Ōshū Kaidō on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
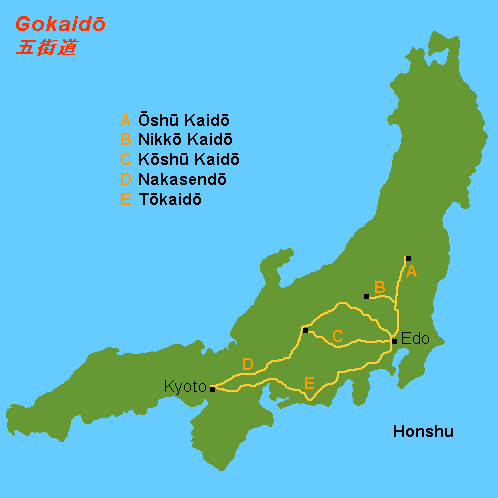 The was one of the five routes of the
The was one of the five routes of the
Yumekaidō. Accessed September 4, 2007. there were over 100 designated post stations when the subroutes are included.
 :Starting Location:
:Starting Location:
Ōshū Kaidō Travel Journal
dead link] {{DEFAULTSORT:Oshu Kaido Road transport in Japan 17th-century establishments in Japan Japan-related lists
 The was one of the five routes of the
The was one of the five routes of the Edo period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was character ...
. It was built to connect Edo
Edo ( ja, , , "bay-entrance" or "estuary"), also romanized as Jedo, Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of Tokyo.
Edo, formerly a ''jōkamachi'' (castle town) centered on Edo Castle located in Musashi Province, became the ''de facto'' capital of ...
(modern-day Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.46 ...
) with Mutsu Province
was an old province of Japan in the area of Fukushima, Miyagi, Iwate and Aomori Prefectures and the municipalities of Kazuno and Kosaka in Akita Prefecture.
Mutsu Province is also known as or . The term is often used to refer to the co ...
and the present-day city of Shirakawa, Fukushima Prefecture
Fukushima Prefecture (; ja, 福島県, Fukushima-ken, ) is a prefecture of Japan located in the Tōhoku region of Honshu. Fukushima Prefecture has a population of 1,810,286 () and has a geographic area of . Fukushima Prefecture borders Miyagi ...
, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
. It was established by Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first ''shōgun'' of the Tokugawa Shogunate of Japan, which ruled Japan from 1603 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was one of the three "Great Unifiers" of Japan, along with his former lord Oda Nobunaga and fello ...
for government officials traveling through the area.
Subroutes
In addition to the established use of traveling from Edo to Mutsu Province, there were also many roads that connected from the Ōshū Kaidō. One such sub-route was the Sendaidō (仙台道), which connected Mutsu Province withSendai
is the capital city of Miyagi Prefecture, the largest city in the Tōhoku region. , the city had a population of 1,091,407 in 525,828 households, and is one of Japan's 20 designated cities. The city was founded in 1600 by the ''daimyō'' Date M ...
. The terminus for the Sendaidō is in Aoba-ku in modern Sendai. From there, the Matsumaedō (松前道) connected Sendai with Hakodate
is a city and port located in Oshima Subprefecture, Hokkaido, Japan. It is the capital city of Oshima Subprefecture. As of July 31, 2011, the city has an estimated population of 279,851 with 143,221 households, and a population density of 412.8 ...
, Hokkaidō
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
. Though the Ōshū Kaidō has only 27 post stations,Ōshū Kaidō MapYumekaidō. Accessed September 4, 2007. there were over 100 designated post stations when the subroutes are included.
Travel
In the early Edo period, travel along the road mostly consisted of magistrates heading towards Edo in order to take part in '' sankin kōtai''. After Hakodate's development, the late Edo period saw travel further increase as a result of increasing trade withRussia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
.
Nowadays, the path of the Ōshū Kaidō and its extensions is followed by National Route 4 from Tokyo to Aomori via Sendai and National Route 280 from Aomori to Minamya.
Stations of the Ōshū Kaidō
The 27 stations of the Ōshū Kaidō are listed below in order and are divided by their modern-day prefecture. The first seventeen stations are shared with the Nikkō Kaidō. The present day municipality is listed afterwards in parentheses.Tokyo
 :Starting Location:
:Starting Location: Nihonbashi
is a business district of Chūō, Tokyo, Japan which grew up around the bridge of the same name which has linked two sides of the Nihonbashi River at this site since the 17th century. The first wooden bridge was completed in 1603. The curre ...
