2018 World Cup on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In October 2014, on their first official visit to Russia, FIFA's inspection committee and its head, Chris Unger, visited St. Petersburg, Sochi, Kazan and both Moscow venues. They were satisfied with the progress. On 8 October 2015, FIFA and the local organising committee agreed on the official names of the stadiums to be used during the tournament. Of the twelve venues, the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow and the Saint Petersburg Stadium—the two largest stadiums in Russia—were used most; both hosted seven matches. Sochi, Kazan, Nizhny Novgorod and Samara each hosted six matches, including one quarter-final match each, while the Spartak Stadium in Moscow and Rostov-on-Don hosted five matches, including one round-of-16 match each. Volgograd, Kaliningrad, Yekaterinburg and Saransk each hosted four matches, but did not host any knockout stage games.
In October 2014, on their first official visit to Russia, FIFA's inspection committee and its head, Chris Unger, visited St. Petersburg, Sochi, Kazan and both Moscow venues. They were satisfied with the progress. On 8 October 2015, FIFA and the local organising committee agreed on the official names of the stadiums to be used during the tournament. Of the twelve venues, the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow and the Saint Petersburg Stadium—the two largest stadiums in Russia—were used most; both hosted seven matches. Sochi, Kazan, Nizhny Novgorod and Samara each hosted six matches, including one quarter-final match each, while the Spartak Stadium in Moscow and Rostov-on-Don hosted five matches, including one round-of-16 match each. Volgograd, Kaliningrad, Yekaterinburg and Saransk each hosted four matches, but did not host any knockout stage games.
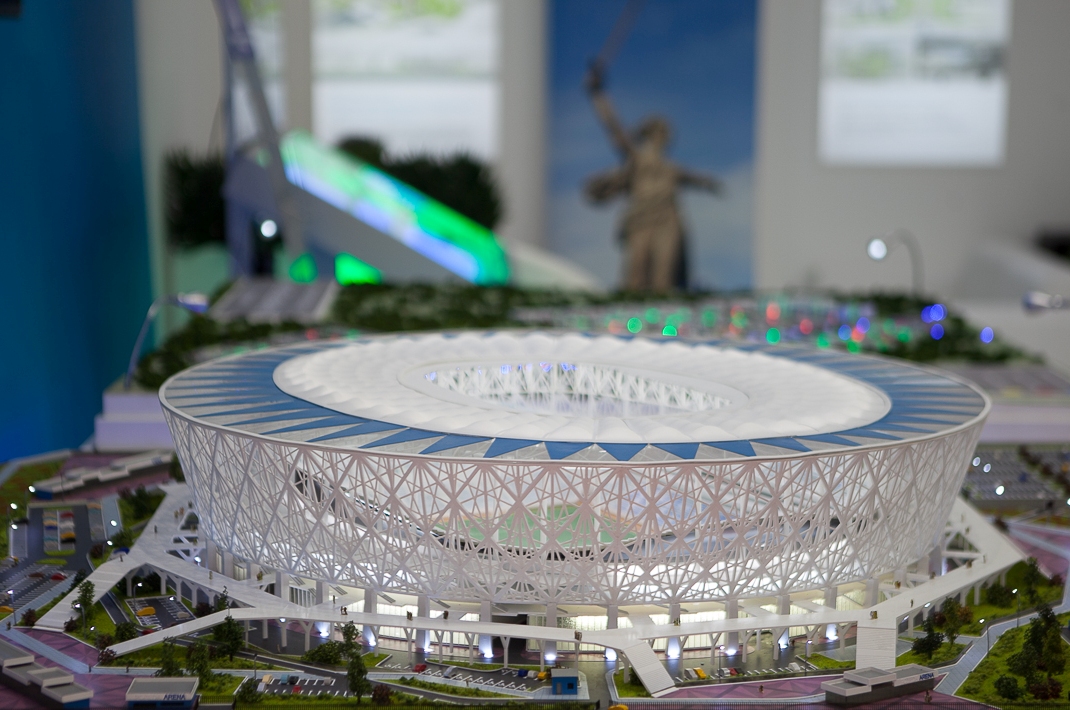
 Twelve stadiums in eleven Russian cities were built or renovated for the FIFA World Cup. Between 2010 (when Russia were announced as hosts) and 2018, nine of the twelve stadiums were built (some in place of older, outdated venues) and the other three were renovated for the tournament.
* Kaliningrad: Kaliningrad Stadium (new). The first piles were driven into the ground in September 2015. On 11 April 2018 it hosted its first match.
* Kazan: Kazan Arena (new). The stadium was built for the 2013 Summer
Twelve stadiums in eleven Russian cities were built or renovated for the FIFA World Cup. Between 2010 (when Russia were announced as hosts) and 2018, nine of the twelve stadiums were built (some in place of older, outdated venues) and the other three were renovated for the tournament.
* Kaliningrad: Kaliningrad Stadium (new). The first piles were driven into the ground in September 2015. On 11 April 2018 it hosted its first match.
* Kazan: Kazan Arena (new). The stadium was built for the 2013 Summer
 At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion , the 2018 FIFA event was the most expensive World Cup in history, surpassing the $11.6 billion cost of the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil.
The Russian government had originally earmarked a Federal budget of Russia, budget of around $20 billion, which was later slashed to $10 billion, for World Cup preparations. Half was spent on transportation infrastructure. As part of the program to prepare for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, a federal sub-program—"Construction and Renovation of Transport Infrastructure"—was implemented with a total budget of ₽352.5 billion (rubles), with ₽170.3 billion coming from the federal budget, ₽35.1 billion from regional budgets, and ₽147.1 billion from investors. The biggest item of federal spending was the aviation infrastructure costing ₽117.8 billion. Construction of new hotels was a crucial area of infrastructure development in World Cup host cities. Costs continued to mount as preparations were underway.
At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion , the 2018 FIFA event was the most expensive World Cup in history, surpassing the $11.6 billion cost of the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil.
The Russian government had originally earmarked a Federal budget of Russia, budget of around $20 billion, which was later slashed to $10 billion, for World Cup preparations. Half was spent on transportation infrastructure. As part of the program to prepare for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, a federal sub-program—"Construction and Renovation of Transport Infrastructure"—was implemented with a total budget of ₽352.5 billion (rubles), with ₽170.3 billion coming from the federal budget, ₽35.1 billion from regional budgets, and ₽147.1 billion from investors. The biggest item of federal spending was the aviation infrastructure costing ₽117.8 billion. Construction of new hotels was a crucial area of infrastructure development in World Cup host cities. Costs continued to mount as preparations were underway.
 Volunteer applications to the 2018 Russia Local Organising Committee opened on 1 June 2016. The 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia Volunteer Program received about 177,000 applications, and engaged a total of 35,000 volunteers. They received training at 15 Volunteer Centres of the local organising committee based in 15 universities, and in volunteer centres in the host cities. Preference, especially in key areas, was given to those with knowledge of a foreign language and volunteering experience, but not necessarily to Russian nationals.
Volunteer applications to the 2018 Russia Local Organising Committee opened on 1 June 2016. The 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia Volunteer Program received about 177,000 applications, and engaged a total of 35,000 volunteers. They received training at 15 Volunteer Centres of the local organising committee based in 15 universities, and in volunteer centres in the host cities. Preference, especially in key areas, was given to those with knowledge of a foreign language and volunteering experience, but not necessarily to Russian nationals.
 The opening ceremony took place on Thursday, 14 June 2018, at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow, preceding the 2018 FIFA World Cup Group A#Russia vs Saudi Arabia, opening match of the tournament between hosts Russia and Saudi Arabia.
At the start of the ceremony, Russian president Vladimir Putin gave a speech, welcoming the countries of the world to Russia and calling football a uniting force. Brazilian World Cup-winning striker Ronaldo (Brazilian footballer), Ronaldo entered the stadium with a child in a Russia jersey. Pop singer Robbie Williams then sang two of his songs solo before he and Russian soprano Aida Garifullina performed a duet. Dancers dressed in the flags of the 32 competing teams appeared carrying a sign with the name of each nation. At the end of the ceremony Ronaldo reappeared with the official match ball which had returned from the International Space Station in early June.
Young participants of the international children's social programme Football for Friendship from 211 countries and regions took part in the opening ceremony of the FIFA World Cup at the Luzhniki stadium.
The opening ceremony took place on Thursday, 14 June 2018, at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow, preceding the 2018 FIFA World Cup Group A#Russia vs Saudi Arabia, opening match of the tournament between hosts Russia and Saudi Arabia.
At the start of the ceremony, Russian president Vladimir Putin gave a speech, welcoming the countries of the world to Russia and calling football a uniting force. Brazilian World Cup-winning striker Ronaldo (Brazilian footballer), Ronaldo entered the stadium with a child in a Russia jersey. Pop singer Robbie Williams then sang two of his songs solo before he and Russian soprano Aida Garifullina performed a duet. Dancers dressed in the flags of the 32 competing teams appeared carrying a sign with the name of each nation. At the end of the ceremony Ronaldo reappeared with the official match ball which had returned from the International Space Station in early June.
Young participants of the international children's social programme Football for Friendship from 211 countries and regions took part in the opening ceremony of the FIFA World Cup at the Luzhniki stadium.
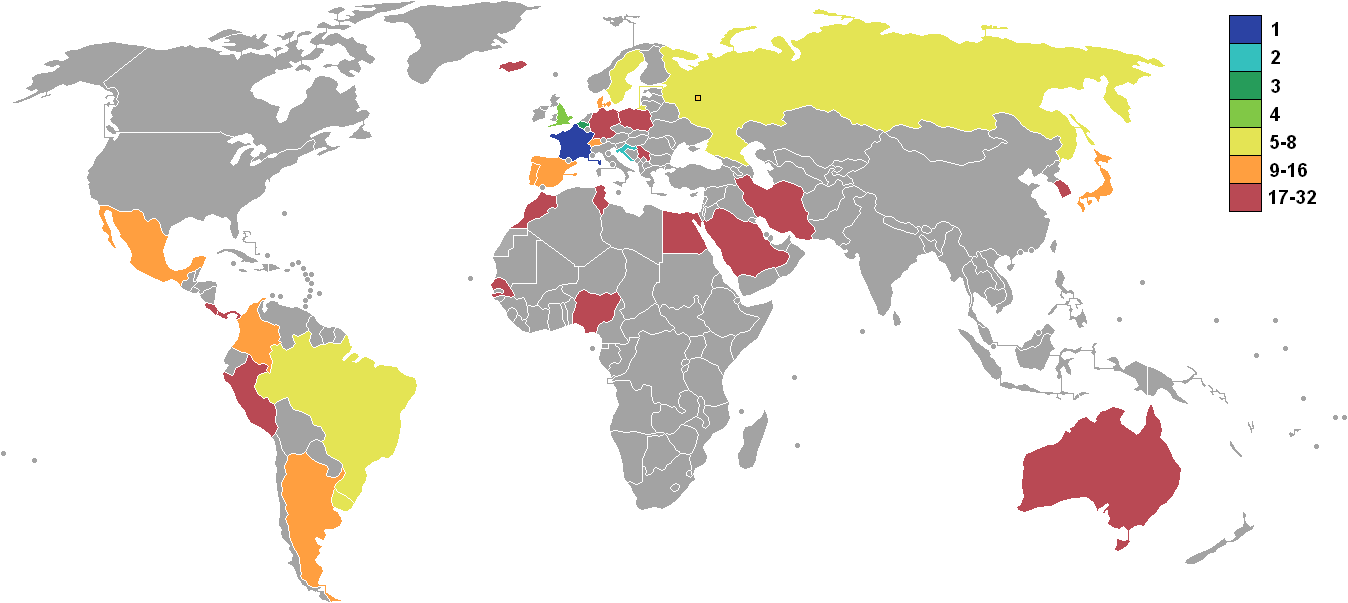 Competing countries were divided into eight groups of four teams (groups A to H). Teams in each group played one another in a round-robin tournament, round-robin, with the top two teams advancing to the #Knockout stage, knockout stage. Ten European teams and four South American teams progressed to the knockout stage, together with Japan and Mexico.
For the first time since 1938, Germany, the reigning champions, were eliminated in the first round. This was the third consecutive tournament in which the holders were eliminated in the first round, after Italy in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 and Spain in
Competing countries were divided into eight groups of four teams (groups A to H). Teams in each group played one another in a round-robin tournament, round-robin, with the top two teams advancing to the #Knockout stage, knockout stage. Ten European teams and four South American teams progressed to the knockout stage, together with Japan and Mexico.
For the first time since 1938, Germany, the reigning champions, were eliminated in the first round. This was the third consecutive tournament in which the holders were eliminated in the first round, after Italy in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 and Spain in
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 ----
----
----
----
 The tournament's FIFA World Cup mascot, official mascot was unveiled on 21 October 2016, and selected through a design competition among university students. A public vote was used to select the mascot from three finalists—a cat, a tiger, and a wolf. The winner, with 53% or approximately 1 million votes, was Zabivaka—an anthropomorphic wolf dressed in the colours of the Russian national team. Zabivaka's name is a portmanteau of the Russian words :wikt:забияка#Russian, забияка ("hothead") and :wikt:забивать#Russian, забивать ("to score"), and his official backstory states that he is an aspiring football player who is "charming, confident and social".
The tournament's FIFA World Cup mascot, official mascot was unveiled on 21 October 2016, and selected through a design competition among university students. A public vote was used to select the mascot from three finalists—a cat, a tiger, and a wolf. The winner, with 53% or approximately 1 million votes, was Zabivaka—an anthropomorphic wolf dressed in the colours of the Russian national team. Zabivaka's name is a portmanteau of the Russian words :wikt:забияка#Russian, забияка ("hothead") and :wikt:забивать#Russian, забивать ("to score"), and his official backstory states that he is an aspiring football player who is "charming, confident and social".
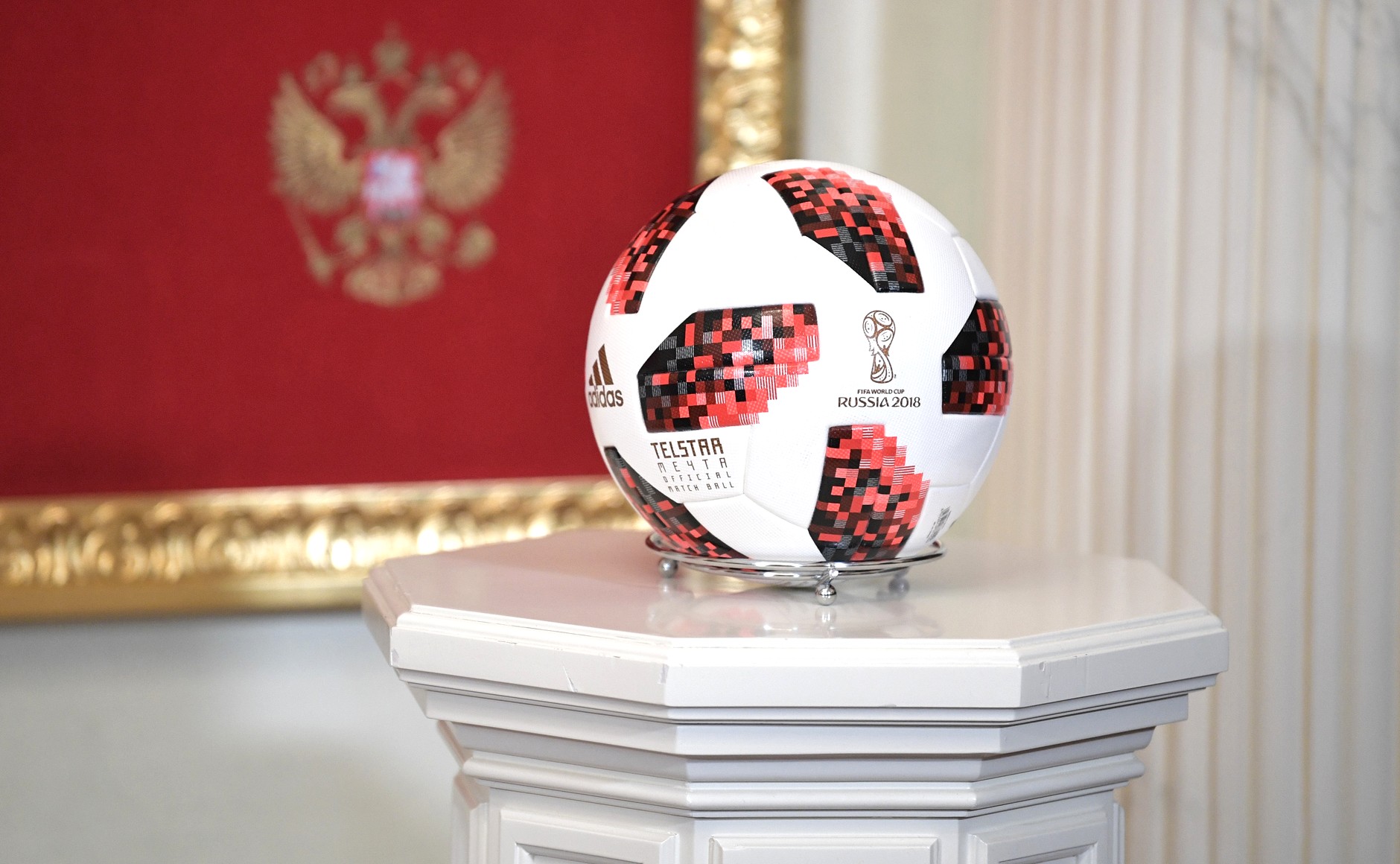
 The official match ball, the "Adidas Telstar 18, Telstar 18", was unveiled on 9 November 2017. It was based on the name and design of the first Adidas World Cup ball from 1970 FIFA World Cup, 1970. A special red-coloured variation, "Telstar Mechta", was used for the knockout stage of the tournament. The word ''mechta'' (Russian: :wikt:мечта#Russian, мечта) means "dream" or "ambition".
Goalkeepers noted that the ball was slippery and prone to having unpredictable trajectory. In addition, two Telstar 18 balls popped in the midst of a first-round 2018 FIFA World Cup Group C#France vs Australia, match between
The official match ball, the "Adidas Telstar 18, Telstar 18", was unveiled on 9 November 2017. It was based on the name and design of the first Adidas World Cup ball from 1970 FIFA World Cup, 1970. A special red-coloured variation, "Telstar Mechta", was used for the knockout stage of the tournament. The word ''mechta'' (Russian: :wikt:мечта#Russian, мечта) means "dream" or "ambition".
Goalkeepers noted that the ball was slippery and prone to having unpredictable trajectory. In addition, two Telstar 18 balls popped in the midst of a first-round 2018 FIFA World Cup Group C#France vs Australia, match between
 At the close of the World Cup, Russia was widely praised for its success in hosting the tournament, with Steve Rosenberg of the
At the close of the World Cup, Russia was widely praised for its success in hosting the tournament, with Steve Rosenberg of the
deeming it "a resounding public relations success" for Putin, adding: "The stunning new stadiums, free train travel to venues and the absence of crowd violence has impressed visiting supporters. Russia has come across as friendly and hospitable: a stark contrast with the country's authoritarian image. All the foreign fans I have spoken to are pleasantly surprised."
Despite the British Foreign Office and MPs repeatedly warning English football fans travelling to Russia of "racist or homophobic intimidation, hooligan violence and anti-British hostility", fans who did travel said they received a warm welcome from ordinary citizens after arriving in Russia.
FIFA president
The 2018 FIFA World Cup was the 21st

 The bidding procedure to host the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cup tournaments began in January 2009, and national associations had until 2 February 2009 to register their interest. Initially, nine countries placed bids for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, but Mexico later withdrew from the proceedings, and Indonesia's bid was rejected by FIFA in February 2010 after the Indonesian government failed to submit a letter to support the bid. During the bidding process, the three remaining non-
The bidding procedure to host the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cup tournaments began in January 2009, and national associations had until 2 February 2009 to register their interest. Initially, nine countries placed bids for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, but Mexico later withdrew from the proceedings, and Indonesia's bid was rejected by FIFA in February 2010 after the Indonesian government failed to submit a letter to support the bid. During the bidding process, the three remaining non-

 The draw was held on 1 December 2017 at 18:00 MSK at the
The draw was held on 1 December 2017 at 18:00 MSK at the
released an investigation conducted by a Ghanaian journalist which implicated him in a bribery scandal.
FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
, the quadrennial world championship for men's national football teams organized by FIFA. It took place in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
from 14 June to 15 July 2018, after the country was awarded the hosting rights in 2010. It was the eleventh time the championships had been held in Europe, and the first time they were held in Eastern Europe. At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion, it was the most expensive World Cup ever held until it was surpassed by the 2022 World Cup
The 2022 FIFA World Cup is an international football tournament contested by the men's national teams of FIFA's member associations. The 22nd FIFA World Cup is taking place in Qatar from 20 November to 18 December 2022; it is the first ...
in Qatar.
The tournament phase involved 32 teams, of which 31 came through qualifying competitions, while as the host nation Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
qualified automatically. Of the 32, 20 had also appeared in the 2014 event, while Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
and Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
each made their first appearance at the World Cup. 64 matches were played in 12 venues across 11 cities. Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, the defending champions, were eliminated in the group stage for the first time since 1938. Host nation Russia was eliminated in the quarter-finals. In the final
Final, Finals or The Final may refer to:
* Final (competition), the last or championship round of a sporting competition, match, game, or other contest which decides a winner for an event
** Another term for playoffs, describing a sequence of con ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
played Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
on 15 July at the Luzhniki Stadium
Luzhniki Stadium ( rus, стадион «Лужники», p=stədʲɪˈon lʊʐnʲɪˈkʲi, ''Stadion Luzhniki'') is the national stadium of Russia, located in its capital city, Moscow. The full name of the stadium is Grand Sports Arena of the ...
in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
. France won the match 4–2, claiming their second World Cup.
Croatian player Luka Modrić
Luka Modrić (; born 9 September 1985) is a Croatian professional footballer who plays as a midfielder for La Liga club Real Madrid and captains the Croatia national team. He plays mainly as a central midfielder, but can also play as an a ...
was voted the tournament's best player, winning the Golden Ball. England's Harry Kane
Harry Edward Kane (born 28 July 1993) is an English professional footballer who plays as a striker for club Tottenham Hotspur and captains the England national team. A prolific goalscorer with strong link play, Kane is regarded as one of ...
won the Golden Boot as he scored the most goals during the tournament with six. Belgium's Thibaut Courtois
Thibaut Nicolas Marc Courtois (born 11 May 1992) is a Belgian professional footballer who plays as a goalkeeper for La Liga club Real Madrid and the Belgium national team. He is considered one of the best goalkeepers in world football.
Courto ...
won the Golden Glove, awarded to the goalkeeper
In many team sports which involve scoring goals, the goalkeeper (sometimes termed goaltender, netminder, GK, goalie or keeper) is a designated player charged with directly preventing the opposing team from scoring by blocking or intercepting o ...
with the best performance. It has been estimated that more than 3 million people attended games during the tournament.
Host selection

 The bidding procedure to host the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cup tournaments began in January 2009, and national associations had until 2 February 2009 to register their interest. Initially, nine countries placed bids for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, but Mexico later withdrew from the proceedings, and Indonesia's bid was rejected by FIFA in February 2010 after the Indonesian government failed to submit a letter to support the bid. During the bidding process, the three remaining non-
The bidding procedure to host the 2018 and 2022 FIFA World Cup tournaments began in January 2009, and national associations had until 2 February 2009 to register their interest. Initially, nine countries placed bids for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, but Mexico later withdrew from the proceedings, and Indonesia's bid was rejected by FIFA in February 2010 after the Indonesian government failed to submit a letter to support the bid. During the bidding process, the three remaining non-UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
nations (Australia, Japan, and the United States) gradually withdrew from the 2018 bids, and thus were ruled out of the 2022 bid. As such, there were eventually four bids for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, two of which were joint bids: England, Russia, Netherlands/Belgium, and Portugal/Spain.
The 22-member FIFA Executive Committee
The FIFA Council (formerly the FIFA Executive Committee) is an institution of FIFA (the governing body of association football, futsal and beach football). It is the main decision-making body of the organization in the intervals of FIFA Congress. ...
convened in Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
on 2 December 2010 to vote to select the hosts of both tournaments. Russia won the right to be the 2018 host in the second round of voting. The Portugal/Spain bid came second, and that from Belgium/Netherlands third. England, which was bidding to host its second tournament, was eliminated in the first round.
The voting results were:
Host selection criticism
The choice of Russia as host was controversial. Issues included the level ofracism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonis ...
in Russian football, human rights abuses
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
by Russian authorities, and discrimination against LGBT
' is an initialism that stands for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender. In use since the 1990s, the initialism, as well as some of its common variants, functions as an umbrella term for sexuality and gender identity.
The LGBT term ...
people in wider Russian society. Russia's involvement in the ongoing conflict in Ukraine had also prompted calls for the tournament to be moved, particularly following the annexation of Crimea. In 2014, FIFA president Sepp Blatter stated that "the World Cup has been given and voted to Russia and we are going forward with our work".
Russia was criticised for alleged abuse of migrant labourers in the construction of World Cup venues, with Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
reporting cases where workers were left unpaid, made to work in dangerously cold conditions, or suffering reprisals for raising concerns. A few pundits claimed it was slave labour. On May 2017, FIFA president Gianni Infantino
Giovanni Vincenzo Infantino (; born 23 March 1970) is a Swiss football administrator with Italian citizenship and the current president of FIFA. He was elected President of FIFA during the 2016 FIFA Extraordinary Congress in February 2016. H ...
admitted there had been human rights abuses of North Korean workers involved in the construction of Saint Petersburg's Zenit Arena. By June 2017, at least 17 workers had died on World Cup construction sites, according to Building and Wood Workers’ International. In August, a group of eight US senators called on FIFA to consider dismissing Russia as the World Cup host if an independent investigation verified allegations of North Koreans being subjected to forced labor.
Racism and Neo-nazi symbols displayed in the past by some Russian football fans drew criticism, with documented incidents of racial chants, banners spewing hate-filled messages, and sometimes assaults on people from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
and Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
. On March 2015, FIFA's then Vice President Jeffrey Webb said that Russia posed a huge challenge from a racism standpoint, and that a World Cup could not be held there under the current conditions. On July, United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
anti-discrimination official Yuri Boychenko said that Russian soccer authorities had failed to fully grasp what racism was and needed to do more to combat it. To address this as well as concerns of hooliganism
Hooliganism is disruptive or unlawful behavior such as rioting, bullying and vandalism, usually in connection with crowds at sporting events.
Etymology
There are several theories regarding the origin of the word ''hooliganism,'' which is a d ...
in general, Russian intelligence services blacklisted over 400 fans from entering the stadiums by June 2018, with 32 other countries also sending officers to help local police screen attendees for valid ID cards.
Allegations of corruption in the bidding processes and concerns over bribery on the part of the Russian team and corruption by FIFA members for the 2018 and 2022 World Cups led to threats from England's FA to boycott the tournament. They claimed that four members of the executive committee had requested bribes to vote for England, and Sepp Blatter had said it had already been arranged before the vote that Russia would win. FIFA appointed Michael J. Garcia, a US attorney, to investigate and produce a report on the corruption allegations. Although the report was never published, FIFA released a 42-page summary of its findings as determined by German judge Hans-Joachim Eckert
Hans-Joachim Eckert (born 1948, in Plochingen
Plochingen (Swabian: ''Blocheng'' or ''Blochenga'') is a town in the district of Esslingen in Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. It lies on the river Neckar, on which it has a river port. With ab ...
. Eckert's summary cleared Russia and Qatar of any wrongdoing, but was denounced by critics as a whitewash. Because of the controversy, the FA refused to accept Eckert's absolving Russia from blame. Greg Dyke
Gregory Dyke (born 20 May 1947) is a British media executive, football administrator, journalist, and broadcaster. Since the 1960s, Dyke has had a long career in the UK in print and then broadcast journalism. He is credited with introducing ' ...
called for a re-examination of the affair and David Bernstein called for a boycott of the World Cup. Garcia criticised the summary as being "materially incomplete" with "erroneous representations of the facts and conclusions", and appealed to FIFA's Appeal Committee. The committee declined to hear his appeal, so Garcia resigned to protest of FIFA's conduct, citing a "lack of leadership" and lack of confidence in Eckert's independence.
On 3 June 2015, the FBI
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. Operating under the jurisdiction of the United States Department of Justice, t ...
confirmed that federal authorities were investigating the bidding and awarding processes for the 2018 and 2022 World Cups. In an interview published on 7 June 2015, Domenico Scala, the head of FIFA's Audit And Compliance Committee, stated that "should there be evidence that the awards to Qatar and Russia came only because of bought votes, then the awards could be cancelled". Prince William of Wales and former British Prime Minister David Cameron attended a meeting with FIFA vice-president Chung Mong-joon
Chung Mong-joon or Chung Mong Joon ( ko, 정몽준, born October 17, 1951) is a South Korean businessman and politician. He is the sixth son of Chung Ju-yung, founder of Hyundai, the second-largest South Korean '' chaebol'' before its breakup in ...
in which a vote-trading deal for the right to host the 2018 World Cup in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
was discussed.
Teams
Qualification
For the first time in the history of the FIFA World Cup, all eligible nations—the 209 FIFA member associations except automatically qualified hosts Russia—applied to enter the qualifying process.Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
were later disqualified before playing their first matches, while Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
and Kosovo
Kosovo ( sq, Kosova or ; sr-Cyrl, Косово ), officially the Republic of Kosovo ( sq, Republika e Kosovës, links=no; sr, Република Косово, Republika Kosovo, links=no), is a partially recognised state in Southeast Euro ...
