naos" within which is a cella, a windowless room originally housing the statue of the god. The cella generally has a porch or "pronaos" before it, and perhaps a second chamber or "antenaos" serving as a treasury or repository for trophies and gifts. The chambers were lit by a single large doorway, fitted with a wrought iron grill. Some rooms appear to have been illuminated by skylights.
On the stylobate, often completely surrounding the naos, stand rows of columns. Each temple is defined as being of a particular type, with two terms: one describing the number of columns across the entrance front, and the other defining their distribution.
Examples:
*''Distyle in antis
In classical architecture, distyle in antis denotes a temple with the side walls extending to the front of the porch and terminating with two antae, the pediment being supported by two columns or sometimes caryatids. This is the earliest ty ...
'' describes a small temple with two columns at the front, which are set between the projecting walls of the ''pronaos'' or porch, like the Temple of Nemesis at Rhamnus. (see above, figure 1.)
*''Amphiprostyle tetrastyle'' describes a small temple that has columns at both ends which stand clear of the ''naos''. ''Tetrastyle'' indicates that the columns are four in number, like those of the Temple on the Ilissus in Athens. (figure 4.)
*''Peripteral hexastyle'' describes a temple with a single row of peripheral columns around the ''naos'', with six columns across the front, like the Theseion in Athens. (figure 7.)
*''Peripteral octastyle'' describes a temple with a single row of columns around the ''naos'', (figure 7.) with eight columns across the front, like the Parthenon, Athens. (figures 6 and 9.)
*''Dipteral decastyle'' describes the huge temple of Apollo at Didyma, with the ''naos'' surrounded by a double row of columns, (figure 6.) with ten columns across the entrance front.
* The Temple of Zeus Olympius at Agrigentum, is termed ''Pseudo-periteral heptastyle'', because its encircling colonnade has ''pseudo'' columns that are attached to the walls of the ''naos''. (figure 8.) ''Heptastyle'' means that it has seven columns across the entrance front.
Proportion and optical illusion
The ideal of proportion that was used by ancient Greek architects in designing temples was not a simple mathematical progression using a square module. The math involved a more complex geometrical progression, the so-called golden mean. The ratio is similar to that of the growth patterns of many spiral forms that occur in nature such as rams' horns,nautilus
A nautilus (; ) is any of the various species within the cephalopod family Nautilidae. This is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and the suborder Nautilina.
It comprises nine living species in two genera, the type genus, ty ...
shells, fern fronds, and vine tendrils and which were a source of decorative motifs employed by ancient Greek architects as particularly in evidence in the volutes of capitals of the Ionic and Corinthian Orders..
:
The ancient Greek architects took a philosophic approach to the rules and proportions. The determining factor in the mathematics of any notable work of architecture was its ultimate appearance. The architects calculated for perspective, for the optical illusions that make edges of objects appear concave and for the fact that columns that are viewed against the sky look different from those adjacent that are viewed against a shadowed wall. Because of these factors, the architects adjusted the plans so that the major lines of any significant building are rarely straight. The most obvious adjustment is to the profile of columns, which narrow from base to top. However, the narrowing is not regular, but gently curved so that each column appears to have a slight swelling, called ''entasis'' below the middle. The ''entasis'' is never sufficiently pronounced as to make the swelling wider than the base; it is controlled by a slight reduction in the rate of decrease of diameter.
The Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
, the Temple to the Goddess Athena
Athena or Athene, often given the epithet Pallas, is an ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek goddess associated with wisdom, warfare, and handicraft who was later syncretism, syncretized with the Roman goddess Minerva. Athena was regarde ...
on the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens ...
in Athens, is referred to by many as the pinnacle of ancient Greek architecture. Helen Gardner refers to its "unsurpassable excellence", to be surveyed, studied and emulated by architects of later ages. Yet, as Gardner points out, there is hardly a straight line in the building. Banister Fletcher calculated that the ''stylobate'' curves upward so that its centres at either end rise about above the outer corners, and on the longer sides. A slightly greater adjustment has been made to the entablature. The columns at the ends of the building are not vertical but are inclined towards the centre, with those at the corners being out of plumb by about . These outer columns are both slightly wider than their neighbours and are slightly closer than any of the others..
Style
Orders
Ancient Greek architecture of the most formal type, for temples and other public buildings, is divided stylistically into threeClassical order
An order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform.
Coming down to the present from Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek and Ancient Roman civiliz ...
s, first described by the Roman architectural writer Vitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
. These are: the Doric order
The Doric order is one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of t ...
, the Ionic order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric) ...
, and the Corinthian order
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric or ...
