|
Temple Of Apollo (Syracuse)
The Temple of Apollo ( grc-gre, Ἀπολλώνιον ''Apollonion'') is one of the most important ancient Greek monuments on Ortygia, in front of the Piazza Pancali in Syracuse, Sicily, Italy. History Dating to the 6th century B.C., this temple is one of the most ancient Doric temples in Sicily, and among the first with the layout consisting of a peripteros of stone columns. This layout became standard for Greek temples.Mertens 2006, pp. 104-109. The temple underwent several transformations: closed during the persecution of pagans in the late Roman Empire, it was a Byzantine church, from which period the front steps and traces of a central door are preserved, and then an Islamic mosque during the Emirate of Sicily. After the Norman defeat of the Saracens, it was reconsecrated at the Church of the Saviour, which was then incorporated into a 16th-century Spanish barracks and into private houses, though some architectural elements remained visible. For instance, in 1778, Dominique ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of Aragon
The Crown of Aragon ( , ) an, Corona d'Aragón ; ca, Corona d'Aragó, , , ; es, Corona de Aragón ; la, Corona Aragonum . was a composite monarchy ruled by one king, originated by the dynastic union of the Kingdom of Aragon and the County of Barcelona and ended as a consequence of the War of the Spanish Succession. At the height of its power in the 14th and 15th centuries, the Crown of Aragon was a thalassocracy controlling a large portion of present-day eastern Spain, parts of what is now southern France, and a Mediterranean empire which included the Balearic Islands, Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia, Malta, Southern Italy (from 1442) and parts of Greece (until 1388). The component realms of the Crown were not united politically except at the level of the king, who ruled over each autonomous polity according to its own laws, raising funds under each tax structure, dealing separately with each ''Corts'' or ''Cortes'', particularly the Kingdom of Aragon, the Principality of Catalonia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Greece
Archaic Greece was the period in Greek history lasting from circa 800 BC to the second Persian invasion of Greece in 480 BC, following the Greek Dark Ages and succeeded by the Classical period. In the archaic period, Greeks settled across the Mediterranean and the Black Seas, as far as Marseille in the west and Trapezus (Trebizond) in the east; and by the end of the archaic period, they were part of a trade network that spanned the entire Mediterranean. The archaic period began with a massive increase in the Greek population and of significant changes that rendered the Greek world at the end of the 8th century entirely unrecognisable from its beginning. According to Anthony Snodgrass, the archaic period was bounded by two revolutions in the Greek world. It began with a "structural revolution" that "drew the political map of the Greek world" and established the ''poleis'', the distinctively Greek city-states, and it ended with the intellectual revolution of the Classical peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
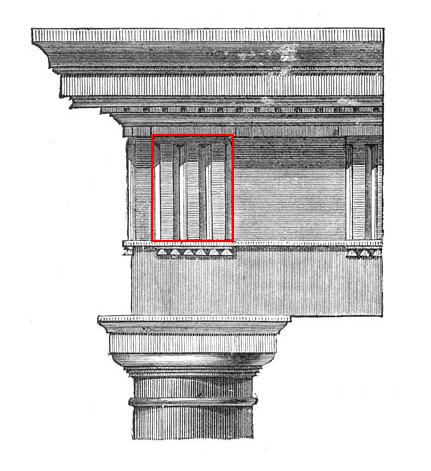
Triglyph
Triglyph is an architectural term for the vertically channeled tablets of the Doric frieze in classical architecture, so called because of the angular channels in them. The rectangular recessed spaces between the triglyphs on a Doric frieze are called metopes. The raised spaces between the channels themselves (within a triglyph) are called ''femur'' in Latin or ''meros'' in Greek. In the strict tradition of classical architecture, a set of guttae, the six triangular "pegs" below, always go with a triglyph above (and vice versa), and the pair of features are only found in entablatures of buildings using the Doric order. The absence of the pair effectively converts a building from being in the Doric order to being in the Tuscan order. The triglyph is largely thought to be a tectonic and skeuomorphic representation in stone of the wooden beam ends of the typical primitive hut, as described by Vitruvius and Renaissance writers. The wooden beams were notched in three separate plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercolumniation
In architecture, intercolumniation is the proportional spacing between columns in a colonnade, often expressed as a multiple of the column diameter as measured at the bottom of the shaft. In Classical, Renaissance, and Baroque architecture, intercolumniation was determined by a system described by the first-century BC Roman architect Vitruvius (Vitruvius, ''De architectura'', iii.3.3-10). Vitruvius named five systems of intercolumniation (Pycnostyle, Systyle, Eustyle, Diastyle, and Araeostyle), and warned that when columns are placed three column-diameters or more apart, stone architraves break. According to Vitruvius, the Hellenistic architect Hermogenes (ca. 200 BC) formulated these proportions ("''symmetriae''") and perfected the Eustyle arrangement, which has an enlarged bay in the center of the façade. Standard intercolumniations The standard intercolumniations are: ; Pycnostyle : One and a half diameters ; Systyle : Two diameters ; Eustyle : Two and a quarter diam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Style
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Dori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adyton
The adyton ( , 'innermost sanctuary, shrine', ) or (Latin) was a restricted area within the cella of a Greek or Roman temple. The ''adyton'' was frequently a small area at the farthest end of the cella from the entrance: at Delphi it measured just . The ''adyton'' often would house the cult image of the deity. ''Adyta'' were spaces reserved for oracles, priestesses, priests, or acolytes, and not for the general public. ''Adyta'' were found frequently associated with temples of Apollo, as at Didyma, Bassae, Clarus, Delos, and Delphi, although they were also said to have been natural phenomena (see the story of Nyx). Those sites often had been dedicated to deities whose worship preceded that of Apollo and may go back to prehistoric eras, such as Delphi, but who were supplanted by the time of Classical Greek culture. In modern usage, the term is sometimes extended to similar spaces in other cultural contexts, as in Egyptian temples or the Western mystery school, Builders of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cella
A cella (from Latin for small chamber) or naos (from the Ancient Greek, Greek ναός, "temple") is the inner chamber of an ancient Greek temple, Greek or Roman temple in classical antiquity. Its enclosure within walls has given rise to extended meanings, of a Monastery, hermit's or monk's cell, and since the 17th century, of a Cell (biology), biological cell in plants or animals. Greek and Roman temples In ancient Greek temple, Greek and Roman temples the cella was a room at the center of the building, usually containing a cult image or statue representing the particular deity venerated in the temple. In addition, the cella may contain a table to receive supplementary votive offerings such as votive statues of associated deities, precious and semi-precious stones, helmets, spear and arrow heads, swords, and war trophy, war trophies. No gatherings or sacrifices took place in the cella as the altar for sacrifices was always located outside the building along the axis and tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronaos
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexastyle
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cultures, including most Western cultures. Some noteworthy examples of porticos are the East Portico of the United States Capitol, the portico adorning the Pantheon in Rome and the portico of University College London. Porticos are sometimes topped with pediments. Palladio was a pioneer of using temple-fronts for secular buildings. In the UK, the temple-front applied to The Vyne, Hampshire, was the first portico applied to an English country house. A pronaos ( or ) is the inner area of the portico of a Greek or Roman temple, situated between the portico's colonnade or walls and the entrance to the ''cella'', or shrine. Roman temples commonly had an open pronaos, usually with only columns and no walls, and the pronaos could be as long as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylobate
In classical Greek architecture, a stylobate ( el, στυλοβάτης) is the top step of the crepidoma, the stepped platform upon which colonnades of temple columns are placed (it is the floor of the temple). The platform was built on a leveling course that flattened out the ground immediately beneath the temple. Etymology The term ''stylobate'' comes from the Ancient Greek στυλοβάτης, consisting of στῦλος stylos, "column", and βατός batos, "walkable, mountable", itself derived from βαίνω baino "to stride, to walk". Terminology Some methodologies use the word ''stylobate'' to describe only the topmost step of the temple's base, while stereobate is used to describe the remaining steps of the platform beneath the stylobate and just above the leveling course. Others, like John Lord, use the term to refer to the entire platform. Architectural use The stylobate was often designed to relate closely to the dimensions of other elements of the temple. In Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |