Acetyl-CoA carboxylase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a
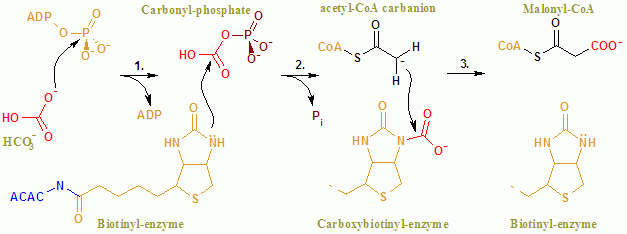 In the
In the
 The regulation of mammalian ACC is complex, in order to control two distinct pools of malonyl CoA that direct either the inhibition of beta oxidation or the activation of lipid biosynthesis.
Mammalian ACC1 and ACC2 are regulated transcriptionally by multiple promoters which mediate ACC abundance in response to the cells nutritional status. Activation of gene expression through different promoters results in
The regulation of mammalian ACC is complex, in order to control two distinct pools of malonyl CoA that direct either the inhibition of beta oxidation or the activation of lipid biosynthesis.
Mammalian ACC1 and ACC2 are regulated transcriptionally by multiple promoters which mediate ACC abundance in response to the cells nutritional status. Activation of gene expression through different promoters results in
biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bo ...
-dependent enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
() that catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation
Carboxylation is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid is produced by treating a substrate with carbon dioxide. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation. In chemistry, the term carbonation is sometimes used synonymously with carboxylatio ...
of acetyl-CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
to produce malonyl-CoA
Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.
Functions
It plays a key role in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis.
Fatty acid biosynthesis
Malonyl-CoA provides 2-carbon units to fatty acids and com ...
through its two catalytic activities, biotin carboxylase
In enzymology, a biotin carboxylase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
: ATP + biotin-carboxyl-carrier protein + CO2 \rightleftharpoons ADP + phosphate + carboxybiotin-carboxyl-carrier protein
The three substrates of this ...
(BC) and carboxyltransferase (CT). ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in most prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
and in the chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it i ...
s of most plants and algae, whereas it is a large, multi-domain enzyme in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
of most eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
. The most important function of ACC is to provide the malonyl-CoA substrate for the biosynthesis of fatty acids
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is co ...
. The activity of ACC can be controlled at the transcriptional level as well as by small molecule modulators and covalent modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosome ...
. The human genome contains the genes for two different ACCs—''ACACA
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 also known as ACC-alpha or ACCa is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ACACA'' gene.
Function
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a complex multifunctional enzyme system. ACC is a biotin-containing enzyme which c ...
'' and ''ACACB
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2 also known as ACC-beta or ACC2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''ACACB'' gene.
Function
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a complex multifunctional enzyme system. ACC is a biotin-containing enzyme which cat ...
''.
Structure
Prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
and plants
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
have multi-subunit ACCs composed of several polypeptides. Biotin carboxylase (BC) activity, biotin carboxyl carrier protein
Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein (BCCP) refers to proteins containing a biotin attachment domain that carry biotin and carboxybiotin throughout the ATP-dependent carboxylation by biotin-dependent carboxylases. In the case of ''E. coli'' Acetyl-Co ...
(BCCP), and carboxyl transferase (CT) activity are each contained on a different subunit. The stoichiometry of these subunits in the ACC holoenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. ...
differs amongst organisms. Humans and most eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacter ...
have evolved an ACC with CT and BC catalytic domains and BCCP domains on a single polypeptide. Most plants also have this homomeric form in cytosol. ACC functional regions, starting from the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
to C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein i ...
are the biotin carboxylase (BC), biotin binding (BB), carboxyl transferase (CT), and ATP-binding (AB). AB lies within BC. Biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bo ...
is covalently attached through an amide bond to the long side chain
In organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called the "main chain" or backbone. The side chain is a hydrocarbon branching element of a molecule that is attached to a ...
of a lysine reside in BB. As BB is between BC and CT regions, biotin can easily translocate to both of the active sites where it is required.
In mammals where two isoforms of ACC are expressed, the main structural difference between these isoforms is the extended ACC2 N-terminus containing a mitochondrial targeting sequence
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used t ...
.
Genes
The polypeptides composing the multi-subunit ACCs ofprokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Con ...
and plants
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude ...
are encoded by distinct genes. In ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Esc ...
'', ''accA'' encodes the alpha subunit of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and ''accD'' encodes its beta subunit.
Mechanism
The overall reaction of ACAC(A,B) proceeds by a two-step mechanism. The first reaction is carried out by BC and involves the ATP-dependent carboxylation ofbiotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bo ...
with bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemi ...
serving as the source of CO2. The carboxyl group is transferred from biotin
Biotin (or vitamin B7) is one of the B vitamins. It is involved in a wide range of metabolic processes, both in humans and in other organisms, primarily related to the utilization of fats, carbohydrates, and amino acids. The name ''biotin'', bo ...
to acetyl CoA
Acetyl-CoA (acetyl coenzyme A) is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Its main function is to deliver the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for ...
to form malonyl CoA in the second reaction, which is catalyzed by CT.