, the names reflecting their regional origins within the Greek world. While the three orders are most easily recognizable by their capitals, they also governed the form, proportions, details and relationships of the columns, entablature, pediment
Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an ...
, and the stylobate. The different orders were applied to the whole range of buildings and monuments.
The Doric order developed on mainland Greece and spread to Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia refers to the Greek-speaking areas of southern Italy, encompassing the modern Regions of Italy, Italian regions of Calabria, Apulia, Basilicata, Campania, and Sicily. These regions were Greek colonisation, extensively settled by G ...
(Italy). It was firmly established and well-defined in its characteristics by the time of the building of the Temple of Hera at Olympia, c. 600 BC. The Ionic order co-existed with the Doric, being favoured by the Greek cities of Ionia
Ionia ( ) was an ancient region encompassing the central part of the western coast of Anatolia. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionians who ...
, in Asia Minor
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
and the Aegean Islands. It did not reach a clearly defined form until the mid 5th century BC. The early Ionic temples of Asia Minor were particularly ambitious in scale, such as the Temple of Artemis
The Temple of Artemis or Artemision (; ), also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to an ancient, localised form of the goddess Artemis (equated with the Religion in ancient Rome, Roman goddess Diana (mythology), Diana) ...
at Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital ...
. The Corinthian order was a highly decorative variant not developed until the Hellenistic
In classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Greek history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the death of Cleopatra VII in 30 BC, which was followed by the ascendancy of the R ...
period and retaining many characteristics of the Ionic. It was popularised by the Romans.
Doric order
The Doric order is recognised by its capital, of which the ''echinus'' is like a circular cushion rising from the top of the column to the square ''abacus'' on which rest the lintels. The echinus appears flat and splayed in early examples, deeper and with greater curve in later, more refined examples, and smaller and straight-sided in Hellenistic examples. A refinement of the Doric column is the entasis, a gentle convex swelling to the profile of the column, which prevents an optical illusion of concavity. This is more pronounced in earlier examples. Doric columns are almost always cut with grooves, known as "fluting", which run the length of the column and are usually 20 in number, although sometimes fewer. The flutes meet at sharp edges called '' arrises''. At the top of the columns, slightly below the narrowest point, and crossing the terminating arrises, are three horizontal grooves known as the '' hypotrachelion''. Doric columns have no bases, until a few examples in the Hellenistic period. The columns of an early Doric temple such as the Temple of Apollo at Syracuse, Sicily, may have a height to base diameter ratio of only 4:1 and a column height to entablature ratio of 2:1, with relatively crude details. A column height to diameter of 6:1 became more usual, while the column height to entablature ratio at the Parthenon is about 3:1. During the Hellenistic period, Doric conventions of solidity and masculinity dropped away, with the slender and unfluted columns reaching a height to diameter ratio of 7.5:1.. The Doric entablature is in three parts, the architrave, thefrieze
In classical architecture, the frieze is the wide central section of an entablature and may be plain in the Ionic order, Ionic or Corinthian order, Corinthian orders, or decorated with bas-reliefs. Patera (architecture), Paterae are also ...
and the cornice
In architecture, a cornice (from the Italian ''cornice'' meaning "ledge") is generally any horizontal decorative Moulding (decorative), moulding that crowns a building or furniture element—for example, the cornice over a door or window, ar ...
. The architrave is composed of the stone lintels which span the space between the columns, with a joint occurring above the centre of each abacus. On this rests the frieze, one of the major areas of sculptural decoration. The frieze is divided into ''triglyphs'' and ''metopes'', the triglyphs, as stated elsewhere in this article, are a reminder of the timber history of the architectural style. Each triglyph has three vertical grooves, similar to the columnar fluting, and below them, seemingly connected, are guttae, small strips that appear to connect the triglyphs to the architrave below. A triglyph is located above the centre of each capital, and above the centre of each lintel. However, at the corners of the building, the triglyphs do not fall over the centre the column. The ancient architects took a pragmatic approach to the apparent "rules", simply extending the width of the last two metopes at each end of the building.
The cornice is a narrow jutting band of complex molding, which overhangs and protects the ornamented frieze, like the edge of an overhanging wooden-framed roof. It is decorated on the underside with projecting blocks, ''mutules'', further suggesting the wooden nature of the prototype. At either end of the building the pediment rises from the cornice, framed by moulding of similar form.