(日本橋) ( Chūō-ku)
:1. Senju-shuku (千住宿) ( Adachi-ku)
Saitama Prefecture
:2. Sōka-shuku (草加宿) ( Sōka) :3. Koshigaya-shuku (越ヶ谷宿) (Koshigaya
is a city located in Saitama Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 345,353 in 158,022 households and a population density of 5700 persons per km². The total area of the city is . It is famous for producing daruma dolls. ...
)
:4. Kasukabe-shuku (粕壁宿) ( Kasukabe)
:5. Sugito-shuku (杉戸宿) ( Sugito, Kitakatsushika District)
:6. Satte-shuku (幸手宿) ( Satte)
:7. Kurihashi-shuku (栗橋宿) ( Kuki)
Ibaraki Prefecture
:8. Nakada-shuku (中田宿) ( Koga) :9. Koga-shuku (古河宿) (Koga)Tochigi Prefecture
:10. Nogi-shuku (野木宿) ( Nogi, Shimotsuga District) :11. Mamada-shuku (間々田宿) ( Oyama) :12. Oyama-shuku (小山宿) (Oyama) :13. Shinden-shuku (新田宿) (Oyama) :14. Koganei-shuku (小金井宿) ( Shimotsuke) :15. Ishibashi-shuku (石橋宿) (Shimotsuke) :16. Suzumenomiya-shuku (雀宮宿) (Utsunomiya
is the prefectural capital city of Tochigi Prefecture in the northern Kantō region of Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 519,223, and a population density of . The total area of the city is . Utsunomiya is famous for its '' gyoza' ...
)
:17. Utsunomiya-shuku (宇都宮宿) (Utsunomiya)
:18. Shirosawa-shuku (白澤宿) (Utsunomiya)
:19. Ujiie-shuku (氏家宿) (Sakura
A cherry blossom, also known as Japanese cherry or sakura, is a flower of many trees of genus ''Prunus'' or ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus''. They are common species in East Asia, including China, Korea and especially in Japan. They generally ...
)
:20. Kitsuregawa-shuku (喜連川宿) (Sakura)
:21. Sakuyama-shuku (佐久山宿) (Ōtawara
270px, View from the ruins of Ōtawara Castle
is a city located in Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 72,189 in 30,136 households, and a population density of 210 persons per km2. The total area of the city is ...
)
:*Yagisawa-shuku (八木沢宿) (Ōtawara) (''ai no shuku
{{nihongo, Ai no Shuku, 間の宿, mid-station were unofficial post stations along historical routes in Japan. These post stations formed organically along routes (such as the Tōkaidō and the Nakasendō) when the distance between two places w ...
'')
:22. Ōtawara-shuku (大田原宿) (Ōtawara)
:23. Nabekake-shuku (鍋掛宿) ( Nasushiobara)
:24. Koebori-shuku (越堀宿) (Nasushiobara)
:*Terago-shuku (寺子宿) (Nasushiobara) (''ai no shuku'')
:25. Ashino-shuku (芦野宿) ( Nasu, Nasu District)
:*Tani-shuku (谷宿) (Nasu, Nasu District) (''ai no shuku'')
:*Yorii-shuku (寄居宿) (Nasu, Nasu District) (''ai no shuku'')
Fukushima Prefecture
:26. Shirosaka-shuku (白坂宿) ( Shirakawa) :27. Shirakawa-shuku (白川宿) (Shirakawa) :Ending Location: Shirakawa Castle (白河城) (Shirakawa)See also
* Edo Five Routes ** Tōkaidō (or53 Stations of the Tōkaidō
The are the rest areas along the Tōkaidō, which was a coastal route that ran from Nihonbashi in Edo (modern-day Tokyo) to Sanjō Ōhashi in Kyoto.. There were originally 53 government post stations along the Tōkaidō, where travelers ...
)
** Nakasendō (or 69 Stations of the Nakasendō
The are the rest areas along the Nakasendō, which ran from Nihonbashi in Edo (modern-day Tokyo) to Sanjō Ōhashi in Kyoto.Yama to Keikoku Publishing (2006). Nakasendō o Aruku (Revised ed.). Osaka: Yama to Keikoku Publishing. .Kōshū Kaidō
The was one of the five routes of the Edo period. It was built to connect Edo (modern-day Tokyo) with Kai Province in modern-day Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan. The route continues from there to connect with the Nakasendō's Shimosuwa-shuku in ...
** Nikkō Kaidō
*Other routes
** Hokkoku Kaidō
** Kisoji
** Mikuni Kaidō
** Tanabu Kaidō
References
External links
Ōshū Kaidō Travel Journal
dead link] {{DEFAULTSORT:Oshu Kaido Road transport in Japan 17th-century establishments in Japan Japan-related lists