 In the
In the active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate ( binding site) ...
, the reaction proceeds with extensive interaction of the residues Glu296 and positively charged Arg338 and Arg292 with the substrates. Two Mg2+ are coordinated by the phosphate groups on the ATP, and are required for ATP binding to the enzyme. Bicarbonate is deprotonated by Glu296, although in solution, this proton transfer is unlikely as the pKa
PKA may refer to:
* Professionally known as:
** Pen name
** Stage persona
* p''K''a, the symbol for the acid dissociation constant at logarithmic scale
* Protein kinase A, a class of cAMP-dependent enzymes
* Pi Kappa Alpha, the North-American so ...
of bicarbonate is 10.3. The enzyme apparently manipulates the pKa to facilitate the deprotonation of bicarbonate. The pKa of bicarbonate is decreased by its interaction with positively charged side chains of Arg338 and Arg292. Furthermore, Glu296 interacts with the side chain of Glu211, an interaction that has been shown to cause an increase in the apparent pKa. Following deprotonation of bicarbonate, the oxygen of the bicarbonate acts as a nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they ar ...
and attacks the gamma phosphate on ATP. The carboxyphosphate intermediate quickly decomposes to CO2 and PO43−. The PO43− deprotonates biotin, creating an enolate, stabilized by Arg338, that subsequently attacks CO2 resulting in the production of carboxybiotin. The carboxybiotin translocates to the carboxyl transferase (CT) active site, where the carboxyl group is transferred to acetyl-CoA. In contrast to the BC domain, little is known about the reaction mechanism of CT. A proposed mechanism is the release of CO2 from biotin, which subsequently abstracts a proton from the methyl group from acetyl CoA carboxylase. The resulting enolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds.
Bonding and structure
Enolate anions are electr ...
attacks CO2 to form malonyl CoA. In a competing mechanism, proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
abstraction is concerted with the attack of acetyl CoA.
Function
The function of ACC is to regulate the metabolism of fatty acids. When the enzyme is active, the product, malonyl-CoA, is produced which is a building block for new fatty acids and can inhibit the transfer of the fatty acyl group from acyl CoA tocarnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, an ...
with carnitine acyltransferase, which inhibits the beta-oxidation
In biochemistry and metabolism, beta-oxidation is the catabolic process by which fatty acid molecules are broken down in the cytosol in prokaryotes and in the mitochondria in eukaryotes to generate acetyl-CoA, which enters the citric acid cycle, ...
of fatty acids in the mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is used ...
.
In mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur o ...
, two main isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ...
of ACC are expressed, ACC1 and ACC2, which differ in both tissue distribution and function. ACC1 is found in the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
of all cells but is enriched in lipogenic tissue, such as adipose
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
tissue and lactating mammary glands, where fatty acid synthesis is important. In oxidative tissues, such as the skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m ...
and the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
, the ratio of ACC2 expressed is higher. ACC1 and ACC2 are both highly expressed in the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it i ...
where both fatty acid oxidation and synthesis are important. The differences in tissue distribution indicate that ACC1 maintains regulation of fatty acid synthesis
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is co ...
whereas ACC2 mainly regulates fatty acid oxidation (beta oxidation).
Regulation
 The regulation of mammalian ACC is complex, in order to control two distinct pools of malonyl CoA that direct either the inhibition of beta oxidation or the activation of lipid biosynthesis.
Mammalian ACC1 and ACC2 are regulated transcriptionally by multiple promoters which mediate ACC abundance in response to the cells nutritional status. Activation of gene expression through different promoters results in
The regulation of mammalian ACC is complex, in order to control two distinct pools of malonyl CoA that direct either the inhibition of beta oxidation or the activation of lipid biosynthesis.
Mammalian ACC1 and ACC2 are regulated transcriptionally by multiple promoters which mediate ACC abundance in response to the cells nutritional status. Activation of gene expression through different promoters results in alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be i ...
; however, the physiological significance of specific ACC isozymes In biochemistry, isozymes (also known as isoenzymes or more generally as multiple forms of enzymes) are enzymes that differ in amino acid sequence but catalyze the same chemical reaction. Isozymes usually have different kinetic parameters (e.g. dif ...
remains unclear. The sensitivity to nutritional status results from the control of these promoters by transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The fun ...
such as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1
Sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) also known as sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SREBF1'' gene.
This gene is located within the Smith–Mageni ...
, controlled by insulin at the transcriptional level, and ChREBP, which increases in expression with high carbohydrates
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or m ...
diets.