, who joined FIFA on 13 May 2016 after the qualifying draw but before European qualifying had begun, also entered the competition. Places in the tournament were allocated to continental confederations, with the allocation unchanged from the 2014 World Cup. The first qualification game, between Timor-Leste
East Timor (), also known as Timor-Leste (), officially the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island country in Southeast Asia. It comprises the eastern half of the island of Timor, the exclave of Oecusse on the island's north-west ...
and Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
, began in Dili on 12 March 2015 as part of the AFC's qualification, and the main qualifying draw took place at the Konstantinovsky Palace
Strelna ( rus, Стре́льна, p=ˈstrʲelʲnə) is a municipal settlement in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of Saint Petersburg, Russia, about halfway between Saint Petersburg proper and Petergof, and overlooking the shore of ...
in Strelna
Strelna ( rus, Стре́льна, p=ˈstrʲelʲnə) is a municipal settlement in Petrodvortsovy District of the federal city of Saint Petersburg, Russia, about halfway between Saint Petersburg proper and Petergof, and overlooking the shore o ...
, Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, on 25 July 2015.
Of the 32 nations qualified to play at the 2018 FIFA World Cup, 20 countries competed at the previous tournament in 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wat ...
. Both Iceland and Panama qualified for the first time, with the former becoming the smallest country in terms of population to reach the World Cup. Other teams returning after absences of at least three tournaments included: Egypt, returning to the finals after their last appearance in 1990; Morocco, who last competed in 1998; Peru, who last appeared in 1982; and Senegal, competing for the second time after reaching the quarter-finals in 2002. It was the first time three Nordic countries (Denmark, Iceland and Sweden) and four Arab nations
The Arab world ( ar, اَلْعَالَمُ الْعَرَبِيُّ '), formally the Arab homeland ( '), also known as the Arab nation ( '), the Arabsphere, or the Arab states, refers to a vast group of countries, mainly located in Western As ...
(Egypt, Morocco, Saudi Arabia and Tunisia) qualified for the World Cup.
Notable teams that failed to qualify included: four-time champions Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
(for the first time since 1958), who were knocked out in a qualification play-off by quarter-finalists Sweden and were the highest-ranked team to not qualify; and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, who were three-time runners-up and had finished in third place in 2014, and had qualified for the last three World Cups. Four reigning continental champions: 2017 Africa Cup of Nations
The 2017 Africa Cup of Nations (abbreviated as AFCON 2017 or CAN 2017), known as the Total 2017 Africa Cup of Nations for sponsorship reasons, was the 31st edition of the Africa Cup of Nations, the biennial international men's football champions ...
winners Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
; two-time Copa América champions and 2017 Confederations Cup runners-up Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
; 2016 OFC Nations Cup
The 2016 OFC Nations Cup was the tenth edition of the OFC Nations Cup, the quadrennial international men's football championship of Oceania organised by the Oceania Football Confederation (OFC). The tournament was played between 28 May and 11 Jun ...
winners New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
; and 2017 CONCACAF Gold Cup
The 2017 CONCACAF Gold Cup was the 14th edition of the CONCACAF Gold Cup, the biennial international men's soccer championship of the North, Central American and Caribbean region organized by CONCACAF, and 24th CONCACAF regional championship ove ...
champions the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
(for the first time since 1986) also failed to qualify. The other notable qualifying streaks broken were for Ghana
Ghana (; tw, Gaana, ee, Gana), officially the Republic of Ghana, is a country in West Africa. It abuts the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean to the south, sharing borders with Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, and To ...
and Ivory Coast, both of which had qualified for the three previous tournaments. The lowest-ranked team to qualify was the host nation, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
Note: Numbers in parentheses indicate positions in the FIFA World Rankings
The FIFA Men's World Ranking is a ranking system for men's national teams in association football, led by Brazil . The teams of the men's member nations of FIFA, football's world governing body, are ranked based on their game results with the ...
at the time of the tournament.
AFC (5)
* (43)
* (34)
* (44)
* (63)
* (62)
CAF (5)
* (30)
* (48)
* (41)
* (34)
* (28)
CONCACAF
The Confederation of North, Central America and Caribbean Association Football,, ; french: Confédération de football d'Amérique du Nord, d'Amérique centrale et des Caraïbes, . Dutch language, Dutch uses the English name. abbreviated as CON ...
(3)
* (22)
* (16)
* (49)
CONMEBOL (5)
* (4)
* (2)
* (13)
* (10)
* (17)
OFC (0)
*''None qualified''
UEFA
Union of European Football Associations (UEFA ; french: Union des associations européennes de football; german: Union der europäischen Fußballverbände) is one of six continental bodies of governance in association football. It governs f ...
(14)
* (3)
* (20)
* (19)
* (12)
* (7)
* (1)
* (21)
* (6)
* (5)
* (70) (hosts)
* (38)
* (8)
* (25)
* (11)

Draw
 The draw was held on 1 December 2017 at 18:00 MSK at the
The draw was held on 1 December 2017 at 18:00 MSK at the State Kremlin Palace
The State Kremlin Palace (russian: Государственный Кремлёвский Дворец), formerly and unofficially still better known as the Kremlin Palace of Congresses (Кремлёвский Дворец съездов), is a ...
in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
. The 32 teams were drawn into eight groups of four, by selecting one team from each of the four ranked pots.
For the draw, the teams were allocated to four pots based on the FIFA World Rankings
The FIFA Men's World Ranking is a ranking system for men's national teams in association football, led by Brazil . The teams of the men's member nations of FIFA, football's world governing body, are ranked based on their game results with the ...
of October 2017. Pot one contained the hosts Russia (who were automatically assigned to position A1) and the best seven teams. Pot two contained the next best eight teams, and so on for pots three and four. This was different from previous draws, when only pot one was based on FIFA rankings while the remaining pots were based on geographical considerations. However, teams from the same confederation still were not drawn against each other for the group stage, except that two UEFA teams could be in each group. The pots for the draw are shown below.
Squads
Initially, each team had to name a preliminary squad of 30 players, but in February 2018 this was increased to 35. From the preliminary squad, the team had to name a final squad of 23 players (three of whom had to be goalkeepers) by 4 June. Players in the final squad could be replaced for serious injury up to 24 hours prior to kickoff of the team's first match. These replacements did not need to have been named in the preliminary squad. For players named in the 35-player preliminary squad, there was a mandatory rest period between 21 and 27 May 2018, except for those involved in the2018 UEFA Champions League Final
The 2018 UEFA Champions League Final was the final match of the 2017–18 UEFA Champions League, the 63rd season of Europe's premier club football tournament organised by UEFA, and the 26th season since it was renamed from the European Cup to the ...
played on 26 May.
Officiating
On 29 March 2018, FIFA released the list of 36 referees and 63 assistant referees selected to oversee matches. On 30 April 2018, FIFA released the list of 13 video assistant referees, who acted solely in this capacity in the tournament. RefereeFahad Al-Mirdasi
Fahad Al-Mirdasi (born 16 August 1985) is a Saudi Arabian football referee who served as a full international for FIFA from 2011 to 2018, when he was banned for life for match fixing.
Refereeing career
Al-Mirdasi was one of the referees for t ...
of Saudi Arabia was removed on 30 May 2018 over a match-fixing
In organized sports, match fixing is the act of playing or officiating a match with the intention of achieving a pre-determined result, violating the rules of the game and often the law. There are many reasons why match fixing might take place, ...
attempt, along with his two assistant referees, compatriots Mohammed Al-Abakry and Abdulah Al-Shalwai. A new referee was not appointed, but two assistant referees, Hasan Al Mahri of the United Arab Emirates
The United Arab Emirates (UAE; ar, اَلْإِمَارَات الْعَرَبِيَة الْمُتَحِدَة ), or simply the Emirates ( ar, الِْإمَارَات ), is a country in Western Asia ( The Middle East). It is located at t ...
and Hiroshi Yamauchi of Japan, were added to the list. Assistant referee Marwa Range of Kenya also withdrew after the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Video assistant referees
Shortly after theInternational Football Association Board
The International Football Association Board (IFAB) is the body that determines the Laws of the Game of association football. IFAB was founded in 1886 to agree standardised Laws for international competition, and has since acted as the "guardia ...
's decision to incorporate video assistant referee
The video assistant referee (VAR) is a match official in association football who reviews decisions made by the referee.
The assistant video assistant referee (AVAR) is a current or former referee appointed to assist the VAR in the video ope ...
s (VARs) into the Laws of the game (LOTG) on 16 March 2018, the FIFA Council
The FIFA Council (formerly the FIFA Executive Committee) is an institution of FIFA (the governing body of association football, futsal and beach football). It is the main decision-making body of the organization in the intervals of FIFA Congress. ...
took the much-anticipated step of approving the use of VAR for the first time in a FIFA World Cup tournament.
VAR operations for all games were operated from a single headquarters in Moscow, which received live video of the games and were in radio contact with the on-field referees. Systems were in place for communicating VAR-related information to broadcasters and visuals on stadiums' large screens were used for the fans in attendance.
VAR had a significant impact on several games. On 15 June 2018, Diego Costa
Diego da Silva Costa (, ; born 7 October 1988), commonly known as Diego Costa, is a professional footballer who plays as a striker for Premier League club Wolverhampton Wanderers and the Spain national team.
Costa began his football care ...
's first goal against Portugal became the first World Cup goal based on a VAR decision; the first penalty as a result of a VAR decision was awarded to France in their match against Australia on 16 June and resulted in a goal by Antoine Griezmann
Antoine Griezmann (; born 21 March 1991) is a French professional footballer who plays as a forward for La Liga club Atlético Madrid and the France national team. A versatile player, Griezmann is known for his attacking, passing, and supporti ...
. A record number of penalties were awarded in the tournament, a phenomenon partially attributed to VAR. Overall, the new technology was both praised and criticised by commentators. FIFA declared the implementation of VAR a success after the first week of competition.
Venues
Russia proposed the following host cities:Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
, Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an ...
, Krasnodar
Krasnodar (; rus, Краснода́р, p=krəsnɐˈdar; ady, Краснодар), formerly Yekaterinodar (until 1920), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Krasnodar Krai, Russia. The city stands on the Kuban River in southe ...
, Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
, Nizhny Novgorod
Nizhny Novgorod ( ; rus, links=no, Нижний Новгород, a=Ru-Nizhny Novgorod.ogg, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪj ˈnovɡərət ), colloquially shortened to Nizhny, from the 13th to the 17th century Novgorod of the Lower Land, formerly known as Gork ...
, Rostov-on-Don, Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, Samara, Saransk
Saransk (russian: Саранск, p=sɐˈransk; mdf, Саранск ошсь, Saransk oš; myv, Саран ош, Saran oš) is the capital city of the Republic of Mordovia, Russia, as well as its financial and economic centre. It is located ...
, Sochi, Volgograd
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) ...
, Yaroslavl
Yaroslavl ( rus, Ярослáвль, p=jɪrɐˈsɫavlʲ) is a city and the administrative center of Yaroslavl Oblast, Russia, located northeast of Moscow. The historic part of the city is a World Heritage Site, and is located at the confluenc ...
, and Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
. Each chosen city was located in European Russia (except Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
, which lies very close to the Europe-Asia border) in order to reduce travel time for the teams in the huge country. The bid evaluation report stated: "The Russian bid proposes 13 host cities and 16 stadiums, thus exceeding FIFA's minimum requirement. Three of the 16 stadiums would be renovated, and 13 would be newly constructed."
In October 2011, Russia reduced the number of stadiums from 16 to 14. Construction of the proposed Podolsk
Podolsk ( rus, Подольск, p=pɐˈdolʲsk) is an industrial city, center of Podolsk Urban Okrug, Moscow Oblast, Russia, located on the Pakhra River (a tributary of the Moskva River).
History
The first mentions of the village of Podol, ...
stadium in the Moscow region was cancelled by the regional government. Also, in the capital, Otkritie Arena
Otkritie Bank Arena ( rus, «Открытие Арена», p=ɐtˈkrɨtʲɪjə ɐˈrʲenə, ), also known as Spartak Stadium (the stadium's official name during the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup and 2018 FIFA World Cup), is a multi-purpose sta ...
was competing with Dynamo Stadium Dynamo Stadium or Dinamo Stadium is a stadium that often associated with the Dynamo (sports society).
It may also refer to:
Albania
* Selman Stërmasi Stadium, Tirana, formerly "Dinamo Stadium"
Belarus
*Dinamo Stadium (Brest), Belarus
*Dinamo St ...
over which would be constructed first.
The final choice of host cities was announced on 29 September 2012. The number of cities was reduced further to 11 and the number of stadiums to 12 as Krasnodar and Yaroslavl were dropped from the final list. Of the 12 stadiums used for the tournament, three (Luzhniki, Yekaterinburg and Sochi) had been extensively renovated and the other nine were brand new; $11.8 billion was spent on hosting the tournament.
Sepp Blatter had said in July 2014 that, given the concerns over the completion of venues in Russia, the number of venues for the tournament may be reduced from 12 to 10. He also said, "We are not going to be in a situation, as is the case of one, two or even three stadiums in South Africa, where it is a problem of what you do with these stadiums".
 In October 2014, on their first official visit to Russia, FIFA's inspection committee and its head, Chris Unger, visited St. Petersburg, Sochi, Kazan and both Moscow venues. They were satisfied with the progress. On 8 October 2015, FIFA and the local organising committee agreed on the official names of the stadiums to be used during the tournament. Of the twelve venues, the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow and the Saint Petersburg Stadium—the two largest stadiums in Russia—were used most; both hosted seven matches. Sochi, Kazan, Nizhny Novgorod and Samara each hosted six matches, including one quarter-final match each, while the Spartak Stadium in Moscow and Rostov-on-Don hosted five matches, including one round-of-16 match each. Volgograd, Kaliningrad, Yekaterinburg and Saransk each hosted four matches, but did not host any knockout stage games.
In October 2014, on their first official visit to Russia, FIFA's inspection committee and its head, Chris Unger, visited St. Petersburg, Sochi, Kazan and both Moscow venues. They were satisfied with the progress. On 8 October 2015, FIFA and the local organising committee agreed on the official names of the stadiums to be used during the tournament. Of the twelve venues, the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow and the Saint Petersburg Stadium—the two largest stadiums in Russia—were used most; both hosted seven matches. Sochi, Kazan, Nizhny Novgorod and Samara each hosted six matches, including one quarter-final match each, while the Spartak Stadium in Moscow and Rostov-on-Don hosted five matches, including one round-of-16 match each. Volgograd, Kaliningrad, Yekaterinburg and Saransk each hosted four matches, but did not host any knockout stage games.
Stadiums
 Twelve stadiums in eleven Russian cities were built or renovated for the FIFA World Cup. Between 2010 (when Russia were announced as hosts) and 2018, nine of the twelve stadiums were built (some in place of older, outdated venues) and the other three were renovated for the tournament.
* Kaliningrad: Kaliningrad Stadium (new). The first piles were driven into the ground in September 2015. On 11 April 2018 it hosted its first match.
* Kazan: Kazan Arena (new). The stadium was built for the 2013 Summer
Twelve stadiums in eleven Russian cities were built or renovated for the FIFA World Cup. Between 2010 (when Russia were announced as hosts) and 2018, nine of the twelve stadiums were built (some in place of older, outdated venues) and the other three were renovated for the tournament.
* Kaliningrad: Kaliningrad Stadium (new). The first piles were driven into the ground in September 2015. On 11 April 2018 it hosted its first match.
* Kazan: Kazan Arena (new). The stadium was built for the 2013 Summer Universiade
The Universiade is an international multi-sport event, organized for university athletes by the International University Sports Federation (FISU). The name is a portmanteau of the words "University" and " Olympiad".
The Universiade is referred ...
. It has since hosted the 2015 World Aquatics Championships
The 16th FINA World Championships (russian: Чемпионат мира по водным видам спорта 2015), also Aquatics 2015, were held in Kazan, Russia from 24 July to 9 August 2015. Russia hosted this event for the first time. T ...
and the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup
The 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup was the 10th and final edition of the FIFA Confederations Cup, a quadrennial international men's football tournament organised by FIFA. It was held in Russia, from 17 June to 2 July 2017, as a prelude to the 201 ...
. It serves as a home arena for FC Rubin Kazan
FC Rubin Kazan (russian: Футбо́льный клуб Руби́н Каза́нь, ''Futbolny klub Rubin Kazan'' , Tatar: Рубин Казан) is a Russian professional football club based in the city of Kazan. They play in the second-tier ...
.
* Moscow: Luzhniki Stadium (heavily renovated). The largest stadium in the country, it was closed for renovation in 2013. It was commissioned in November 2017.
* Moscow: Spartak Stadium (new). This stadium is the home arena to its namesake FC Spartak Moscow
FC Spartak Moscow (russian: Футбольный клуб «Спартак» Москва, Futbolʹnyy klub «Spartak» Moskva, ) is a Russian professional football club based in Moscow. Having won 12 Soviet championships (second only to Dyn ...
. In accordance with FIFA requirements, during the 2018 World Cup, it was called Spartak Stadium instead of its usual name Otkritie Arena. It hosted its first match on 5 September 2014.
* Nizhny Novgorod: Nizhny Novgorod Stadium (new). Construction of this stadium commenced in 2015 and was completed in December 2017.
* Rostov-on-Don: Rostov Arena (new). The stadium is located on the left bank of the Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
. Construction was completed on 22 December 2017.
* Saint Petersburg: Saint Petersburg Stadium (new). Construction commenced in 2007 after the site, formerly occupied by Kirov Stadium
Kirov may refer to:
* Sergei Kirov (1886–1934), Soviet Bolshevik leader in Leningrad after whom all other entries are named
* Kirov (surname)
Places Armenia
*Amrakits or Kirov
*Taperakan or Kirov
Azerbaijan
* Kirov, Baku
* Kirov, Lankaran
* Kir ...
, was cleared. The project was officially completed on 29 December 2016. It has hosted 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup games and served as a venue for UEFA Euro 2020
The 2020 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2020 (stylised as UEFA EURO 2020) or simply Euro 2020, was the 16th UEFA European Championship, the quadrennial international men's football championship of Europe ...
.
* Samara: Samara Arena (new). Construction officially started on 21 July 2014 and was completed on 21 April 2018.
* Saransk: Mordovia Arena (new). The stadium in Saransk was scheduled to be commissioned in 2012 in time for the opening of the all-Russian Spartakiad
The Spartakiad (or Spartakiade) was an international sports event that was sponsored by the Soviet Union. Five international Spartakiades were held from 1928 to 1937. Later Spartakiads were organized as national sport events of the Eastern Bloc ...
, but the plan was revised. The opening was rescheduled to 2017. The arena hosted its first match on 21 April 2018.
* Sochi: Fisht Stadium (slightly renovated). This stadium hosted the opening and closing ceremonies of the 2014 Winter Olympics. Afterwards, it was renovated in preparation for the 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup and the 2018 World Cup.
* Volgograd: Volgograd Arena (new). The main Volgograd arena was built on the demolished Central Stadium site, at the foot of the Mamayev Kurgan
Mamayev Kurgan (russian: Мамаев Курган) is a dominant height overlooking the city of Volgograd (formerly Stalingrad) in Southern Russia. The name in Russian means "tumulus of Mamai".
The formation is dominated by a memorial complex ...
memorial complex. It was commissioned on 3 April 2018.
* Yekaterinburg: Ekaterinburg Arena (heavily renovated). The Central Stadium of Yekaterinburg had been renovated for the FIFA World Cup. Its stands have a capacity of 35,000 spectators. The renovation project was completed in December 2017.
Team base camps
Base camps were used by the 32 national squads to stay and train before and during the World Cup tournament. On 9 February 2018, FIFA announced the base camps for each participating team. * Argentina:Bronnitsy
Bronnitsy (russian: Бро́нницы) is a town in Moscow Oblast, Russia, located southeast of central Moscow and west of the Bronnitsy station on the Moscow–Ryazan railroad. The town is surrounded by Ramensky District but is administrative ...
, Moscow Oblast
* Australia: Kazan
Kazan ( ; rus, Казань, p=kɐˈzanʲ; tt-Cyrl, Казан, ''Qazan'', IPA: ɑzan is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Tatarstan in Russia. The city lies at the confluence of the Volga and the Kazanka rivers, covering an ...
, Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
* Belgium: Krasnogorsky, Moscow Oblast
* Brazil: Sochi, Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai (russian: Краснода́рский край, r=Krasnodarsky kray, p=krəsnɐˈdarskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of ...
* Colombia: Verkhneuslonsky, Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
* Costa Rica: Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
* Croatia: Roshchino
Roshchino (russian: Рощино) is the name of several types of inhabited localities in Russia, inhabited localities in Russia.
Modern localities
;Urban localities
*Roshchino, Leningrad Oblast, an urban-type settlement under the administrative ...
, Leningrad Oblast
Leningrad Oblast ( rus, Ленинградская область, Leningradskaya oblast’, lʲɪnʲɪnˈgratskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ, , ) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). It was established on 1 August 1927, although it was not until 194 ...
* Denmark: Anapa
Anapa (russian: Ана́па, ) is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the northern coast of the Black Sea near the Sea of Azov. Population:
History
The area around Anapa was settled in antiquity. It was originally a major seaport ( ...
, Krasnodar Krai
* Egypt: Grozny
Grozny ( rus, Грозный, p=ˈgroznɨj; ce, Соьлжа-ГӀала, translit=Sölƶa-Ġala), also spelled Groznyy, is the capital city of Chechnya, Russia.
The city lies on the Sunzha River. According to the 2010 census, it had a po ...
, Chechnya
* England: Repino Repino (russian: Репино) is the name of several inhabited localities in Russia.
Modern localities
;Urban localities
* Repino, Saint Petersburg, a municipal settlement in Kurortny District of the federal city of St. Petersburg
;Rural ...
, Saint Petersburg
* France: Istra, Moscow Oblast
* Germany: Vatutinki
Vatutinki (russian: Вату́тинки) is a rural locality (a village) in Novomoskovsky Administrative Okrug of the federal city of Moscow, Russia, located on the Desna River. Its population as of the 2010 Census was 11,081; up from ...
, Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
* Iceland: Gelendzhik
Gelendzhik (russian: Геленджи́к) is a resort town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the Gelendzhik Bay of the Black Sea, between Novorossiysk ( to the northwest) and Tuapse ( to the southeast). Greater Gelendzhik sprawls for alon ...
, Krasnodar Krai
* Iran: Bakovka, Moscow Oblast
* Japan: Kazan, Tatarstan
The Republic of Tatarstan (russian: Республика Татарстан, Respublika Tatarstan, p=rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə tətɐrˈstan; tt-Cyrl, Татарстан Республикасы), or simply Tatarstan (russian: Татарстан, tt ...
* Mexico: Khimki
Khimki ( rus, Химки, p=ˈxʲimkʲɪ) is a city in Moscow Oblast, Russia, 18.25 kilometres northwest of central Moscow, and immediately beyond the Moscow city boundary.
History Origins and formation
Khimki was initially a railway station th ...
, Moscow Oblast
* Morocco: Voronezh
Voronezh ( rus, links=no, Воро́неж, p=vɐˈronʲɪʂ}) is a city and the administrative centre of Voronezh Oblast in southwestern Russia straddling the Voronezh River, located from where it flows into the Don River. The city sits on ...
, Voronezh Oblast
Voronezh Oblast (russian: Воронежская область, Voronezhskaya oblast) is a federal subject of Russia (an oblast). Its administrative center is the city of Voronezh. Its population was 2,308,792 as of the 2021 Census.
Geography
V ...
* Nigeria: Yessentuki, Stavropol Krai
* Panama: Saransk
Saransk (russian: Саранск, p=sɐˈransk; mdf, Саранск ошсь, Saransk oš; myv, Саран ош, Saran oš) is the capital city of the Republic of Mordovia, Russia, as well as its financial and economic centre. It is located ...
, Republic of Mordovia, Mordovia
* Peru: Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 millio ...
* Poland: Sochi, Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai (russian: Краснода́рский край, r=Krasnodarsky kray, p=krəsnɐˈdarskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of ...
* Portugal: Ramenskoye, Moscow Oblast, Ramenskoye, Moscow Oblast
* Russia: Khimki, Moscow Oblast
* Saudi Arabia: Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
* Senegal: Kaluga, Kaluga Oblast
* Serbia: Svetlogorsk, Kaliningrad Oblast, Svetlogorsk, Kaliningrad Oblast
* South Korea: Saint Petersburg
* Spain: Krasnodar
Krasnodar (; rus, Краснода́р, p=krəsnɐˈdar; ady, Краснодар), formerly Yekaterinodar (until 1920), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Krasnodar Krai, Russia. The city stands on the Kuban River in southe ...
, Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai (russian: Краснода́рский край, r=Krasnodarsky kray, p=krəsnɐˈdarskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of ...
* Sweden: Gelendzhik, Krasnodar Krai
Krasnodar Krai (russian: Краснода́рский край, r=Krasnodarsky kray, p=krəsnɐˈdarskʲɪj kraj) is a federal subject of Russia (a krai), located in the North Caucasus region in Southern Russia and administratively a part of ...
* Switzerland: Tolyatti, Togliatti, Samara Oblast
* Tunisia: Pervomayskoye, Moscow Oblast
* Uruguay: Bor, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Bor, Nizhny Novgorod Oblast
Preparation and costs
Budget
 At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion , the 2018 FIFA event was the most expensive World Cup in history, surpassing the $11.6 billion cost of the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil.
The Russian government had originally earmarked a Federal budget of Russia, budget of around $20 billion, which was later slashed to $10 billion, for World Cup preparations. Half was spent on transportation infrastructure. As part of the program to prepare for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, a federal sub-program—"Construction and Renovation of Transport Infrastructure"—was implemented with a total budget of ₽352.5 billion (rubles), with ₽170.3 billion coming from the federal budget, ₽35.1 billion from regional budgets, and ₽147.1 billion from investors. The biggest item of federal spending was the aviation infrastructure costing ₽117.8 billion. Construction of new hotels was a crucial area of infrastructure development in World Cup host cities. Costs continued to mount as preparations were underway.
At an estimated cost of over $14.2 billion , the 2018 FIFA event was the most expensive World Cup in history, surpassing the $11.6 billion cost of the 2014 FIFA World Cup in Brazil.
The Russian government had originally earmarked a Federal budget of Russia, budget of around $20 billion, which was later slashed to $10 billion, for World Cup preparations. Half was spent on transportation infrastructure. As part of the program to prepare for the 2018 FIFA World Cup, a federal sub-program—"Construction and Renovation of Transport Infrastructure"—was implemented with a total budget of ₽352.5 billion (rubles), with ₽170.3 billion coming from the federal budget, ₽35.1 billion from regional budgets, and ₽147.1 billion from investors. The biggest item of federal spending was the aviation infrastructure costing ₽117.8 billion. Construction of new hotels was a crucial area of infrastructure development in World Cup host cities. Costs continued to mount as preparations were underway.
Infrastructure spending
Platov International Airport in Rostov-on-Don was upgraded with automated air traffic control systems. Modern surveillance, navigation, communication, control, and Meteorology, meteorological support systems were also installed. Koltsovo Airport inYekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg ( ; rus, Екатеринбург, p=jɪkətʲɪrʲɪnˈburk), alternatively romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( rus, Свердло́вск, , svʲɪrˈdlofsk, 1924–1991), is a city and the administra ...
was upgraded with radio-engineering tools for flight operation and received a second runway. Saransk Airport received a new navigation system; two new hotels were constructed in the city—the Mercure Saransk Centre (Accor Hotels) and Four Points by Sheraton Saransk as well as few other smaller accommodation facilities. In Samara, new tram lines were laid. Khrabrovo Airport in Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
was upgraded with radio navigation and weather equipment. Renovation and upgraded radio-engineering tools for flight operations was completed in the Myachkovo Airport, Moscow, Pulkovo Airport, Saint Petersburg, Volgograd International Airport, Volgograd, Kurumoch International Airport, Samara, Yekaterinburg, Kazan International Airport, Kazan and Sochi International Airport, Sochi airports. On 27 March, the Russian Ministry of Construction Industry, Housing and Utilities Sector of reported that all communications within its area of responsibility had been commissioned. The last facility commissioned was a waste treatment station in Volgograd. In Yekaterinburg, where four matches were hosted, hosting costs increased to over ₽7.4 billion, exceeding the ₽5.6 billion rubles originally allocated from the state and regional budget.
Volunteers
 Volunteer applications to the 2018 Russia Local Organising Committee opened on 1 June 2016. The 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia Volunteer Program received about 177,000 applications, and engaged a total of 35,000 volunteers. They received training at 15 Volunteer Centres of the local organising committee based in 15 universities, and in volunteer centres in the host cities. Preference, especially in key areas, was given to those with knowledge of a foreign language and volunteering experience, but not necessarily to Russian nationals.
Volunteer applications to the 2018 Russia Local Organising Committee opened on 1 June 2016. The 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia Volunteer Program received about 177,000 applications, and engaged a total of 35,000 volunteers. They received training at 15 Volunteer Centres of the local organising committee based in 15 universities, and in volunteer centres in the host cities. Preference, especially in key areas, was given to those with knowledge of a foreign language and volunteering experience, but not necessarily to Russian nationals.
Transport
Free public transport services were offered for ticketholders during the World Cup, including additional trains linking host cities, as well as services such as bus services within them.Schedule
The full schedule was announced by FIFA on 24 July 2015 without kick-off times, which were confirmed later. On 1 December 2017, following the final draw, FIFA adjusted six kick-off times. Russia was placed in position A1 in the group stage and played in the opening match at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow on 14 June against Saudi Arabia national football team, Saudi Arabia, the two lowest-ranked teams of the tournament at the time of the final draw. The Luzhniki Stadium also hosted the second semi-final on 11 July and the final on 15 July. The Krestovsky Stadium in Saint Petersburg hosted the first semi-final on 10 July and the third place play-off on 14 July.Opening ceremony
 The opening ceremony took place on Thursday, 14 June 2018, at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow, preceding the 2018 FIFA World Cup Group A#Russia vs Saudi Arabia, opening match of the tournament between hosts Russia and Saudi Arabia.