The pediment is decorated with figures that are in relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
in the earlier examples, though almost free-standing by the time of the sculpture on the Parthenon. Early architectural sculptors found difficulty in creating satisfactory sculptural compositions in the tapering triangular space. By the Early Classical period, with the decoration of the Temple of Zeus at Olympia (486–460 BC), the sculptors had solved the problem by having a standing central figure framed by rearing centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
s and fighting men who are falling, kneeling and lying in attitudes that fit the size and angle of each part of the space.. The famous sculptor Phidias
Phidias or Pheidias (; , ''Pheidias''; ) was an Ancient Greek sculptor, painter, and architect, active in the 5th century BC. His Statue of Zeus at Olympia was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Phidias also designed the statues of ...
fills the space at the Parthenon (448–432 BC) with a complex array of draped and undraped figures of deities, who appear in attitudes of sublime relaxation and elegance.
Ionic order
TheIonic order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric) ...
is recognized by its voluted capital, in which a curved ''echinus'' of similar shape to that of the Doric order, but decorated with stylised ornament, is surmounted by a horizontal band that scrolls under to either side, forming spirals or ''volutes'' similar to those of the nautilus
A nautilus (; ) is any of the various species within the cephalopod family Nautilidae. This is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and the suborder Nautilina.
It comprises nine living species in two genera, the type genus, ty ...
shell or ram's horn. In plan, the capital is rectangular. It is designed to be viewed frontally but the capitals at the corners of buildings are modified with an additional scroll so as to appear regular on two adjoining faces. In the Hellenistic period, four-fronted Ionic capitals became common..
Like the Doric order, the Ionic order retains signs of having its origins in wooden architecture. The horizontal spread of a flat timber plate across the top of a column is a common device in wooden construction, giving a thin upright a wider area on which to bear the lintel, while at the same time reinforcing the load-bearing strength of the lintel itself. Likewise, the columns always have bases, a necessity in wooden architecture to spread the load and protect the base of a comparatively thin upright. The columns are fluted with narrow, shallow flutes that do not meet at a sharp edge but have a flat band or ''fillet'' between them. The usual number of flutes is twenty-four but there may be as many as forty-four. The base has two convex mouldings called ''torus'', and from the late Hellenic period stood on a square plinth similar to the ''abacus''.
The architrave of the Ionic order is sometimes undecorated, but more often rises in three outwardly-stepped bands like overlapping timber planks. The frieze, which runs in a continuous band, is separated from the other members by rows of small projecting blocks. They are referred to as dentils, meaning "teeth", but their origin is clearly in narrow wooden slats which supported the roof of a timber structure. The Ionic order is altogether lighter in appearance than the Doric, with the columns, including base and capital, having a 9:1 ratio with the diameter, while the whole entablature was also much narrower and less heavy than the Doric entablature. There was some variation in the distribution of decoration. Formalised bands of motifs such as alternating forms known as egg-and-dart
Egg-and-dart, also known as egg-and-tongue, egg-and-anchor, or egg-and-star, is an Ornament (architecture), ornamental device adorning the fundamental quarter-round, convex ovolo profile of molding (decorative), moulding, consisting of alternating ...
were a feature of the Ionic entablatures, along with the bands of dentils. The external frieze often contained a continuous band of figurative sculpture or ornament, but this was not always the case. Sometimes a decorative frieze occurred around the upper part of the ''naos'' rather than on the exterior of the building. These Ionic-style friezes around the ''naos'' are sometimes found on Doric buildings, notably the Parthenon. Some temples, like the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus, had friezes of figures around the lower drum of each column, separated from the fluted section by a bold moulding.
Caryatids, draped female figures used as supporting members to carry the entablature, were a feature of the Ionic order, occurring at several buildings including the Siphnian Treasury
The Siphnian Treasury was a building at the Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek cult centre of Delphi, erected to host the offerings of the polis, or city-state, of Sifnos, Siphnos. It was one of a number of treasuries lining the "Sacred Way", the proc ...
at Delphi in 525 BC and at the Erechtheion, about 410 BC.
Corinthian order
The Corinthian order does not have its origin in wooden architecture. It grew directly out of the Ionic in the mid 5th century BC, and was initially of much the same style and proportion, but distinguished by its more ornate capitals.. The capital was very much deeper than either the Doric or the Ionic capital, being shaped like a large ''krater'', a bell-shaped mixing bowl, and being ornamented with a double row of acanthus leaves above which rose voluted tendrils, supporting the corners of the abacus, which, no longer perfectly square, splayed above them. According toVitruvius
Vitruvius ( ; ; –70 BC – after ) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work titled . As the only treatise on architecture to survive from antiquity, it has been regarded since the Renaissan ...
, the capital was invented by a bronze founder, Callimachus
Callimachus (; ; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar, and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works, most of which ...
of Corinth, who took his inspiration from a basket of offerings that had been placed on a grave, with a flat tile on top to protect the goods. The basket had been placed on the root of an acanthus plant which had grown up around it. The ratio of the column height to diameter is generally 10:1, with the capital taking up more than 1/10 of the height. The ratio of capital height to diameter is generally about 1.16:1.
The Corinthian order was initially used internally, as at the Temple of Apollo Epicurius at Bassae (c. 450–425 BC). In 334 BC, it appeared as an external feature on the Choragic Monument of Lysicrates
The Choragic Monument of Lysicrates near the Acropolis of Athens was erected by the ''Choregos (ancient Greece), choregos'' Lysicrates, a wealthy patron of musical performances in the Theater of Dionysus, to commemorate the prize in the dithyram ...
in Athens, and then on a huge scale at the Temple of Zeus Olympia in Athens (174 BC–132 AD). It was popularised by the Romans, who added a number of refinements and decorative details. During the Hellenistic period, Corinthian columns were sometimes built without fluting.
Decoration
Architectural ornament
Early wooden structures, particularly temples, were ornamented and in part protected by fired and painted terracotta revetments in the form of rectangular panels, and ornamental discs. Many fragments of these have outlived the buildings that they decorated and demonstrate a wealth of formal border designs of geometric scrolls, overlapping patterns and foliate motifs. With the introduction of stone-built temples, the revetments no longer served a protective purpose and sculptured decoration became more common. The clay ornaments were limited to the roof of buildings, decorating the cornice, the corners and surmounting the pediment. At the corners of pediments they were called acroteria and along the sides of the building, antefixes. Early decorative elements were generally semi-circular, but later of roughly triangular shape with moulded ornament, often palmate... Ionic cornices were often set with a row of lion's masks, with open mouths that ejected rainwater. From the Late Classical period, acroteria were sometimes sculptured figures (see Architectural sculpture). In the three orders of ancient Greek architecture, the sculptural decoration, be it a simple half round astragal, a frieze of stylised foliage or the ornate sculpture of the pediment, is all essential to the architecture of which it is a part. In the Doric order, there is no variation in its placement. Reliefs never decorate walls in an arbitrary way. The sculpture is always located in several predetermined areas, the metopes and the pediment. In later Ionic architecture, there is greater diversity in the types and numbers of mouldings and decorations, particularly around doorways, where volutedbrackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. They come in four main pairs of shapes, as given in the box to the right, which also gives their n ...
sometimes occur supporting an ornamental cornice over a door, such as that at the Erechtheion. A much applied narrow moulding is called "bead and reel" and is symmetrical, stemming from turned wooden prototypes. Wider mouldings include one with tongue-like or pointed leaf shapes, which are grooved and sometimes turned upward at the tip, and "egg and dart" moulding which alternates ovoid shapes with narrow pointed ones.
Architectural sculpture
Architectural sculpture showed a development from early Archaic examples through Severe Classical, High Classical, Late Classical and Hellenistic. Remnants of Archaic architectural sculpture (700–500 BC) exist from the early 6th century BC with the earliest survivingpedimental sculpture
Pedimental sculpture is a form of architectural sculpture designed for installation in the Tympanum (architecture), tympanum, the space enclosed by the architectural element called the pediment. Originally a feature of Ancient Greek architecture, ...
s being fragments of a Gorgon flanked by heraldic panthers from the centre of the pediment of the Artemis Temple of Corfu.. A metope from a temple known as "Temple C" at Selinus, Sicily, shows, in a better preserved state, Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
slaying the Gorgon Medusa.. Both images parallel the stylised depiction of the Gorgons on the black figure name vase decorated by the Nessos painter (c. 600 BC), with the face and shoulders turned frontally, and the legs in a running or kneeling position. At this date, images of terrifying monsters have predominance over the emphasis on the human figure that developed with Humanist philosophy.
Early pedimental sculptures, and those on smaller temples, were usually in relief
Relief is a sculpture, sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces remain attached to a solid background of the same material. The term ''wikt:relief, relief'' is from the Latin verb , to raise (). To create a sculpture in relief is to give ...
, and the late free-standing ones were often in terracotta, which has survived only in fragments. The sculptures were covered with a layer of stucco and painted or, if terracotta, painted with the more restrained fired colours of Greek pottery.