Through a feed-forward loop, citrate
Citric acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula HOC(CO2H)(CH2CO2H)2. It is a colorless weak organic acid. It occurs naturally in citrus fruits. In biochemistry, it is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle, which occurs in the ...
allosterically activates ACC. Citrate may increase ACC polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many f ...
to increase enzymatic activity; however, it is unclear if polymerization is citrate's main mechanism of increasing ACC activity or if polymerization is an artifact of in vitro experiments. Other allosteric activators include glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
and other dicarboxylic acids
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or aromatic. In general, dicarboxylic acids show ...
. Long and short chain fatty acyl CoAs are negative feedback inhibitors of ACC.
Phosphorylation can result when the hormones glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to tre ...
or epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
bind to cell surface receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
, but the main cause of phosphorylation is due to a rise in AMP levels when the energy status of the cell is low, leading to the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase
5' AMP-activated protein kinase or AMPK or 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase is an enzyme (EC 2.7.11.31) that plays a role in cellular energy homeostasis, largely to activate glucose and fatty acid uptake and oxidation when cell ...
(AMPK). AMPK is the main kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
regulator of ACC, able to phosphorylate a number of serine residues on both isoforms of ACC. On ACC1, AMPK phosphorylates Ser79, Ser1200, and Ser1215. Protein kinase A
In cell biology, protein kinase A (PKA) is a family of enzymes whose activity is dependent on cellular levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP). PKA is also known as cAMP-dependent protein kinase (). PKA has several functions in the cell, including regulatio ...
also has the ability to phosphorylate ACC, with a much greater ability to phosphorylate ACC2 than ACC1. However, the physiological significance of protein kinase A in the regulation of ACC is currently unknown. Researchers hypothesize there are other ACC kinases important to its regulation as there are many other possible phosphorylation sites on ACC.
When insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
binds to its receptors on the cellular membrane
The cell membrane (also known as the plasma membrane (PM) or cytoplasmic membrane, and historically referred to as the plasmalemma) is a biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of all cells from the outside environment (th ...
, it activates a phosphatase enzyme called protein phosphatase 2A Protein phosphatase 2A may refer to:
* Protein phosphatase 2
Protein phosphatase 2 (PP2), also known as PP2A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPP2CA'' gene. The PP2A heterotrimeric protein phosphatase is ubiquitously expressed ...
(PP2A) to dephosphorylate the enzyme; thereby removing the inhibitory effect. Furthermore, insulin induces a phosphodiesterase that lowers the level of cAMP in the cell, thus inhibiting PKA, and also inhibits AMPK directly.
This protein may use the morpheein
Morpheeins are proteins that can form two or more different homo-oligomers (morpheein forms), but must come apart and change shape to convert between forms. The alternate shape may reassemble to a different oligomer. The shape of the subunit ...
model of allosteric regulation
In biochemistry, allosteric regulation (or allosteric control) is the regulation of an enzyme by binding an effector molecule at a site other than the enzyme's active site.
The site to which the effector binds is termed the ''allosteric sit ...
.
Clinical implications
At the juncture of lipid synthesis and oxidation pathways, ACC presents many clinical possibilities for the production of novelantibiotics
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and preventio ...
and the development of new therapies for diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level ( hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, and other manifestations of metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndro ...
. Researchers aim to take advantage of structural differences between bacterial and human ACCs to create antibiotics specific to the bacterial ACC, in efforts to minimize side effects to patients. Promising results for the usefulness of an ACC inhibitor include the finding that mice with no expression of ACC2 have continuous fatty acid oxidation, reduced body fat mass, and reduced body weight despite an increase in food consumption. These mice are also protected from diabetes. A lack of ACC1 in mutant mice is lethal already at the embryonic stage. However, it is unknown whether drugs targeting ACCs in humans must be specific for ACC2.
Firsocostat (formerly GS-976, ND-630, NDI-010976) is a potent allosteric ACC inhibitor, acting at the BC domain of ACC. Firsocostat is under development in 2019 (Phase II) by the pharmaceutical company Gilead
Gilead or Gilad (; he, גִּלְעָד ''Gīləʿāḏ'', ar, جلعاد, Ǧalʻād, Jalaad) is the ancient, historic, biblical name of the mountainous northern part of the region of Transjordan.''Easton's Bible Dictionary'Galeed''/ref> ...
as part of a combination treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), also known as metabolic (dysfunction) associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), is excessive fat build-up in the liver without another clear cause such as alcohol use. There are two types; non-alcoholic ...
(NASH), believed to be an increasing cause of liver failure.
In addition, plant-selective ACC inhibitors are in widespread use as herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page f ...
s, which suggests clinical application against Apicomplexa
The Apicomplexa (also called Apicomplexia) are a large phylum of parasitic alveolates. Most of them possess a unique form of organelle that comprises a type of non-photosynthetic plastid called an apicoplast, and an apical complex structure. Th ...
parasites that rely on a plant-derived ACC isoform, including malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
.
See also
* ACCase inhibitor herbicides * Malonyl-CoA decarboxylaseReferences
Further reading
* * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Acetyl-Coa Carboxylase EC 6.4.1