At the start of the ceremony, Russian president Vladimir Putin gave a speech, welcoming the countries of the world to Russia and calling football a uniting force. Brazilian World Cup-winning striker Ronaldo (Brazilian footballer), Ronaldo entered the stadium with a child in a Russia jersey. Pop singer Robbie Williams then sang two of his songs solo before he and Russian soprano Aida Garifullina performed a duet. Dancers dressed in the flags of the 32 competing teams appeared carrying a sign with the name of each nation. At the end of the ceremony Ronaldo reappeared with the official match ball which had returned from the International Space Station in early June.
Young participants of the international children's social programme Football for Friendship from 211 countries and regions took part in the opening ceremony of the FIFA World Cup at the Luzhniki stadium.
The opening ceremony took place on Thursday, 14 June 2018, at the Luzhniki Stadium in Moscow, preceding the 2018 FIFA World Cup Group A#Russia vs Saudi Arabia, opening match of the tournament between hosts Russia and Saudi Arabia.
At the start of the ceremony, Russian president Vladimir Putin gave a speech, welcoming the countries of the world to Russia and calling football a uniting force. Brazilian World Cup-winning striker Ronaldo (Brazilian footballer), Ronaldo entered the stadium with a child in a Russia jersey. Pop singer Robbie Williams then sang two of his songs solo before he and Russian soprano Aida Garifullina performed a duet. Dancers dressed in the flags of the 32 competing teams appeared carrying a sign with the name of each nation. At the end of the ceremony Ronaldo reappeared with the official match ball which had returned from the International Space Station in early June.
Young participants of the international children's social programme Football for Friendship from 211 countries and regions took part in the opening ceremony of the FIFA World Cup at the Luzhniki stadium.
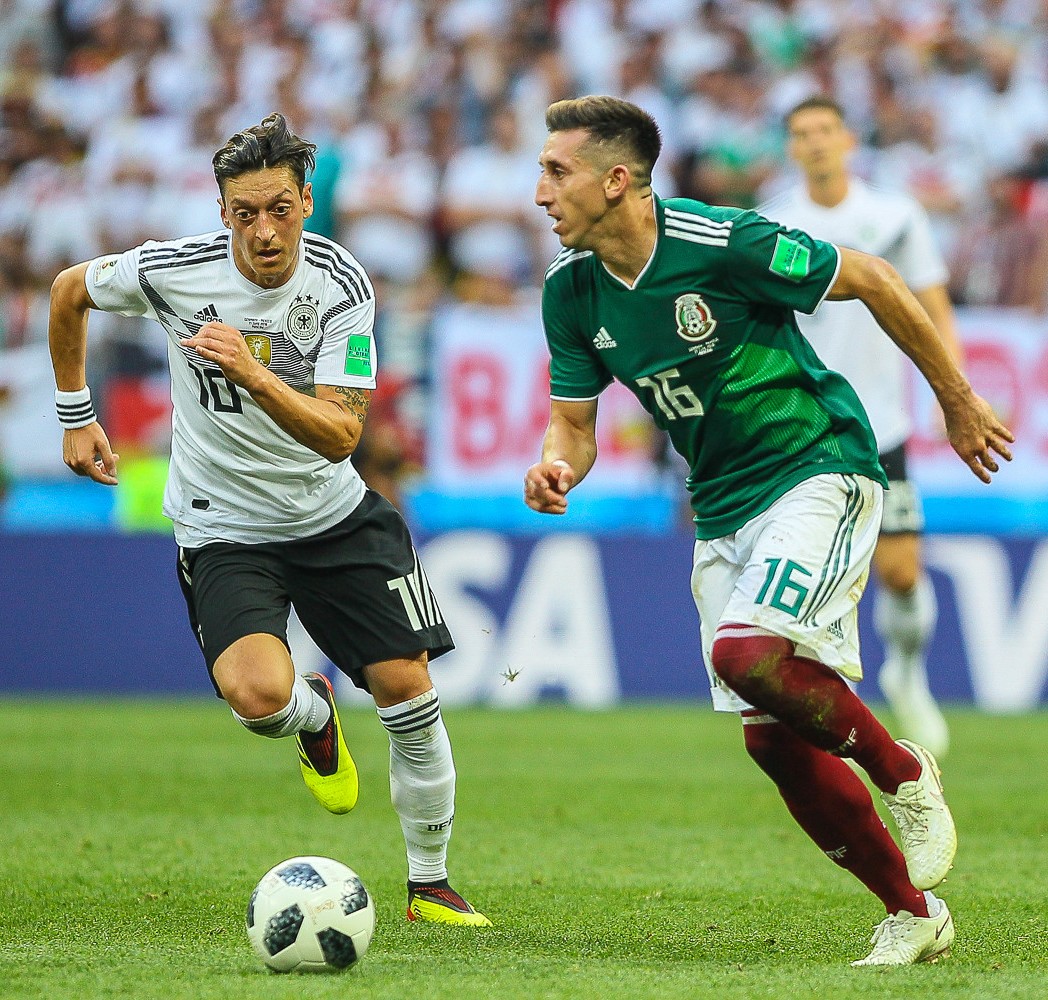
Group stage
 Competing countries were divided into eight groups of four teams (groups A to H). Teams in each group played one another in a round-robin tournament, round-robin, with the top two teams advancing to the #Knockout stage, knockout stage. Ten European teams and four South American teams progressed to the knockout stage, together with Japan and Mexico.
For the first time since 1938, Germany, the reigning champions, were eliminated in the first round. This was the third consecutive tournament in which the holders were eliminated in the first round, after Italy in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 and Spain in
Competing countries were divided into eight groups of four teams (groups A to H). Teams in each group played one another in a round-robin tournament, round-robin, with the top two teams advancing to the #Knockout stage, knockout stage. Ten European teams and four South American teams progressed to the knockout stage, together with Japan and Mexico.
For the first time since 1938, Germany, the reigning champions, were eliminated in the first round. This was the third consecutive tournament in which the holders were eliminated in the first round, after Italy in 2010 FIFA World Cup, 2010 and Spain in 2014
File:2014 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Stocking up supplies and personal protective equipment (PPE) for the Western African Ebola virus epidemic; Citizens examining the ruins after the Chibok schoolgirls kidnapping; Bundles of wat ...
. No African team progressed to the second round for the first time since 1982 FIFA World Cup, 1982. The fair play criteria came into use for the first time when Japan qualified over Senegal because the team had received fewer yellow cards. Only one match, France versus Denmark, was goalless. Until then there were a record 36 straight games in which at least one goal was scored. All times listed below are Time in Russia, local time.
Group A
 ----
----
----
----
Group B
 ----
----
----
----
Group C
 ----
----
----
----
Group D
 ----
----
----
----
Group E
 ----
----
----
----
Group F
 ----
----
----
----
Group G
 ----
----
----
----
Group H
 ----
----
----
----
Knockout stage
In the knockout stages, if a match was level at the end of normal playing time, Overtime (Association football), extra time was played (two periods of 15 minutes each) and followed, if necessary, by a Penalty shoot-out (association football), penalty shoot-out to determine the winners. If a match went into extra time, each team was allowed to make a fourth substitution, the first time this had been allowed in a FIFA World Cup tournament. Below is the bracket for the knockout round of the tournament, teams in bold denote match winners.Bracket
Round of 16
---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ---- ----Quarter-finals
---- ---- ----Semi-finals
----Third place play-off
Final
Statistics
Goal scorers
Discipline
Awards
The following FIFA World Cup awards, awards were given at the conclusion of the tournament. The Golden Boot (top scorer), Golden Ball (best overall player) and Golden Glove (best goalkeeper) awards were all sponsored by Adidas. Additionally, FIFA.com shortlisted 18 goals for users to vote on as the tournament's best. The poll closed on 23 July. The award was sponsored by Hyundai Group, Hyundai.All-Star Team
FIFA published an FIFA World Cup awards#All-Star Team, All-Star Team, this year called the ''Fantasy Team'', based on player performances evaluated through statistical data.Dream Team
The users of FIFA.com elected their Fan Dream Team.Prize money
Prize money amounts were announced in October 2017.Marketing
Branding
The tournament logo was unveiled on 28 October 2014 by cosmonauts at the International Space Station and then projected onto Moscow's Bolshoi Theatre during an evening television programme. Russian Sports Minister Vitaly Mutko said the logo was inspired by "Russia's rich artistic tradition and its history of bold achievement and innovation", and FIFA president Sepp Blatter stated that it reflected the "heart and soul" of the country. For branding, Portuguese design agency Brandia Central created materials in 2014, with a typeface called ''Dusha'' (from , ) designed by Brandia Central and edited by Adotbelow of the DSType Foundry in Portugal.Ticketing
The first phase of ticket sales started on 14 September 2017, 12:00 Moscow Time, and lasted until 12 October 2017. The general visa policy of Russia did not apply to participants and spectators, who were able to visit Russia without a visa right before and during the competition regardless of their citizenship. Spectators were nonetheless required to register for a "Fan-ID", a special photo identification pass. A Fan-ID was required to enter the country visa-free, while a ticket, Fan-ID and a valid passport were required to enter stadiums for matches. Fan-IDs also granted World Cup attendees free access to public transport services, including buses, and Rail transport in Russia, train service between host cities. Fan-ID was administered by the Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media (Russia), Ministry of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Media, which could revoke this accreditation at any time to "ensure the defence capability or security of the state or public order".Merchandise
On 29 May 2018, Electronic Arts released a free update to their video game ''FIFA 18'' that added content related to the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The expansion pack, expansion included a World Cup tournament mode with all teams and stadiums from the event, official television presentation elements, and World Cup-related content for the Ultimate Team mode. Panini Group, Panini continued their partnership with FIFA by producing stickers for their World Cup sticker album. Panini also developed an app for the 2018 World Cup where fans could collect and swap virtual stickers, with 5 million fans gathering digital stickers for the tournament.Symbols
Mascot
 The tournament's FIFA World Cup mascot, official mascot was unveiled on 21 October 2016, and selected through a design competition among university students. A public vote was used to select the mascot from three finalists—a cat, a tiger, and a wolf. The winner, with 53% or approximately 1 million votes, was Zabivaka—an anthropomorphic wolf dressed in the colours of the Russian national team. Zabivaka's name is a portmanteau of the Russian words :wikt:забияка#Russian, забияка ("hothead") and :wikt:забивать#Russian, забивать ("to score"), and his official backstory states that he is an aspiring football player who is "charming, confident and social".
The tournament's FIFA World Cup mascot, official mascot was unveiled on 21 October 2016, and selected through a design competition among university students. A public vote was used to select the mascot from three finalists—a cat, a tiger, and a wolf. The winner, with 53% or approximately 1 million votes, was Zabivaka—an anthropomorphic wolf dressed in the colours of the Russian national team. Zabivaka's name is a portmanteau of the Russian words :wikt:забияка#Russian, забияка ("hothead") and :wikt:забивать#Russian, забивать ("to score"), and his official backstory states that he is an aspiring football player who is "charming, confident and social".
Match ball

 The official match ball, the "Adidas Telstar 18, Telstar 18", was unveiled on 9 November 2017. It was based on the name and design of the first Adidas World Cup ball from 1970 FIFA World Cup, 1970. A special red-coloured variation, "Telstar Mechta", was used for the knockout stage of the tournament. The word ''mechta'' (Russian: :wikt:мечта#Russian, мечта) means "dream" or "ambition".
Goalkeepers noted that the ball was slippery and prone to having unpredictable trajectory. In addition, two Telstar 18 balls popped in the midst of a first-round 2018 FIFA World Cup Group C#France vs Australia, match between
The official match ball, the "Adidas Telstar 18, Telstar 18", was unveiled on 9 November 2017. It was based on the name and design of the first Adidas World Cup ball from 1970 FIFA World Cup, 1970. A special red-coloured variation, "Telstar Mechta", was used for the knockout stage of the tournament. The word ''mechta'' (Russian: :wikt:мечта#Russian, мечта) means "dream" or "ambition".
Goalkeepers noted that the ball was slippery and prone to having unpredictable trajectory. In addition, two Telstar 18 balls popped in the midst of a first-round 2018 FIFA World Cup Group C#France vs Australia, match between France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
and Australia national football team, Australia, leading to further discussions over the ball's performance.
Music
The official song of the tournament was "Live It Up", with vocals by Will Smith, Nicky Jam and Era Istrefi, released on 25 May 2018. Its music video was released on 8 June 2018.Other controversies
Thirty-three footballers who were alleged to be part of the Russian steroid programme are listed in the McLaren Report. On 22 December 2017, it was reported that FIFA had fired a doctor who had been investigating Doping in Russia, doping in Russian football. On 22 May 2018 FIFA confirmed that the investigations concerning all Russian players named for the provisional squad of the FIFA World Cup in Russia had been completed, with the result that insufficient evidence was found to support anti-doping rule violations. FIFA's medical committee also decided that Russian personnel would not be involved in performing drug testing procedures at the tournament, an action taken to reassure teams that samples would not be tampered with. Russia relaxed its visa rules during the World Cup, allowing Fan ID holders to enter and exit Russia without a visa through 31 December 2018. Traffickers exploited this system to bring foreign sex trafficking victims into the country, especially from Nigeria. Reuters had raised concerns about the victims' conditions, who had allegedly been forced into prostitution, with some of them enduring violent abuse. Russian authorities were accused of doing little to fix to the issue, allegedly because many locals blamed the victims for falling into prostitution.Response to Skripal poisoning
In response to the March 2018 poisoning of Sergei and Yulia Skripal, British prime minister Theresa May announced that no British ministers or members of the royal family would attend the World Cup, and issued a warning to any travelling England fans. Russia responded to the comments from the UK Parliament claiming that the West are trying to "take the World Cup out of Russia". The Russian Foreign Ministry denounced Boris Johnson's statements that compared the event to the 1936 Summer Olympics, 1936 Olympics held in Nazi Germany as "poisoned with venom of hate, unprofessionalism and boorishness" and "unacceptable and unworthy" parallel towards Russia, a "nation that World War II casualties of the Soviet Union, lost millions of lives in fighting Nazism".Critical reception
 At the close of the World Cup, Russia was widely praised for its success in hosting the tournament, with Steve Rosenberg of the
At the close of the World Cup, Russia was widely praised for its success in hosting the tournament, with Steve Rosenberg of the BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...Gianni Infantino
Giovanni Vincenzo Infantino (; born 23 March 1970) is a Swiss football administrator with Italian citizenship and the current president of FIFA. He was elected President of FIFA during the 2016 FIFA Extraordinary Congress in February 2016. H ...
stated: "Everyone discovered a beautiful country, a welcoming country, that is keen to show the world that everything that has been said before might not be true. A lot of preconceived ideas have been changed because people have seen the true nature of Russia." Infantino has proclaimed Russia 2018 to be "the best World Cup ever", as 98 per cent of the stadiums were sold out, there were 3 billion viewers on TV around the world and 7 million fans visited the fan fests. It was the most viewed World Cup to date, and the third List of most-watched television broadcasts#List, most viewed television broadcast, surpassing the Beijing Olympics in 2008.
However, some Western media outlets called the tournament a distraction from the international isolation and economic difficulties Russia has been facing.
Broadcasting rights
FIFA, through several companies, sold the broadcasting rights for the 2018 FIFA World Cup to various local broadcasters. After having tested the technology at limited matches of the 2013 FIFA Confederations Cup, and the 2014 FIFA World Cup (via private tests and public viewings in the host city of Rio de Janeiro), the 2018 World Cup was the first World Cup in which all matches were produced in 4K resolution, 4K Ultra-high-definition television, ultra high definition. Host Broadcast Services (HBS) stated that at least 75% of the broadcast cut of each match would come from 4K cameras (covering the majority of main angles), with instant replays and some camera angles being converted up from 1080p high definition sources with limited degradation in quality. These broadcasts were made available from selected rightsholders and television providers. In February 2018, Ukrainian rightsholder UA:PBC stated that it would not broadcast the World Cup. This came in the wake of growing boycotts of the tournament among the Football Federation of Ukraine and sports minister Ihor Zhdanov. Additionally, the Football Federation of Ukraine refused to accredit journalists for the World Cup and waived their quota of tickets. However, the Ukrainian state TV still broadcast the World Cup, and more than 4 million Ukrainians watched the opening match. Broadcast rights to the tournament in the Middle East were hampered by an ongoing 2017–18 Qatar diplomatic crisis, diplomatic crisis in Qatar, which saw Bahrain, Egypt, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates cut diplomatic ties with Qatar—the home country of FIFA's Middle East and Africa rightsholder beIN Sports—in June 2017, over its Qatar and state-sponsored terrorism, alleged state support of terrorist groups. On 2 June 2018, beIN pulled its channels from Du (company), Du and Etisalat, but with service to the latter restored later that day. Etisalat subsequently announced that it would air the World Cup in the UAE, and continue to offer beIN normally and without interruptions. In Saudi Arabia, beIN was banned from doing business; as a result, its channels and other content have been widely and illegally repackaged by a broadcaster identifying itself as "beoutQ". While FIFA attempted to negotiate the sale of a package consisting of Saudi matches and the final indirectly, they were unable to do so. On 12 July 2018, FIFA stated that it had "engaged counsel to take legal action in Saudi Arabia and is working alongside other sports rights owners that have also been affected to protect its interests." In the United States, the 2018 World Cup was the first men's World Cup whose English rights were held by Fox Sports (United States), Fox Sports, and Spanish rights held by Telemundo Deportes, Telemundo. The elimination of the United States in qualifying led to concerns that US interest and viewership of this World Cup would be reduced, noting that "casual" viewers of U.S. matches caused them to peak at 16.5 million viewers in 2014, and determined how much Fox paid for the rights. During a launch event prior to the elimination, Fox stated that it had planned to place a secondary focus on the Mexican team in its coverage to take advantage of their popularity among Hispanic and Latino Americans. Fox stated that it was still committed to broadcasting a significant amount of tournament coverage. Viewership was down overall over 2014; match scheduling was not as favourable to viewers in the Americas as it was in 2014. Many matches aired in the morning hours, although Telemundo's broadcast of the Mexico-Sweden Group F match was announced as being its most-watched weekday Daytime television, daytime program in network history. Unlike previous tournaments, where the rights were bundled with those of South Korea, Korean Central Television acquired rights to the 2018 World Cup within North Korea. Broadcasts only began with the round of 16, and matches were tape delayed and edited for time. In addition, matches involving Japan were excluded from the broadcasts, due to Japan–North Korea relations, strained relations and campaigns against the country.Sponsorship
Audience
A combined 3.572 billion viewers – more than half of the global population aged four and over – tuned in to world football's ultimate competition, according to audience data for official broadcast coverage of the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The average global live audience of for the tournament was 191 million viewers, a 2.1% increase over the 2014 tournament average of 187 million viewers, including that average audience in the early stages (group stage and round of 16) were bigger than in 2014. However, in 2018, the audience was 15 percent smaller for the semi-finals, 17 percent for the third place play-off, and 5.1 percent for the final, which was watched by 517 million people on average, compared to 545 million in 2014. Presumably, the reason for that is the smaller countries involved in the top four games compared to those in 2014, and only one global region (Europe) being represented in 2018 (compared to South America and Europe in 2014).See also
*FIFA World Cup
The FIFA World Cup, often simply called the World Cup, is an international association football competition contested by the senior men's national teams of the members of the ' ( FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament ha ...
* FIFA World Cup hosts
* 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup
The 2017 FIFA Confederations Cup was the 10th and final edition of the FIFA Confederations Cup, a quadrennial international men's football tournament organised by FIFA. It was held in Russia, from 17 June to 2 July 2017, as a prelude to the 201 ...
* 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup
References
External links
FIFA.com 2018 website
Official Technical Report
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Fifa World Cup 2018 2018 FIFA World Cup, 2018 in association football 2017–18 in Russian football FIFA World Cup tournaments, 2018 International association football competitions hosted by Russia, 2018 Fifa World Cup June 2018 sports events in Russia July 2018 sports events in Russia Association football controversies