The ''Severe Classical Style'' (500–450 BC) is represented by the pedimental sculptures of the Temple of Zeus at Olympia (470–456 BC). The eastern pediment shows a moment of stillness and "impending drama" before the beginning of a chariot race, the figures of Zeus and the competitors being severe and idealised representations of the human form. The western pediment has Apollo as the central figure, "majestic" and "remote", presiding over a battle of Lapiths and Centaur
A centaur ( ; ; ), occasionally hippocentaur, also called Ixionidae (), is a creature from Greek mythology with the upper body of a human and the lower body and legs of a horse that was said to live in the mountains of Thessaly. In one version o ...
s, in strong contrast to that of the eastern pediment for its depiction of violent action, and described by Donald E. Strong as the "most powerful piece of illustration" for a hundred years..
 The reliefs and three-dimensional sculpture which adorned the frieze and pediments, respectively, of the Parthenon, are the lifelike products of the High Classical style (450–400 BC) and were created under the direction of the sculptor
The reliefs and three-dimensional sculpture which adorned the frieze and pediments, respectively, of the Parthenon, are the lifelike products of the High Classical style (450–400 BC) and were created under the direction of the sculptor Phidias
Phidias or Pheidias (; , ''Pheidias''; ) was an Ancient Greek sculptor, painter, and architect, active in the 5th century BC. His Statue of Zeus at Olympia was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Phidias also designed the statues of ...
.. The pedimental sculpture represents the Gods of Olympus, while the frieze shows the Panathenaic procession and ceremonial events that took place every four years to honour the titular Goddess of Athens. The frieze and remaining figures of the eastern pediment show a profound understanding of the human body, and how it varies depending upon its position and the stresses that action and emotion place upon it. Benjamin Robert Haydon described the reclining figure of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, myth, Dionysus (; ) is the god of wine-making, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, festivity, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, and theatre. He was also known as Bacchus ( or ; ...
as "the most heroic style of art, combined with all the essential detail of actual life".
The names of many famous sculptors are known from the Late Classical period (400–323 BC), including Timotheos, Praxiteles, Leochares and Skopas, but their works are known mainly from Roman copies. Little architectural sculpture of the period remains intact. The Temple of Asclepius at Epidauros had sculpture by Timotheos working with the architect Theodotos. Fragments of the eastern pediment survive, showing the Sack of Troy. The scene appears to have filled the space with figures carefully arranged to fit the slope and shape available, as with the earlier east pediment of the Temple of Zeus at Olympus. But the figures are more violent in action, the central space taken up, not with a commanding God, but with the dynamic figure of Neoptolemos as he seizes the aged king Priam
In Greek mythology, Priam (; , ) was the legendary and last king of Troy during the Trojan War. He was the son of Laomedon. His many children included notable characters such as Hector, Paris, and Cassandra.
Etymology
Most scholars take the e ...
and stabs him. The remaining fragments give the impression of a range of human emotions, fear, horror, cruelty and lust for conquest.. The ''acroteria'' were sculptured by Timotheus, except for that at the centre of the east pediment which is the work of the architect. The palmate acroteria have been replaced here with small figures, the eastern pediment being surmounted by a winged Nike, poised against the wind.
Hellenistic architectural sculpture (323–31 BC) was to become more flamboyant, both in the rendering of expression and motion, which is often emphasised by flowing draperies, the Nike Samothrace which decorated a monument in the shape of a ship being a well-known example. The Pergamon Altar (c. 180–160 BC) has a frieze (120 metres long by 2.3 metres high) of figures in very high relief. The frieze represents the battle for supremacy of Gods and Titans, and employs many dramatic devices: frenzy, pathos and triumph, to convey the sense of conflict..
See also
*Ancient Greek art
Ancient Greek art stands out among that of other ancient cultures for its development of naturalistic but idealized depictions of the human body, in which largely nude male figures were generally the focus of innovation. The rate of stylistic d ...
* Ancient Roman architecture
Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often consi ...
* Byzantine architecture
Byzantine architecture is the architecture of the Byzantine Empire, or Eastern Roman Empire, usually dated from 330 AD, when Constantine the Great established a new Roman capital in Byzantium, which became Constantinople, until the Fall of Cons ...
* Classical architecture
Classical architecture typically refers to architecture consciously derived from the principles of Ancient Greek architecture, Greek and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture of classical antiquity, or more specifically, from ''De archit ...
* Greek culture
* Greek technology
* List of ancient architectural records
* List of ancient Greek temples
* Modern Greek architecture
* Outline of classical architecture
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*The Foundations of Classical Architecture Part Two: Greek Classicism
– Free educational program by the ICAA (published August 29, 2018) * Joseph Woods (1828)
Letters of an Architect, From France, Italy, and Greece
{{DEFAULTSORT:Architecture Of Ancient Greece Architectural history